Electrolytic plating method and device for a wiring board
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
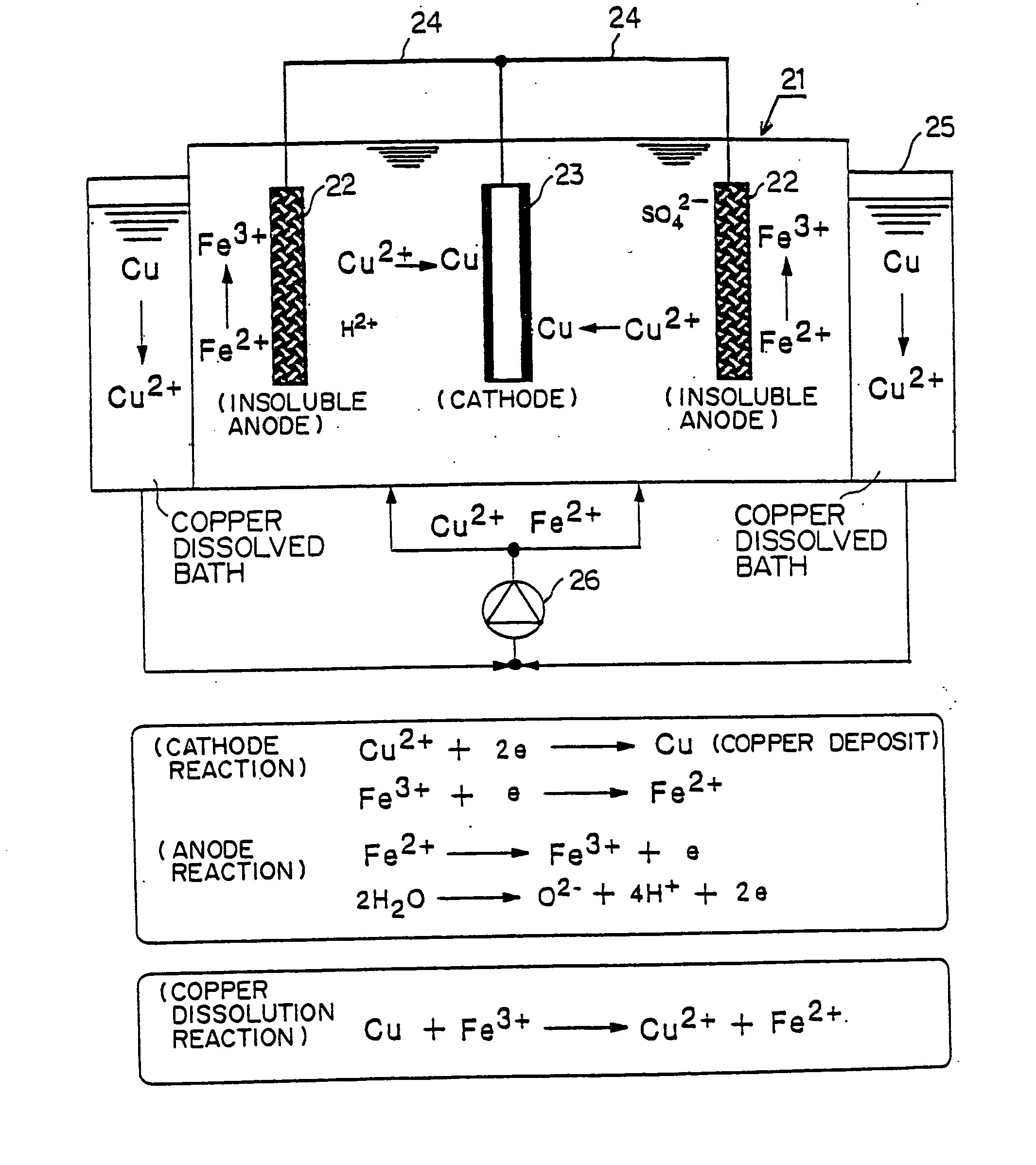
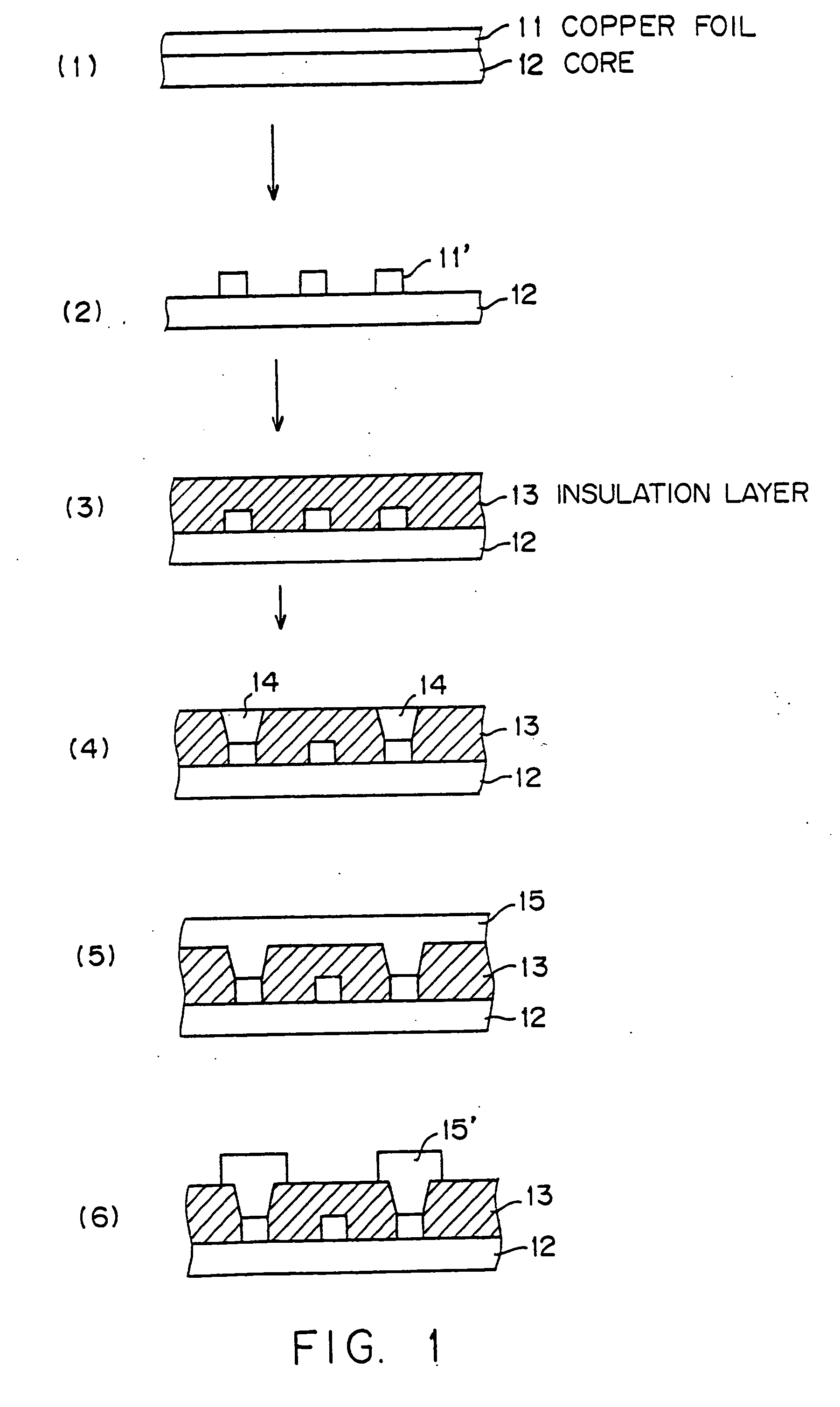
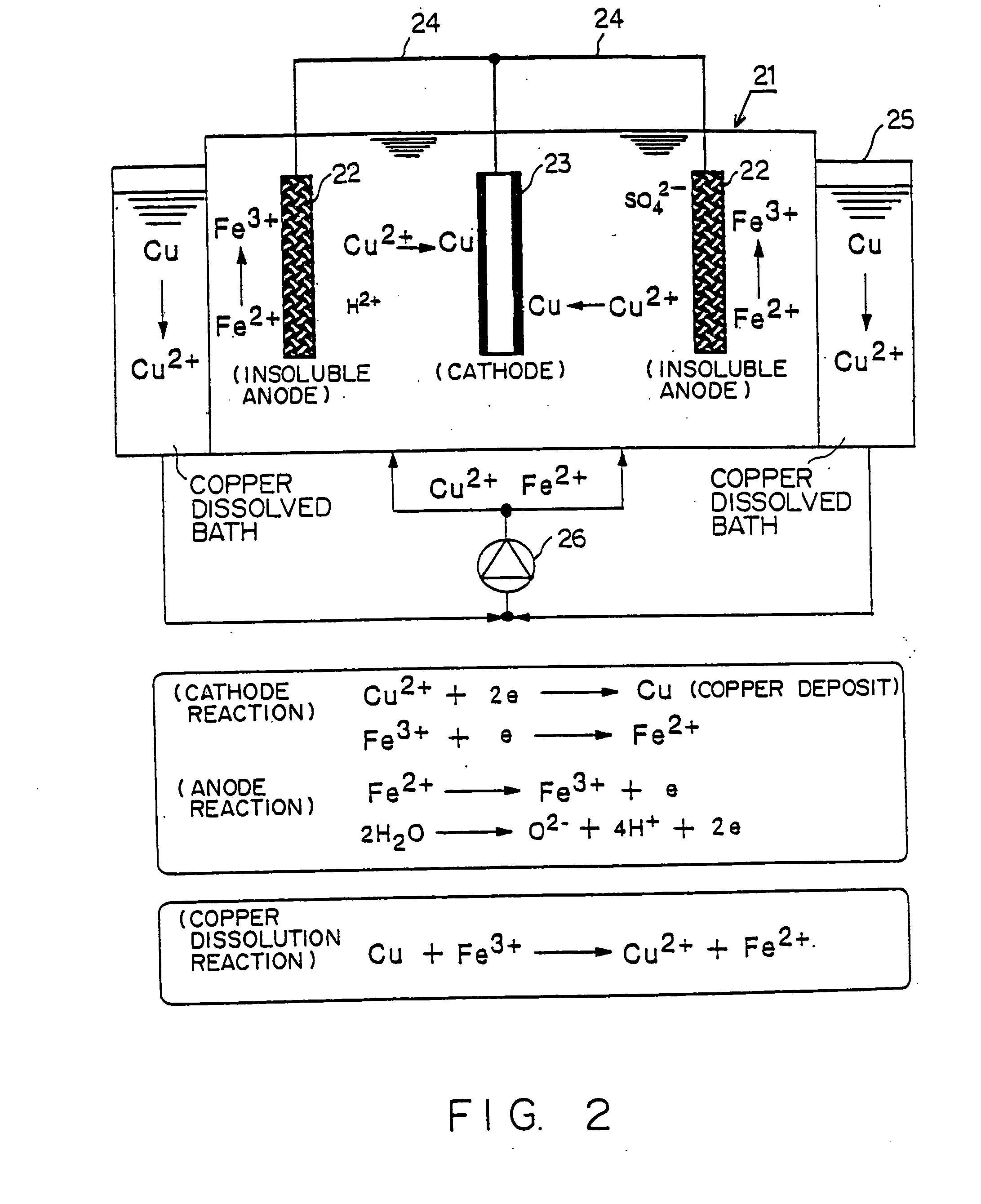
[0025] Hereinafter, a preferred embodiment according to the present invention will be described by referencing drawings. First of all, the manufacturing process of a multi-layer printed-circuit board is explained by referencing FIG. 1.
[0026] A wiring pattern (wiring layer) 11′ is formed by etching a copper foil (conductor layer) stacked onto a core resin 12 such as glass epoxy, etc. (process steps (1) and (2) in FIG. 1). Next, an insulation layer 13 is formed on the wiring pattern (process step (3) in FIG. 1). Holes are drilled in the insulation layer 13 with laser, etc., so that microvia holes 14 are formed (process step (4) in FIG. 1). Next, a copper plated layer 15 is formed with electrolytic plating, etc. to fill up the microvia holes (process step (5) in FIG. 1). In the plating process step (5) in FIG. 1, after a thin conductor layer is formed with chemical plating, etc. on the wiring pattern 11′ at the bottom of the insulation layer 13 and the microvia holes 14, the microvia ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com