Lens driving unit
A lens driving device, lens technology, applied in installation, instrument, TV and other directions, can solve the problems of increased power consumption, easy breakage, large stepping motor, etc., to eliminate tilt, improve impact resistance, and reduce power consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
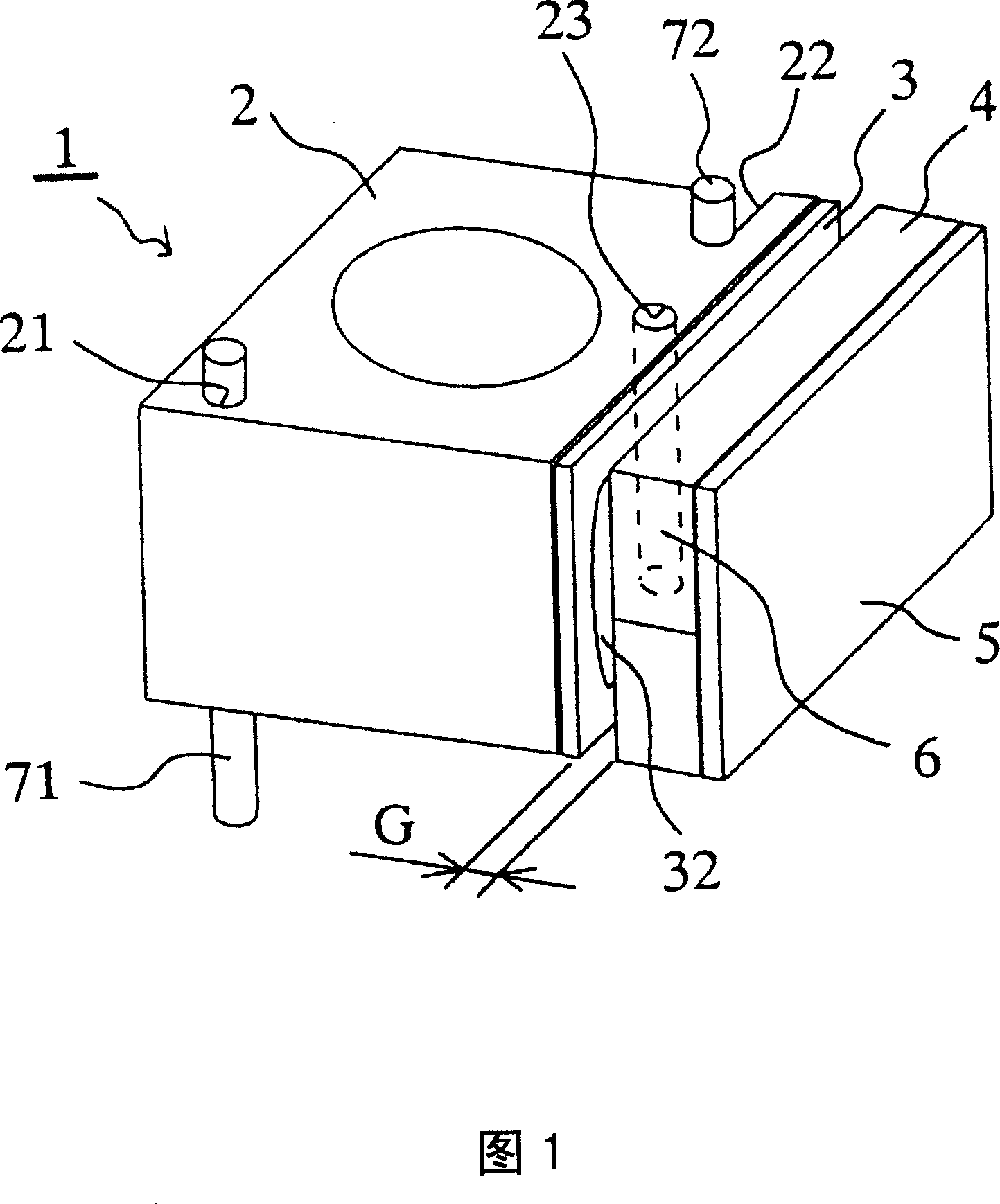
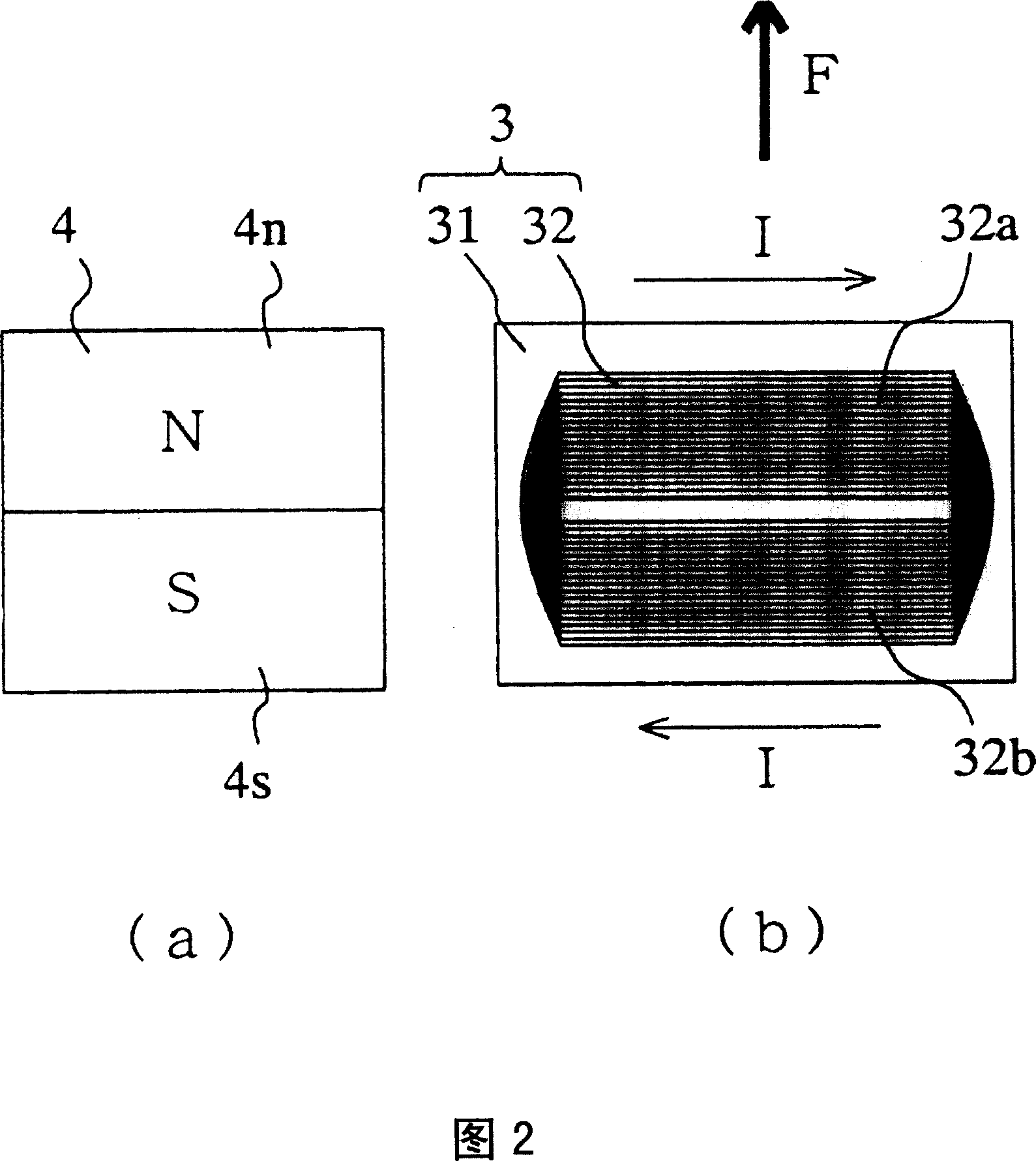
[0027] FIG. 1 shows a lens driving device 1 of a camera device. A lens group (not shown) is provided inside the lens holder 2 . On one side of the lens holder 2, the FP coil 3 is disposed, and the coil pattern 32 is exposed. In addition, a magnet 4 is arranged with a gap G at a position facing the FP coil 3 . The front surface of the magnet 4 faces the FP coil 3 , but the yoke 5 as a magnetic body is attached to the back surface by attraction. The yoke 5 attached to the magnet 4 is fixed to a housing (not shown) of the camera device, although not shown.
[0028] Two shaft-shaped guide mechanisms 71 and 72 are vertically provided as guide mechanisms on a housing (not shown). In addition, the lens holder 2 is provided with a cylindrical through-hole 21 , a notch 22 , and a cylindrical through-hole 23 . The diameter of the through-hole 21 is substantially the same as or slightly larger than the diameter of the first shaft-shaped guide mechanism 71 , and the first shaft-shaped...
