High loft low density nonwoven webs of crimped filaments and methods of making same
a technology of crimped filament and nonwoven webs, which is applied in the field of high loft low density nonwoven webs of crimped filament and methods of making same, and achieves the effects of high loft, greater open space and high lo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
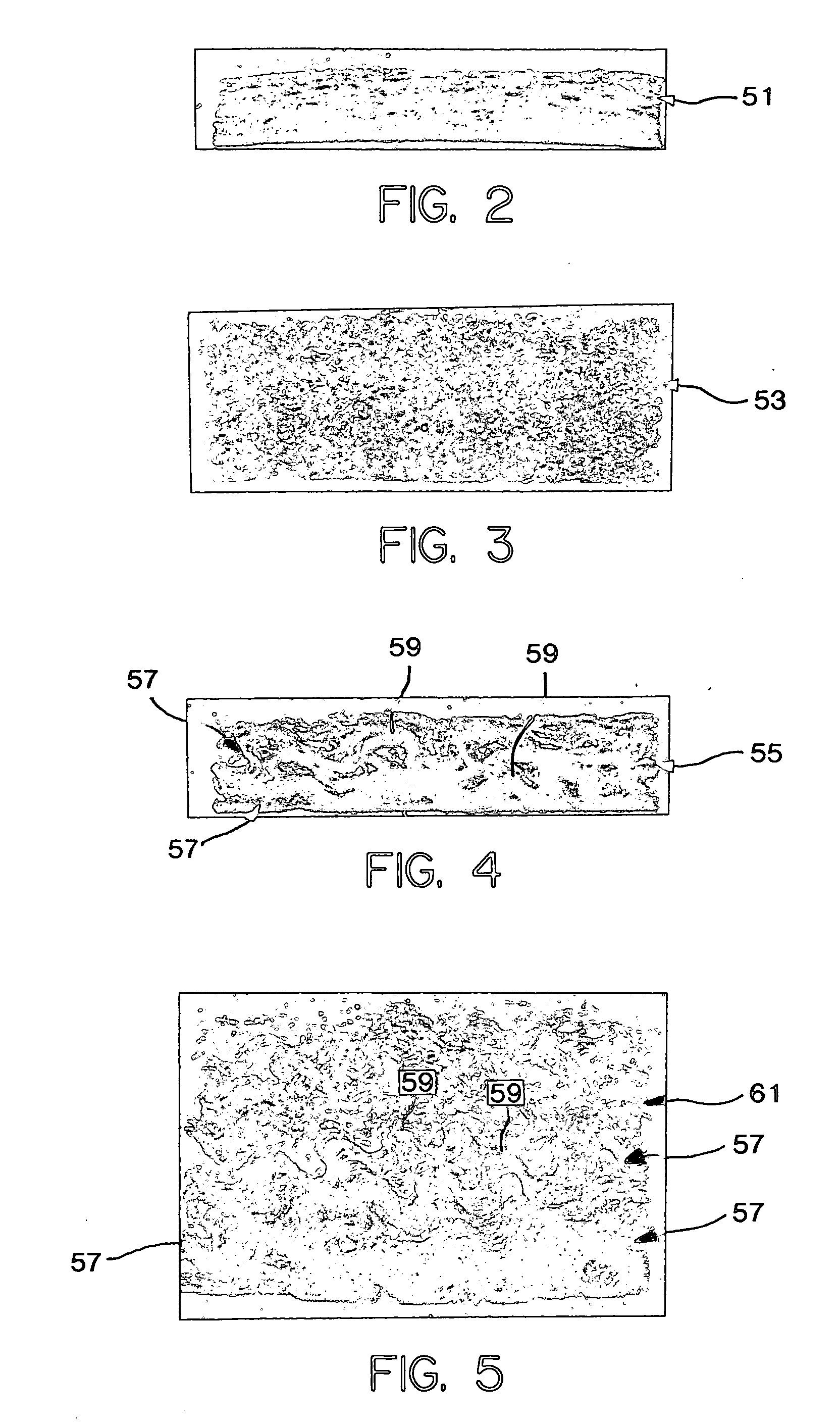
Examples
example 1
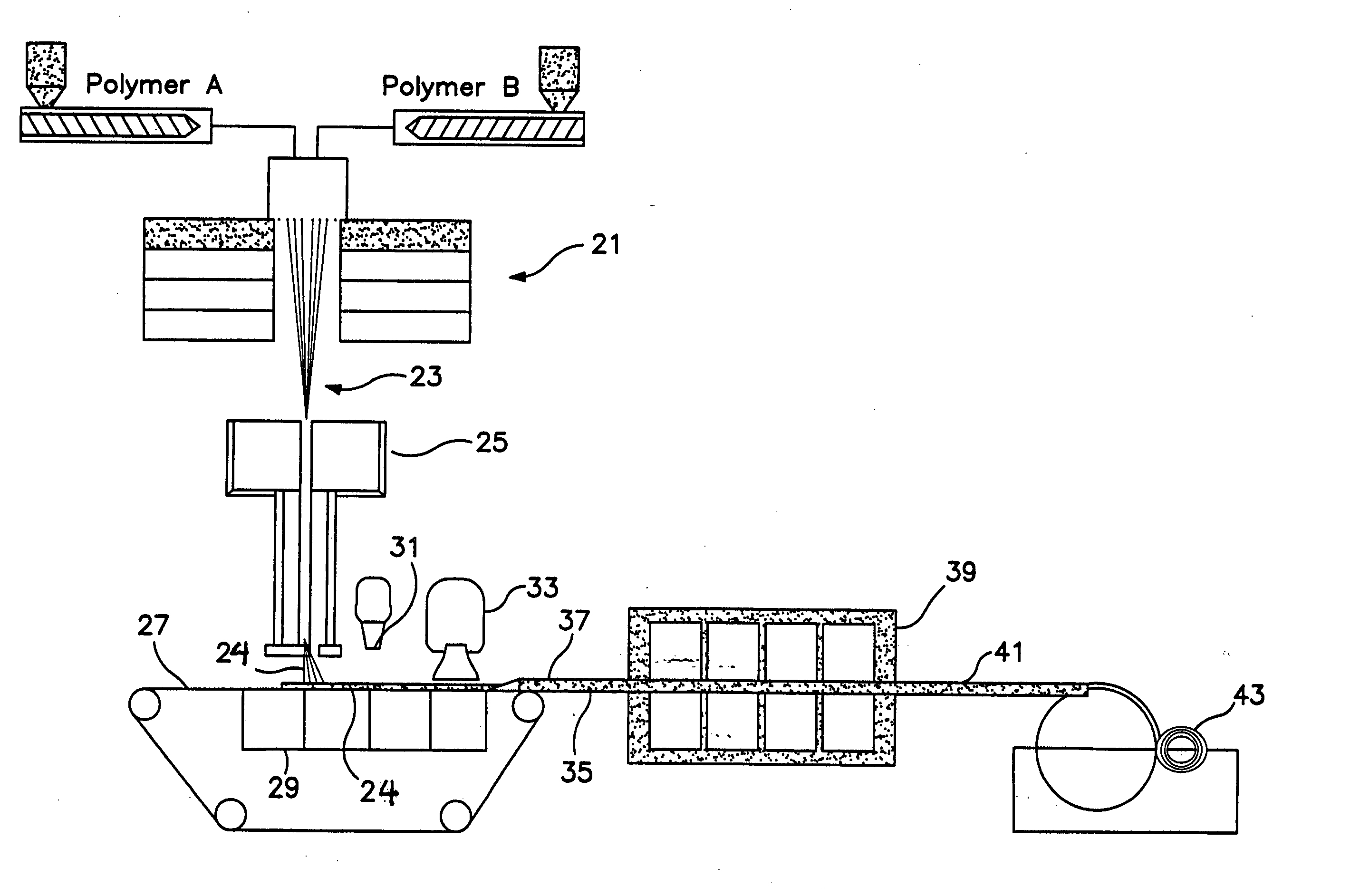
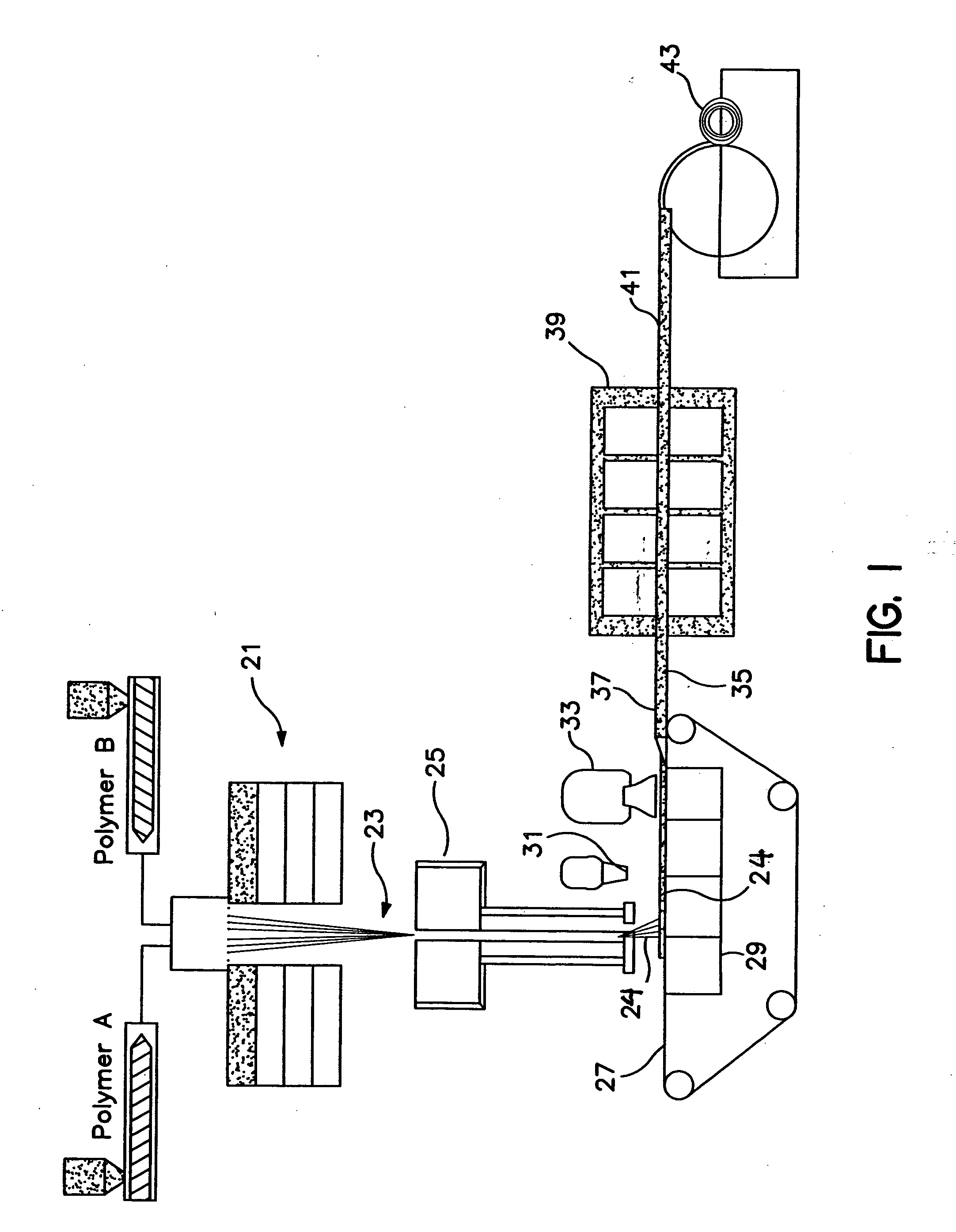
[0094] Example 1, was produced according to the present invention to a basis weight of 202 gsm (5.96 osy), with a bulk of 12.6 mm (0.5 inch) and density of 0.016 g / cc. The average denier was measured to be approximately 3.3 dpf (denier per fiber). The fibers were side by side bicomponent, featuring polymer A of Dow 61800.41 polyethylene (PE) and polymer B of Exxon 3155 polypropylene (PP). A TiO.sub.2 additive from the Standridge Color Corporation, of Social Circle, Ga., tradenamed SCC-4837, was added to the polymer prior to extrusion at 2% by weight to provide