Adhesive-containing wound closure device and method
a wound closure and adhesive technology, applied in the field of medical and surgical wound closure and management, can solve the problems of additional pain and trauma to the patient, cosmetically unattractive wound closure marks, and additional trauma to the wound, so as to improve wound approximation, improve wound closure, and improve wound approximation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0137] A patient is presented having a one inch cut on the arm. The cut does not extend fully through the dermal layers of the skin.
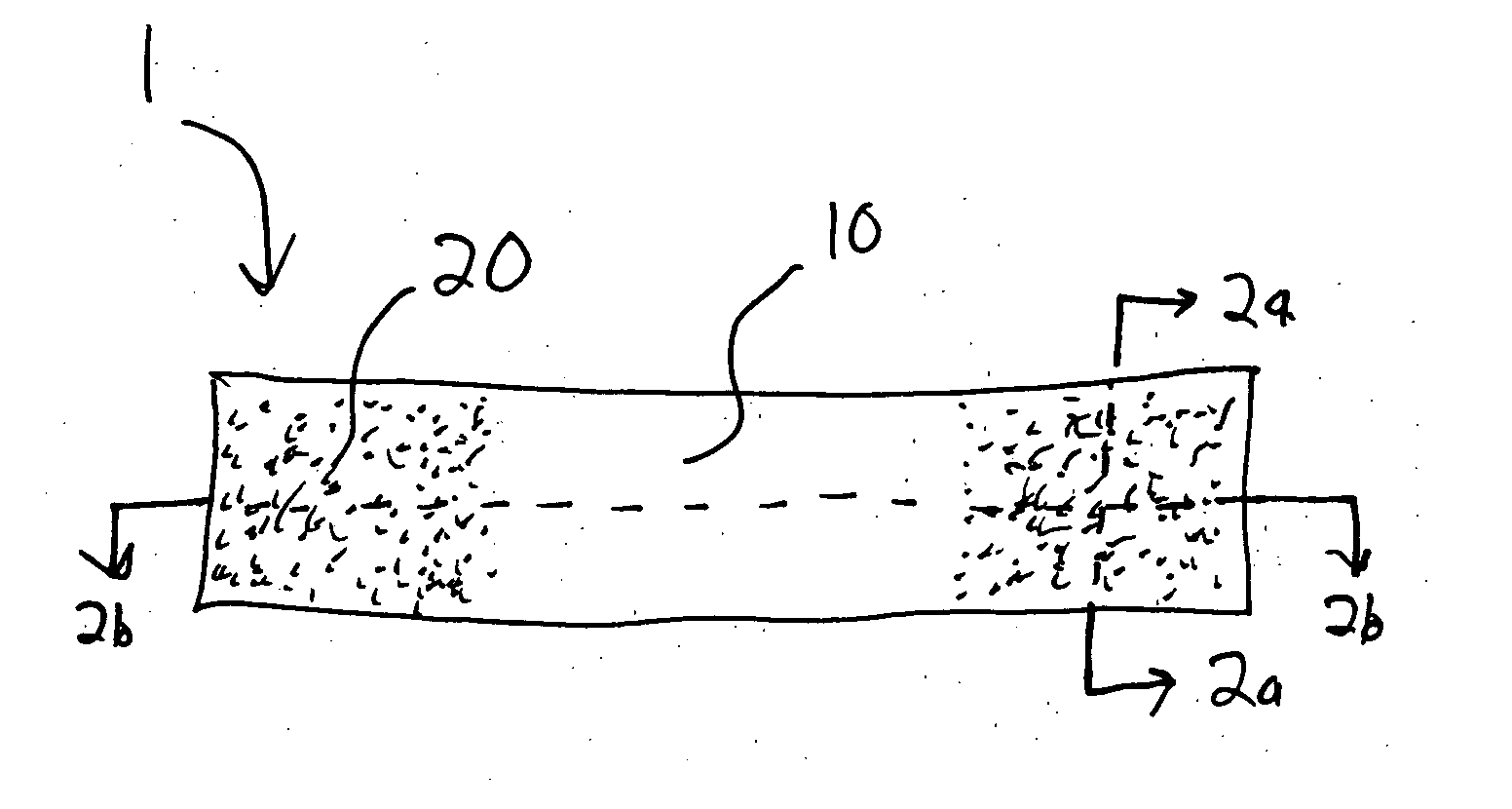
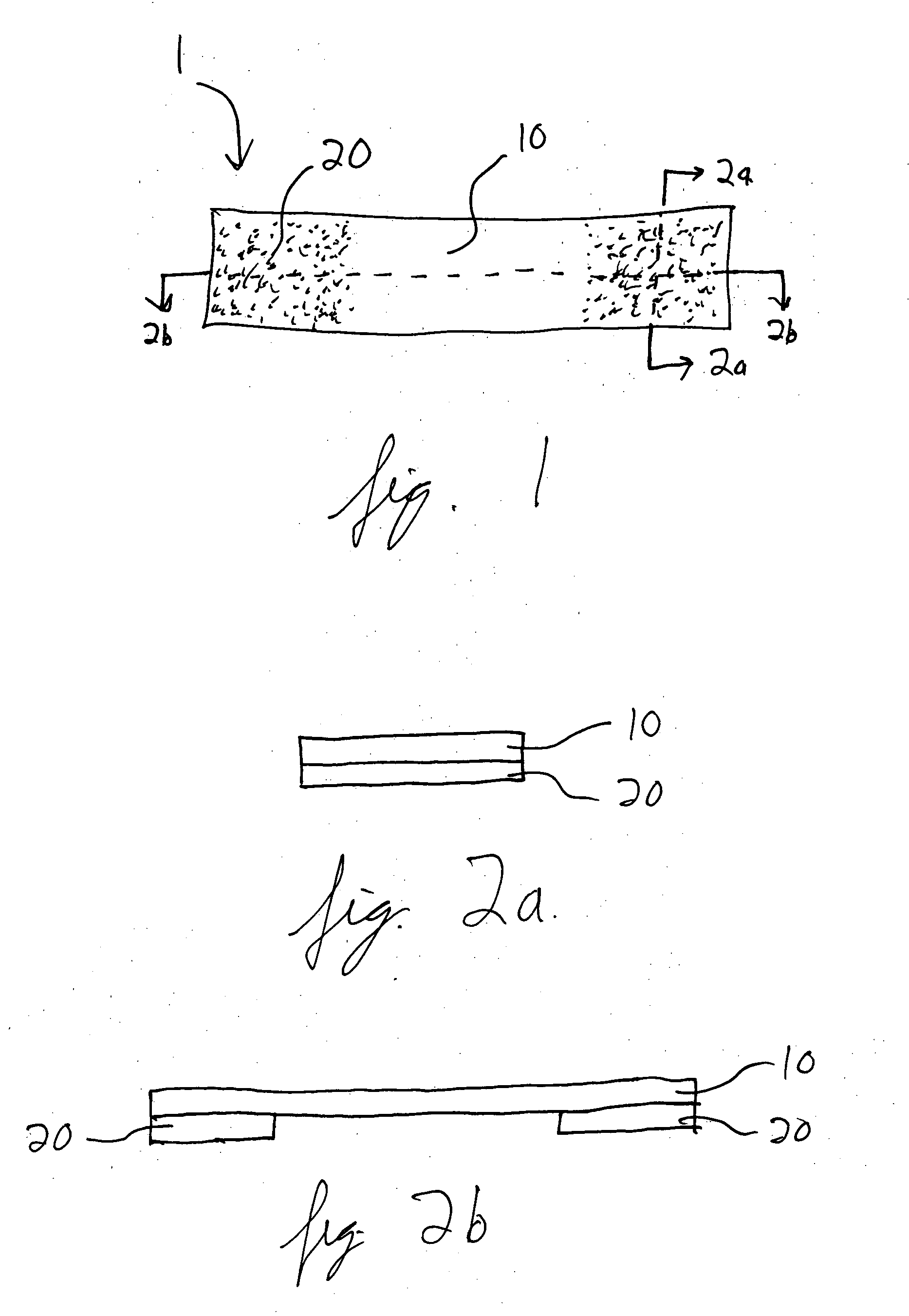
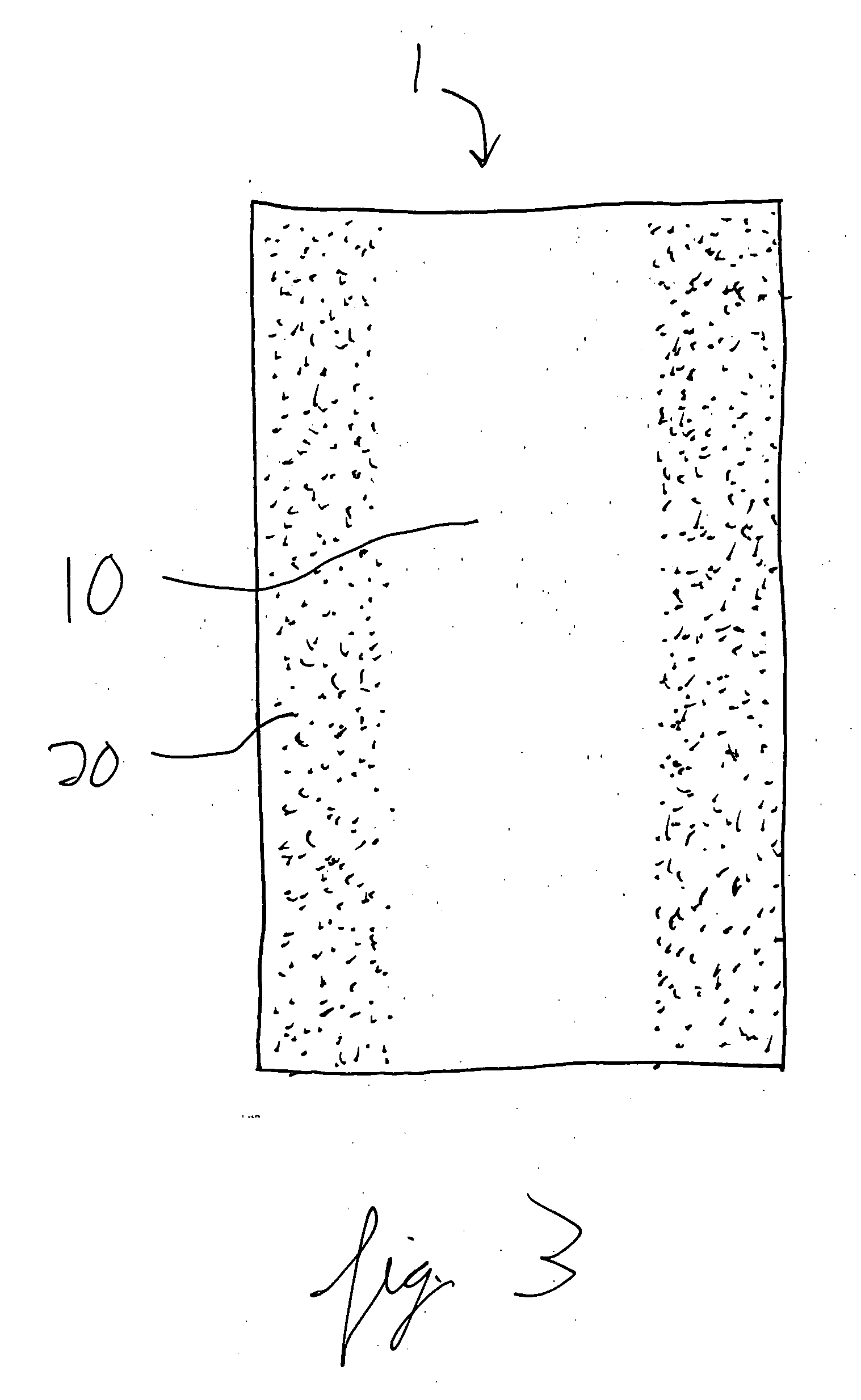
[0138] Following suitable washing, disinfecting and drying of the area around the cut, a 2-inch length of the prepared flexible substrate is applied to the wound site. The