Co2 refrigerant system with booster circuit
a refrigerant system and booster circuit technology, applied in the field of refrigerant systems, can solve the problems of refrigerant system designers, refrigerant systems utilizing cosub>2/sub>as a refrigerant do not always operate at the efficiency level of traditional refrigerant systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 44
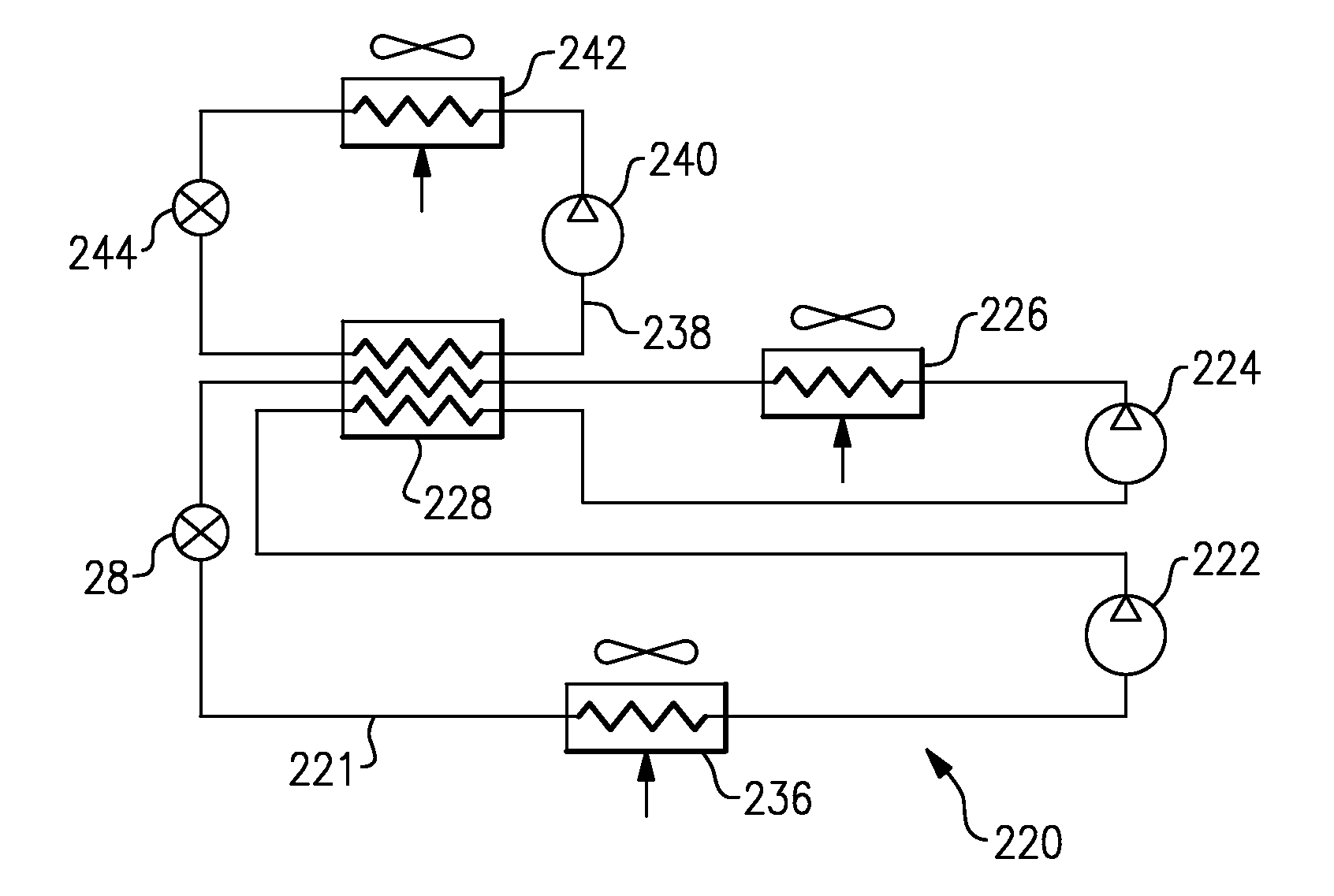
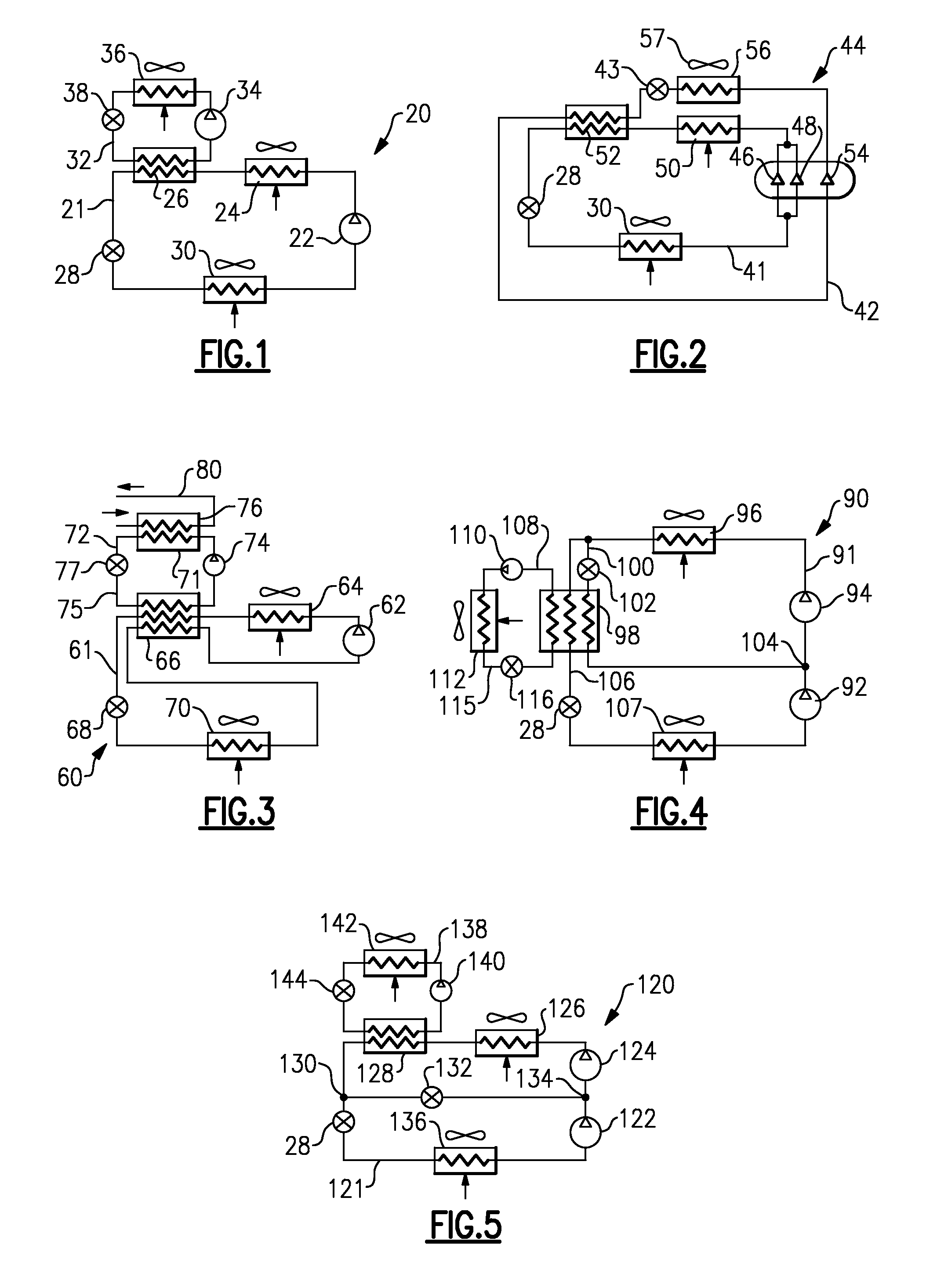
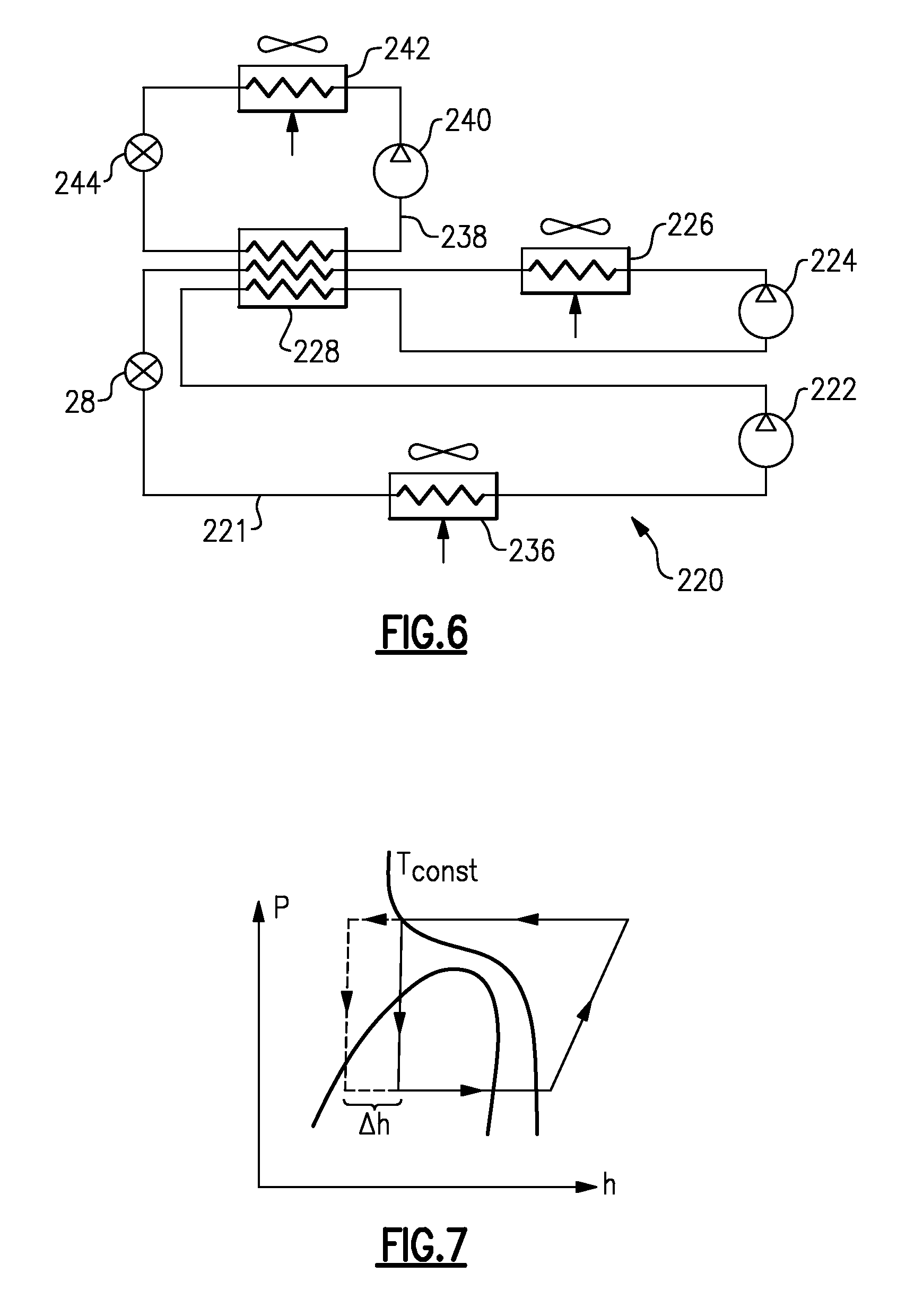
[0021]As shown in FIG. 2, another embodiment 44 provides tandem compressor stages 46 and 48 which circulate refrigerant through a main circuit 41, including a heat rejection heat exchanger 50, a heat exchanger 52, the expansion device 28, and the evaporator 30. A separate compressor stage 54 compresses the refrigerant in a booster circuit 42 and