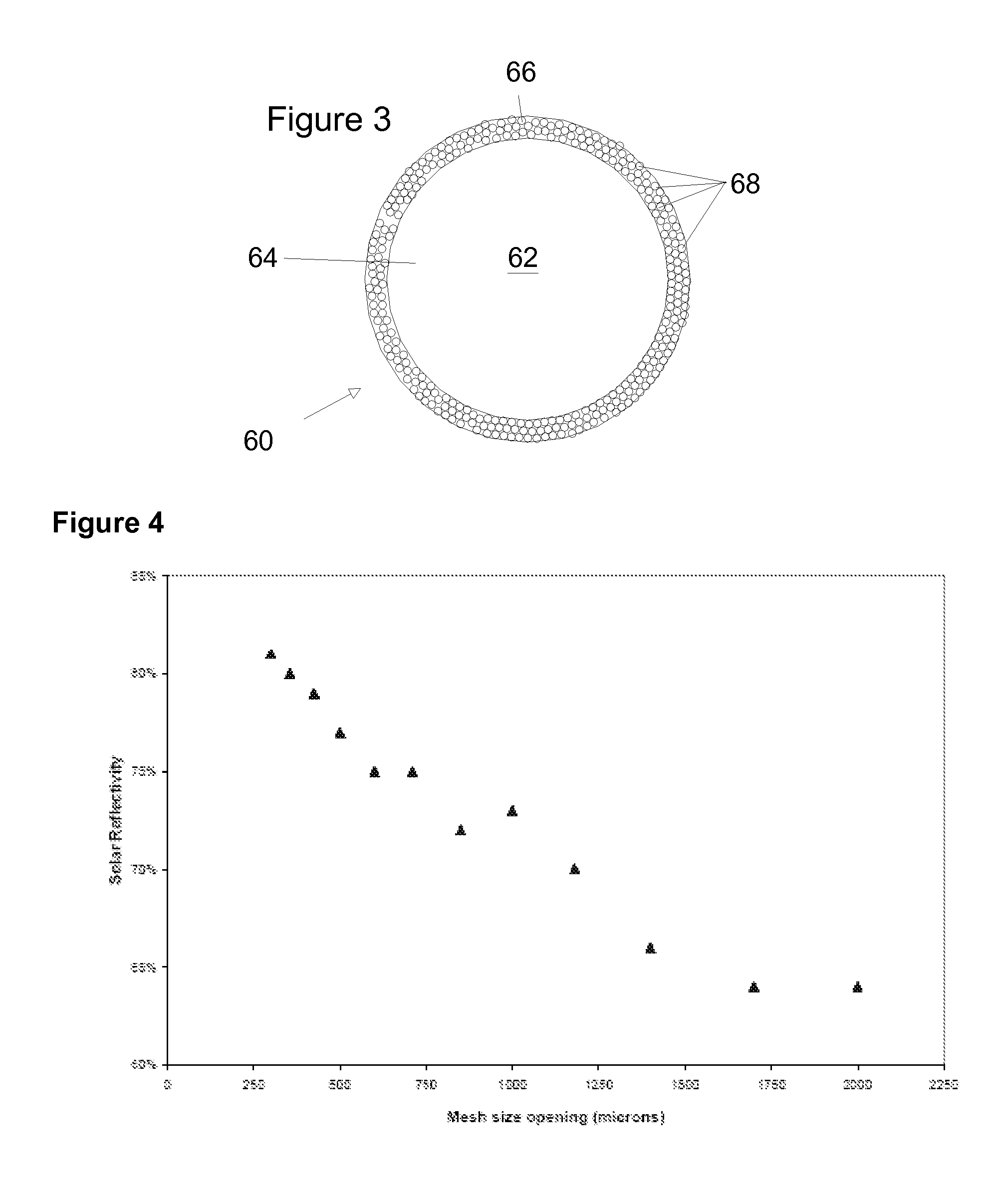
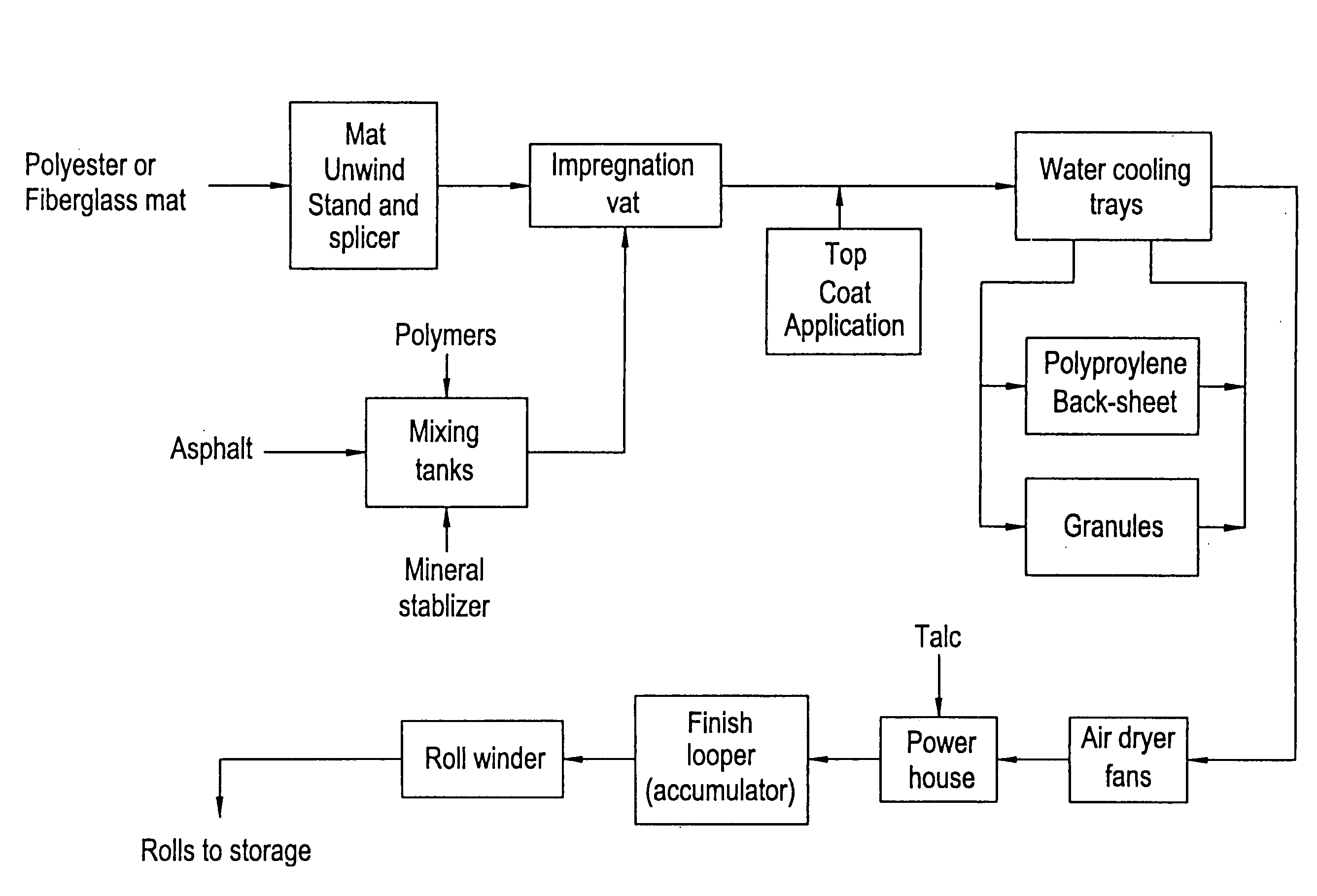
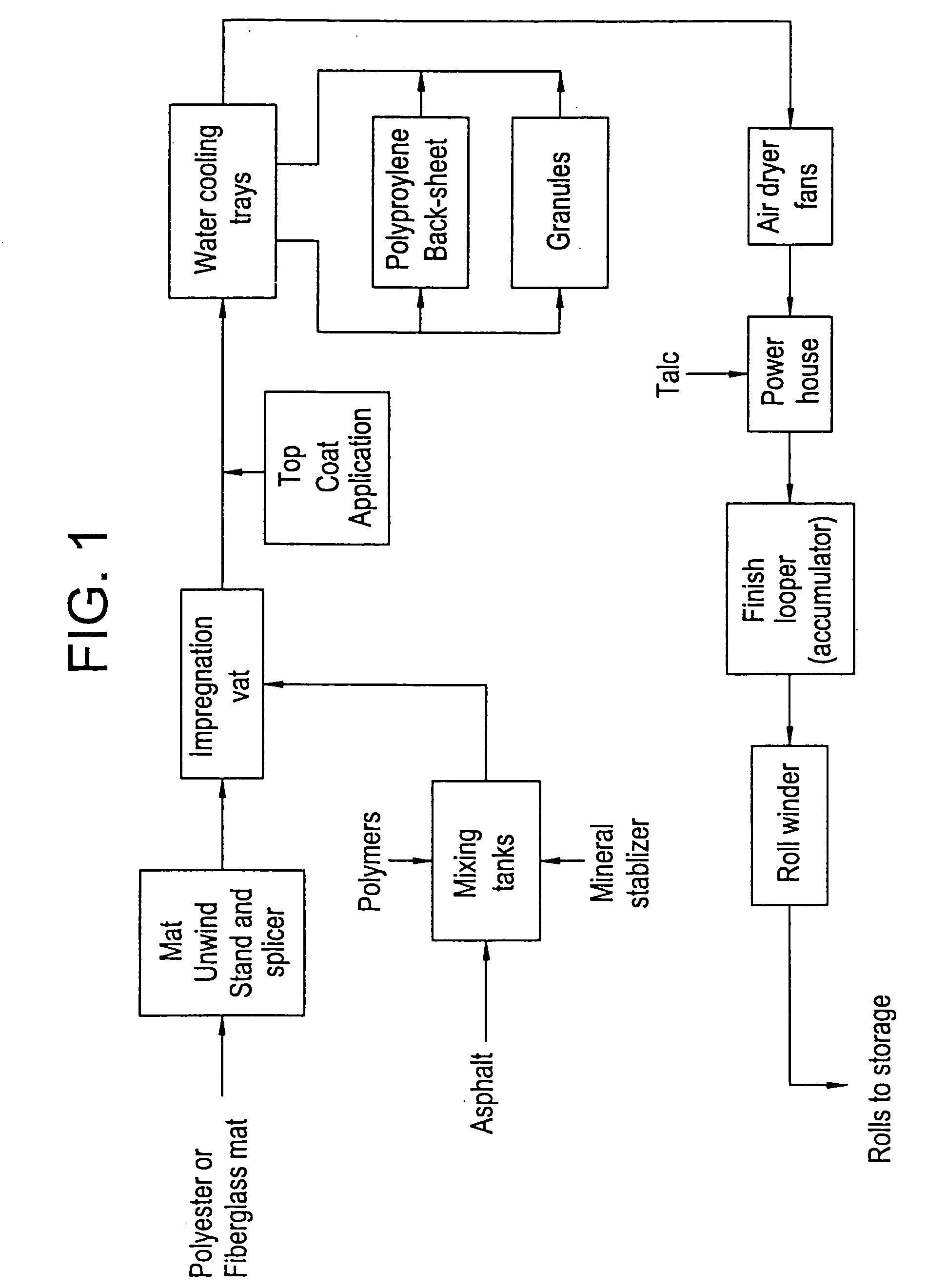
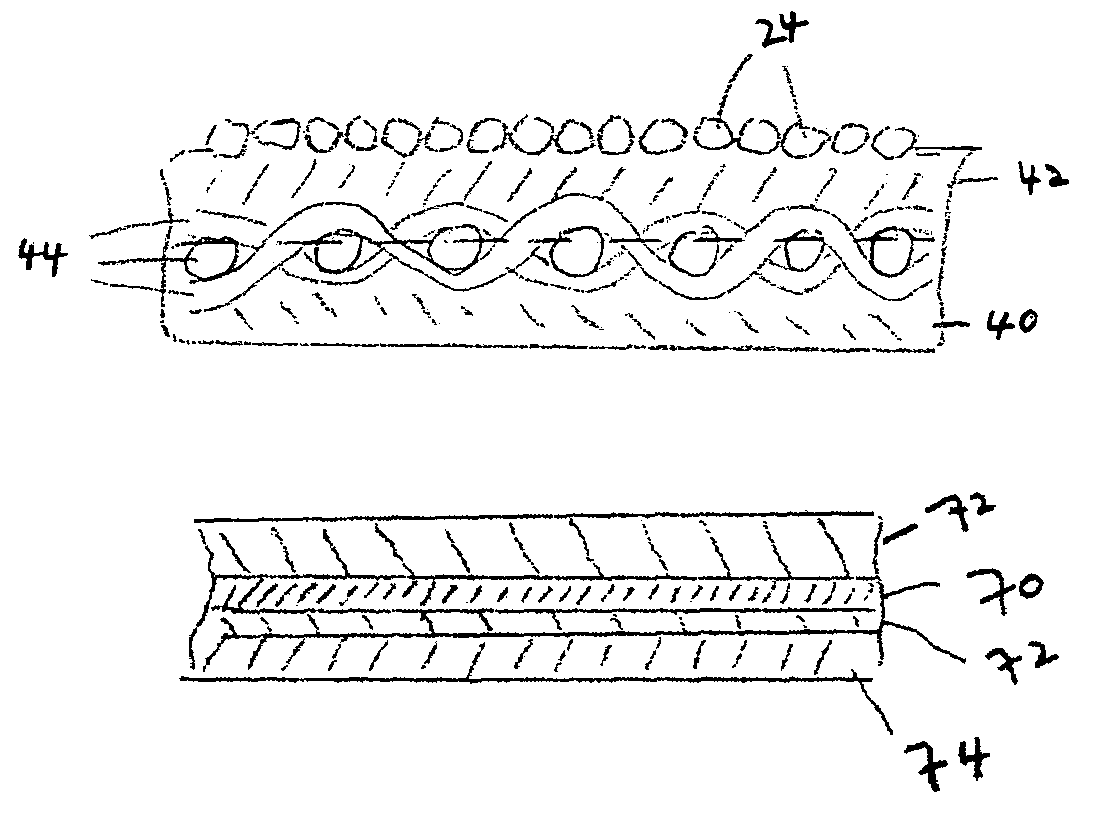
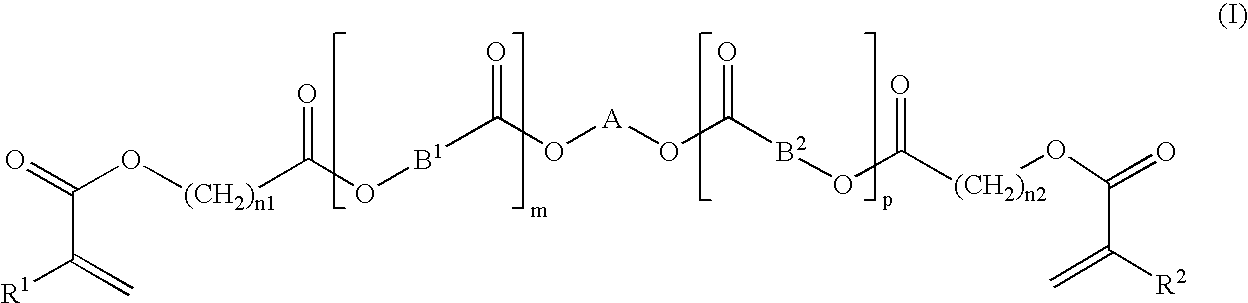
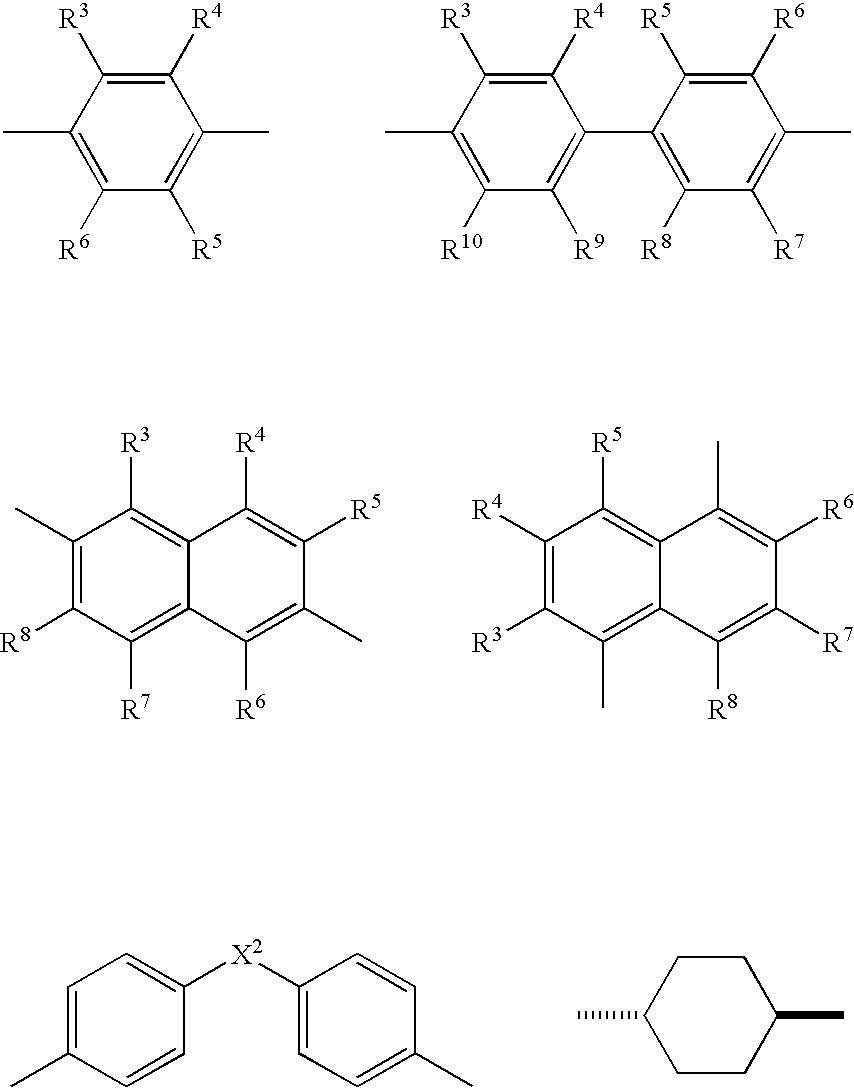
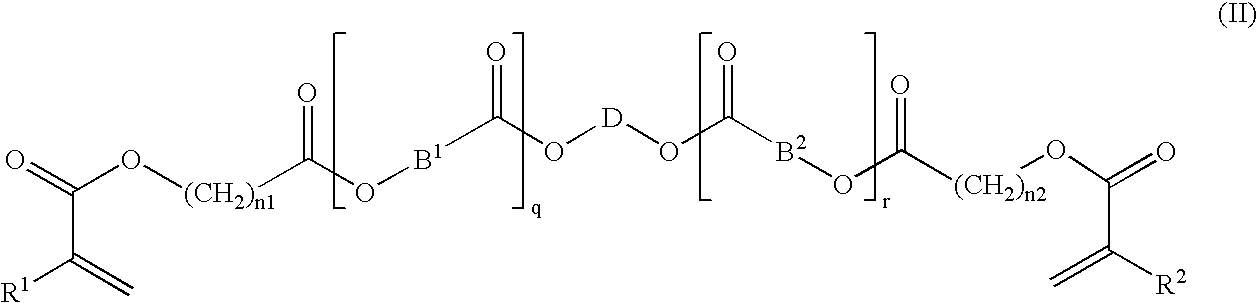
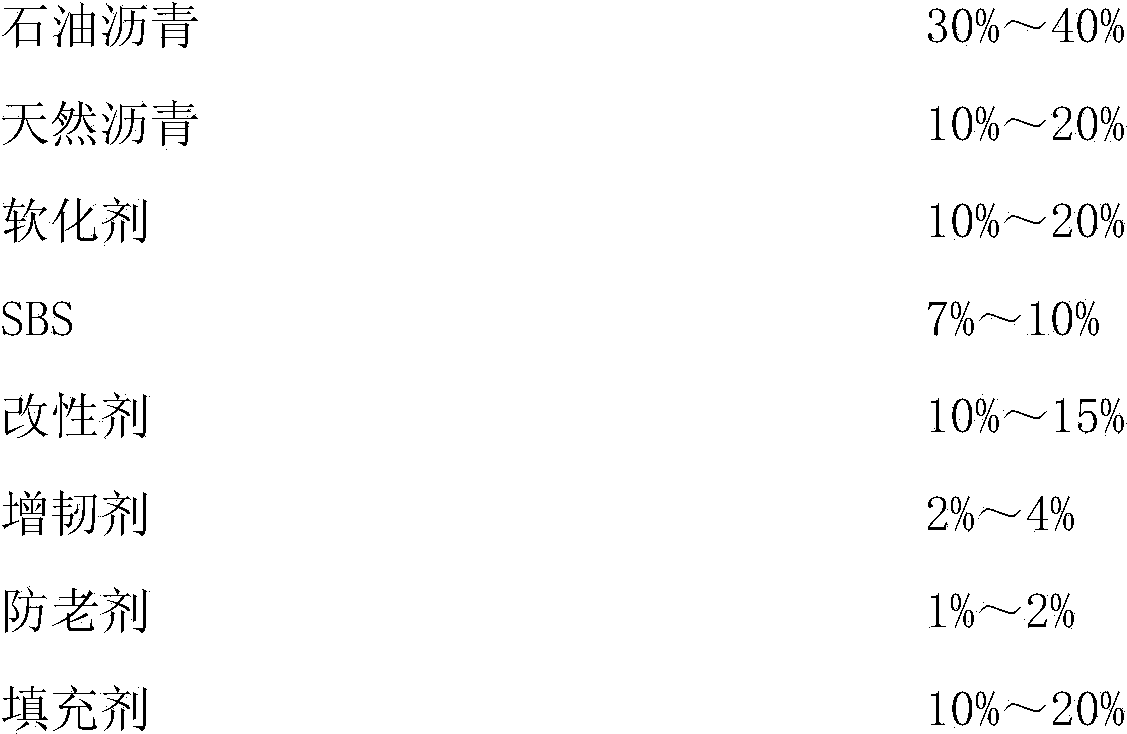Patents
Literature
971results about "Bituminous layered products" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthetic fiber
InactiveUS6135987AFormed easily and efficientlyCeramic shaping apparatusBaby linensPolyesterVitrification
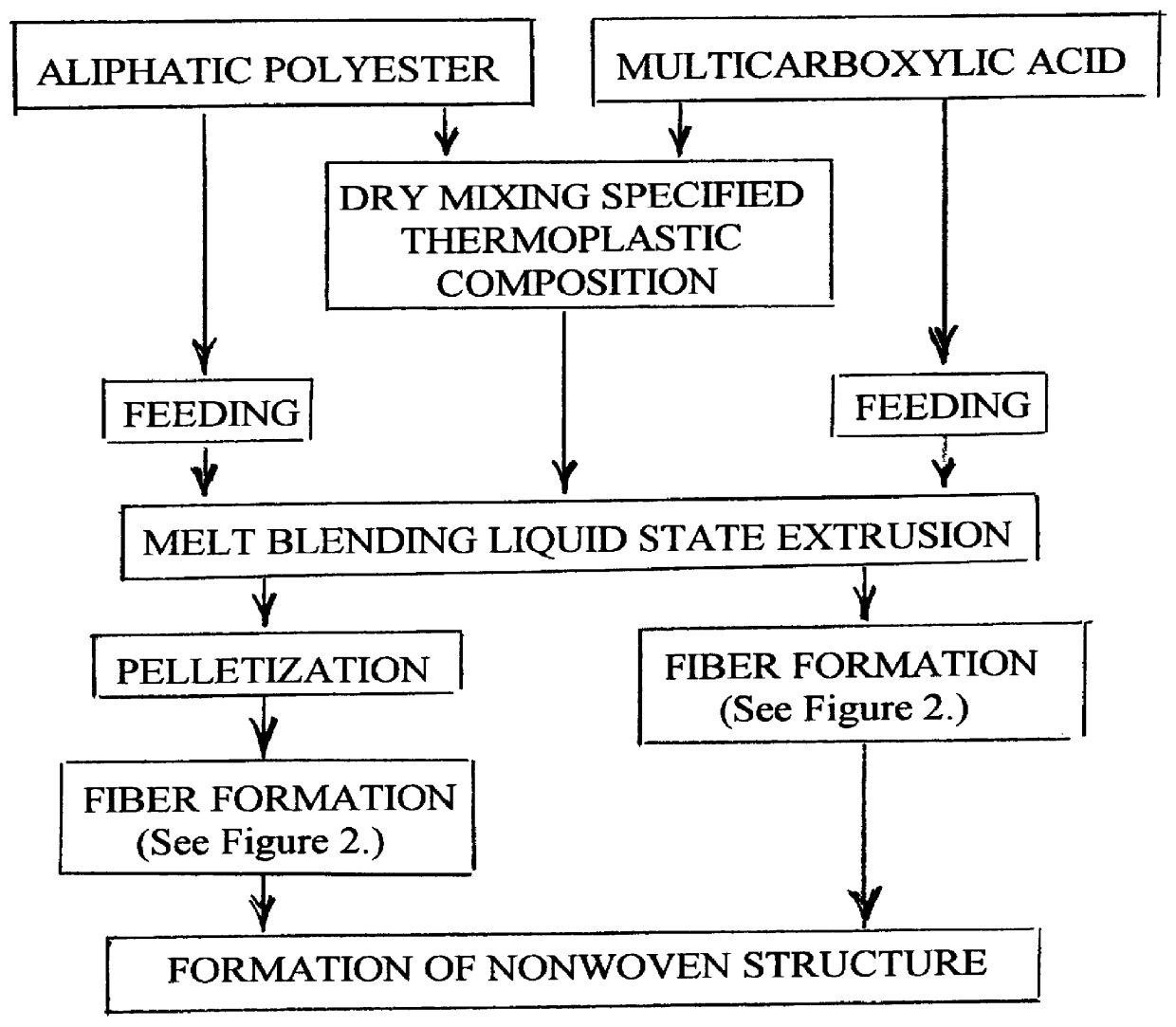
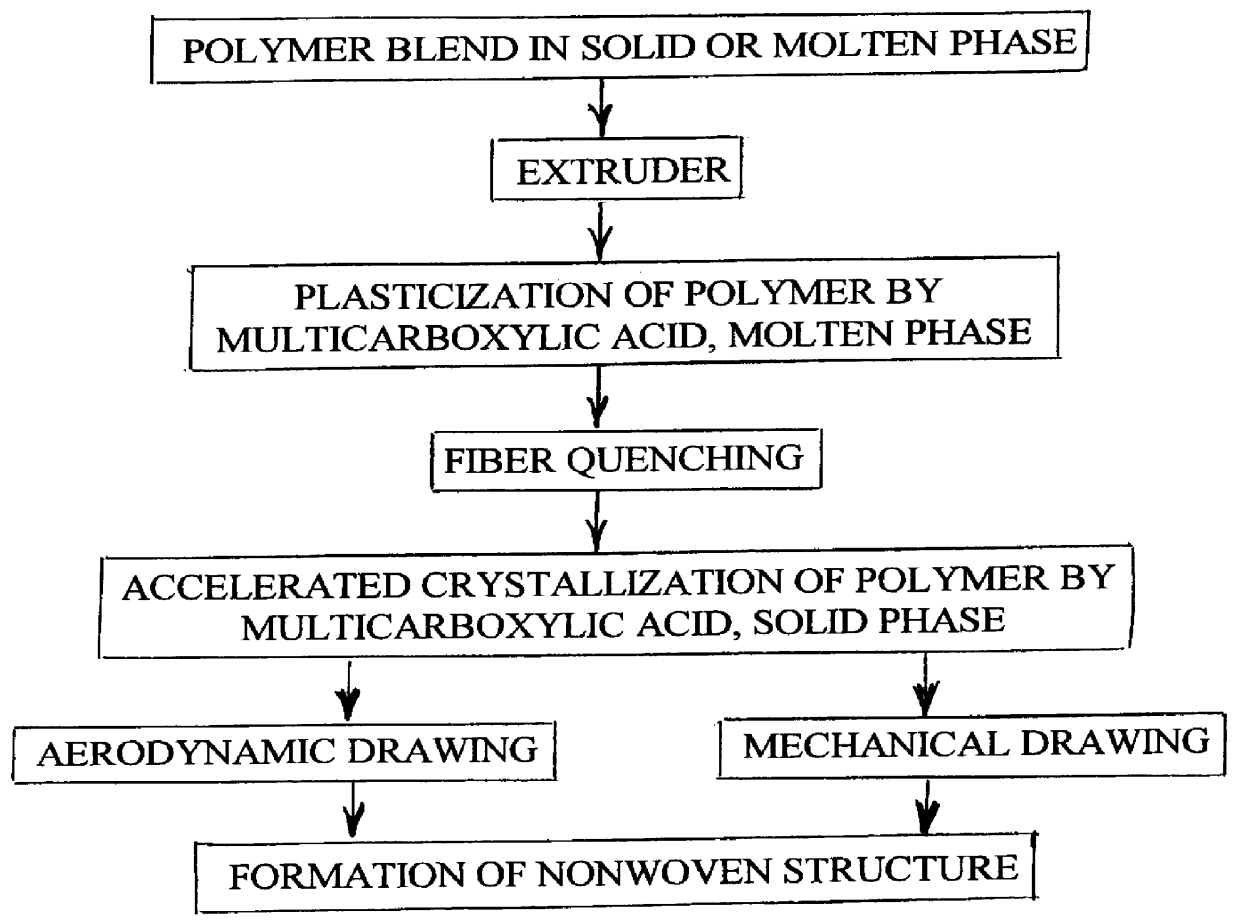
A process is disclosed for forming a synthetic fiber including providing a first component of an aliphatic polyester polymer a second component of a multicarboxylic acid, mixing the first component aliphatic polyester polymer and the second component multicarboxylic acid to form an unreacted specified thermoplastic composition, and melt blending the unreacted specified thermoplastic composition in an extruder or a mixer. The second component multicarboxylic acid lubricates the extruder and provides a nucleating agent for crystallizing the specified thermoplastic composition to form a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. Fiber composed of the specified thermoplastic composition has a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. The fiber has a glass transition temperature (Tg) less than about 55 DEG