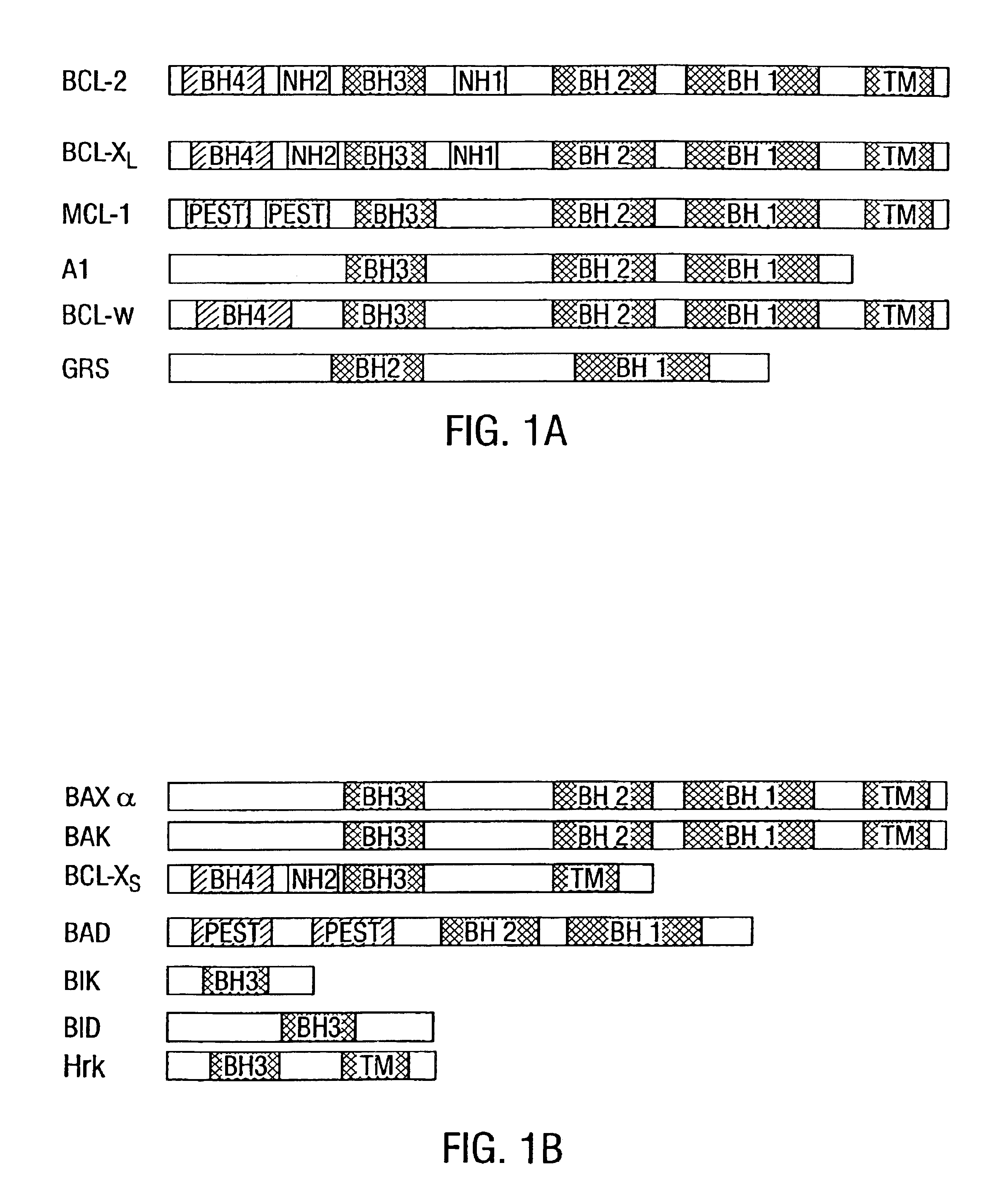
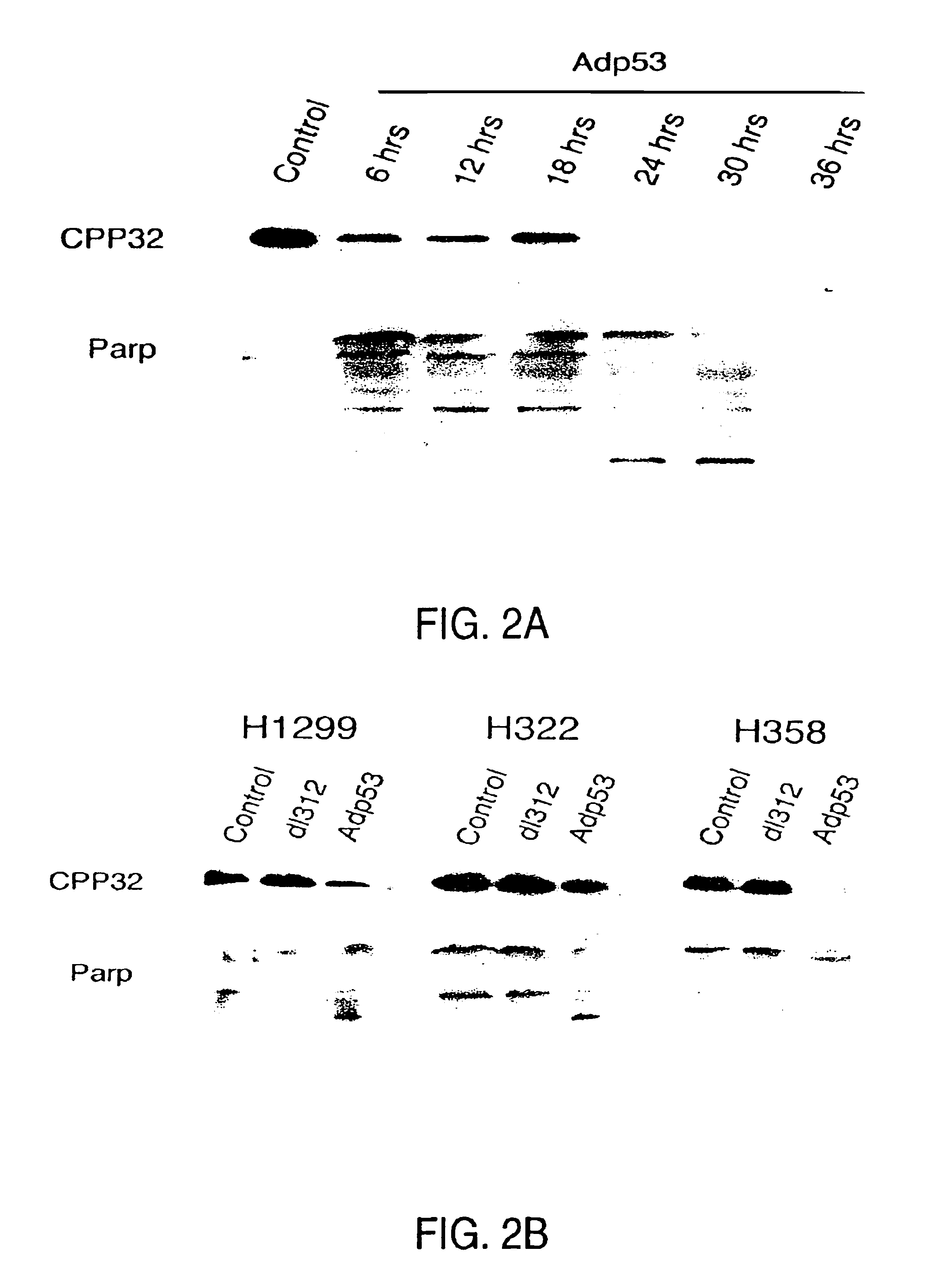
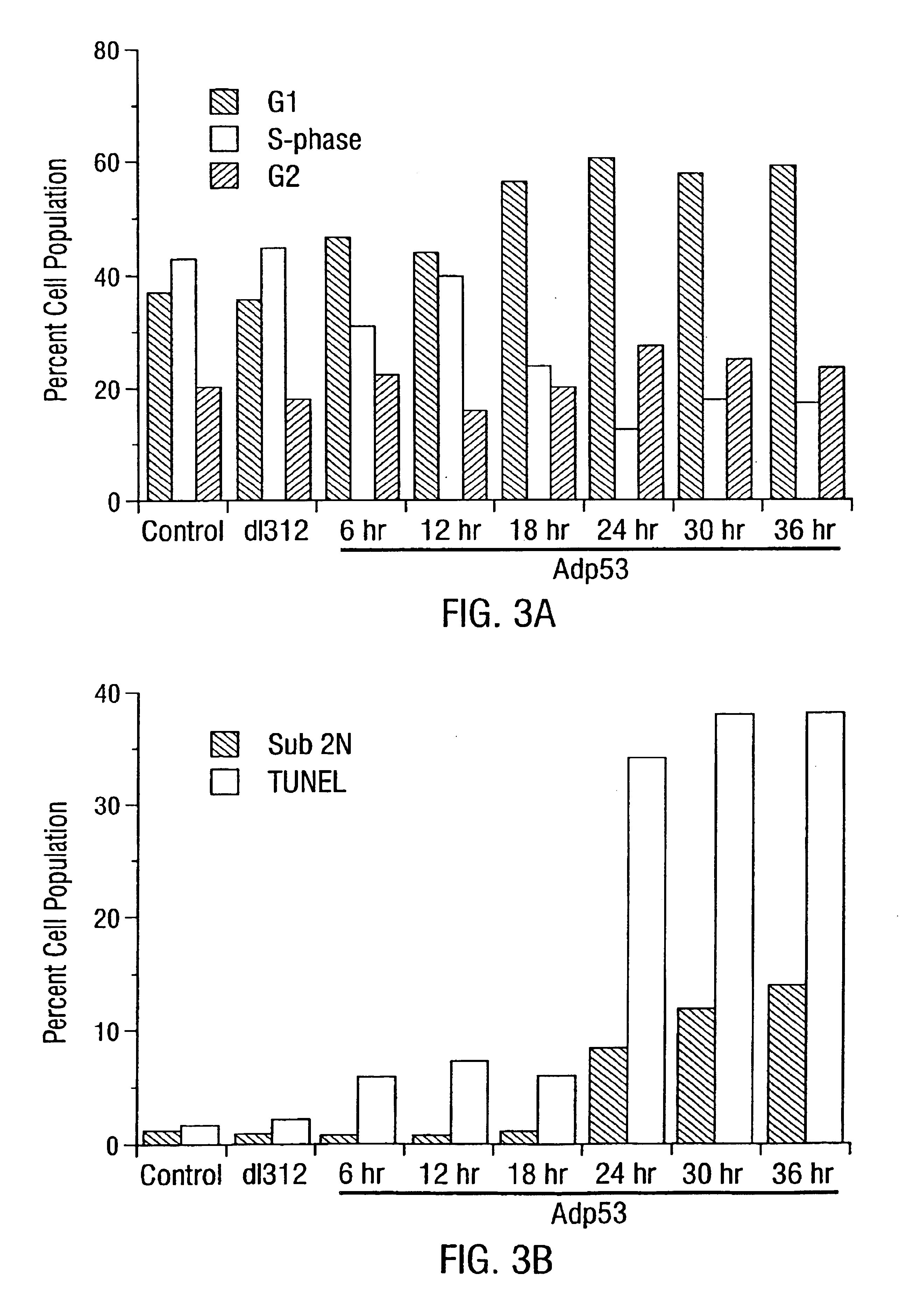
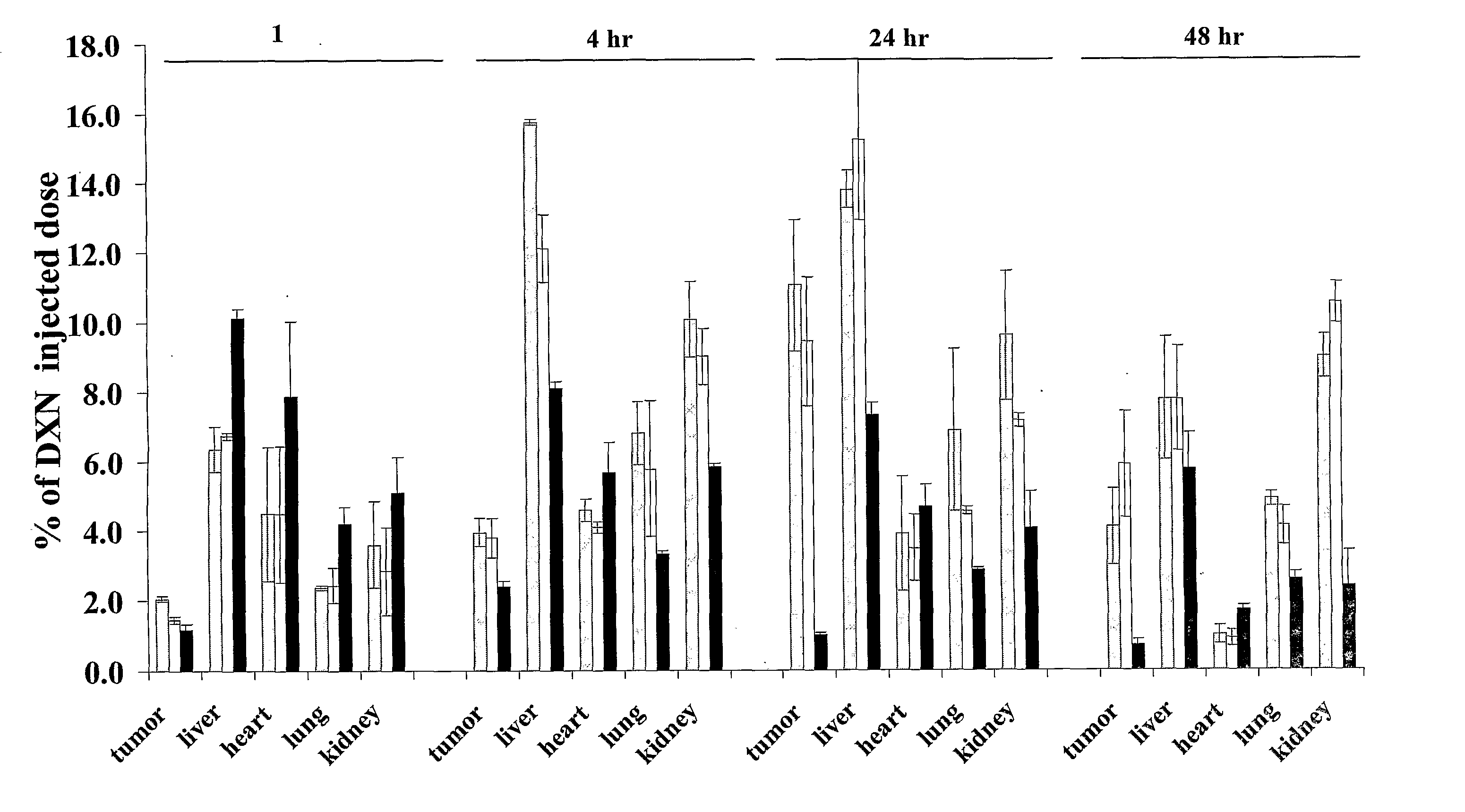
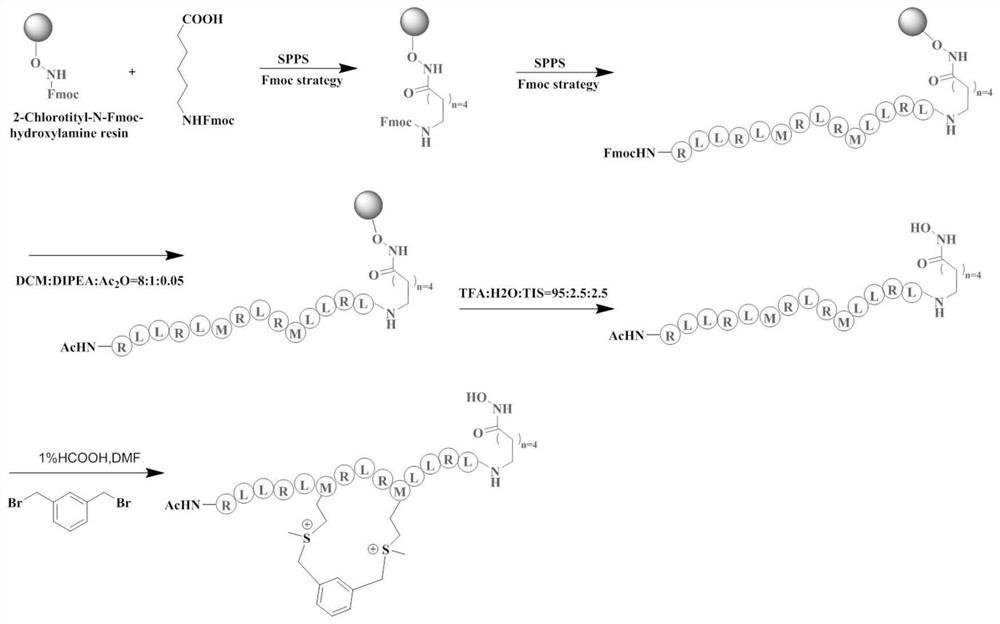
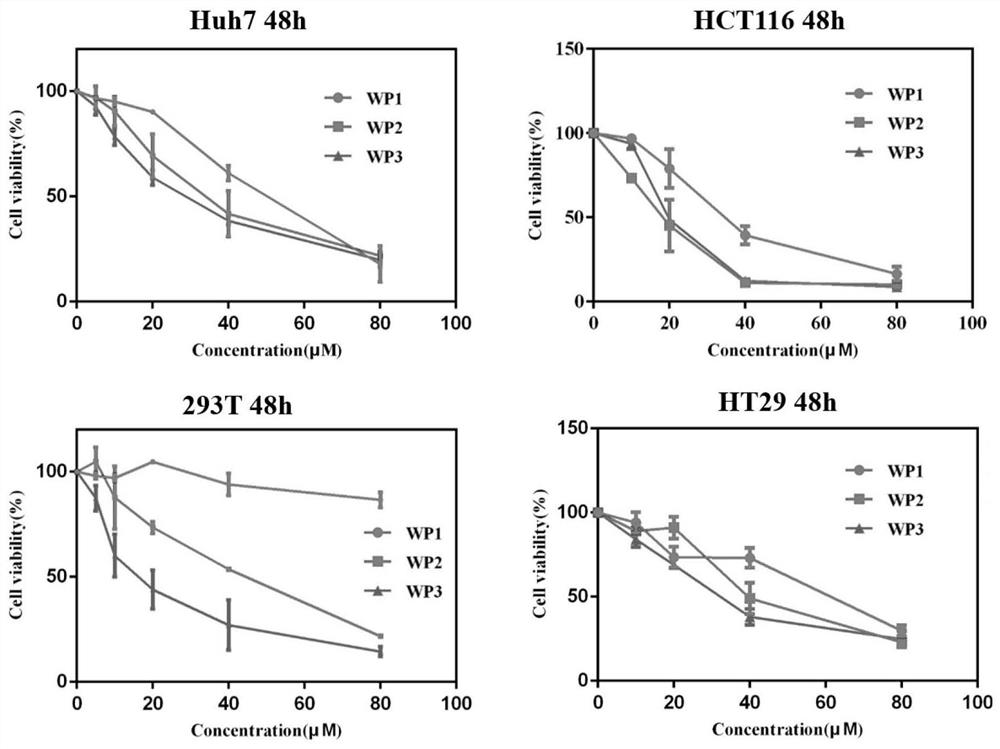
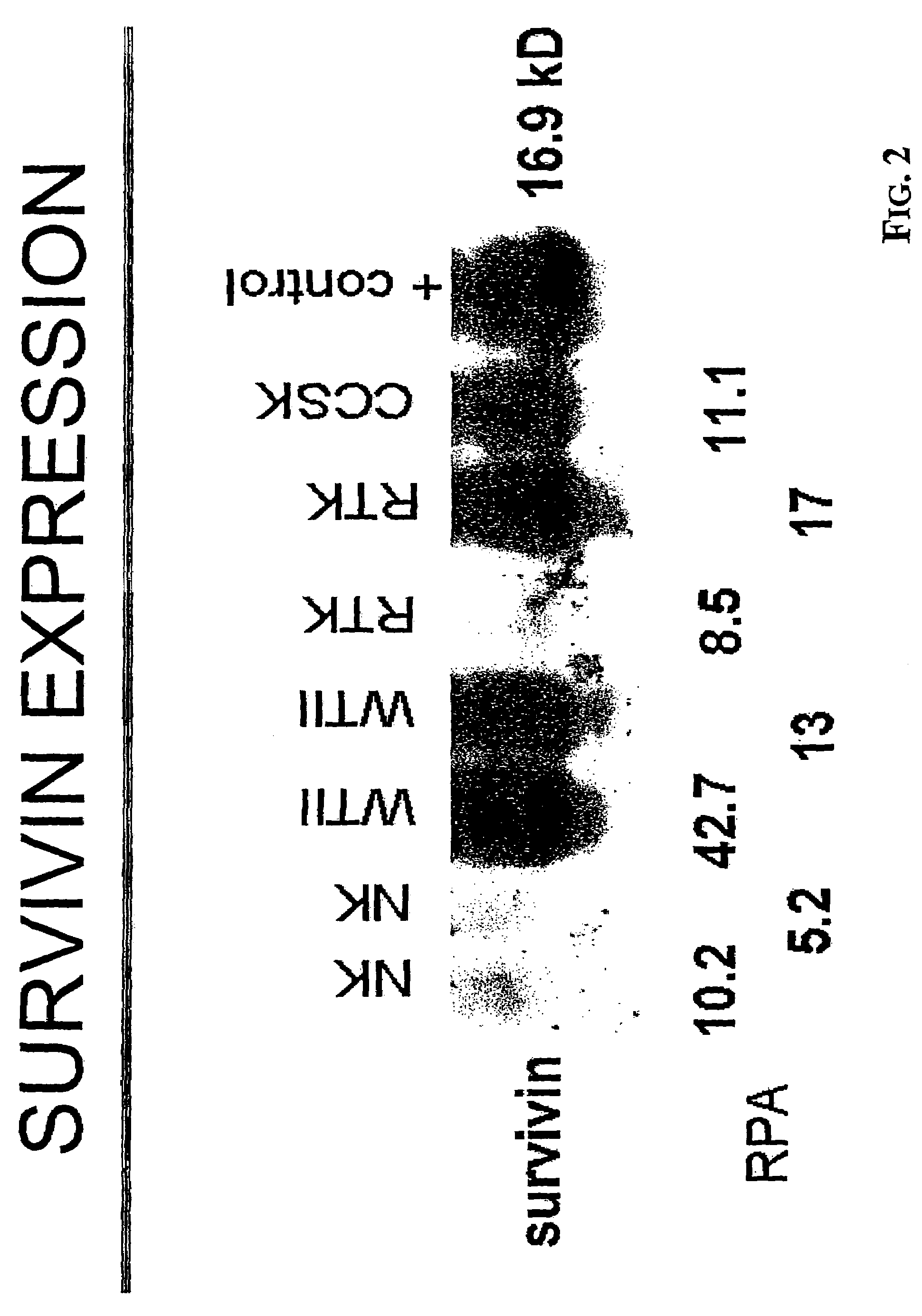
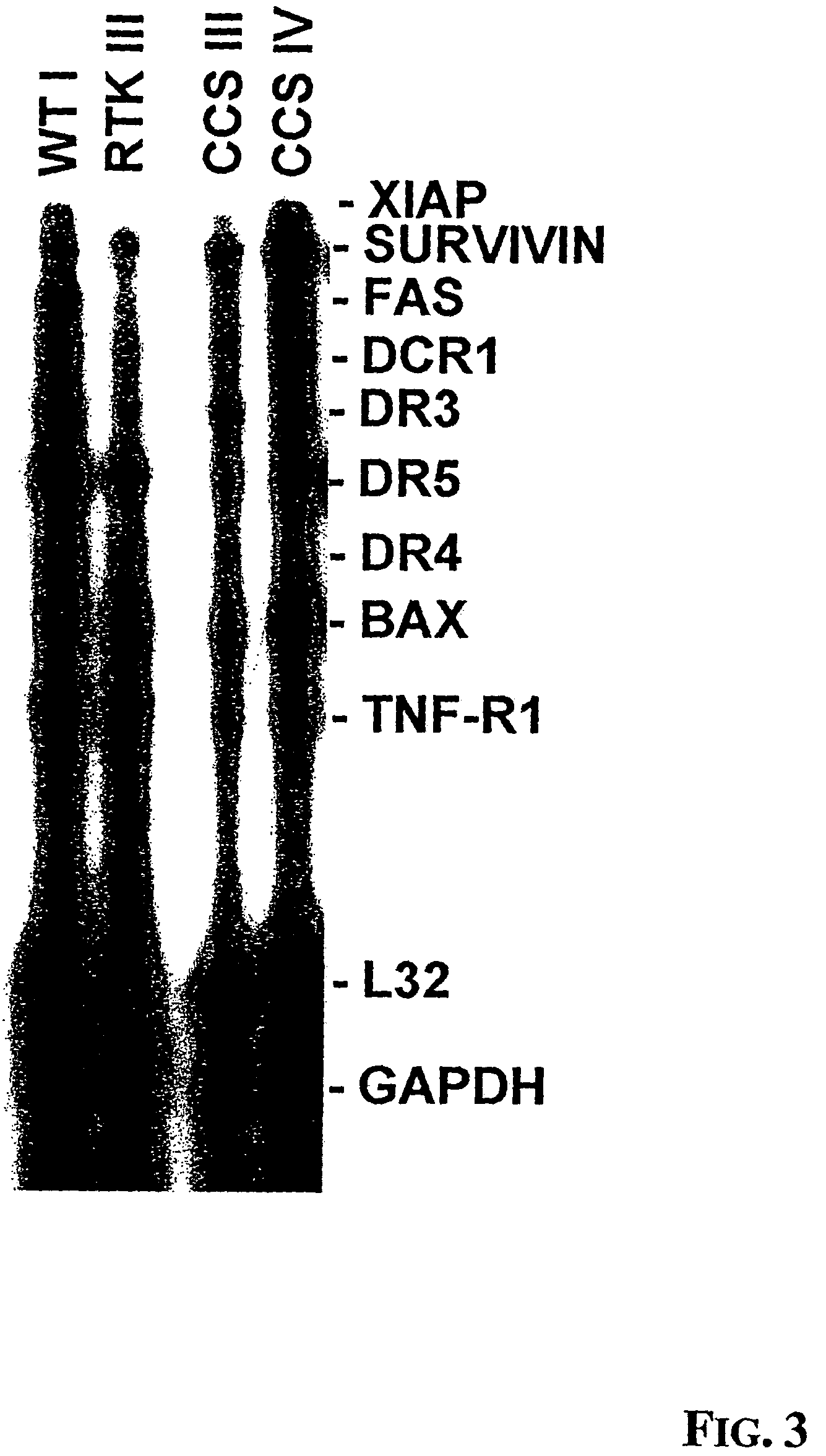
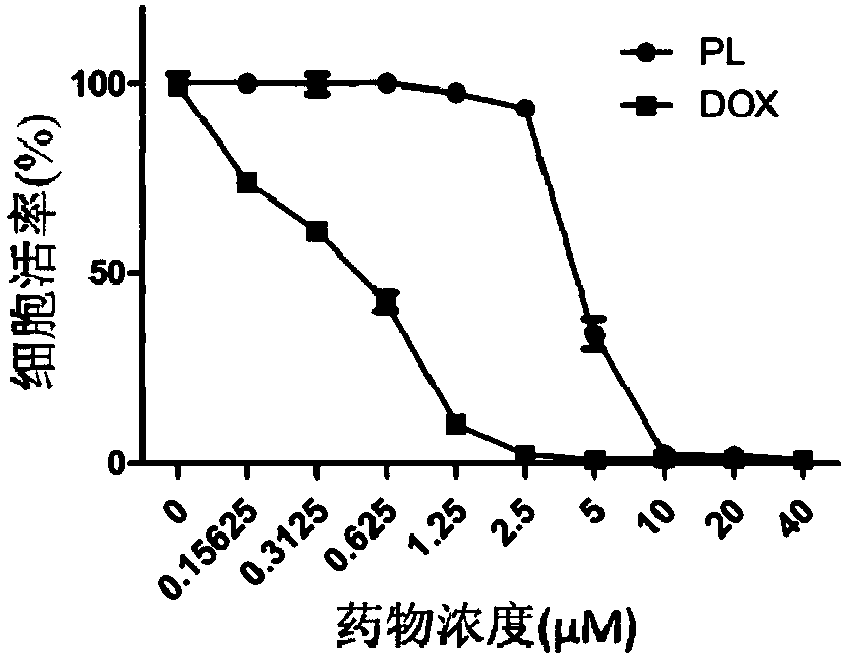
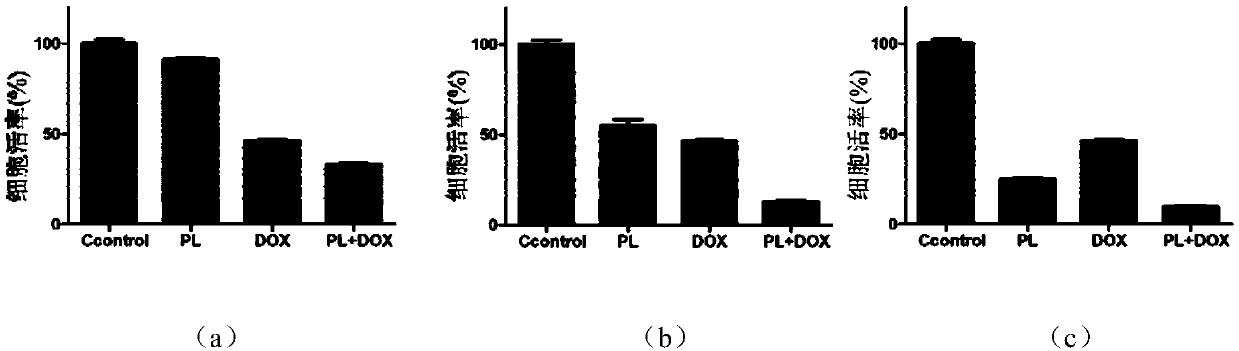
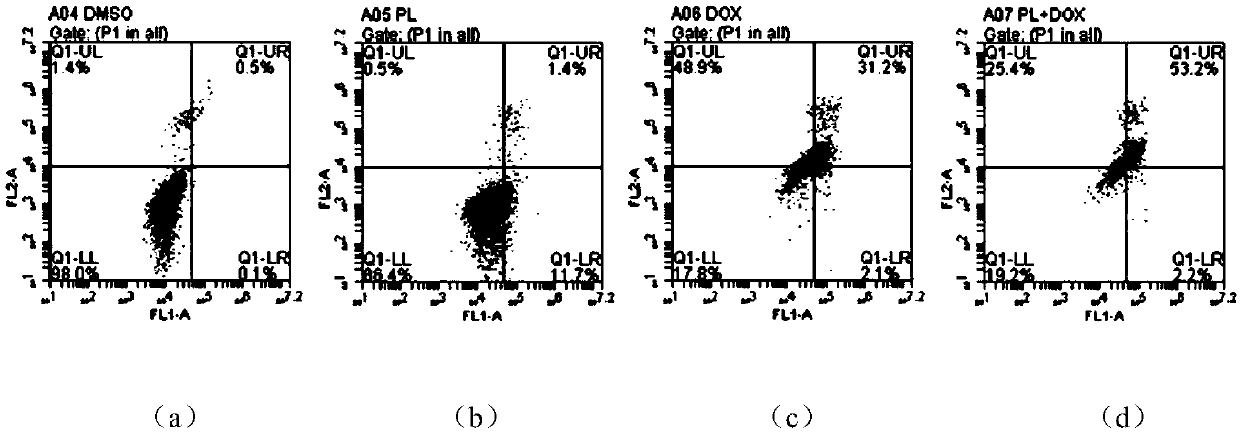
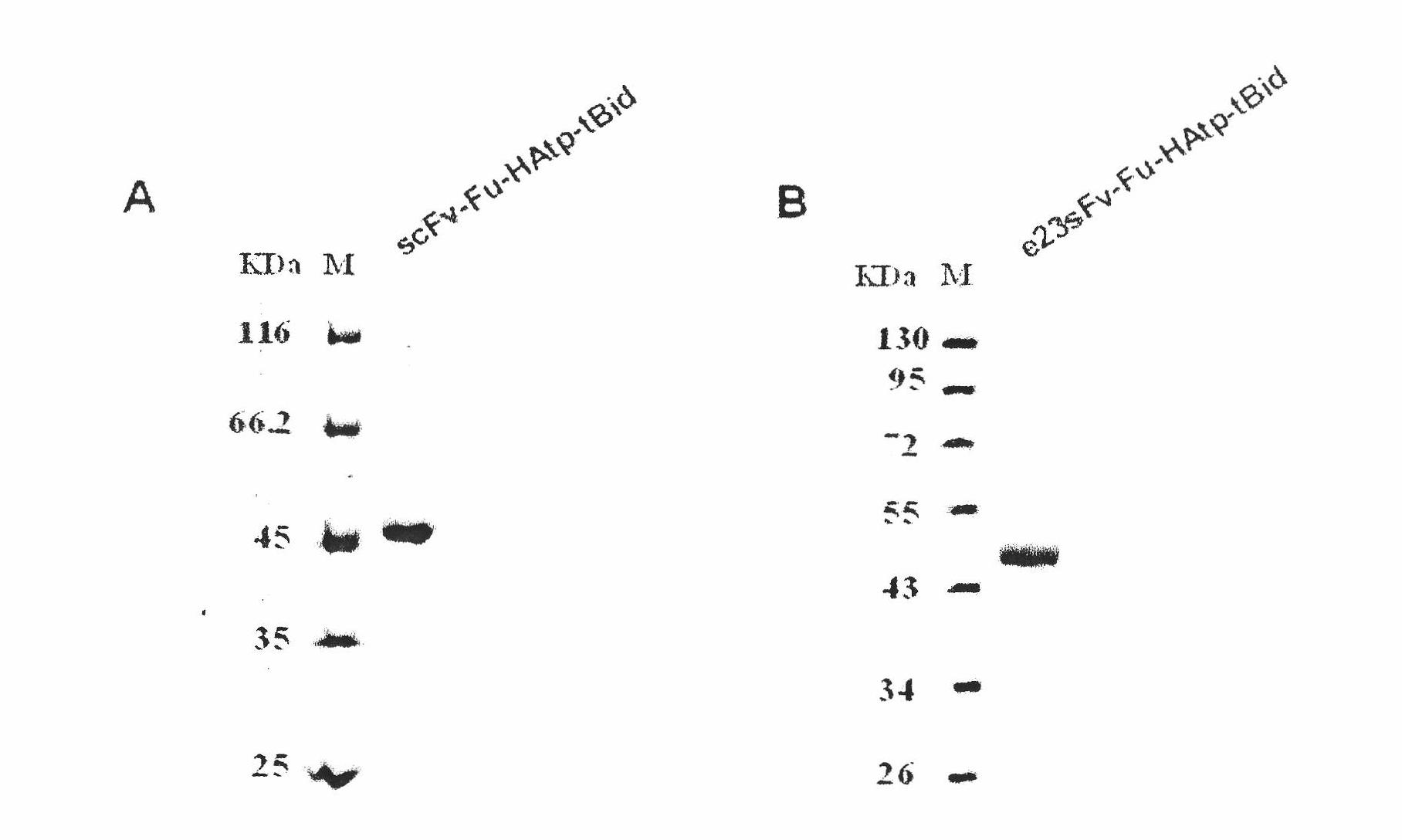
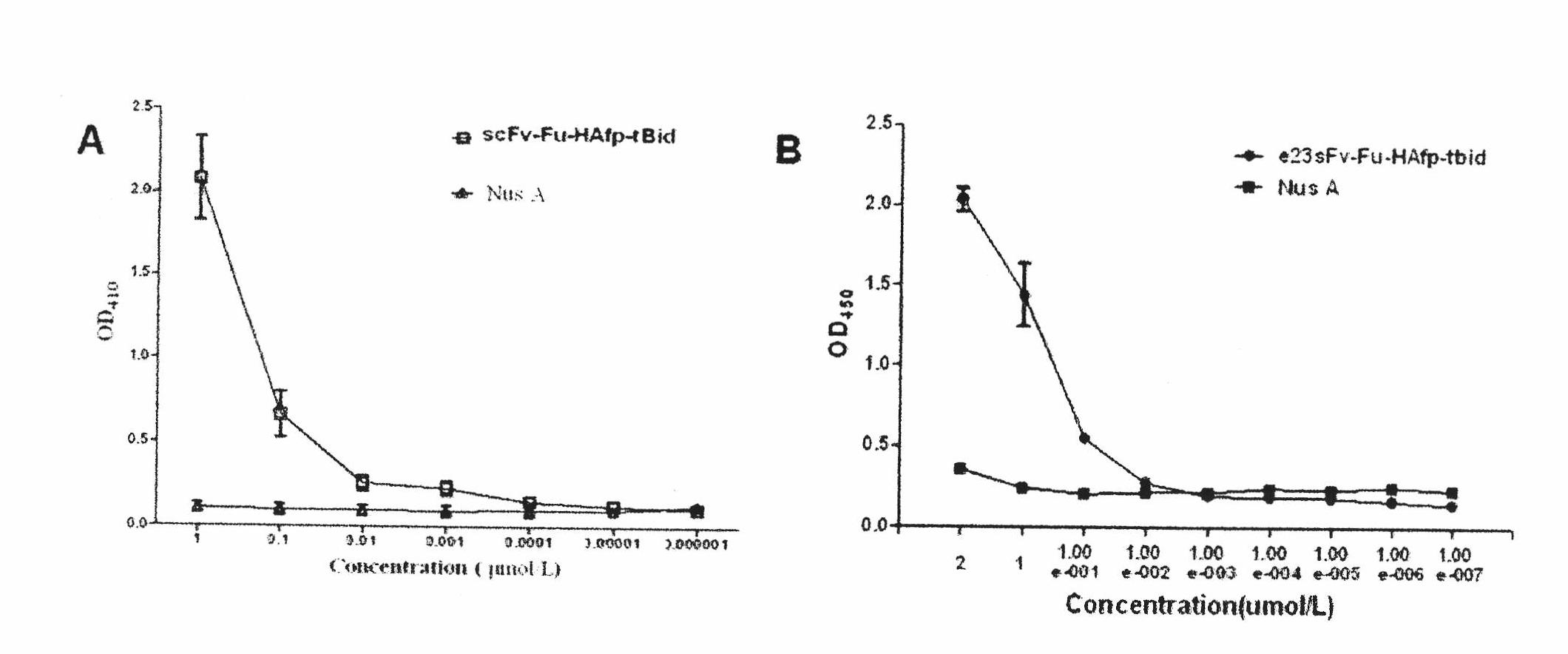
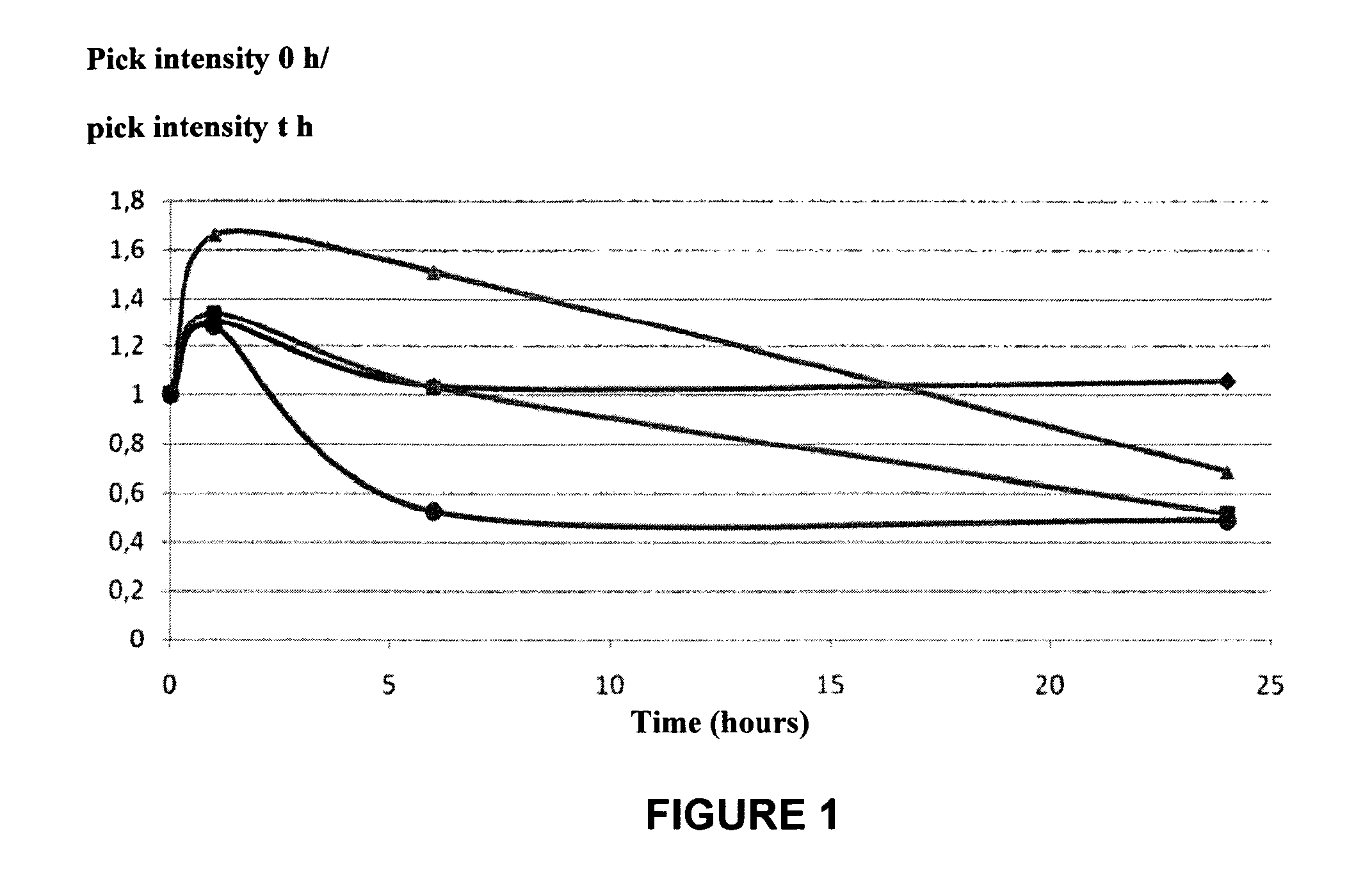
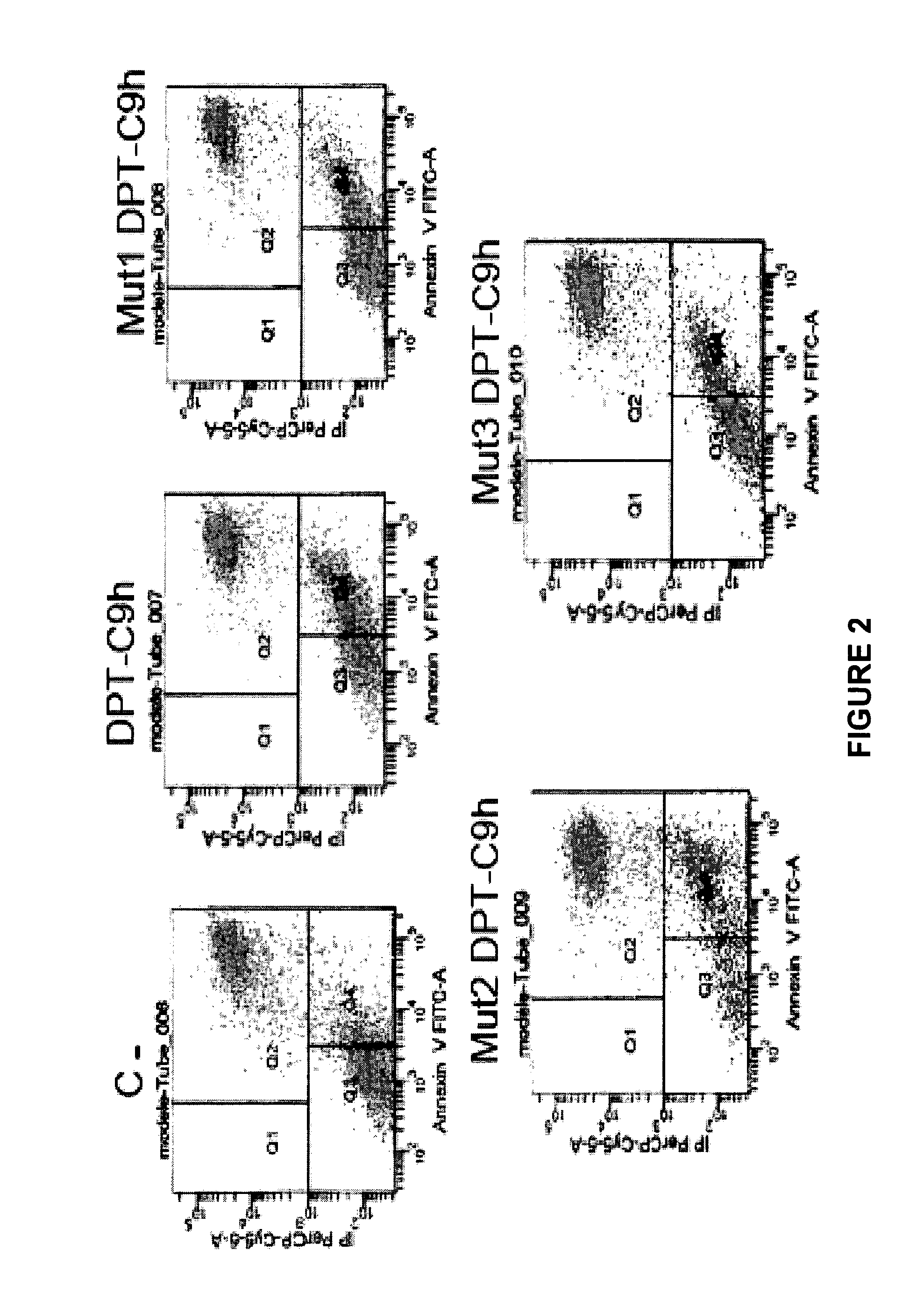
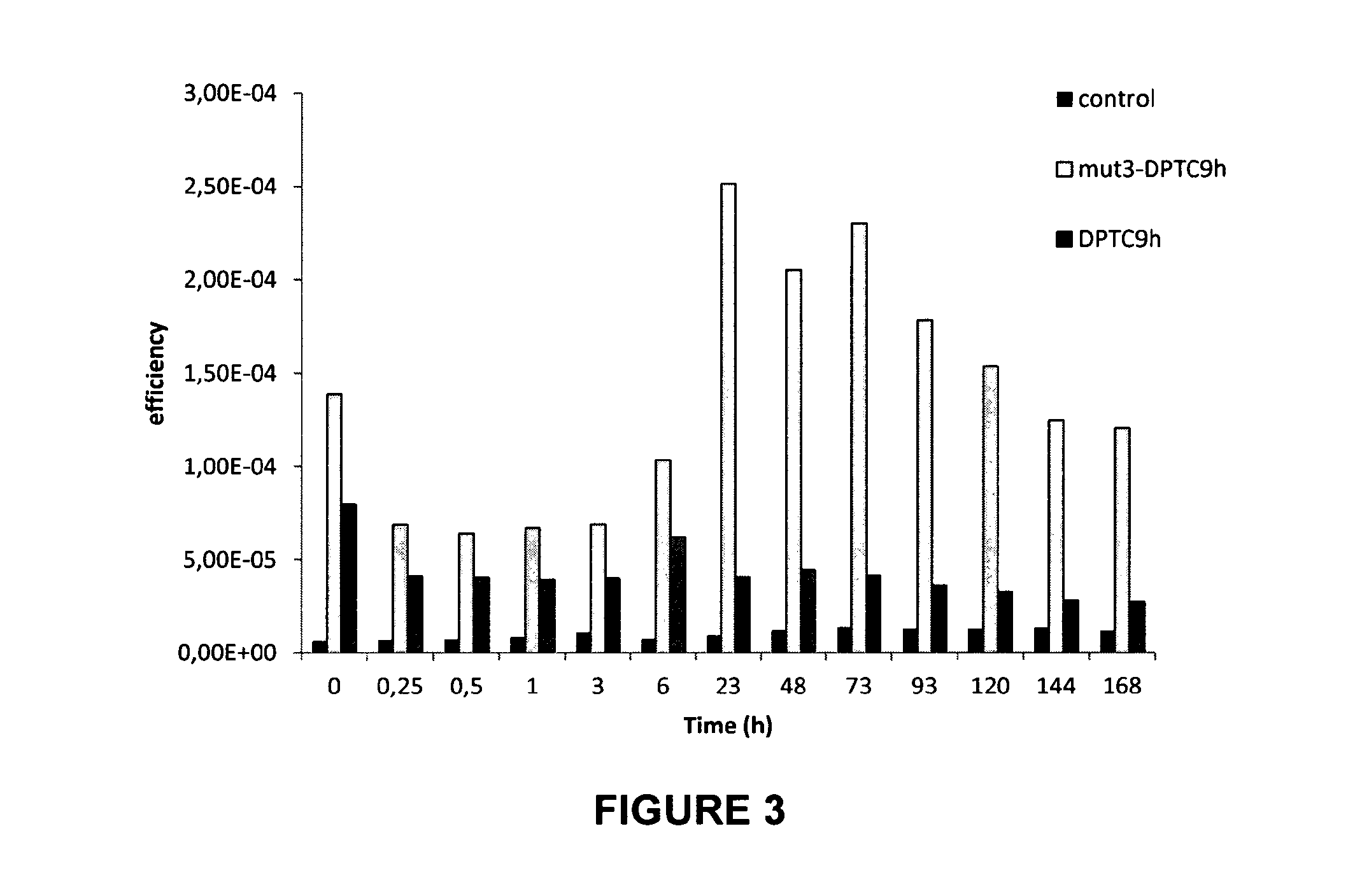
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Pro-apoptosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
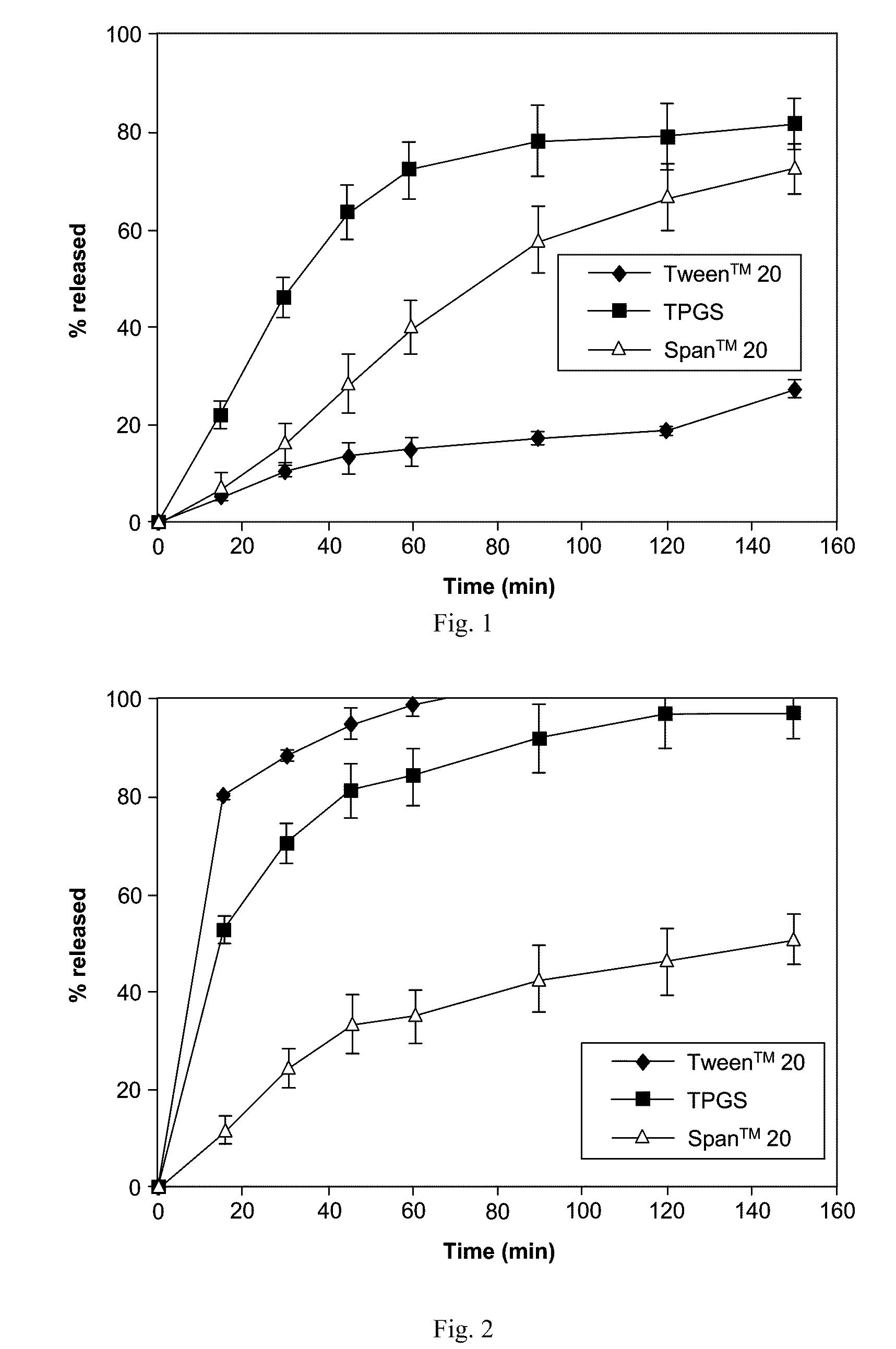
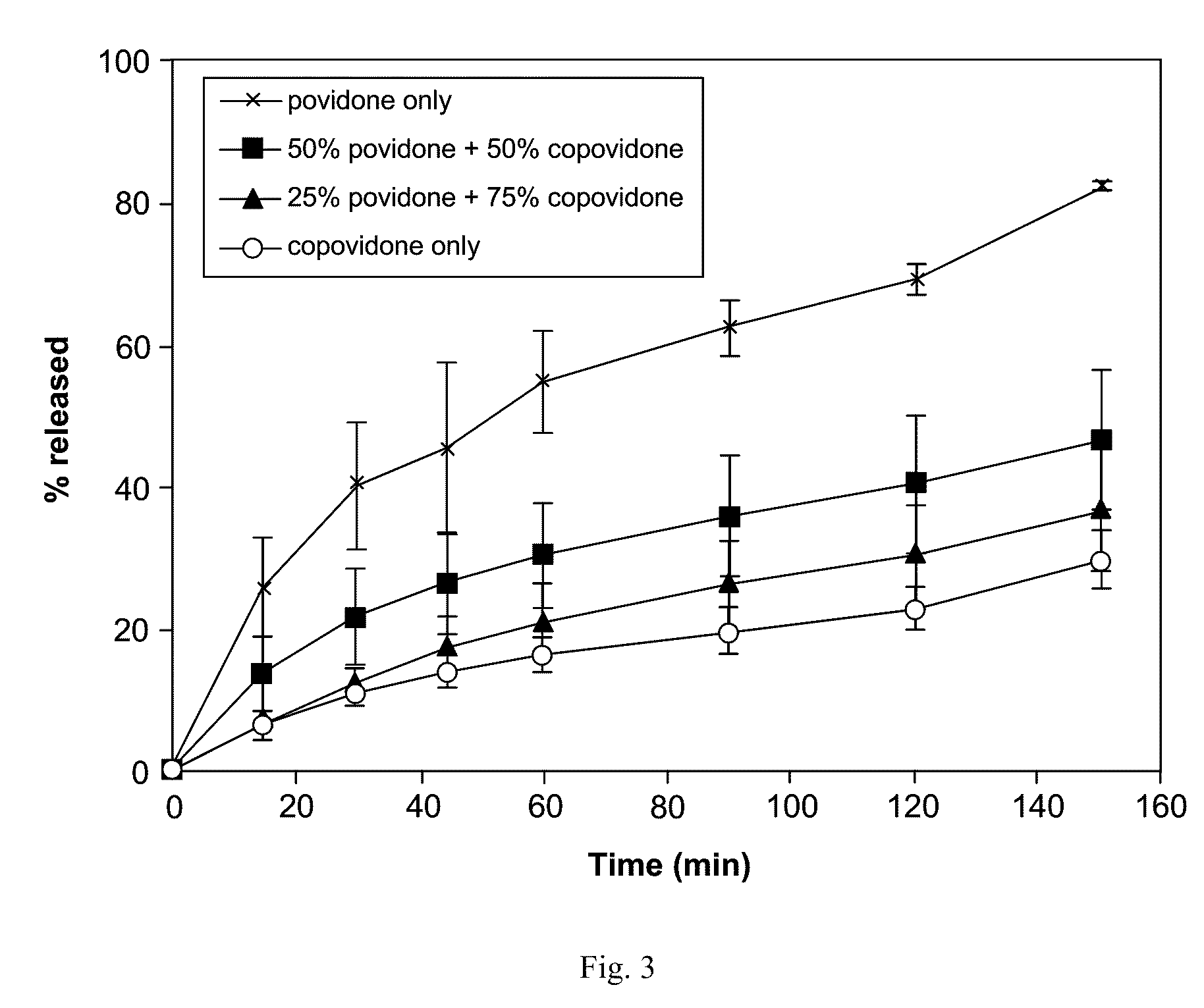
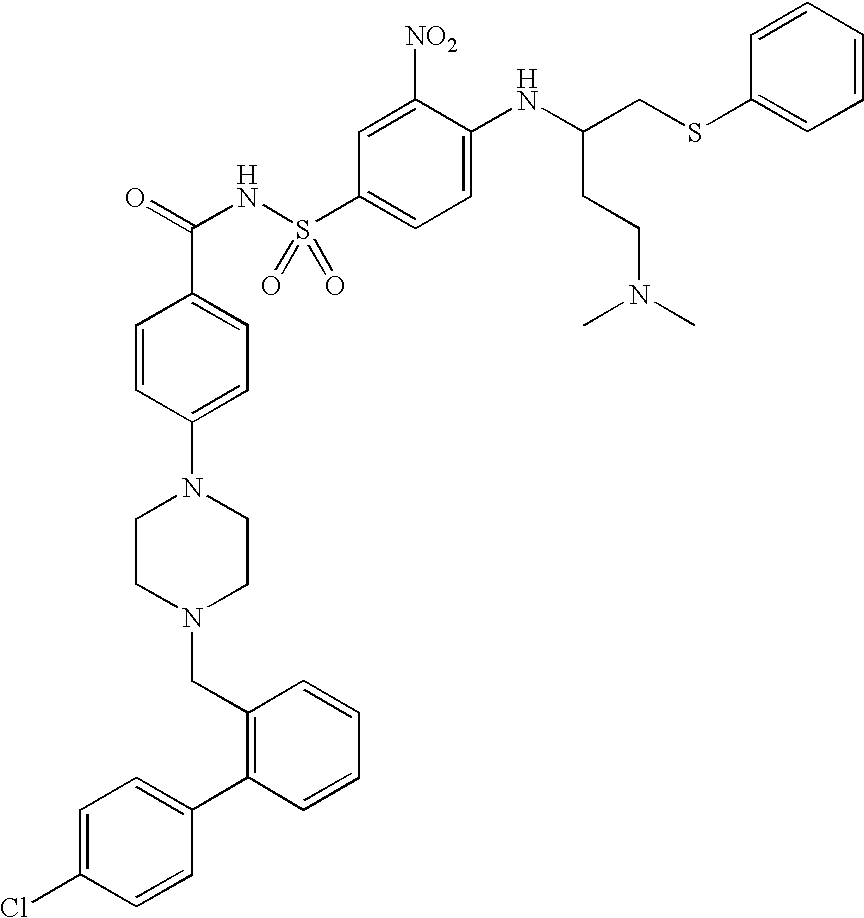
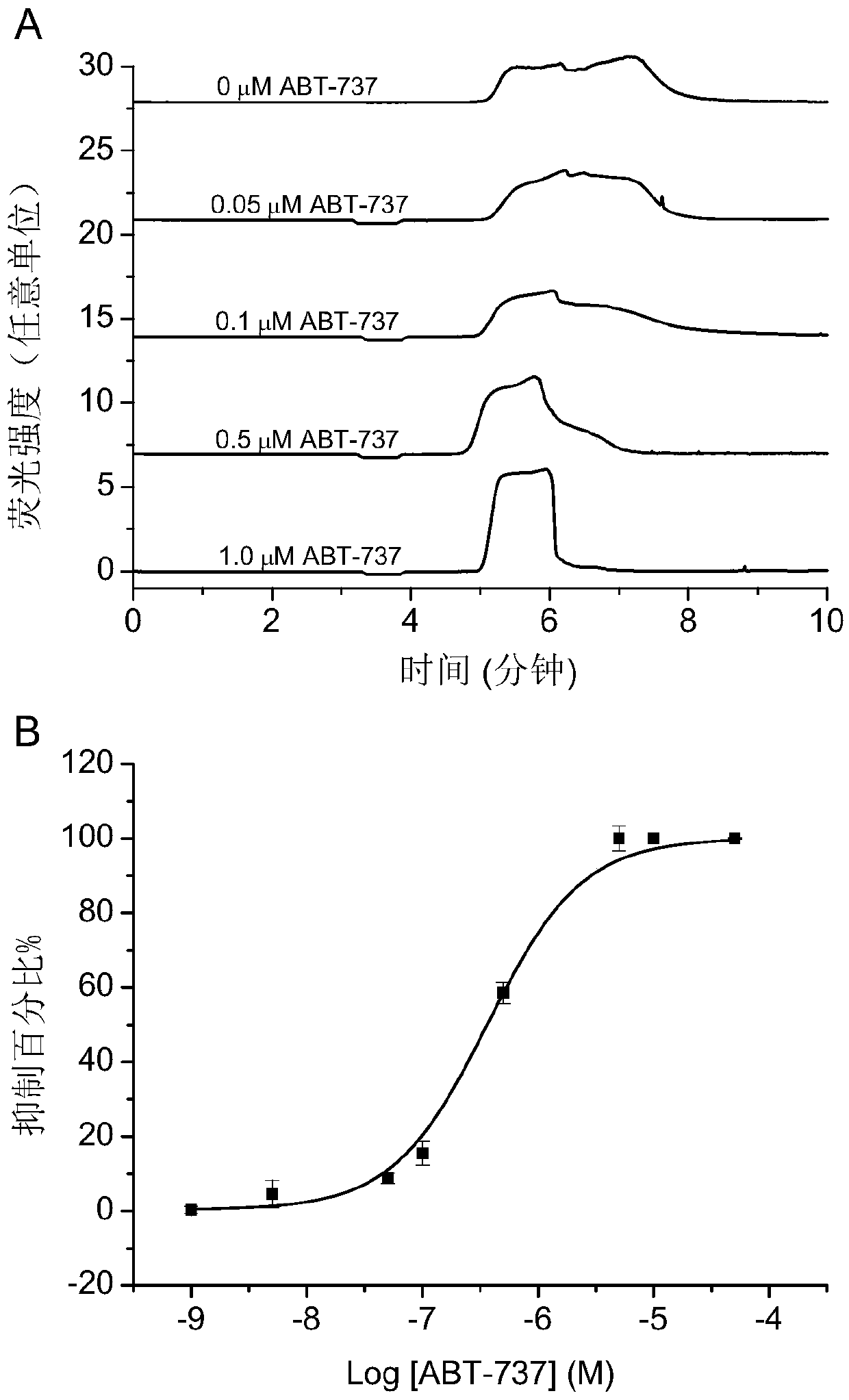
