Methods for acquiring and processing seismic data from quasi-simultaneously activated translating energy sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
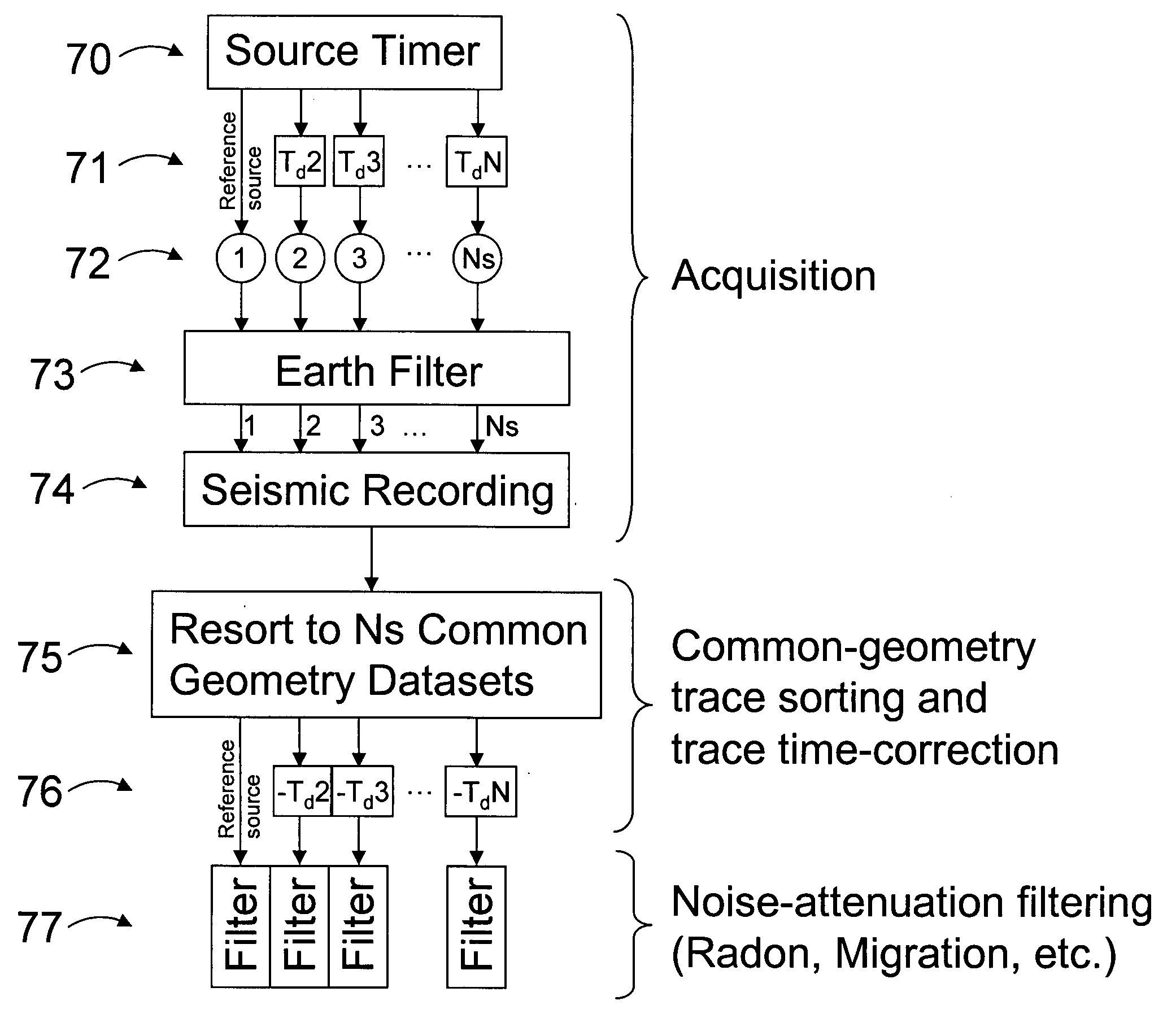
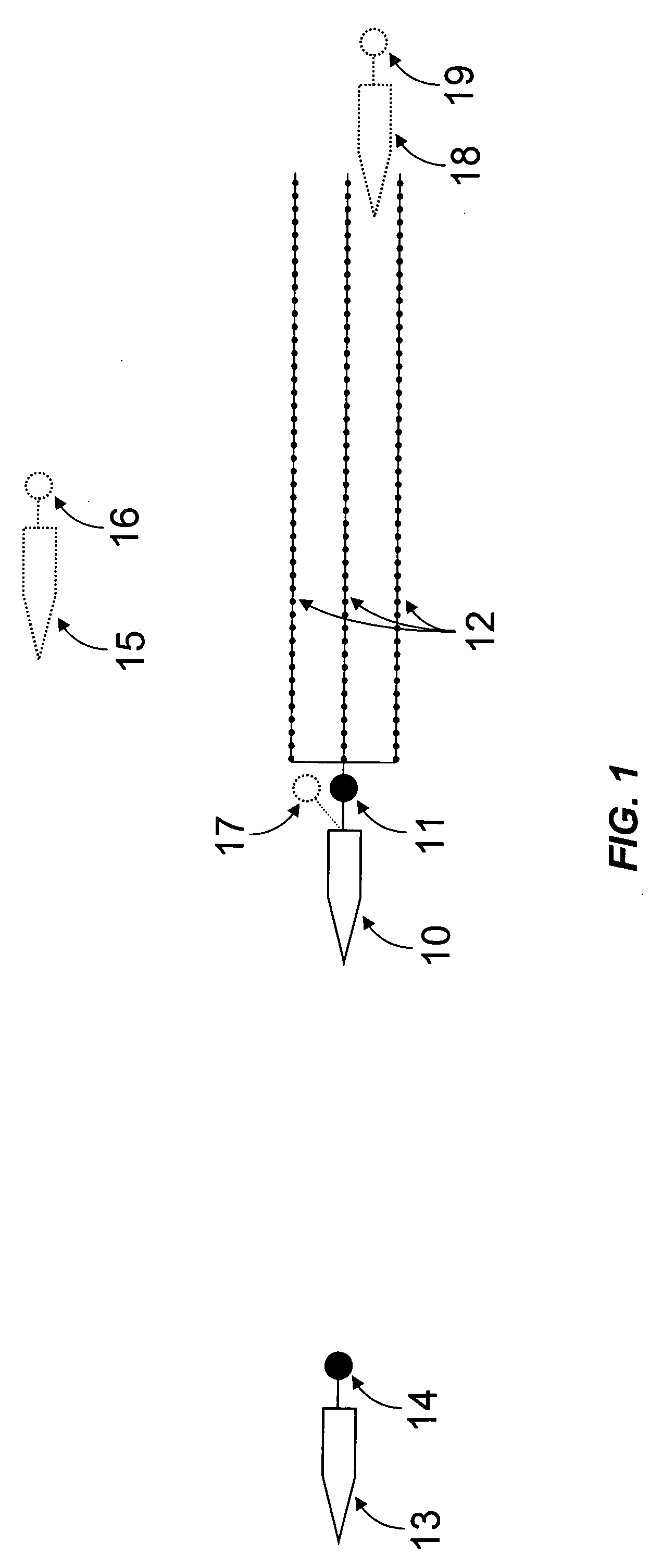
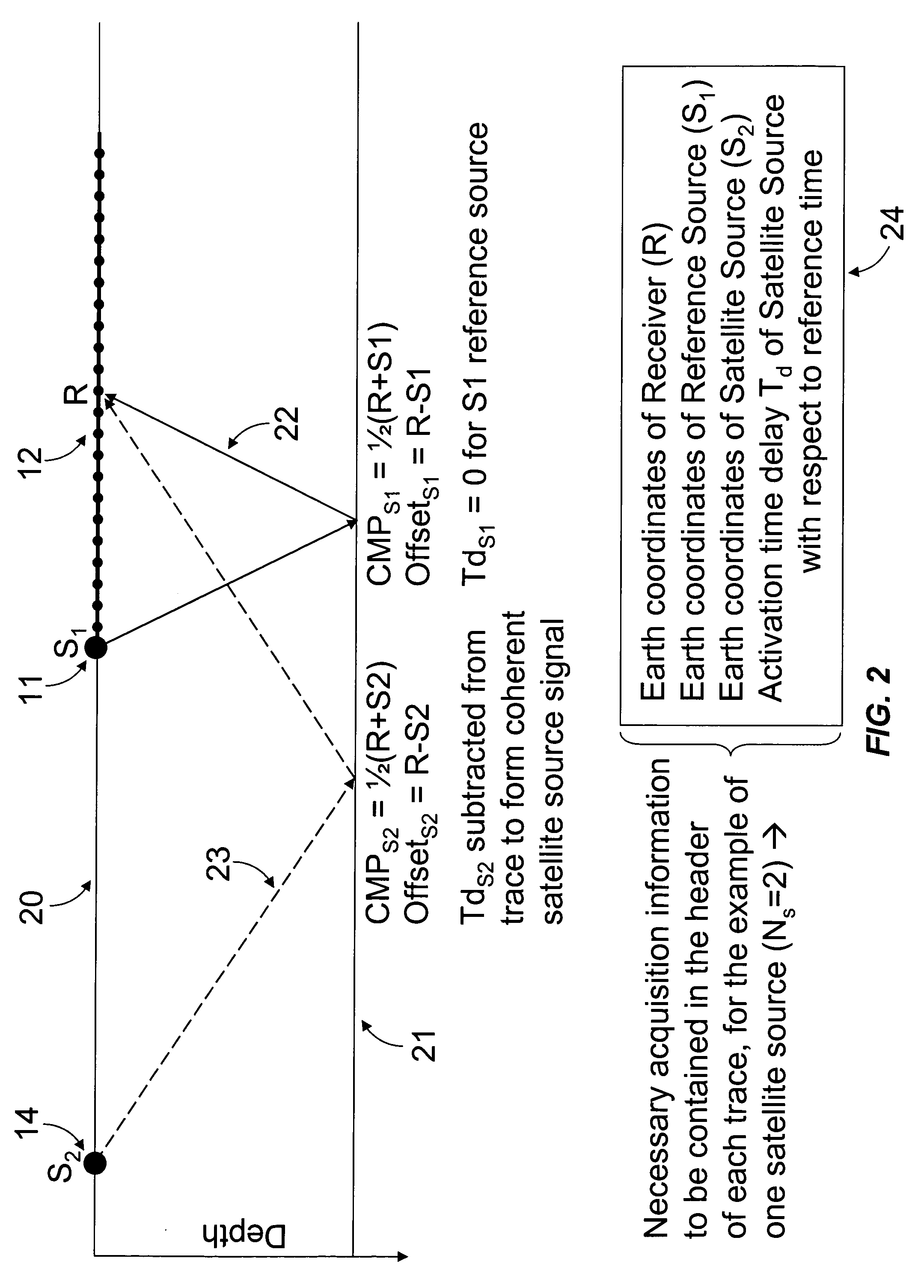
[0021] This invention teaches a method for the acquisition of seismic data using quasi-simultaneous sources, as well as the processing of the superposed signals in order to separate the energy due to each source from the energy due to every other source in the constellation. For the purposes of this invention, the term “constellation” shall mean the set of spaced apart seismic sources bearing any relative spatial relationship among themselves, and able to move as a whole from one location to another as part of a seismic survey.
[0022] Quasi-simultaneous acquisition and its associated processing as described herein enable high quality seismic data to be acquired at a much greater operational efficiency as compared to a conventional seismic survey. The term “quasi-simultaneous” shall mean that the activation-time differences among the several sources in a constellation are not zero (thus the prefix “quasi”), but yet small enough (typically less than several seconds) so as not to inter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com