Device for Freezing,Transporting and Thawing Fluids
a technology for transporting and thawing fluids, which is applied in the direction of fluid heaters, air heaters, stationary conduit assemblies, etc. it can solve the problems of inconvenient thawing process, inconvenient thawing, and insufficient thawing speed, so as to achieve rapid thawing, increase the number of operating options, and reduce the effect of thawing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
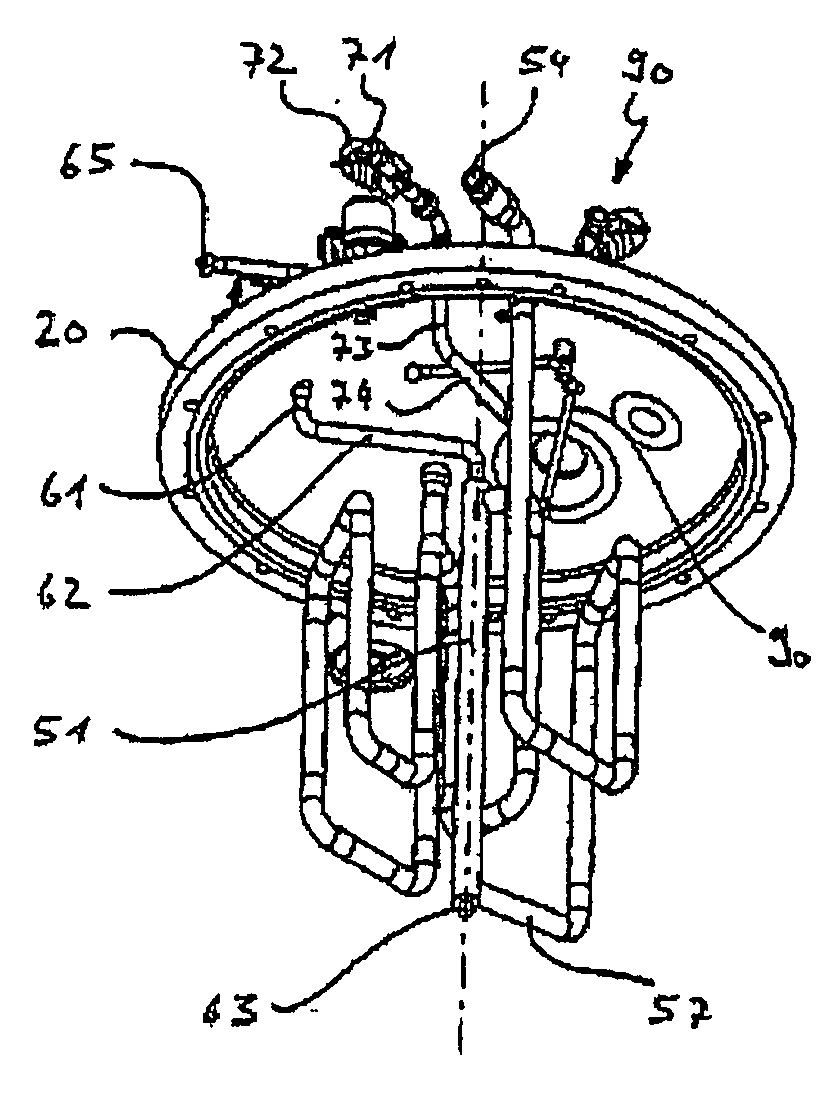
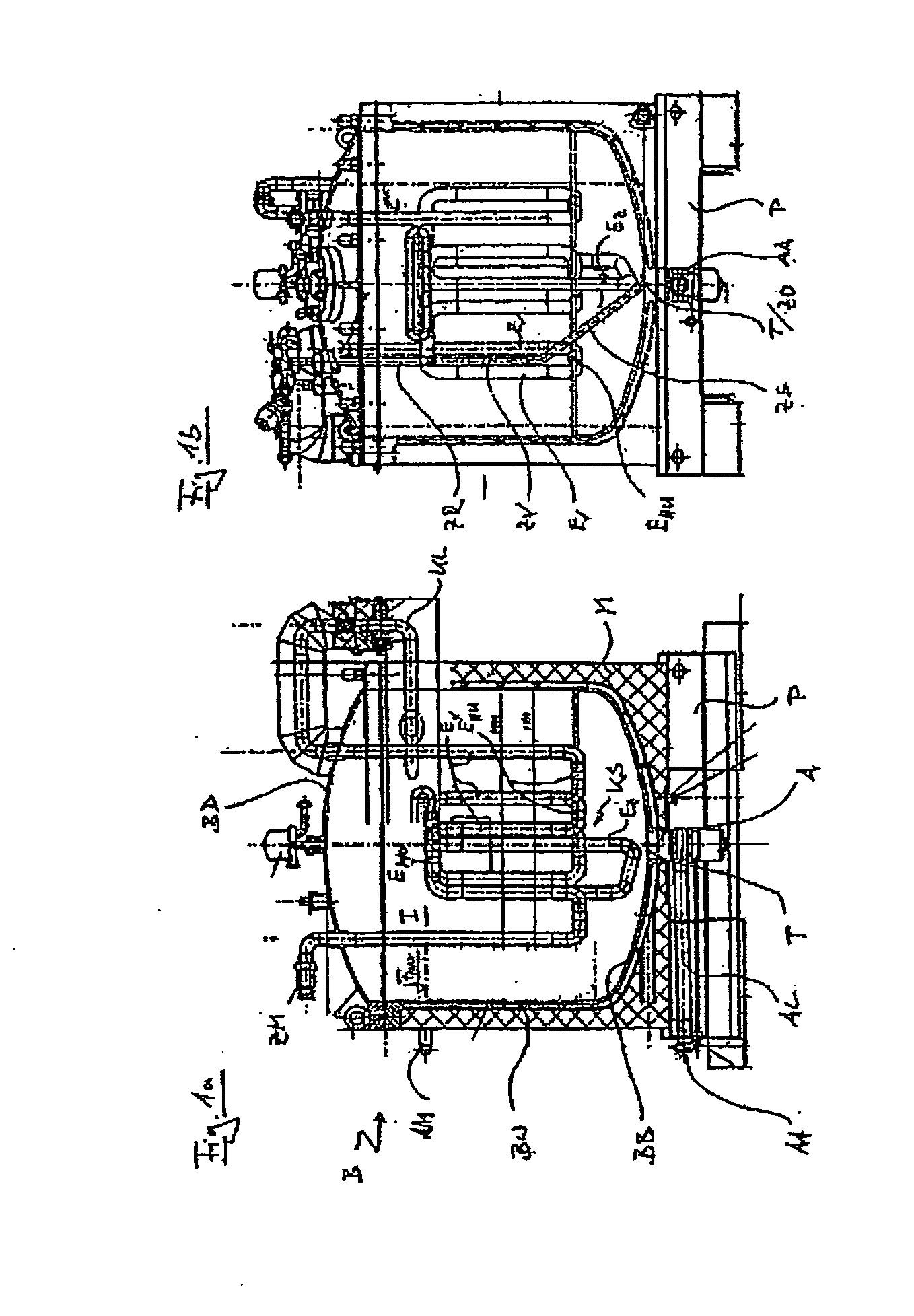
