Catoptric and catadioptric imaging system with pellicle and aperture-array beam-splitters and non-adaptive and adaptive catoptric surfaces
a technology of pellicle aperture and aperture array, applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, instruments, interferometers, etc., can solve the problem of introducing the possibility of non-common path phase error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
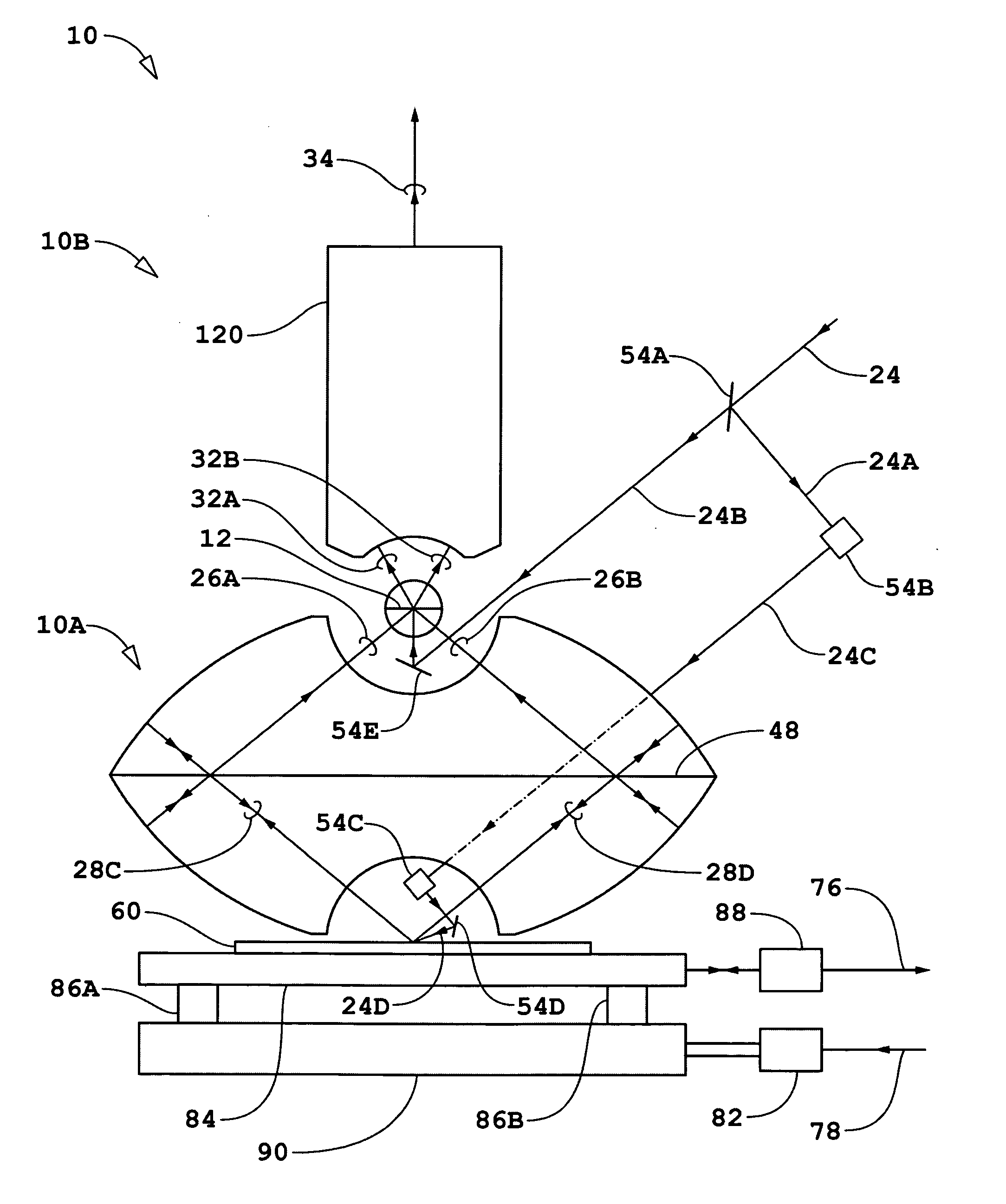
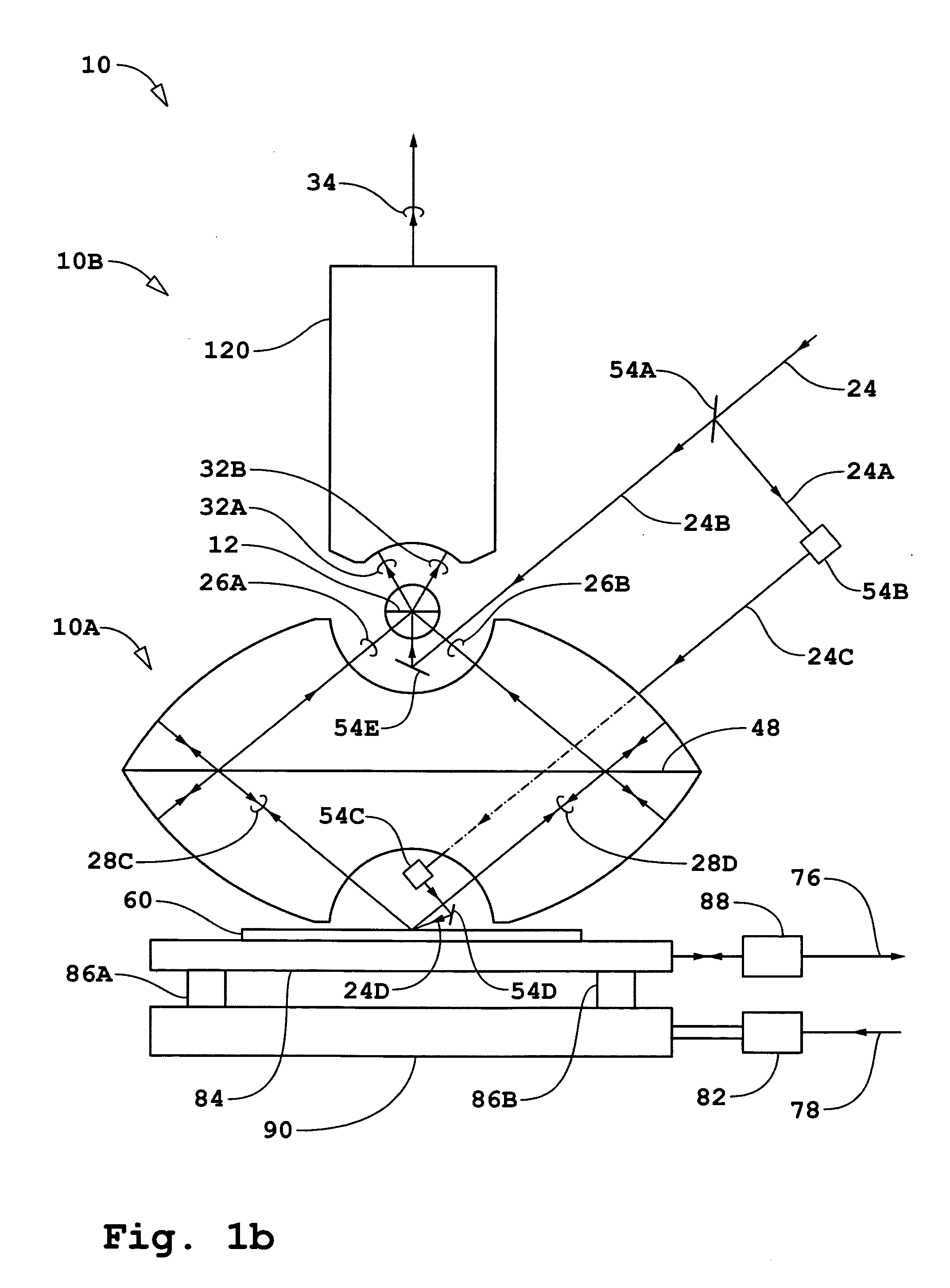
[0102] Adaptive reflecting surfaces 42A-1, 42A-2, 42A-3, 42C-1, 42C-2, and 42C-3 and adaptive reflecting surfaces 46A-1, 46A-2, 46C-1, and 46C-2 shown in FIG. 1c may each be representative of annular rings or of sections of annular rings. The remaining description of the first embodiment will be based on the simple configuration wherein there are no additional reflecting surfaces beyond those described as a non-limiting example without departing from the scope and spirit of the present invention. The number of corresponding adaptive reflecting surfaces defines of the values of N that may be used in the N-dimensional bi- and quad-homodyne detection methods. In the non-limiting example of the simple configuration shown in FIG. 1c, the maximum value for N is 6.
[0103] Referring to FIG. 1d, the locations and orientations of adaptive reflecting surfaces are controlled by transducers according to servo control signal 98 from servo controller 96. For each of the adaptive reflective surfaces...
third embodiment
[0184] The location of the object plane of catadioptric imaging system 210A may also be on the plane surface of piano convex lens 258. In this case, the measurement beam can be arranged to probe substrate 60 as an evanescent field when h is of the order of λ / 4. The third embodiment can change rapidly from using the evanescent field as a probe beam to using the non-evanescent fields as a probe beam by use of the high speed vertical scan feature of the present invention.
