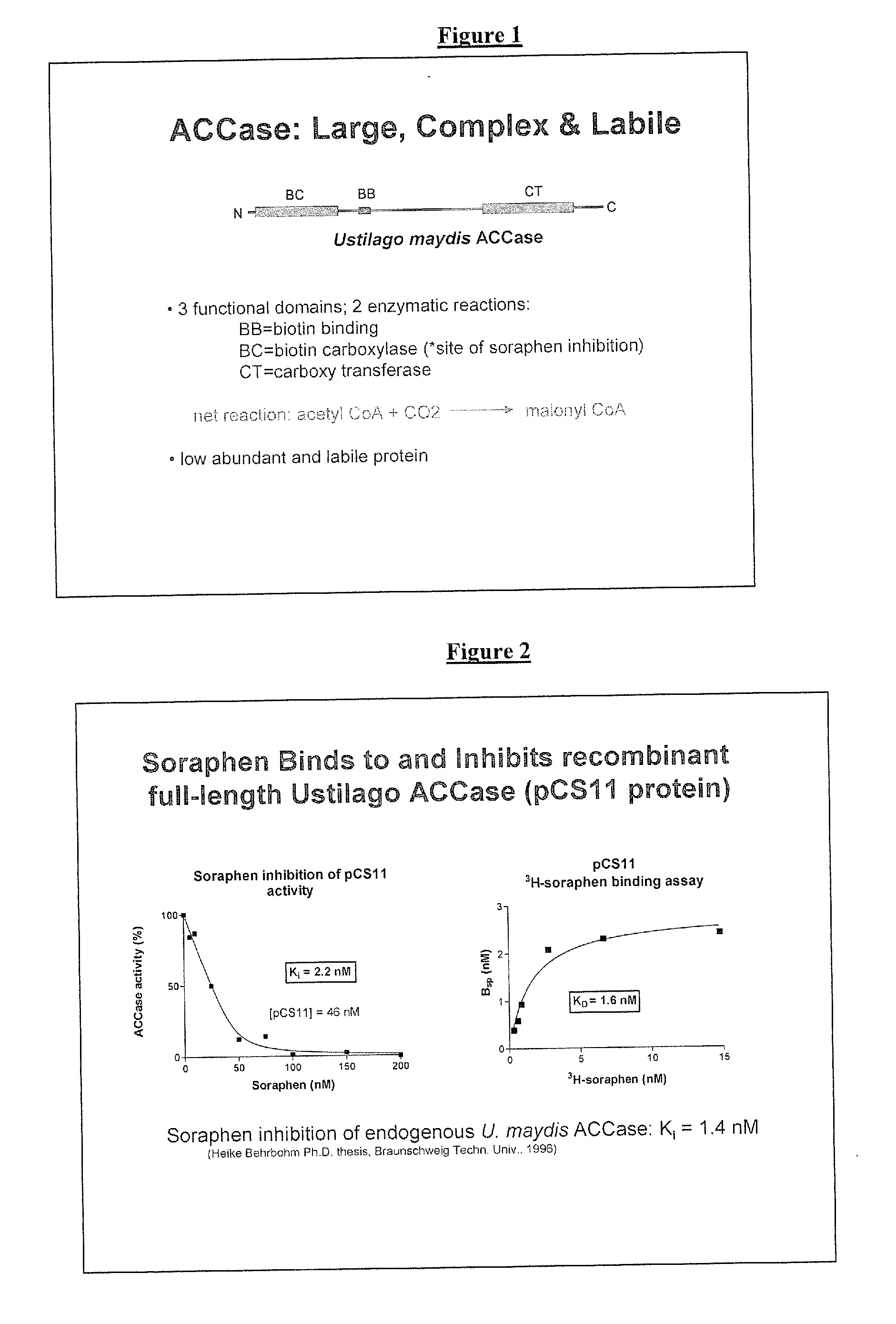
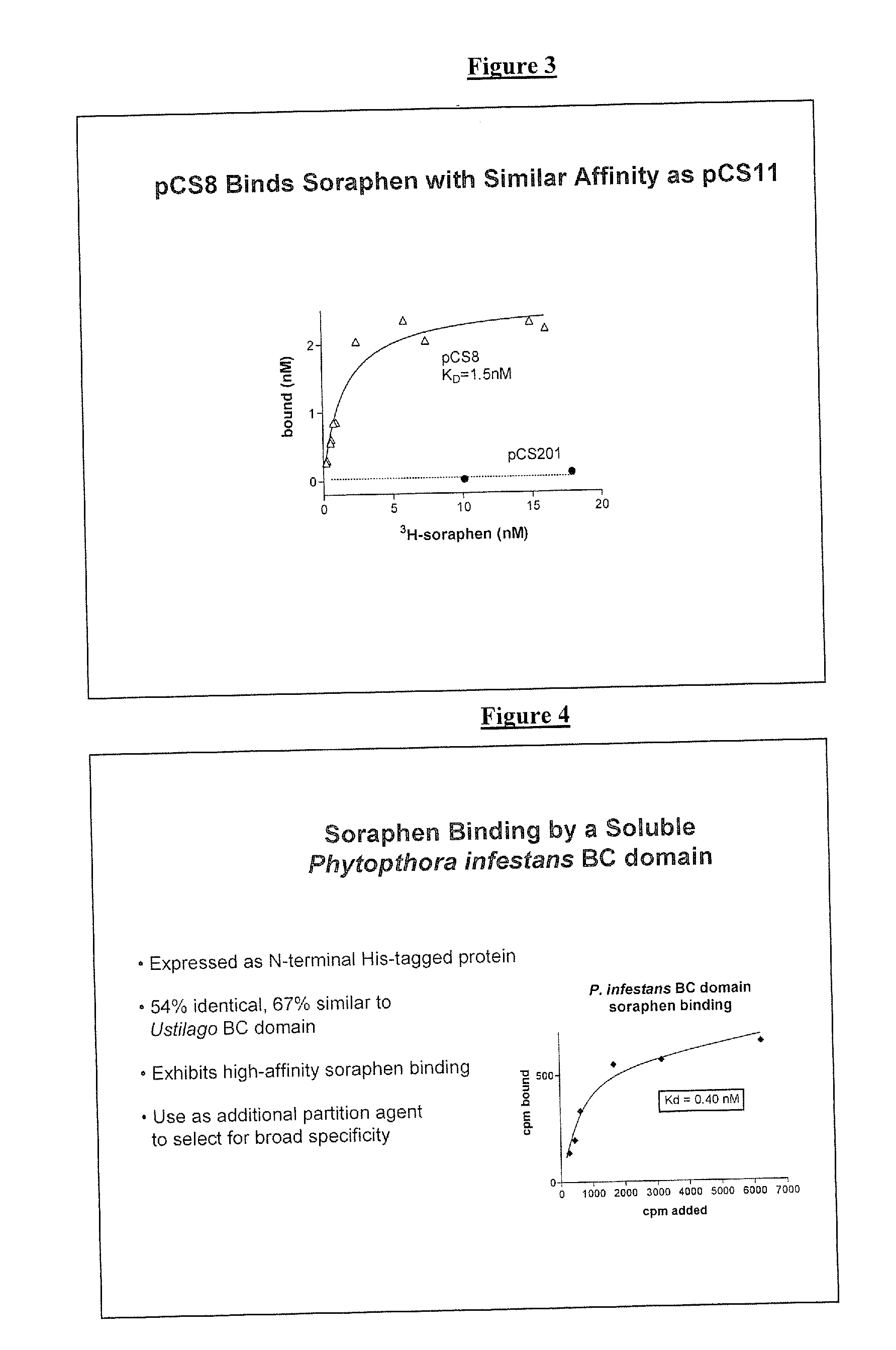
RECOMBINANT BIOTIN CARBOXYLASE DOMAINS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF ACETYL CoA CARBOXYLASE INHIBITORS
a technology recombinant biotin, which is applied in the field of recombinant biotin carboxylase domains for identification of acetyl coa carboxylase inhibitors, can solve problems such as preventing the identification of new accase inhibitors, and achieve the effect of inhibiting detection of inhibition of acetyl coa carboxylase activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0082]A. Preparation of BC Domain Peptide. E. coli cultures transformed with protein expression constructs for BC domains with either N or C terminal his-tags (as illustrated in FIG. 5 for pCS8) were induced by the addition of IPTG (0.2 mM) at an OD600=0.5. The cultures were grown overnight at 18° C., harvested and stored at −80° C. The bacterial pellet was resuspended in a buffer containing 50 mM NaH2PO4 (pH8), 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, protease inhibitor and 1 mg / mL lysozyme. The lysate was sonicated and nuclease was added. The lysate was then incubated with Ni-NTA resin (Novagen) for 1 hour at 4° C. pCS8 was eluted with a buffer containing 50 mM NaH2PO4 (pH8), 300 mM NaCl, and 250 mM imidazole. Fractions containing pCS8 were combined and ammonium sulfate precipitated (40% ammonium sulfate). The pellet from the ammonium sulfate precipitation was resuspended in SB (SB=200 mM NaH2PO4 pH 7.0, 10% glycerol). Protein concentrations were determined by Bradford analysis. The purified...
example 2
[0084]ACCase Activity Assays. The following methods were employed to detect ACCase activity. See also FIGS. 9A and 9B.
