Articles Including High Modulus Fibrous Material
a high modulus, fibrous material technology, applied in the field of textile products, can solve the problems of nonwoven sheet materials exposed to varying temperature conditions, products can suffer various drawbacks, and many products, such as roofing membranes, are subject to stress in all directions of products, so as to improve strength, stability and abrasion resistance, and improve the effect of properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
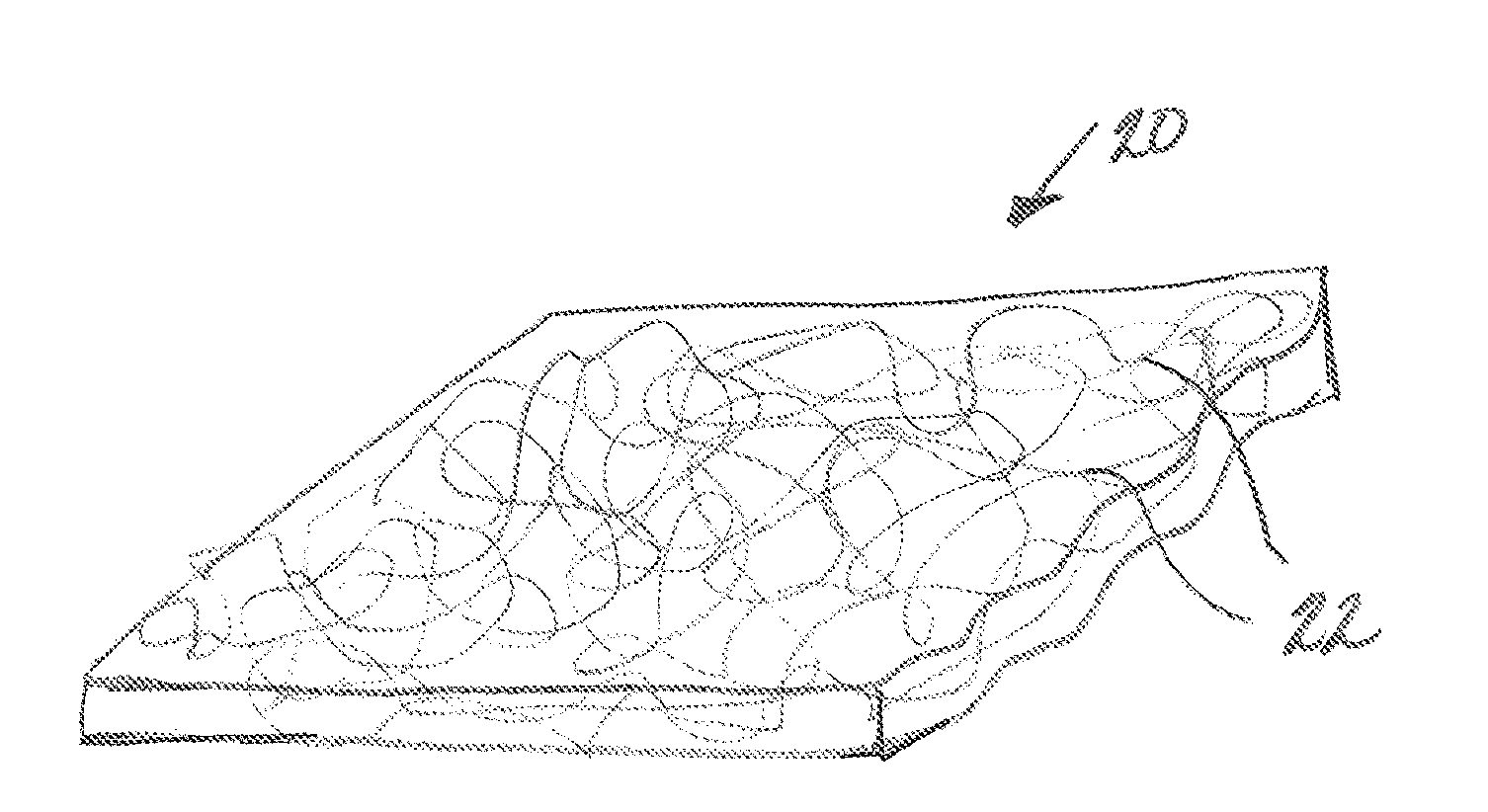
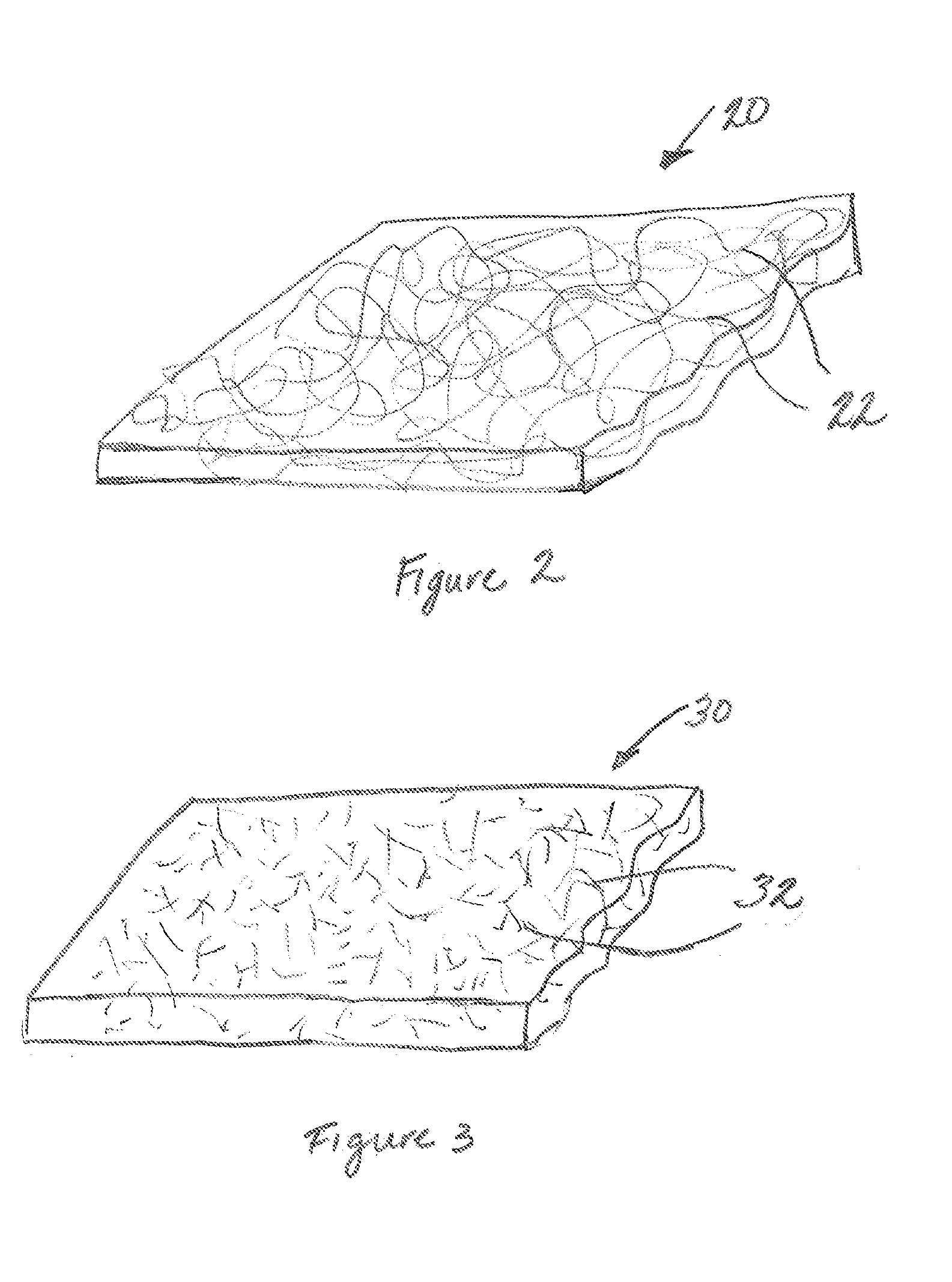
[0049]A nonwoven composite sheet material in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be prepared using a continuous multi-spinning beam process as follows. A nonwoven sheet of polyester fibrous materials can be produced using a continuous filament process such as spunbonding. Thereafter high modulus fibrous materials, such as glass staple fibers or glass cut yarns, are sprayed or otherwise applied onto a surface of the spunbonded polyester web. An additional layer of continuous filament polyester material, such as a second polyester spunbonded web, can thereafter be formed on the exposed surface of the glass fibrous web to form a sandwich structure including outer polyester spunbonded webs and an inner glass fibrous web. The webs can be bonded to form a coherent laminate structure using any suitable bonding technique, including chemical adhesion, thermal bonding, mechanical bonding (such as needling or hydroentanglement), and combinations thereof.
example 2
[0050]A nonwoven composite sheet material in accordance with another exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be prepared as follows. A nonwoven sheet of polyester staple fibers can be produced using a carding process. High modulus fibrous materials, such as glass staple fibers or glass cut yarns, are sprayed or otherwise applied onto a surface of a lower (inferior) crosslapper and prior to this lower web being combined with a web of polyester staple fibers being formed by an upper (superior) crosslapper, to form a composite sheet material including outer layers of polyester staple fibers sandwiching an inner layer of glass staple fibers. The webs can be bonded to form a coherent laminate structure using any suitable bonding technique, including chemical adhesion, thermal bonding, mechanical bonding (such as needling or hydroentanglement), and combinations thereof.
example 3
[0051]A nonwoven composite sheet material in accordance with yet another exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be prepared as follows. High modulus fibers, such as glass fibers, can be commingled with thermoplastic fibers, such as polyester fibers, in a mixing device and the commingled fibers thereafter laid on a web forming belt. The web of commingled polyester and glass fibers can be bonded to form a coherent laminate structure using any suitable bonding technique, including chemical adhesion, thermal bonding, mechanical bonding (such as needling or hydroentanglement), and combinations thereof.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoplasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Polymeric | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com