Position and electromagnetic field sensor
a sensor and electromagnetic field technology, applied in the field of position and electromagnetic field sensors, can solve the problems of sensor not necessarily allowing monitoring of moving objects, electromagnetic energy loss variation within the oscillator, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing spatial resolution and insensitive to amplitude nois
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
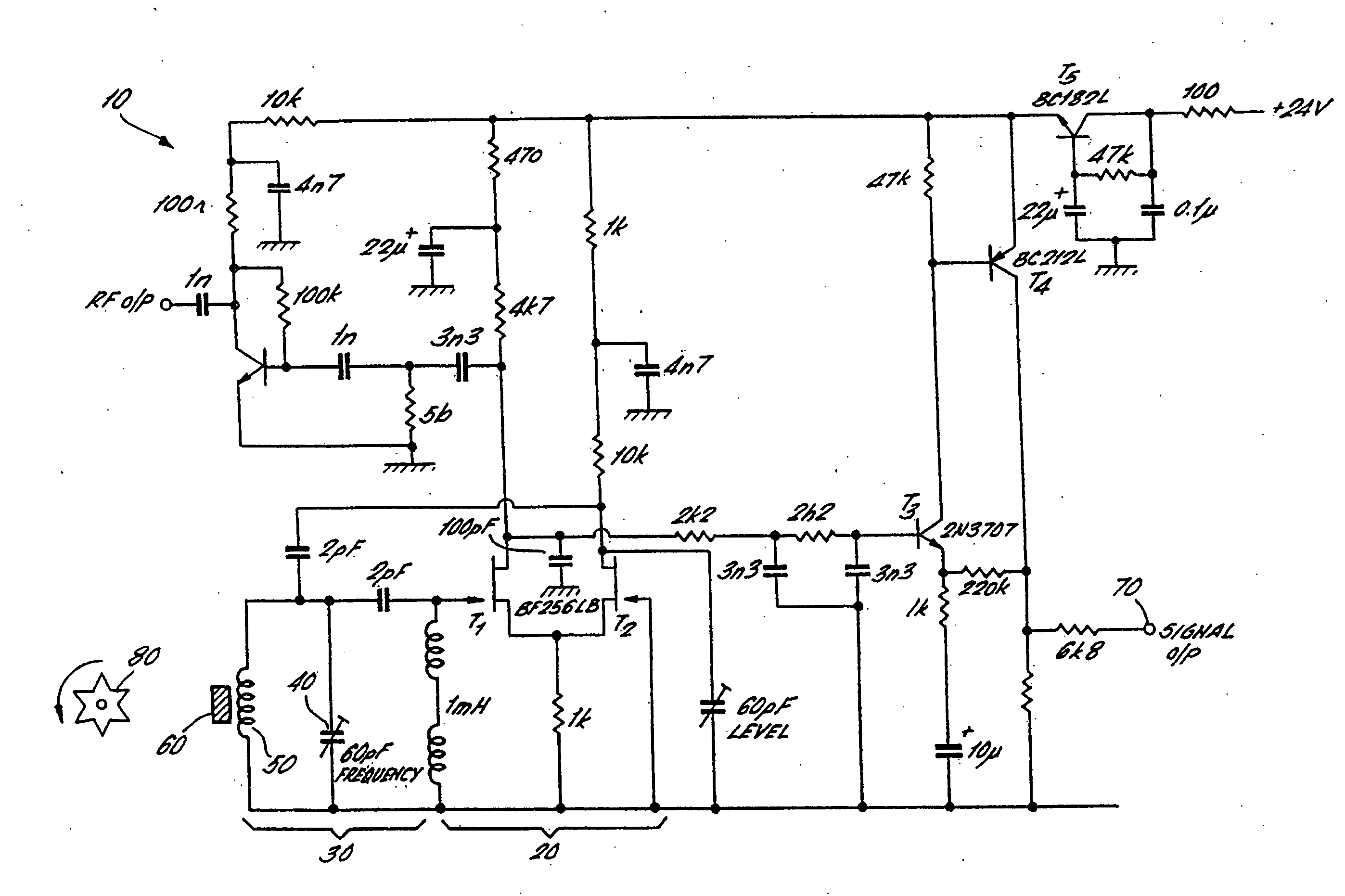
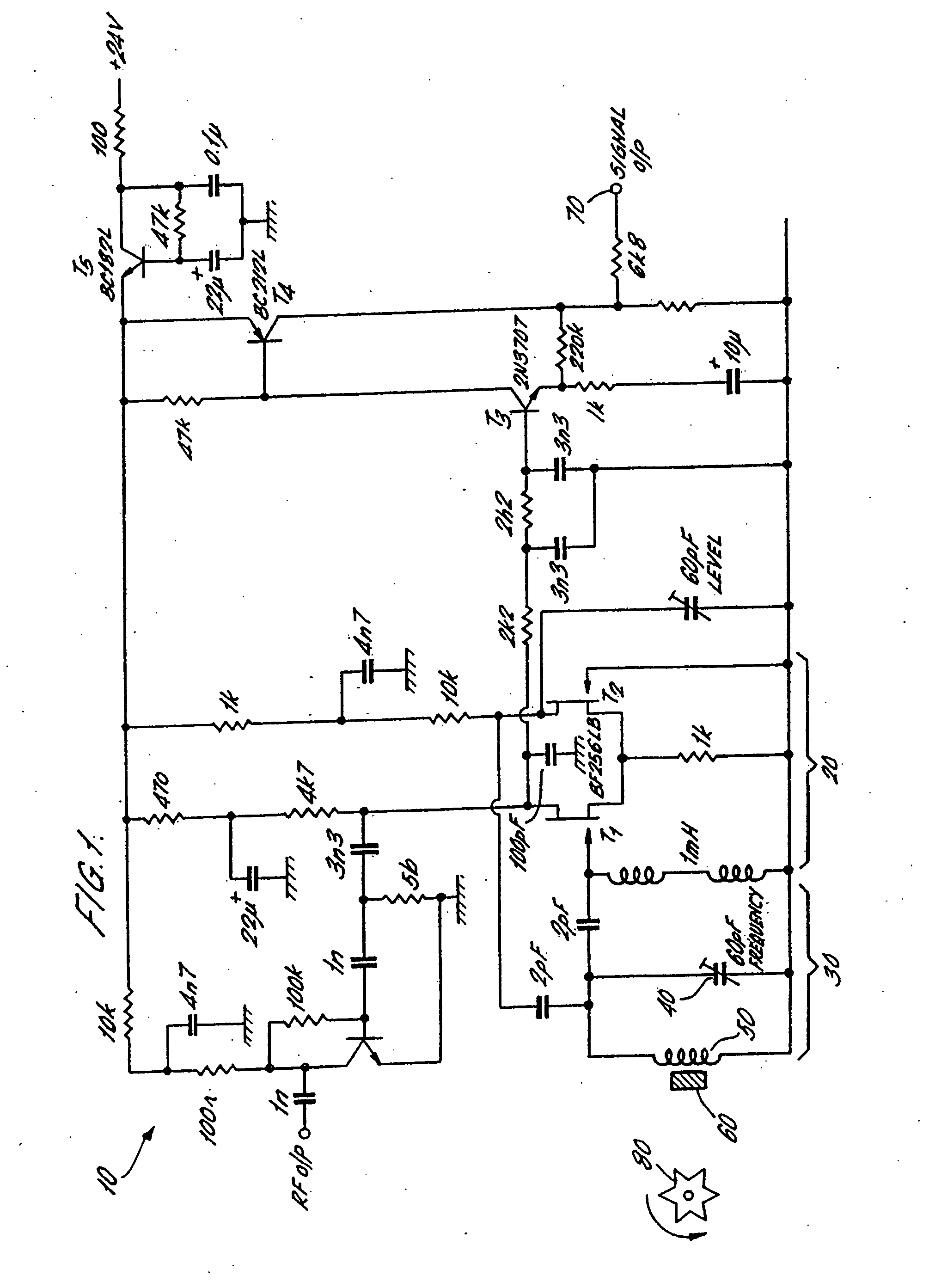