C. In one aspect, a first component of polylactic acid and a second component of adipic acid provide synthetic fibers in a nonwoven structure used in a biodegradable and compostable disposable absorbent product for the absorption and removal of body fluids.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Three-dimensionally reinforced multifunctional nanocomposites
ActiveUS20070128960A1Improve structural reinforcementSimple structureMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsFiberGeometric stability
A three-dimensional composite reinforcement, a three-dimensionally reinforced multifunctional nanocomposite, and methods of manufacture of each are disclosed. The three dimensional reinforcement comprises a two dimensional fiber cloth upon which carbon nanotubes have been grown, approximately perpendicular to the plane of the fiber cloth. The nanocomposite comprises the three-dimensional reinforcement and a surrounding matrix material. Examples illustrate improvements in the through-thickness mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of the nanocomposite, in addition to substantial improvements in geometrical stability upon temperature changes and vibrational damping, compared to baseline composites reinforced with the two-dimensional fiber cloth alone. Embodiments of the nanocomposite may also be configured to perform multiple functions simultaneously, such as bearing a thermal or mechanical load simultaneously or bearing a mechanical load while also monitoring the state of damage within the nanocomposite.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Low odor faced insulation assembly
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
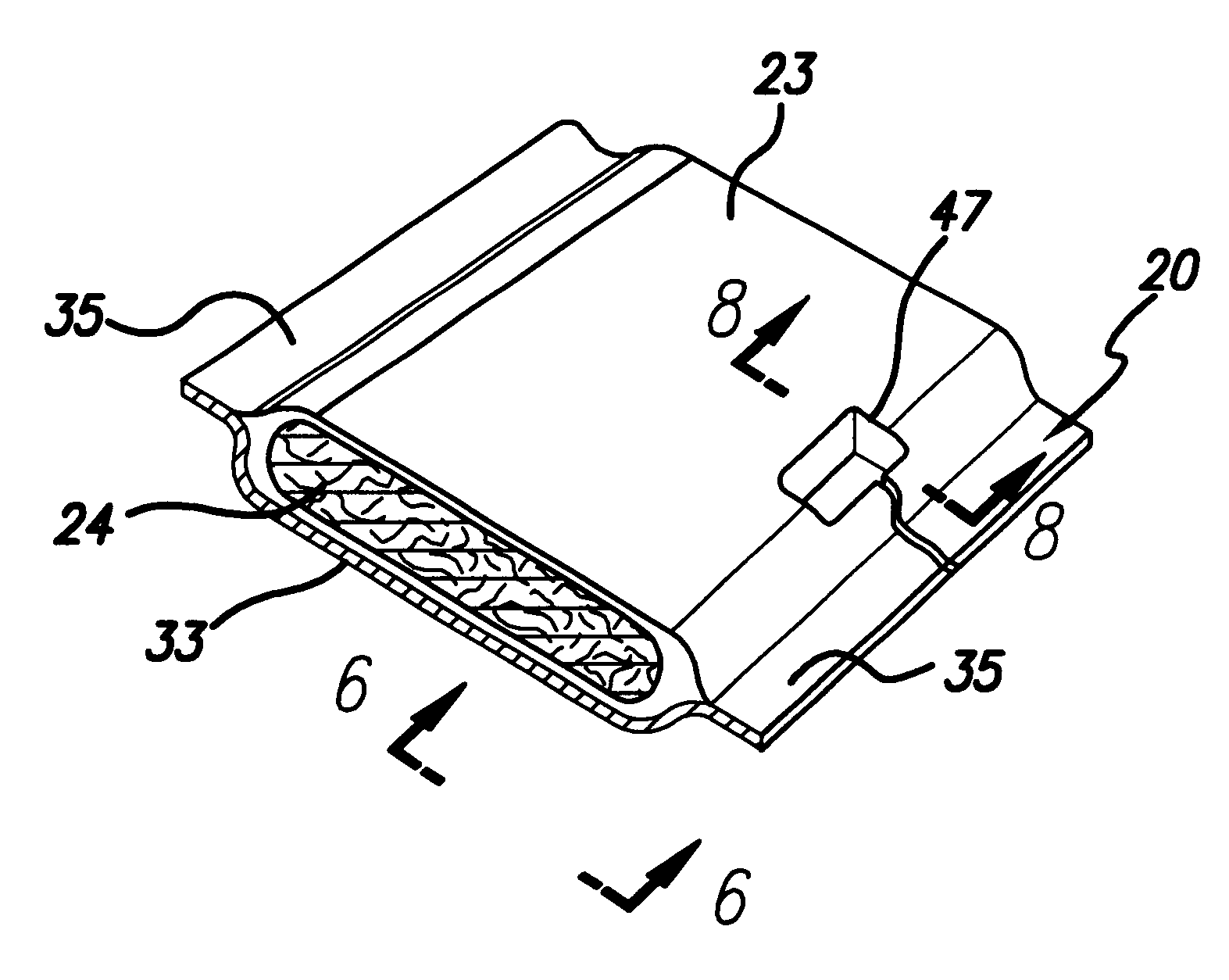
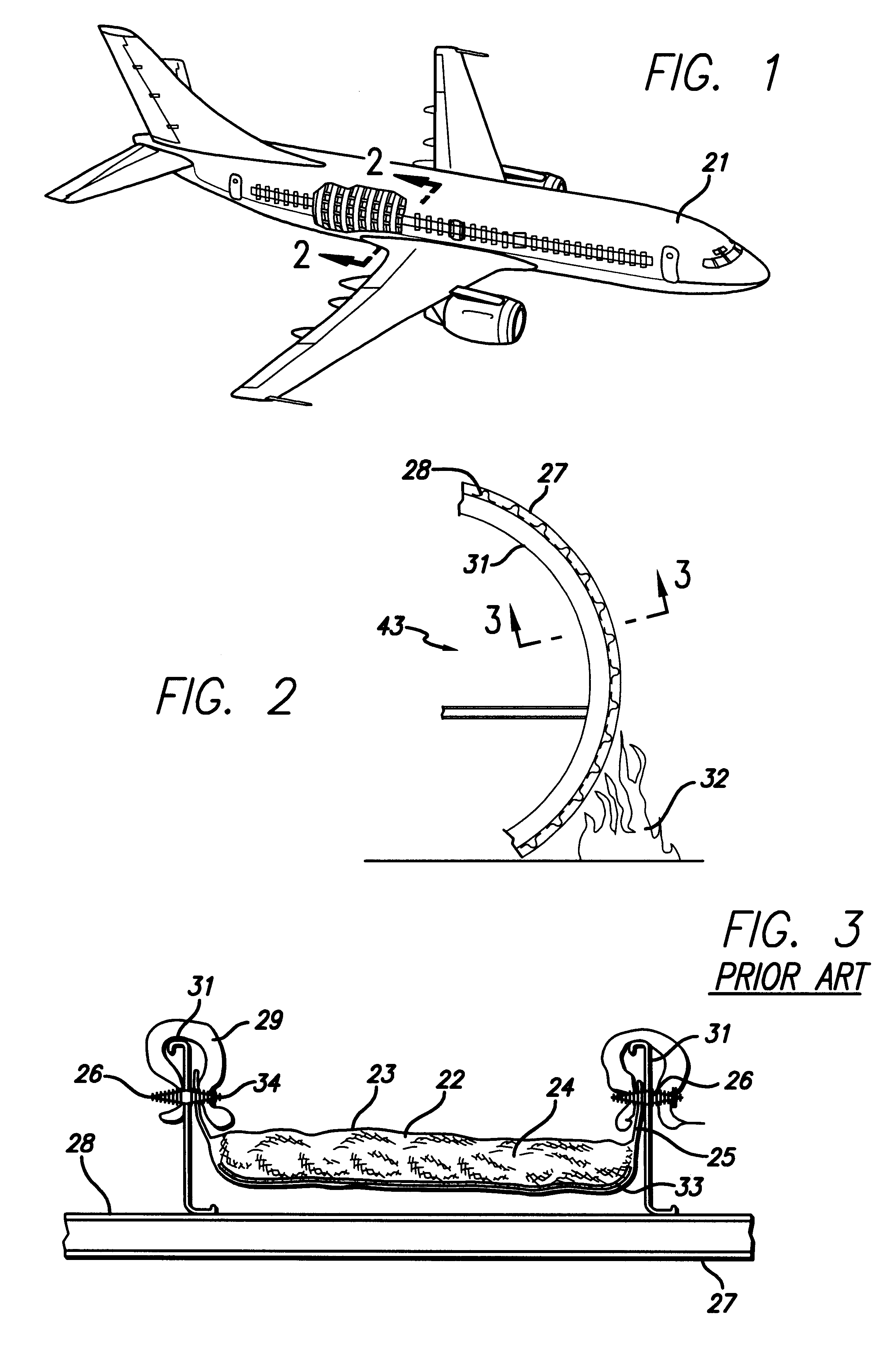
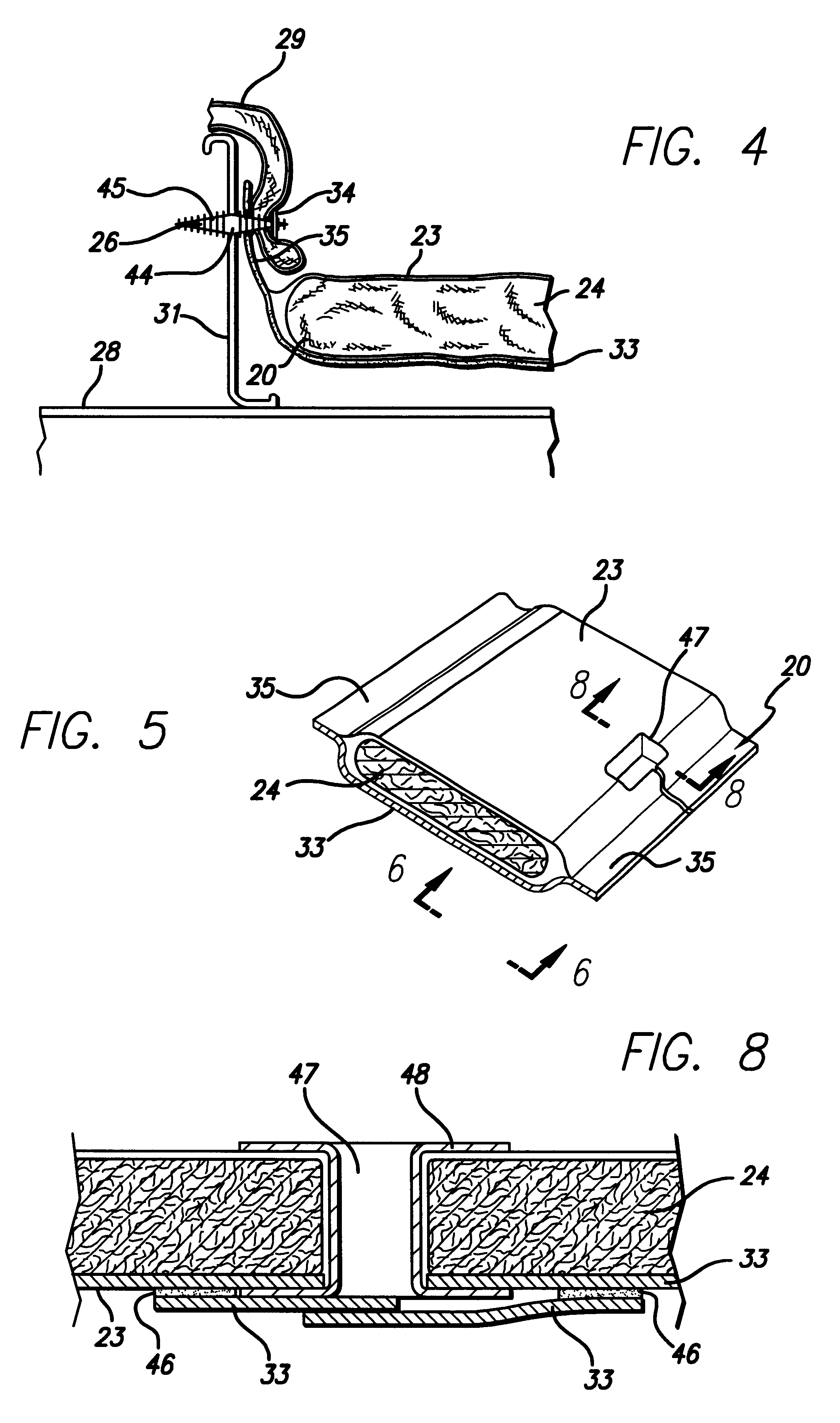
Fire-blocking insulation blanket
InactiveUS6358591B1Improve protectionLow costSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsGlass fiberFuselage
An insulation blanket is disclosed that contains fire-blocking materials for preventing rapid penetration of fire into an aircraft fuselage in case of a fire outside the aircraft. The insulation blanket contains at least one layer of fiberglass or other thermal-acoustic insulation material without fire-blocking properties, and one or more layers of fire-blocking material. The fire blocking material is wider than the thermal-acoustic insulation so that it may be folded against and attached to adjacent structural frame members of the fuselage. In the alternative, a thermal-acoustic insulation material is used that has fire-blocking properties instead of the separate layers of fire-blocking and thermal-acoustic insulation materials. A method for installing insulation blankets according to the present invention is disclosed, whereby a fire-blocking insulation portion of the blanket is folded against and attached to frame members of the aircraft using attachment posts or spring clips.
