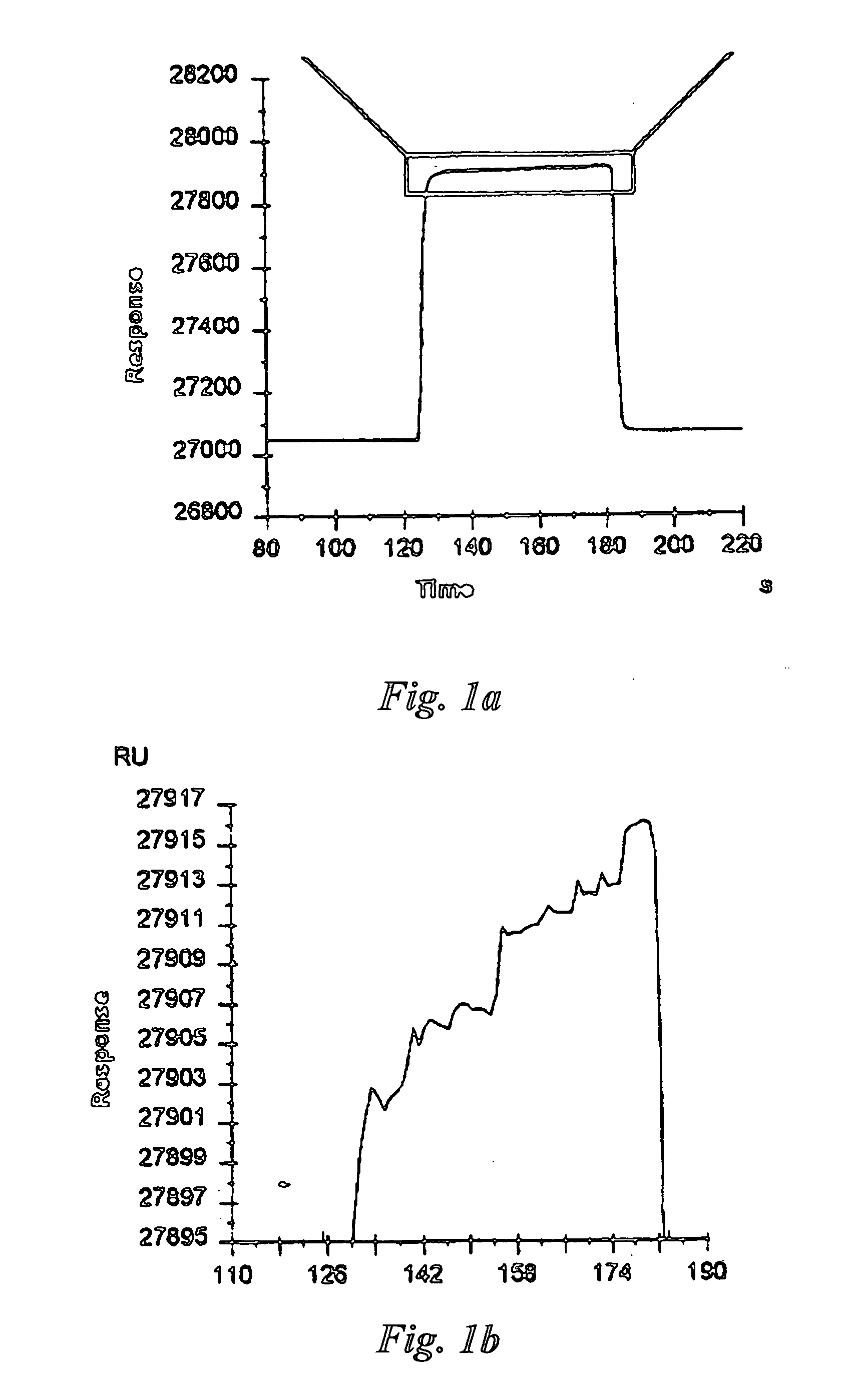
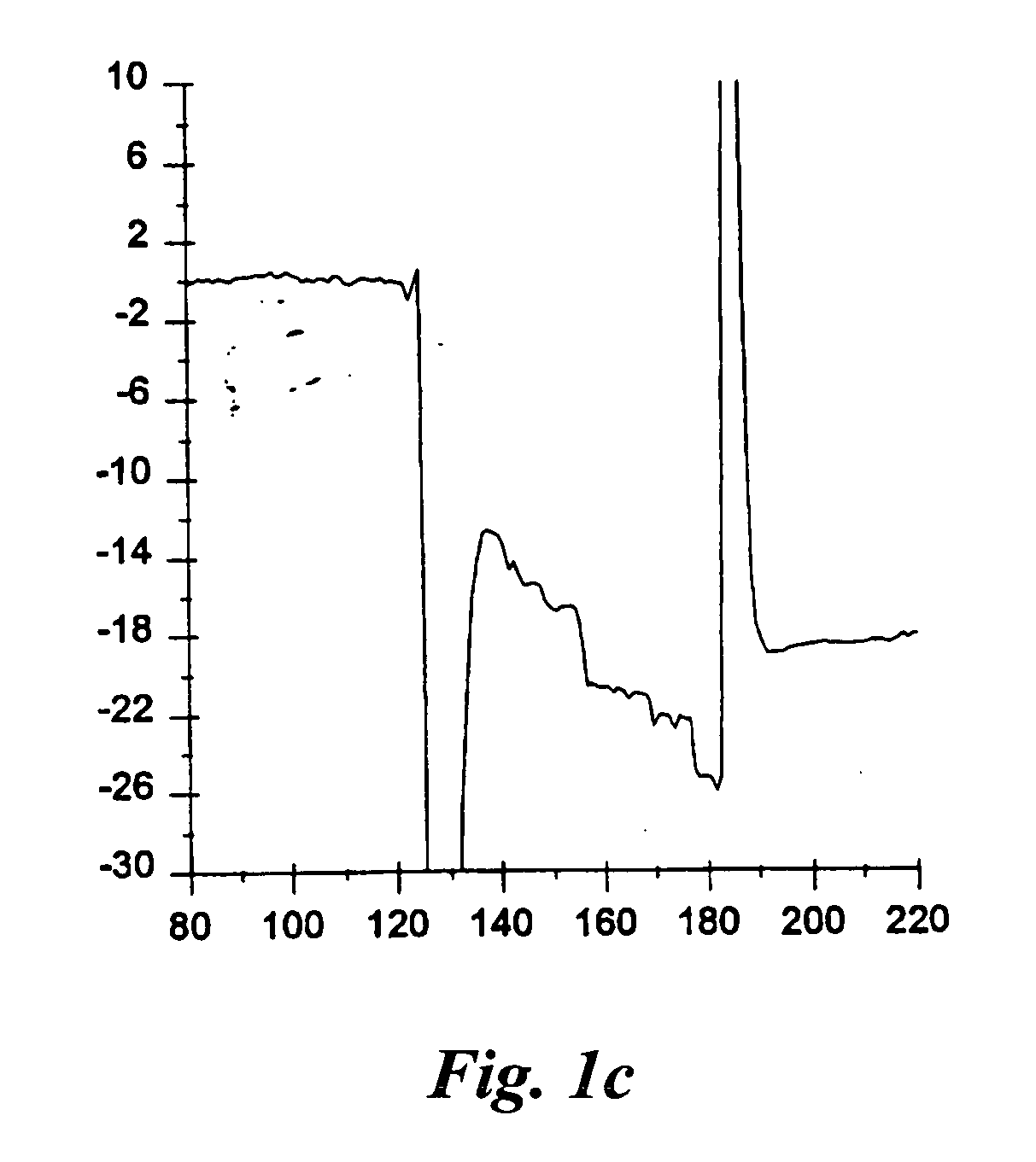
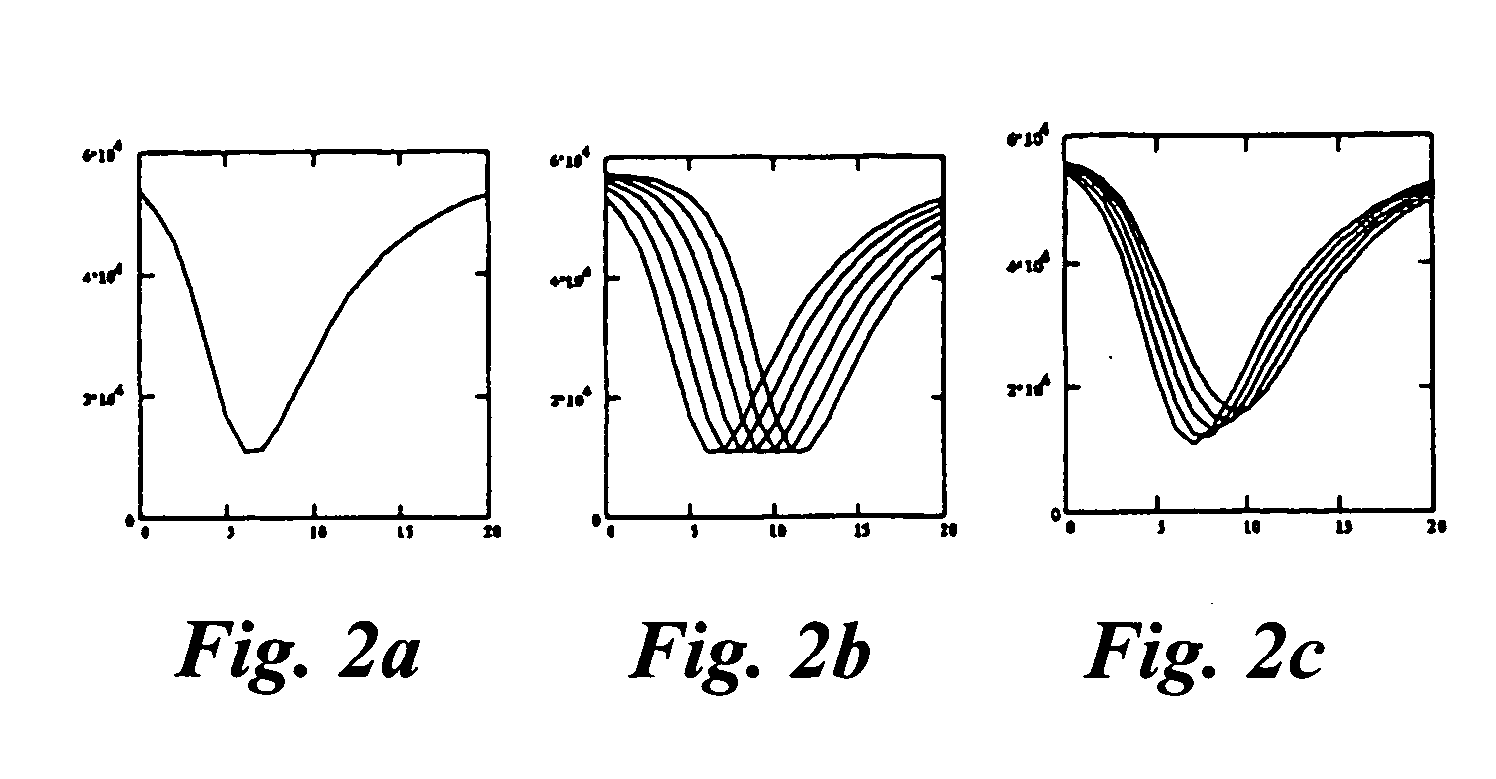Method and apparatus for assaying a drug candidate to estimate a pharmacokinetic parameter associated therewith
a drug candidate and parameter technology, applied in the field of method and apparatus for assaying a drug candidate, can solve the problems of difficult to accurately predict the pharmacological effect of promising new drug candidates, limited number of useful models, and difficult experimentally obtained information to adequately describe such pharmacokinetic physiologic models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Simultaneous Measurement of Solubility, Plasma Protein Binding Lipophilicity and Intestinal Absorption for Three Drug Candidates A-C
