Fin-tube heat exchanger, fin for heat exchanger, and heat pump apparatus
a heat exchanger and fin technology, applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatuses, refrigeration machines, etc., to achieve the effects of improving heat transfer performance, increasing heat transfer area, and increasing flow velocity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0079]Hereinbelow, one embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to the appended drawings.
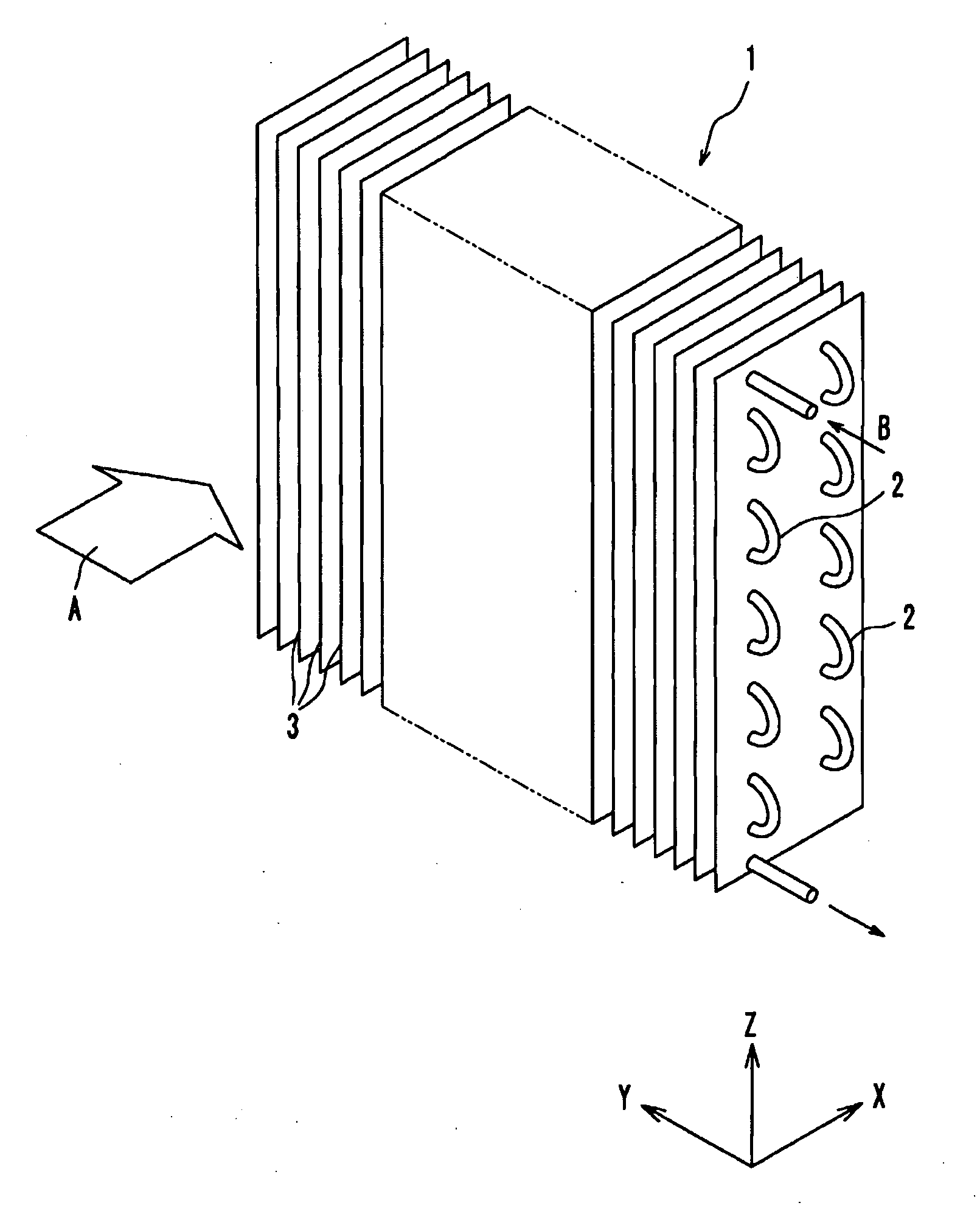
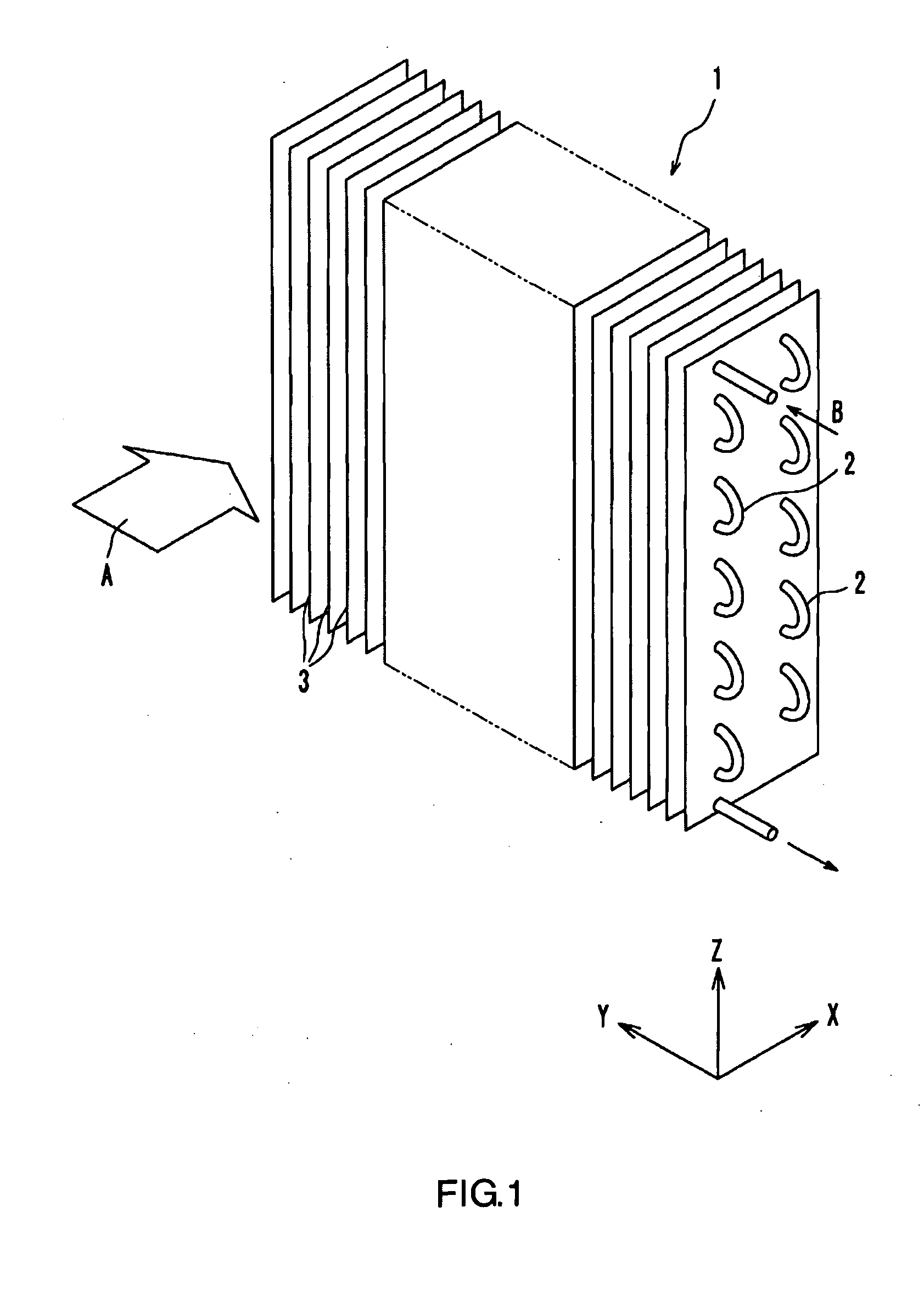
[0080]FIG. 1 is an overall perspective view illustrating a fin-tube heat exchanger according to the present embodiment. The fin-tube heat exchanger 1 has a plurality of fins 3 arranged parallel to each other with a predetermined gap for forming spaces for allowing the first fluid to flow therethrough, and a plurality of heat transfer tubes 2 penetrating these fins 3. The heat exchanger 1 is for exchanging heat between the first fluid flowing along the principal surfaces of the fins 3 and the second fluid flowing inside the heat transfer tubes 2. In the present embodiment, air A flows along the principal surfaces of the fins 3, and refrigerant B flows inside the heat transfer tubes 2. The plurality of heat transfer tubes 2 penetrating the fins 3 are connected in a single line so that the refrigerant B flows therein in turn. It should be noted that the type and state of the ...
