Refrigeration apparatus
a technology of refrigerating apparatus and heat exchanger, which is applied in the direction of refrigeration machines, gas cycle refrigeration machines, corrosion prevention, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve high operating efficiency, large heat radiation loss of heat exchangers, and temperature difference between refrigerants, so as to reduce the loss of defrosting capacity, reduce the loss of defrosting time, and minimize the loss of defrosting capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
modification 1
(3) Modification 1
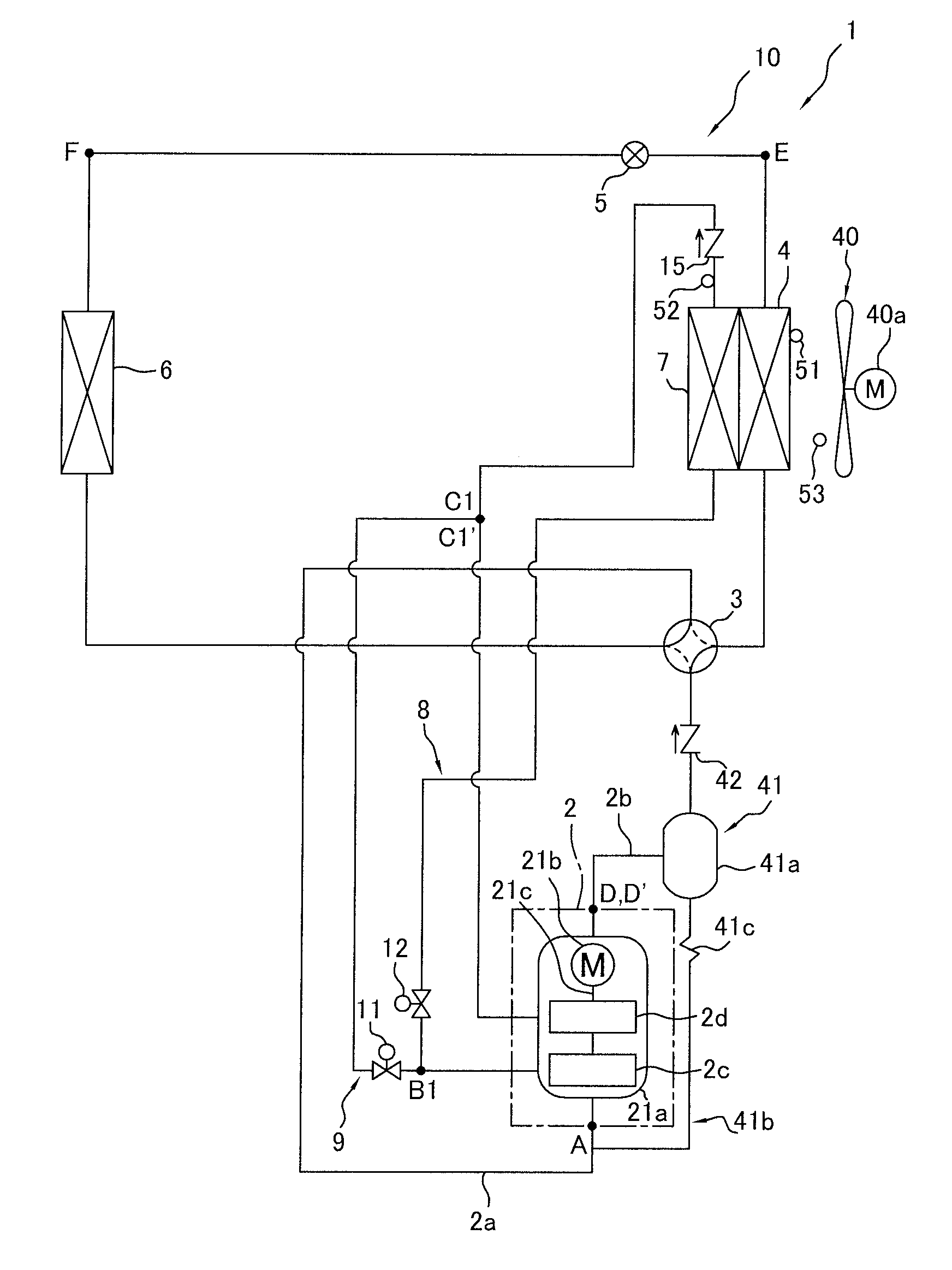
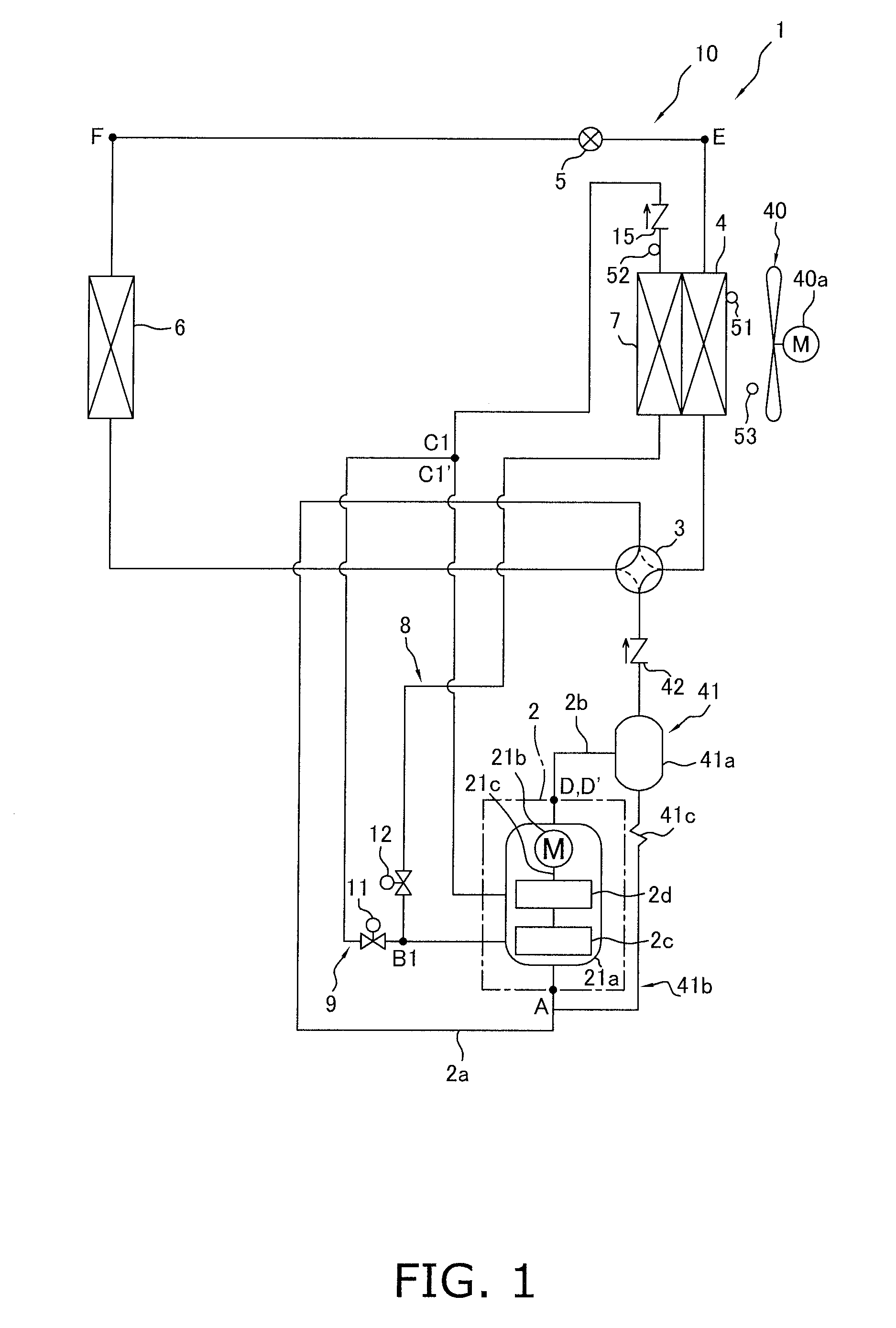
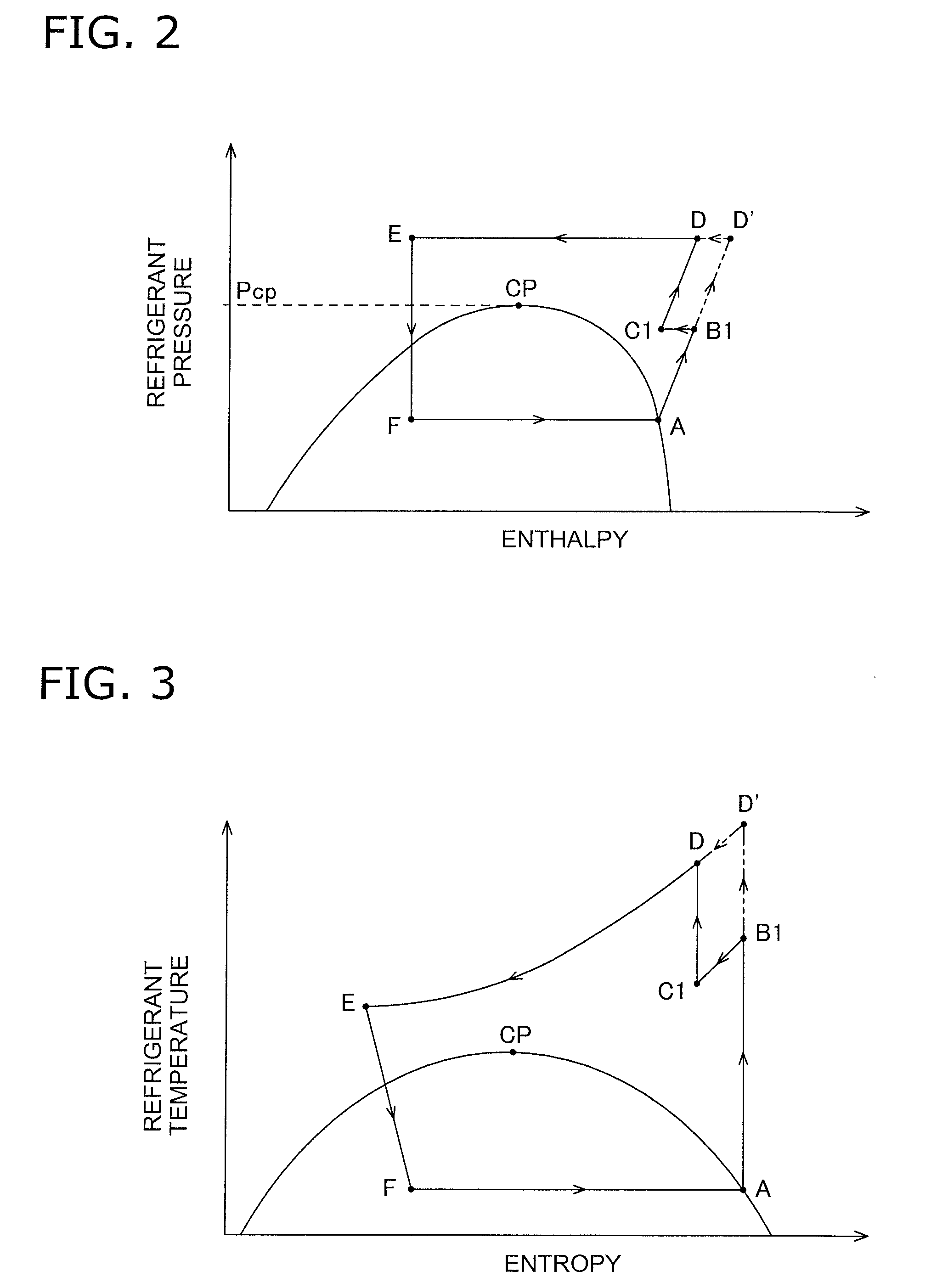
[0078]In the embodiment described above, in the air-conditioning apparatus 1 configured to be capable of being switched between the air-cooling operation and the air-warming operation by the switching mechanism 3, the air-cooling intercooler 7 integrated with the heat source-side heat exchanger 4 and the intercooler bypass tube 9 were provided. Using the intercooler 7 and the intercooler bypass tube 9, the intercooler 7 was made to function as a cooler when the switching mechanism 3 was set to a cooling operation state and the intercooler 7 was