Logic circuit with single charge pulling out transistor and semiconductor integrated circuit using the same
a logic circuit and transistor technology, applied in logic circuits, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as serious impedement and delay in the operation of a preceding logic circuit stag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
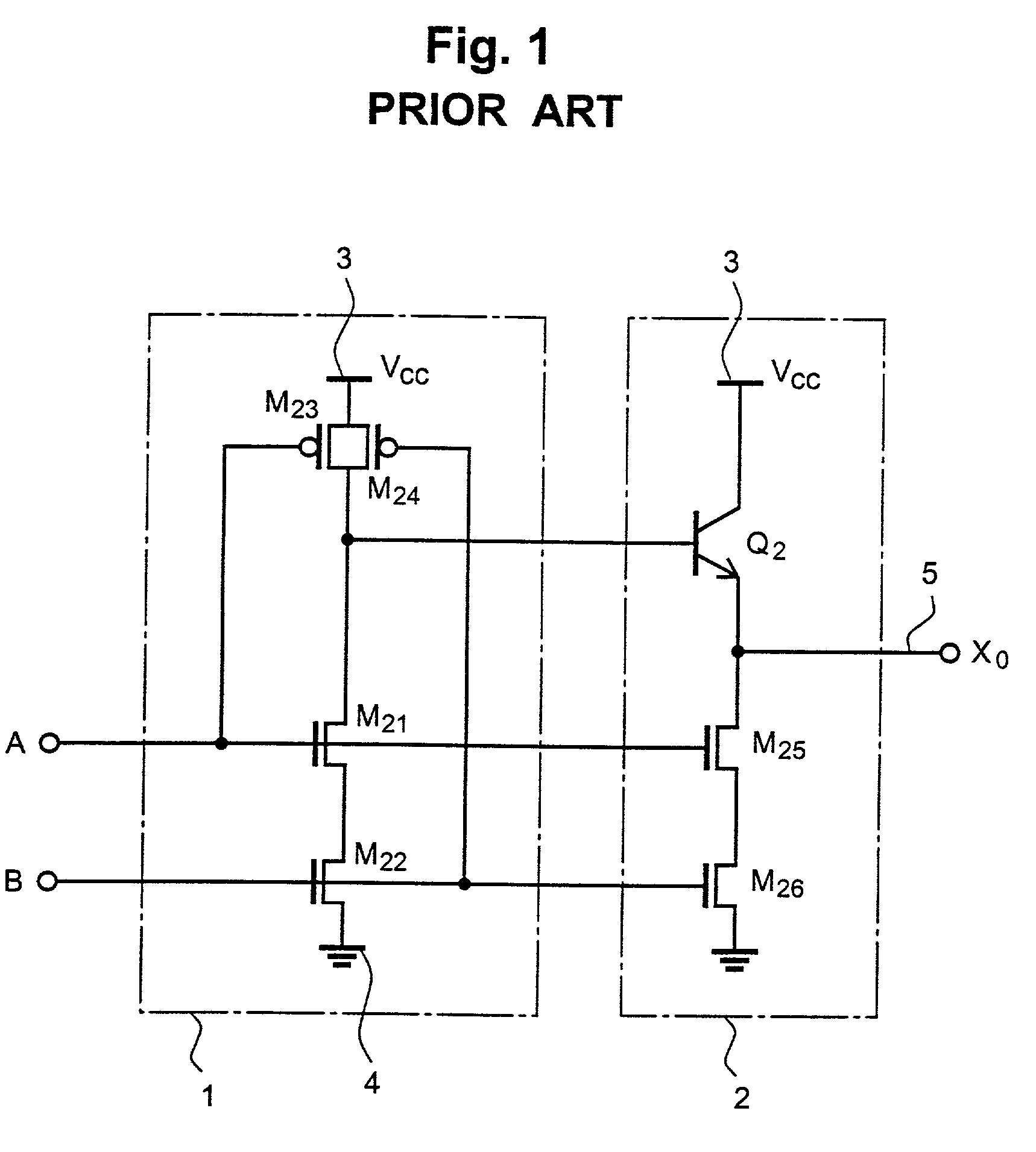
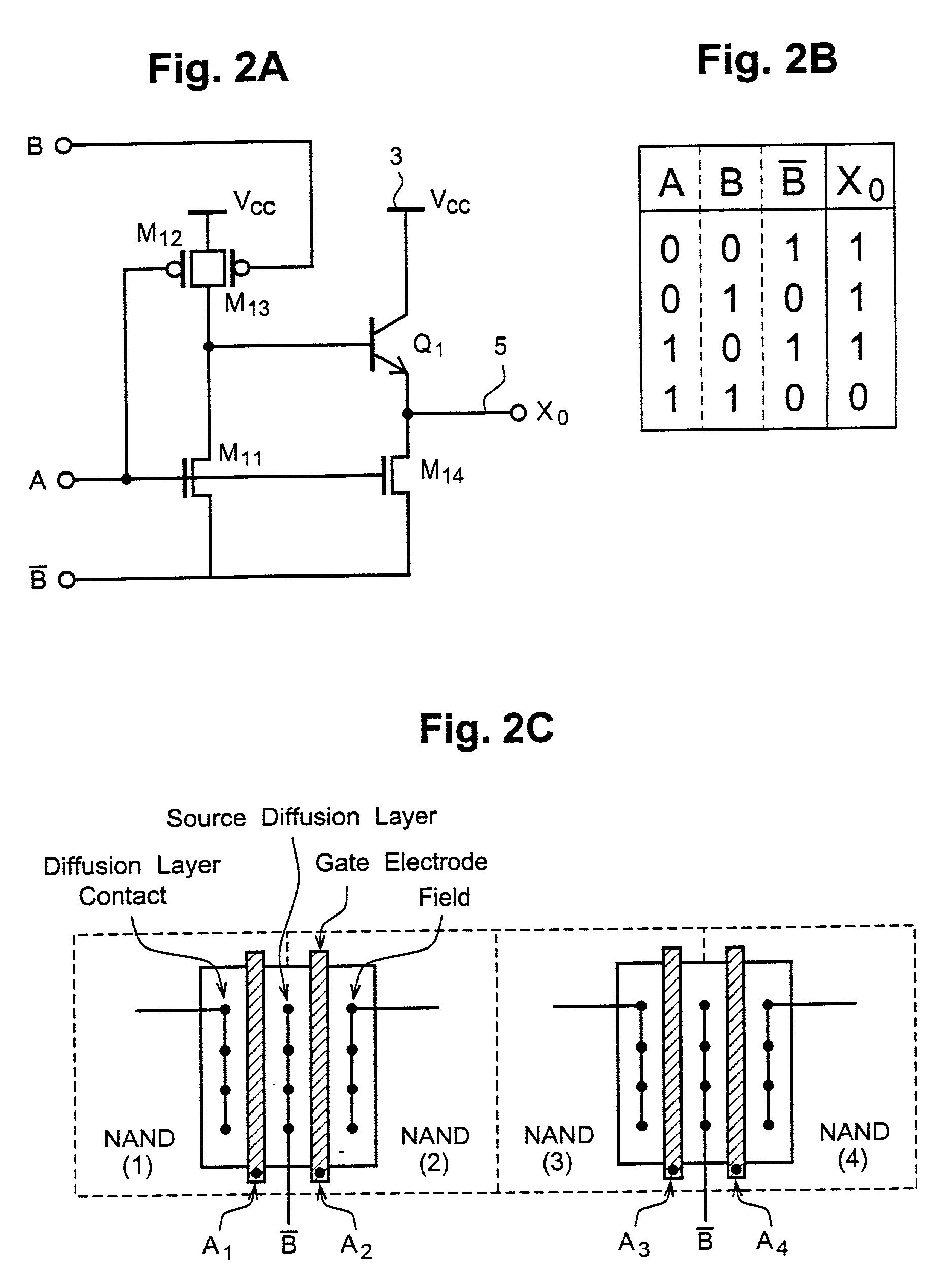
[0041] FIG. 2A is a circuit diagram showing the logic circuit according to the invention applied to a two-input NAND logic circuit having the BiCMOS structure. Comparing FIGS. 2A and 1, this embodiment of the invention is significantly different from the prior art NAND circuit in that the current paths for pulling down output stage BiP transistor base potential and pulling out charge from the load are constituted by independent n-channel MOS transistors M.sub.11 and M.sub.14, respectively, instead of the series n-channel MOS transistors M.sub.21 and M.sub.22 and the series n-channel MOS transistors M.sub.25 and M.sub.26 in the prior art.
[0042] In this embodiment, an input signal A is inputted to the gate of a p-channel MOS transistor M.sub.12 as well as the gate of the n-channel MOS transistor M.sub.11. The source of the p-channel MOS transistor M.sub.12 is connected to a high potential power supply line 3 (at V.sub.cc). A separate input signal B is inputted to the gate of a p-chann...