circulates it through a heat rejection heat exchanger 56, the heat exchanger 52, an expansion device 43 and back to the compressor 54. As shown, a fan system 57 may be designed to move air over both heat rejection heat exchangers 50 and 56. In this manner, there is not the requirement of a separate air-moving device for each heat exchanger. Although heat rejection heat exchangers 50 and 56 are shown in a sequential arrangement, with respect to the airflow, they can also be positioned in a parallel configuration.
[0022]The tandem compressors 46 and 48 of the main circuit 41 and the compressor 54 of the booster circuit 42 may all be receiving p...
embodiment 60
[0023]FIG. 3 shows an embodiment 60, wherein the compressor 62 of the main circuit 61 delivers refrigerant sequentially to a heat rejection heat exchanger 64, a heat exchanger 66, an expansion device 68 and an evaporator 70. As shown in FIG. 3, the refrigerant in the main circuit 61 flows from the evaporator 70 back through the heat exchanger 66, before returning to the compressor 62. In this manner, the heat exchanger 66 performs a function similar to a “liquid-to-suction” heat exchanger function (since, in transcritical operation, there may not be any liquid at the exit of the heat rejection heat exchanger 64 of the main circuit 61). This function is assisted and enhanced by a booster circuit 75, since extra cooling is obtained by the main circuit refrigerant entering an expansion device 68. This increase in the cooling capacity would normally be substantially higher then subsequent decrease in the cooling capacity caused by density reduction of the refrigerant vapor entering the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com