made to not function as a cooler when the switching mechanism 3 was set to a heating operation state, thereby reducing the heat radiation loss in the heat source-side heat exchanger 4 functioning as a refrigerant cooler and improving operating efficiency during the air-cooling operation, and minimizing heat radiation to the exterior to minimize the loss of heating performance during the air-warming operation. In addition to ...
modification 2
(4) Modification 2
[0117]In the defrosting operation in Modification 1 described above, although only temporarily until defrosting of the intercooler 7 is complete, the refrigerant flowing through the intercooler 7 condenses and the refrigerant drawn into the compression element 2d becomes wet, presenting a risk that wet compression will occur in the second-stage compression element 2d and the compression mechanism 2 will be overloaded.
[0118]In view of this, in the present modification, as shown in FIG. 16, in cases in which it is detected in step S7 that the refrigerant has condensed in the refrigerant flowing through the intercooler 7, intake wet prevention control is performed in step S8 for reducing the flow rate of refrigerant returned to the second-stage compression element 2d via the second-stage injection tube 19.
[0119]The decision of whether or not the refrigerant has condensed in the refrigerant flowing through the intercooler 7 in step S7 is based on the degree of superhea...
modification 3
(5) Modification 3
[0122]In the defrosting operation in Modifications 1 and 2 described above, after it has been detected that defrosting of the intercooler 7 is complete, the operation is performed to ensure that the intercooler 7 does not function as a cooler by closing the cooler on / off valve 12 and opening the intercooler bypass on / off valve 11 while the heat source-side heat exchanger 4 continues to be defrosted by the reverse cycle defrosting operation, heat radiation from the intercooler 7 to the exterior is prevented, and the decrease in defrosting capacity of the heat source-side heat exchanger 4 can be minimized.
[0123]However, when refrigerant does not flow to the intercooler 7, the temperature of the refrigerant drawn into the second-stage compression element 2d suddenly increases; therefore, there is a tendency for the refrigerant drawn into the second-stage compression element 2d to become less dense and for the flow rate of refrigerant drawn into the second-stage compre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com