Link adaptation
a technology of link adaptation and adapter, applied in the field of link adaptation, can solve the problems of no signaling mechanism specified which would allow a receiver, and does not provide any protocol means for a receiver, and achieve the effects of reducing data rate, excellent performance, and fast changing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
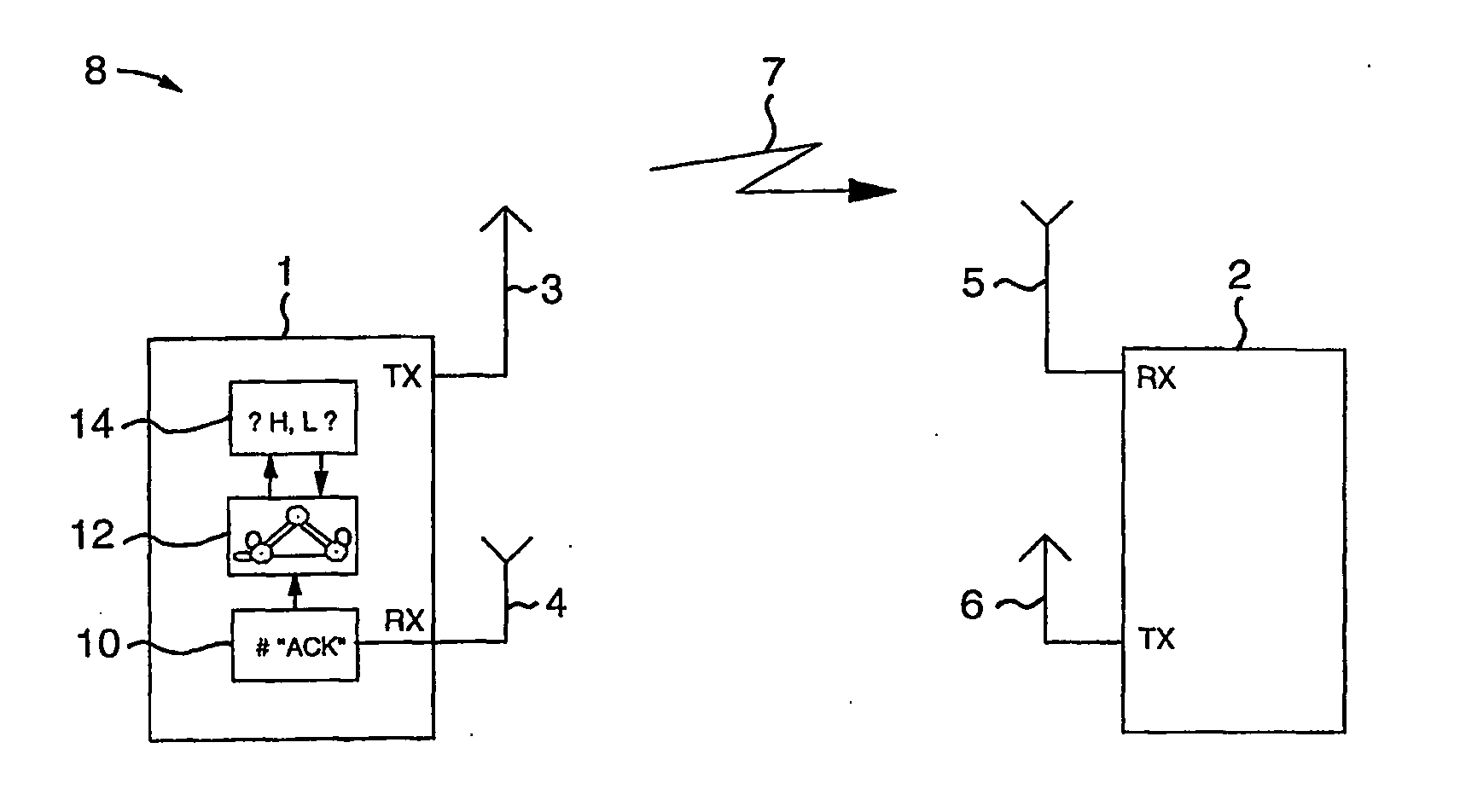
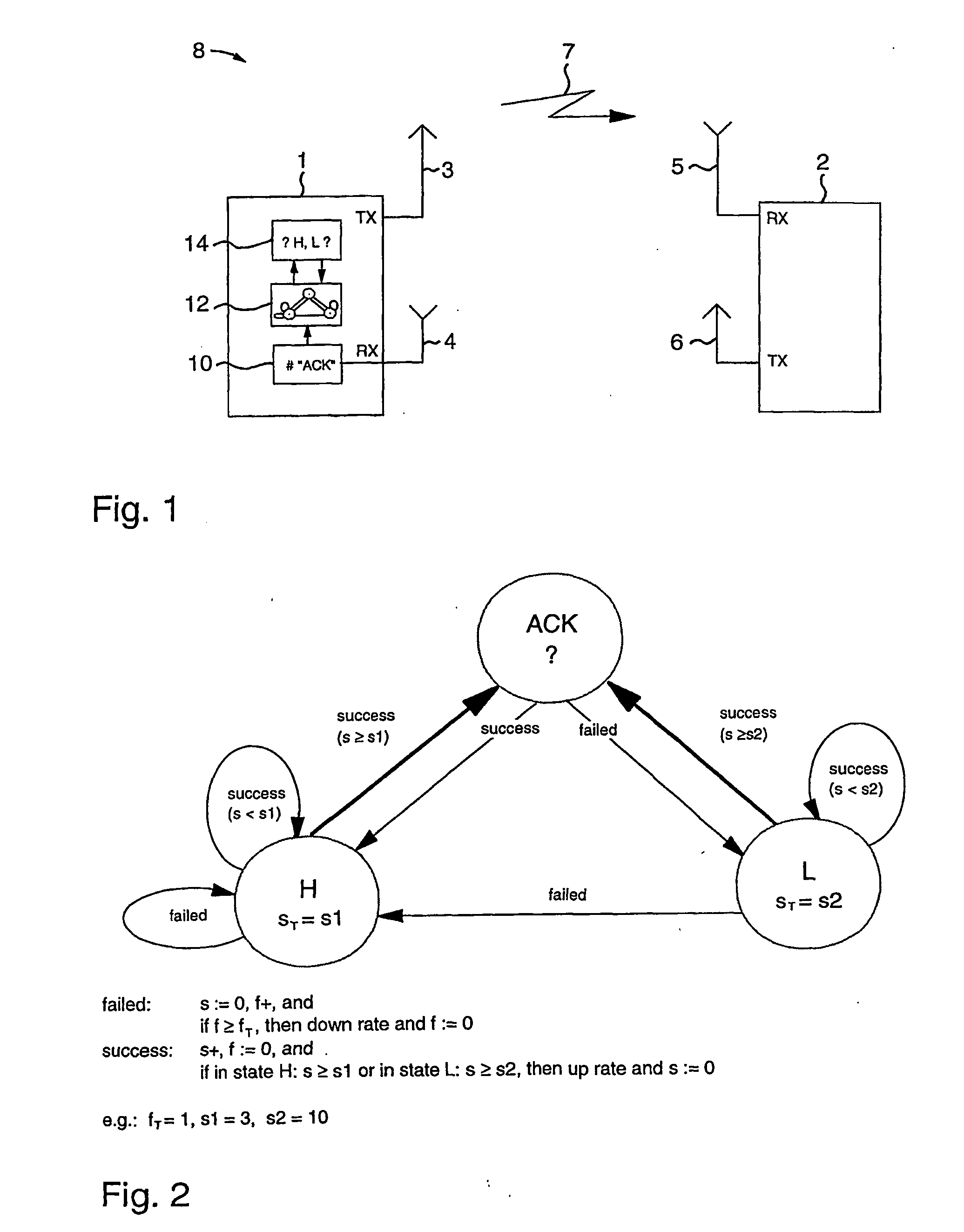
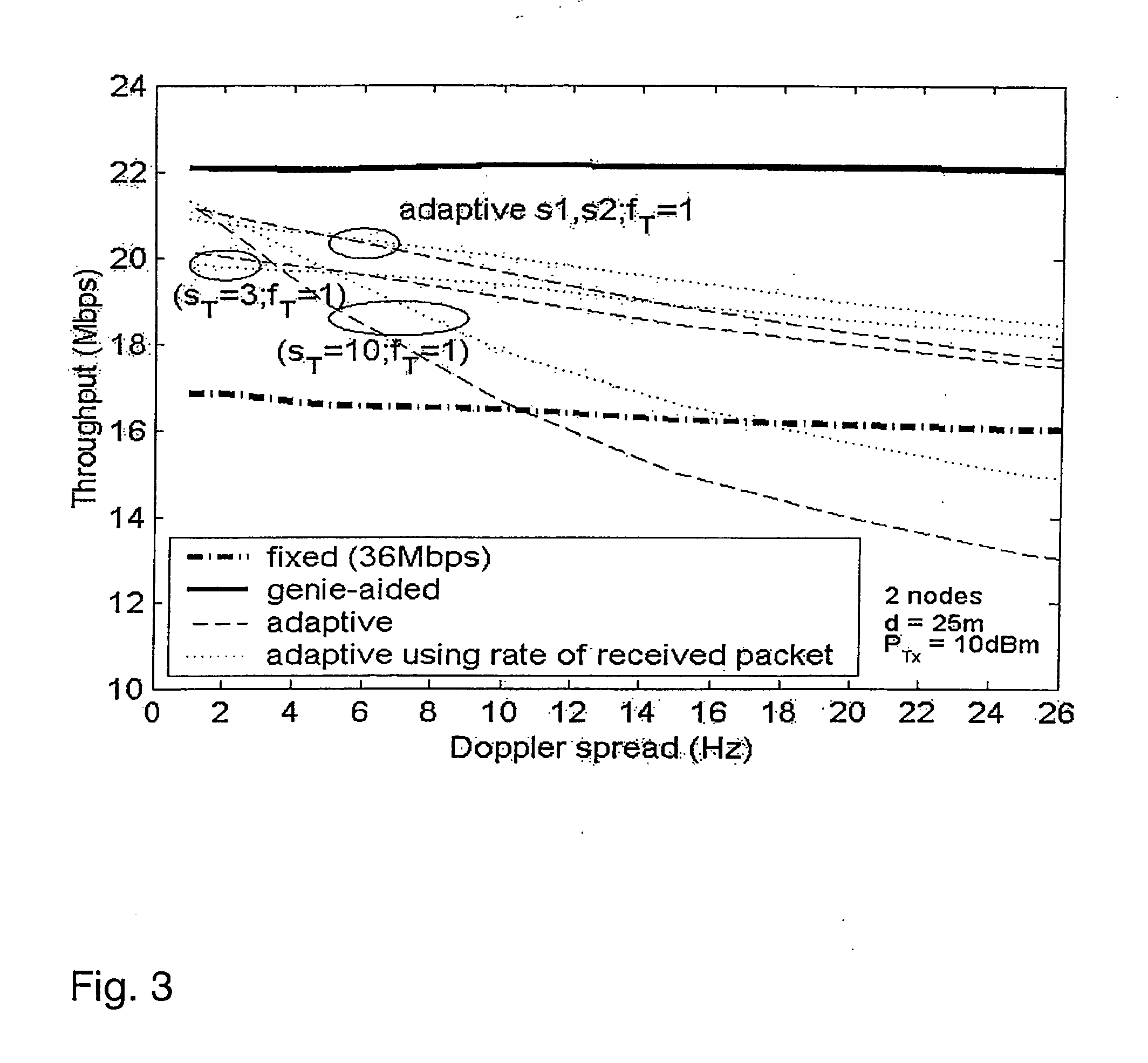
[0029] Although the present invention is applicable in a broad variety of transmission applications it will be described with the focus put on an application to wireless systems, i.e. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN), using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) as employed in the WLAN standards IEEE 802.11a and HIPERLAN / 2. Before embodiments of the present invention are described, some basics, in accordance with the present invention, are addressed.
[0030] As the invention takes advantage of the so-called error recovery procedure defined in the MAC (medium access control) layer of the IEEE 802.11 standard, this error recovery procedure is described in more detail below.
[0031] The IEEE 802.11 basic access procedure is a distributed procedure based on the known Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) method used in Ethernet LANs (local area networks). A station with a pending data packet has to sense the state of the wireless medium before it can transmit. If the medium i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com