Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties
a technology of fc variants and receptors, applied in the field of fc variants with optimized fc receptor binding properties, can solve the problems of major challenges in obtaining variants that selectively increase or reduce the affinity of fcr, and the anti-cancer potential is unsatisfactory, so as to achieve the effect of increasing affinity and increasing affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design of Fc Variants with Selective FcγR Affinity
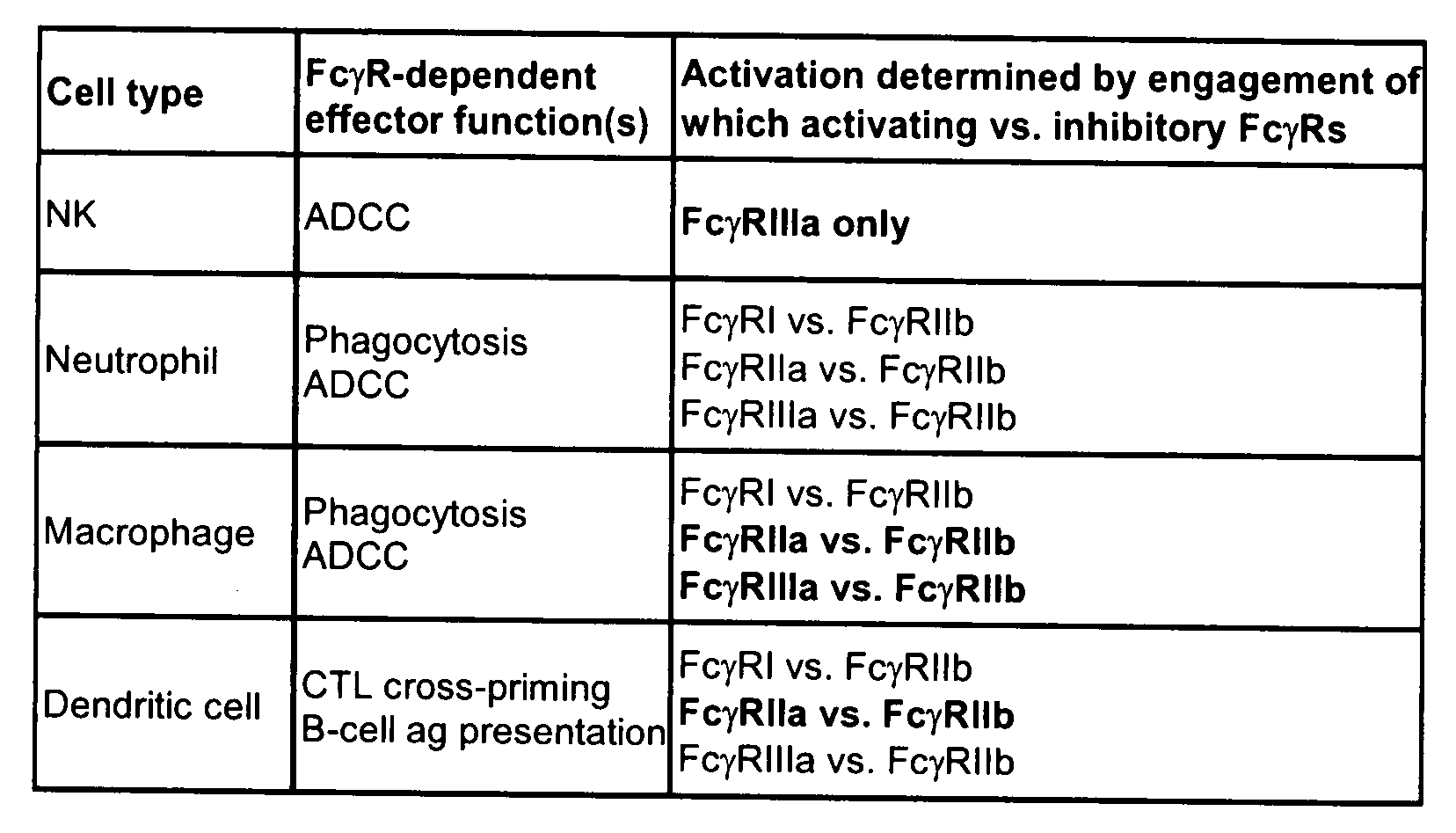
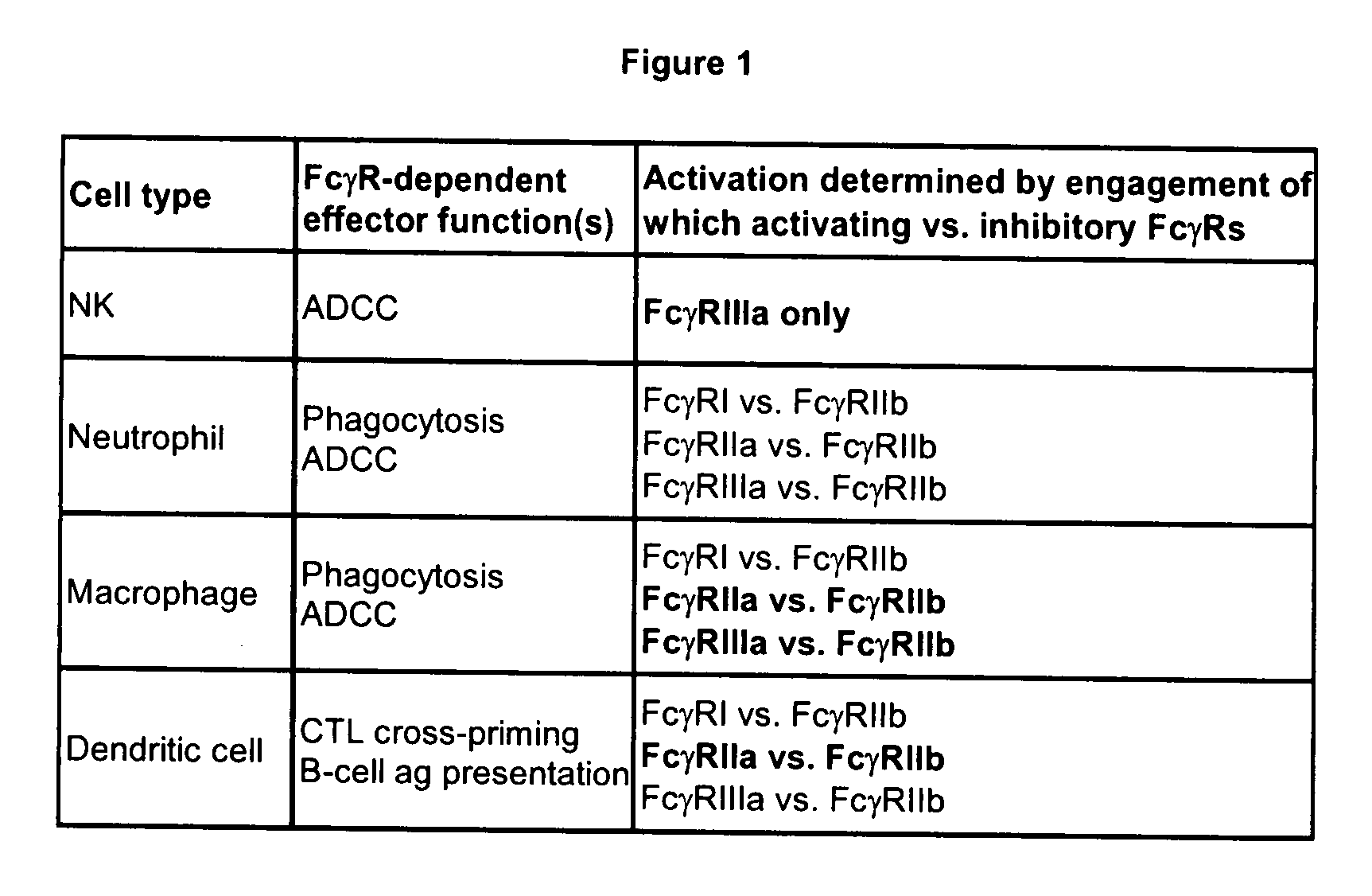
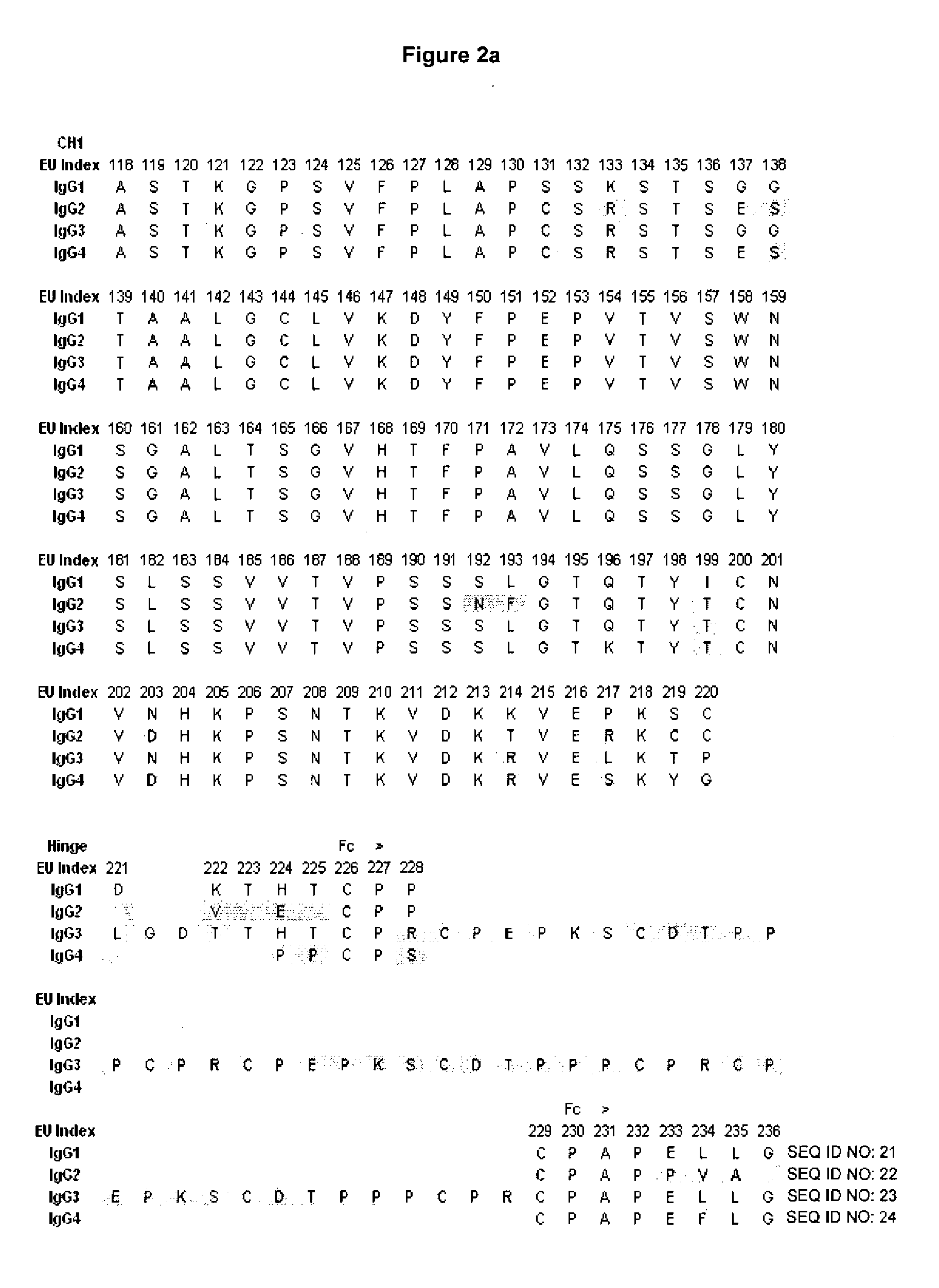
[0174]Sequence and structural analysis of the Fc / FcγR interface was carried out for the different human FcγRs. A central goal was to generate variants with selectively increased affinity for the activating receptors FcγRI, FcγRIIa, FcγRIIc, and FcγRIIIa relative to the inhibitory receptor FcγRIIb, and selectively increased affinity for FcγRIIb relative to the activating receptors. FIG. 4 shows an alignment of the sequences of the human FcγRs, highlighting the differences from FcγRIIb and positions at the Fc interface. The analysis indicates that although there is extensive