Method for using a sensor to register a biometric for use with a transponder-reader system related applications
a transponder-reader system and biometric technology, applied in computer control, program control, securing communication, etc., can solve the problems of initiation and completion of unwanted transactions, undue overhead, and limited conventional fobs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
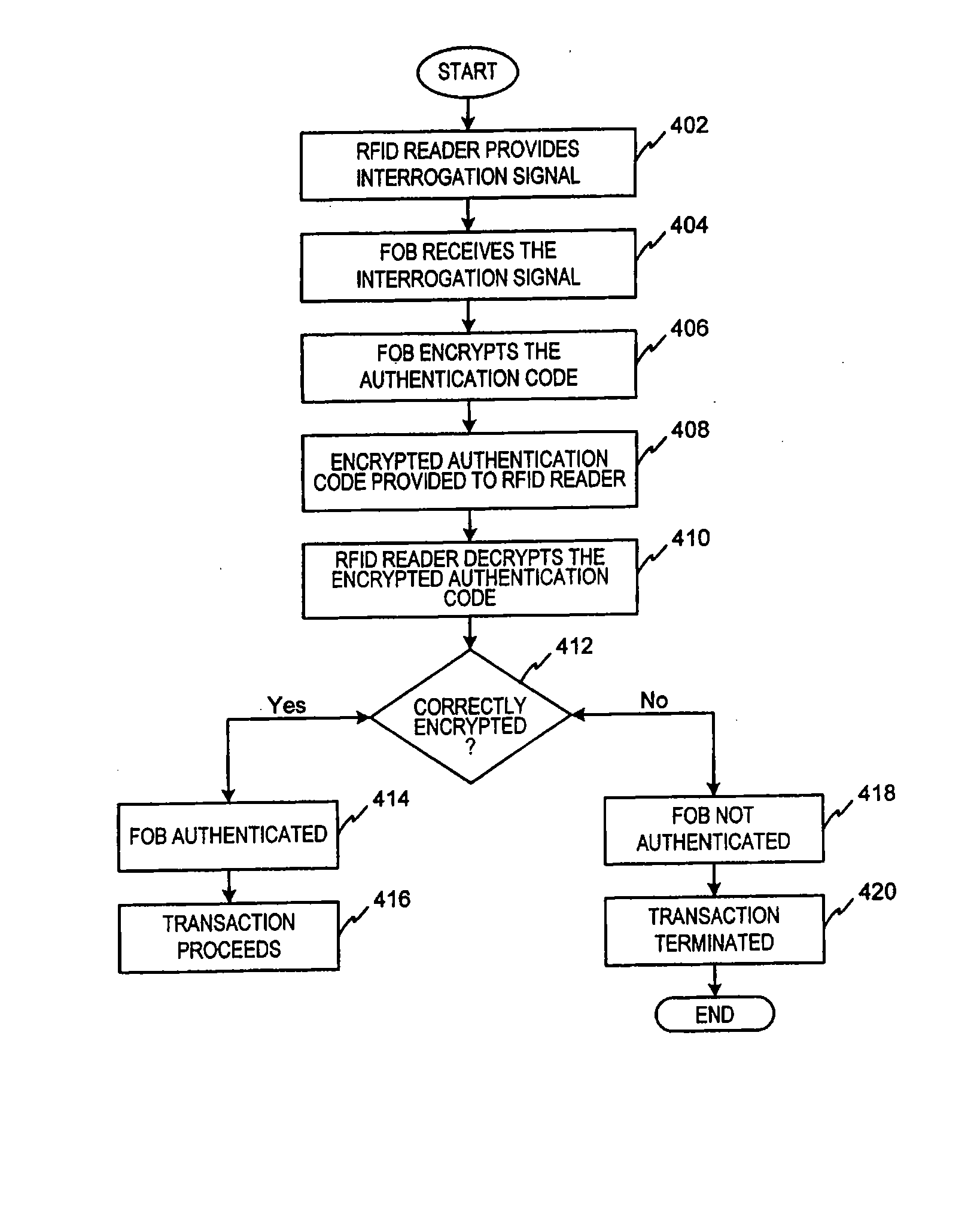
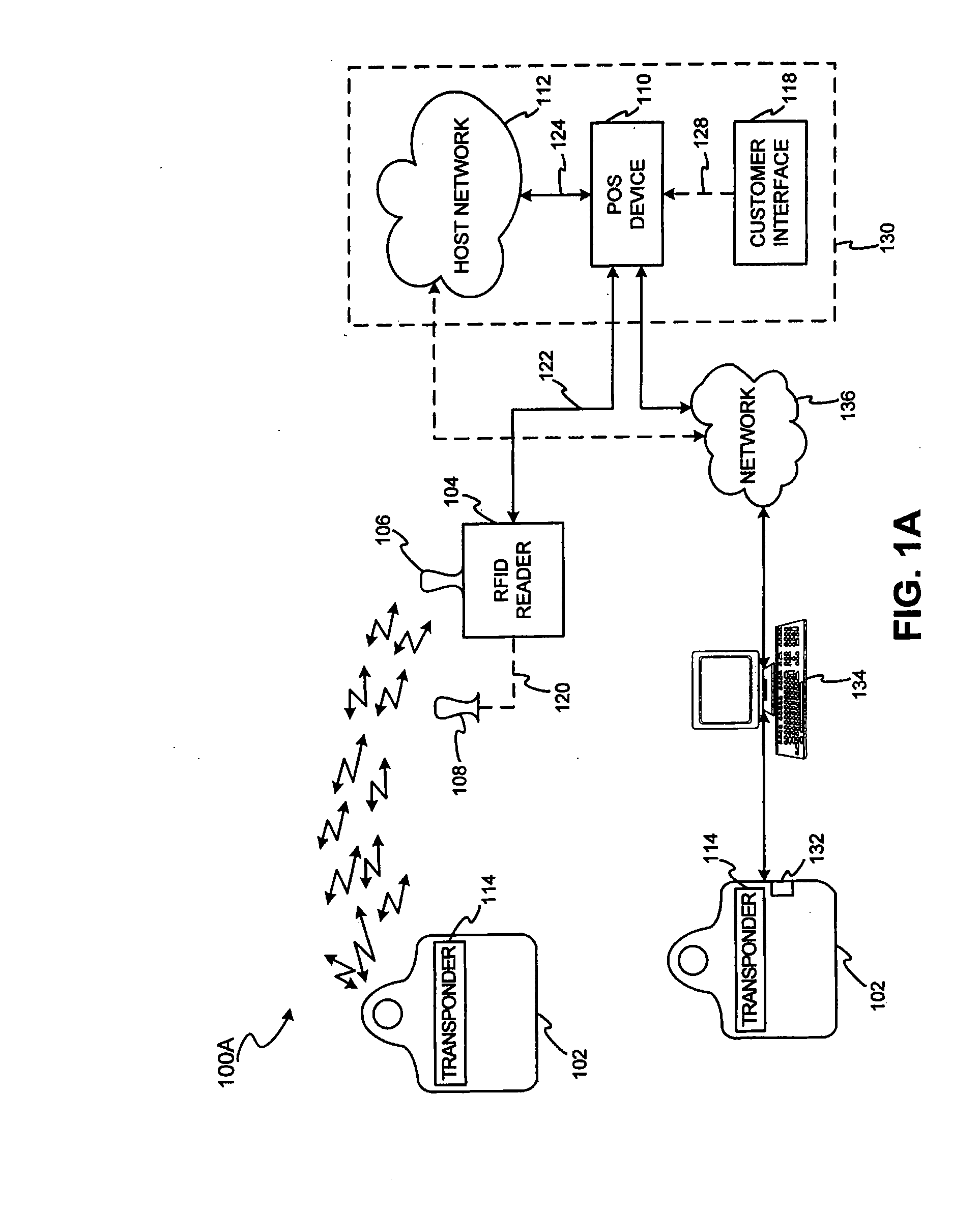
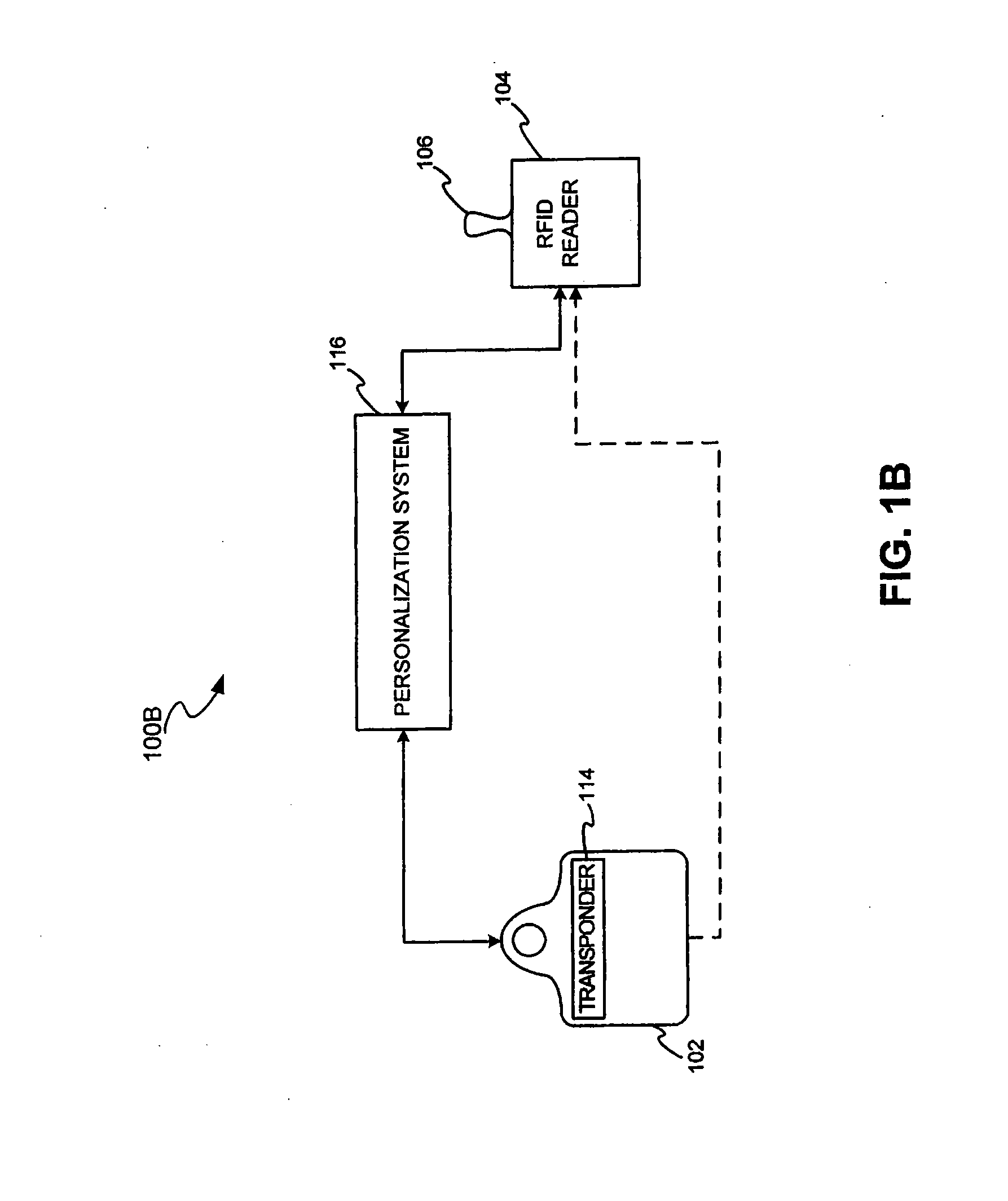
[0048] The present invention may be described herein in terms of functional block components, screen shots, optional selections and various processing steps. Such functional blocks may be realized by any number of hardware and / or software components configured to perform to specified functions. For example, the present invention may employ various integrated circuit components, (e.g., memory elements, processing elements, logic elements, look-up tables, and the like), which may carry out a variety of functions under the control of one or more microprocessors or other control devices. Similarly, the software elements of the present invention may be implemented with any programming or scripting language such as C, C++, Java, COBOL, assembler, PERL, extensible markup language (XML), JavaCard and MULTOS with the various algorithms being implemented with any combination of data structures, objects, processes, routines or other programming elements. Further, it should be noted that the pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com