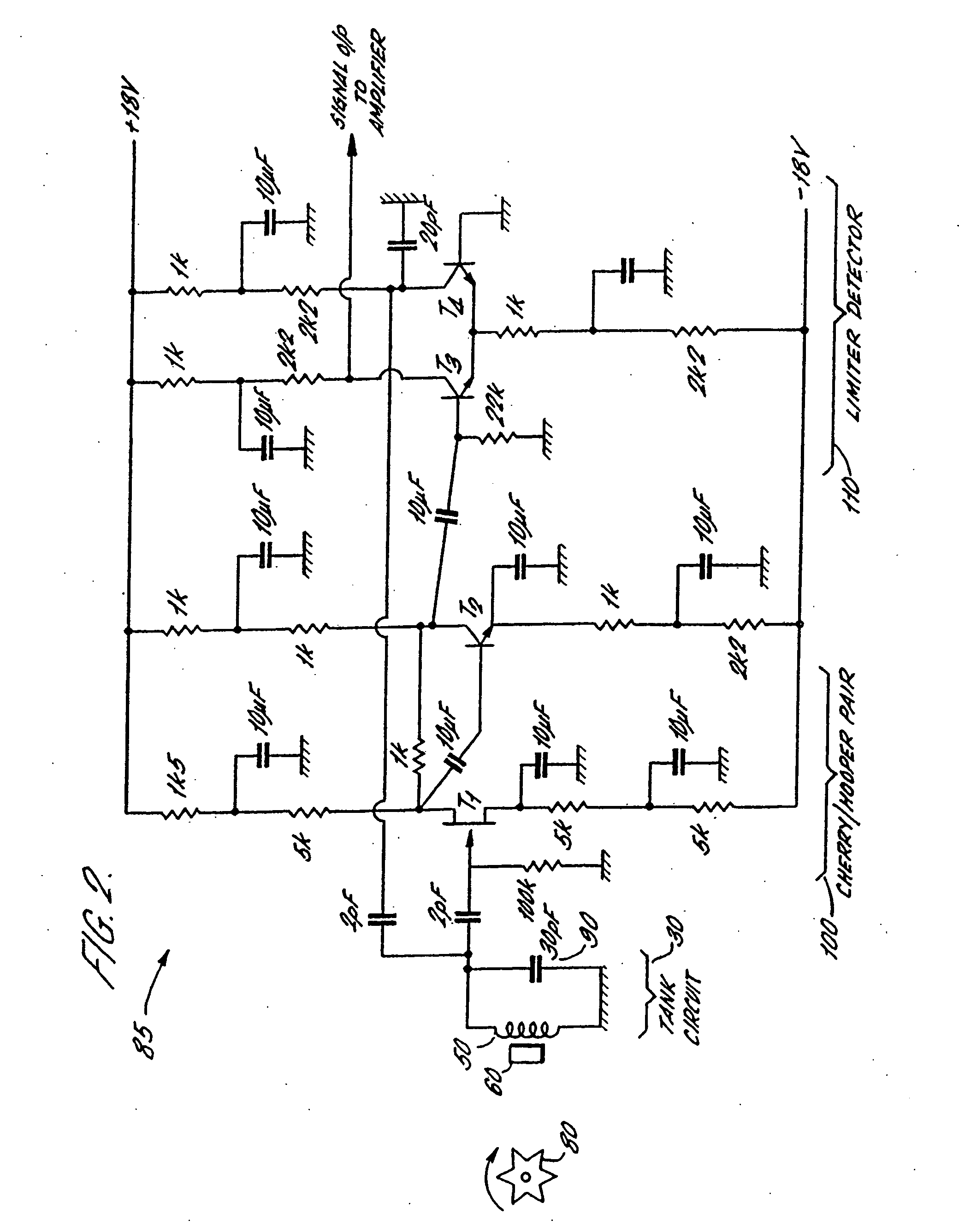
[0032]FIG. 1 shows a circuit diagram of a sensor according to a first embodiment of the invention. The circuit 10 comprises a closed loop Robinson-type oscillator 20 connected with a tank circuit 30. The tank circuit 30 comprises a capacitor and inductor provided by a variable capacitor 40 in parallel with a coil 50. The coil 50 is wrapped around a sensor element 60 and comprises a piece of colossal magnetoresistive material such as lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO). This material has a strong variation in the imaginary part of its susceptibility, as a magnetic field applied to it varies.
[0033] In the circuit of FIG. 1, transistors T1 and T2 have a triple function. Firstly, they provide the gain to keep the closed loop Robinson oscillator 20 running, secondly they provide a limiting action which makes the feedback independent of amplitude noise, and thirdly they perform detection to generate an output signal. These three functions provided by transistors T1 and T2 may be separat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com