Embodiment 2
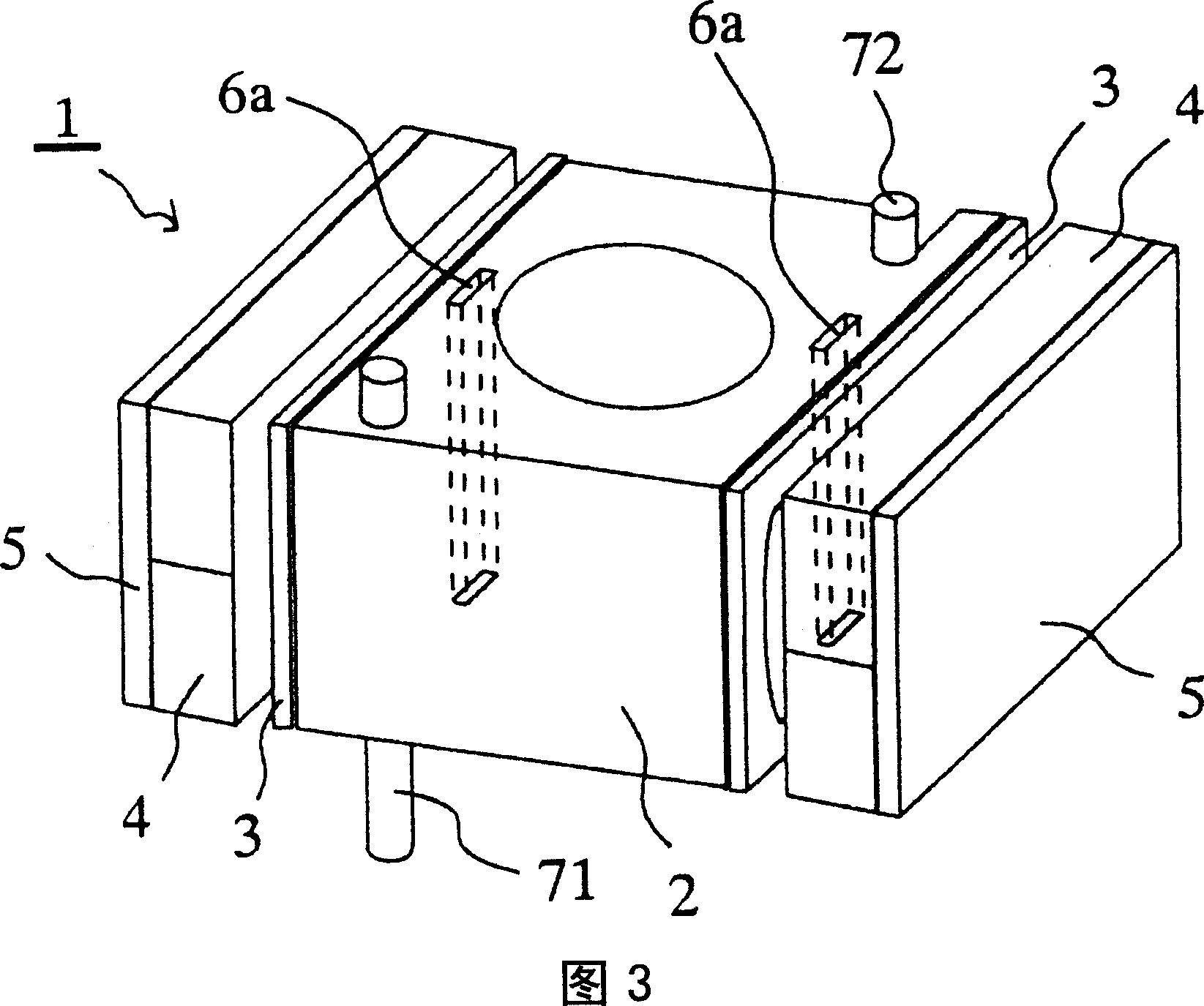
[0033] FIG. 3 shows a perspective view of Example 2. FIG. In addition, in Embodiment 2 and below, the same components and portions as in Embodiment 1 are assigned the same reference signs as in Embodiment 1, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0034] FP coils 3 are respectively arranged on two side surfaces parallel to each other of the lens holder 2 , and magnets 4 with yokes 5 as magnetic bodies attached to the back are arranged at intervals from the respective FP coils 3 . In addition, in the vicinity of the FP coil 3 of the lens holder 2, two magnetic members 6a in the shape of square columns are arranged and fixed with an adhesive (not shown) or the like.
[0035] In Example 2, since two sets of magnetic member 6a, FP coil 3, magnet 4, and yoke 5 are arranged, lens holder 2 can be held more precisely than in Example 1. In addition, instead of providing two magnetic members 6a, only one magnetic member 6a may be provided.
Embodiment 3
[0037] FIG. 4 shows a perspective view of Example 3. FIG. As can be seen from this figure (a), as the guide mechanism of the lens holder 2, instead of using a shaft-shaped guide mechanism, a through hole or a cutout, the first and second convex guide mechanisms provided on the side of the lens holder are used. 26 and 27 are different from Embodiment 1 in that Figure (b) is a plan view of a device in which the lens driving device 1 of Embodiment 3 is incorporated into the frame 8 of the camera device viewed from the moving direction of the lens holder 2 . The cross section of the first convex guiding mechanism 26 is triangular, and the cross section of the second convex guiding mechanism 27 is quadrangular. In addition, at positions corresponding to the convex guides 26 and 27 of the housing 8, a first concave guide 81 having a triangular cross section and a second concave guide 82 having a square cross section are formed.
[0038] The lens holder 2 moves along the optical axi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com