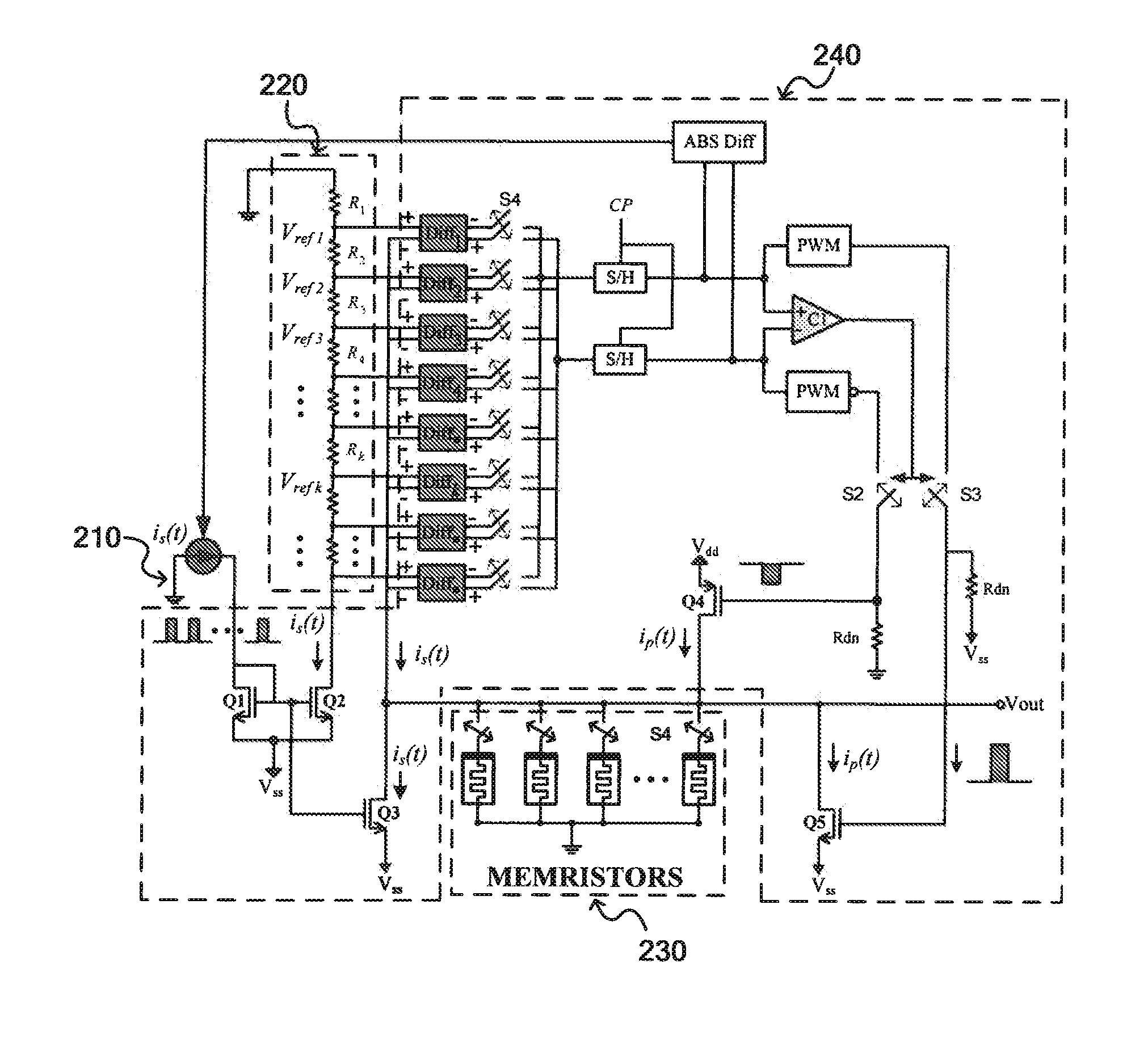
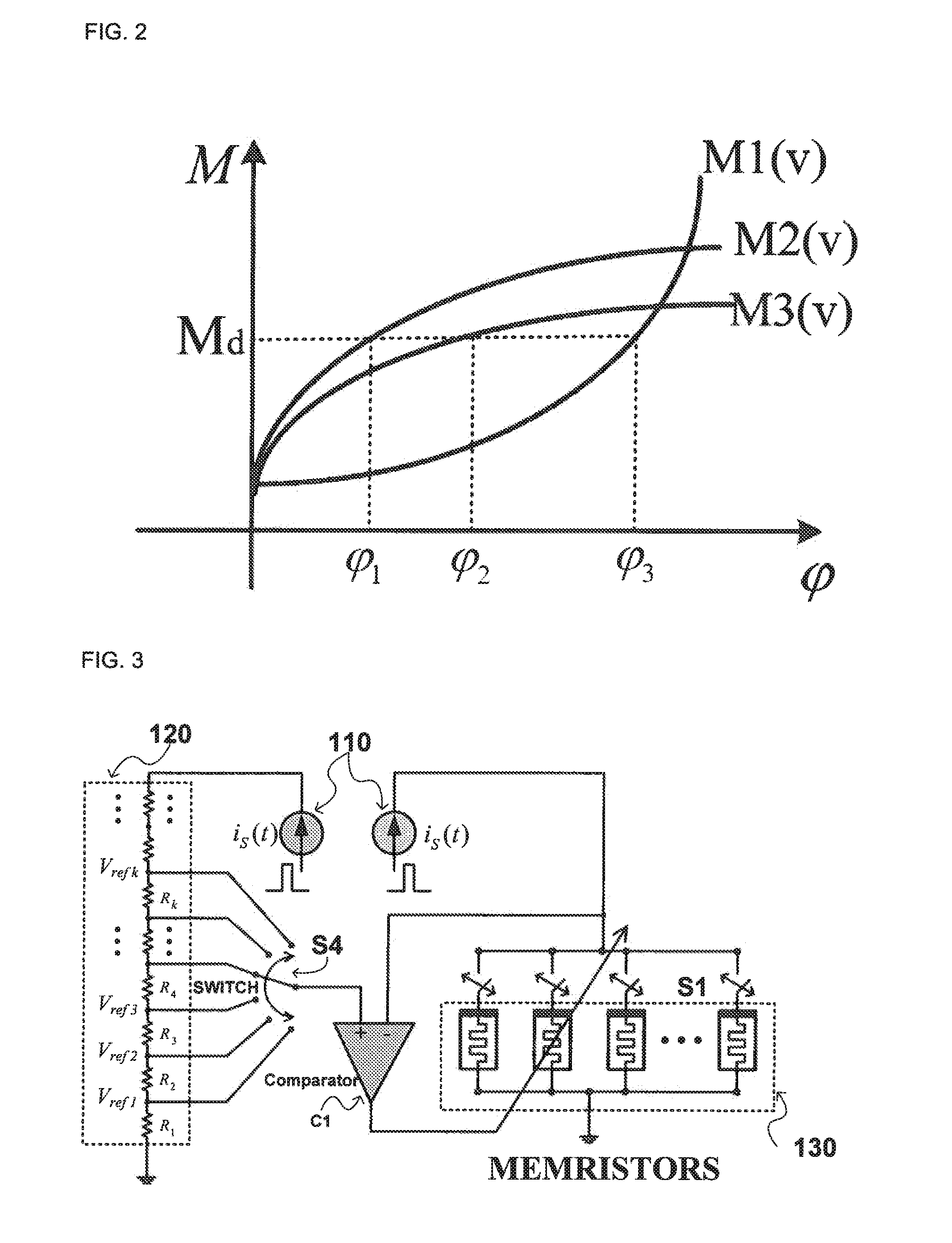
Method of implementing memristor-based multilevel memory using reference resistor array
a multi-level memory and reference resistor technology, applied in the field of memristors, can solve the problems of difficult to determine the proper pulse width for difficulty in achieving the desired resistance value, and several weaknesses of the memristor, so as to prevent the resistance of the memristor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041]Reference will be now made in detail to the preferred embodiment of the present invention with reference to the attached drawings.
