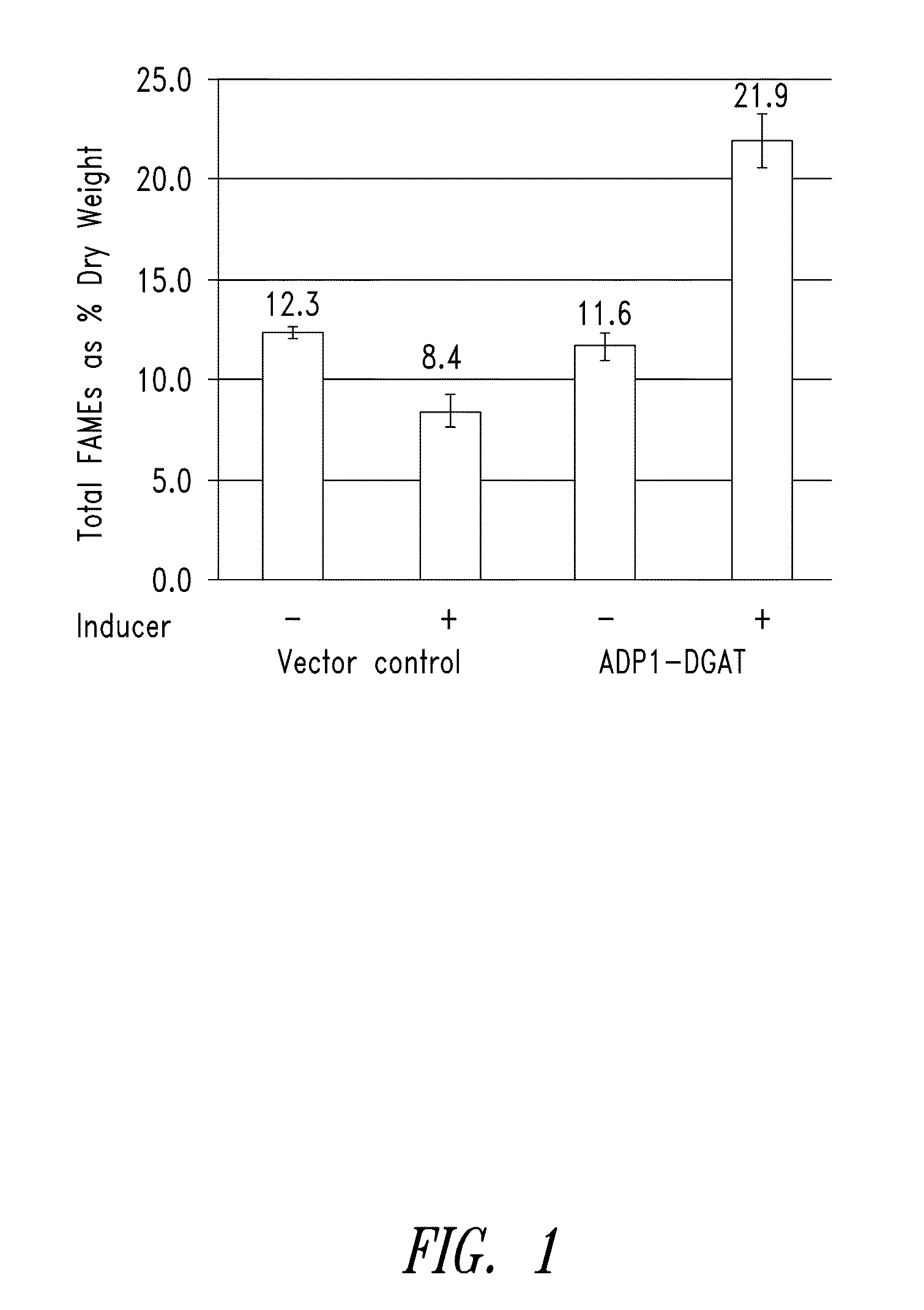
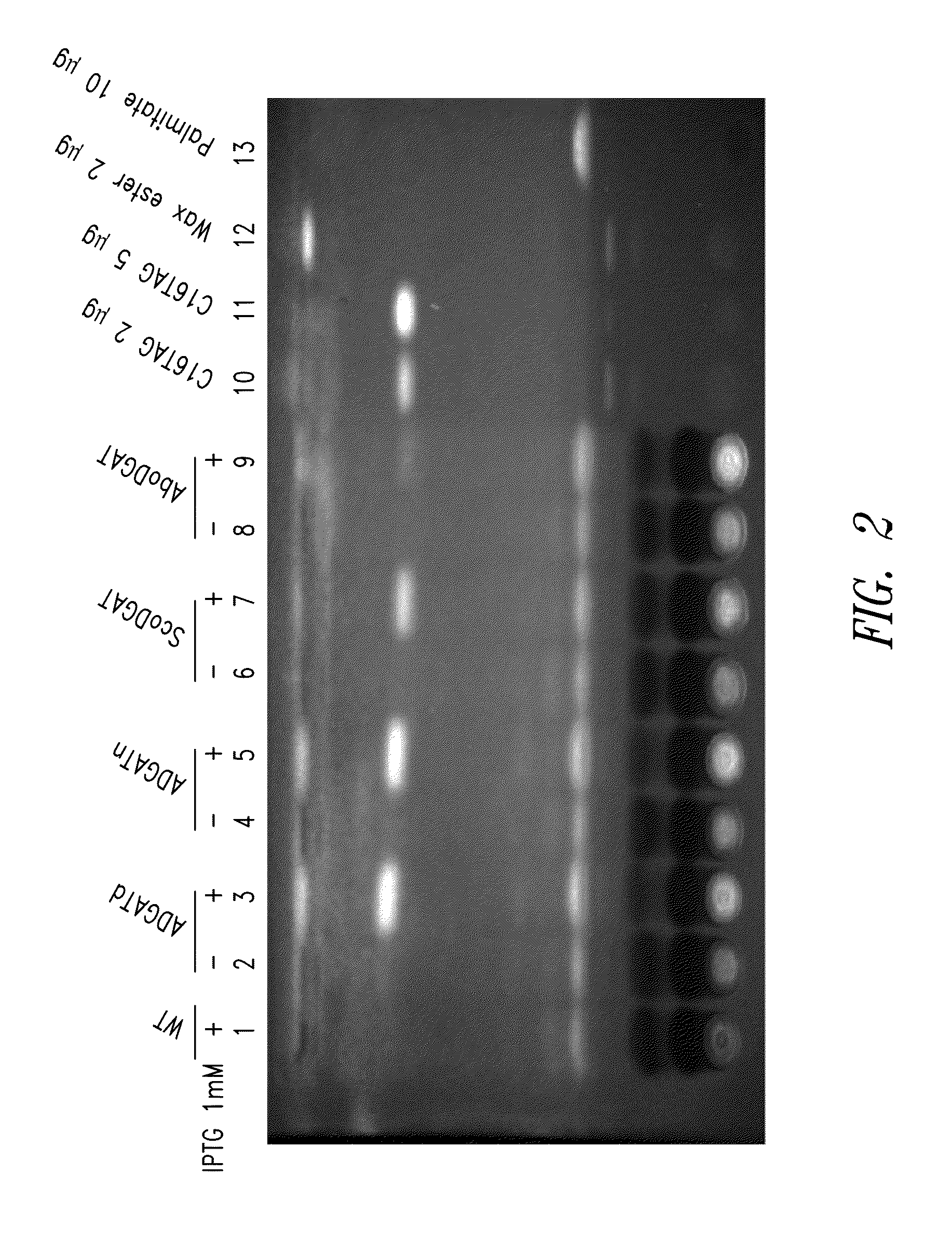
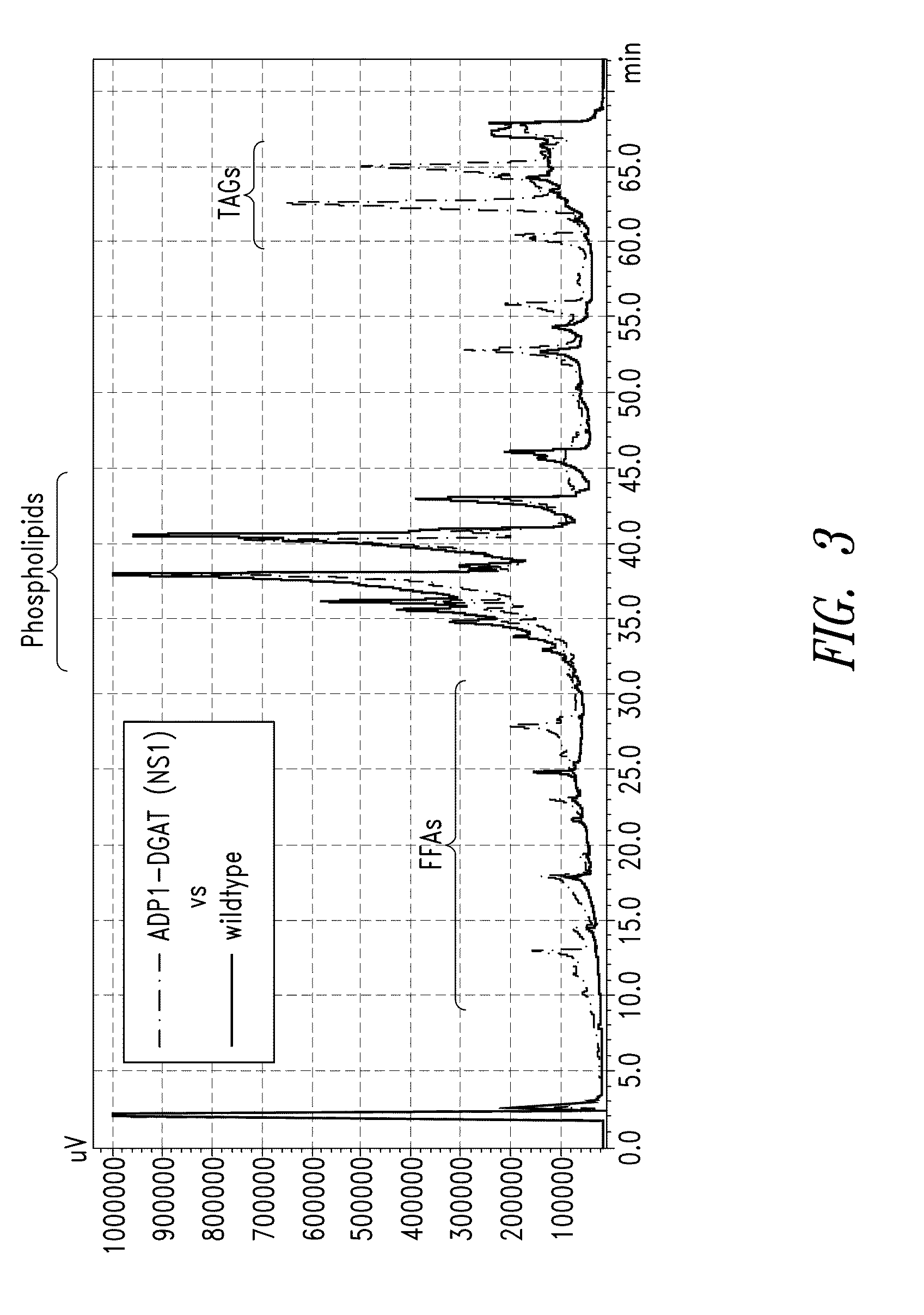
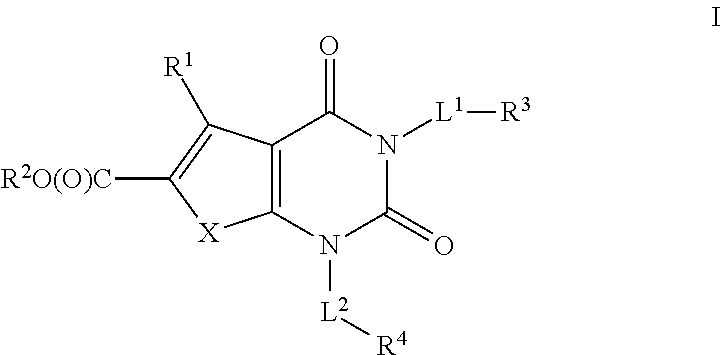
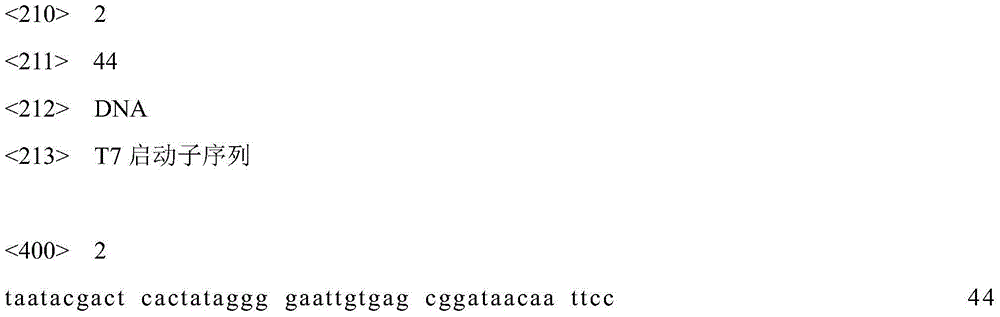Patents
Literature
88 results about "Acetyl-CoA carboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
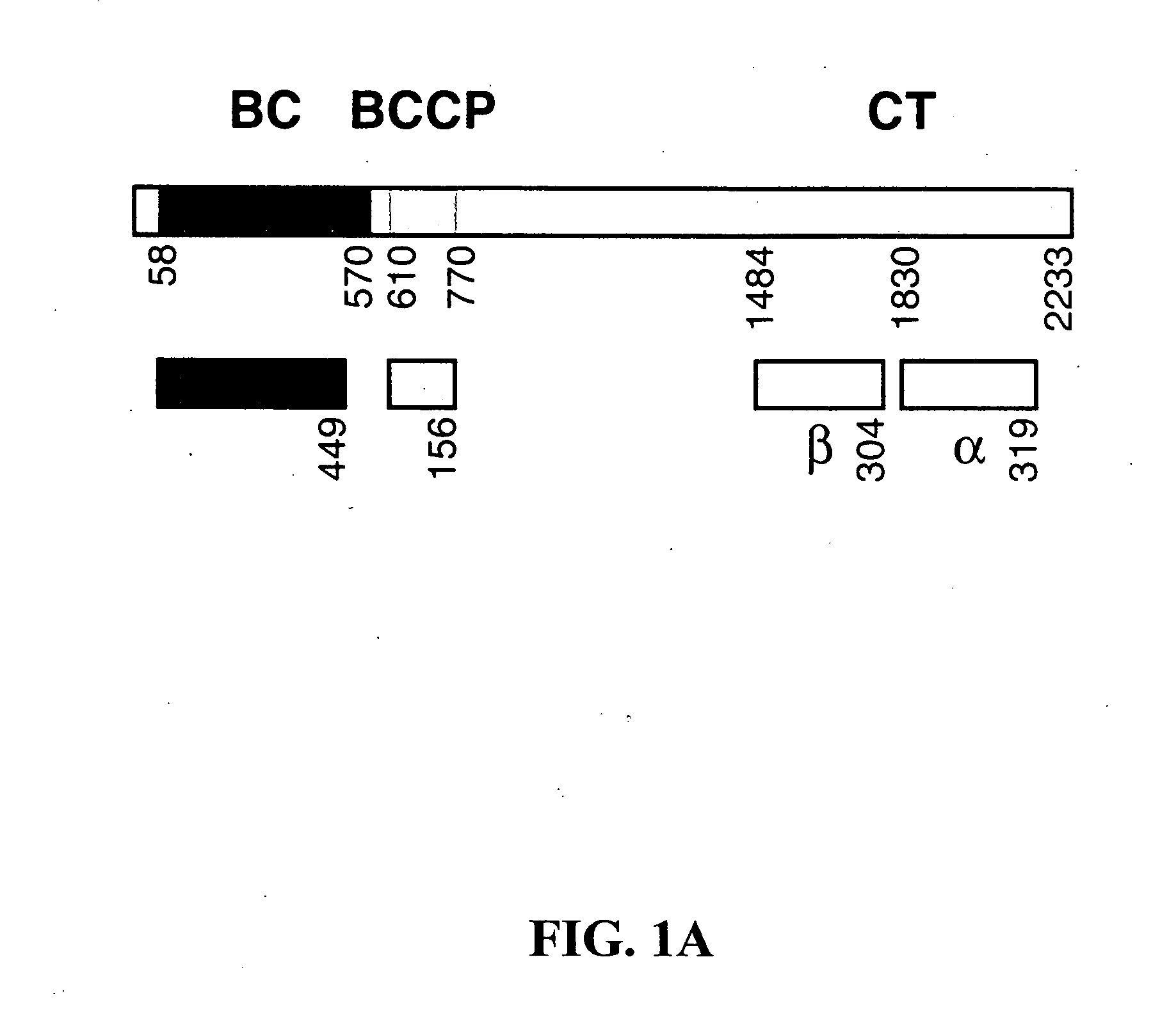
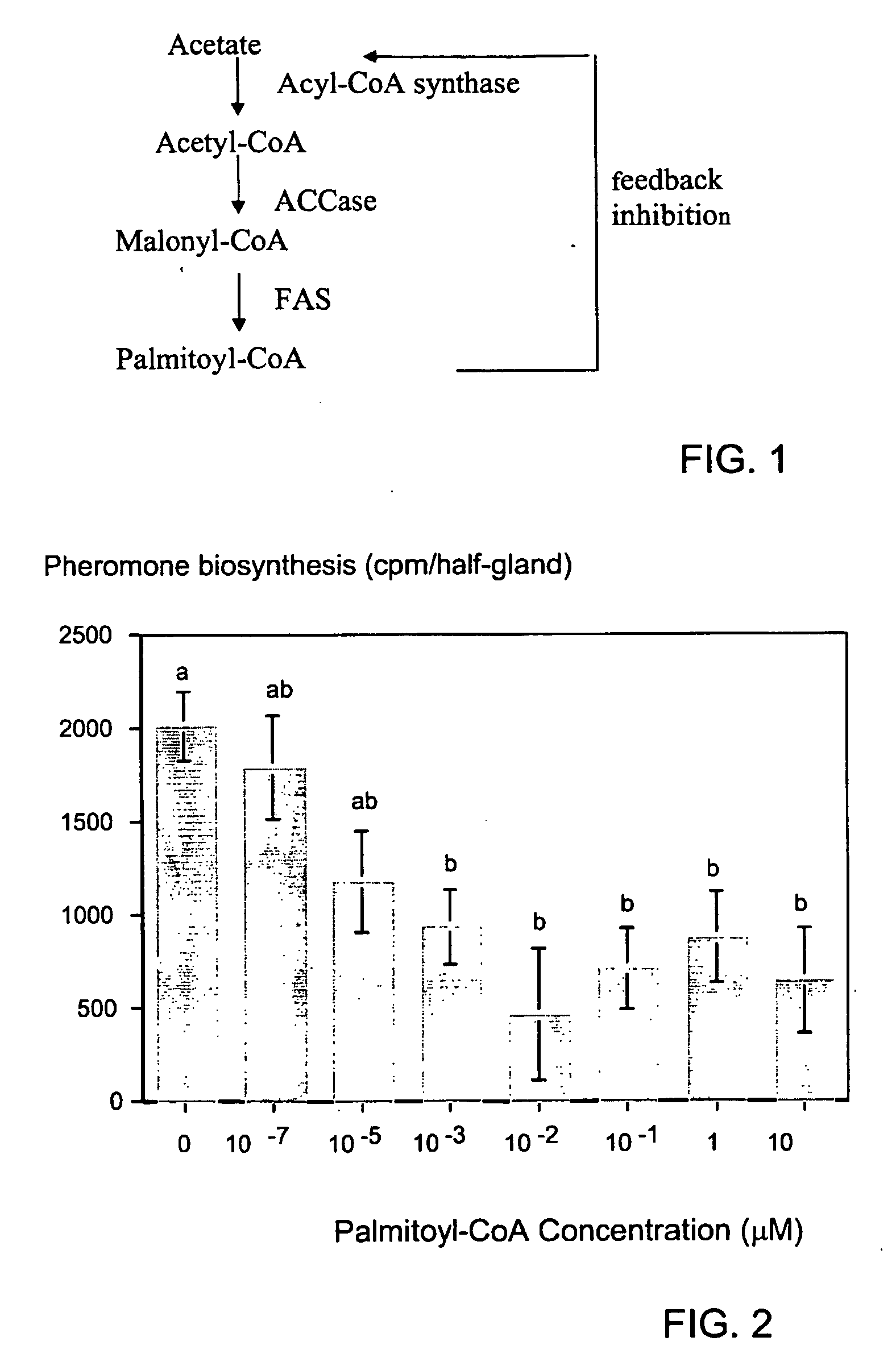
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum of most eukaryotes. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—ACACA and ACACB.
