Semiconductor memory
A memory and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of static memory, read-only memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problems of shrinking chips, increasing manufacturing costs, and high unit price of chips, so as to meet high-speed operation, increase operating margin, and shorten memory. The effect of taking time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
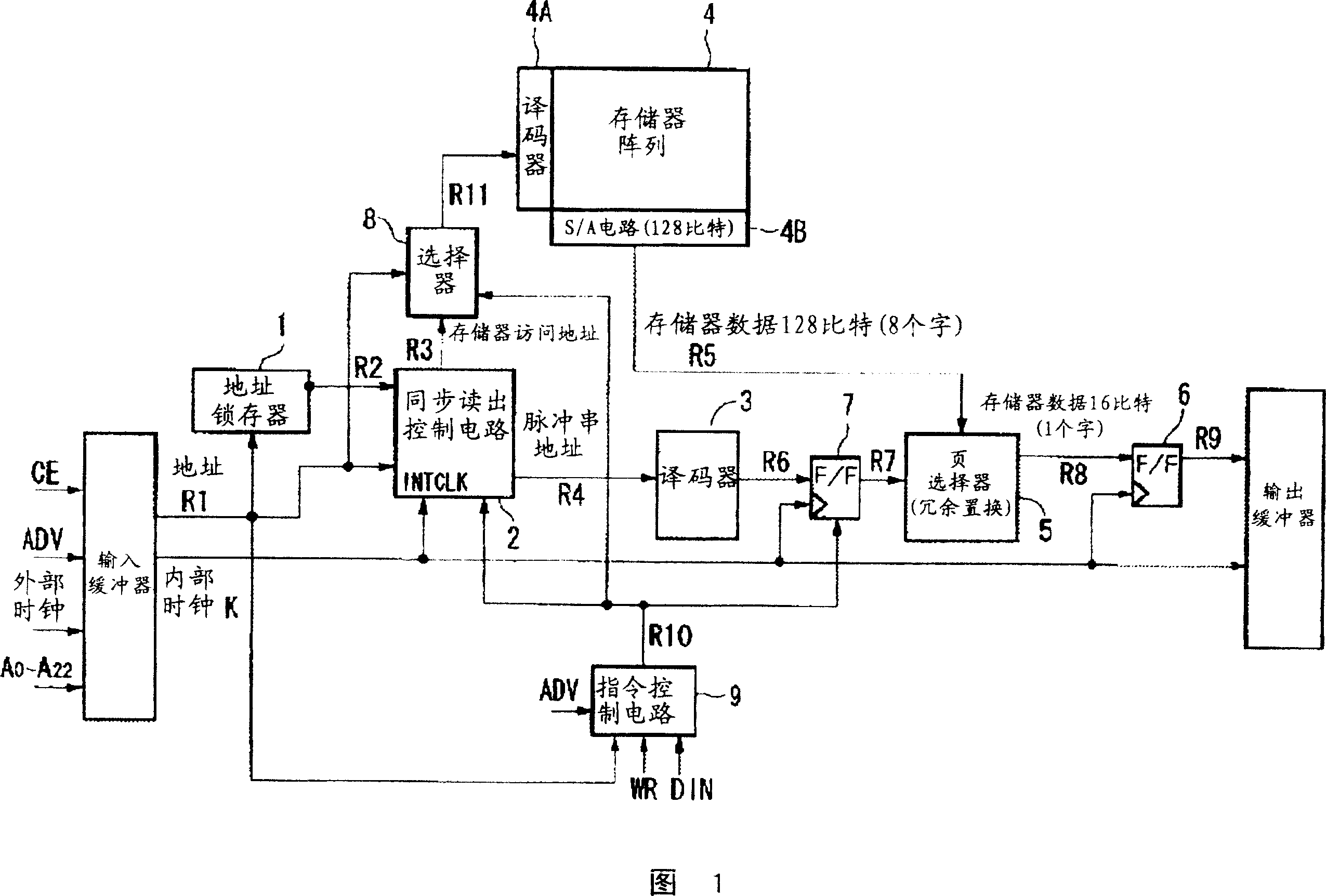
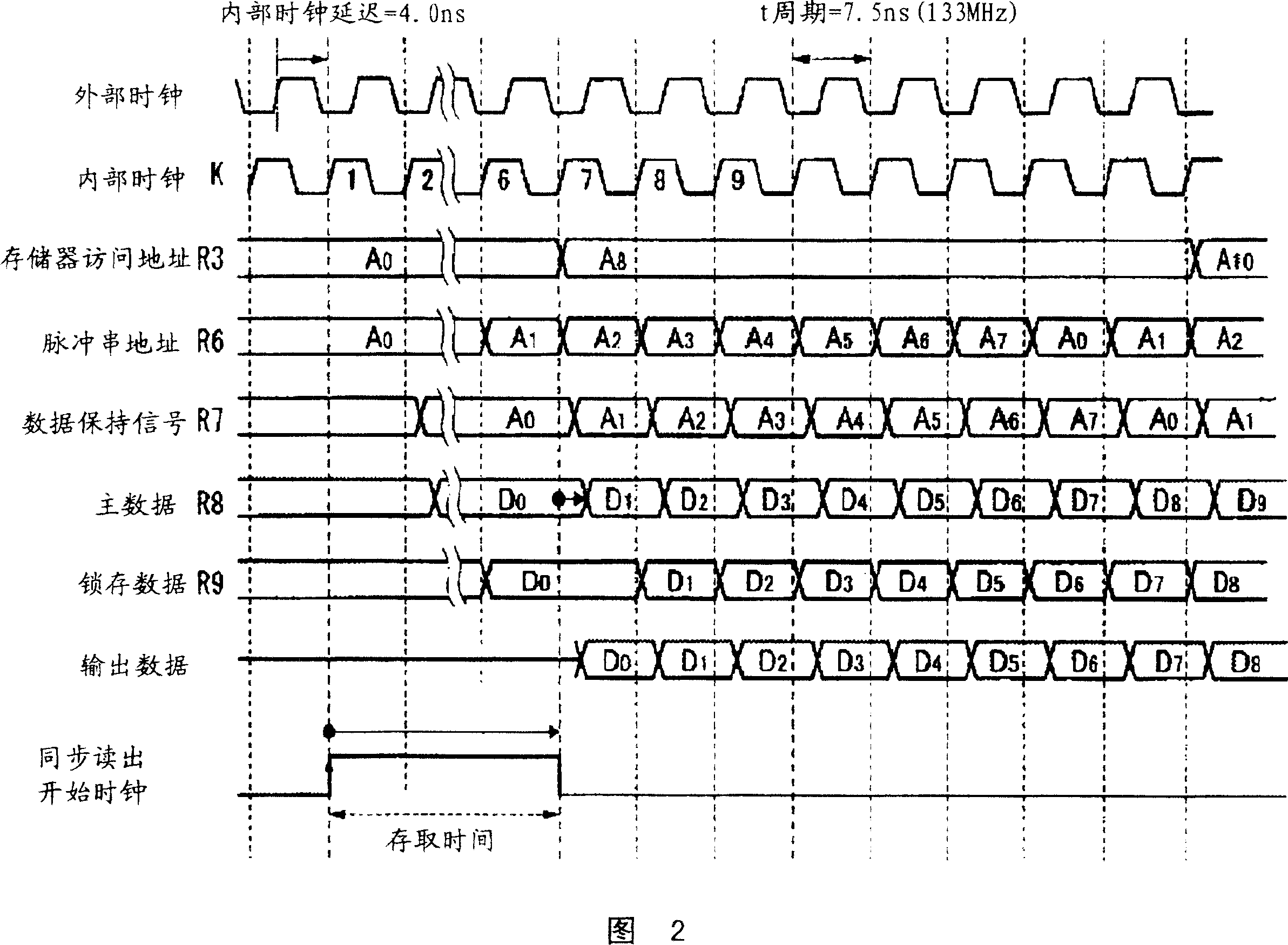
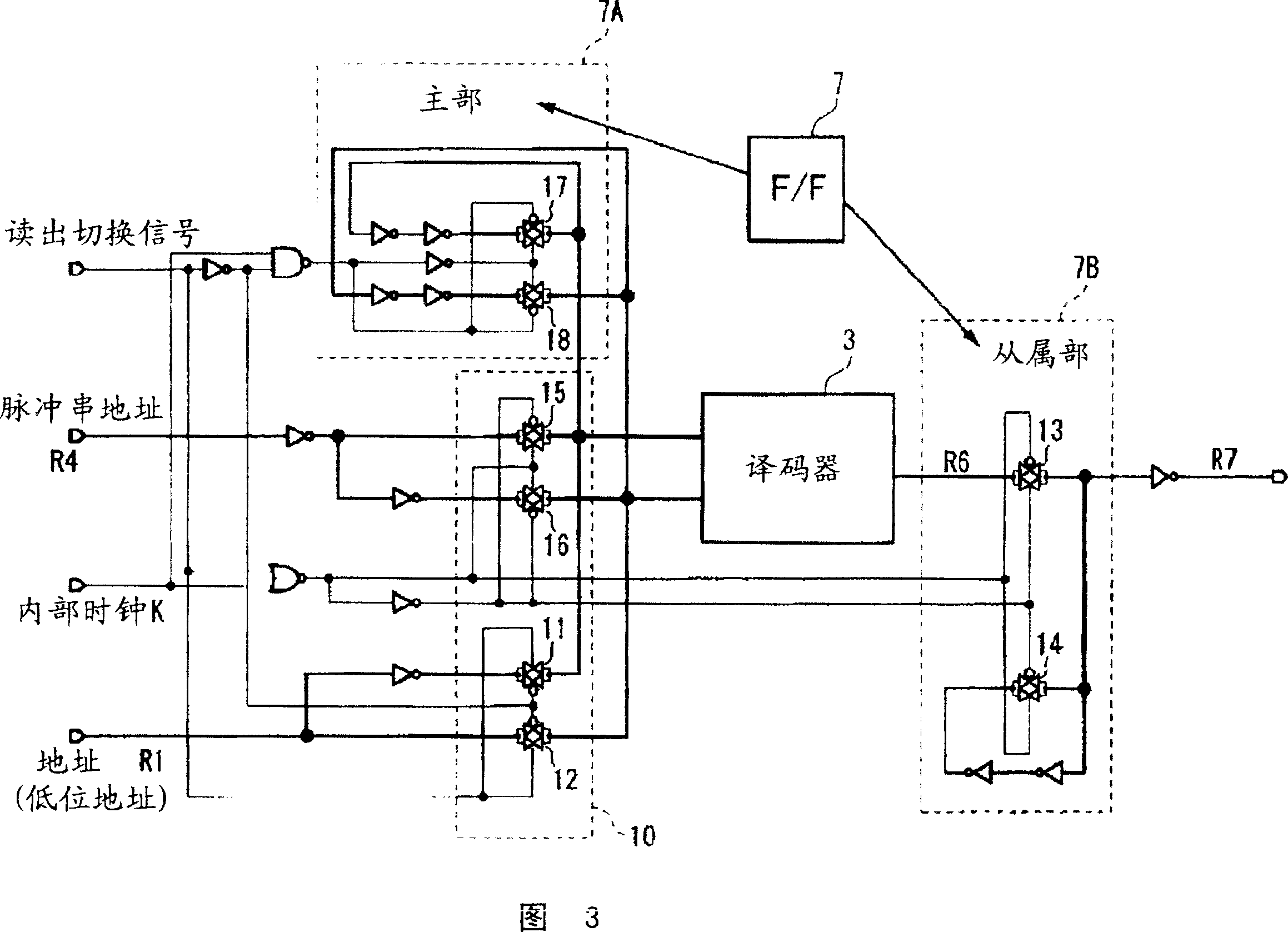
[0064] In the present invention, as shown in FIG. 1, in the synchronous read operation in multiple read modes of the semiconductor memory, a lock for time adjustment is provided at a predetermined position between the synchronous read control circuit 2 and the output latch 6. Register 7, in the past, the increase of the burst address of the synchronous read control circuit 2 is performed from the timing of the predetermined number of clock pulses from the start of synchronous read to the output of data. The internal clock K which is one cycle earlier than the set number of clock pulses starts incrementing the burst address R4.
[0065] That is, in the clock cycle of the internal clock pulse K (minimum number of pulses is the number of internal clock pulses of the above access time plus 1 internal The synchronous readout control circuit 2 changes the burst address R4 at a timing earlier than one internal clock cycle by the number of pulses after the cycle of the clock pulse.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com