flexible substrate is applied by first removing one of the two release strip papers and affixing the pressure sensitive adhesive edge to one side of the cut, about 7 / 8 inch from the edge of the cut. The second release strip paper is then removed from the flexible substrate. After approximating the wound edges using slight pressure applied by two fingers, the remaining pressure sensitive adhesive edge of the flexible substrate is applied to the other side of the cut, about 7 / 8 inch from the edge of the cut. The flexible substrate extends about ½ inch beyond each end of the wound.
[0139] A quantity of a stabilized 2-octyl cyanoacrylate adhesive is applied to the exposed surface of the ...
example 2
[0141] A patient is presented having a four inch cut on the leg. The cut extends fully through the dermal layers of the skin.
[0142] Following suitable washing, disinfecting and drying of the area around the cut, subcutaneous dissolvable sutures are used to approximate and close the subcutaneous layers in the wound. Next, a 5-inch length of the prepared flexible substrate is applied to the wound site. The flexible substrate is applied by first removing one of the two release strip papers and affixing the pressure sensitive adhesive edge to one side of the cut, about 7 / 8 inch from the edge of the cut. The second release strip paper is then removed from the flexible substrate. After approximating the wound edges using slight pressure applied by the hands, the remaining pressure sensitive adhesive edge of the flexible substrate is applied to the other side of the cut, about 7 / 8 inch from the edge of the cut. The flexible substrate extends about ½ inch beyond each end of the wound.
[014...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com