Owner:ORCON CORP
Method of forming an improved roofing material
InactiveUS6933007B2Improve reflectivityIncrease temperatureRoof covering using tiles/slatesCovering/liningsMaterials scienceReflectivity
A method of coating highly reflective granules on an adhering material of a roofing or siding material to form a roofing or siding material having an average resulting reflectivity on an upper surface of at least about 45%. The method includes the selecting of highly reflective granules and applying the highly reflective granules on an adhering material until over about 95% of a top surface of the adhering material is covered by the granules.
Owner:GARLAND INDS
Shingle with improved blow-off resistance
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Impact resistant shingle
InactiveUS20050204675A1Resistance to crackingDissipate energyRoof covering using tiles/slatesConstructions elementsCrack resistanceShingles
An impact resistant shingle is provided, wherein the base mat is impregnated with an asphaltic material, with an asphaltic material on the upper surface of the shingle, and wherein another asphaltic material is disposed on the rear surface of the shingle, which other asphaltic material is softer with greater elongation than the asphaltic material used elsewhere in the shingle, such that crack resistance is afforded because energy from impact on the shingle is dissipated.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Solar heat-reflective roofing granules, solar heat-reflective shingles, and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20110086201A1Improve solar heat reflectivityRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof improvementMetallurgyDegree Celsius
A process for preparing roofing granules includes forming kaolin clay into green granules and sintering the green granules at a temperature of at least 900 degrees Celsius to cure the green granules until the crystalline content of the sintered granules is at least ten percent as determined by x-ray diffraction.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Solar Heat Reflective Roofing Membrane and Process For Making the Same
ActiveUS20070054129A1High solar heat resistanceRoof covering using flexible materialsClimate change adaptationEngineeringSolar heat
A roofing membrane with high solar heat reflectance includes a bituminous base sheet, a tie-layer with a reinforcement material, and a solar heat-reflective upper layer.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Sealing sheet assembly for construction surfaces and methods of making and applying same
InactiveUS6586080B1Low costReduce thicknessBuilding roofsRoof covering using flexible materialsRelative displacementClassical mechanics
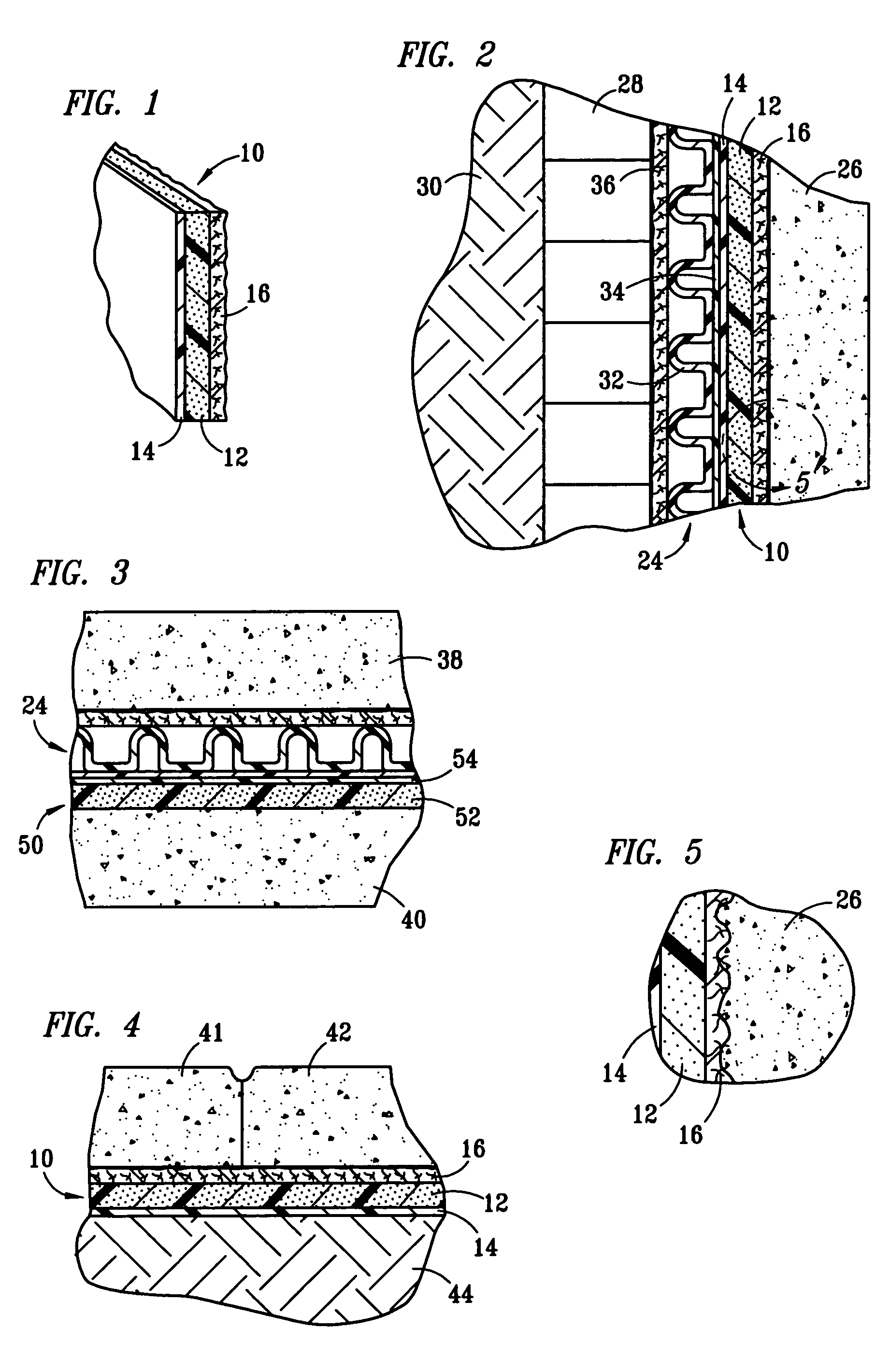
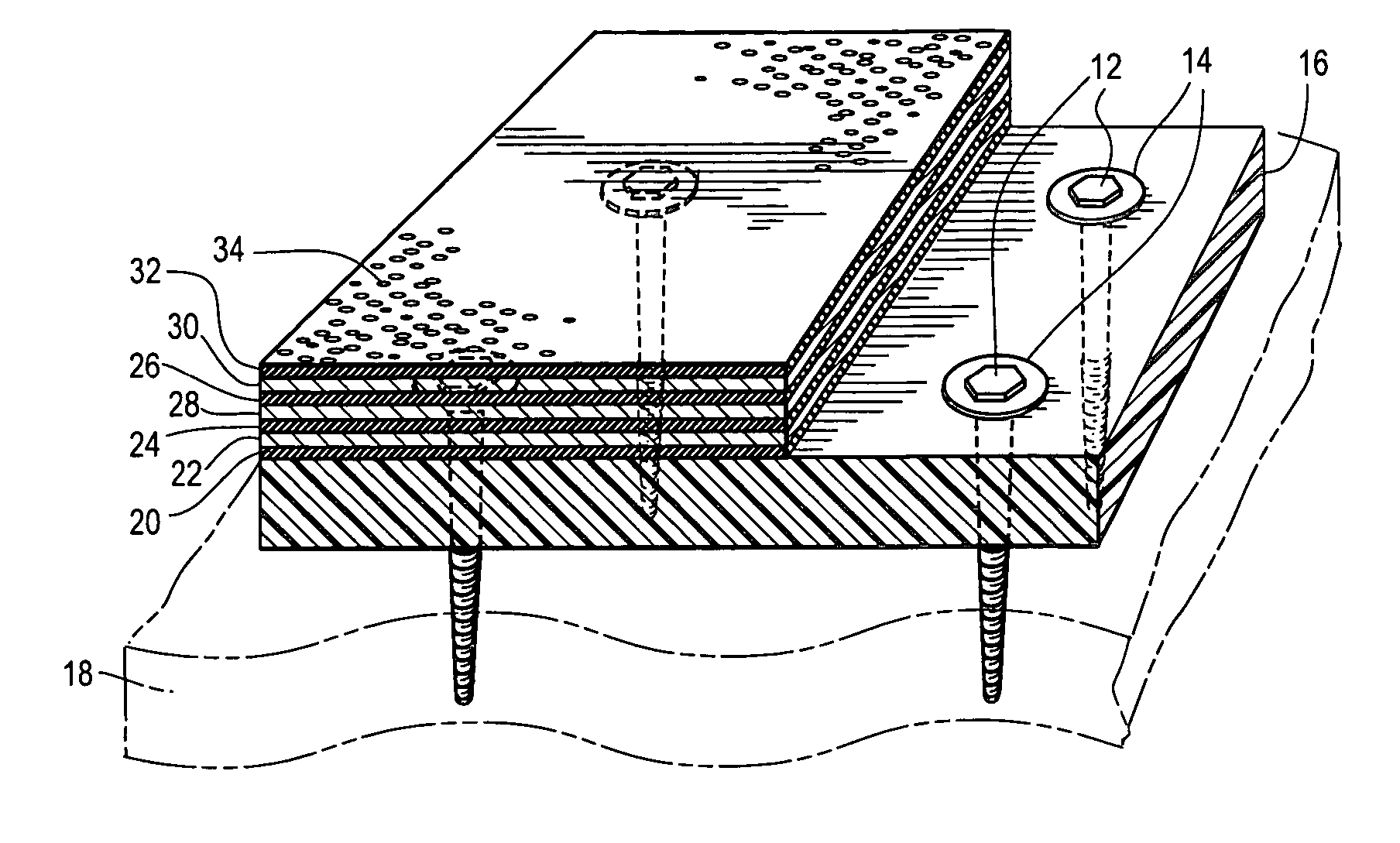
