Data transmission method adapted to network system for broadcasting distribution of streaming contents
a data transmission and content technology, applied in the field of data transmission methods, can solve the problems of random error, displaced burst error, and broken stream content reproduction, so as to reduce the range of packets, reduce the error resistance of transmission, and reduce the time lag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] This invention will be described in further detail by way of examples with reference to the accompanying drawings.
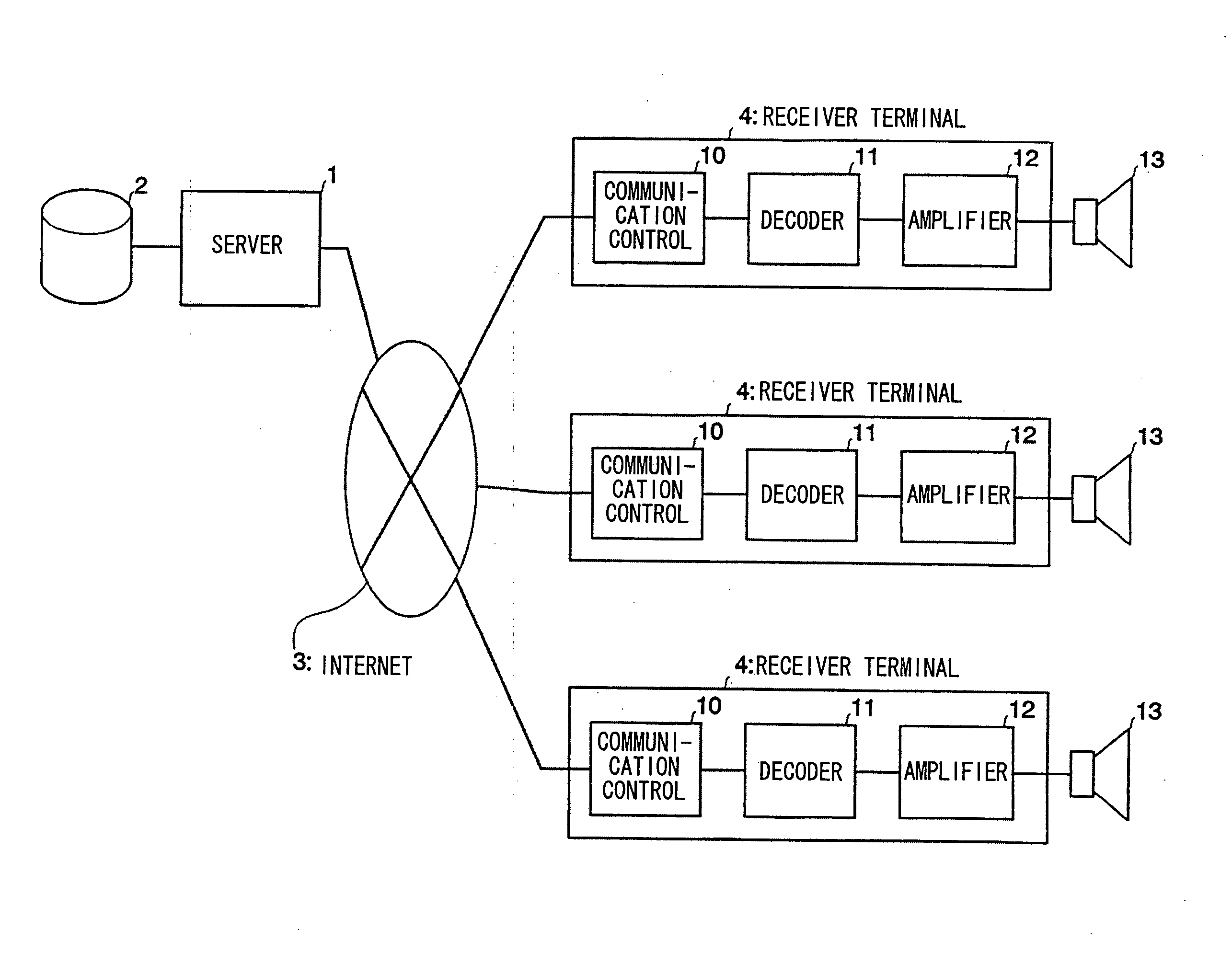
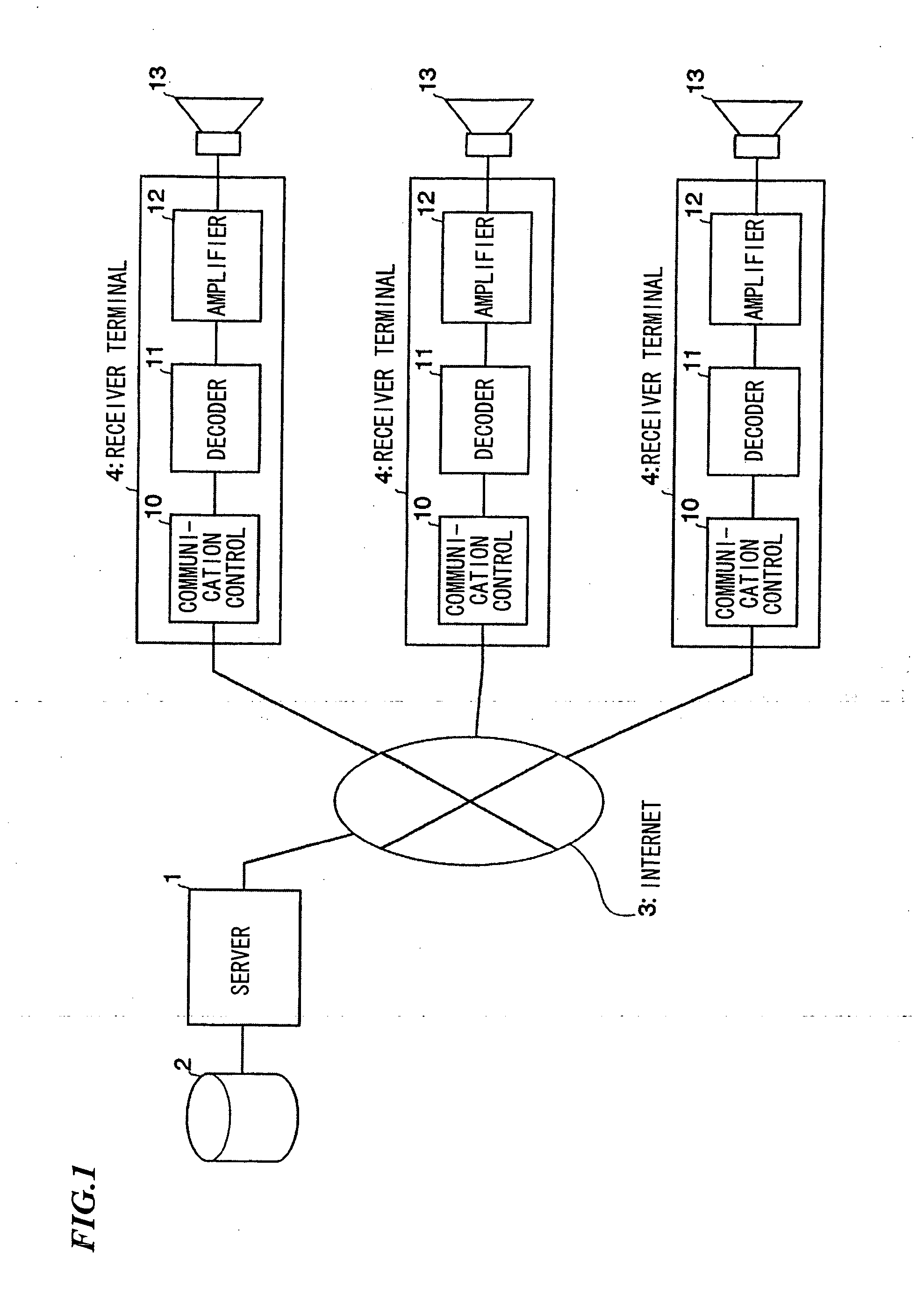
[0039]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the overall constitution of an audio distribution system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the invention. A server 1 is equipped with a storage 2 for storing and accumulating various data regarding audio contents. The storage 2 is configured using hard disks, for example. The server 1 is connected with an Internet 3, via which audio contents are subjected to streaming broadcasting (or broadcasting distribution).