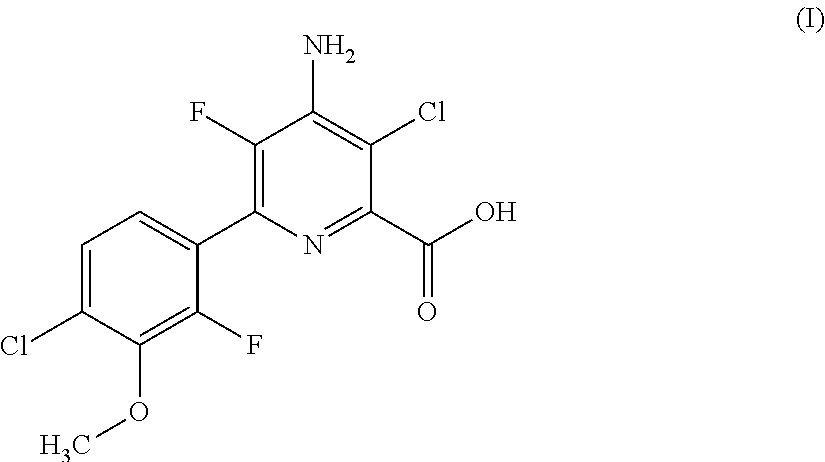
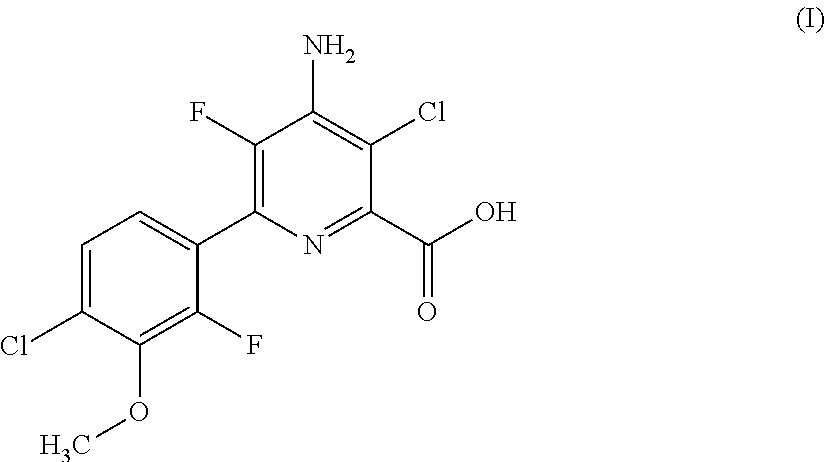
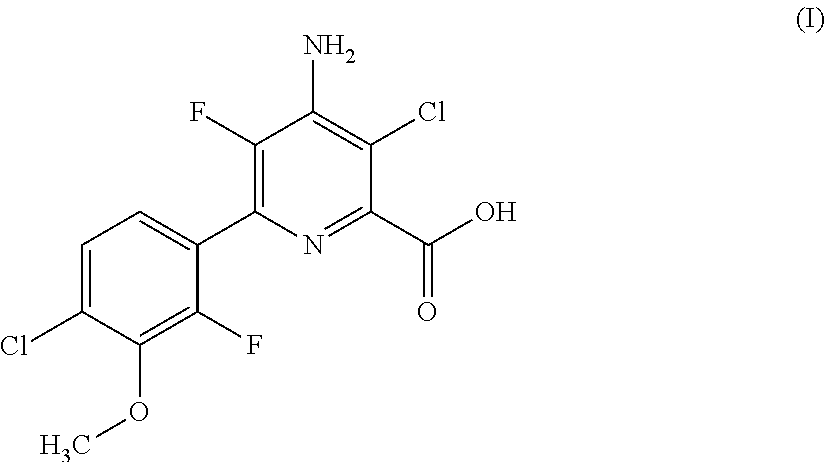
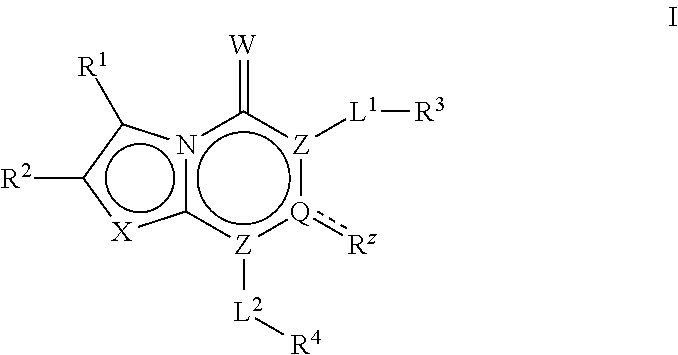
HERBICIDAL COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING 4-AMINO-3-CHLORO-5-FLUORO-6-(4-CHLORO-2-FLUORO-3-METHOXYPHENYL) PYRIDINE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID OR A DERIVATIVE THEREOF AND ACETYL-CoA CARBOXYLASE (ACCASE) INHIBITORS
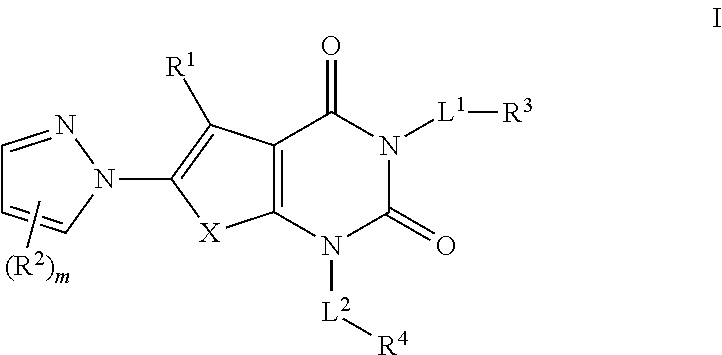
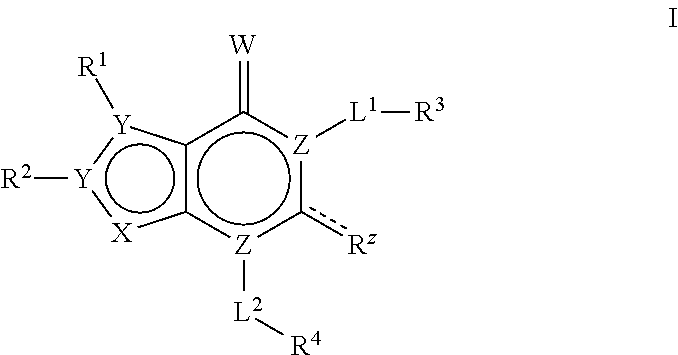
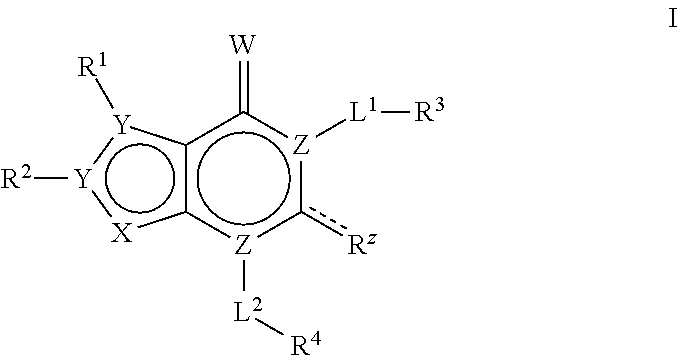
Provided herein are synergistic herbicidal compositions containing and methods utilizing (a) a compound of formula (I):or an agriculturally acceptable salt or ester thereof and (b) an ACCase inhibitors, including. e.g., clethodim, clodinafop-propargyl, cyhalofop-R-butyl, diclofop-methyl, fenoxaprop-P-ethyl, fluazifop-P-butyl, haloxyfop-R-methyl, metamifop, pinoxaden, profoxydim, quizalofop-P-ethyl, sethoxydim and tralkoxydim, provide synergistic weed control of undesirable vegetation in rice, cereals, wheat, barley, oats, rye, sorghum, corn / maize, sugarcane, sunflower, oilseed rape, canola, sugar beet, soybean, cotton, pineapple, pastures, grasslands, rangelands, fallowland, turf, tree and vine orchards, aquatics, plantation crops, vegetables, industrial vegetation management (IVM) or rights of way (ROW).
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
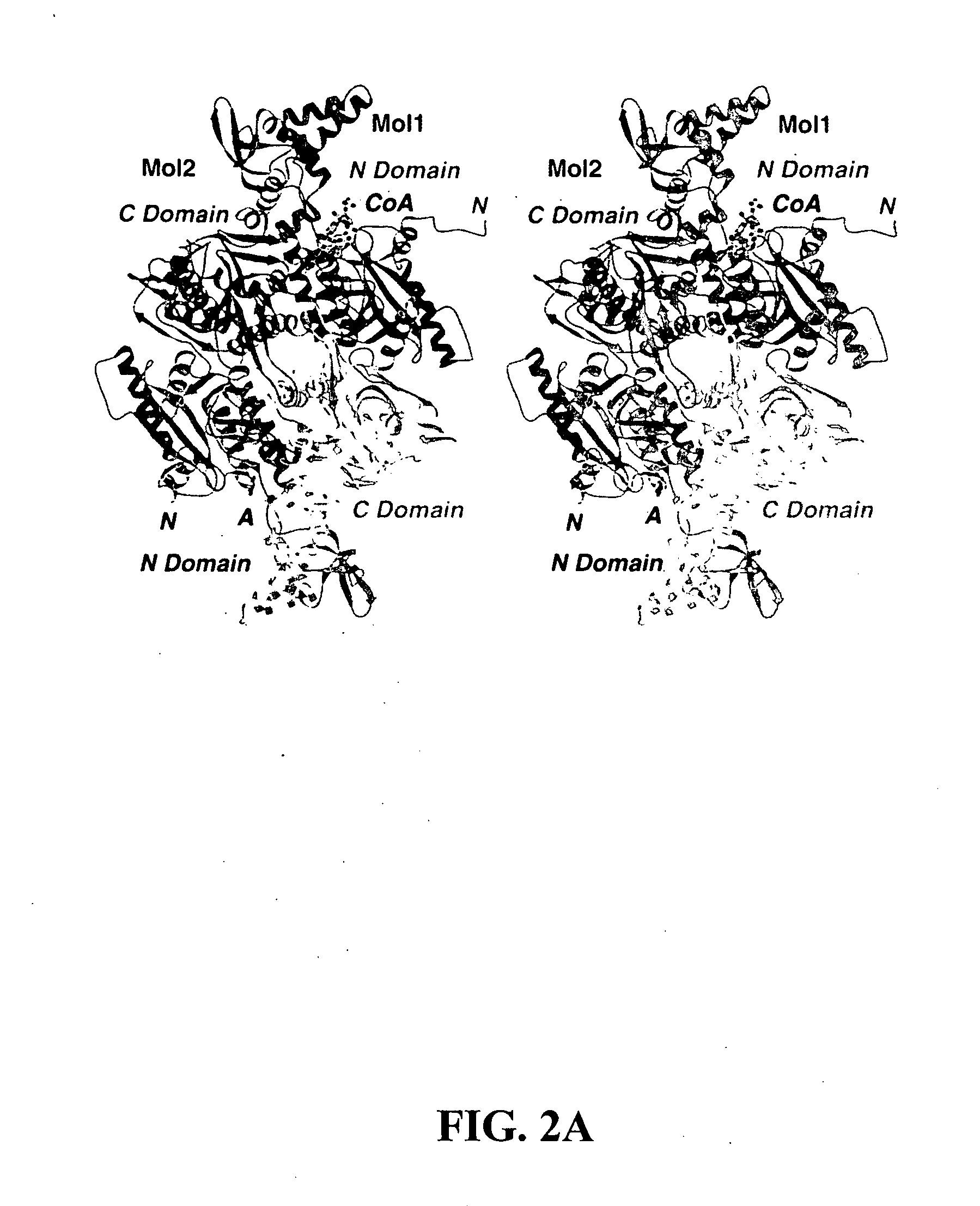
Methods of using crystal structure of carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, modulators thereof, and computer methods
InactiveUS20050009163A1Increase and decreases acetyl-CoA carboxylase activityTransferasesPeptide preparation methodsX-rayCrystal structure
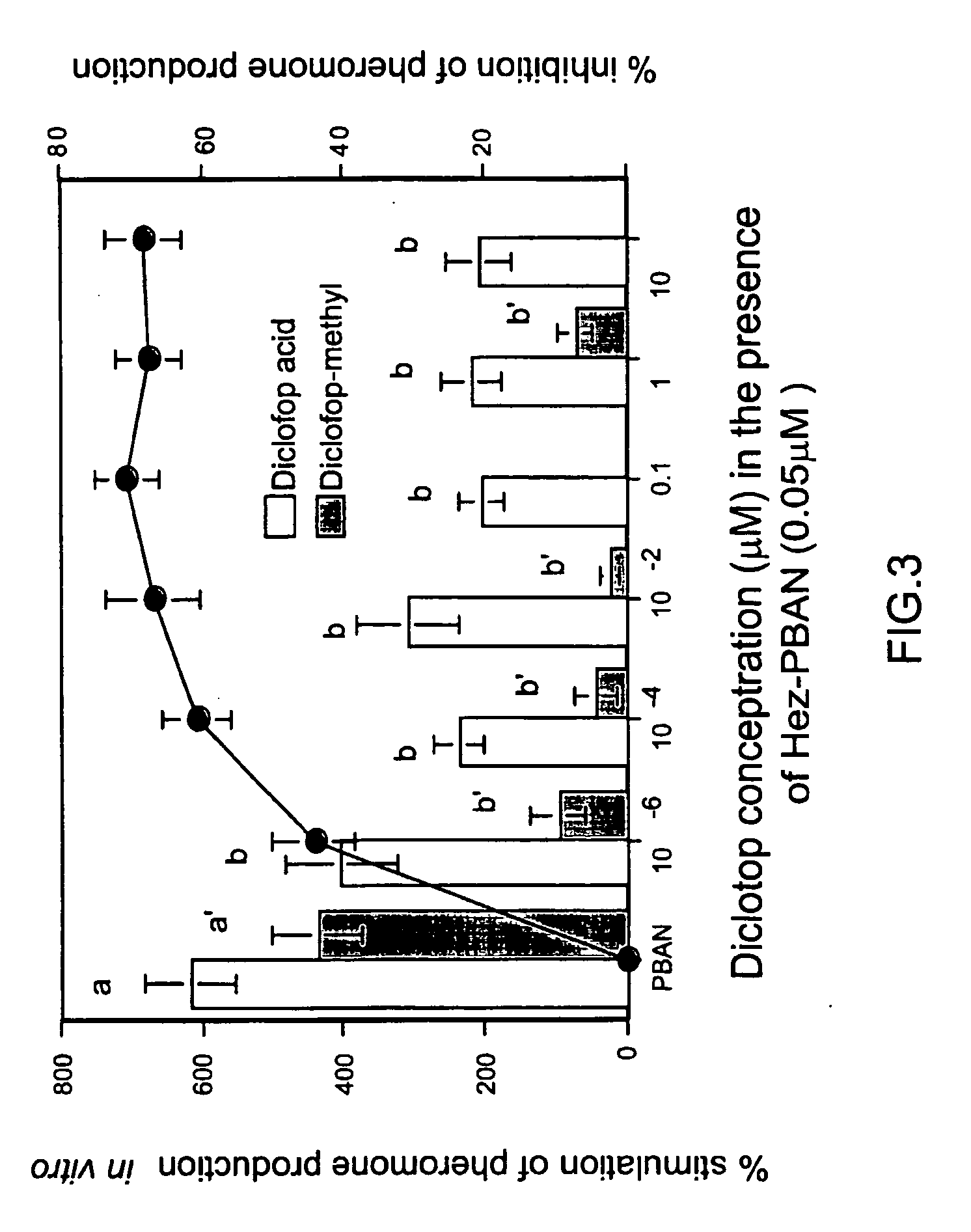
The present invention provides compositions and crystals of the carboxyltransferase (CT) domain (the C-terminal ˜90 kDa fragment) of various acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) proteins, including yeast, mouse and human ACCs. Further, the present invention provides methods for identifying and designing compounds that can modulate ACC activity. These methods are based, in part, on the X-ray crystallographic structures of the CT domain of yeast ACC, either alone or bound to acetyl-CoA or a CT inhibitor, such as haloxyfop or diclofop or CP-640186. Thus, the present invention relates to the crystal structures of the carboxyltransferase (“CT”) domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (“ACC”), and to the use of these structures in the design of anti-obesity compounds, anti-diabetes compounds, antibiotic compounds, herbicide compounds, and in the design of herbicide resistant plants.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
