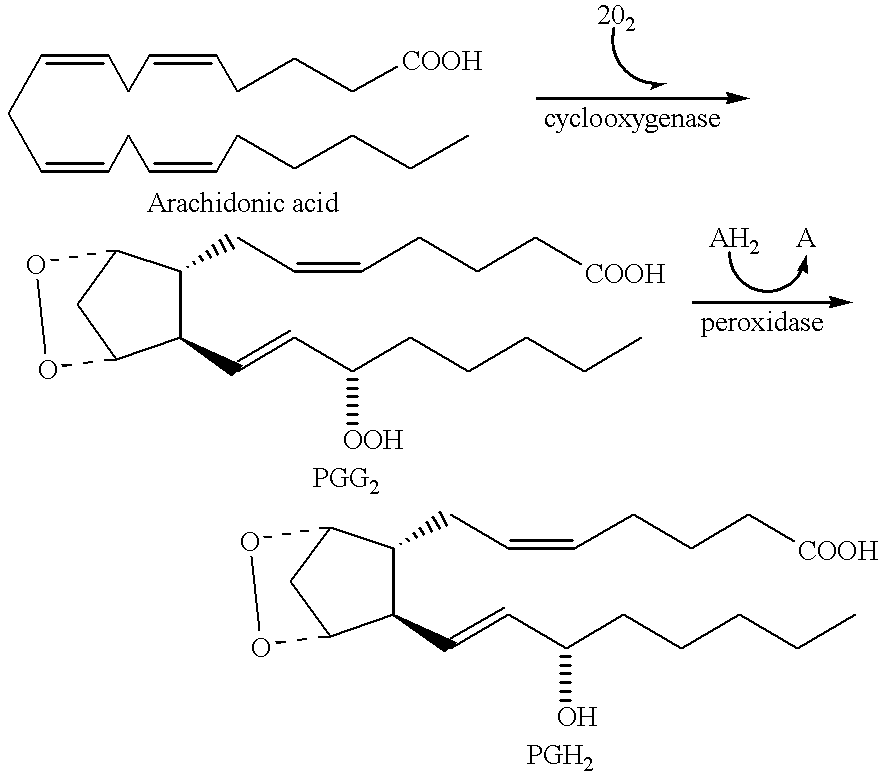
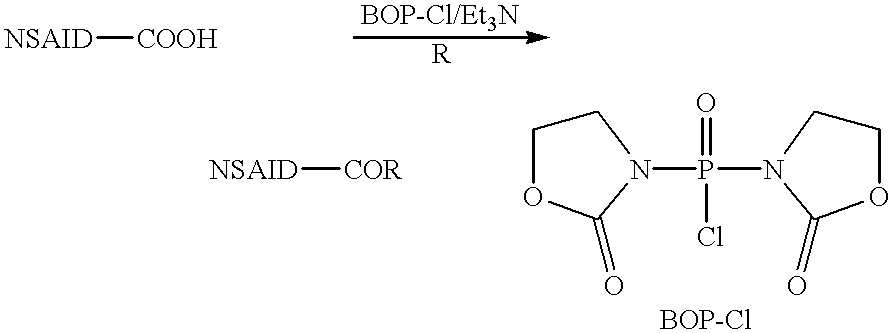
Amide derivatives for antiangiogenic and/or antitumorigenic use
a technology of amide derivatives and amides, applied in the direction of biocide, heterocyclic compound active ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of easy hydrolysis of hydroxamates and patents that fail to address cox inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
[0054] The following carboxylic acid amide derivatives of indomethacin, designated as compounds 1 through 31, were made. (Note: compounds 1, 2, and 9 through 13 are also disclosed in the above-discussed U.S. Pat. Nos. 3,285,908 and 3,336,194, both to Shen, assignor to Merck & Co., Inc.)
[0055] Indomethacin-N-methyl amide (compound 1) was obtained upon chromatography on silica gel (EtOAc:hexanes; 10:90 then 50:50) as a bright yellow solid (271 mg, 79%). mp=187-189.degree. C.; .sup.1H NMR (CDCl.sub.3) .delta. 7.64-7.67 (dd, 2H, J=6.6 Hz and 1.9 Hz, ArH), 7.47-7.50 (dd, 2H, J=6.7 Hz and 1.9 Hz, ArH), 6.88-6.89 (dd, 1H, J=9.1 Hz and 2.5 Hz, ArH), 6.84-6.87 (d, 1H, J=9.0 Hz, ArH), 6.68-6.72 (dd, 1H, J=9.1 Hz and 2.5 Hz, ArH), 5.22 (bs, 1H, NH), 3.83 (s, 3H, CH.sub.3), 3.65 (s, 2H, CH.sub.2), 2.75-2.76 (d, 3H, J=4.8 Hz, CH.sub.3), 2.39 (s, 3H, CH.sub.3).
