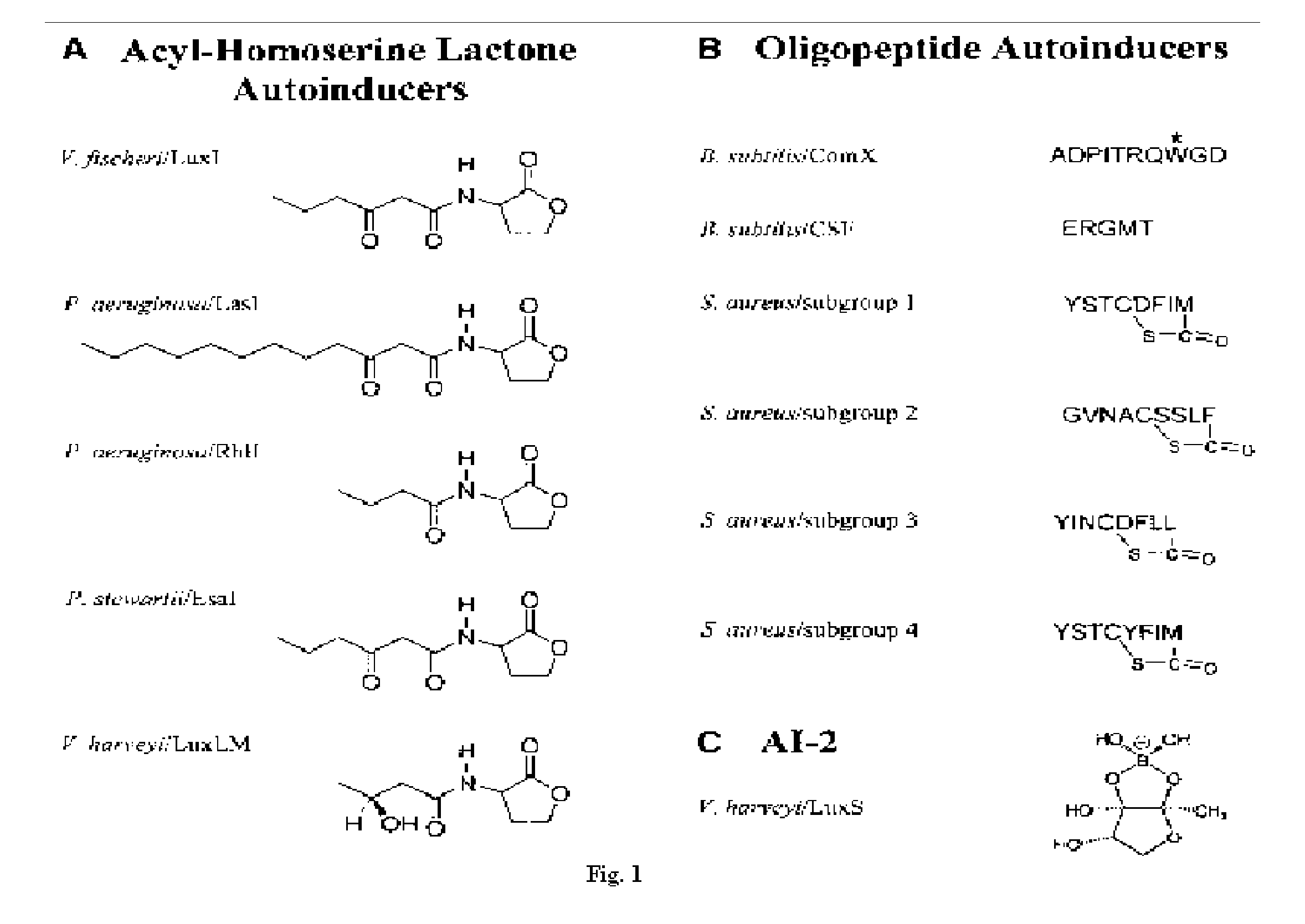
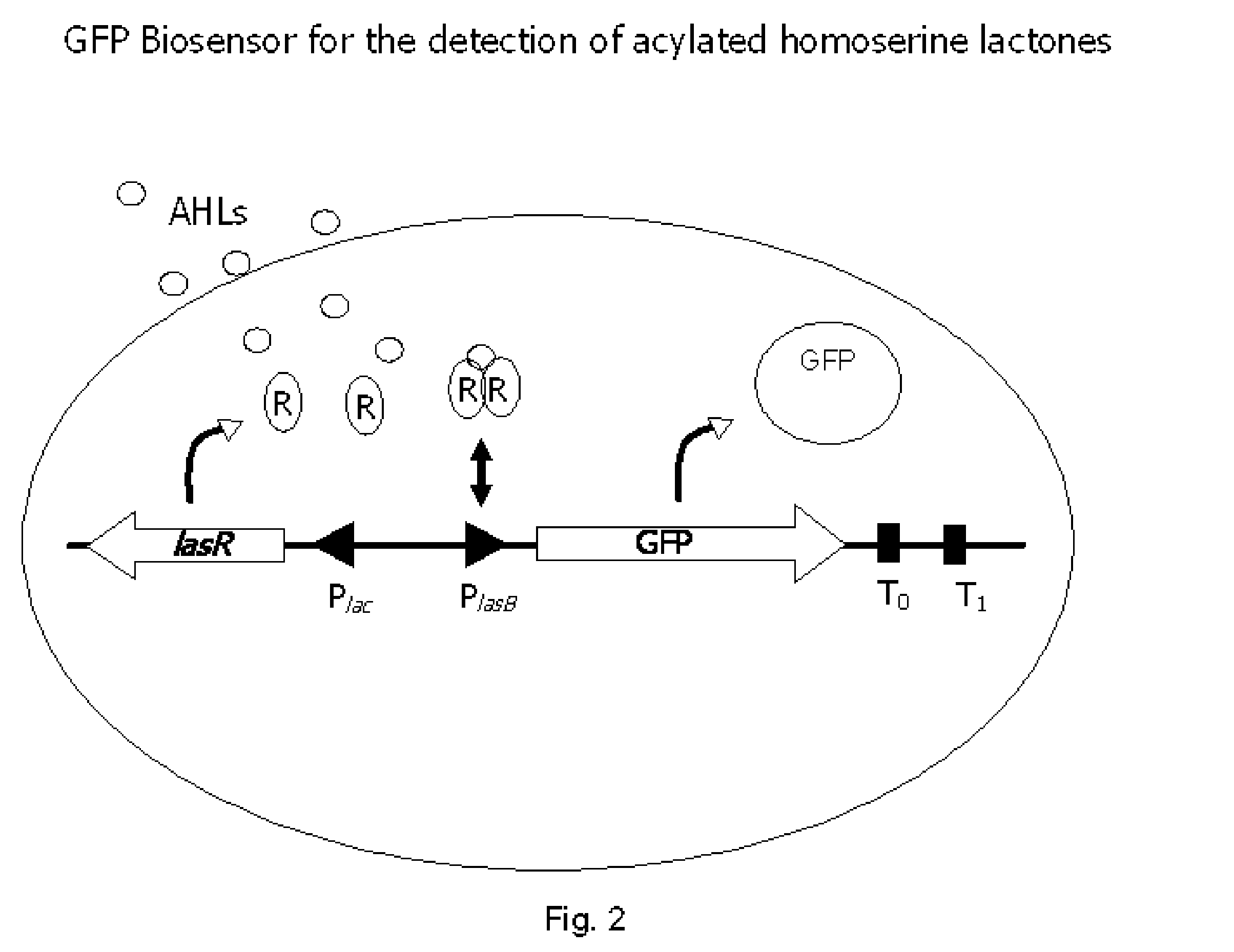
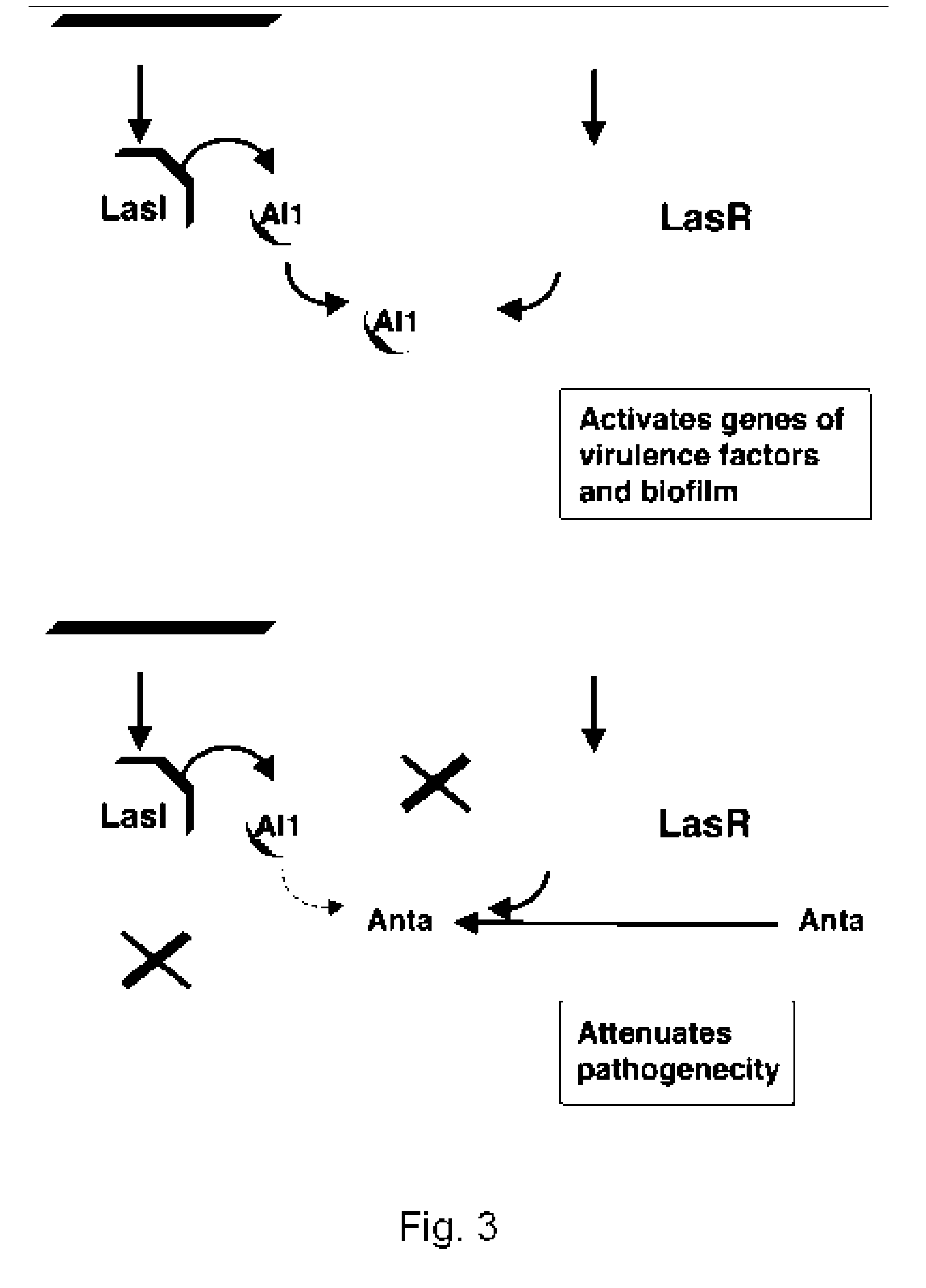
Method for modulating microbial quorum sensing
a quorum sensing and microbial technology, applied in the field ofquorum sensing, can solve the problems of no antibacterial compound that targets bacterial, no specific target for rational drug design, and huge damage worldwide, and achieve the effect of regulating microbial disease resistance or susceptibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Activity of Antagonists Compared in the Presence of Synthetic AHLs
[0110] This example presents representative results of experiments designed to test the activity of putative antagonists when challenged with different concentrations of synthetic AHLs, particularly 3oxoC12HSL. Assays were conducted with P. putida F117 pKRC12 reporter strain as described in the methods for secondary screens.
[0111] Representative results of experiments designed to test the effects of increasing concentrations of synthetic AHLs are presented in FIG. 14 and suggest that increasing the concentration of 3oxoC12HSL to extremely high levels diminishes the activity of the antagonistic compounds. This reduction