RNAi-mediated inhibition of HIF1A for treatment of ocular angiogenesis
a technology of hif1a and rnai, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, extracellular fluid disorders, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problems of hyperglycemia in a number of ways, tissue damage, accumulation of sorbitol, etc., and achieve the effect of lowering the transcriptional activity of hif-1 inducible genes and reducing the pre-angiogenic and angiogenic cellular activity of the ocular
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Interfering RNA for Specifically Silencing HIF1A
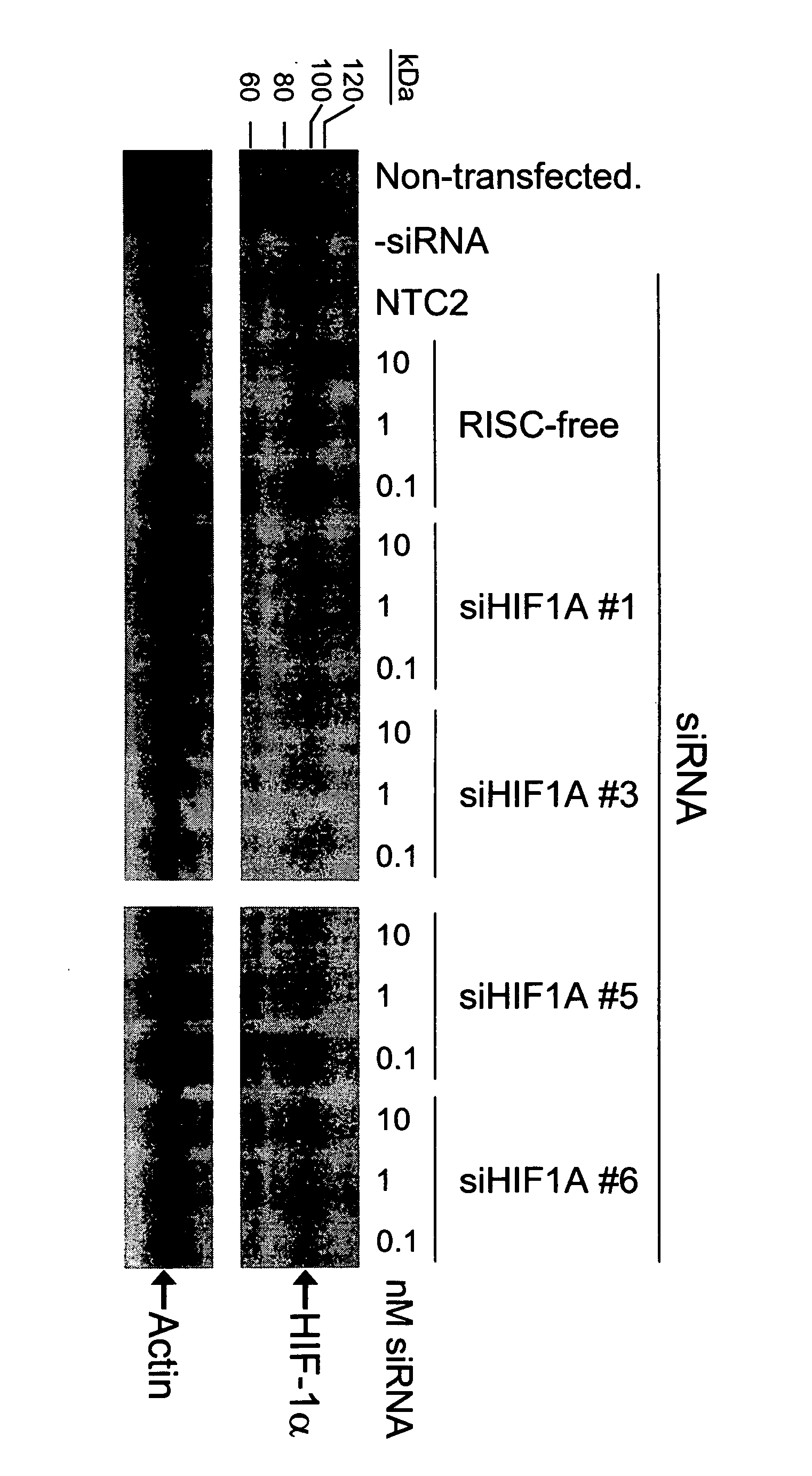
[0101] The present study examines the ability of HIF1A-interfering RNA to knock down the levels of endogenous HIF-1α protein expression in cultured HeLa cells.
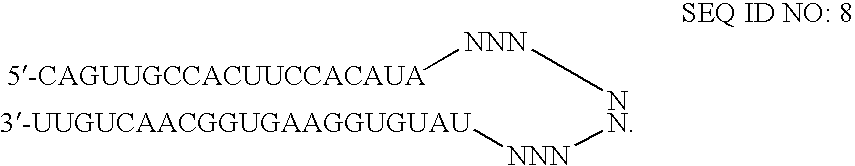
[0102] Transfection of HeLa cells was accomplished using standard in vitro concentrations (0.1-10 nM) of HIF1A siRNAs, siCONTROL RISC-free siRNA #1, or siCONTROL Non-targeting siRNA #2 (NTC2) and DHARMAFECT® #1 transfection reagent (Dharmacon, Lafayette, Colo.). All siRNAs were dissolved in 1× siRNA buffer, an aqueous solution of 20 mM KCl, 6 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.2 mM MgCl2. Control samples included a buffer control in which the volume of siRNA was replaced with an equal volume of 1× siRNA buffer (-siRNA). Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were treated with 100 μM CoCl2 for 4 h to induce HIF-1α protein expression, and western blots were performed to assess HIF-1α level. The HIF1A siRNAs are double-stranded interfering RNAs having specificity for the following targ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com