Therapeutic platelets and methods
a technology of platelets and platelets, which is applied in the field of manipulation or modification of platelets, can solve the problems of blood transfusion centers under considerable pressure to produce platelets, rapid loss of platelet function, and limited shelf life under these conditions, so as to avoid platelet activation, effective platelet loading, and stable shelf life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0070] Washing of Platelets. Platelet concentrations were obtained from the Sacramento blood center or from volunteers in our laboratory. Platelet rich plasma was centrifuged for 8 minutes at 320×g to remove erythrocytes and leukocytes. The supernatant was pelleted and washed two times (480×g for 22 minutes, 480×g for 15 minutes) in buffer A (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM KCl, 10 mM EGTA, 10 mM imidazole, pH 6.8). Platelet counts were obtained on a Coulter counter T890 (Coulter, Inc., Miami, Fla.).
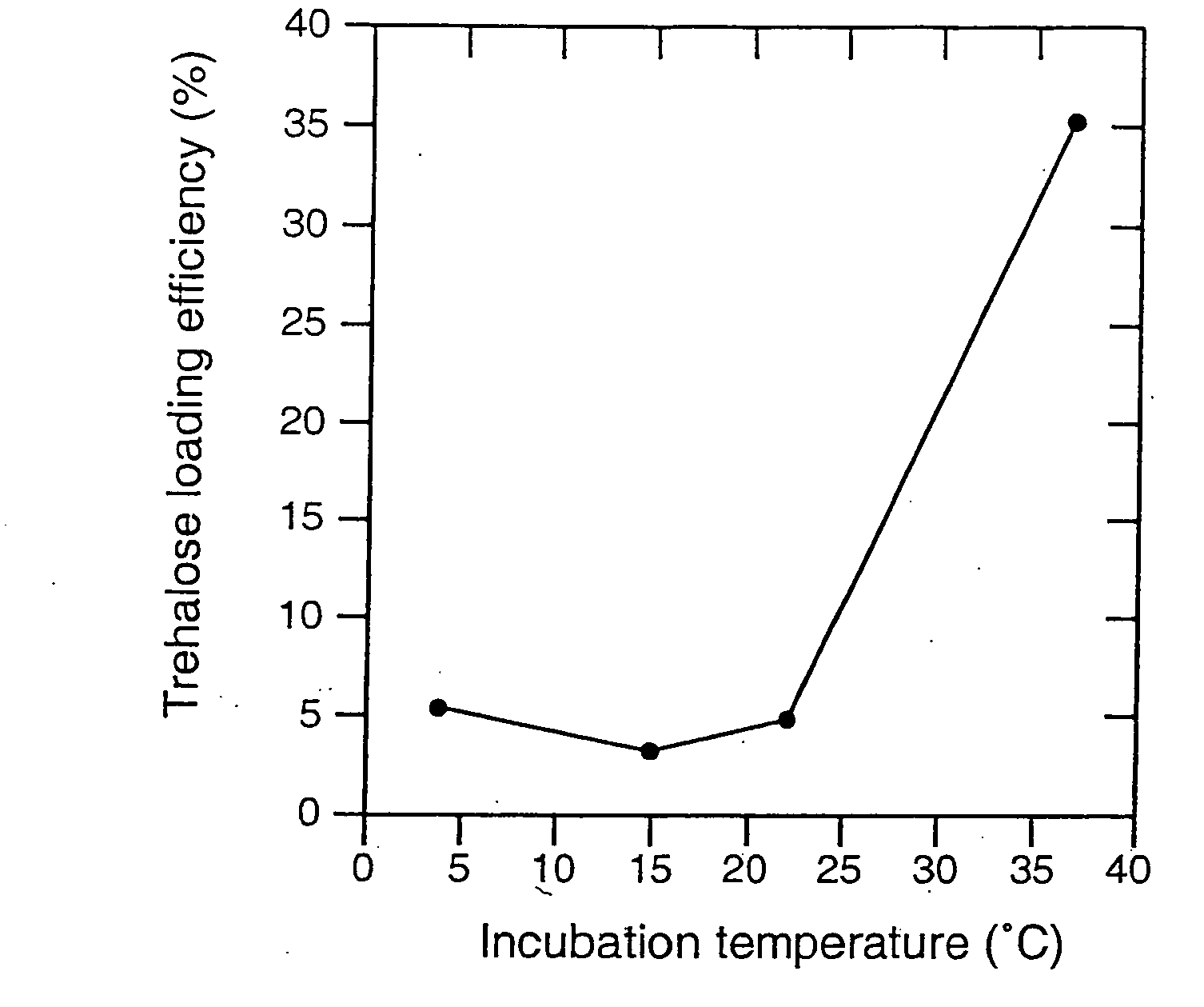
