Processor and compiler for decoding an instruction and executing the instruction with conditional execution flags
a compiler and instruction technology, applied in the field of processors and compilers, can solve problems such as large-scale circuits, and achieve the effect of high speed and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0104]mov r1, 0x23;;
[0105]This instruction description indicates that only an instruction “mov” shall be executed.
example 2
[0106]mov r1, 0x38
[0107]add r0, r1, r2
[0108]sub r3, r1, r2;;
[0109]These instruction descriptions indicate that three instructions of “mov”, “add” and “sub” shall be executed in parallel.
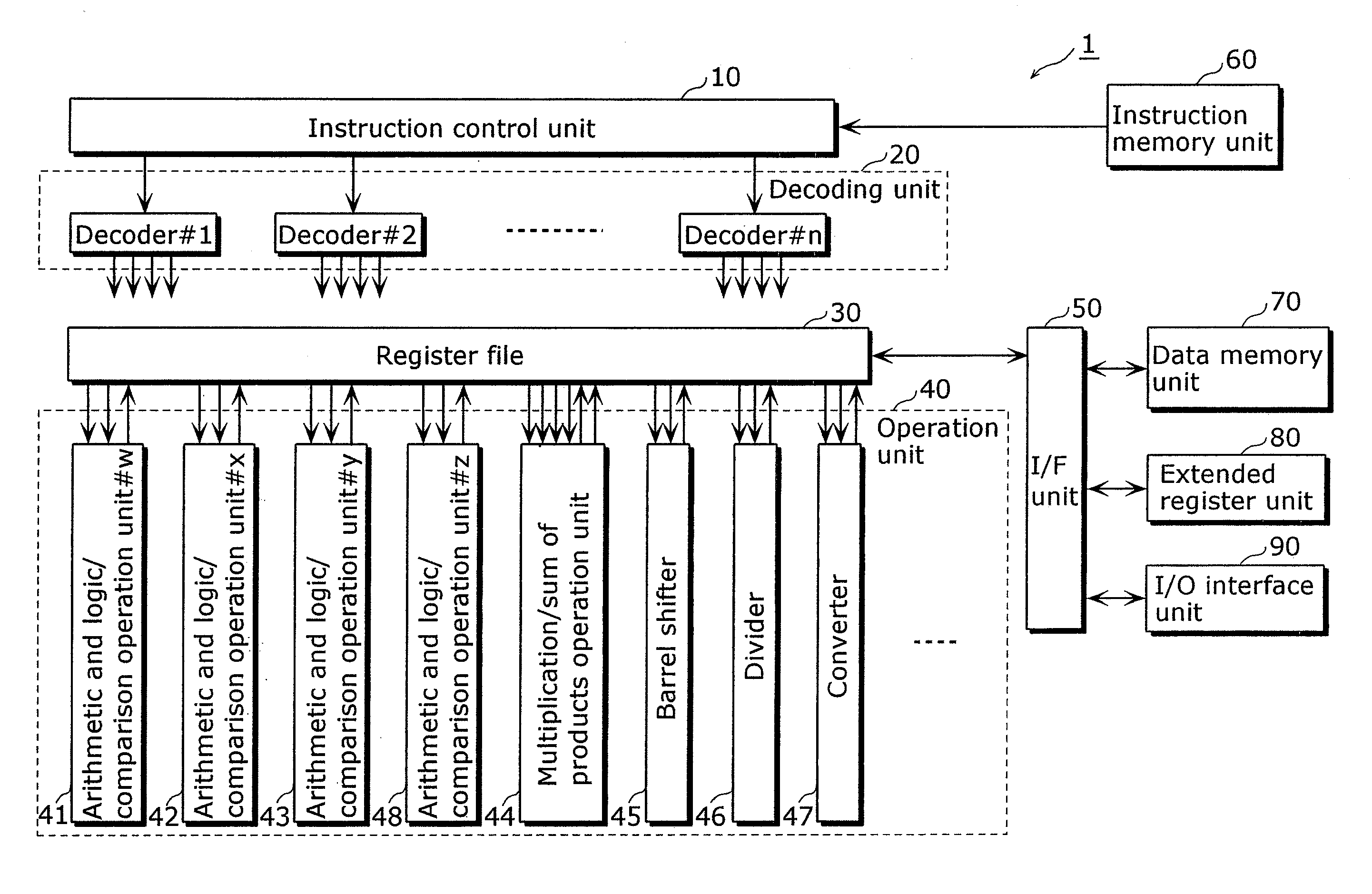
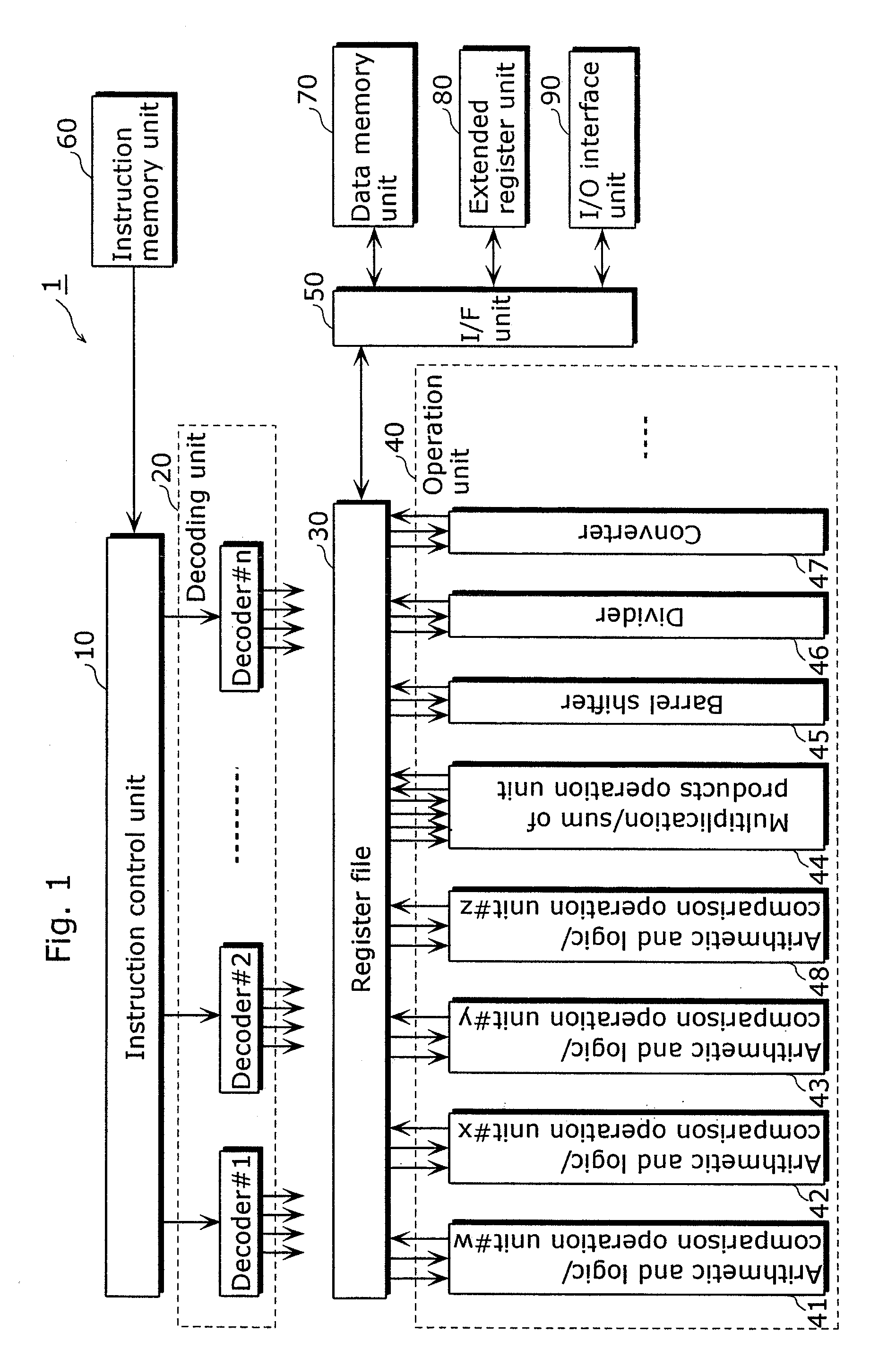
[0110]The instruction control unit 10 identifies an issue group and sends the identified issue group to the decoding unit 20. The decoding unit 20 decodes the instructions in the issue group, and controls resources required for executing such instructions.
[0111]Next, an explanation is given for registers included in the processor 1.
[0112]Table 1 below lists a set of registers of the processor 1.
