Dual function splice component for mechanical splice connector
a technology of mechanical splice connector and component, which is applied in the field of fiber optic connector, can solve the problems of requiring additional materials, affecting the field optical fiber, and unable to reverse and rework the splice, so as to eliminate the effect of positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
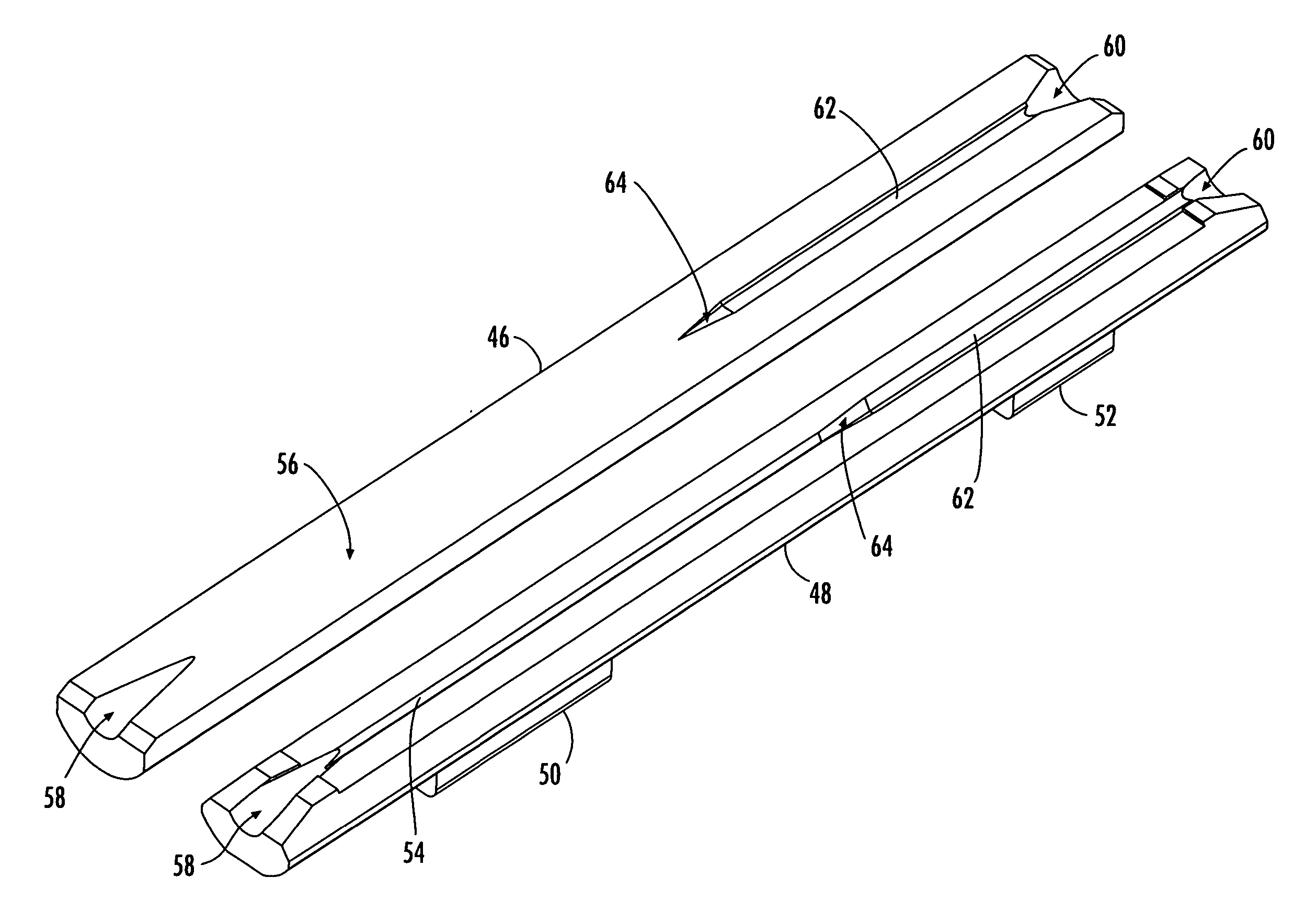
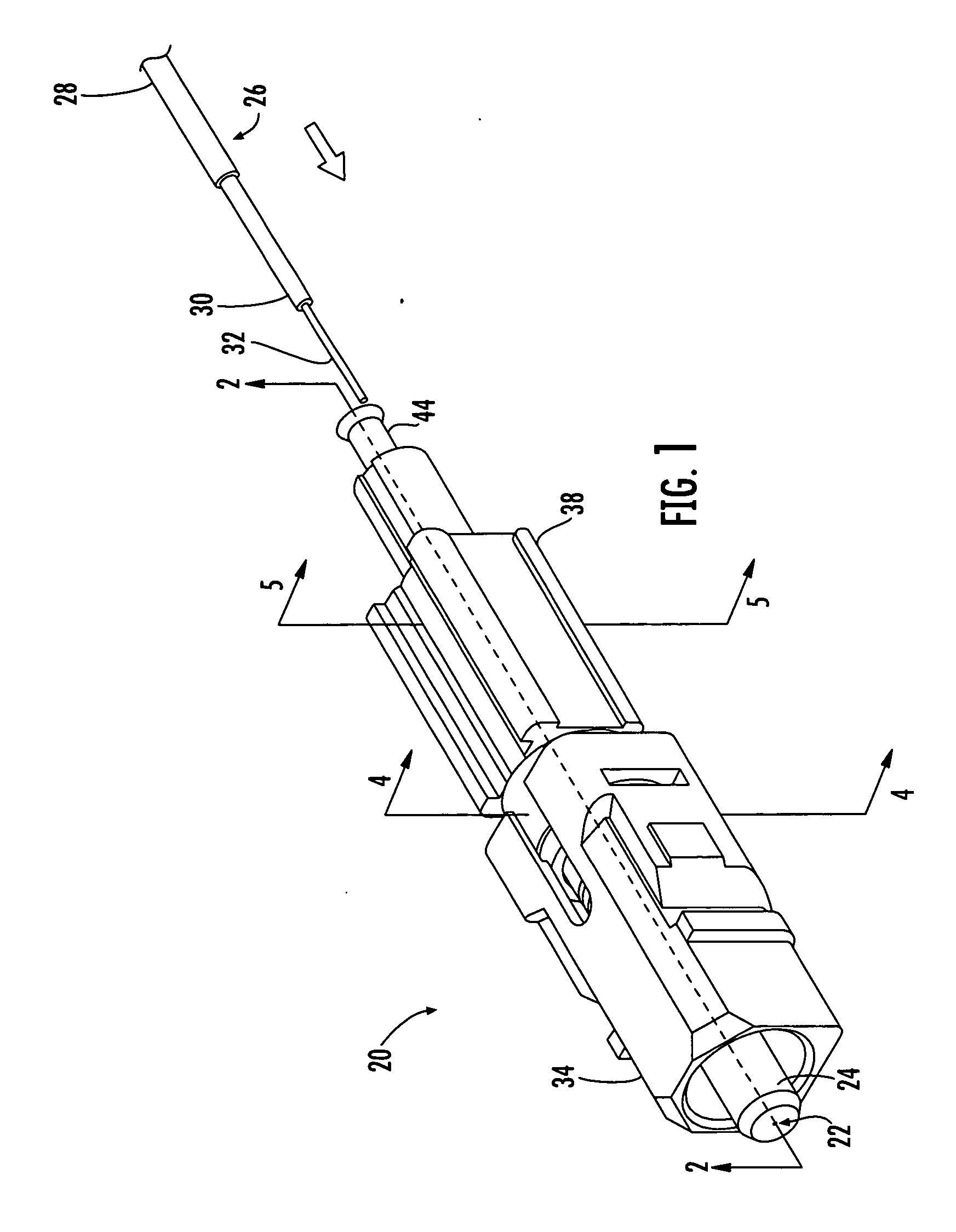
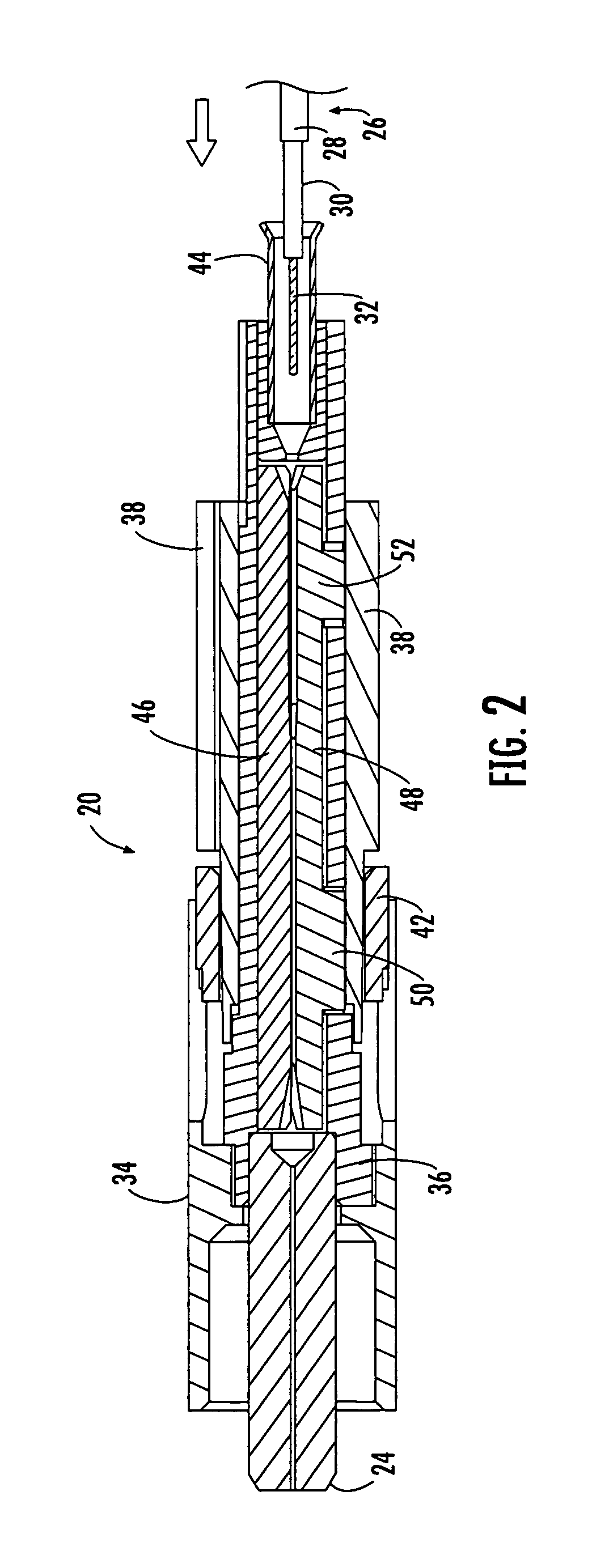
[0018] Reference will now be made in detail to presently preferred embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Whenever possible, the same reference numerals are used throughout the drawings to refer to the same or like parts. Although a dual function connector element operable for providing both optical fiber alignment and strain relief is shown in the accompanying drawings as one or more splice components of a particular fiber optic mechanical splice connector, it is envisioned that the dual function connector element may be any component used in any now known or hereafter devised mechanical splice connector that facilitates the splicing of two or more optical fibers, as well as the retention of one or both of the optical fibers. The broad concepts of the present invention may also be applied to any optical connection between mating optical fibers, such as a mechanical or fusion splice connection utilizing a splice component or spl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com