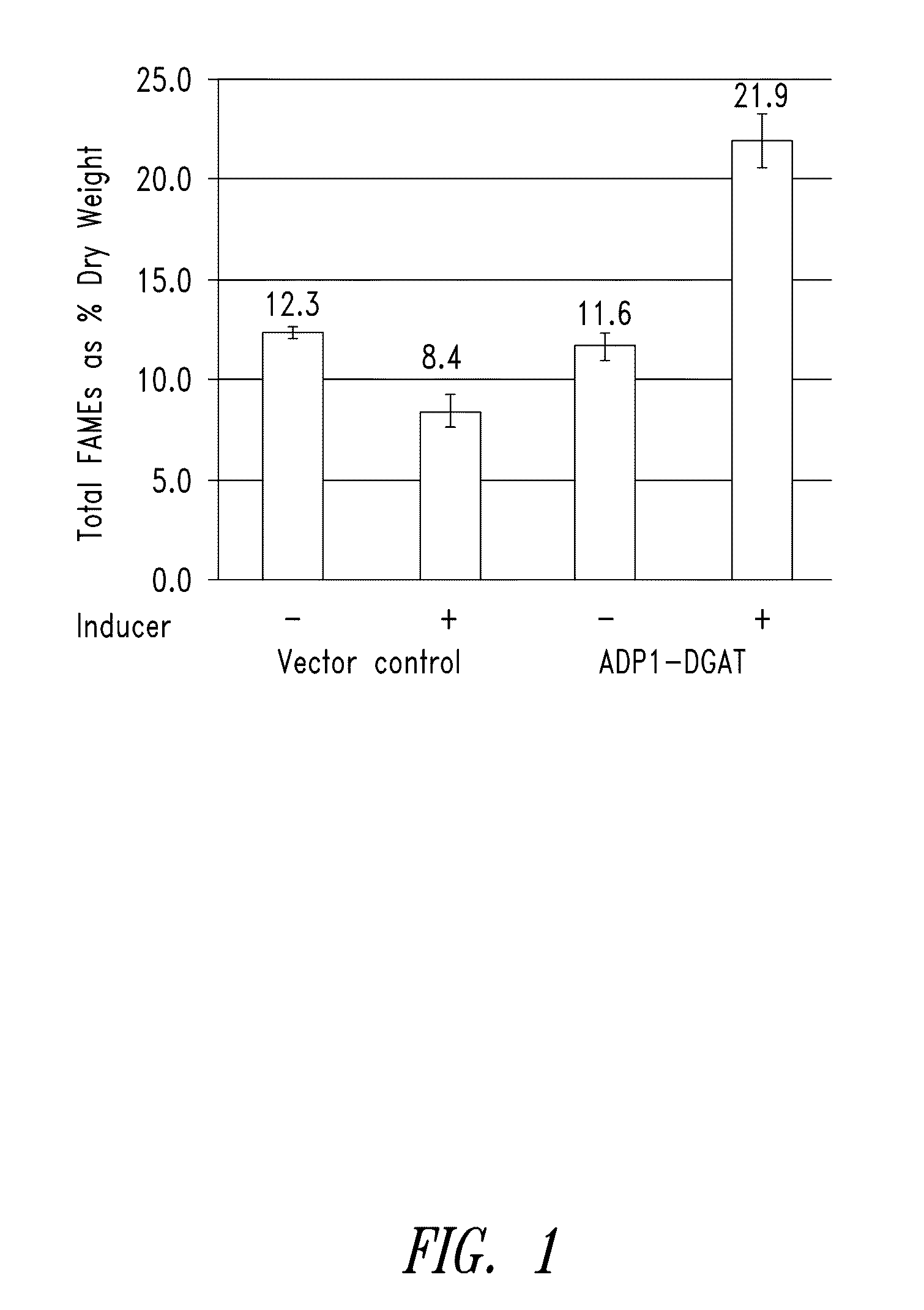
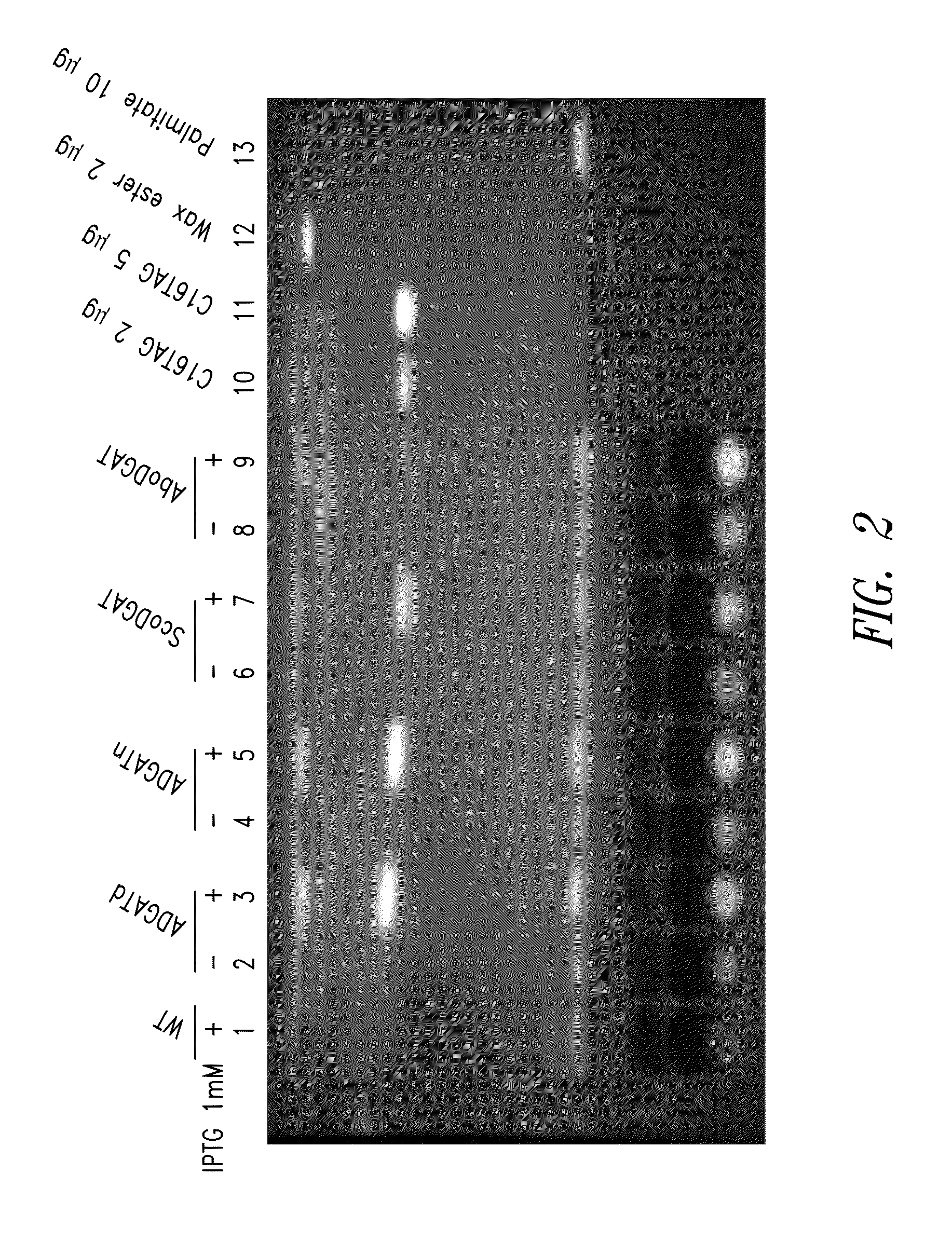
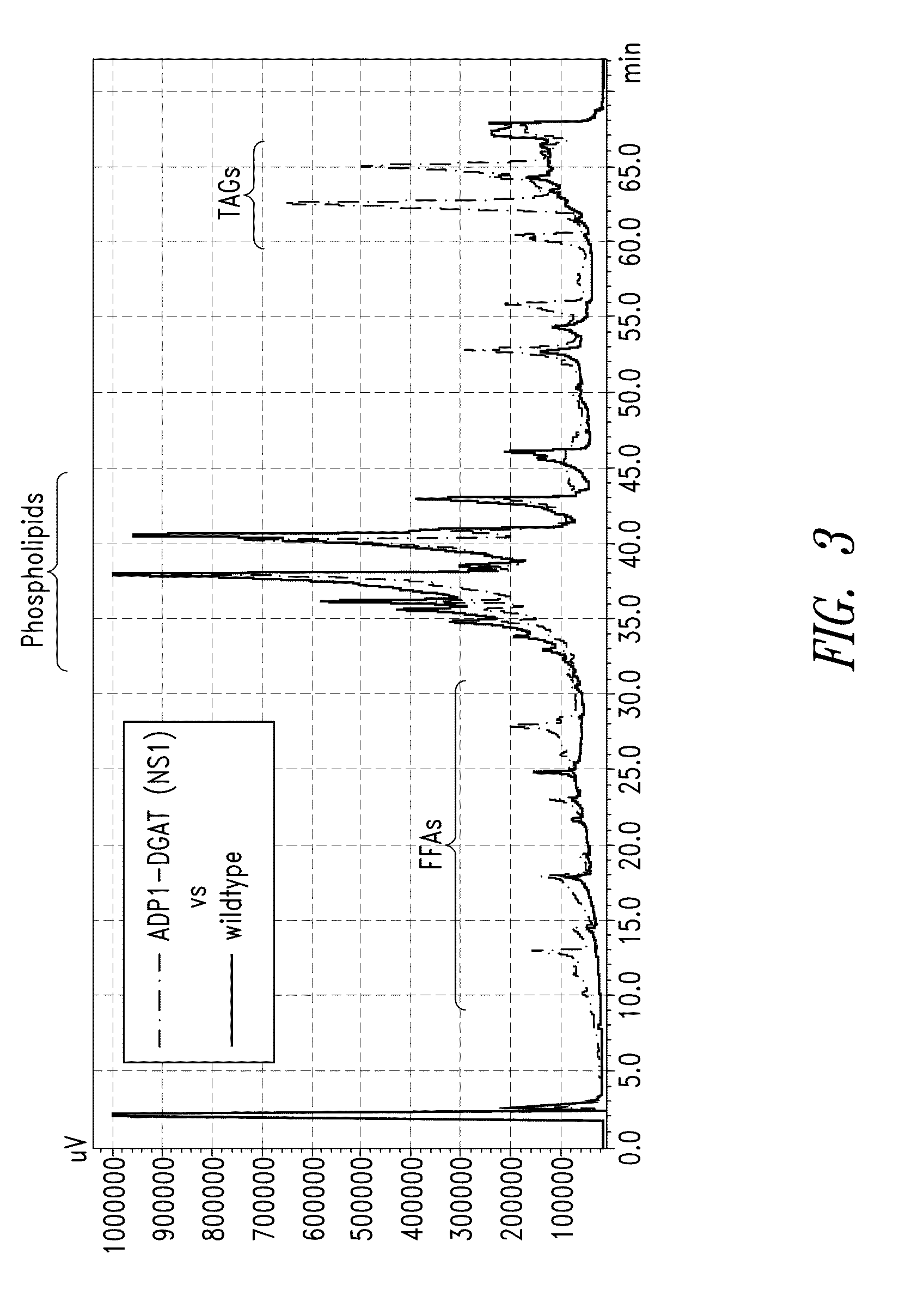
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing triglycerides
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
ACETYL CoA CARBOXYLASE INHIBITORS
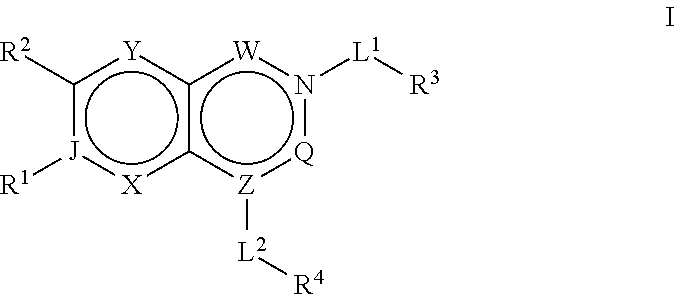
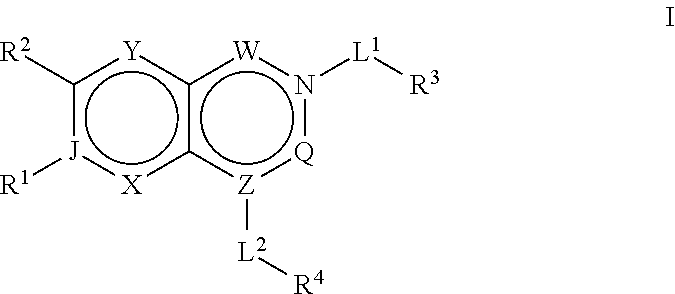
The present invention relates to acetyl coenzyme-A carboxylase (“ACC”) inhibiting compounds of the formulawherein the variables are as defined herein. In particular, the present invention relates to ACC1 and / or ACC2 inhibitors, compositions of matter, kits and articles of manufacture comprising these compounds, methods for inhibiting ACC1 and / or ACC2, and methods of making the inhibitors.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
RNA interference mediated inhibition of acetyl-CoA-carboxylase gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050124568A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesDouble stranded rnaGene expression
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of acetyl-CoA carboxylase genes.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP +1
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors for use as pesticides
InactiveUS20060039943A1Reduce frequencyReduce the populationBiocideAnimal repellantsInsect pestExcipient
The present invention relates to the use of inhibitors of the action of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase for controlling insect pests. The inhibitors are selected from arylphenoxypropionates and cyclohexanedione oximes, or their mixtures which may be used together with suitable additives, excipients and carriers. The invention further relates to an insecticidal composition comprising inhibitors of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and further to a method for controlling undesired insect pests by applying an effective amount of eukaryotic-type Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT +1
Combination therapy for endothelial dysfunction, angina and diabetes
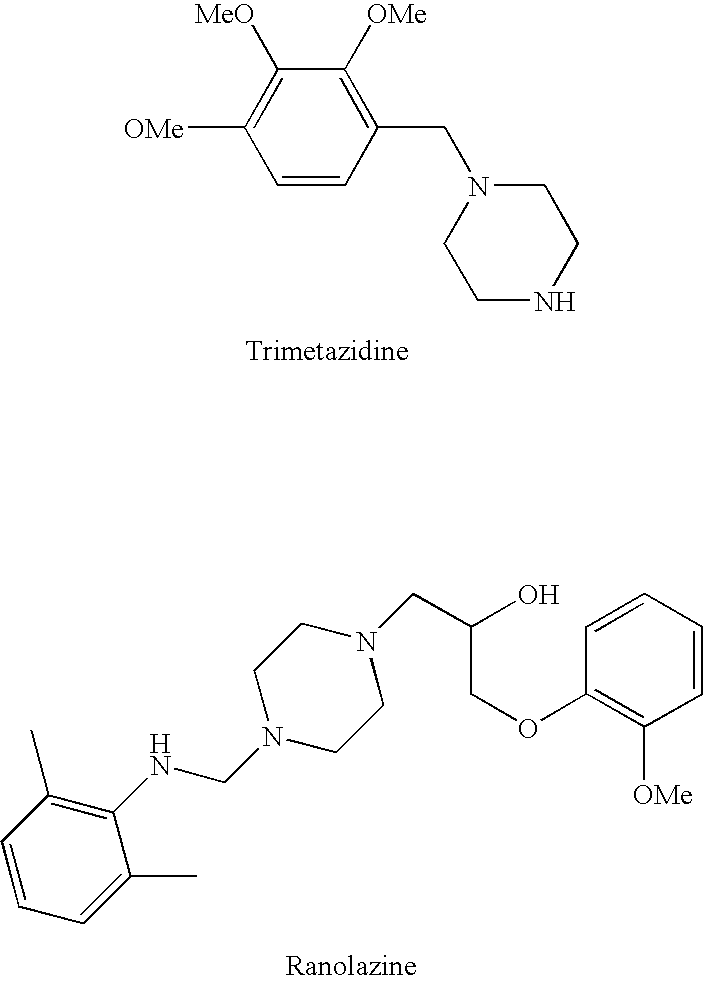