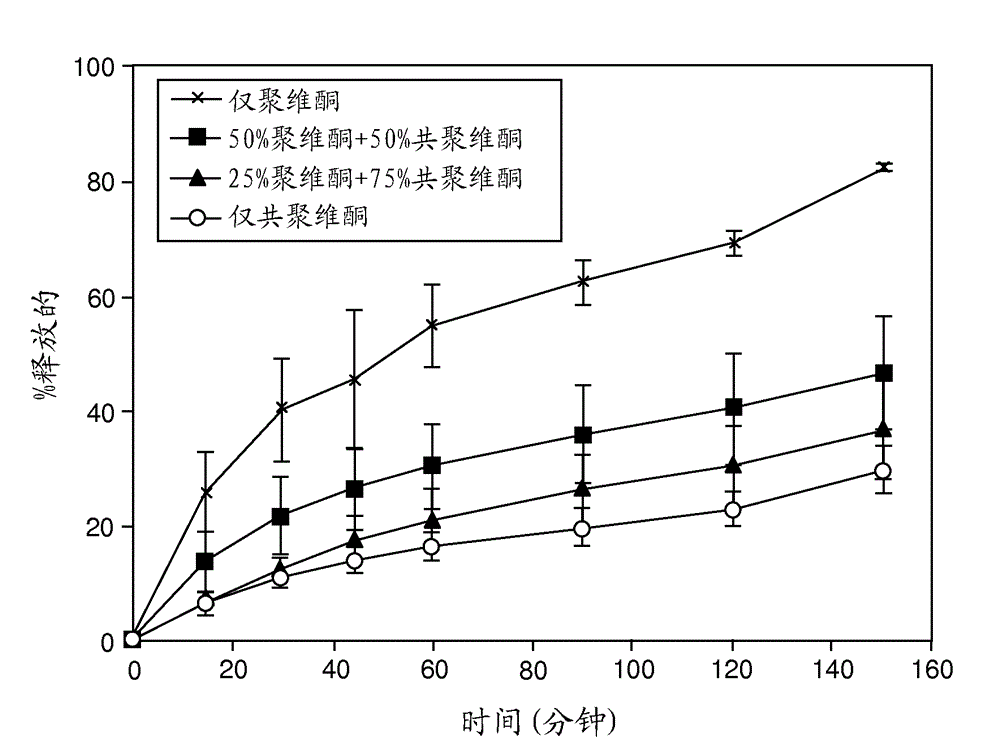
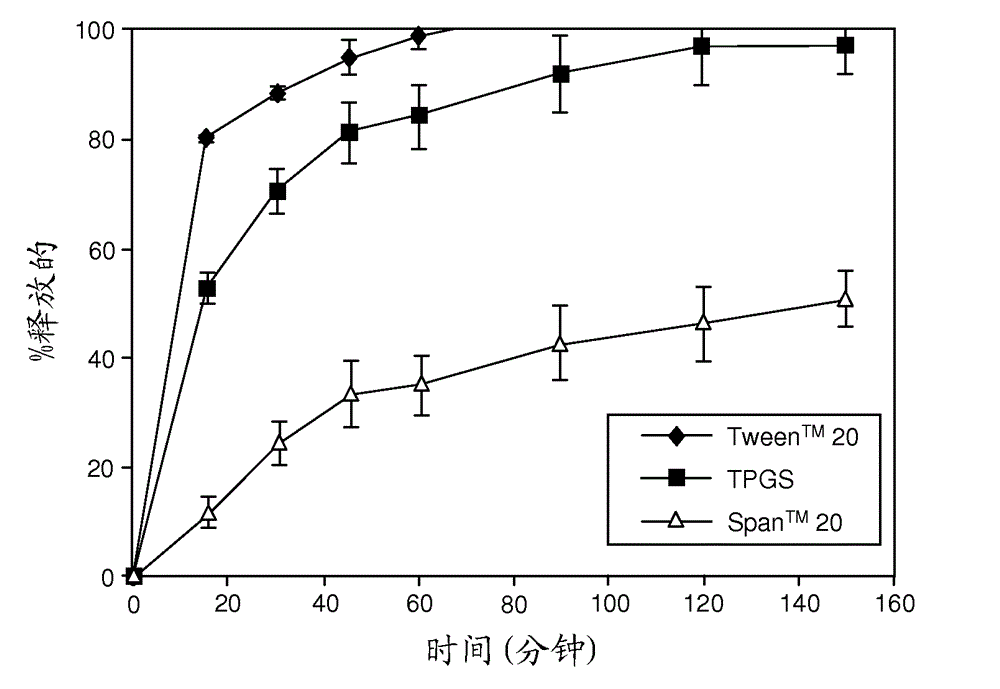
Solid dispersions containing an apoptosis-inducing agent
InactiveUS20120277210A1Improve clinical utilityStay focusedPowder deliveryBiocidePolymer scienceOral medication
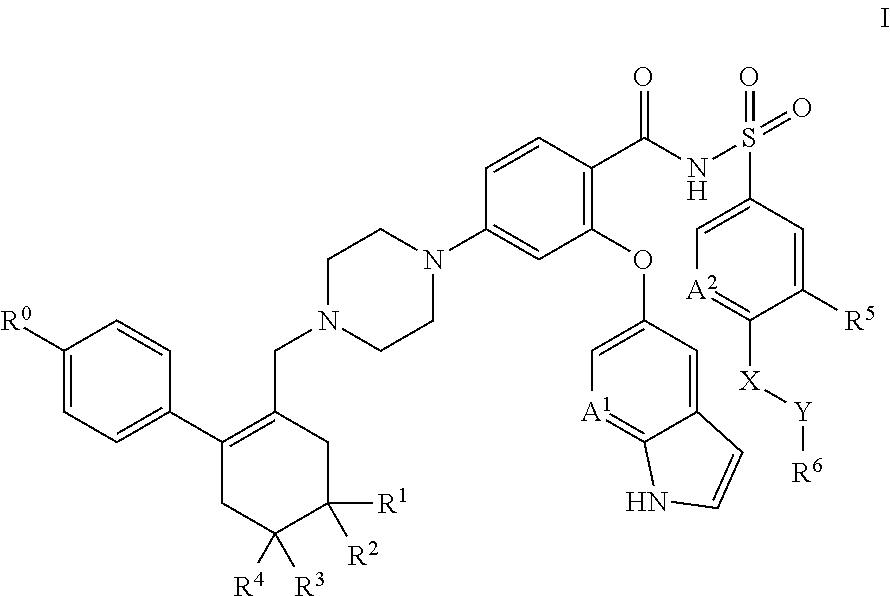
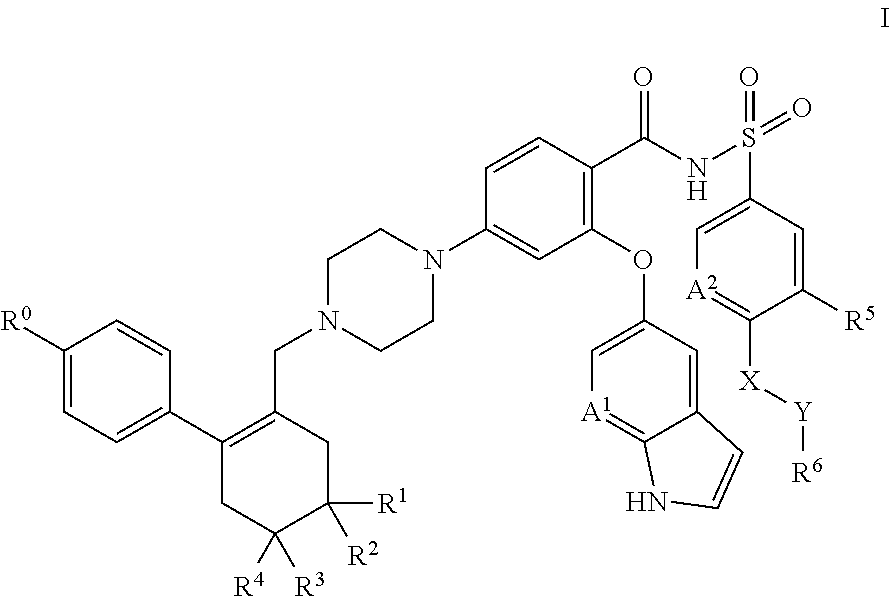
A pro-apoptotic solid dispersion comprises, in essentially non-crystalline form, a Bcl-2 family protein inhibitory compound of Formula I as defined herein, dispersed in a solid matrix that comprises (a) a pharmaceutically acceptable water-soluble polymeric carrier and (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable surfactant. A process for preparing such a solid dispersion comprises dissolving the compound, the polymeric carrier and the surfactant in a suitable solvent, and removing the solvent to provide a solid matrix comprising the polymeric carrier and the surfactant and having the compound dispersed in