Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
a cell cycle and cell cycle technology, applied in the field of biotechnology, can solve the problems of inability to extrapolate the findings relating to the cell cycle, inability to understand the mechanism by which vpr induces apoptosis, and inability to activate the proapoptotic signaling cascad
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
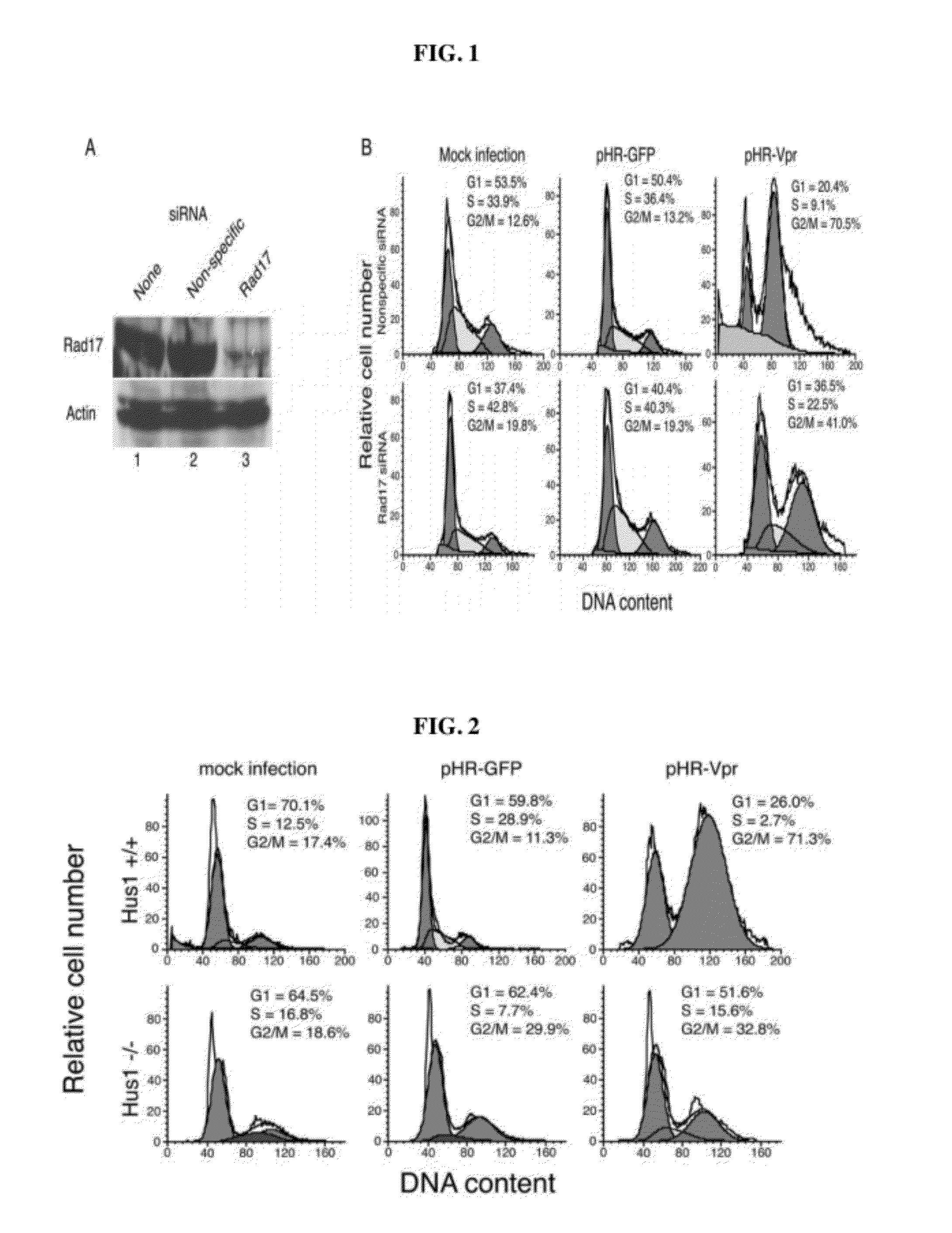
[0085]Rad17 is necessary for Vpr-mediated G2 arrest. To examine the role of Rad17 in Vpr-mediated G2 arrest, RNA interference was used to reduce endogenous Rad17 levels. Transfected siRNA duplex oligonucleotides targeted at Rad17 mRNA (54) were used to knock down Rad17, in parallel, siRNA with a nonspecific target sequence and mock transfection was used as controls. In these experiments, endogenous Rad17 protein levels were reduced by approximately 85%, relative to those of mock-transfected or nonspecific siRNA-transfected cells (FIG. 1A). Following transfection, cells were transduced with lentivirus vectors expressing either Vpr and GFP cDNAs separated by an internal ribosome entry site (pHR-Vpr) or GFP alone (pHRGFP) (40) (79). At 48 h after transduction, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for infection efficiency and DNA content, as reported by GFP expression and propidium iodide staining, respectively. Cell cycle distributions of the various experimental cell populations were...