embodiment 2
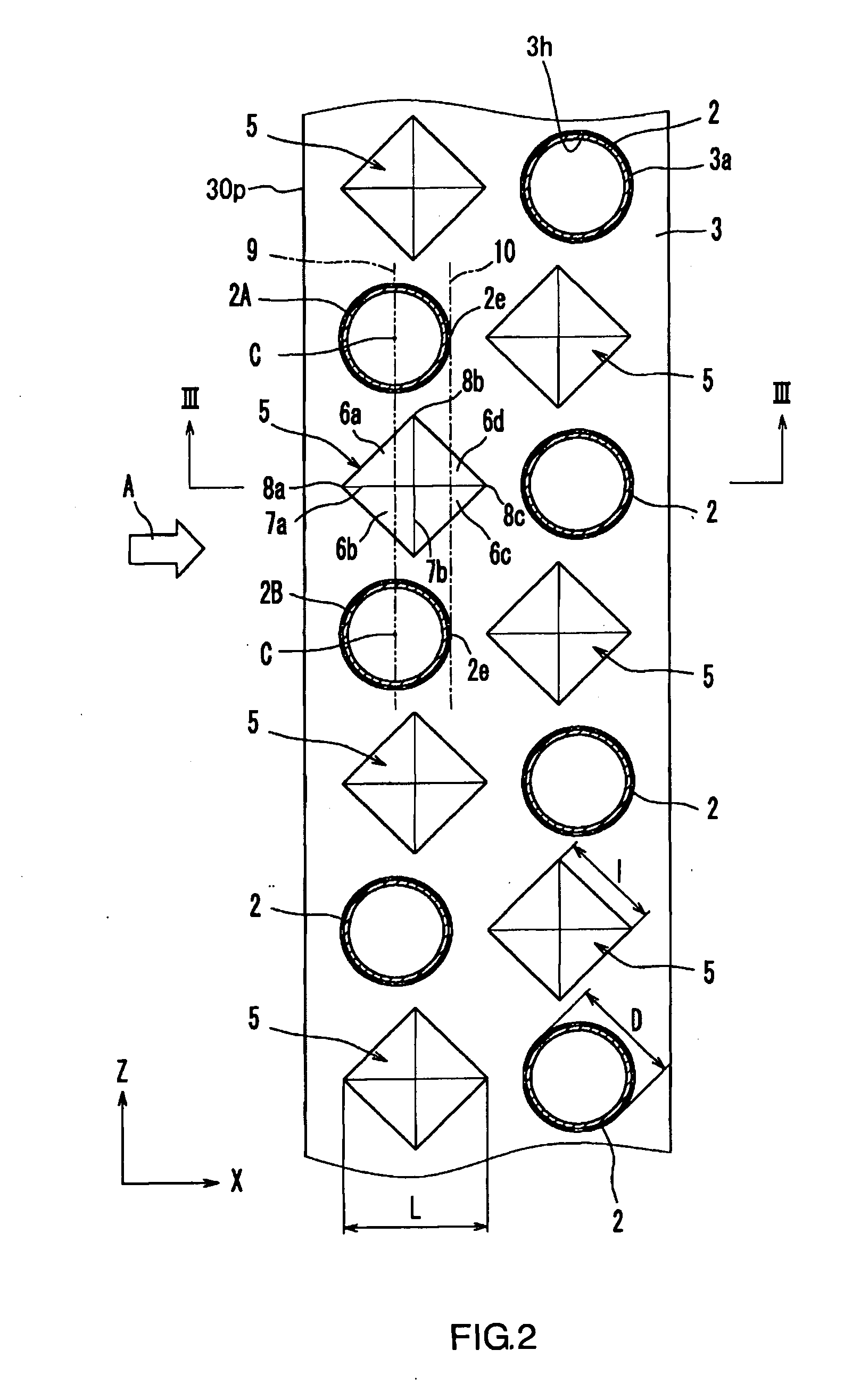
[0110]As illustrated in FIGS. 10 and 11, a fin 13 according to the present embodiment has protrusions 15 formed in a circular conic shape. In the present embodiment, the protrusion 15 has no clear ridge line. However, assuming a virtual line 7a extending from an upstream edge 8a to an apex 11 in the X direction and a virtual line 7b extending through the apex 11 in the Z direction, it is understood that a first slanted surface 6a, which guides the air toward the first heat transfer tube 2A side, and a second slanted surface 6b, which guides the air toward the second heat transfer tube 2B side, are formed between the virtual line 7a and the virtual line 7b.
[0111]In the present embodiment as well, the width of each of the protrusions 15 increases from the upstream edge 8a to the intermediate portion 8b, while it decreases from the intermediate portion 8b to the downstream edge 8c. The upstream edges 8a of the protrusions 15 are located upstream of the centers C of the heat transfer t...
embodiment 3
[0115]As illustrated in FIG. 12, a fin 23 according to Embodiment 3 has protrusions 25 that are formed in an elliptic conic shape. Herein, the ellipticity (the ratio of the major axis to the minor axis) is set at about 2. However, the ellipticity of the protrusions 25 is not particularly limited. The ellipticity may be greater than 1 but equal to or less than 2, or it may be equal to or greater than 0.5 but less than 1. The protrusions 25 may have an elliptic conic shape that is slender in the X direction or an elliptic conic shape that is slender in the Z direction.
[0116]In the present embodiment as well, the protrusion 25 has no clear ridge line. However, as in the case of Embodiment 2, assuming a virtual line 7a extending from an upstream edge 8a to an apex 11 in the X direction and a virtual line 7b extending through the apex 11 in the Z direction, it is understood that a first slanted surface 6a, which guides the air toward the first heat transfer tube 2A side, and a second sla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com