System and method for determining probing locations on IC
a technology of probing location and system, applied in the direction of testing circuits, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to determine the corresponding circuit element that is probed, difficult to determine the corresponding circuit element that emits light, and inconvenient to determine the corresponding circuit elemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
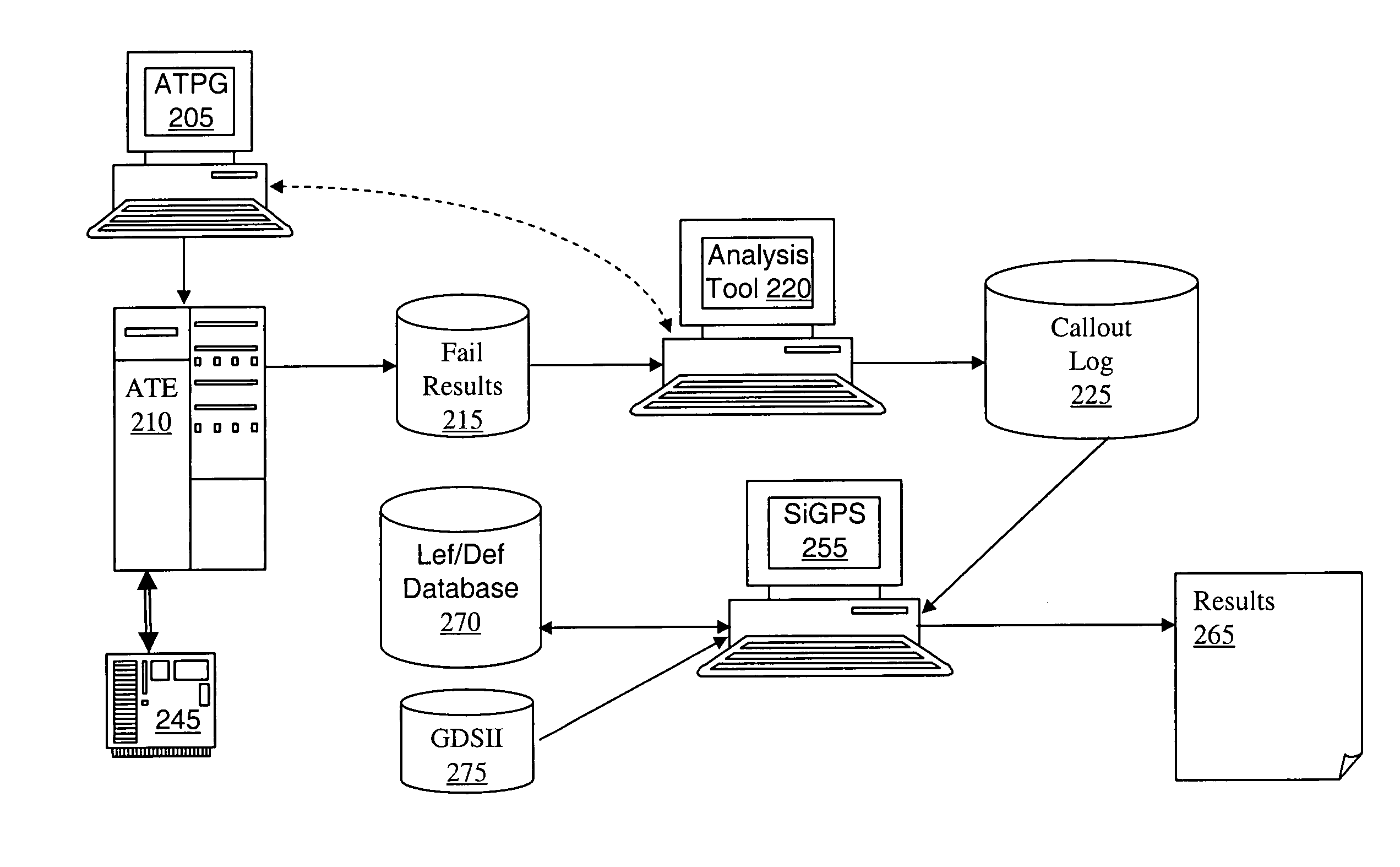
[0045]FIG. 2 depicts an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, all of the equipment and processes leading to the generation of the callout log 225 are the same as in the prior art. However, according to this embodiment, The Def / Lef and GDSII files are interrogated to produce the results of locations for probing, providing the bounding box of the cell, the pins, and the locations within the cell where TRE probing may be performed. This process is referred to herein as SiGPS and may be done automatically using a specifically programmed computer, such as a PC.
[0046] The terms Lef, Def, and GDS are commonly used in the art. Due to increasing size and complexity of the designs, engineers use automated tools to do the floor planning followed by place and route (P&R). During the P&R stage, the design tools have the ability to generate LEF / DEF files. These files are in ASCII format and contain the place and route data. The term Lef is an acronym for Library Exchange Forma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com