Method of treating water with chlorine dioxide
a technology of chlorine dioxide and water treatment, applied in the direction of biocide, water treatment parameter control, specific water treatment objectives, etc., can solve the problem of relatively high time-specific generation rate of chlorine dioxide, inability to store chlorine dioxide in compressed form or in solutions of relatively high concentration, and hazards in the vicinity of generation systems. , to achieve the effect of saving and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
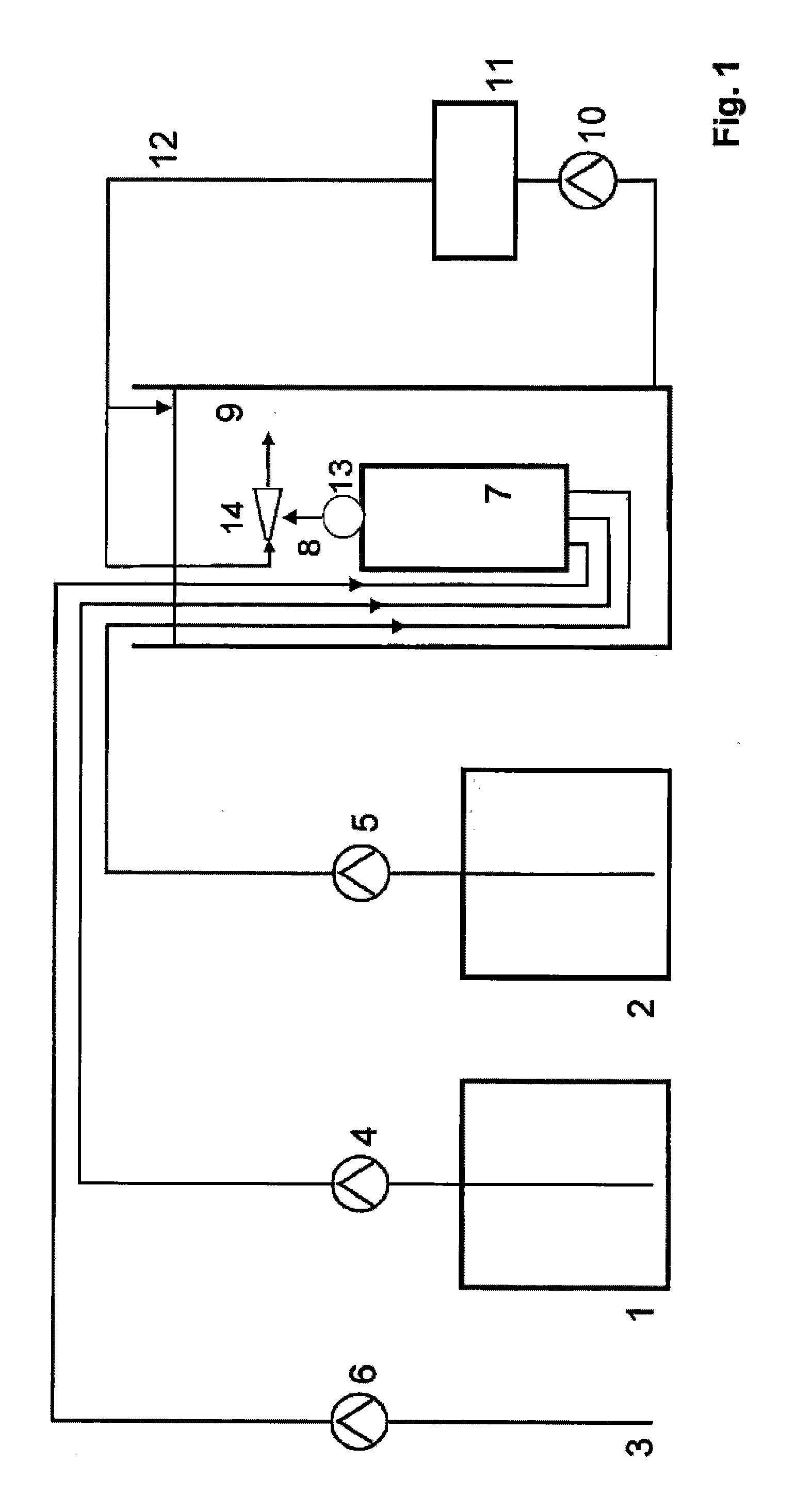
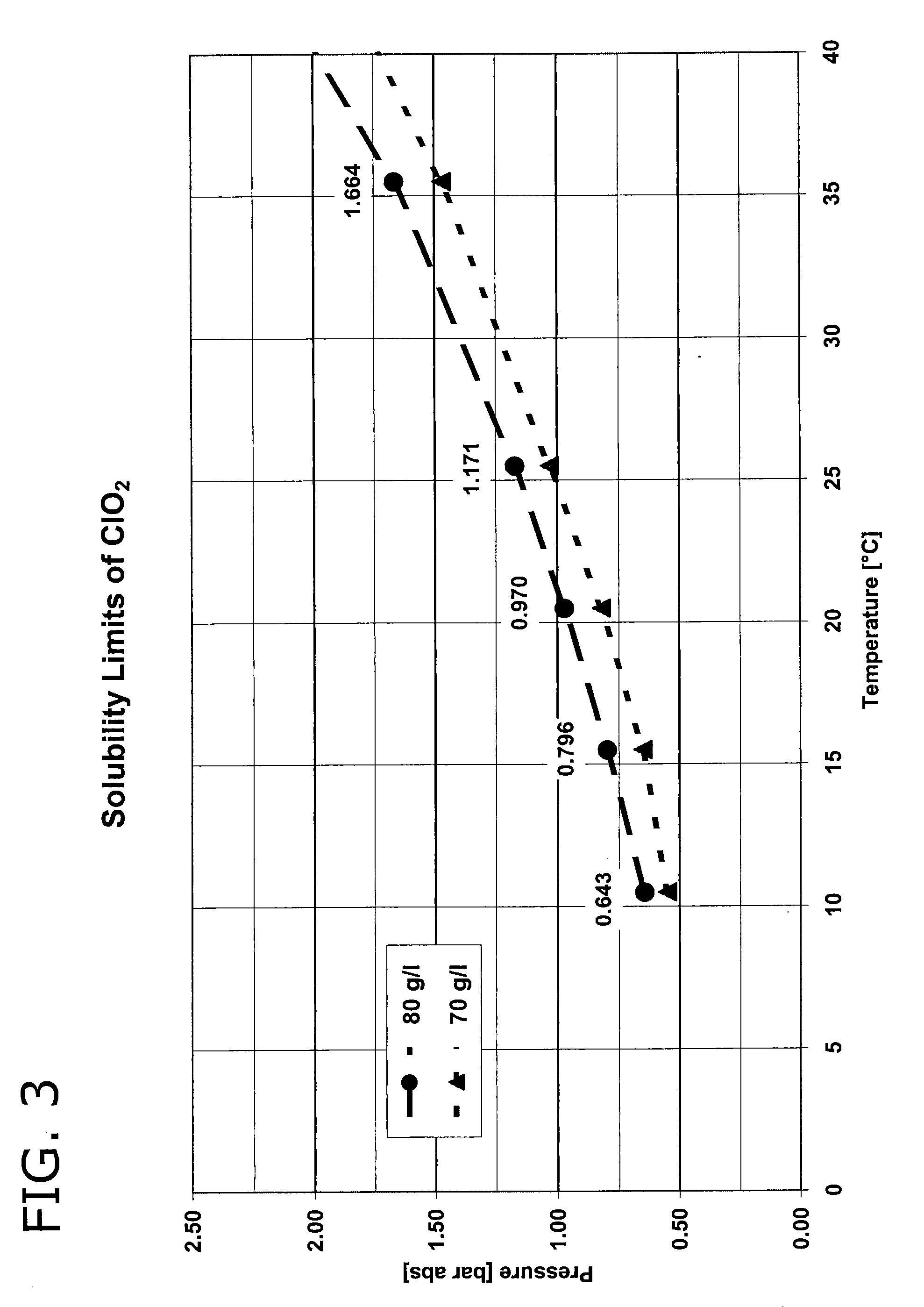
[0086]The device described in FIG. 1 is used. The aqueous solution in the chlorite storage tank 1 contains 25% sodium chlorite and 2.5 l / h of this solution are passed by the transport pump 4 into the reactor 7. From the acid storage tank 2, 2.5 l / h of a 32% strength aqueous hydrochloric acid solution are simultaneously fed to the reactor 7 by the transport pump 5. Via the dilution water rate of 5 l / h, which is likewise simultaneously fed to the reactor 7 from the water connection 3 by the transport pump 6, the concentration of the resultant chlorine dioxide solution is set to 42 g / l [at a yield of 92%]. The reactor has a free volume of 0.33 litres and the residence time of the reaction mixture in the reaction chamber is 2 minutes. 10 litres of chlorine dioxide solution having a content of 42 g / l are fed per hour via the reactor outlet 8 to a water-jet liquid pump 14 which is operated with the water which is to be treated and subsequently mixed with the returned amount of water which...