InactiveUS20060205727A1Control blood sugar levelsIncrease productionBiocideMetabolism disorderHMG-CoA reductaseTrimetazidine
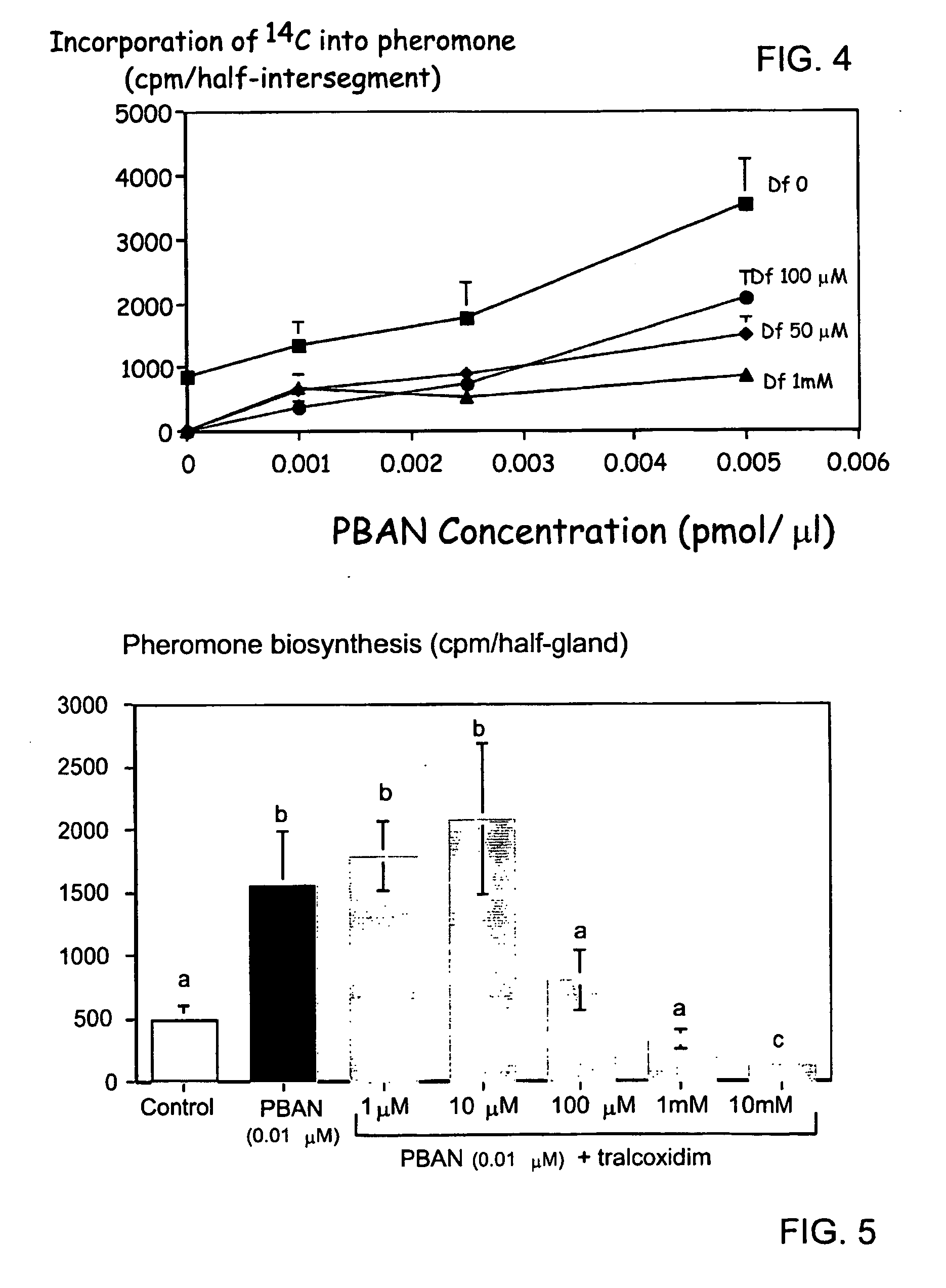
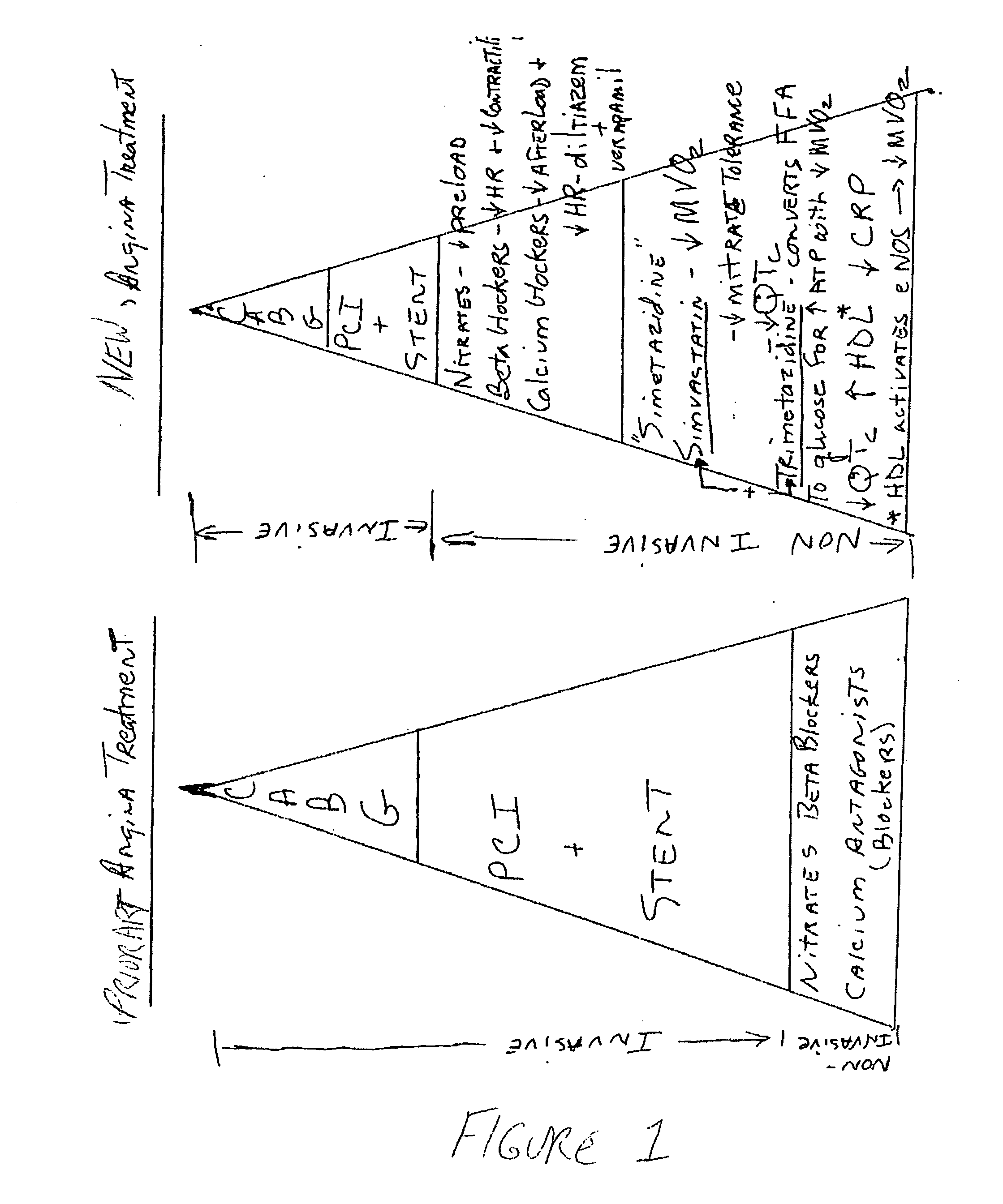
The combination of a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor like a statin, such as simvastatin, with a pFox inhibitor such as trimetazidine (“Simetazidine”) is particularly advantageous for treatment of end-stage complications, such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and chronic angina, especially in type II diabetics. The combination therapy is also useful in the treatment and / or prevention of chronic heart failure (CHF) and peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The combination of a nitric oxide (NO) mechanism with increased NO production with pFox inhibition simultaneously treats both the effect and the cause of angina. One or more oral hypoglycemic compounds (biguanides, insulin sensitizers, such as thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin secretagogues, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors), protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors can also be used in combination with the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and / or pFox inhibitors, especially in type II diabetics, to control glucose levels and treat endothelial dysfunction. The drugs can be given in combination (e.g. a single tablet) or in separate dosage forms, administered simultaneously or sequentially. In the preferred form the statin is given in a dose of between 5 and 80 mg / day in two separate doses, and the pFox inhibitor is administered in a sustained or extended dosage formulation at a dose of 20 mg three times a day or 35 mg two times a day. The dose of the oral hypoglycemic, PKC inhibitor, or acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor varies with the type of drug used.
Owner:HONG KONG NITRIC OXIDE
Modified Photosynthetic Microorganisms With Reduced Glycogen and Their Use in Producing Carbon-Based Products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Solid forms of a thienopyrimidinedione acc inhibitor and methods for production thereof
The present invention provides solid forms of compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, methods of producing the same, and methods of using the same in the treatment of ACC-mediated diseases.
Owner:J P LAWSON CONSULTING LLC +2
