Compensation for Frequency Adjustment in Mobile Communication-Positioning Device With Shared Oscillator
a technology of frequency adjustment and mobile communication, which is applied in the direction of electronic characteristics varying frequency control, wireless commuication services, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the mixing frequency and sampling frequency of the gps receiver used in down-converting and digitizing the gps signal, failure to detect the gps signal, and received signal may yield an error. , to achieve the effect of removing uncertainty, reducing uncertainty and reducing the uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
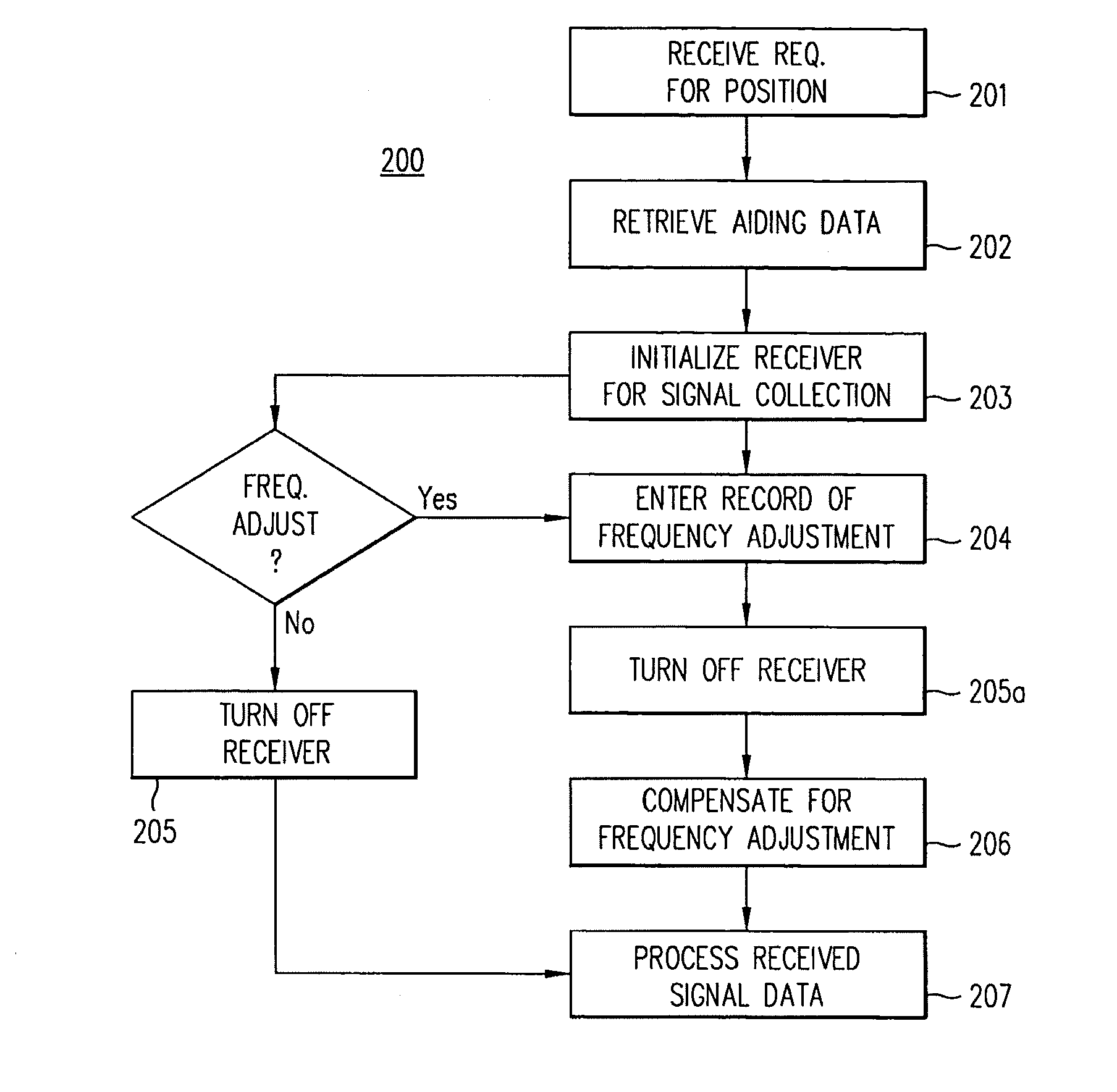
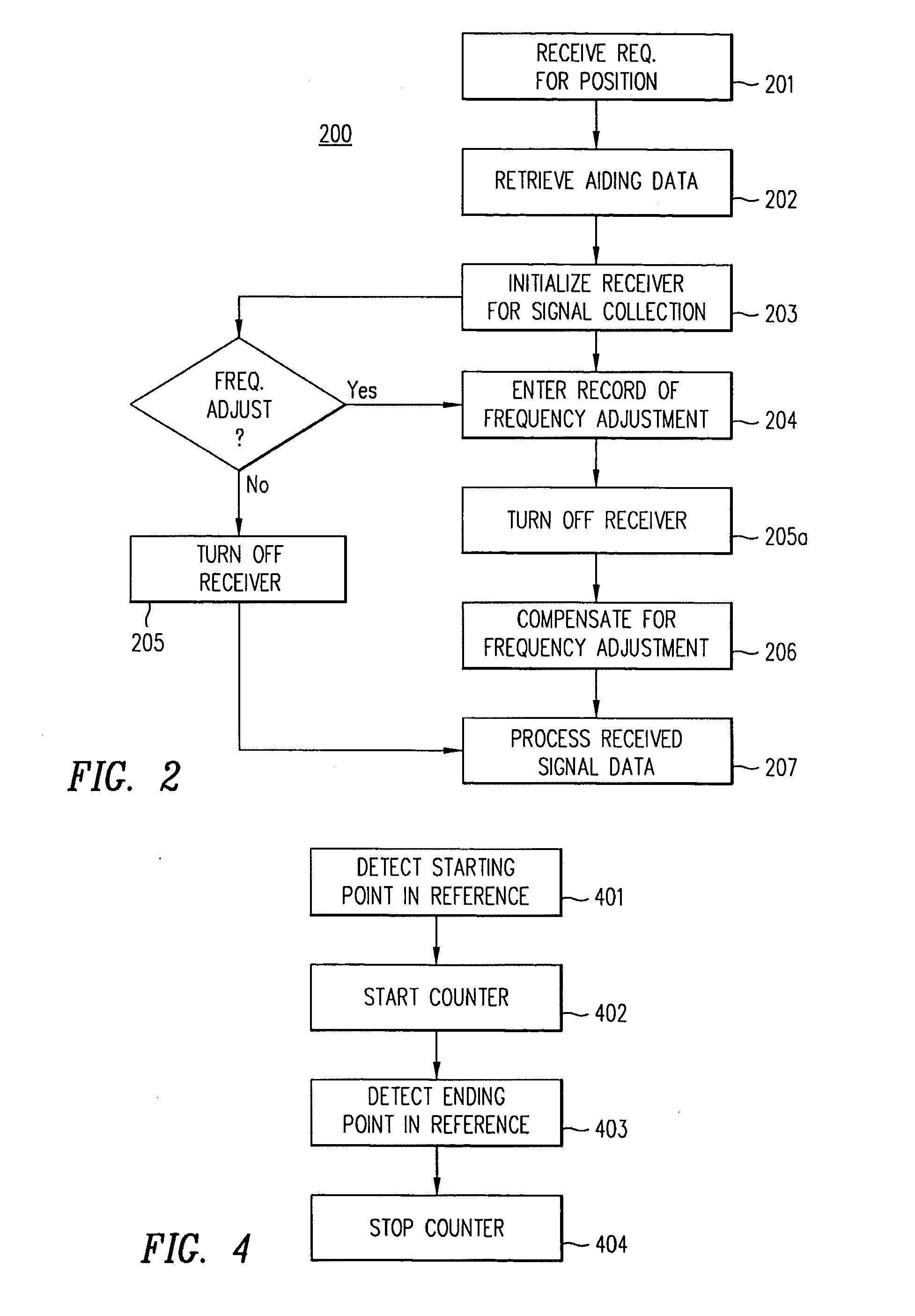
[0020]The present invention provides a method that compensates the frequency adjustment effects in the positioning signal detection process. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method for accurately determining the frequency of a local oscillator is provided.
