Method and device for handling cellulose pulp
a technology of cellulose pulp and cellulose pulp, which is applied in the direction of pulp beating/refining methods, machine wet ends, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of high degree of dryness, inability to achieve a higher degree of consistency, and significant higher cost of other materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
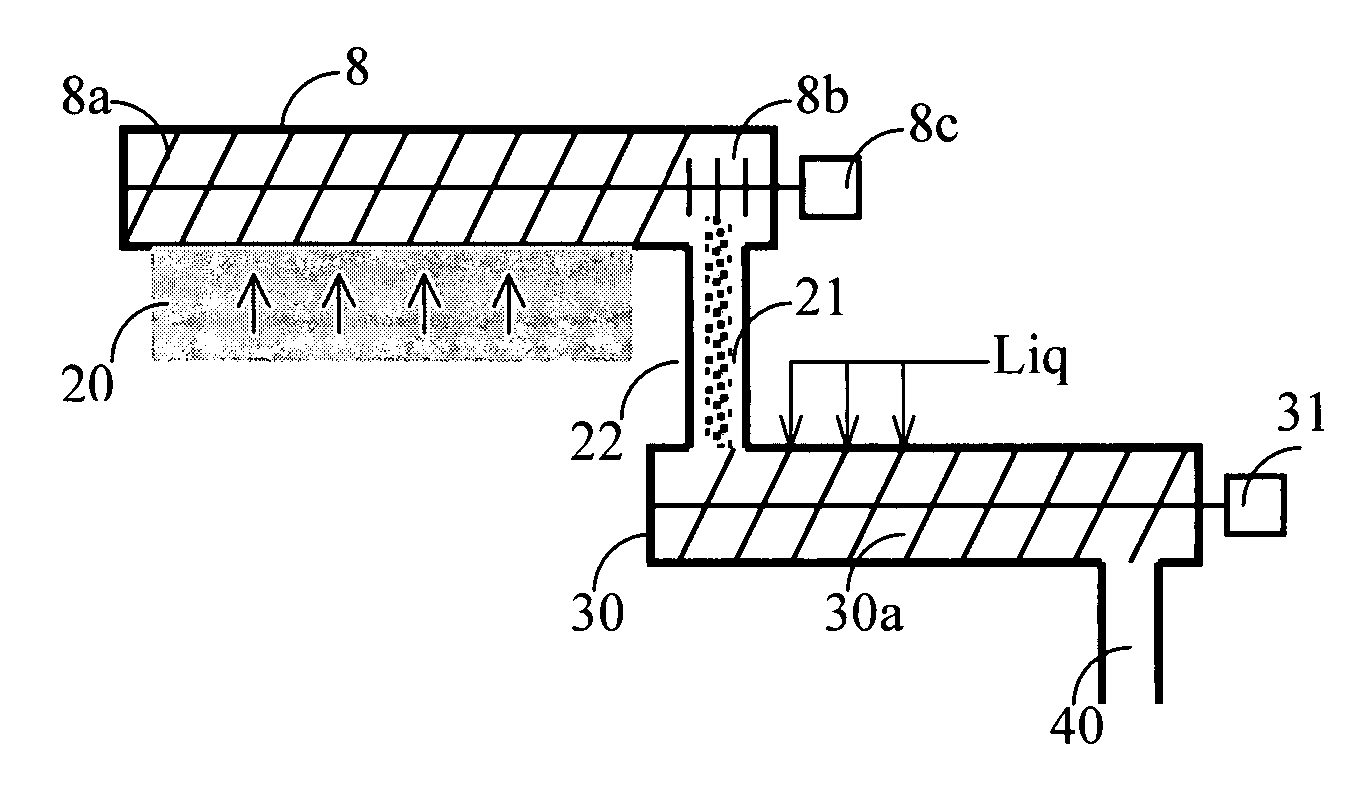
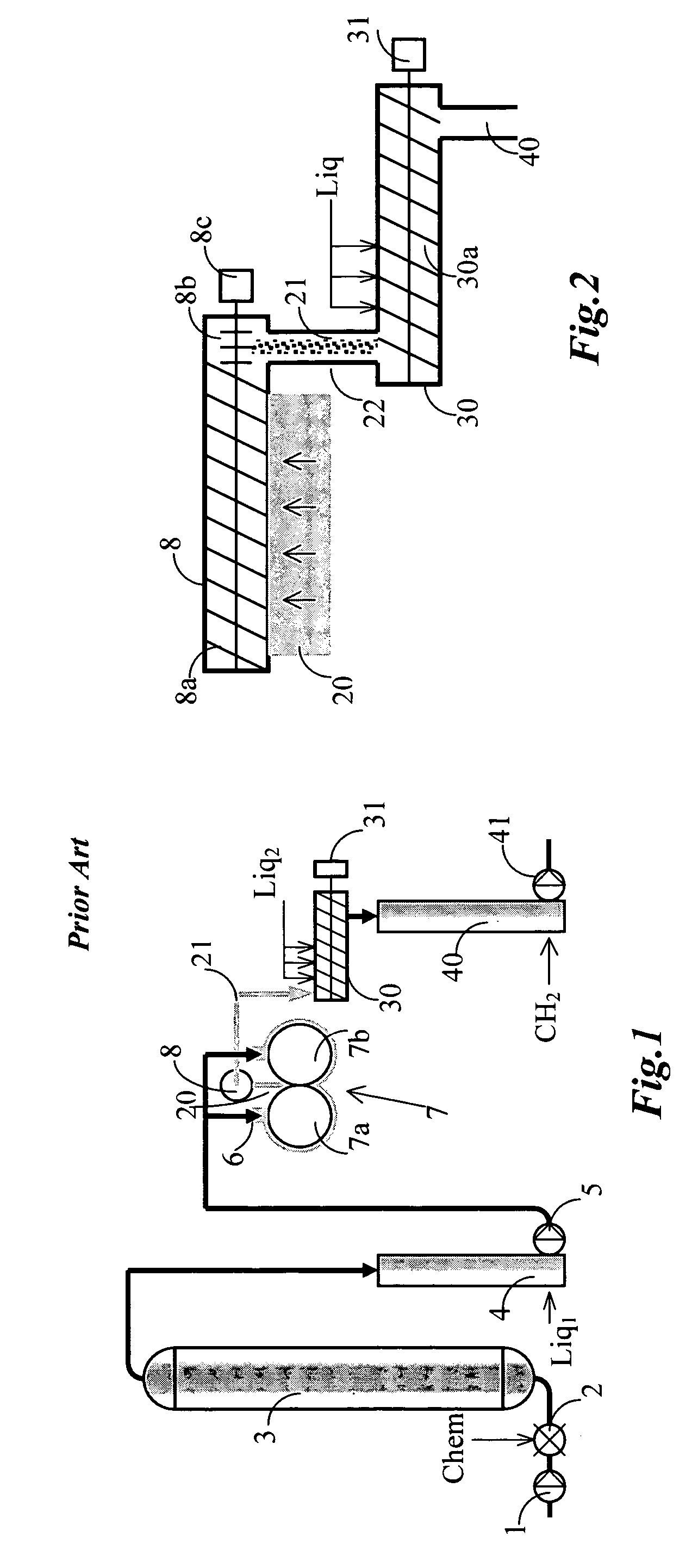
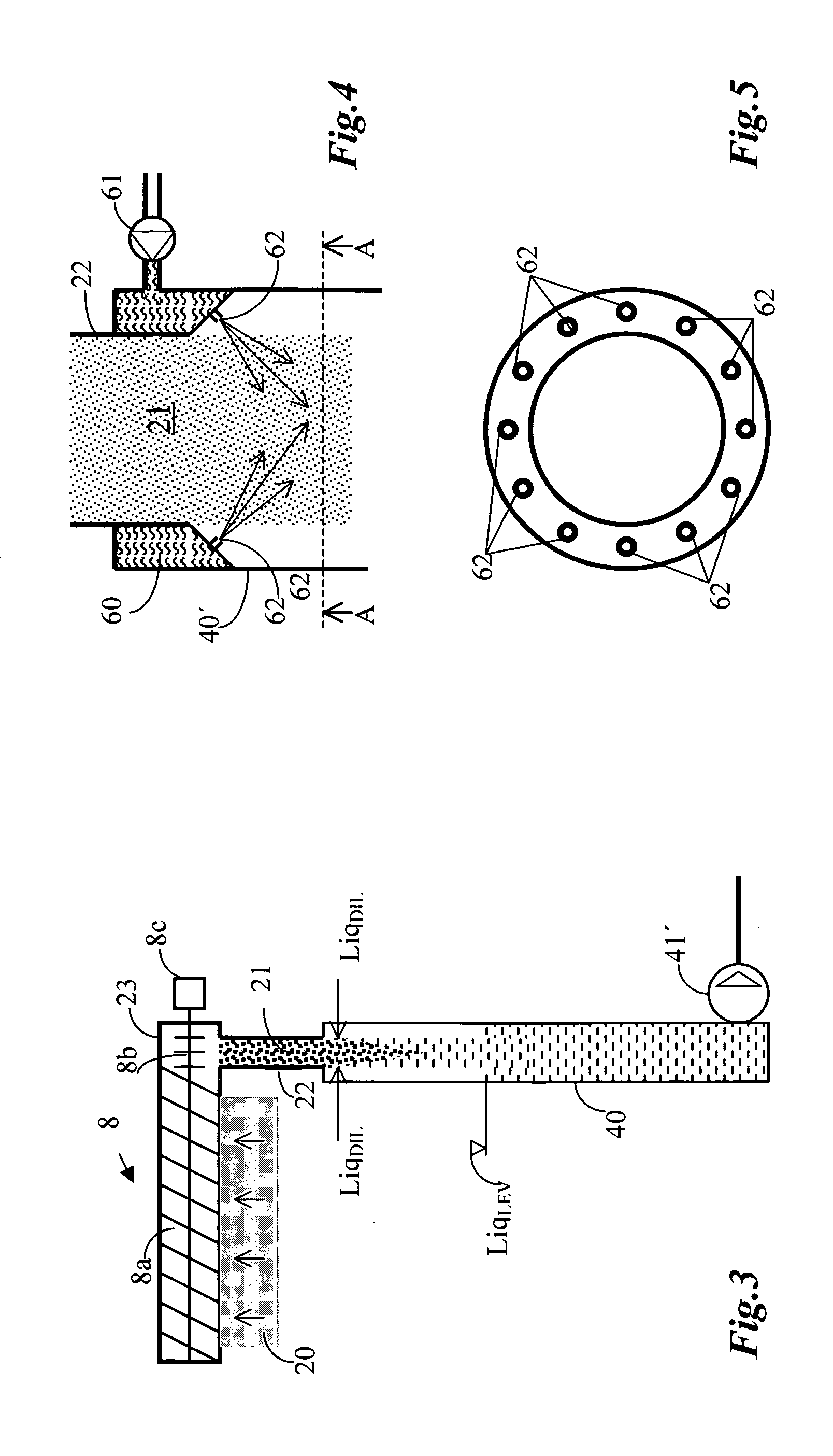
[0031]FIG. 1 shows a conventional treatment step for cellulose pulp, hereafter denoted “pulp”. The pulp is fed by the pump 1 to a mixer 2 in which necessary treatment chemicals are added. These treatment chemicals can be, for example, oxygen gas, ozone, chlorine dioxide, chlorine, peroxide, pure acid or a suitable alkali for an extraction step, or a mixture of these, and possibly other chemical or additives such as a chelating agent. The pulp is transported after the addition of the necessary chemicals by the mixer 2 to a reactor system 3, here shown in the form of a single-vessel tower 3 of upwards flow. The reactor system can, however, be constituted by simple pipes or by one or several reactors in series, and possibly with the batchwise addition of chemicals between the towers in those cases in which the bleaching processes are compatible and do not require washing between the towers. The treated pulp is fed after treatment in the reactor system 3 to a pulp chute / stand pipe 4, wh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| granulate size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com