example ii
[0086]Hus1 is necessary for Vpr-mediated G2 arrest. Finding that Rad17 is necessary for Vpr-induced G2 arrest, another constituent of the ATR signaling pathway, Hus1, was examined. To examine the role of Hus1 in Vpr-induced G2 arrest, Hus1− / − p21− / − mouse embryonic fibroblasts (49) were used. Both Hus1− / − p21− / − cells and Hus1+ / + p21− / − cells exhibited normal cell cycle distributions when mock infected or infected with pHR-GFP (FIG. 2). Hus1− / − p21− / − cells, how however, failed to arrest in G2 after infection with pHR-Vpr, whereas their Hus1+ / + counterparts exhibited robust G2 arrest (FIG. 2). These experiments illustrate a requirement for Hus1 in Vpr-induced G2 arrest.
[0087]Taken together, the observations indicate that HIV-1 Vpr activates the G2 checkpoint in a manner that is mechanistically similar to that of certain genotoxic agents (specifically, HU) that cause replication inhibition. Because recognition of DNA damage via ATR can lead to dramatic cellular changes, other than ch...
example iii
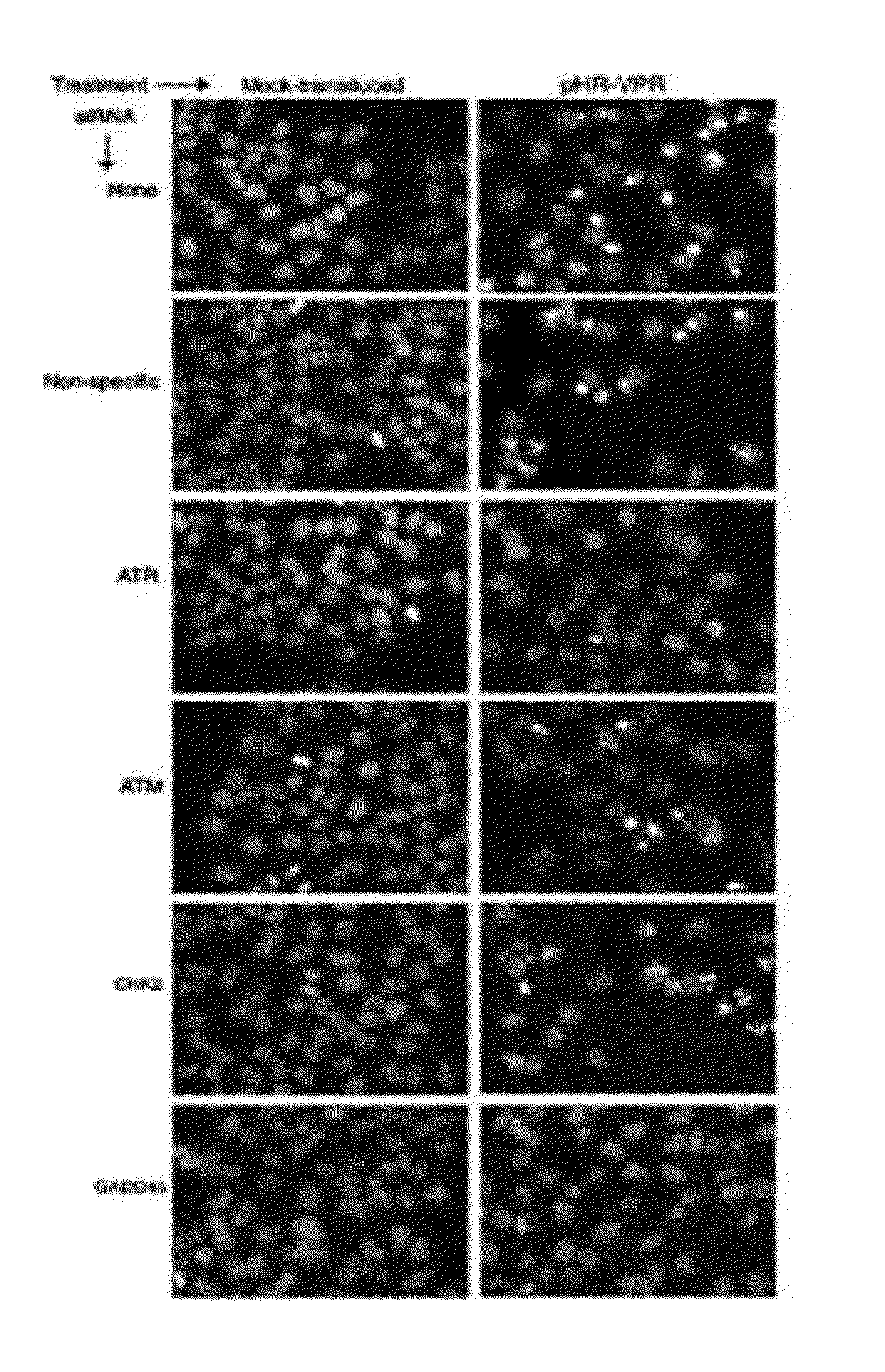