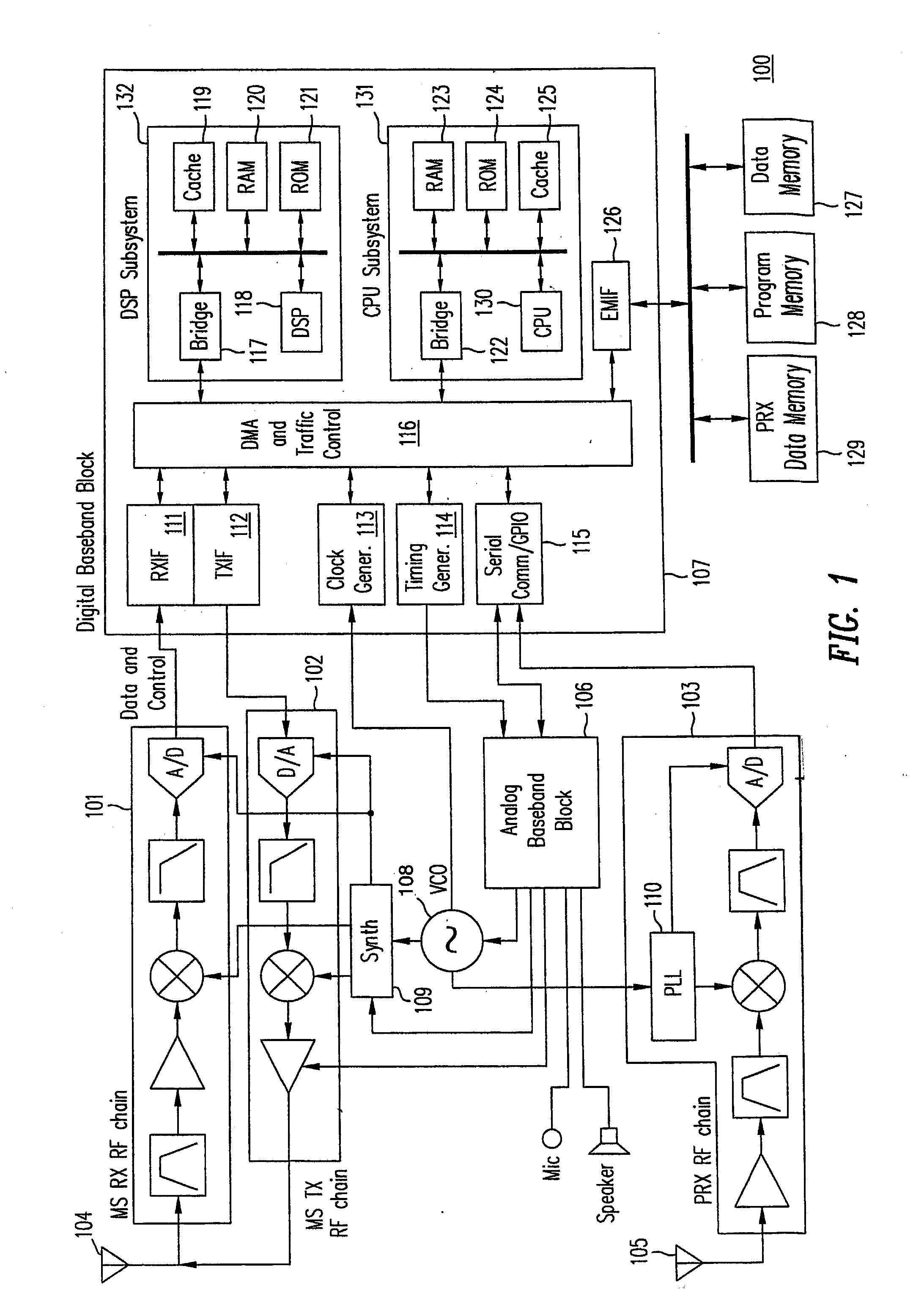
[0021]FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of mobile communication device 100 to which a method of the present invention is applicable. Mobile communication device 100 can be, for example, a cellular telephone handset. As shown in FIG. 1, mobile communication device 100 includes communication receiver 101, communication transmitter 102, positioning signal receiver 103, analog baseband circuit 106, digital baseband circuit 107, shared local oscillator 108 and synthesizer 109. In mobile communication device 100, shared local oscillator 108 is the frequency source for communication receiver 101, communication transmitter 102, and positioning signal receiver 103. Shared local oscillator 108 can be implemented, for exampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com