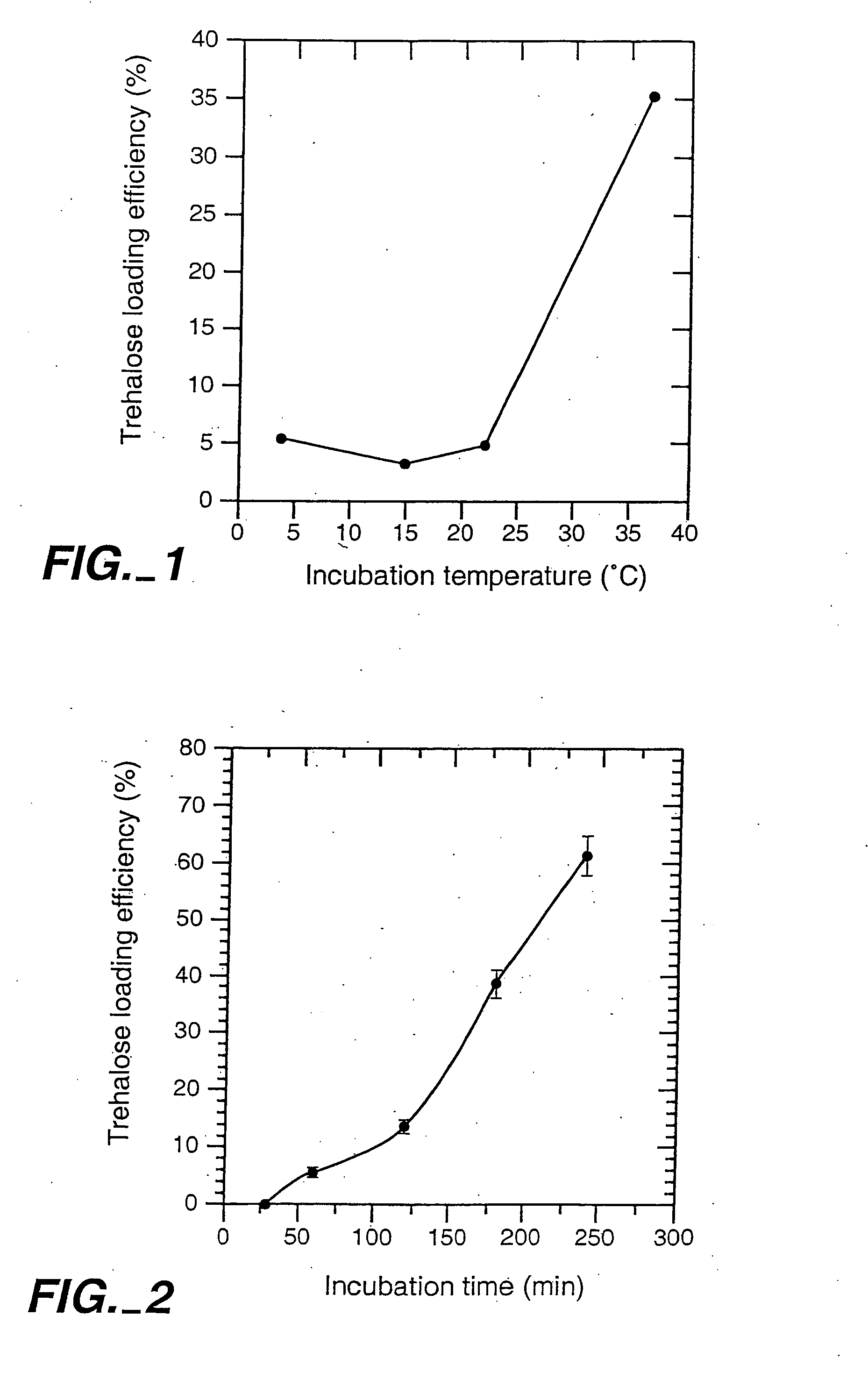
[0071] Loading of Lucifer Yellow CH into Platelets. A fluorescent dye, lucifer yellow CH (LYCH), was used as a marker for penetration of the membrane by a solute. Washed platelets in a concentration of 1-2×109 platelets / ml were incubated at various temperatures in the presence of 1-20 mg / ml LYCH. Incubation temperatures and incubation times were chosen as indicated. After incubation the platelets suspensions were spun down for 20× at 14,000 RPM (table centrifuge), resuspended in buffer A, spun down ...
example 2
[0079] Washing Platelets. Platelets were obtained from volunteers in our laboratory. Platelet rich plasma was centrifuged for 8 minutes at 320×g to remove erythrocytes and leukocytes. The supernatant was pelleted and washed two times (480×g for 22 minutes, 480×g for 15 minutes) in buffer A (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM KCl, 10 mM EGTA, 10 mM imidazole, 10 μg / ml PGE1, pH 6.8). Platelet counts were obtained on a Coulter counter T890 (Coulter, Inc., Miami, Fla.).