This example discloses how combined information from each of four different flow-cells of a biosensor may be represented in a characterization matrix where each of the three drug candidates A-C illustrates a quality pattern (i.e., HSA % Bound, Predicted Lipophilicity, Solubility, and Predicted FA %) which is useful for the selection of lead drug compounds.
Preparation of Sensor Chip
Three of the four discrete sensing surfaces of a CM5 Sensor Chip (Biacore AB, Uppsala, Sweden) were modified such that the CM5 Sensor Chip had surface-bound biomolecules as depicted below in Table 1.
TABLE 1SURFACE-BOUND BIOMOLECULES OF CM5 SENSOR CHIPType ofSurface / Cell No.Flow-CellSurface ModificationFC1Ref-1Unmodified carboxymethyl dextran (CM5)FC2Target-1Human Serum albumin - HSA (9-12 kRU)FC3Target-2DMPC-liposomes (5-7 kRU) captured onstearylamineFC4Target-3POPC-li...
example 2
Demonstrated Correlation Between Biosensor Data and Fraction Absorbed in Humans (FA %)
This example discloses a correlation between biosensor data obtained form the BIACORE instrument (i.e., BIACORE 3000) and known data for the fraction absorbed in humans (FA %) for a number of different drugs, wherein the correlation graph is useful for drug candidate absorption predictions. More specifically, a correlation graph as shown in FIG. 7 was constructed having known fraction absorbed in humans (FA %) plotted along the ordinate (i.e., the y-axis) and corresponding calibrated (i.e., reference subtracted) steady state binding levels for each drug at 500 μM plotted along the abscissa in a 10-logarithm scale (i.e., the x-axis). In this example, the sensing surfaces of the target flow-cells each had 6,000 RU of POPC-GM3 ganglioside (available from Sigma) captured on stearylamine tiles. (Note that an unmodified sensing surface of a CM5 Sensor Chip was used as the reference.) As shown in FIG. 7...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface plasmon resonance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com