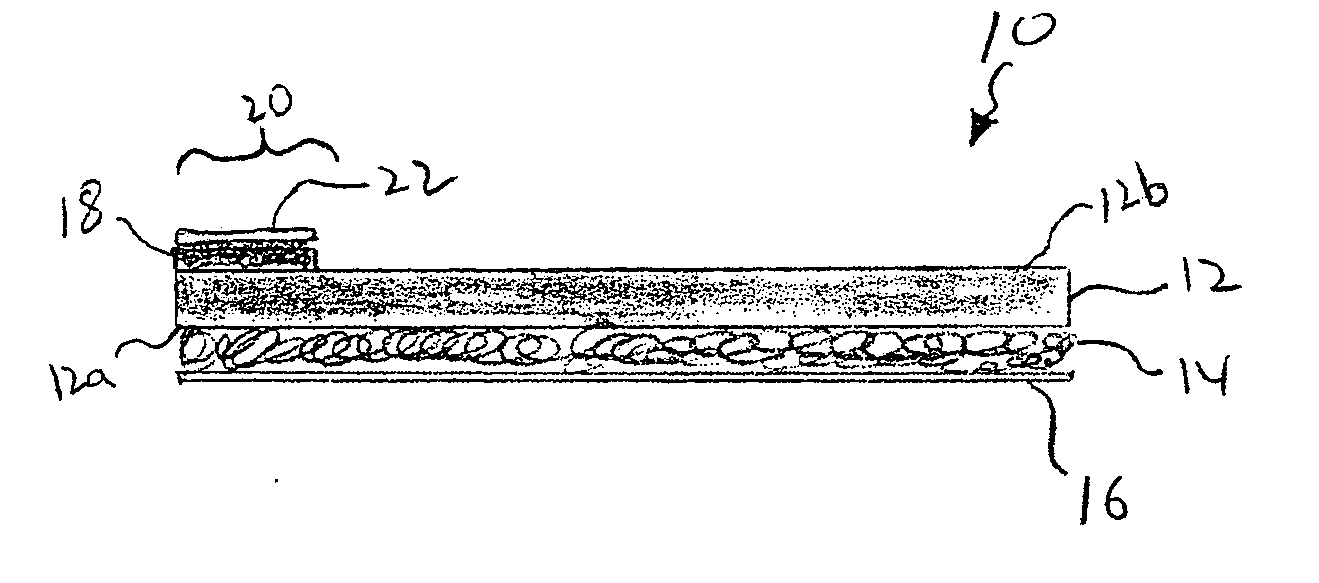
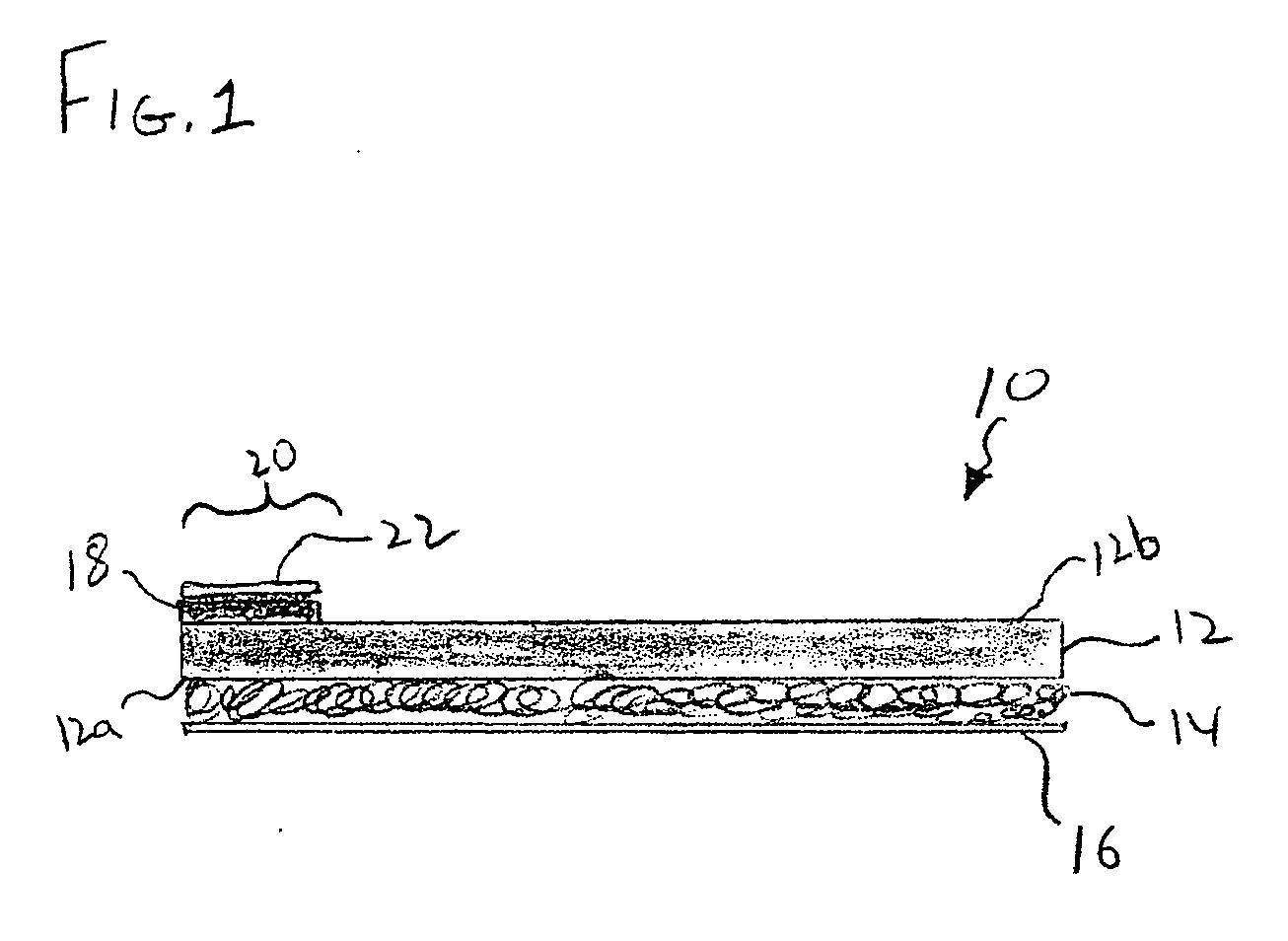
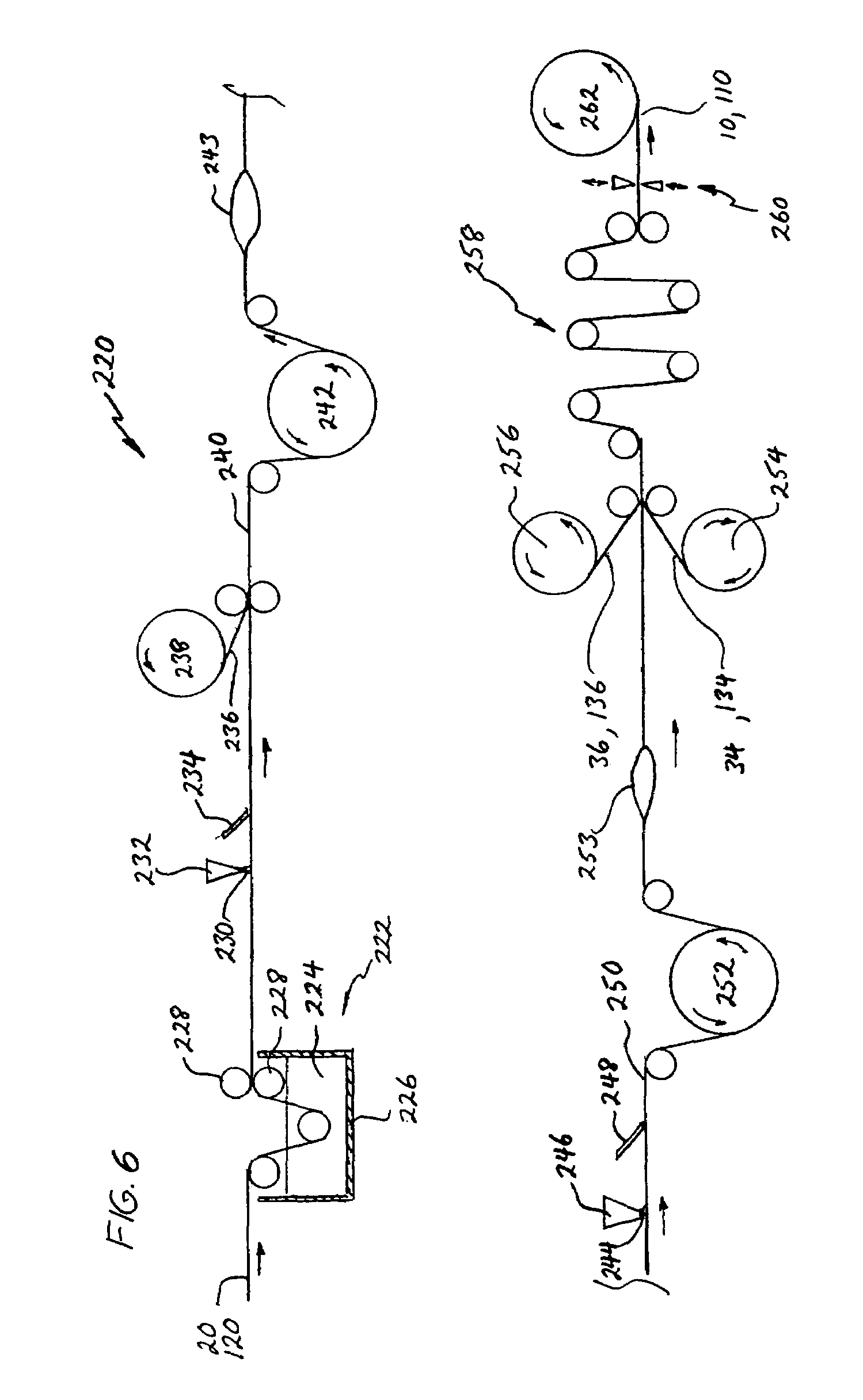
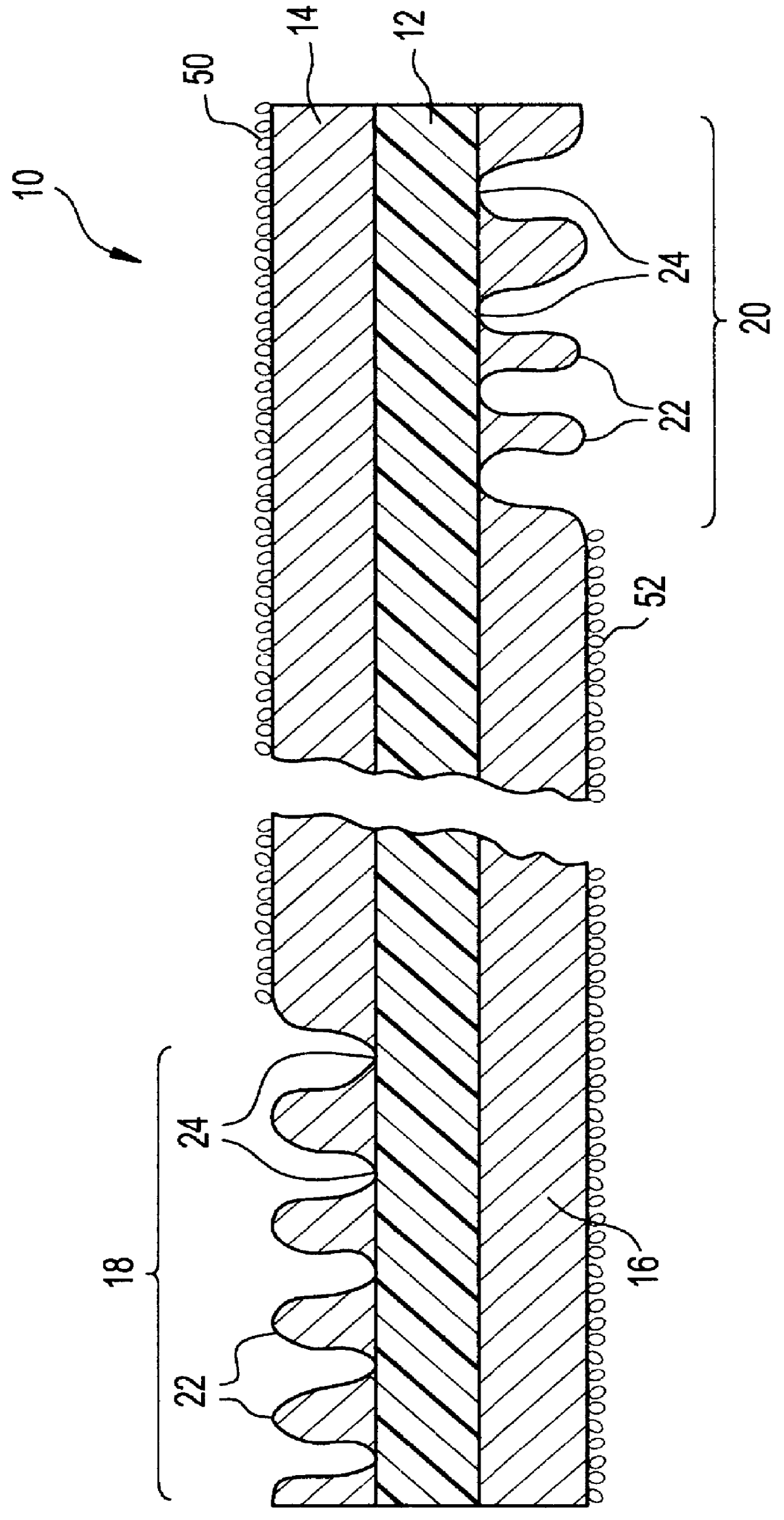
A sealing sheet (10) assembly bondable to a construction surface comprising (a) an upper layer (14) of a first substance, the upper layer being selected fluid impermeable; and (b) a lower flexible layer (16) of a second substance, the lower flexible layer being bondable to the construction surface. The upper layer and the lower flexible layer are at least partially attached to one another, wherein a combination of the upper layer, the lower layer and the attachment or the partial attachment of the layers to one another are selected such that tensile forces resulting from constructional movements acting upon the sealing sheet result in a local detachment or relative displacement of the upper layer and the lower flexible layer, thereby the ability of the lower flexible layer of transmitting the forces onto the upper layer is remarkably reduced, resulting in improved service of the sealing cover as a whole. The attachment is selected such that a spread of a leakage between the layers via a tear formed in the upper layer is locally restricted.
Owner:HEIFETZ RAPHAEL
Multilayer slip resistant sheet material
InactiveUS6925766B2Increase coefficient of frictionGood walkabilityRoof covering using tiles/slatesTreadsEngineeringSlip resistance
There is provided a sheet material having a walking surface with high slip resistance. The sheet material has a flexible structural layer laminated to a mesh layer which has interconnected reinforced strands and protruding nodes to impart a high coefficient of friction. The high coefficient of friction of the sheet material provides a roofing underlayment which is safe to walk upon in dry, wet or dusty conditions, and on steeply sloped surfaces. The sheet material may also be used as an industrial wrapping material or a fabric.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Highly reflective asphalt-based roofing membrane
ActiveUS20050053745A1Efficient use ofImprove reflectivitySpecial ornamental structuresCeramic layered productsEngineeringAsphalt
A prefabricated asphalt-based waterproof roofing membrane for use in a multi-ply asphalt-based commercial roofing system, e.g. a cap sheet that forms the exposed layer of a multi-ply built-up roofing system, is manufactured at a factory to have a highly reflective non-asphalt based elastomeric top coating layer with an upper surface that meets current EPA Energy Star requirements. Preferably, a polymer primer layer is interposed between the highly reflective coating layer and an asphalt saturated and coated reinforcing substrate to keep oils and other colored components in the asphalt from exuding into the highly reflective coating layer.