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing triglycerides
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Ester acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides ester compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:SCHRODINGER INC +1
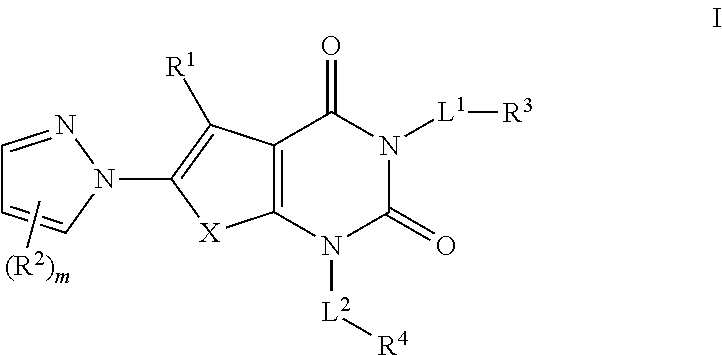
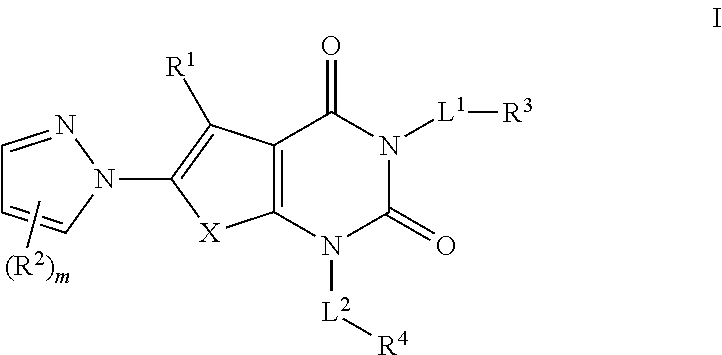
Pyrazole acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides pyrazole compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC +1
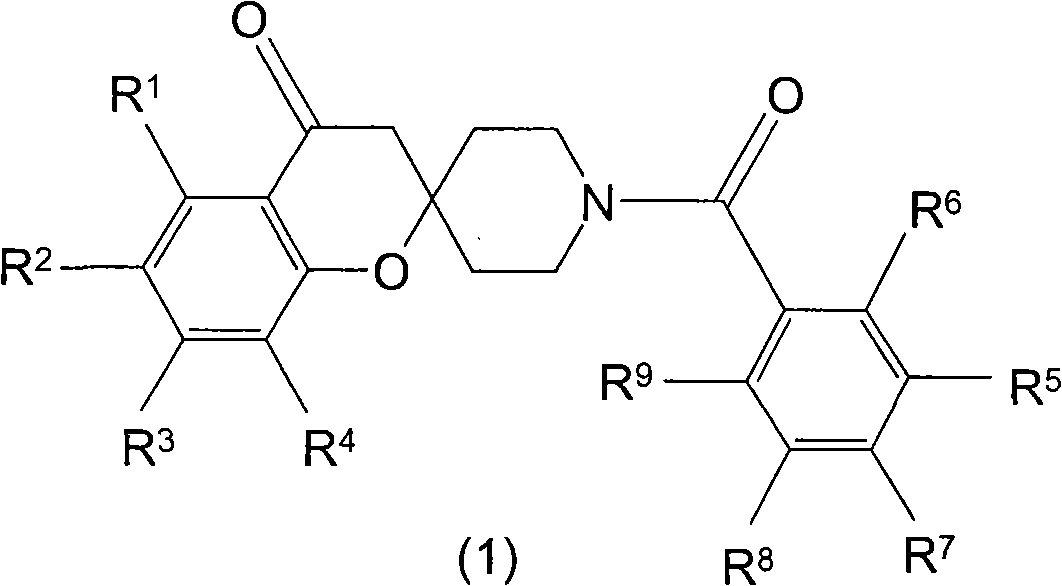
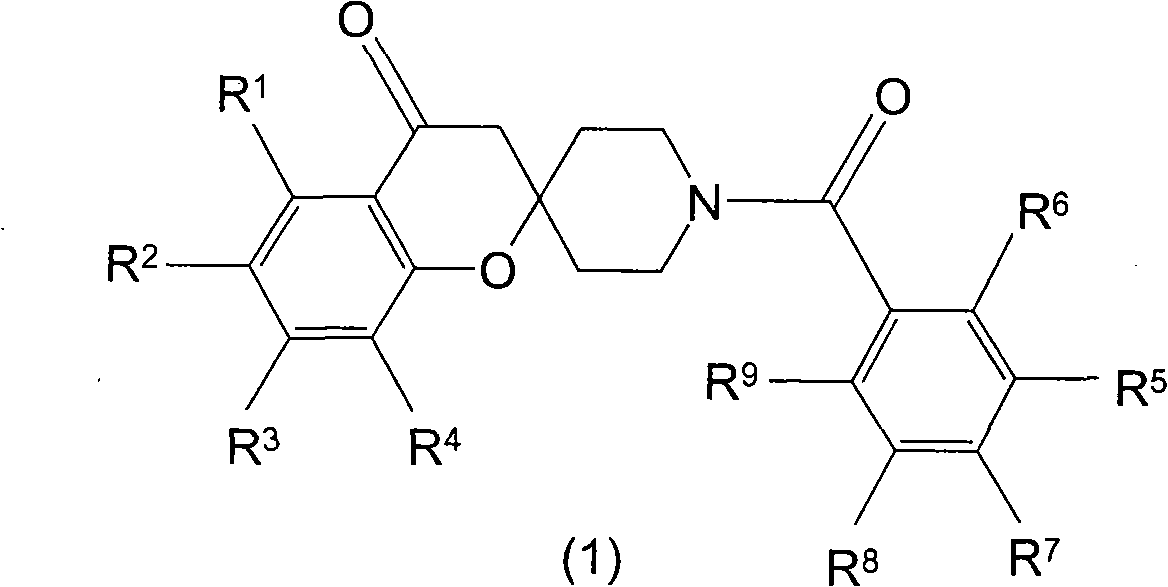
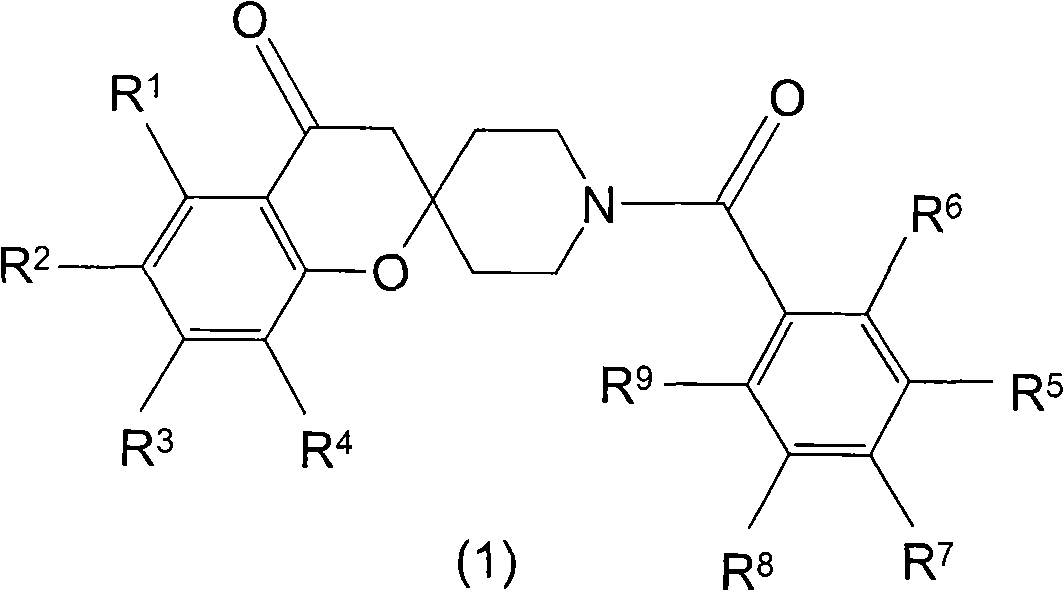
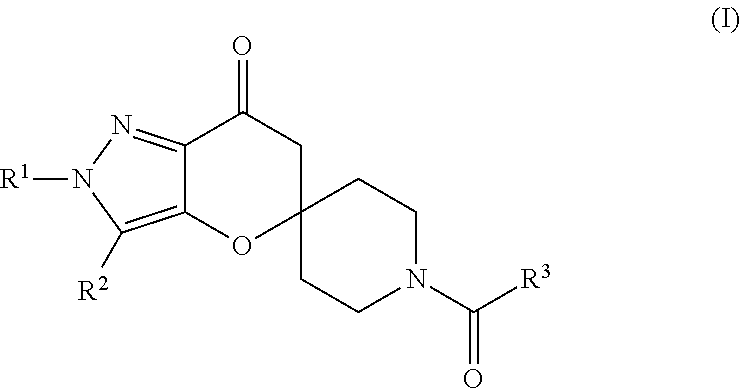
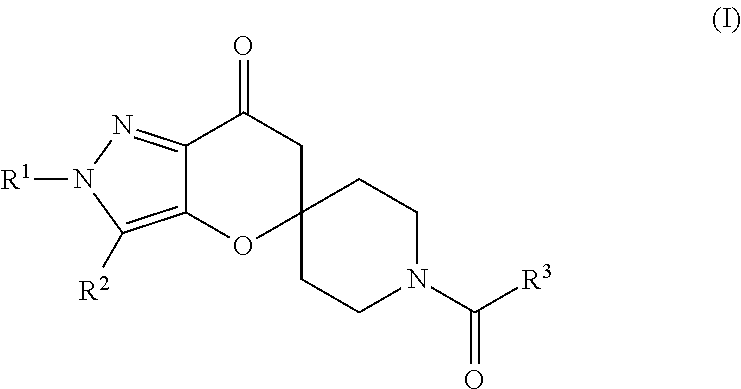
Spiroketone Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitors
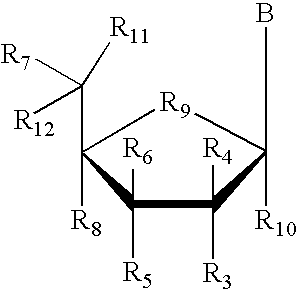
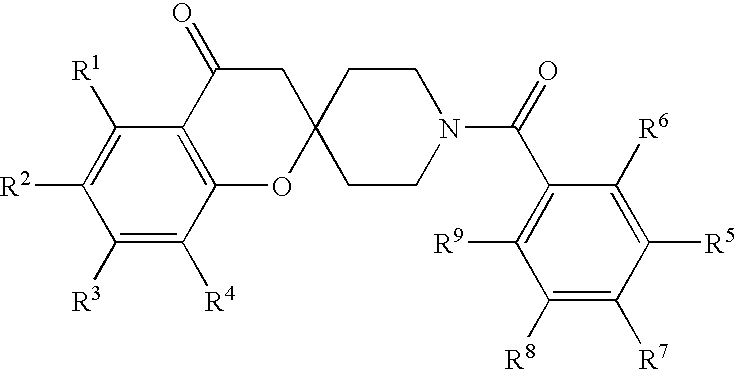
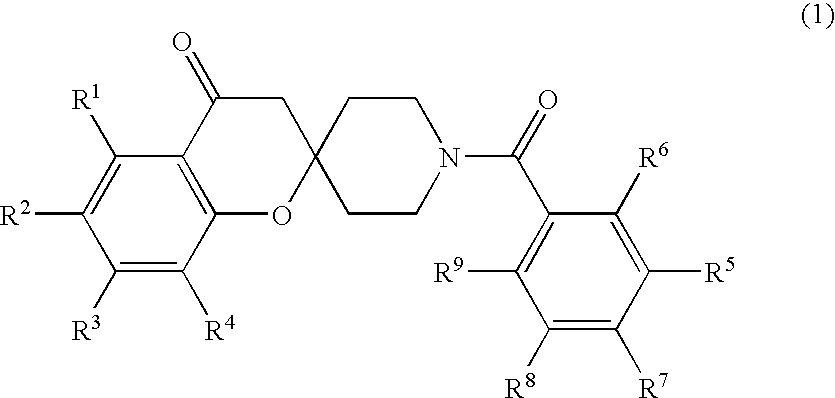
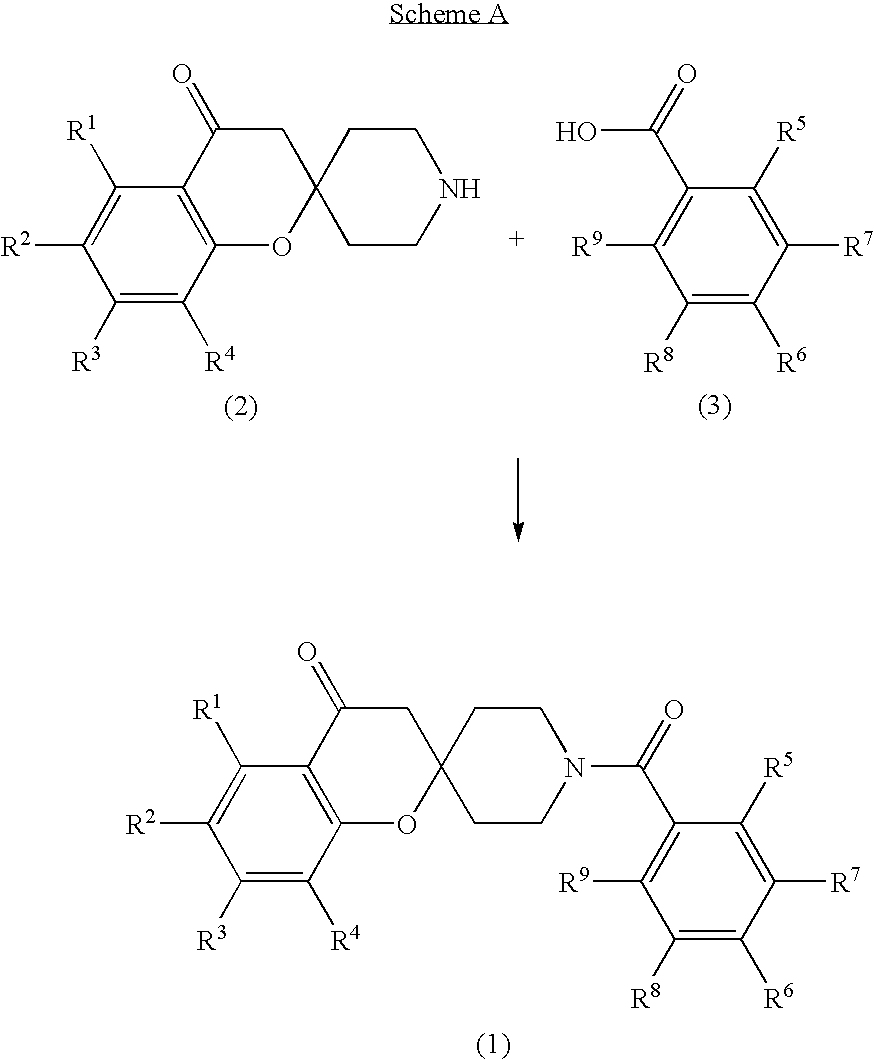
The invention provides compounds of Formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said compound, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8 and R9 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating mammals suffering from the condition of being overweight.
Owner:CORBETT JEFFREY WAYNE +2
Solid forms of a thienopyrimidinedione ACC inhibitor and methods for production thereof
The present invention provides solid forms of compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, methods of producing the same, and methods of using the same in the treatment of ACC-mediated diseases.
Owner:J P LAWSON CONSULTING LLC +2
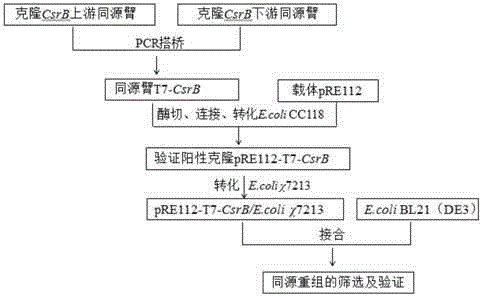
Genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as construction method and application of genetic engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104388371AIncrease productionImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaPeptidesCarbon metabolismCarbon storage
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as a construction method and an application of the genetic engineering bacterium and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium over-expresses carbon storage and regulation factor gene CsrB shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and co-expresses a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor gene marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase. The invention also provides the construction method and the application of