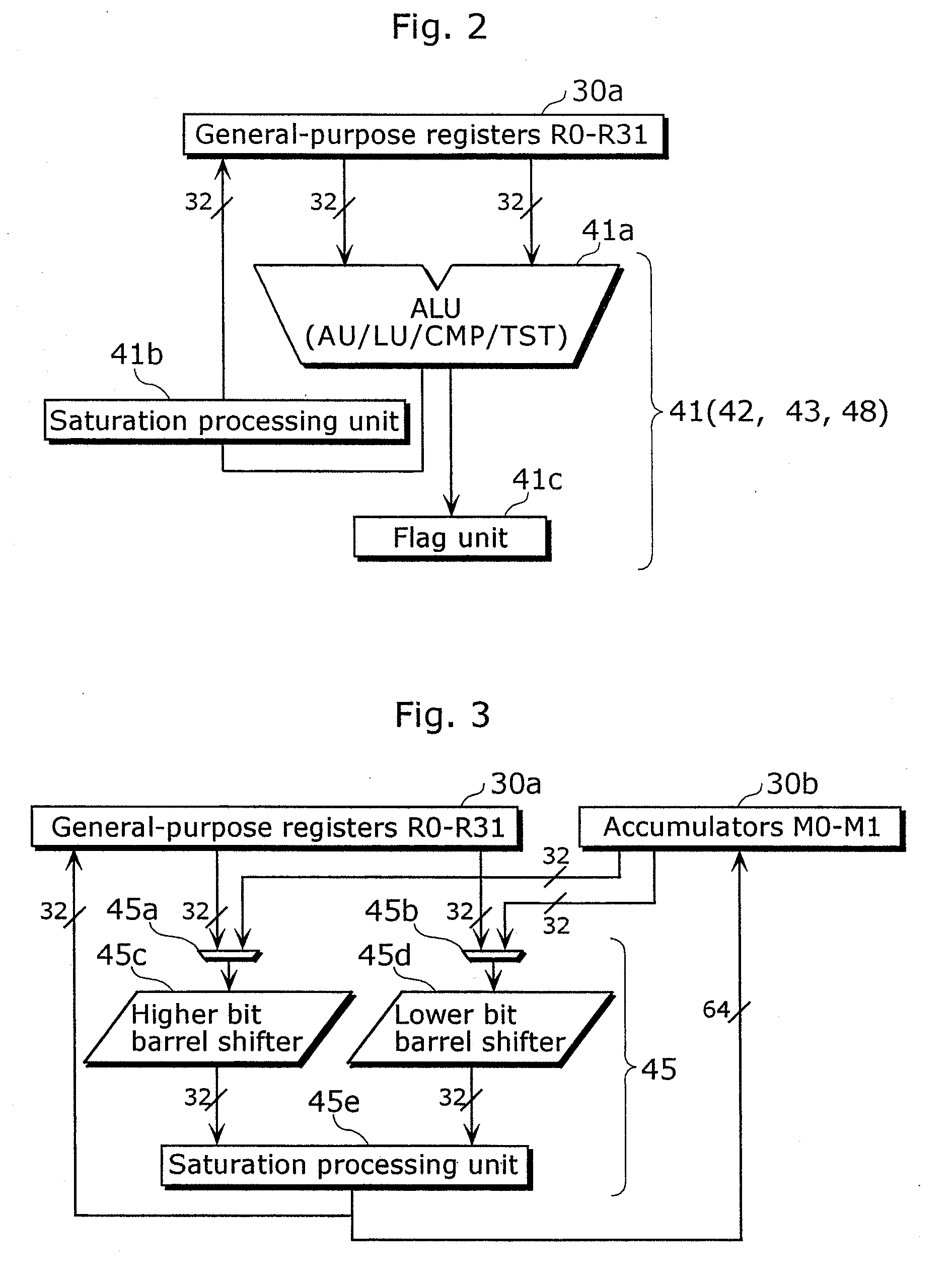
TABLE 1Register nameBit widthNo. of registersUsageR0-R3132 bits32General-purpose registers. Used as datamemory pointer, data storage at the time ofoperation instruction, and the like.TAR32 bits1Branch register. Used as branch addressstorage at branch point.LR32 bits1Link register.SVR16 bits2Save register. Used for saving conditional flag(CFR) and various modes.M0-M164 bits2Operation registers. Used as data sto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com