Elastic spunbonded nonwoven and elastic nonwoven fabric comprising the same
a technology of elastic nonwoven fabric and elastic nonwoven fabric, which is applied in the direction of weaving, conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filaments, weaving, etc., can solve the problems of affecting web uniformity, affecting the uniformity of webs, and troublesome bigger filament bundling, so as to facilitate the whole spunbonding process and reduce friction and polymer tackiness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Perforated Hydroentangled Elastic Nonwoven Fabrics
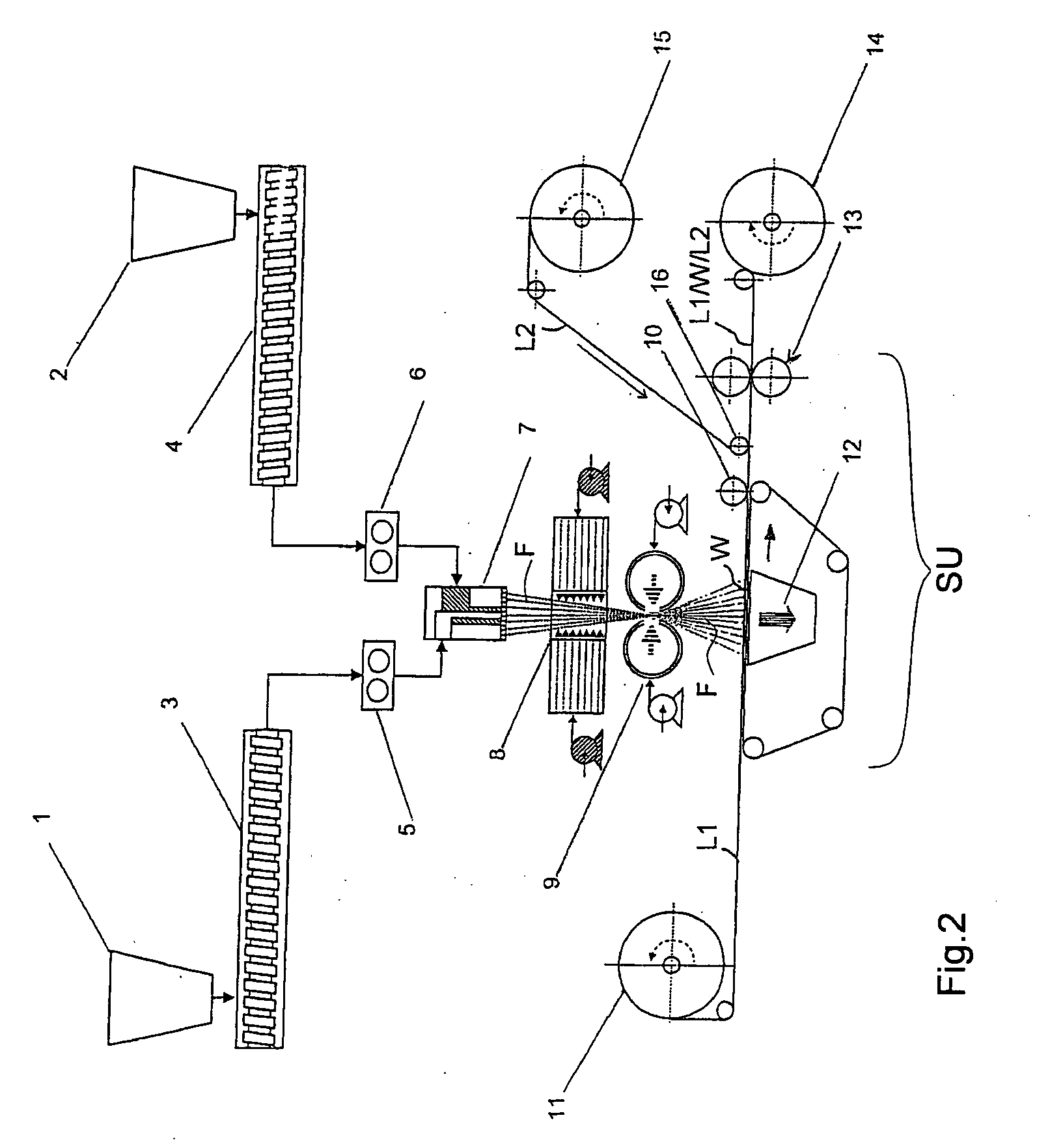
[0142]Different perforated composite nonwoven fabric (C / W, C / W / S and C / W / C) have been produced according to the manufacturing processes of FIGS. 3 and 4 (examples E-150-FP, E-151-FP, E-152-FP, E-153-FP, E-155-FP).
The compositions of these composite nonwoven fabrics are summarized in Table 7.
TABLE 7Perforated hydroentangled elastic nonwoven of the inventionElastictotalBottomspunbondedB.W.Layer,Layer WTop Layer,Examplesstructure(gsm)typegsm(see table 4)gsmtypegsmE-150-C / W60on line30E-7-830NONE0FPcardedPPE-151-C / W / S58on line20E-7-830Spunbonbded8FPcardedPPPPE-152-C / W / S110on line20E-7-1080Spunbonbded10FPcardedPPPPE-153-C / W / S90on line20E-7-660Spunbonbded10FPcardedPPPPE-155-C / W / C94on line20E-7-660Carded PP14FPcardedPPC: carded layerW: Elastic spunbonded layer of the inventionS: Spunbonded layerPP: Polypropylene
[0143]The outer carded layers (C) with low basis weight give textile appearance and soft touch to the final nonwoven fabric. This pr...
example
Elastic Spunbonded Nonwoven (W / M)
[0157]Samples of multilayer nonwoven (C / W / M / C) have been produced on a pilot plant, without bonding the layers together. Then the two outer carded layers were removed in order to keep only the elastic spunbonded (W) and meltblown (M) layers.