Owner:JOHNSON MANVILLE INT
Roofing materials having engineered coatings
InactiveUS7238408B2Improve toughnessImprove impact resistanceRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof improvementPliabilityAsphalt
An asphalt-based roofing material includes a coating having a top portion containing a mixture of asphalt and igneous and / or metamorphic rock particles, while the mat portion of the coating contains a mixture of asphalt and a filler which contains less than 10% igneous and / or metamorphic rock particles. In other embodiments, the top portion but not the bottom portion of the coating meets or exceeds a pliability standard, passes a weathering performance test, or has a high solar reflectance. In another embodiment relating to a laminated roofing material, the top portion but not the bottom portion has viscoelastic properties effective to prevent the coating from sticking to an adjacent shingle in a bundle. The invention also relates to a continuous process of applying first and second coatings to a mat for manufacturing a roofing material. In a first coating operation, a first asphalt-based coating is continuously applied to a first surface of the mat so that the first coating saturates the mat and forms a layer on the first surface. In a second coating operation, a second asphalt-based coating is continuously applied to a second surface of the mat so that the second coating forms a layer on the second surface. The second coating has different properties from the first coating.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Adhesive rubber article having scored released liner and guide to facilitate field application and related methods
An adhesive rubber article of the type having a release liner covering its tacky, adhesive surface to prevent the adhesive rubber article from adhering to various substrates or to itself prior to its intended use includes an impression or mark presented on one or more surfaces for facilitating the alignment and application of the adhesive rubber article on one or more substrates. The release liner has been scored, perforated or otherwise cut in a longitudinal direction of the article such that the scoring of the release liner further produces a visual guide on the adhesive rubber article. Thus, upon removal of the release paper, the guide may be used to align and apply the adhesive rubber article to the various substrates. These adhesive rubber articles are particularly useful within the roofing industry for bonding panels of rubber membranes together or for use as flashing.
Owner:FIRESTONE BUILDING PRODS
Modified bitumen roofing membrane with enhanced sealability
InactiveUS6924015B2Reduce the possibilityImprove the noise reduction effectTreadsRoof covering using flexible materialsThermoplasticEngineering
A self-adhering modified bituminous roof covering composite that comprises a thermoplastic (APP), elastomeric (SBS) or TPO modified bitumen compound on the front side, and a factory-applied self-adhesive compound on the back side of a reinforcement carrier sheet, with factory-applied tracts of adhesive on the side lap and end lap sections of each roll to enhance adhesion. A method of manufacturing such composite comprising coating an APP or SBS or TPO compound on the upper surface and affixing a self-adhesive compound to the lower surface of a reinforcement carrier support sheet, coating an adhesive on the side lap and end lap areas, applying a release liner to the tacky self-adhesive layer, and applying release films to the side and end laps during manufacture, stripping the release liner, selvage release film and end lap film from the membrane immediately prior to use, subsequently placing the exposed self-adhesive side of the membrane directly on to the end lap areas and side lap areas of adjacent rolls and applying force directly to the sheet to enhance the bond between the two sheets, resulting in a continuous roof covering. The present invention relates generally to residential and commercial roofing membranes.
Owner:POLYGLASS
Transparent shock-absorbing laminate and flat panel display using the same
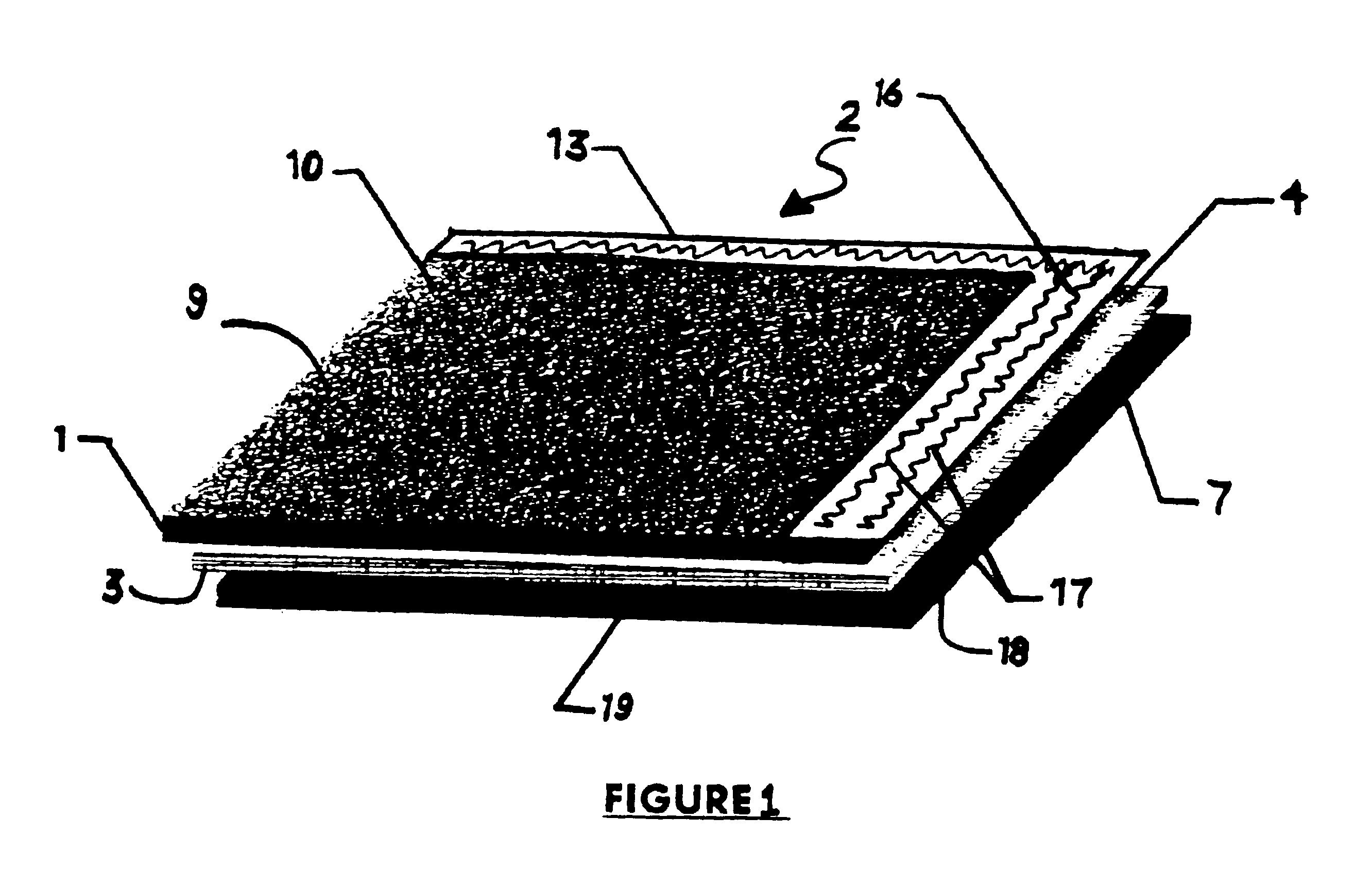
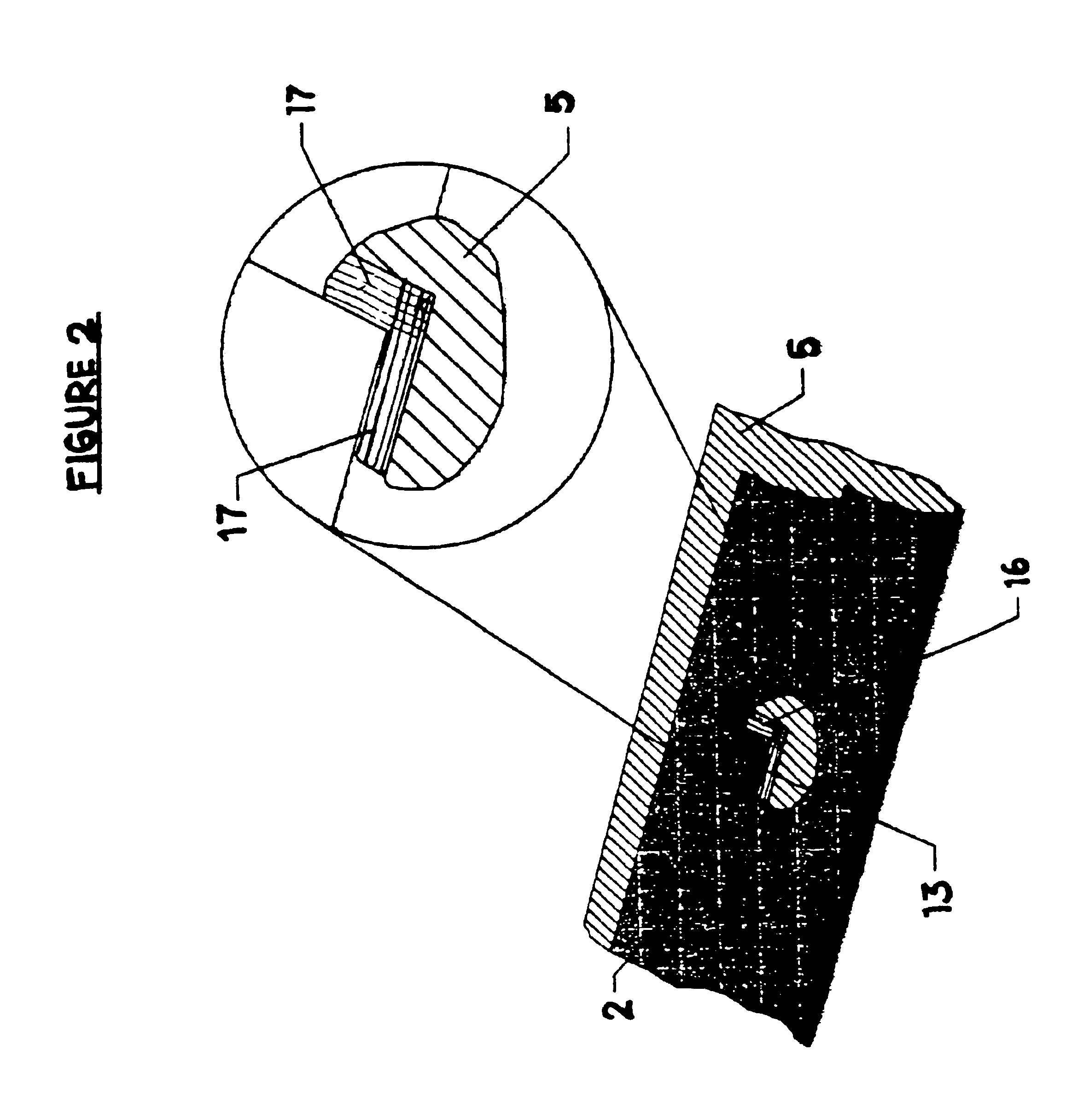
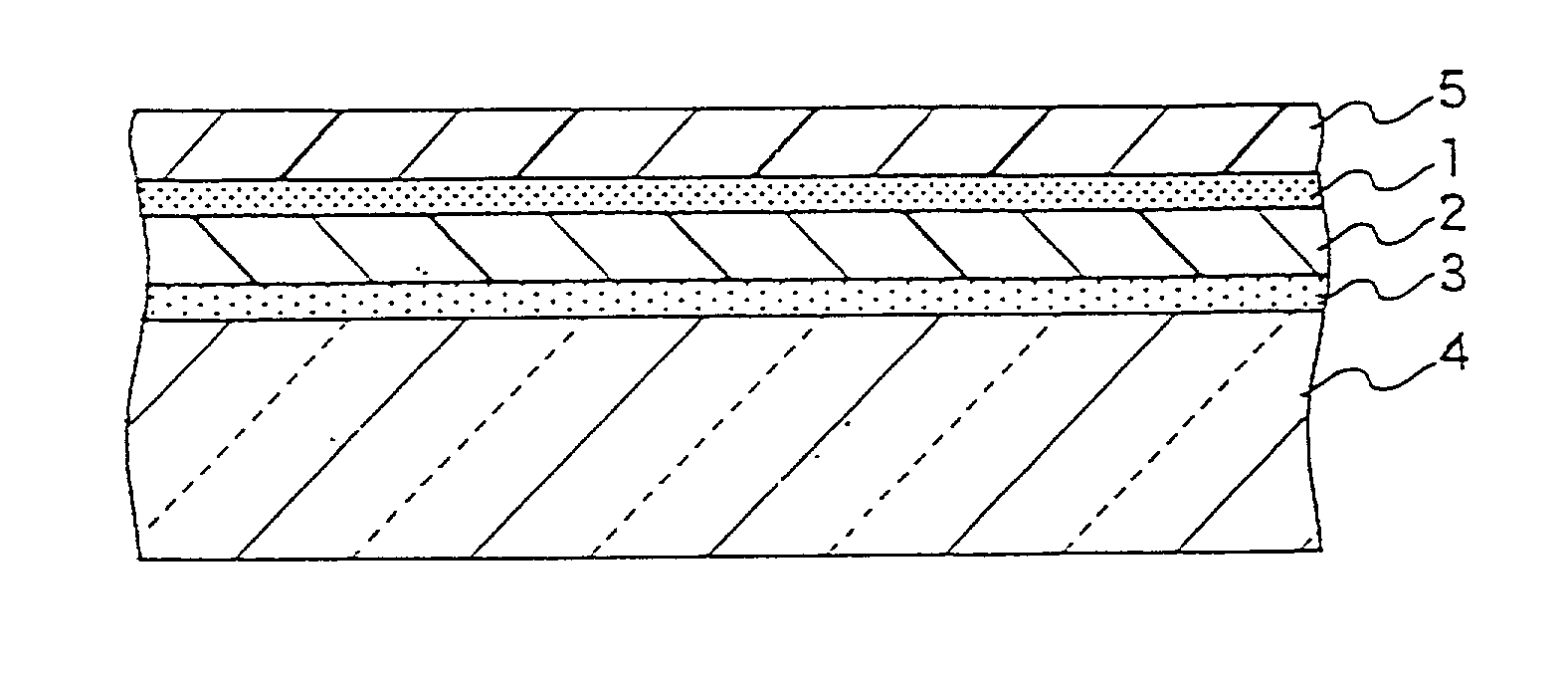
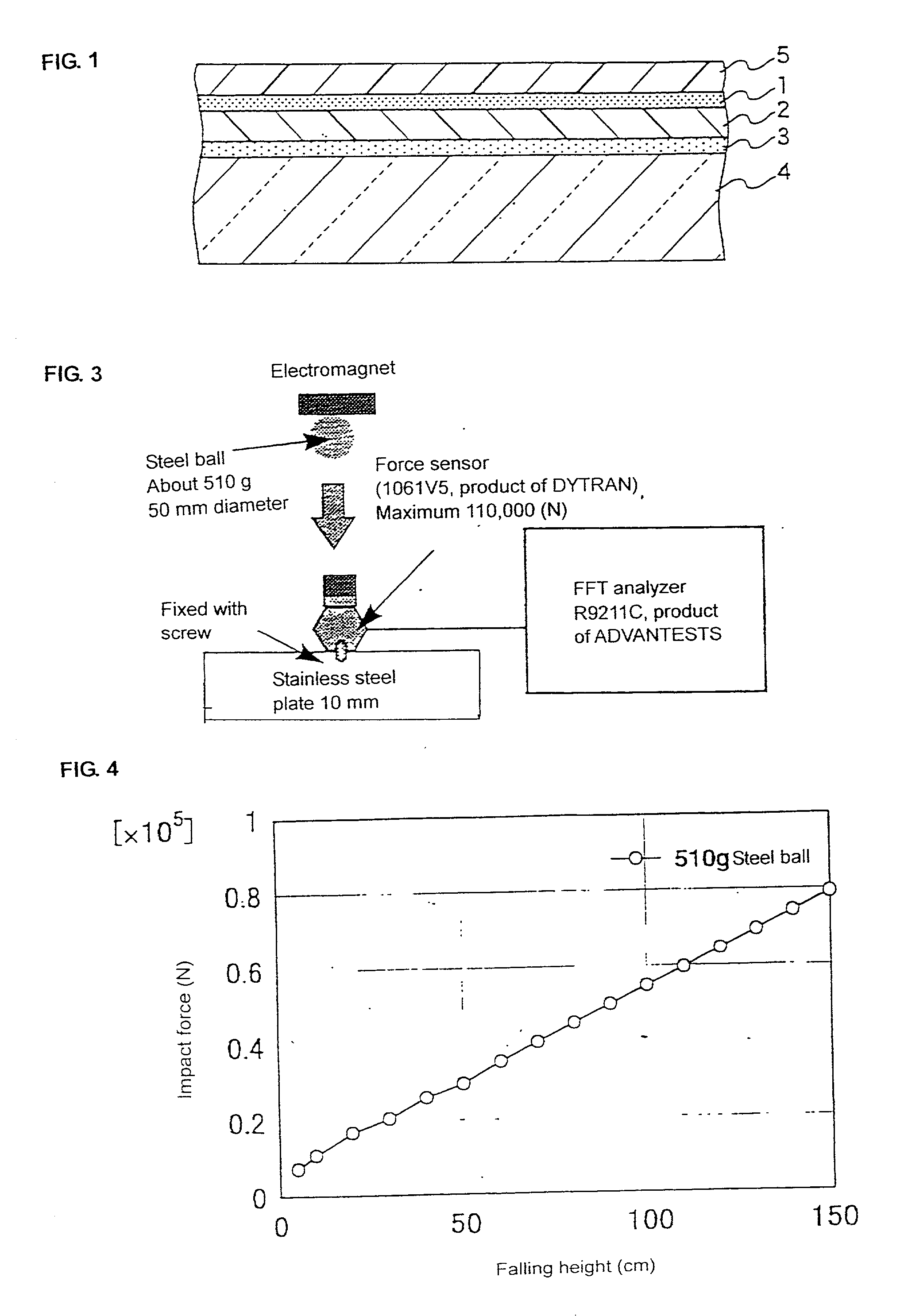
A transparent shock-absorbing laminate to be formed on a glass substrate for a display panel having a fracture strength such that it is fractured by a falling ball impact (drop height: 1.5 m; ball weight: 510 g) corresponding to 79,000 N, the transparent shock-absorbing laminate comprising a shatterproof layer having a shearing modulus of 2x108 Pa or more, at least two fracture-proof layers having a shearing modulus ranging from 1x104 to 2x108 Pa, each having different modulus, and a transparent pressure-sensitive adhesive layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Shingle with improved blow-off resistance
InactiveUS20040083673A1Roof covering using tiles/slatesBuilding repairsEngineeringStructural engineering
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Filamentous carbon particles for cleaning oil spills and method of production
