Extended retention and medium consistency pulp treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
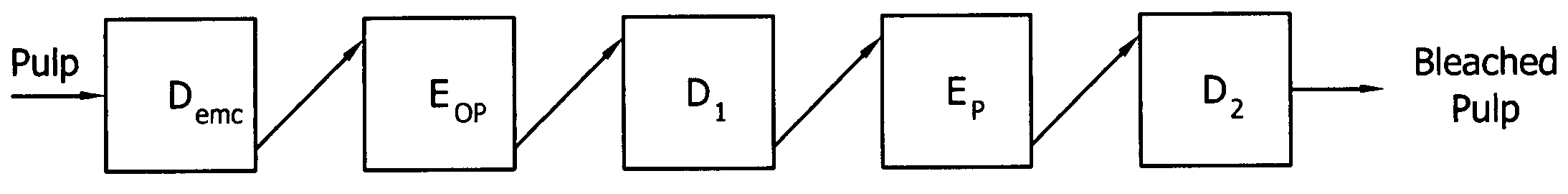
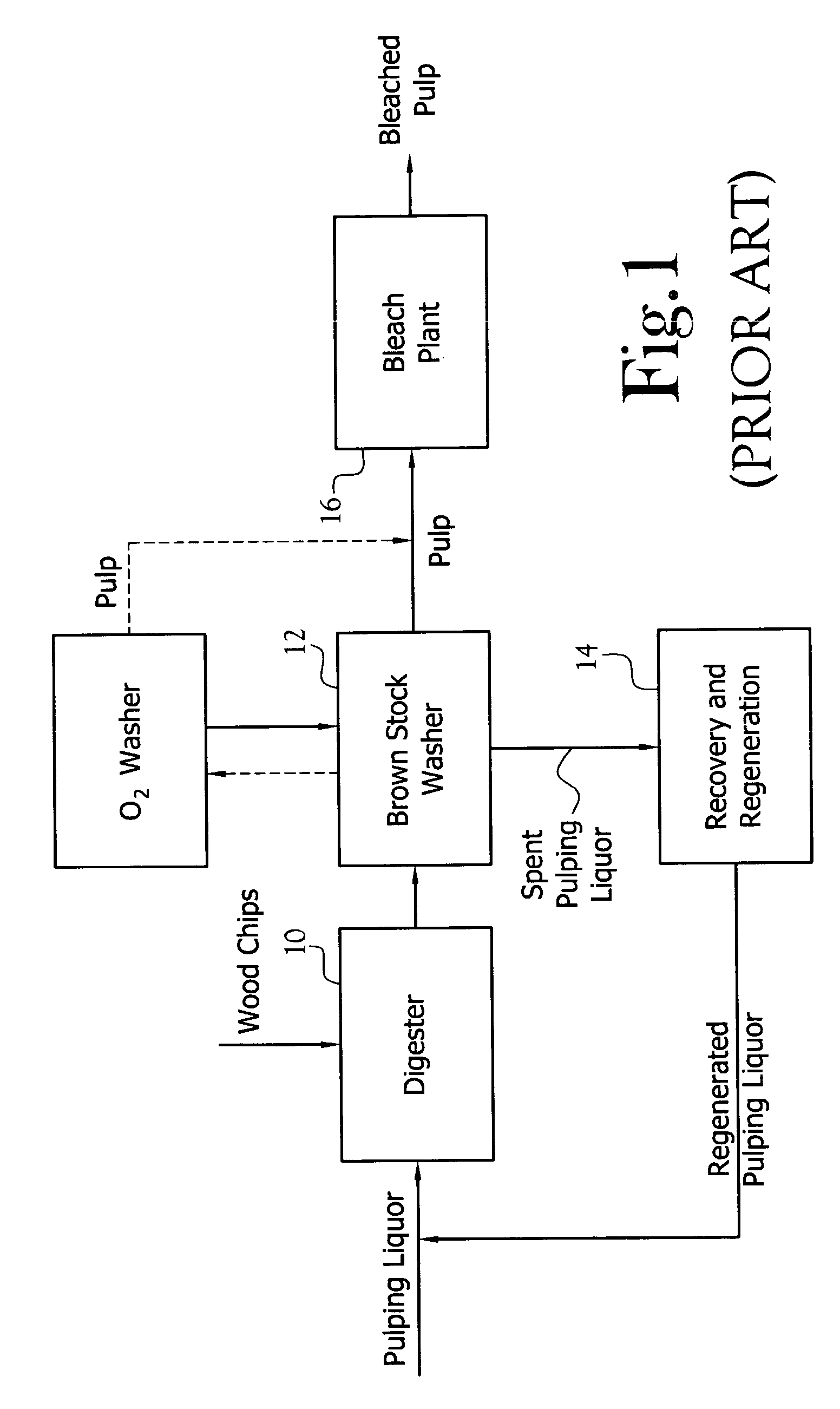
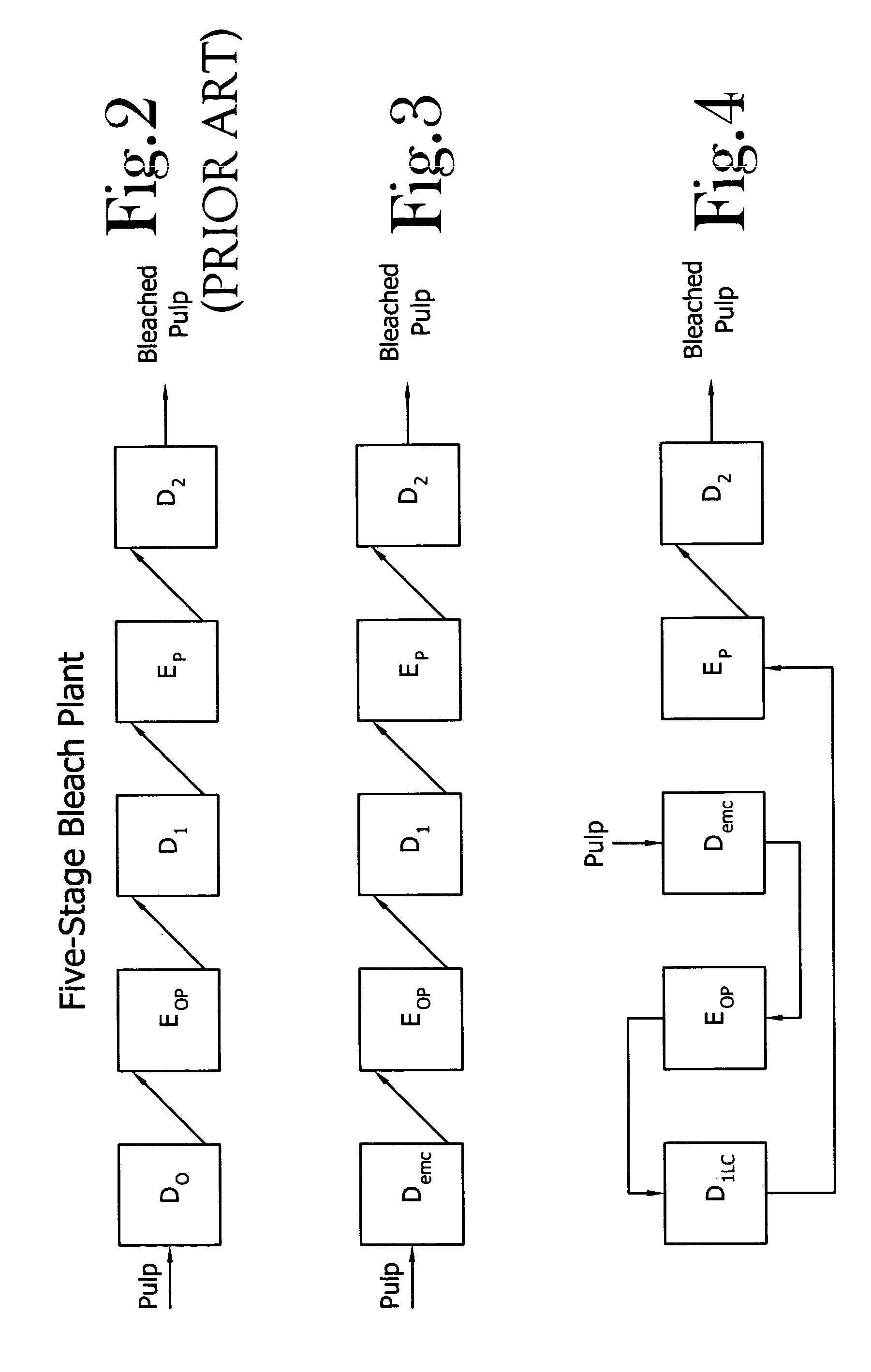
[0056]FIG. 3 schematically depicts a modification to the bleaching plant depicted in FIG. 2 wherein the current Do stage is converted to the Demc stage with the remaining bleaching plant unchanged.
second embodiment
[0057]FIG. 4 depicts a modification to the bleaching plant depicted in FIG. 2 wherein the functions of the current Do and D1 stages are swapped. The D1 stage is converted to a Demc stage, and the Do stage is left in place, but converted to a D1LC stage. In this embodiment, the pulp initially enters the Demc stage, flows through the Eop stage, through the D1LC stage, through the EP stage, through the D2 stage and is stored.
third embodiment
[0058]FIG. 5 depicts a modification to the bleaching plant depicted in FIG. 2 within the Do stage is eliminated, the Ep stage is converted to a P stage, the D2 stage is converted to a Demc stage, and the output from the DEMC stage is piped to the Eop stage. Basically this conversion involves little more than piping modifications.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com