homology among the human FcγRs, there are significant differences. Particularly relevant are differences at the Fc binding interface that may be capitalized on to engineer selective Fc variants.
[0175]The utility of this analysis is illustrated using the example of FcγRIIa vs. FcγRIIb. Engineering an Fc variant that selectively improves binding to FcγRIIa relative t...
example 2
Screening of Fc Variants
[0177]Amino acid modifications were engineered at these positions to generate variants with selective FcγR affinity. Fc variants were engineered in the context of the anti-CD20 antibody PRO70769 (PCT / US2003 / 040426, hereby entirely incorporated by reference). The genes for the variable regions of PRO70769 (SEQ IDs NO: 1 and NO:2, FIGS. 27a and 27b) were constructed using recursive PCR, and subcloned into the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1Zeo (Invitrogen) comprising the full length light kappa (CK) and heavy chain IgG1 constant regions. Amino acid substitutions were constructed in the variable region of the antibody in the pcDNA3.1Zeo vector using quick-change mutagenesis techniques (Stratagene). DNA was sequenced to confirm the fidelity of the sequences. Plasmids containing heavy chain gene (VH-CH1-CH2-CH3) (wild-type or variants) were co-transfected with plasmid containing light chain gene (VL-Cκ) into 293T cells. Media were harvested 5 days after trans...
example 3
Performance of Fc Variants in Cell-Based Assays
[0189]A central goal of improving the activating FcγR vs. inhibitory FcγR profile of an antibody or Fc fusion was to enhance its FcγR-mediated effector function in vitro and ultimately in vivo. To investigate the capacity of antibodies comprising the Fc variants of the present invention to carry out FcγR-mediated effector function, in vitro cell-based ADCC assays were run using human PBMCs as effector cells. ADCC was measured by the release of lactose dehydrogenase using a LDH Cytotoxicity Detection Kit (Roche Diagnostic). Human PBMCs were purified from leukopacks using a ficoll gradient, and the EpCAM+ target gastric adenocarcinoma line LS180. Target cells were seeded into 96-well plates at 10,000 cells / well, and opsonized using Fc variant or WT antibodies at the indicated final concentration. Triton X100 and PBMCs alone were run as controls. Effector cells were added at 40:1 PBMCs:target cells, and the plate was incubated at 37° C. fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com