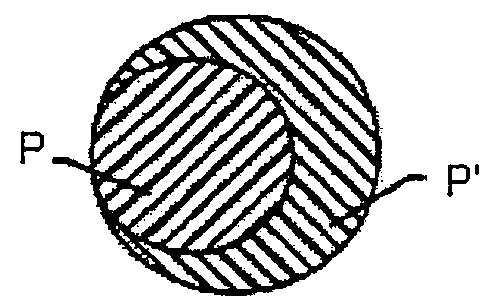
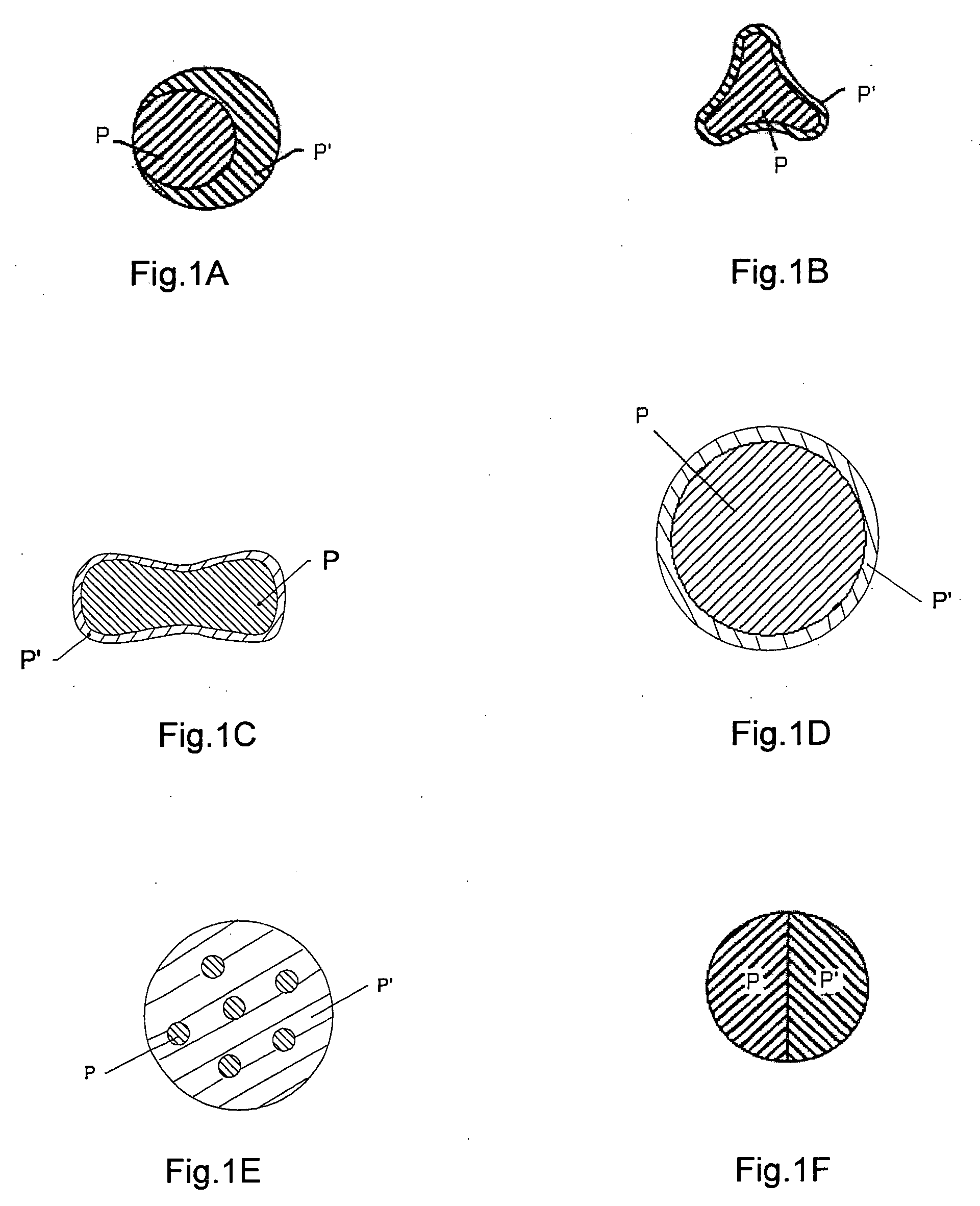
[0158]The elastic spunbonded layer W was made of bicomponent sheath / core filaments having the round cross-section of FIG. 1D. The core of the filaments was made (first polymeric component P) of a blend VM2125 (70 wt %) and VM6100 (30 wt %). The outer sheath of the filaments was made of VM 2125 (second polymeric component P′). The weight of the core was 90% of the total basis weight, and the weight of the sheath was 10% of the total basis weight. The basis weight of the elastic spunbonded layer (W) was 54 gsm.
[0159]In this example the material used for the elastic meltblown layer (M) was VM 2320. The basis weight of the meltblown layer (M) was 10 gsm. The elastic properties of the elastic spunbonded nonwoven (W / M) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com