third embodiment
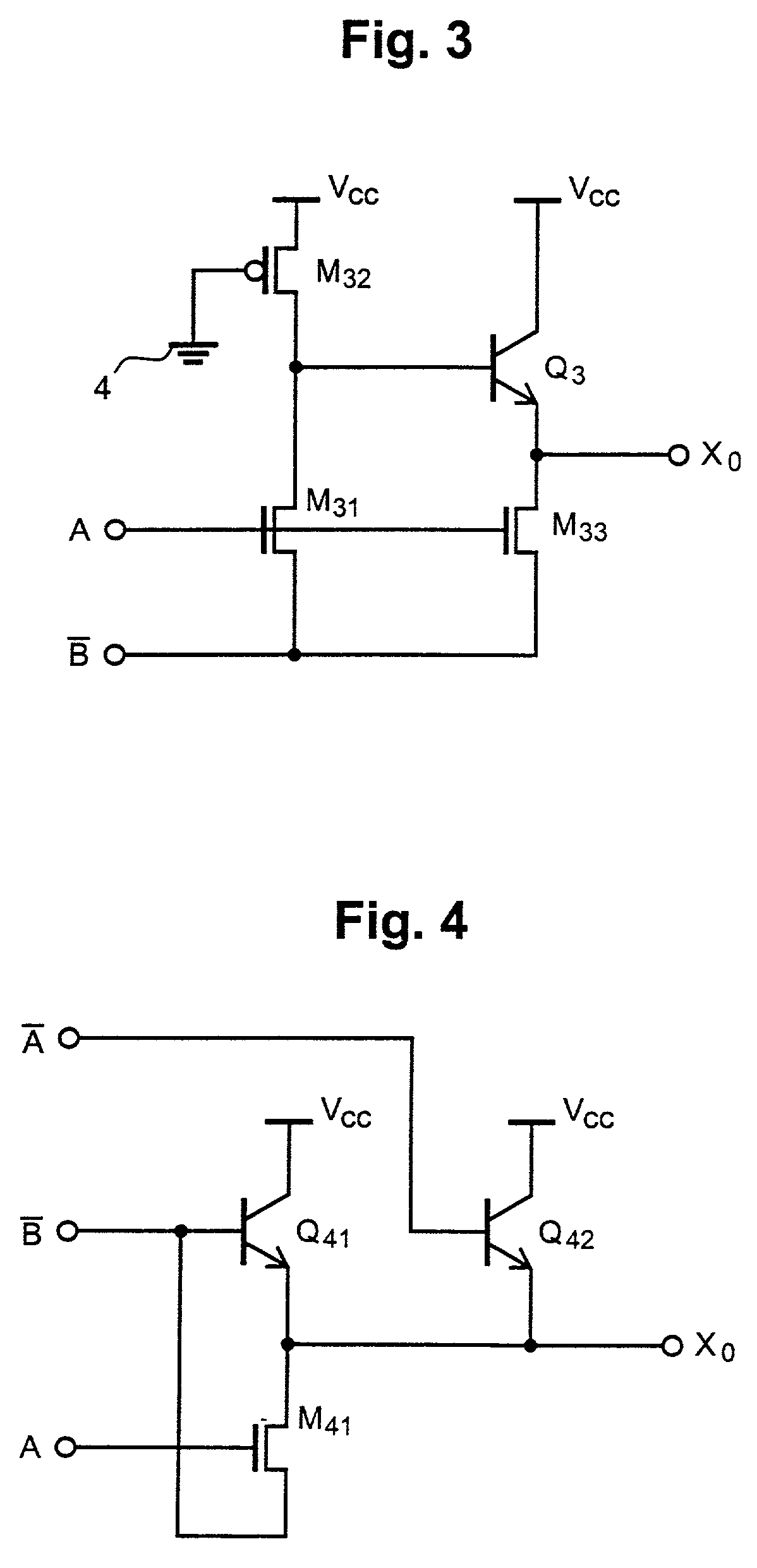
[0053] the invention will now be described with reference to FIG. 4. Referring to the figure, this embodiment is the same as the preceding embodiments in the point wherein the output X.sub.0 is pulled down by using a single n-channel MOS transistor M.sub.41. A feature of this embodiments resides in that the output X.sub.0 is pulled up by using only BiP transistors. The inverse signal .gradient.B which is inputted to the source of the n-channel MOS transistor M.sub.41, is also inputted to the base of the BiP transistor Q.sub.41, and the inverse signal .gradient.A inverse to the signal A is inputted to a base of a BiP transistor Q.sub.42 which is parallel with the transistor Q.sub.41.
[0054] In this embodiment, when the signal A and the inverse signal .gradient.B become "high" and "low", respectively (i.e., A=1, B=1), the n-channel MOS transistor M.sub.41 is turned on. At this time, the inverse signals .gradient.A and .gradient.B both become "low", and the two BiP transistors Q.sub.41 ...
fourth embodiment
[0056] the invention will now be described with reference to FIG. 6. This embodiment is a two-input NOR circuit having the BiCMOS structure. Referring to FIG. 6, the base potential on a BiP transistor Q.sub.6 is pulled down by parallel n-channel MOS transistors M.sub.62 and M.sub.63, to the gates of which input signals A and B are inputted. Transistors M.sub.64 and M.sub.65 are for pulling down an output X.sub.1. For the pull-up of the base potential on the BiP transistor Q.sub.6, a single p-channel MOS transistor M.sub.61 is provided, to the gate and source of which the signal A and the inverse signal .gradient.B are inputted, respectively. In the prior art NOR circuit, this part is constituted by two series p-channel MOS transistors. In such a case, there is a problem in that, when providing the "high" output, the current capacity of the p-channel MOS transistors in the "on" state thereof is low and unable to supply sufficient base current to the transistor Q.sub.6. In other words...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com