the genetic engineering bacterium for the high-yield phloroglucinol. With the adoption of the genetic engineering bacterium, the yield of the phloroglucinol is firstly increased by 115.6 percent by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level of the genetic engineering bacterium, and the genetic engineering bacterium has a high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same. Specifically, bicyclic heteroaryl derivatives containing a imidazole, thiazole or oxazole fused to a pyridinone, pyrimidinone or pyrimidindione are provided. These compounds have therapeutic utility toward treating an ACC enzyme mediated disorder such as obesity in a subject, upon administration in an effective amount to said subject.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
ACC inhibitors and uses thereof
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
InactiveUS6979741B2Ease of preparation and detectabilityGood metabolic stabilityOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderMedicineMetabolic syndrome
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms with reduced glycogen and their use in producing carbon-based products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Bicyclic compounds as ACC inhibitors and uses thereof
The present invention provides compounds useful as inhibitors of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC), compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.
Owner:NIMBUS DISCOVERY INC
ACETYL-CoA CARBOXYLASE HERBICIDE RESISTANT SORGHUM
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for producing crop plants that are resistant to herbicides. In particular, the present invention provides for sorghum plants, plant tissues and plant seeds that contain altered acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) genes and proteins that are resistant to inhibition by herbicides that normally inhibit the activity of the ACC protein.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing triglycerides
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Spiroketone acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
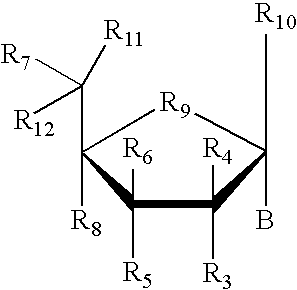
The invention provides compounds of Formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said compound, wherein R, R, R, R, R, R, R, R and R are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating mammals suffering from the condition of being overweight.