white color and opacity to the web. The fibers were spun through a 96 hole per inch (hpi) spinpack, spinning in an A / B side by side (s / s) configuration, at a melt temperature of 410.degree. F.
[0095] Throughput was balanced in a 50 / 50 throughput ratio between the two polymers, with a total throughput of 0.7 grams per hole per minute (ghm). The quench air temperature was 55.degree. F. The fiber spin length was 48 inches. The fib...
example 2
[0097] Example 2, was produced according to the present invention to a basis weight of 79 gsm (2.33 osy), with a bulk of 3.8 mm (0.15 inches) and density of 0.021 g / cc. The average denier was measured to be approximately 3.3 dpf. Polymers and additives were the same as stated for Example 1.
[0098] Fiber and web formation conditions were the same as for Example 1 except the forming wire was moving at 220 ft / min, as measured on the forming wire. The HAK was set at 250.degree. F. and 5.0 inches H.sub.2O of pressure on bank 1, and 240.degree. F. and 3.5 inches H.sub.2O on bank 2, at a height of 5.0 inches above the forming wire. The below wire exhaust under the fiber draw unit was set to vacuum of approximately 1.7 inches H.sub.2O in bank 1, and 3.8 inches H.sub.2O in bank 2.
example 3
[0099] Example 3, was produced according to the present invention to a basis weight of 77 gsm (2.27 osy), with a bulk of 3.3 mm (0.13 inch) and density of 0.023 g / cc. The average denier was measured to be approximately 3.3 dpf.
[0100] Fiber and web formation conditions were the same as for Example 1 except the forming wire was moving at 229 ft / min, as measured on the forming wire. The RAK was set at 250.degree. F. and 5.0 inches H.sub.2O of pressure on bank 1, and 240.degree. F. and 3.5 inches H.sub.2O on bank 2, at a height of 5.0 inches above the forming wire. The below wire exhaust under the fiber draw unit was set to vacuum of approximately 1.6 inches H.sub.2O in bank 1, and 3.8 inches H.sub.2O in bank 2. The web was bonded at approximately 262-269.degree. F. in a through air bonder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| densities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com