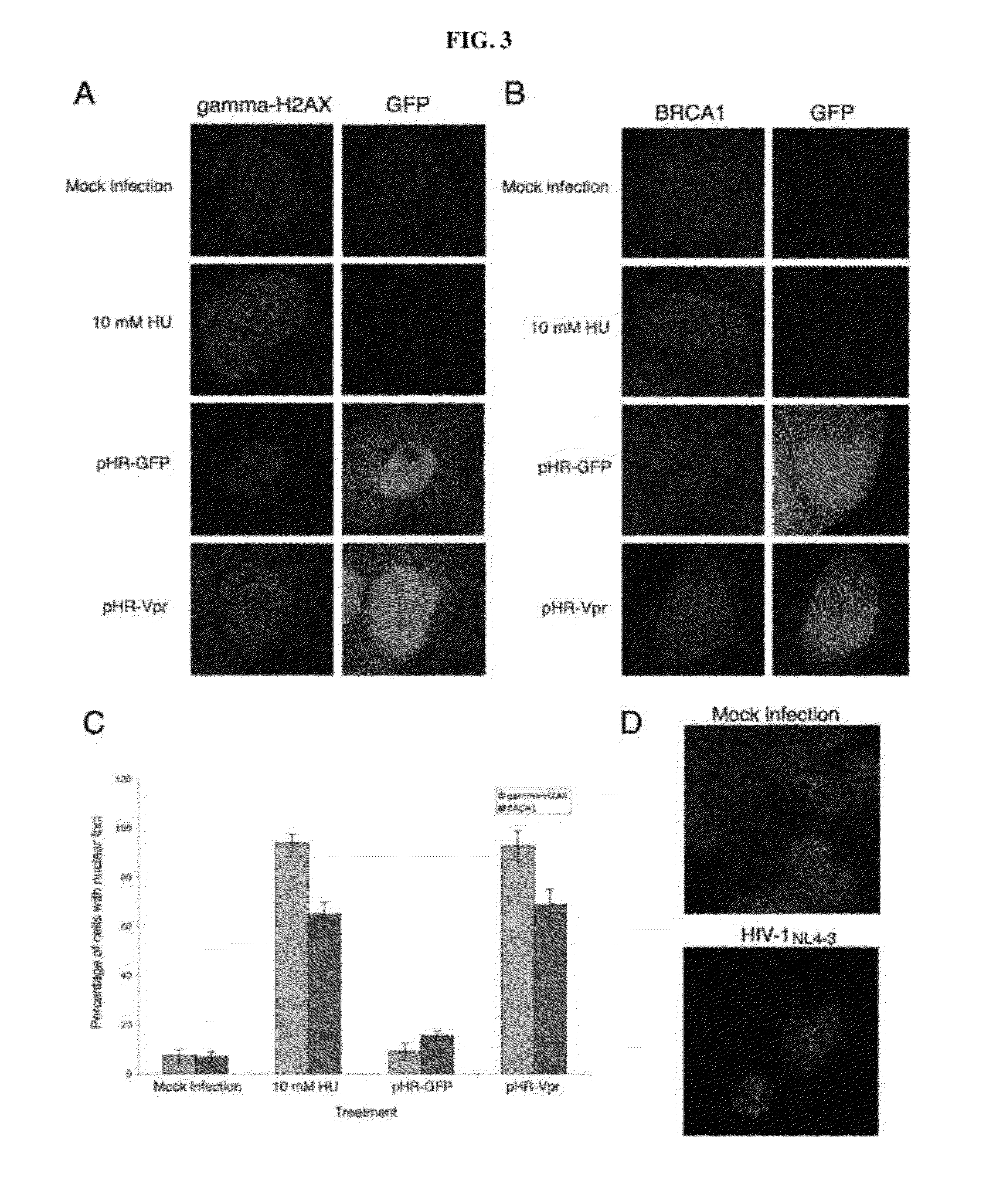
[0088]Vpr expression induces γ-H2AX and BRCA1 focus formation. It was possible that Vpr, through ATR activation, would induce γ-H2AX (9) and. BRCA1 (45) focus formation. To test this hypothesis, HeLa cells were infected with pHR-Vpr or pHR-GFP and, 48 h later, immunostained with γ-H2AX- or BRCA1-specific antibodies. As a positive control, nontransduced cells were treated for 1 h with 10 mM HU 10 min prior to immunostaining (46). Samples then were visualized by fluorescence scanning confocal microscopy (FIGS. 3A and B). Cells with multiple (10 or more), intense nuclear foci were manually counted. These quantitations are presented in FIG. 3C. Approximately 93 or 69% of Vpr-expressing cells exhibited significant γ-H2AX or BRCA1 focal staining, respectively, whereas only 9 or 16% of pHR-GFPinfected cells exhibited any γ-H2AX or BRCA1 foci, respectively. Less than 8% of mock-infected cells exhibited γ-H2AX or BRCA1 foci. Approximately 94 or 65% of HU-treated cells exhibited γ-H2AX or BRC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com