[0042]Characteristics of Memristors
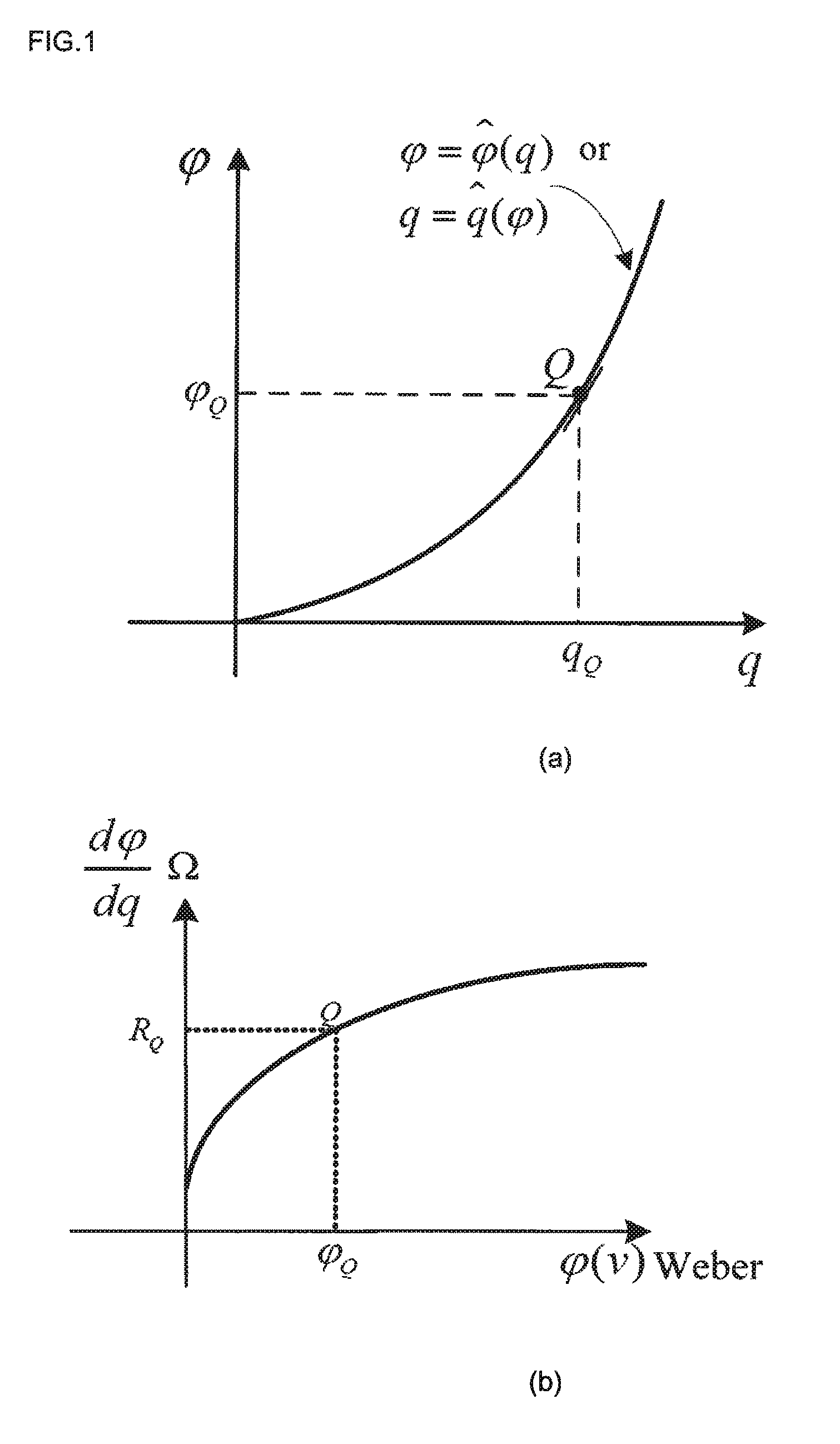
[0043]The principle of the memristor is based on the nonlinear property of basic circuit elements. In the relationships defining basic circuit elements, charge is defined as the time integral of current, namely,
q(t)=∫−∞i(Σ)dτ (1)
[0044]Equivalently, the current i is the time derivative of the charge q; namely,
i=qt(2)
[0045]Similarly, the flux is φ is defined as the time integral of voltage; namely,
φ(t)=∫−∞v(τ)dτ (3)
[0046]Equivalently, the voltage v is the derivative of the flux; namely
v=ϕt(4)
[0047]Dividing (4) by (2), we obtain the resistance
R=vi=ϕt•tq=ϕqq=qQ(5)
[0048]Thus, the resistance can be interpreted as the slope at an operating point on the φ-q curve. If the φ-q curve is nonlinear, the resistance will vary with the operating point. For instance, if the φ-q curve is the nonlinear function shown in FIG. 1(a), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com