Embolization microcatheter
a micro-catheter and catheter technology, applied in the field of micro-catheters, can solve the problems of ischemia and ulceration, damage to healthy tissues, and the inability to access the vessels with a larger and often stiffer catheter, and achieve the effect of increasing local pressur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
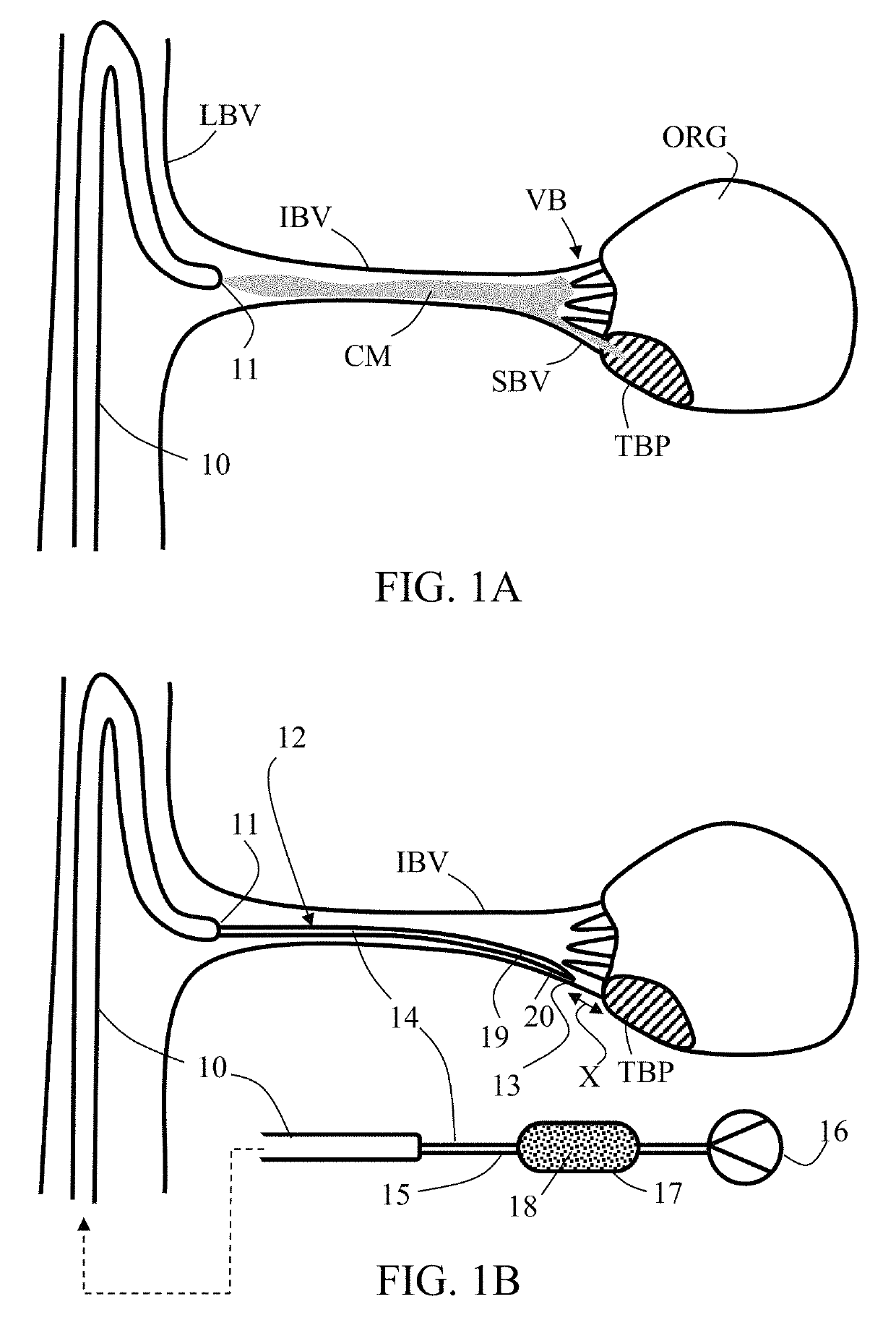
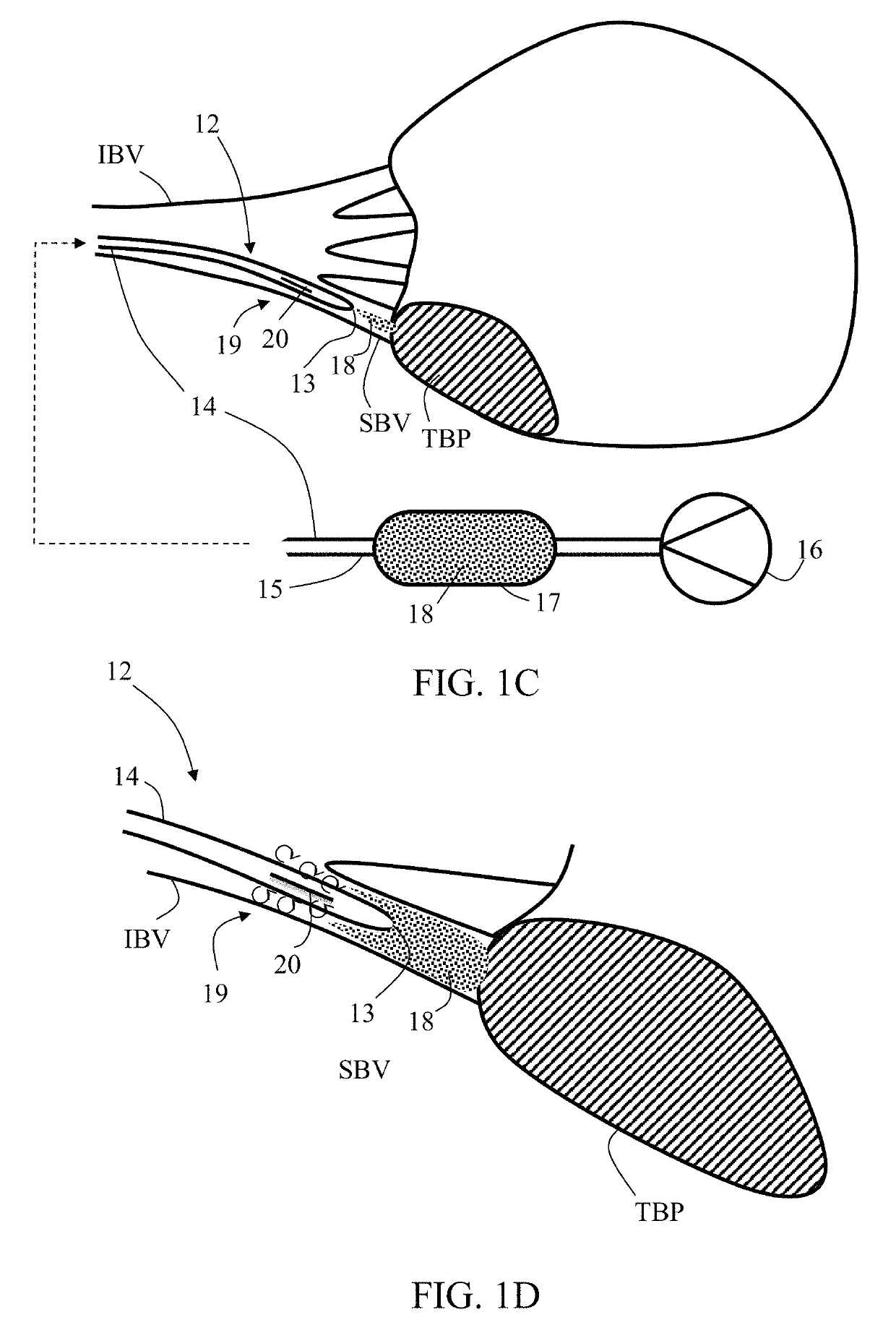
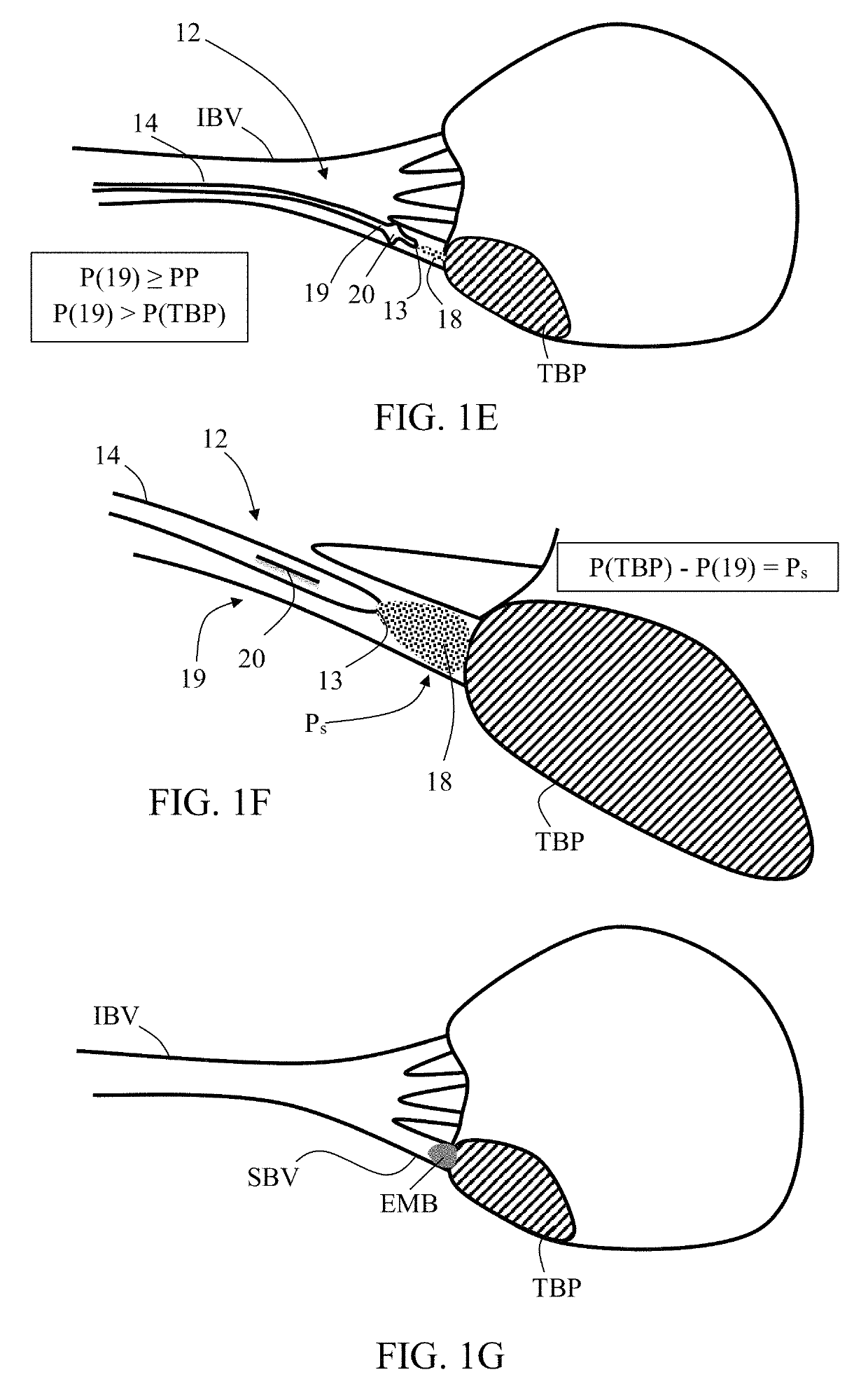
[0049]The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to microcatheters and methods for delivering a substance (e.g., an infusion agent including embolization material and / or contrast enhancing material) to a target bodily part, for example, located within the cardiovascular system, and in particular to an embolization microcatheter, uses thereof in performing local embolization procedures, and delivering an infusion agent (for example, embolization beads with contrast enhancing material). Some embodiments of the invention are applicable for: (i) delivering an infusion agent including embolization material and / or contrast enhancing material in a small blood vessel towards a target bodily part, and (ii) performing local embolization in a small blood vessel feeding a (for example, cancerous) target bodily part, thereby forming emboli in small blood vessels, while preventing or minimizing non-target embolization (associated with contrast enhancing material). Some embodiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com