Method of manufacturing non-volatile memory element
A technology of non-volatile storage and manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of manufacturing electrically rewritable non-volatile storage elements, can solve problems such as the inability to easily realize DRAM storage capacity, and achieve the effect of enhancing heat generation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
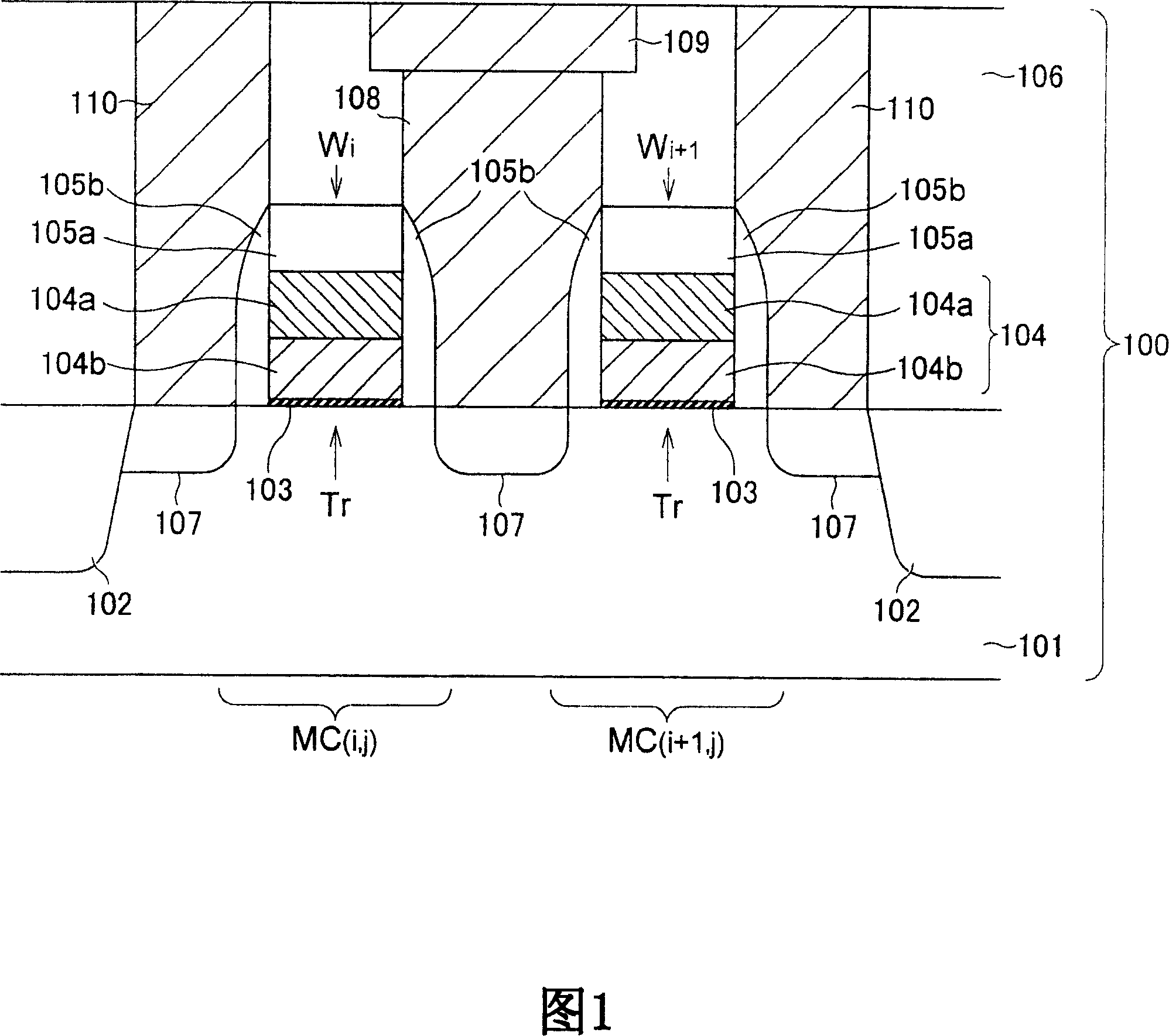
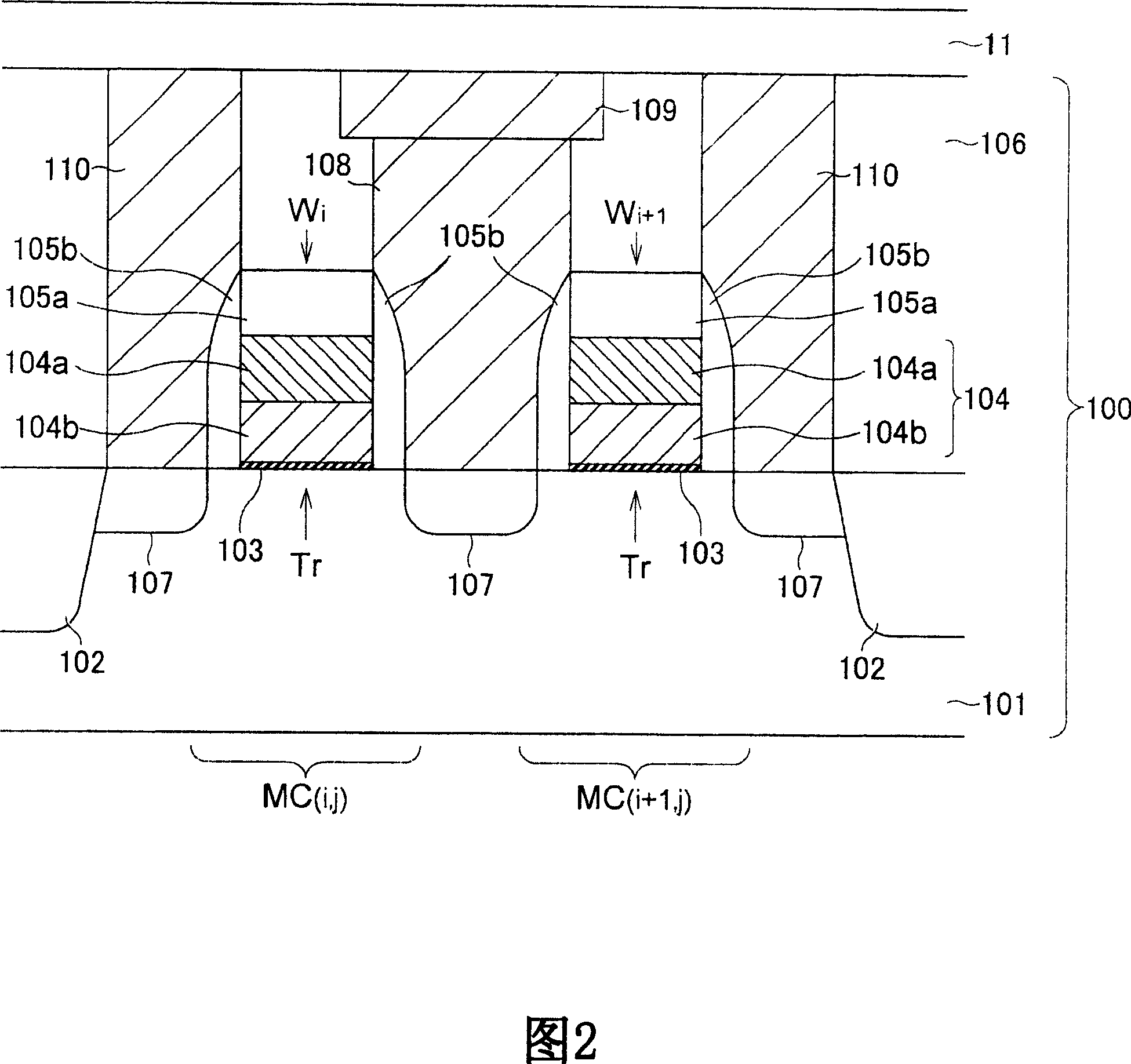
