Aluminum alloy clad sheet for heat exchangers and method of producing the same
a technology of aluminum alloy and heat exchanger, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, soldering devices, light and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult pressing of materials, low processing area, and eroded core materials of filler metals in low processing areas, and achieve excellent brazing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0063]The present invention is described below by way of examples and comparative examples. Note that the following examples merely illustrate several aspects of the present invention. The present invention is not limited to the following examples.
(Test A)
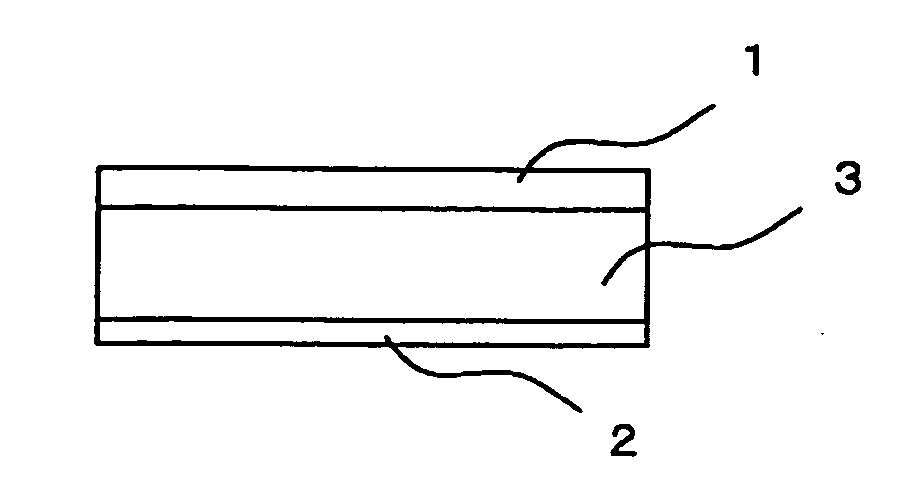
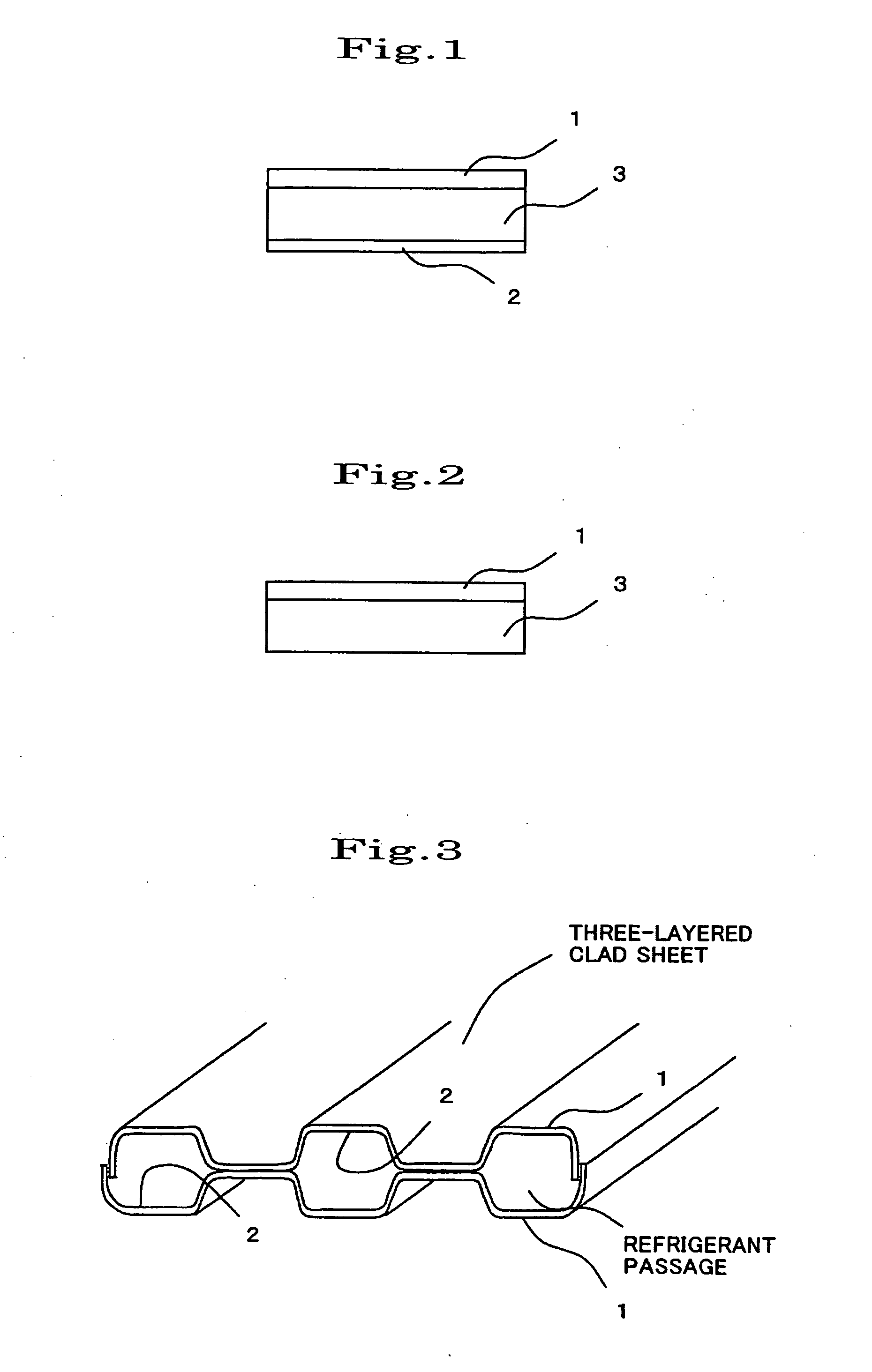