[0056] Indomethacin-N-ethan-2-ol amide (compound 2) was obtained upon chromatography on silica gel (EtOAc) as a pale yellow solid (143 mg,...
example ii
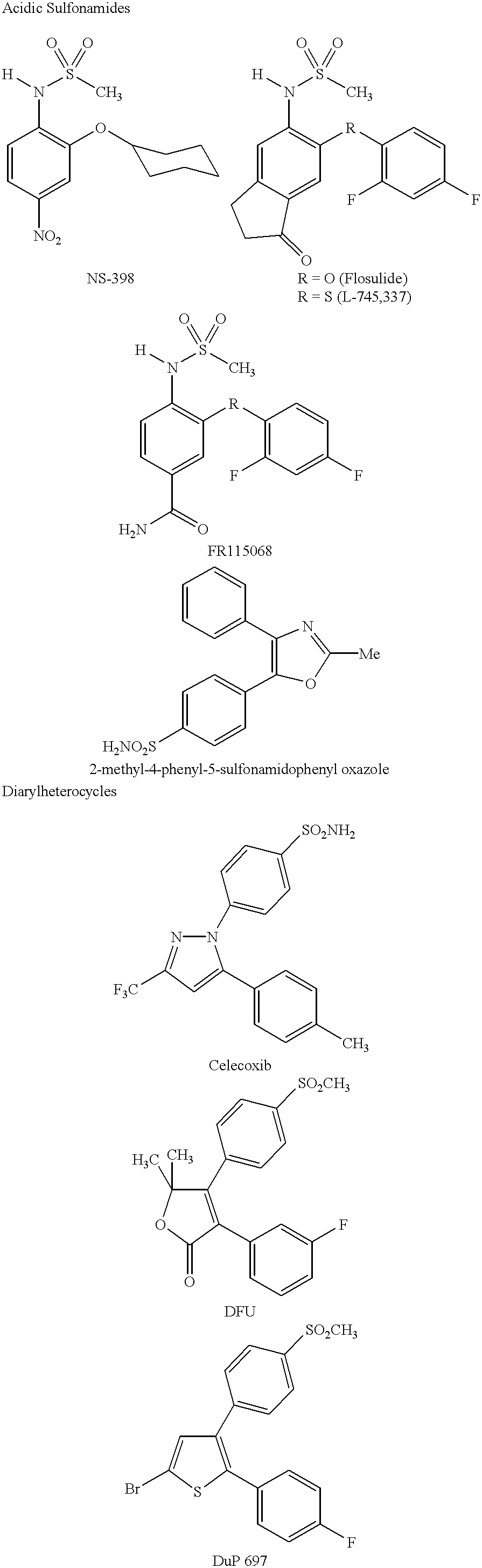
[0097] Comparison with Sulfonamides of Another Study
[0098] A similar SAR study was previously reported in the above-noted journal article by Li et al. for acidic sulfonamides. (See, the structures drawn above for compounds L-745,337 and NS-398.) Specifically, Li et al. found that replacement of the N--H proton in the NHSO.sub.2CH.sub.3 moiety of L-745,337 or NS-398 with a methyl group led to complete loss of inhibitory potency towards either the COX-1 or COX-2 isozyme.
[0099] This behaviour may be explained from the recently solved crystal structure of murine COX-2 complexed with NS-398. See, Kurumbail et al., Abstract 197, Eicosanoids and Other Bioactive Lipids in Cancer, Inflammation and Related Diseases, Fifth International Conference, La Jolla, Calif. (Sep. 17-20, 1997). Unlike the diarylheterocyclics, NS-398 does not utilize the side pocket even though it contains a sulfonamide group. Instead the sulfonamide binds to Arg106 in a fashion similar to the carboxylic acid-containing ...
example iii
[0101] Additional Inhibitory Activity Testing with Mouse COX
[0102] Compound 11
[0103] The structural basis for COX-2 selectivity by compound 11 also was probed by site directed mutagenesis. More particularly, the inhibitory potency of indomethacin as compared to that of indomethacin-N-phenethyl amide (compound 11) was evaluated against site directed murine COX-2 mutants (Arg106Gln and Tyr341Ala) which represent key residues involved in the binding of the carboxylic acid-containing NSAIDs. Arg106 is the only positively charged residue in the fatty acid binding site and is important for binding the carboxylic acid moiety of an NSAID with Tyr341Ala, which is juxtaposed to Arg106 at the constriction site and is responsible for the selective binding of the S-enantiomers but not the R-enantiomers in the 2-phenylpropionate class of NSAIDs including flurbiprofen. In addition to these mutants, also analyzed was the inhibition profile of the Val509IleArg499HisVal420Ile mutant (also known as th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com