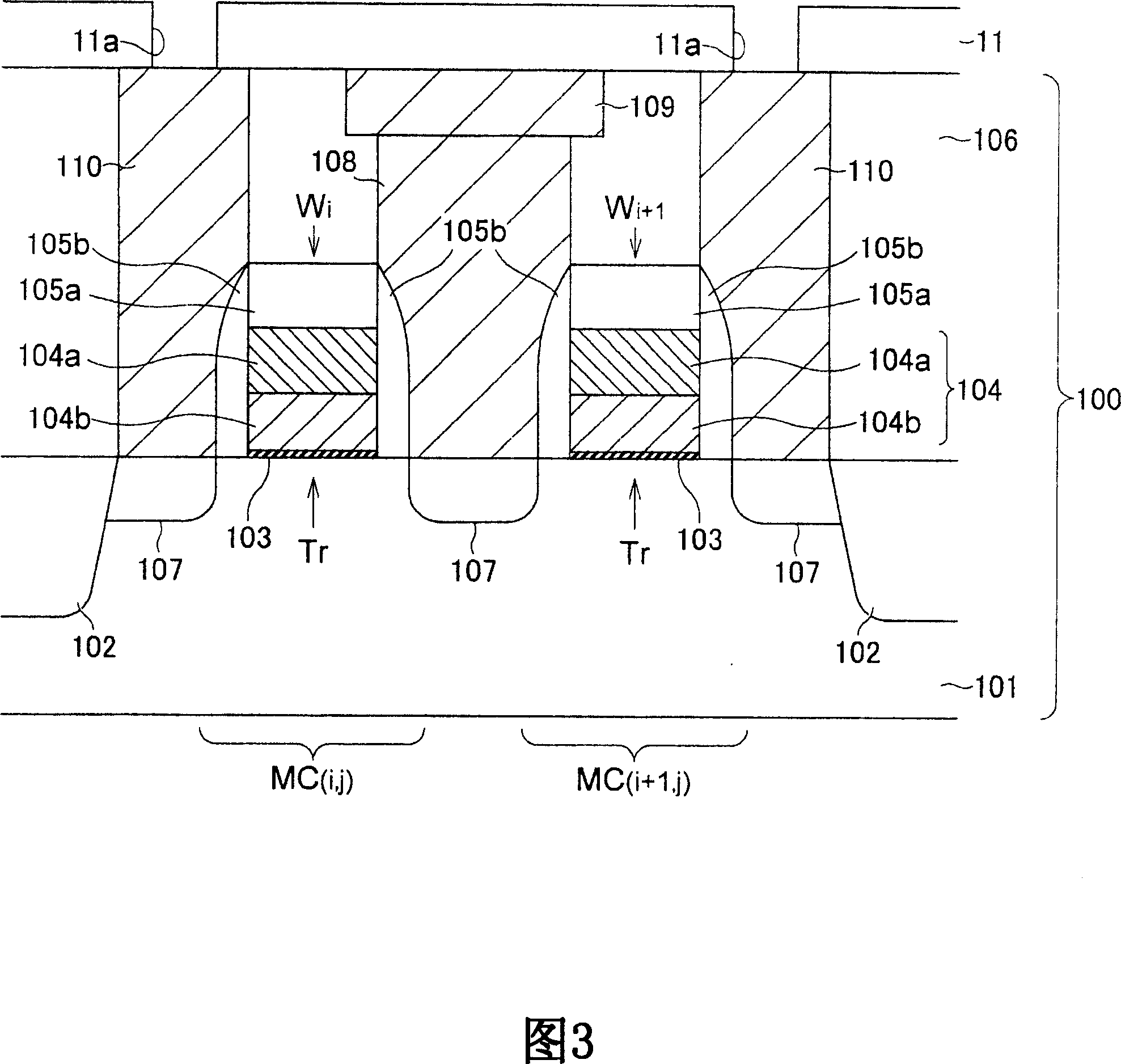
[0039] 1 to 10 are schematic cross-sectional views showing a method of manufacturing a nonvolatile memory element according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention.
[0040] In the method of manufacturing a nonvolatile memory element according to the present embodiment, first, a transistor layer 100 is formed on a semiconductor substrate 101 (FIG. 1). The structure and method for forming the transistor layer 100 are not particularly limited, and the transistor layer 100 can be formed using known methods. The transistor layer 100 as shown has two transistors Tr. The gates 104 of the transistor Tr are respectively configured with word lines Wi and Wi+1. The gate 104 has a polycide structure composed of a polysilicon film 104 a and tungsten silicide (WSi) 104 b, and is formed on the gate insulating film 103 . The grid 104 has a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com