[0080] Loading Platelets with Trehalose. Platelets were loaded with trehalose as described in Example 1. Washed platelets in a concentration of 1-2×109 platelets / ml were incubated at 37° C. in buffer A with 35 mM trehalose added. Incubation times were typically 4 hours. The samples were gently stirred for 1 minute every hour. After incubation the platelet solutions were pelleted (25 sec in a microfuge) and resuspended in drying buffer (9.5 mM HEPES, 142.5 mM NaCl, 4.8 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 30 mM Trehalose, 1% Human Serum Albumin, 10 μg / ml...
example 3
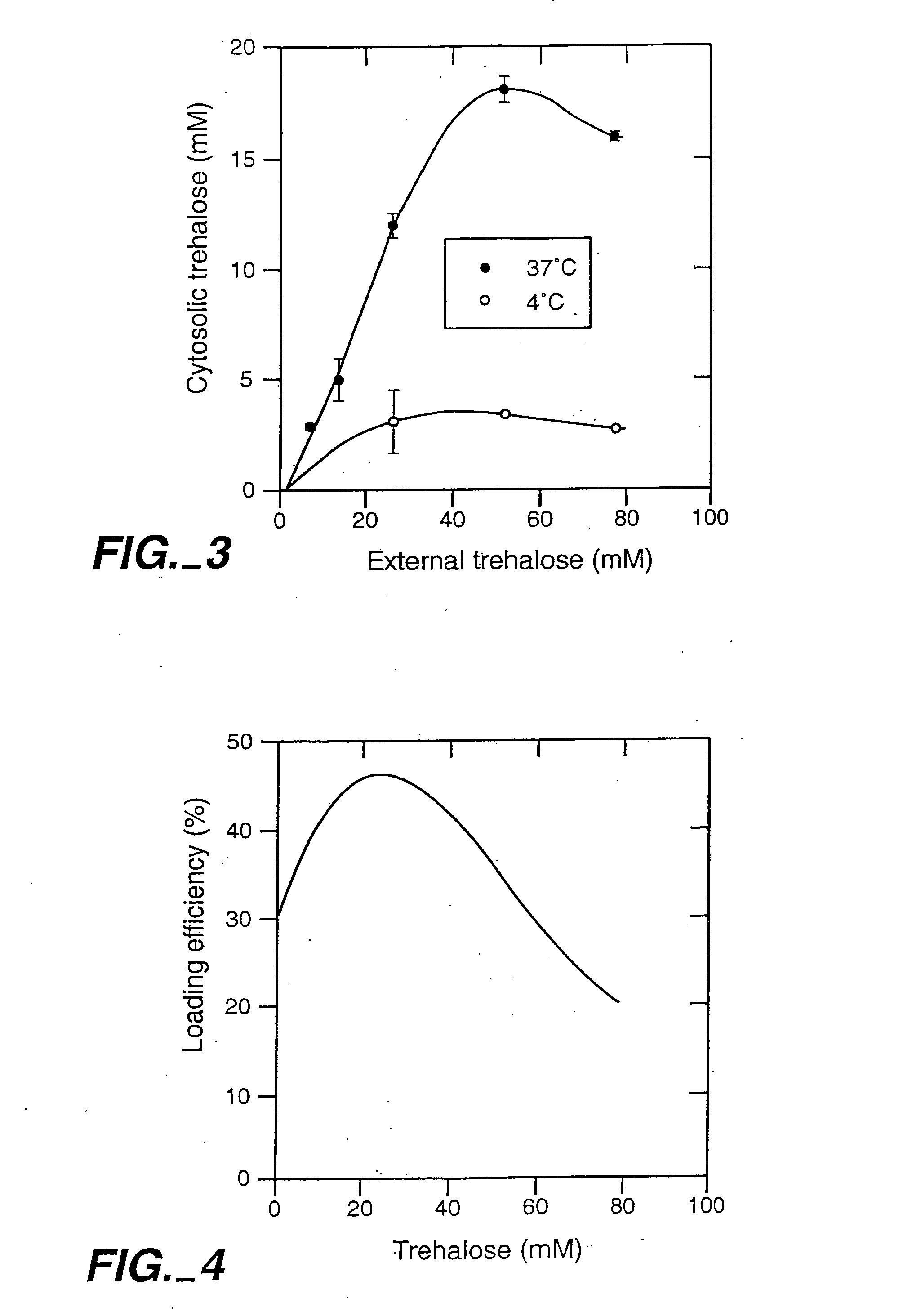
[0092] We view trehalose as the main lyoprotectant in the drying buffer. However, other components in the drying buffer, such as albumin, can improve the recovery. In the absence of external trehalose in drying buffer, the numerical recovery is only 35%. With 30 mM trehalose in the drying buffer the recovery is around 65%. A combination of 30 mM trehalose and 1% albumin gave a numerical recovery of 85%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com