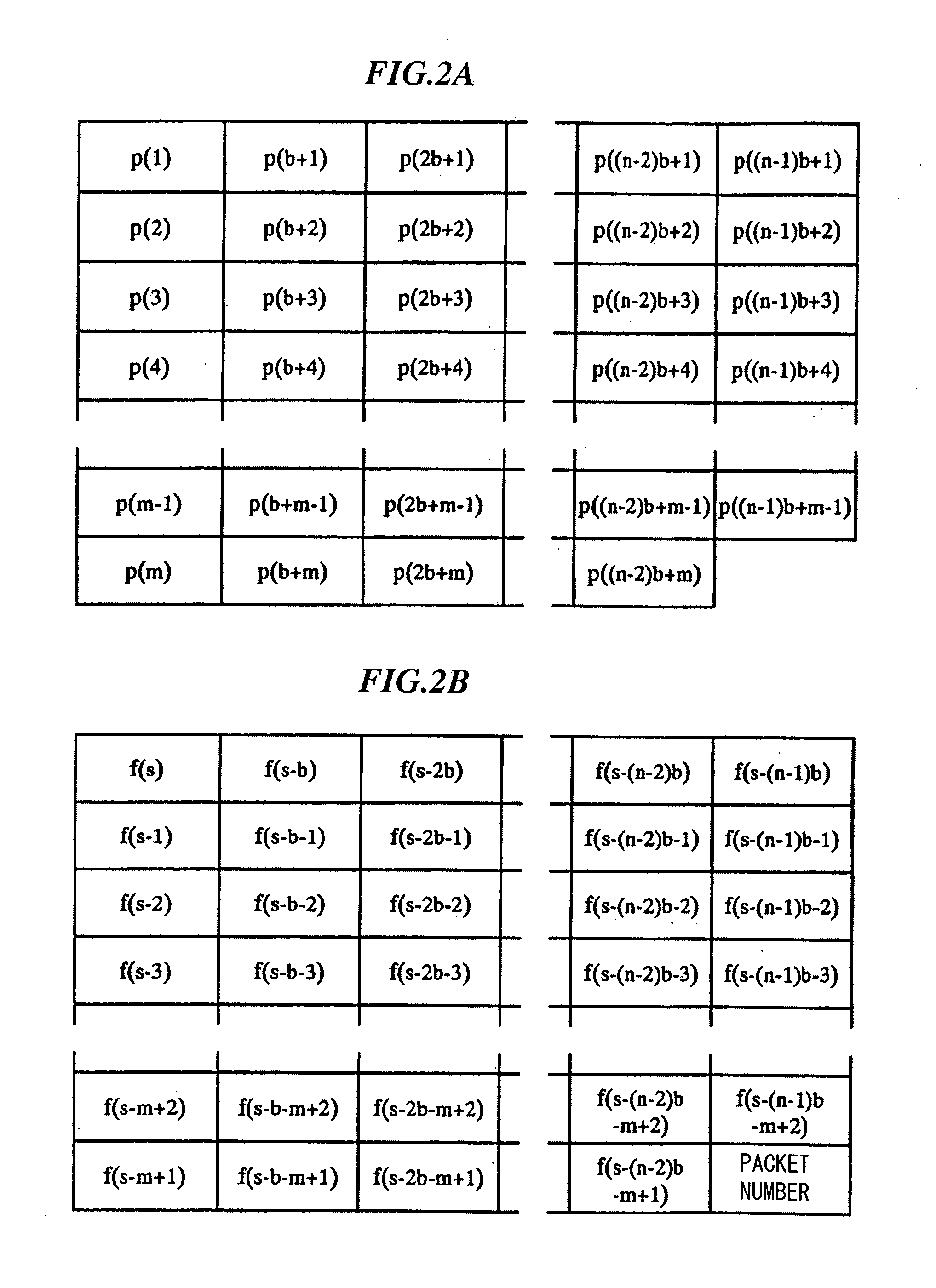
[0040] In the broadcasting distribution, streaming data strings are divided into a plurality of frames each having a prescribed length expressed as (m−1)×(n−1) bytes. In addition, error correction codes are added to frames, which are then subjected to interleaving and converted into packets. The present embodiment uses a prescribed communication protocol that performs ‘order control’ but does not perform ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com