InactiveUS7473466B1Increase specific energy and overall energy efficiencyHydrogen/synthetic gas productionGlass/slag layered productsFiberCarbon nanotube
A compact hydrogen generator is coupled to or integrated with a fuel cell for portable power applications. In the process of producing hydrogen for the generator via thermocatalytic decomposition (cracking, pyrolysis) of hydrocarbon fuels in an oxidant-free environment, novel carbon products are produced with filamentary surfaces, “octopus”-like carbon filaments, single carbon nanotube fibers and the like. Two novel processes are disclosed for the production of carbon filaments and a novel filamentous carbon product useful in the clean-up of oil spills on the surface of water. The apparatus can utilize a variety of hydrocarbon fuels, including natural gas, propane, gasoline, and sulfurous fuels. The hydrogen-rich gas produced is free of carbon oxides or other reactive impurities, so it can be directly fed to any type of a fuel cell. The hydrogen generator can be conveniently integrated with high temperature fuel cells to produce an efficient and self-contained source of electrical power.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Stress-relieving barrier membrane for concrete slabs and foundation walls
ActiveUS7488523B1Relieve pressureReduce crack formationPaving reinforcementsIn situ pavingsStress relievingToxic material
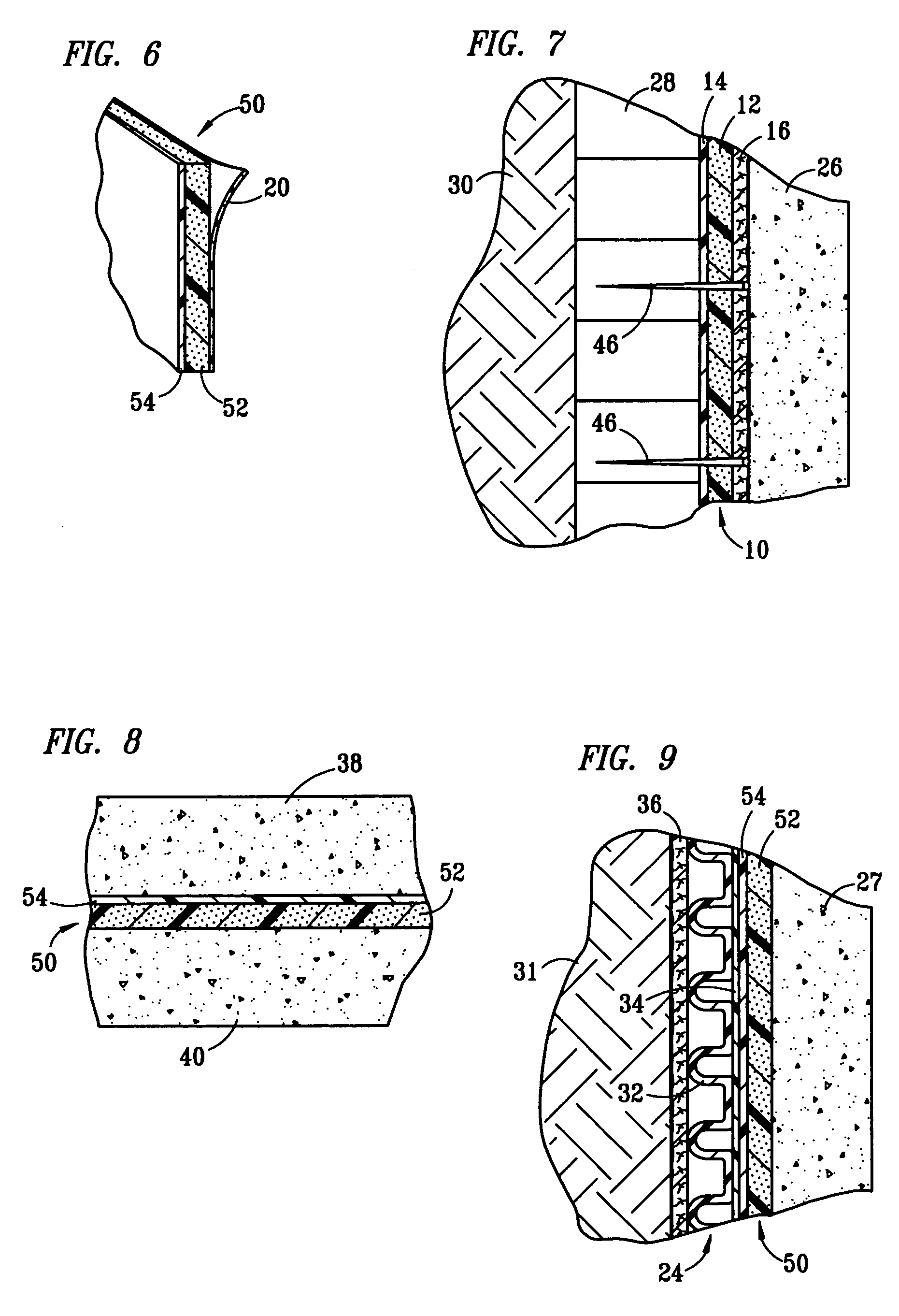
A composite membrane comprising a layer of rubberized asphalt having a heavy duty plastic film layer continuously bonded to one side and, optionally, a layer of nonwoven geotextile continuously bonded to the other side. The membrane can be used in vertical or horizontal applications, and is particularly useful for its stress-relief properties that resist crack formation and propagation in concrete walls and slabs in addition to serving as a barrier to moisture, toxic substances and insects. An appropriate composite membrane of the invention can be advantageously utilized in positive side, blindside, underslab or split slab applications. The thickness of the composite membrane preferably ranges from about 30 mils to about 150 mils.
Owner:POLYGUARD PRODS
Modified asphalt waterproof sheet material
ActiveCN103802380AHigh tensile strengthGood dimensional stabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSynthetic resin layered productsElastomerPolyester
The invention discloses a modified asphalt waterproof sheet material. The modified asphalt waterproof sheet material is of a multilayer structure; the upper surface of the modified asphalt waterproof sheet material is a mineral granule layer; a fiberglass reinforcement basic layer and a polyester reinforcement basic layer are sequentially arranged in the middle part of the modified asphalt waterproof sheet material in sequence; a self-adhesion polymer modification asphalt sizing material layer is arranged in the bottom layer of the modified asphalt waterproof sheet material; adjacent layers are adhered through an elastomer polymer modification asphalt sizing material layer; an isolation film is adhered on the self-adhesion polymer modification asphalt sizing material layer. The structure of the modified asphalt waterproof sheet material provided by the invention can be applicable to small deformation of the basic layers, and has the advantages of higher size stability, convenience in construction, adhesion reliability and self-heating property. The invention provides a reliable and exposed modified asphalt waterproof sheet material, and is particularly applicable to monolayer roofs.
Owner:KUNMING FENGXING WATERPROOF MATERIAL +1
Roofing products including granules with reflective coating
ActiveUS20060240224A1Sufficiently puncture and scuff resistantEnergy efficacyRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHigh reflectivityPigment
A roofing product with a higher reflectivity is provided having a roofing material, and fine granules adhered to the roofing materials that are double-coated with a coating having a white pigment. A top white coating composition can be applied to the granules after the granules are applied to a roofing material. Further, a process of manufacturing a roofing product is provided, where fine granules that are double-coated with a coating having a white pigment are applied to a roofing material, and a top coating composition is then applied to the fine granules.
Owner:BMIC LLC
Dual layer shingle
ActiveUS7048990B2Less costlyEfficient use ofLiquid surface applicatorsWallsPolymer modifiedPliability
A shingle formed from a base sheet, with a layer of polymer modified asphalt coating the top of the base sheet, and a layer of conventional oxidized asphalt, free from polymer additives, coating the bottom of the base sheet. Both layers preferably directly contact the strands of the base sheet for good adhesion. This improves the strength, flexibility and ultraviolet resistance of the shingle, while reducing the cost as compared with a shingle which utilized only polymer modified asphalt, and in addition it increases the stiffness of the shingle as compared with one using only polymer modified asphalt.
