Wireless interface
a wireless interface and cable technology, applied in the field of wireless interfaces, can solve the problems of increasing the number of external connections, adding a significant cost in the manufacture of the display, and the complexity of the display system, so as to achieve the effect of providing sufficient power, sufficient bandwidth, and high speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
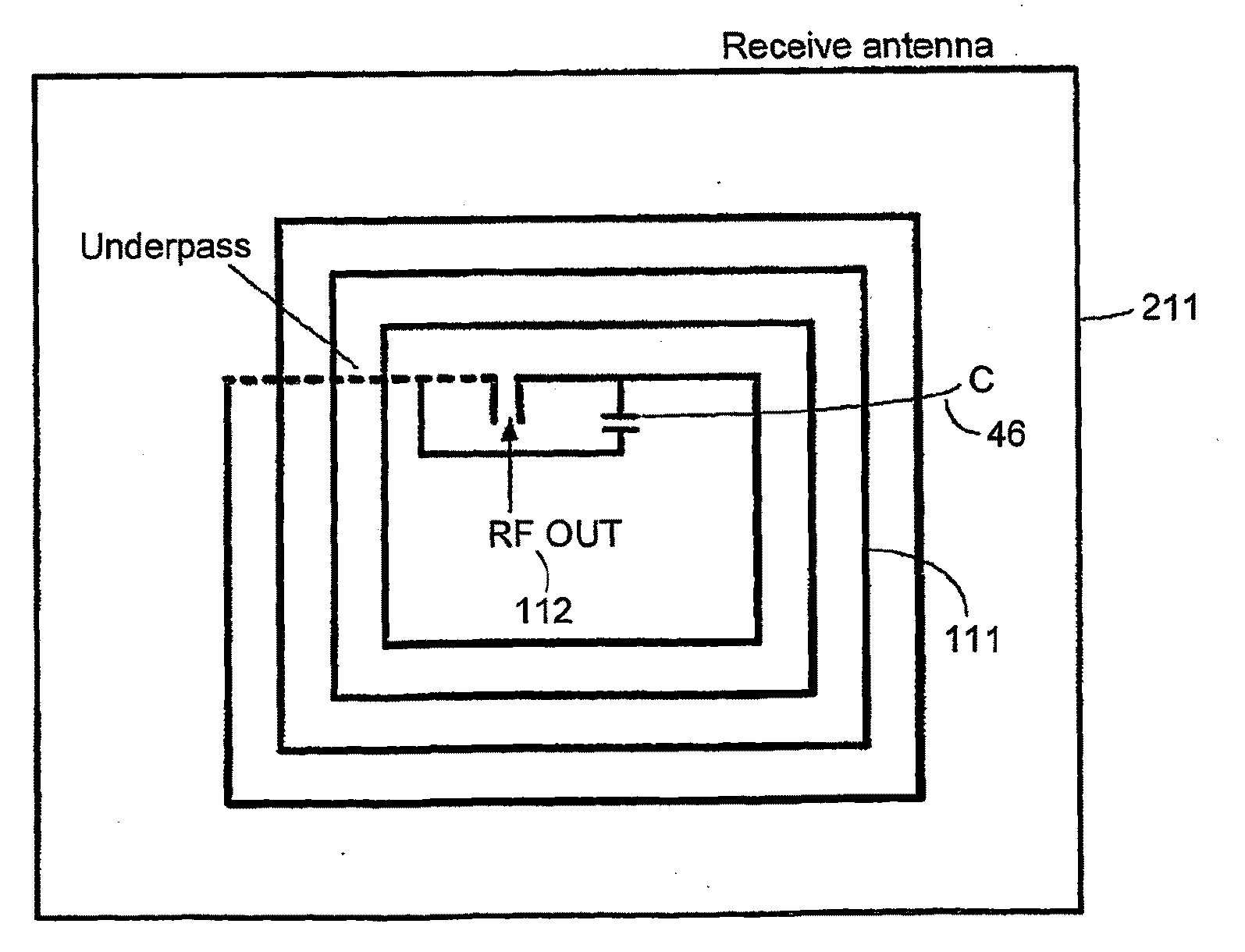
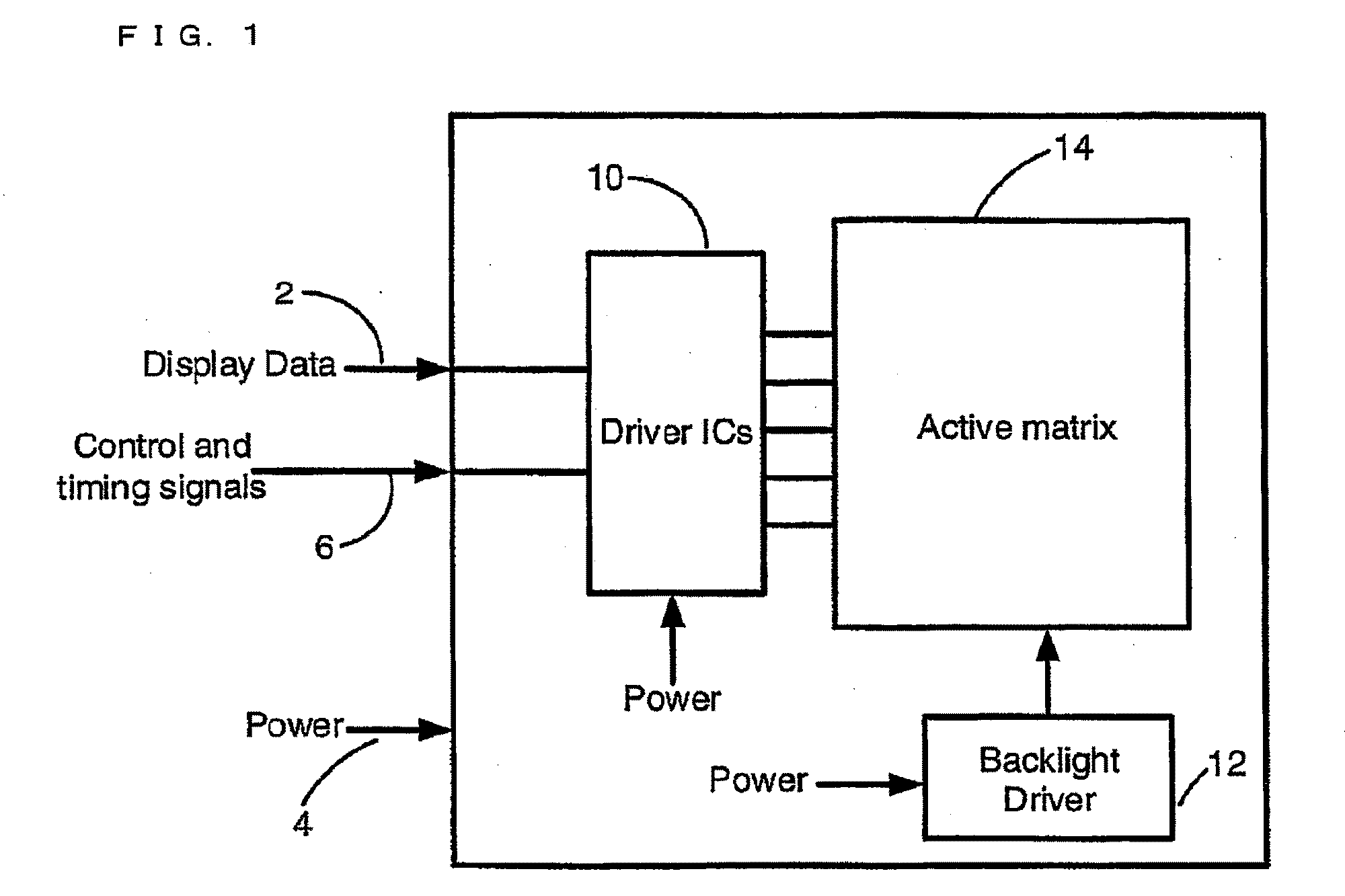
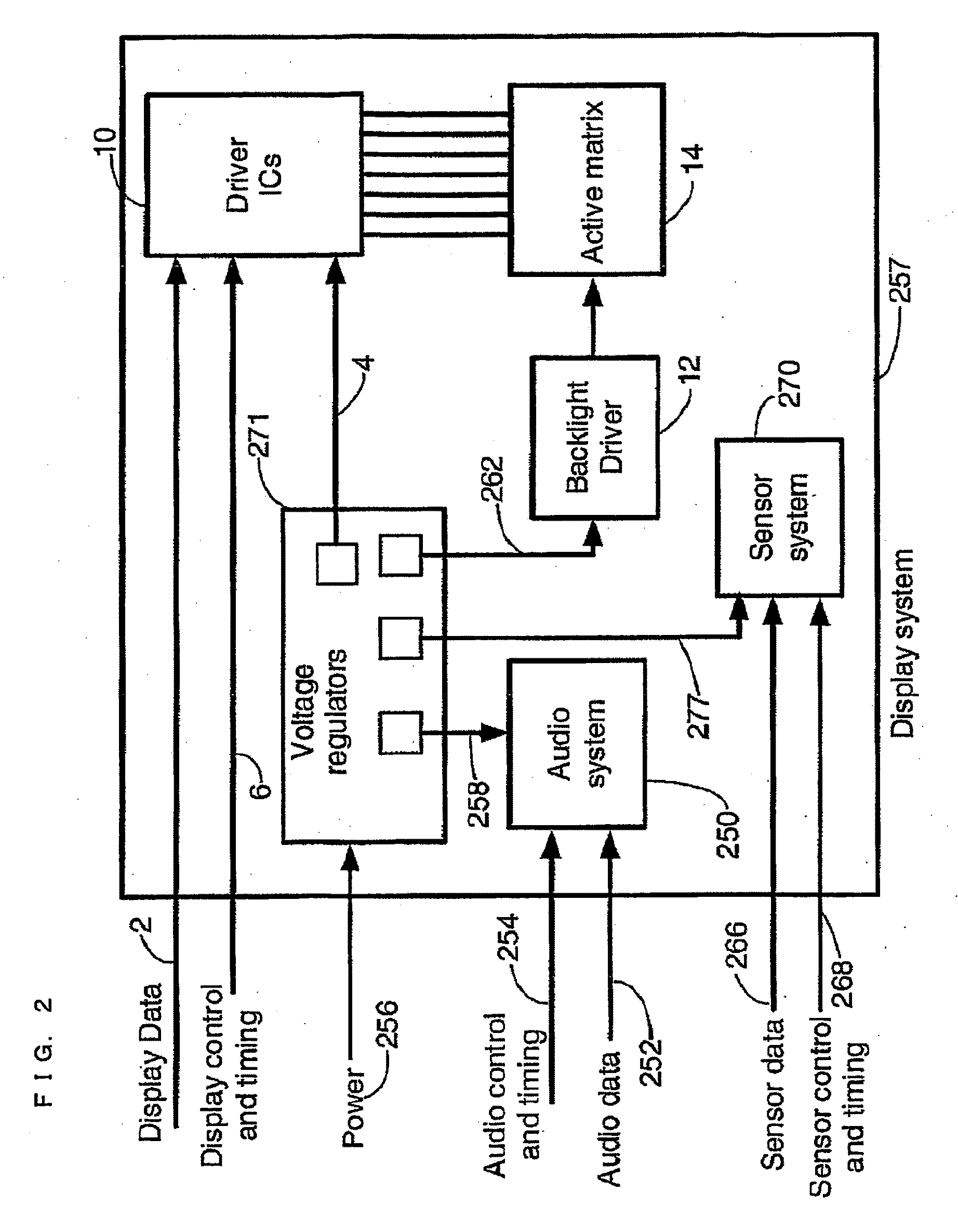
[0078]FIG. 23 shows a complete wireless system comprising a driver system 200 constituting a transmitting section and a wireless display system 220 constituting a receiving section. The driver system 200 comprises a data source 202 to supply the display system data 212 and the control and timing signals 208. These signals are then connected to the transmitter system 210 which is then connected to a transmit antenna 166. The driver system 200 is supplied with power 204 externally to power all the circuitry. After the signal is launched from the transmit antenna 210, it traverses the wireless channel 26 to couple to the wireless display system 220. The wireless display system comprises the receive system 224 which is connected to the display system 257. A receive antenna 211 which captures the transmitted signal is connected to a receiver 255. The receiver extracts the display system data 212, control and timing signals 208 and power 256 from the transmitted signal. These signals are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com