essentially non-crystalline form therein. The solid dispersion is suitable for oral administration to a subject in need thereof for treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
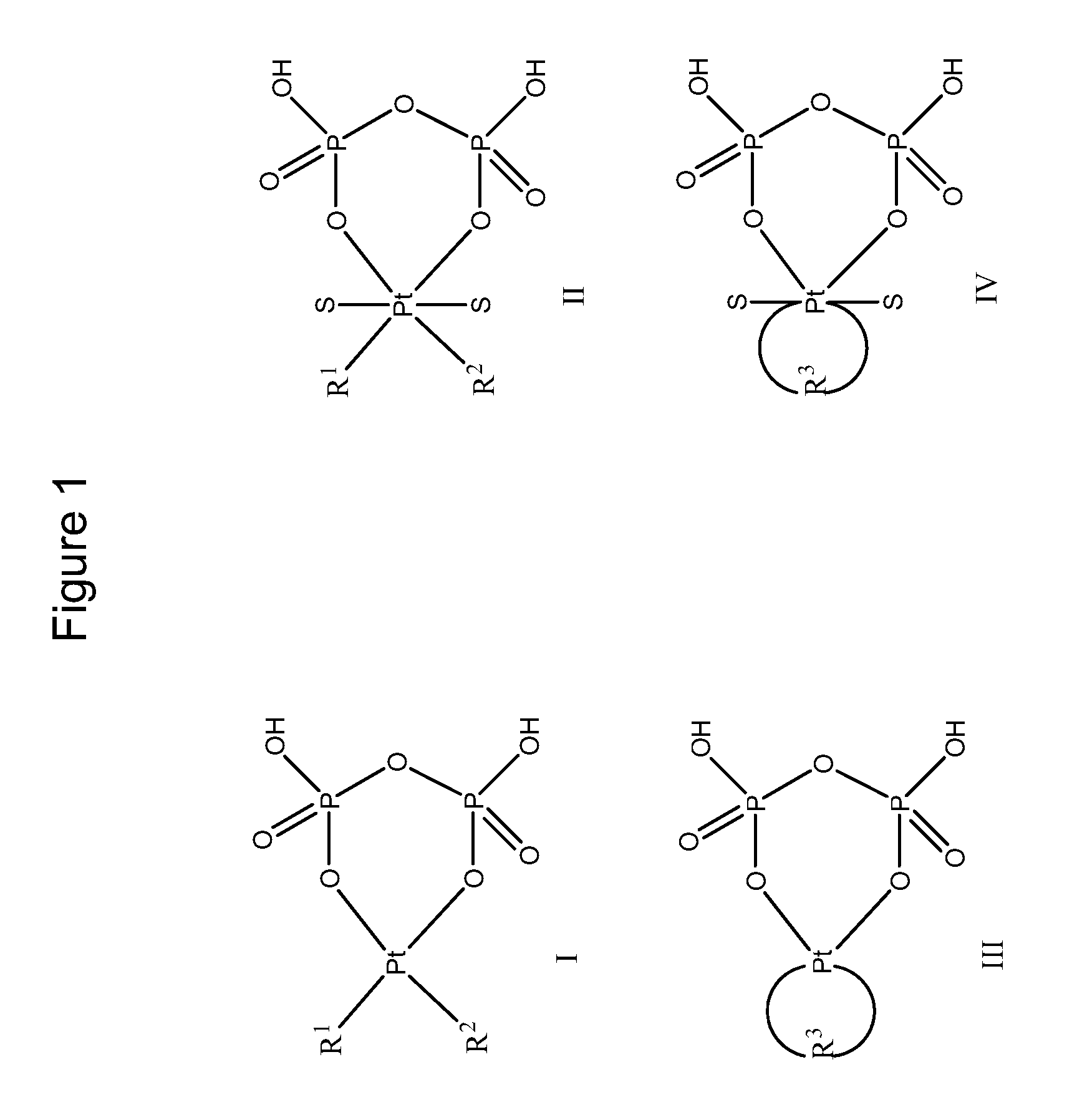
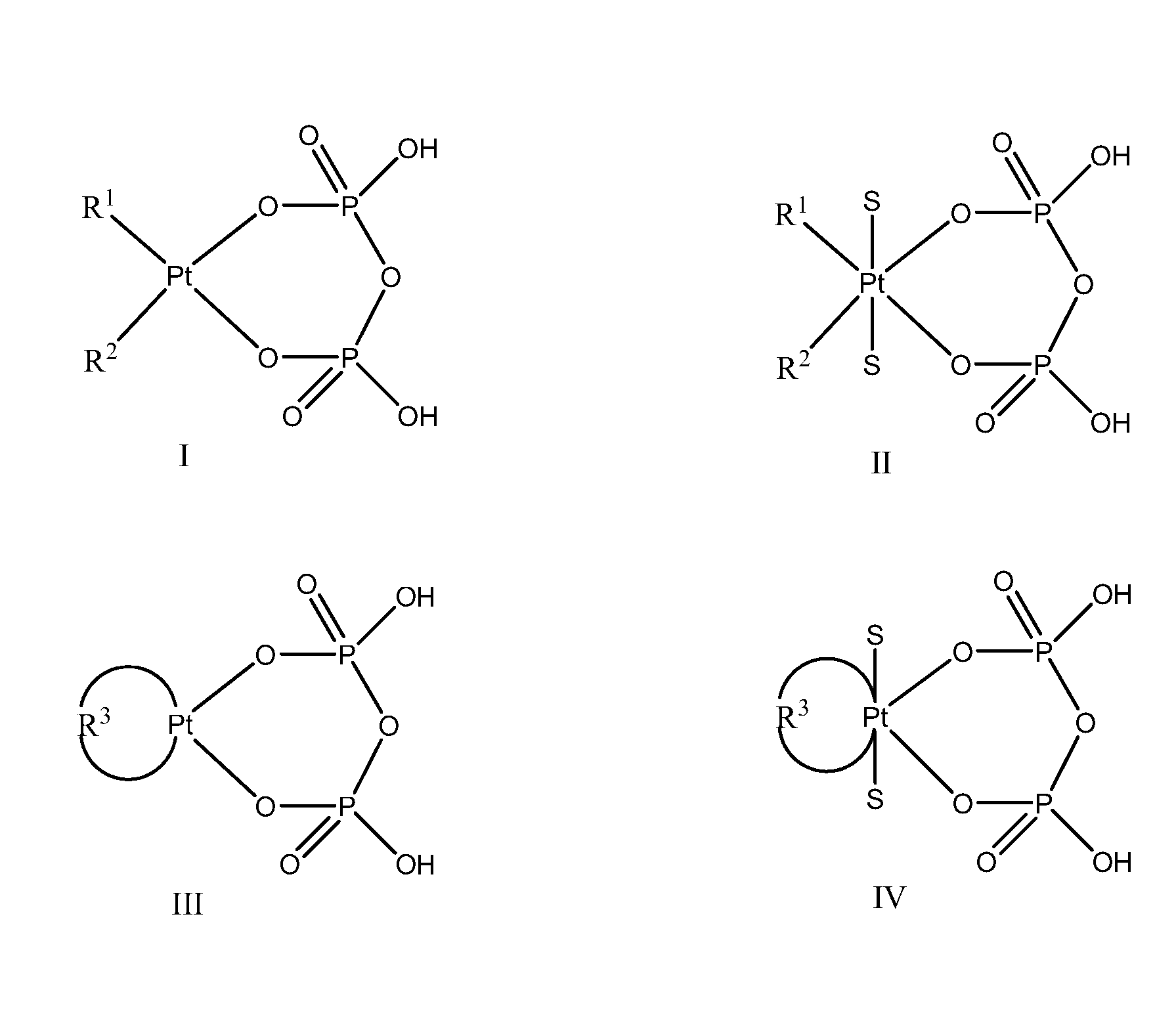
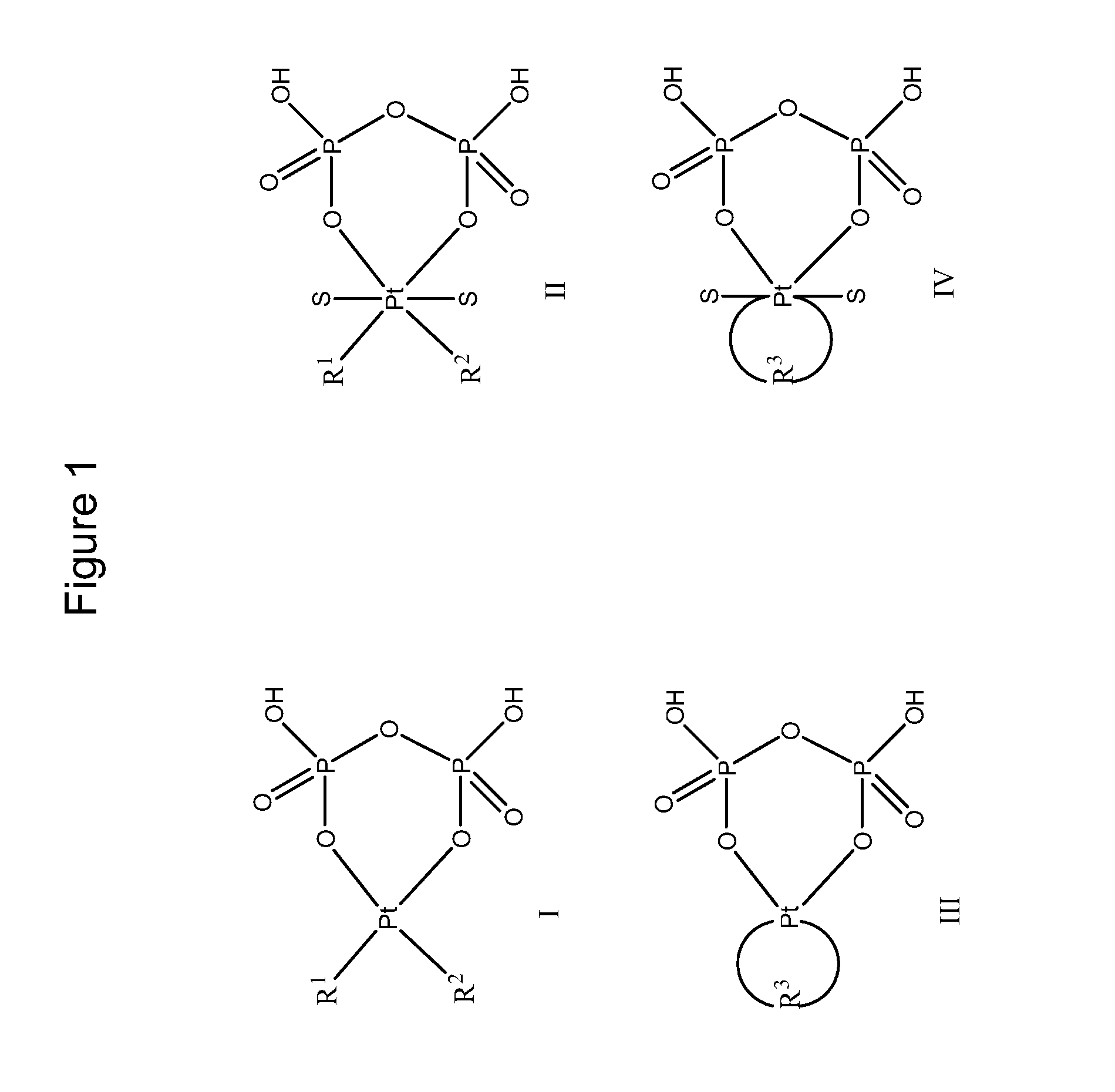
Phosphaplatins and their use in the treatment of cancers resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin
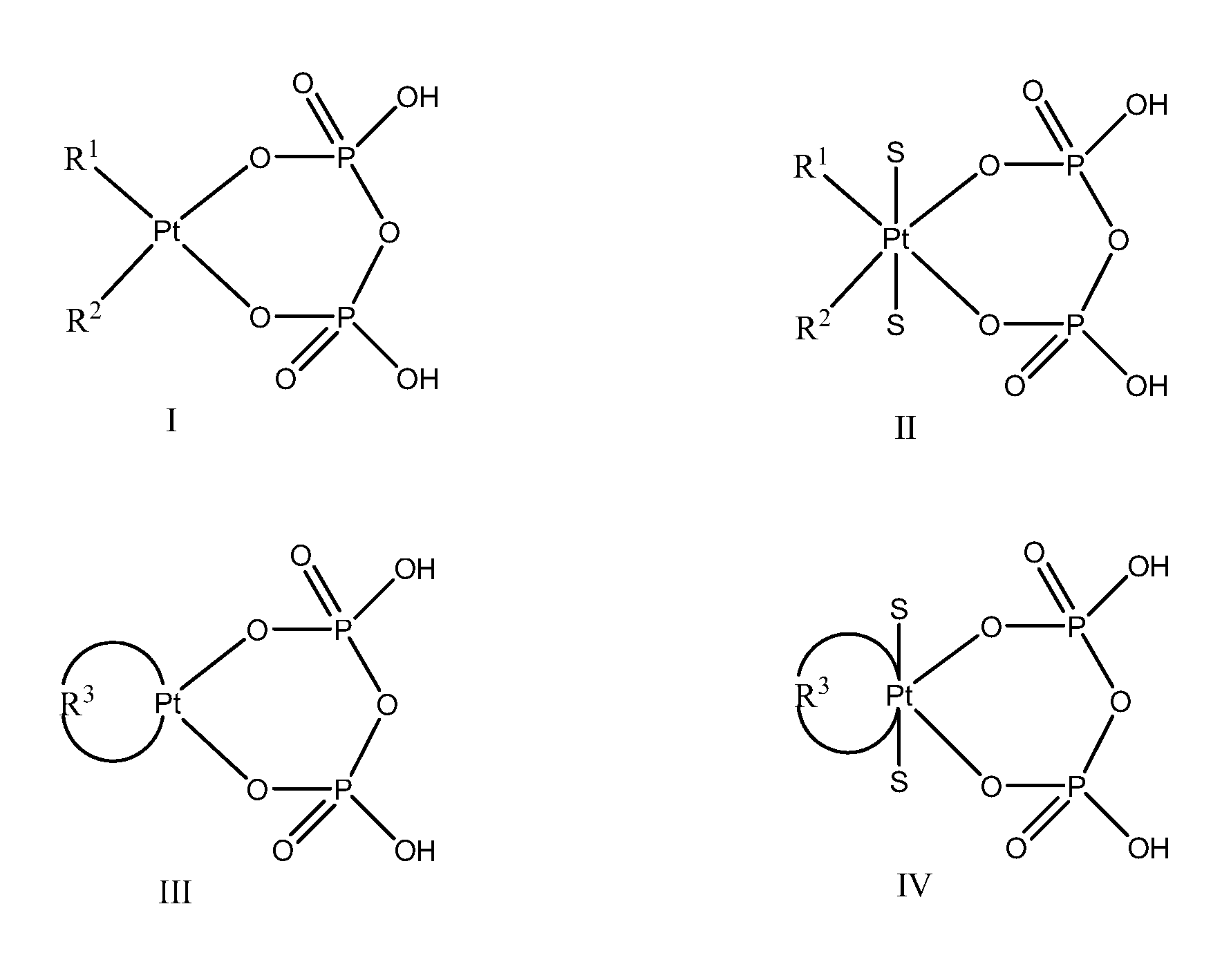
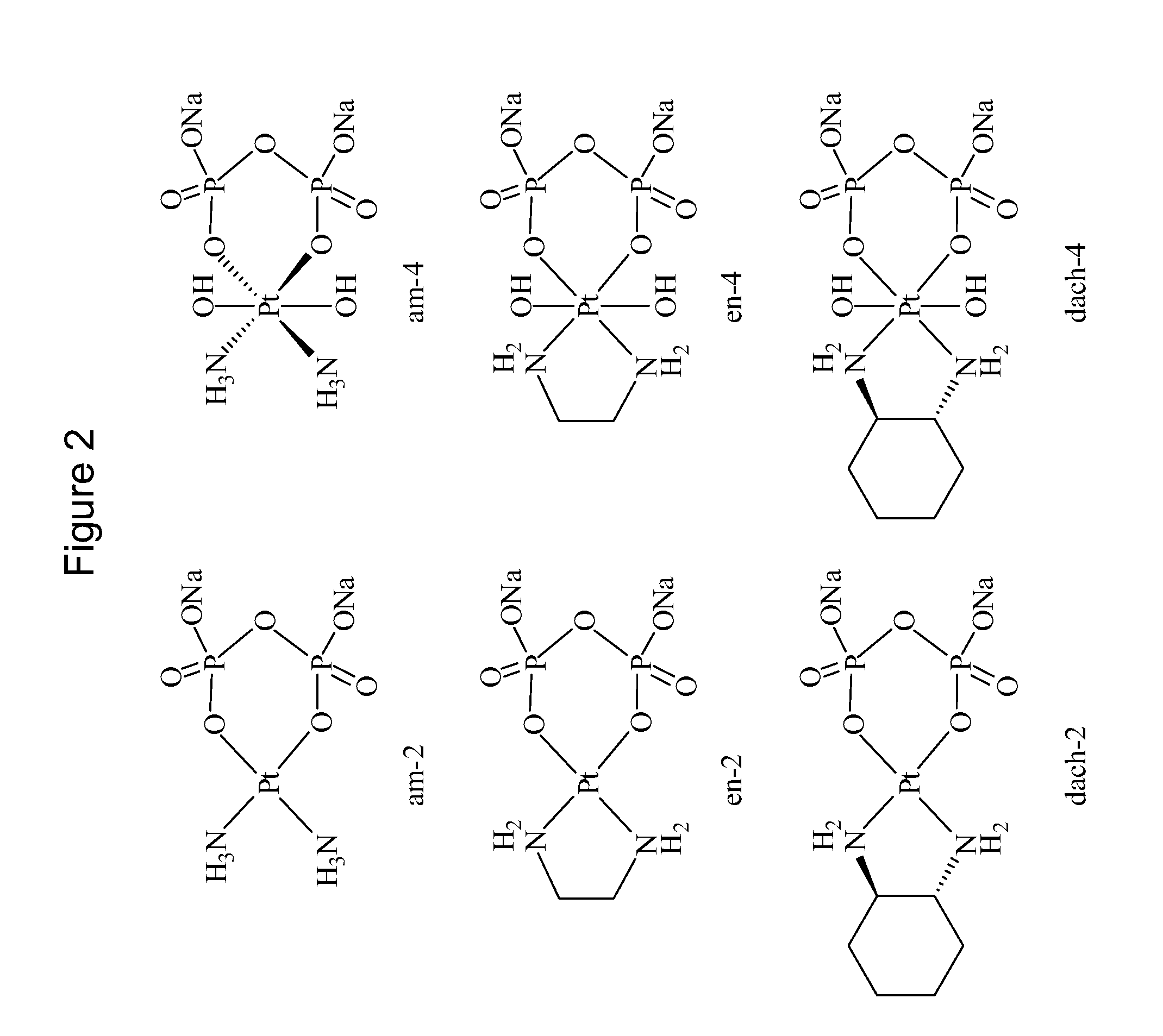
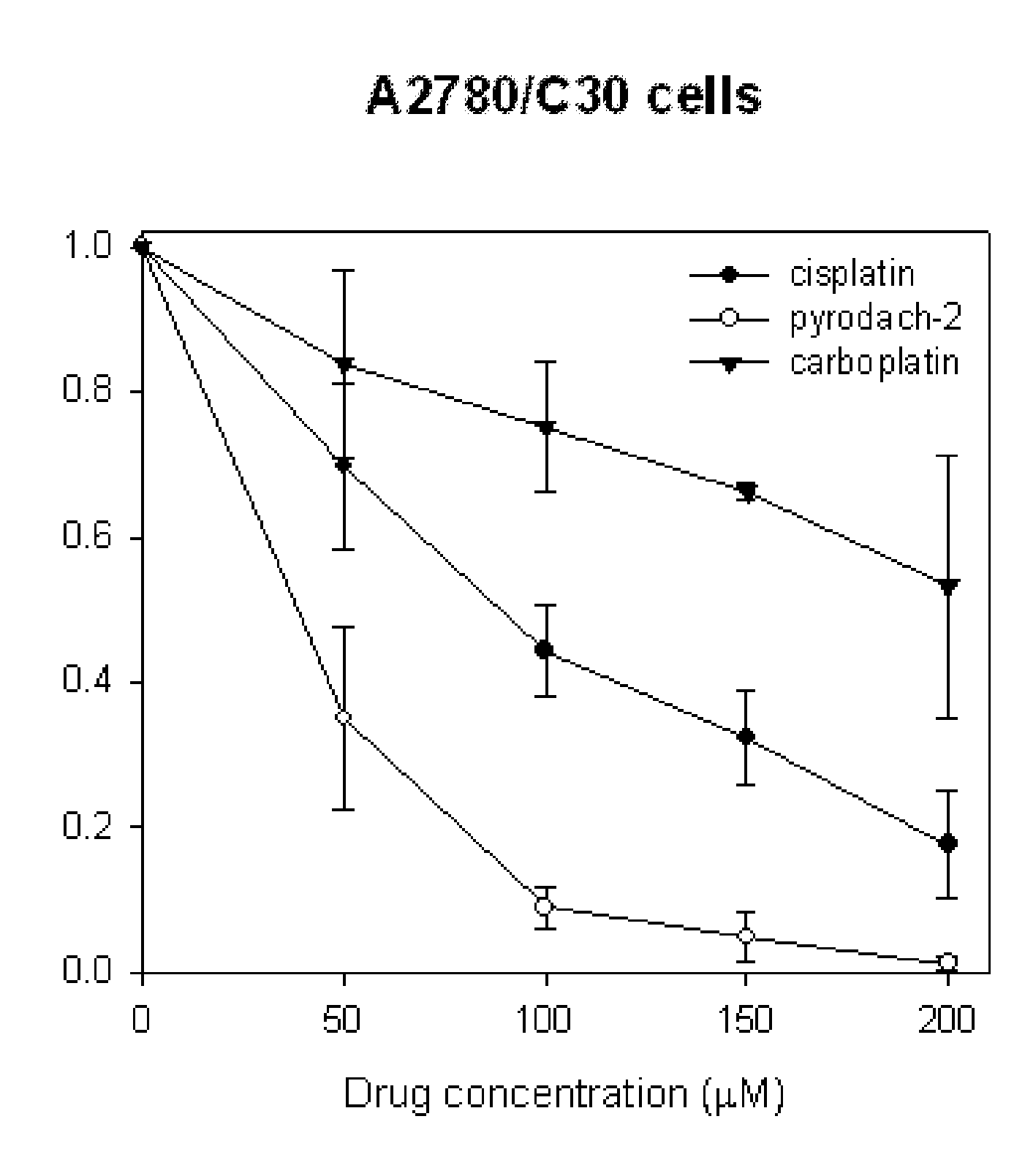
The present invention provides phosphaplatins, stable isolated monomeric phosphate complexes of platinum (II) and (IV), and methods of use thereof for treating cancers, including cisplatin- and carboplatin-resistant cancers. Unlike cisplatin, these complexes do not readily undergo hydrolysis and are quite soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. Moreover, these complexes—unlike