example 2
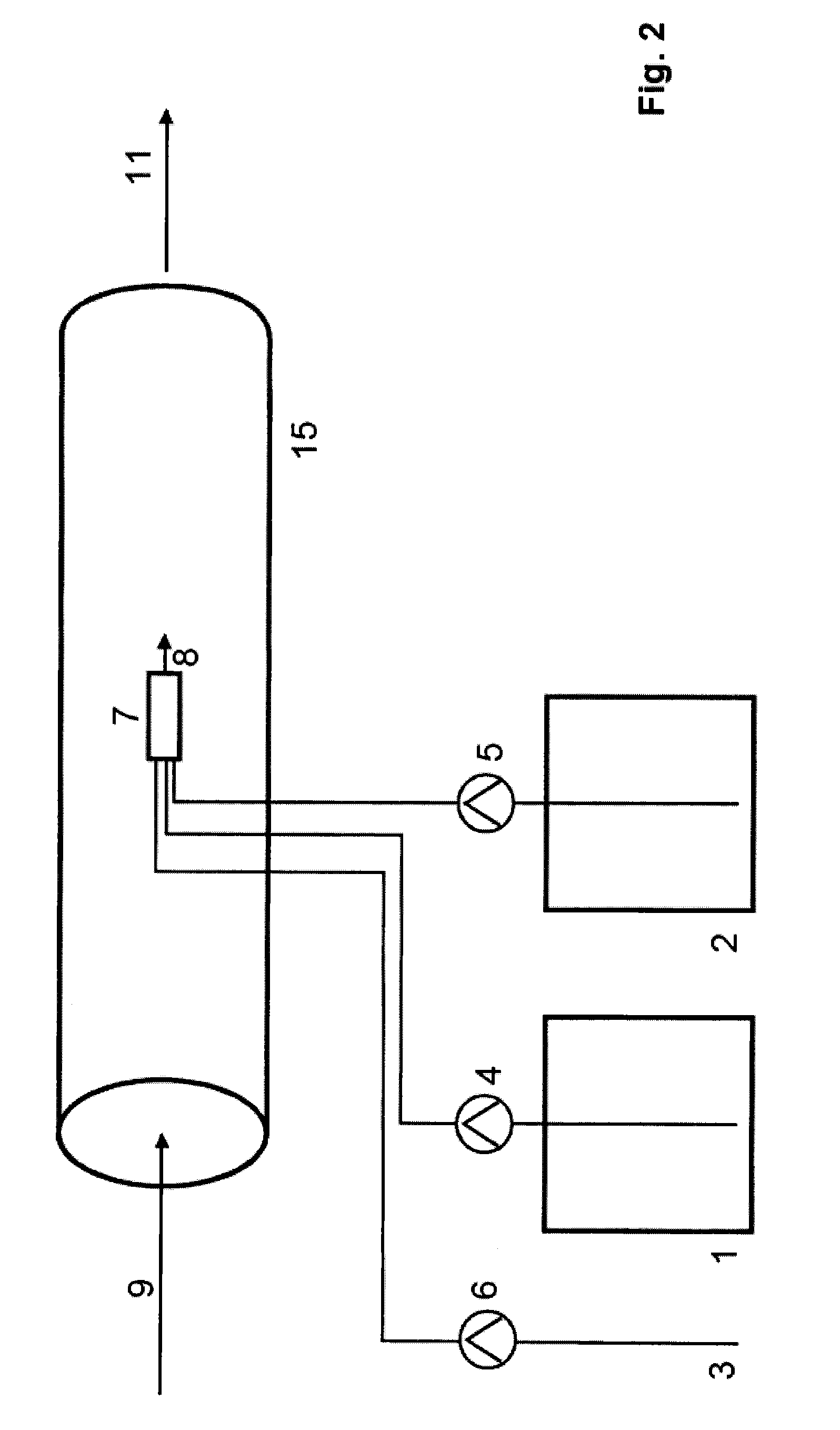
[0087]The device described in FIG. 2 is used. The aqueous solution in the chlorite storage tank 1 contains 25% sodium chloride and 6 l / h of this solution are passed into the reactor 7 by the transport pump 4. From the acid storage tank 2, 5 l / h of a 30% strength aqueous hydrochloric acid solution are simultaneously fed to the reactor 7 by the transport pump 5. The reactor 7 is built into a pipe 14 through which an amount of 100 m3 of water to be treated 9 flows per hour. No dilution water is fed to the reactor via transport pump 6. The reactor has a free volume of 0.075 litres and the residence time of the reaction mixture in the reaction chamber is 0.4 minutes. 11 litres of chlorine dioxide solution having a content of 94 g / l are delivered per hour via the reactor outlet 8 into the water which is to be treated 9 flowing around the reactor 7, as a result of which the concentration of the reaction mixture at the reactor outlet 8 is abruptly reduced to 10 mg / l by mixture with the wate...
example 3
[0088]The device described in FIG. 1 is used. The aqueous solution in the chlorite storage tank 1 contains 24.5% sodium chlorite and 5 l / h of this solution are passed into the reactor 7 by the transport pump 4. From the acid storage tank 2, 5 l / h of a 32% strength aqueous hydrochloric acid solution are simultaneously fed to the reactor 7 by the transport pump 5. Via the dilution water rate of 28 l / h which is likewise simultaneously fed to the reactor 7 from the water connection 3 by the transport pump 6, the concentration of the resultant chlorine dioxide solution is set to 19.7 g / l [at a yield of 83%]. The reactor has a free volume of 6 litres and the residence time of the reaction mixture in the reaction chamber is 9.5 minutes. 38 litres of chlorine dioxide solution having a content of 19.7 g / l are delivered via the reactor outlet 8, which is situated in the vicinity of the suction line of the circulation pump 10, into the water to be treated 9 which surrounds the reactor. 2000 m3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com