of the antagonistic activity with increasing concentrations of the synthetic AHLs suggests that these compounds are outcompeted by saturating concentrations of the cognate AHL and further suggests that these compounds may interact specifically with the LasR transcriptional activator.
[0112]FIG. 15 pre...
example 3
Structure-Activity Analysis of Antagonists
[0113] Following the initial screens to identify strong antagonists of the LasR transcriptional activator, further investigation of additional compounds in the Chembridge library was carried out. In particular, the experiments described in Example 1 identified three compounds that shared a thiocarbamate structure, as also shown in FIG. 16. To further investigate structure-activity relationships, the inventors examined the antagonist activity of 19 additional compounds with related thiocarbamate structures, using the procedures described in Example 1. The results are presented in Table 3, expressed as the percent activity of the AHL induced control. The % activity represents the relative fluorescence, which is the fluorescence observed in each assay divided by bacterial cell density as measured by absorbance at 600 nm. Compounds were assayed at a concentration of 10 μM. Assays were conducted with P. putida F117 pKRC12 reporter strain as desc...
example 4
Caenorhabditis elegans Nematode Model for Testing Compounds
[0117]P. aeruginosa strains, PA01 wild type virulent and a virulent PA01 IasIrhll mutant strain were grown in 5 ml of LB liquid culture in 18 mm testtubes in the presence or absence of 10 μm experimental compound overnight with shaking. 15 μl samples of bacterial culture are spread on 55 mm BHI agar plates containing 10 μm experimental compound or no compound as a control.
[0118] Following overnight incubation at 28° C., ten L4 or adult wild-type Bristol N2 nematodes were transferred to the plates, which were then sealed with parafilm and incubated at 20° C. The number of living worms per plate was determined at various time points with a compound microscope. Nematodes are considered dead when they fail to move in response to the tapping of the plate against the microscope stage.
[0119] Expected Results:
[0120] Nematodes treated with the wild type pathogen PA01 in the absence of antagonistic compounds will suffer 100% morta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| excitation wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com