[0185] The fourth embodiment of the present invention comprises interferometer 10 and catadioptric imaging system 210A of the third embodiment except that thin film fluorescent layer 12 is replaced by a pinhole array beam-splitter 12 the same as in the second embodiment shown schematically in FIG. 1f. Pinhole array beam-splitter 12 is used as the beam-splitter for generating the reference and measurement beams and for the function of combining the reference and measurement beam reflected / scattered by substrate 60. The ...
fifth embodiment
[0191] Referring to FIG. 3b, mirror system 354B redirects and displaces measurement beam 324A such that measurement beam 324C is propagating in a plane displaced out of the plane of FIG. 3b. Mirror system 354C displaces measurement beam 324C such that the transmitted measurement beam subsequently reflected by mirror 354D propagates in the plane of FIG. 3b. The remaining description of the present invention is the same as corresponding descriptions given for the first four embodiments of the present invention and corresponding descriptions given for embodiments given in cited U.S. Pat. No. 6,552,852 (ZI-38) and No. 10 / 366,651 (ZI-43); U.S. Provisional Patent Applications No. 60 / 447,254 (ZI-40), No. 60 / 448,360 (ZI-41), No. 60 / 448,250 (ZI-42), No. 60 / 442,982 (ZI-45), No. 60 / 459,425 (ZI-50), No. 60 / 485,255 (ZI-53), filed Jul. 7, 2003 (ZI-52) and entitled “Apparatus and Method for High Speed Scan for Subwavelength Defects in Semiconductor Metrology,” and filed Sep. 10, 2003 (ZI-54) entit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com