Owner:IKO INDS
Foamed roofing materials and methods of use
InactiveUS20040109983A1Increase heatIncrease resistanceCovering/liningsRoof covering using sealantsPolyesterIsolation layer
Improvements in compositions, composites, and methods for construction of weather resistant and insulated roofs are disclosed. The type of roofs to which these improvements apply are typically known as built up roofs. Built up roofs feature a substrate as an inner layer normally adjacent to and attached to the exterior of an unimproved roof surface. This invention is directed to improved foamed resin substrates used in such roof constructions. Alternating layers of hot asphalt and roofing felt are applied to the foam substrate layer. In prior art roofs, the foamed resin substrates could not withstand the direct application of hot molten asphalt to the foam surface which necessitated use of an isolation layer between the foamed resin layer and the first asphalt layer. This invention discloses compositions, composites, and methods involving direct application of hot asphalt to specially formulated and thermally resistant polyester foam resin substrate layers at temperatures up to 500° F. These improved compositions, composites, and methods not only reduce labor and material costs but also produce roofs that score higher on standard tests used for rating such roofing constructions.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Under roof peel and stick tile underlayment
InactiveUS20060243388A1Easy and hassle-free field applicationAdhesive processesAdhesive articlesEngineeringRelease liner
An under roof peel-and-stick tile underlayment, having a core or substrate having an upper and lower surface. On the lower surface of the substrate, an adhesive compound is layered and then covered with a release liner. On the selvage edge of the upper surface of the substrate, an adhesive coating is layered and then covered with a top release liner. After the underlayment is adhered to a roof surface, ceramic tiles, such as Spanish-style tiles are adhered on the upper surface.
Owner:BUILDING MATERIALS INVESTMENT
Container sealing material having a heat-releasable interlayer
An container sealing material suitable for sealing a container comprises a liner sheet (liner), a sealant sheet, and an interlayer portion (interlayer) bound between the liner and the sealant sheet by individual layers of wax. The material has a closure-contacting surface and a heat-sealable surface. At least one of the surfaces of the liner and the interlayer that contacts a layer of wax is capable of absorbing liquid wax when the layer of wax is melted. At least one of the surfaces of the sealant sheet and interlayer which contacts a layer of wax is capable of absorbing liquid wax when the layer of wax is melted. The liner and the sealant sheet each release from the interlayer when sufficient heat is applied to the container sealing material to melt the layers of wax. The interlayer can include printed matter visible on one or both of its surfaces (e.g., a logo, proof-of-purchase indicator, and the like). The printed matter can include promotional indica for a product, a service, a game and the like. Accordingly, the container sealing material provides a means for including a promotional token, such as a redeemable coupon within a container closure between the liner and the sealant sheet.
Owner:TEKNI PLEX
Highly reflective asphalt-based roofing membrane
InactiveUS7070844B2Good lookingImprove composite effectSpecial ornamental structuresCoatingsThermoplastic elastomerEngineering
A prefabricated asphalt-based waterproof roofing membrane for use in a multi-ply asphalt-based commercial roofing system, e.g. a cap sheet that forms the exposed layer of a multi-ply built-up roofing system, is manufactured at a factory to have a highly reflective thermoplastic elastomeric sheet layer with a top surface that has a reflectance that meets current EPA Energy Star requirements. Preferably, a polymer primer layer is interposed between the highly reflective thermoplastic elastomeric sheet layer and an asphalt saturated and coated reinforcing substrate to keep oils and other colored components in the asphalt from exuding into the highly reflective thermoplastic elastomeric sheet layer.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Multilayer laminates comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals
ActiveUS20070154718A1Low hazeMaintain structureLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsHalf waveEnergy consumption
Provided are multilayer laminates having one or more layers comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals and one or more layers of a polymeric sheet comprising a polymer with a modulus of 20,000 psi (138 MPa) or less. The twisted nematic liquid crystal layers reflect infrared radiation. Thus, the multilayer laminates are useful to reduce the transmission of infrared energy. For example, in some embodiments the multilayer laminates are useful as windows to reduce energy consumption necessary to cool the interior of a structure such as an automobile or building. Preferably, the multilayer laminates retain the beneficial properties of safety glass. The multilayer laminates may include additional layers such as infrared absorbing layers, half wave plates, and the like, to minimize the transmission of infrared energy. The multilayer laminates may also include further additional layers such as polymeric films, polymeric sheets, rigid sheets, and the like.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Using a cleaning cloth impregnated with coupling agent for adhesive films
InactiveUS6106953AAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentGlass/slag layered productsSolventSynthetic rubber
Use of a prior-cleaning cloth for an adhesive bond brought about by means of an adhesive film which is rereleasable without damage by pulling in the direction of the bond plane and which has an adhesive composition based on polymers and / or copolymers of synthetic rubber and / or natural rubber, characterized in that the substrate to be bonded is rubbed with a prior-cleaning cloth of this kind which is impregnated with a moisture-reactive organosilane, the organosilane being dissolved in a solvent or solvent mixture and being present therein in a concentration of 0.1-3% by weight, whereupon, following a waiting time of a few minutes, the adhesive film is pressed onto the treated area and then an article, hook or the like is bonded to the other side of the adhesive film, or else in that, after a waiting time of a few minutes, the adhesive film is pressed onto the treated area, an article, hook or the like already being located in bonded-on form on the reverse of the adhesive film.
Owner:TESA SE
Roll roofing membrane
An improved roll roof membrane for use in commercial applications, i.e., flat and low pitch roof structures, and a method for the preparation thereof. The roof membrane comprises a support sheet, and top and bottom layers comprising APP modified bitumen, the top APP modified bitumen layer having a selvage edge disposed along one side of the membrane and the bottom APP modified bitumen layer having a second selvage edge disposed along the opposite side of the membrane. Each of the selvage edges have a series of embossed ridges and valleys adapted to accept adhesives, the valleys extending substantially through the APP modified bitumen layer to the support sheet. The membrane exhibits excellent peel strength with an adhesive, thereby eliminating the need to use a torch during installation in commercial roofing applications.
Owner:BUILDING MATERIALS CORP OF AMERICA
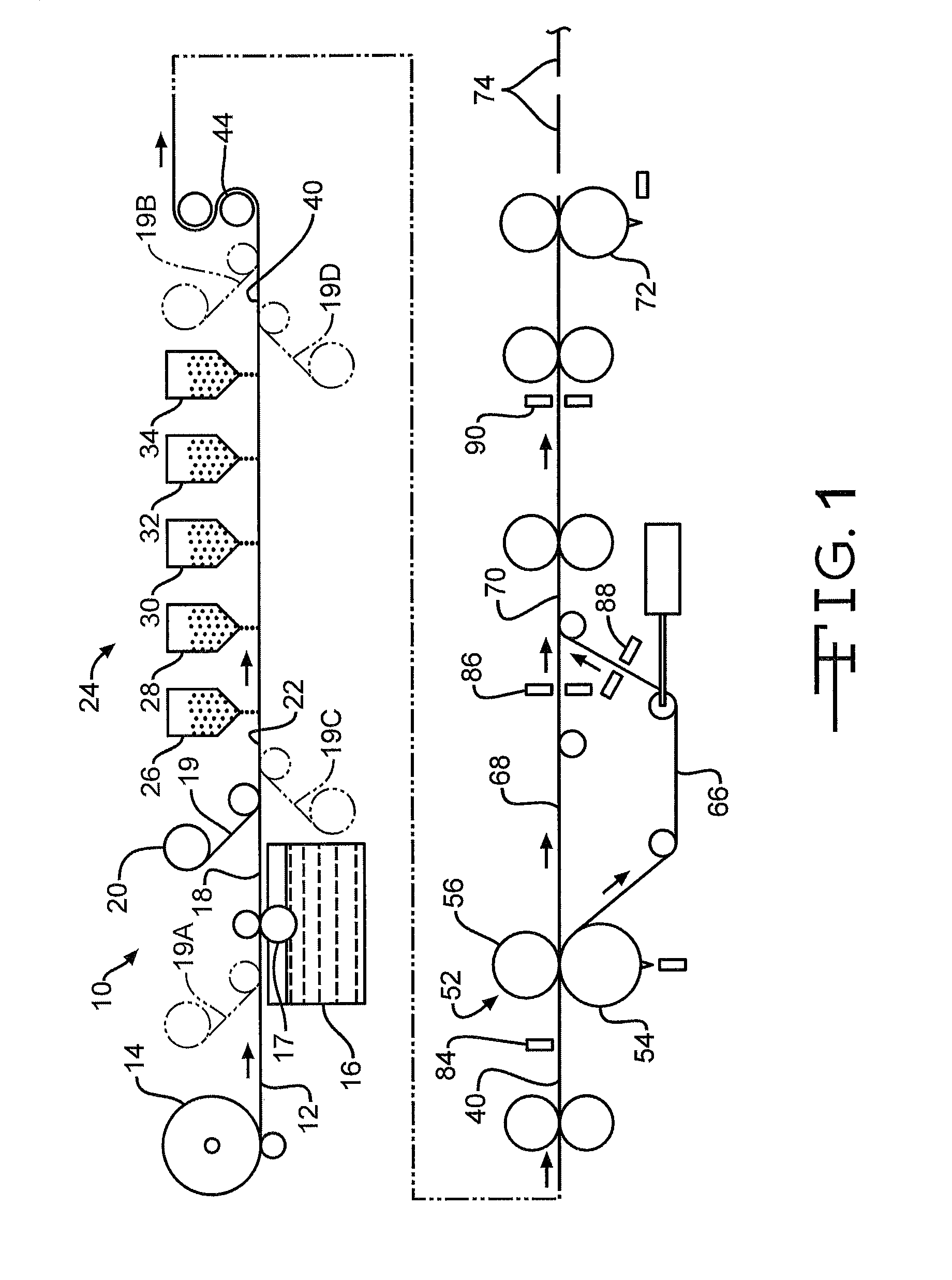
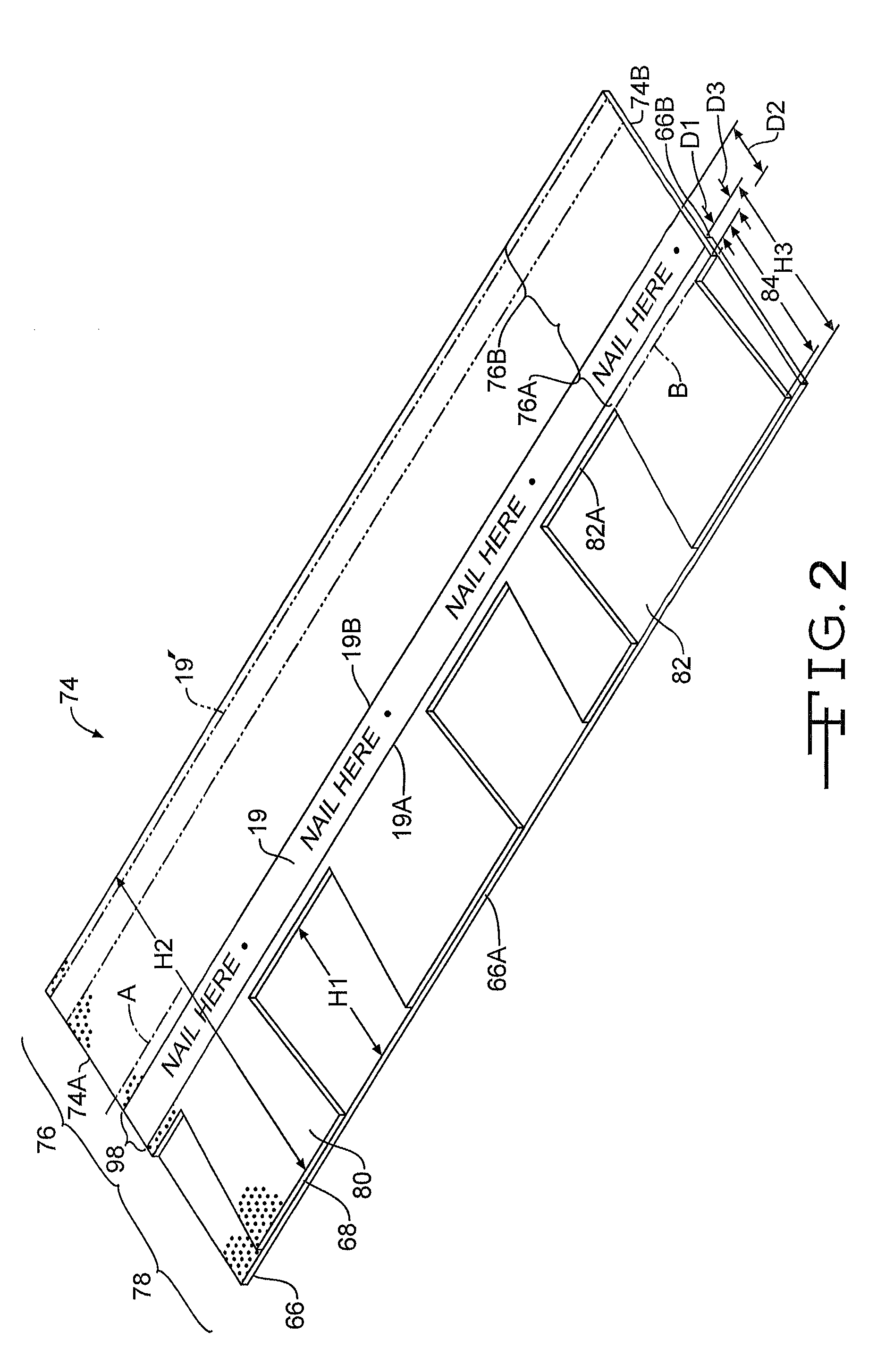
Shingle with reinforced nail zone and method of manufacturing
A method of making a laminated shingle is provided. The method includes coating a shingle mat with roofing asphalt to make an asphalt-coated sheet, adhering a reinforcement member to a portion of the asphalt-coated sheet, covering the asphalt-coated sheet, and optionally covering the reinforcement member, with granules to make a granule-covered sheet, dividing the granule-covered sheet into an overlay sheet and an underlay sheet, wherein the overlay sheet has a tab portion normally exposed on a roof and a headlap portion normally covered-up on a roof, the headlap portion having a lower zone adjacent the tab portion and an upper zone adjacent the lower zone, and wherein the reinforcement member is adhered to the lower zone of the headlap portion and laminating the overlay sheet and the underlay sheet to make the laminated shingle.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com