Owner:PFIZER PRODS ETAT DE CONNECTICUT
Gene modification method for increasing yield of phloroglucinol and application of same
InactiveCN104388457AIncrease productionHigh industrial application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a gene modification method for increasing the yield of phloroglucinol and application of the same, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The gene modification method comprises the following steps: obtaining a mutant strain by virtue of a mode of knocking out or inserting a global regulating factor arcA gene of an original strain, converting the state of the mutant strain to a competent state, introducing recombinant plasmids containing a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase, and obtaining a recombinant cell. The invention also provides a method of producing the phloroglucinol by utilizing the recombinant cell. According to the gene modification method and application disclosed by the invention, the yield of the phloroglucinol after fermentation is firstly increased by 2.06 times by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level, and the gene modification method and application have high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
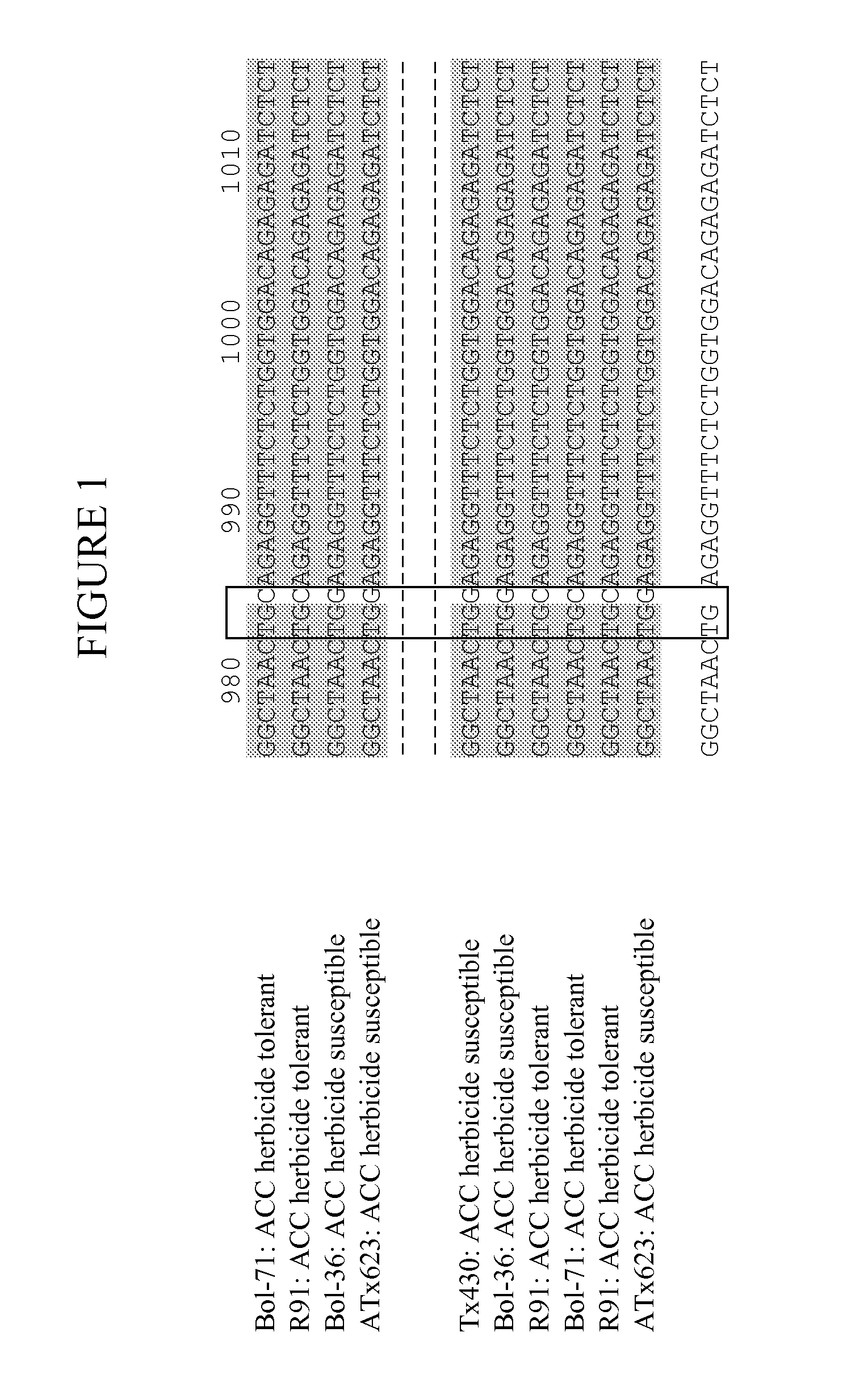
Rice ACCase mutant gene and application thereof in herbicide resistance of plants
The invention discloses a rice ACCase mutant gene and an application thereof in herbicide resistance of plants. The amino acid sequence of the encoding protein of the ACCase mutant gene has the following mutation: the 1731st siteor / and 2276th site of the amino acid sequence corresponding to the wild type rice ACCase is subjected to mutation. The ACCase mutant gene is introduced into herbicide-sensitive rice genome by a transgenic method and is expressed; and receiver plants can have resistance to acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor herbicide. The ACCase mutant gene can be widely applied to the breeding of plants with the herbicide resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Acc inhibitors and uses thereof
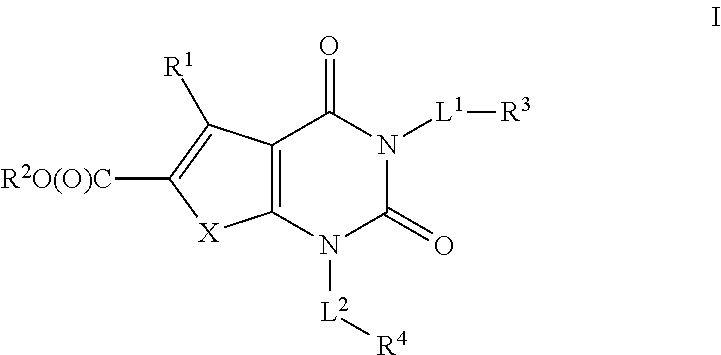
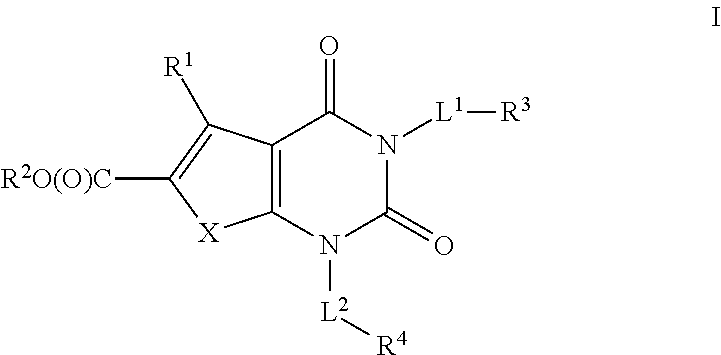
The present invention provides for compounds of formula I as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibitors. The ACC inhibitors are useful for the prevention or treatment of metabolic syndrome, including obesity, dyslipidemia and hyperlipidemia in humans. The inhibitor compounds are also capable of inhibiting the ACC enzyme found in plants, parasites and bacteria.
Owner:GILEAD APOLLO LLC +1
Pyrazolospiroketone acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors
The invention provides compounds of Formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said compound, wherein R1, R2, and R3 are as described herein; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and the use thereof in treating diseases, conditions or disorders modulated by the inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme(s) in an animal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
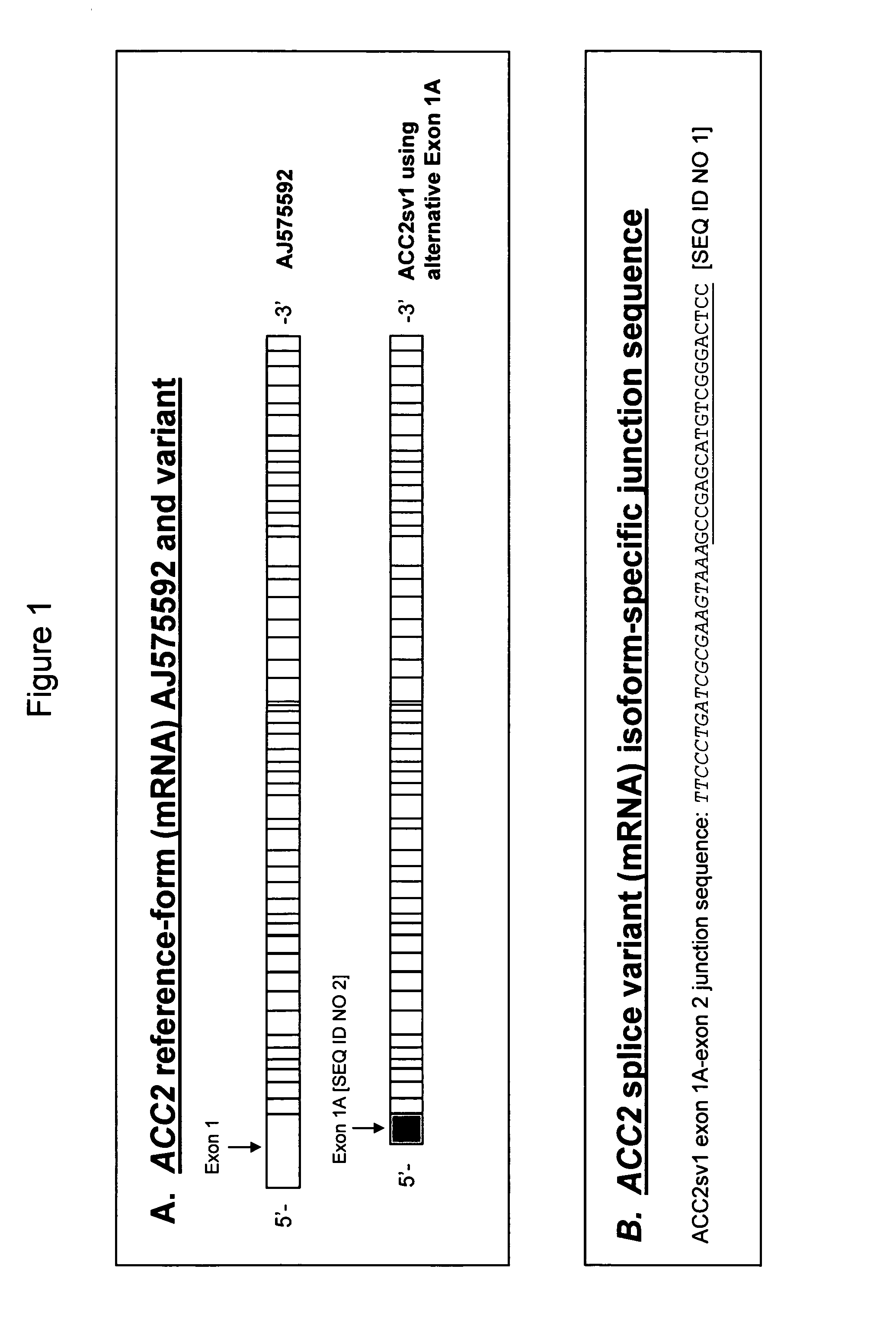
Alternatively spliced isoform of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACC2)
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com