[0085]Method 1: Assay-Spectrophotometric. ACCase activity was measured spectrophotometrically by coupling the production of ADP to the oxidation of NADH using pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase. This assay was used to measure either overall ACCase activity by supplying acetyl CoA as a substrate, or BC activity by supplying free biotin as a substrate (note, however, that this has only been demonstrated with “prokaryotic type” BC's). This assay is best suited for purified protein. This assay would be used to test for enzymatic activity of compounds identified by virtue of their binding to isolated BC domains, including but not limited to the EC process.
[0086]To establish this assay, E. coli biotin carboxylase was first cloned and expressed according to the literature (Biochemistry 38:3393-3400, 1999). As seen in FIG. 9A, the activity of E. coli BC towards a free...
example 3
[0089]Soraphen binding assay. Affinity based screens and selection assays, including but not limited to EC selections, rely on binding of small molecules and not inhibition of enzymatic activity. Therefore, despite the lack of enzymatic activity, pCS8 would be a suitable affinity based screening or selection agent if it retained the high affinity soraphen binding activity of the full-length Ustilago ACCase. Soraphen A was tritium labeled by Sibtech, Inc. (Newington, Conn.) and used for binding experiments with pCS8 protein. Briefly, 6.7 nM purified pCS8 protein was incubated with various concentrations (approximately 0.5-20 nM) of 3H-soraphen in PNT buffer (100 mM NaH2PO4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.01% Triton X-100, pH 7.0) for 45 min at room temperature. pCS8 protein (with bound ligand) was separated from free ligand on NAP-5 desalting columns (Amersham Biosciences) and the amount of bound 3H-soraphen determined by liquid scintillation counting. Non-specific binding was determined with duplic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com