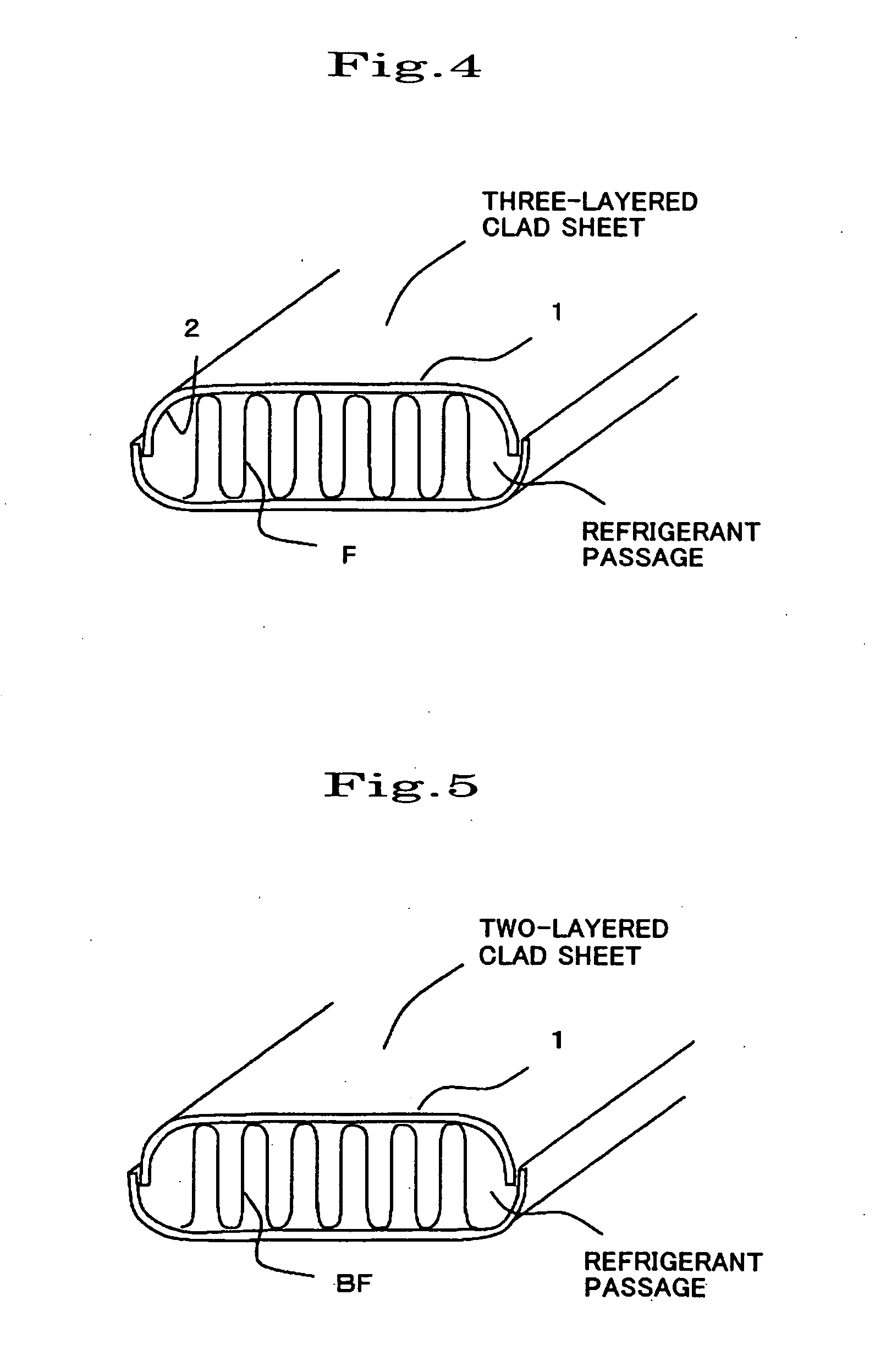
[0064]An aluminum alloy for the cladding material 1 (outer-side cladding material) having a composition shown in Table 1 or 2, an aluminum alloy for the core material shown in Table 3 or 4, and an aluminum alloy for the cladding material 2 (inner-side cladding material) having a composition shown in Table 5 or 6 were continuously cast, and homogenized by a normal method. The aluminum alloy for the cladding material 1 and the aluminum alloy for the cladding material 2 were then hot-rolled, and placed on the aluminum alloy for the core material according to the combination shown in Table 7 or 8 so that the thickness ratio of the cladding material 1, the core material, and the cladding material 2 was 20% / 70% / 10%. The aluminum alloys w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com