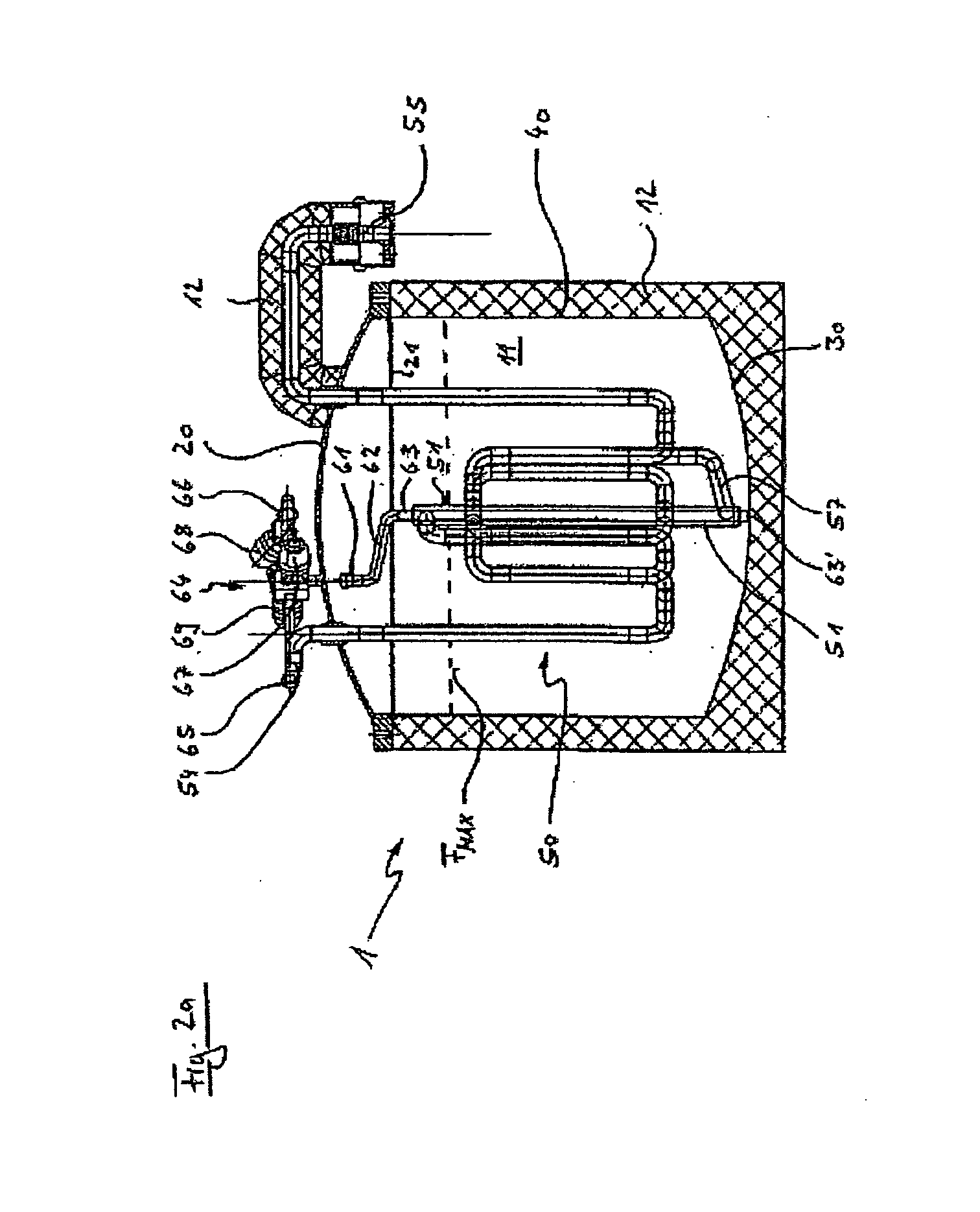
[0022]FIG. 1a is a longitudinal section illustrating a freeze-thaw container B designed by the applicant. As explained above, this container is known from the prior art under the name of FreezeContainer. The container B can be closed and sealed by means of a top lid BD. Together with a bottom base BB and a side wall BS, the lid BD defines an interior I of the container B, in which a cooling coil KS is disposed. As indicated in FIG. 1a, the cooling coil is connected so as to communicate with the double-skin inner container wall by means of an isolated cooling pipe KL. Coolant fed in through an appropriate inlet pipe AM to the double-skin container wall BW, flows through the container wall BW and base BB via the cooling pipe KL and is then directed through the cooling coil KS. It will be clear to the person skilled in the art that technically reversible processes of freezing and thawing can be effected using the device illustrated in FIG. 1 and with other similar generic devices on wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com