cisplatin, carboplatin, and related platinum-based anti-cancer agents—do not bind DNA. Rather, data suggests that phosphaplatins trigger overexpression of fas and fas-related transcription factors and some proapoptotic genes such as Bak and Bax. Nevertheless, the complexes exhibit tremendous cytotoxicity towards cancer cells. Thus, the present invention provides novel platinum anticancer agents that have a different molecular target than those in the art.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Solid dispersions containing an apoptosis-promoting agent
InactiveUS20100311751A1Attenuate induction of apoptosisStrong cytotoxicityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOral medication
A pro-apoptotic solid dispersion comprises, in essentially non-crystalline form, a Bcl-2 family protein inhibitory compound, e.g., ABT-263, dispersed in a solid matrix that comprises (a) a pharmaceutically acceptable water-soluble polymeric carrier and (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable surfactant. A process for preparing such a solid dispersion comprises dissolving the compound, the polymeric carrier and the surfactant in a suitable solvent, and removing the solvent to provide a solid matrix comprising the polymeric carrier and the surfactant and having the compound dispersed in essentially non-crystalline form therein. The solid dispersion is suitable for oral administration to a subject in need thereof for treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Treatment or prevention of oto-pathologies by inhibition of pro-apoptotic genes
InactiveUS7825099B2Prevent ototoxicityIncrease doseSenses disorderSugar derivativesExternal earsPathology diagnosis
The invention relates to one or more inhibitors, in particular siRNAs, which down-regulate the expression of human pro-apoptotic genes. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating or preventing the incidence or severity of hearing impairment (or balance impairment), particularly hearing impairment associated with cell death of the inner ear hair cells or outer ear hair cells, comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Phosphaplatins and their use in the treatment of cancers resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin
The present invention provides phosphaplatins, stable isolated monomeric phosphato complexes of platinum (II) and (IV), and methods of use thereof for treating cancers, including cisplatin- and carboplatin-resistant cancers. Unlike cisplatin, these complexes do not readily undergo hydrolysis and are quite soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. Moreover, these complexes—unlike cisplatin, carboplatin, and related platinum-based anti-cancer agents—do not bind DNA. Rather, data suggests that phosphaplatins trigger overexpression of fas and fas-related transcription factors and some proapoptotic genes such as Bak and Bax. Nevertheless, the complexes exhibit tremendous cytotoxicity towards cancer cells. Thus, the present invention provides novel platinum anticancer agents that have a different molecular target than those in the art.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Phosphaplatins and their use in the treatment of cancers resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin
ActiveUS20090042838A1Stable and effectiveHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCarboplatinAnticarcinogen
The present invention provides phosphaplatins, stable isolated monomeric phosphate complexes of platinum (II) and (IV), and methods of use thereof for treating cancers, including cisplatin- and carboplatin-resistant cancers. Unlike cisplatin, these complexes do not readily undergo hydrolysis and are quite soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. Moreover, these complexes-unlike cisplatin, carboplatin, and related platinum-based anti-cancer agents-do not bind DNA. Rather, data suggests that phosphaplatins trigger overexpression of fas and fas-related transcription factors and some proapoptotic genes such as Bak and Bax. Nevertheless, the complexes exhibit tremendous cytotoxicity towards cancer cells. Thus, the present invention provides novel platinum anticancer agents that have a different molecular target than those in the art.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Induction of apoptic or cytotoxic gene expression by adenoviral mediated gene codelivery
InactiveUS6899870B1Reduce the overall heightBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCytotoxicityHuman cell
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Combination Therapy
InactiveUS20080058274A1Beneficial additive effectGood effectBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDoxorubicinLiposome
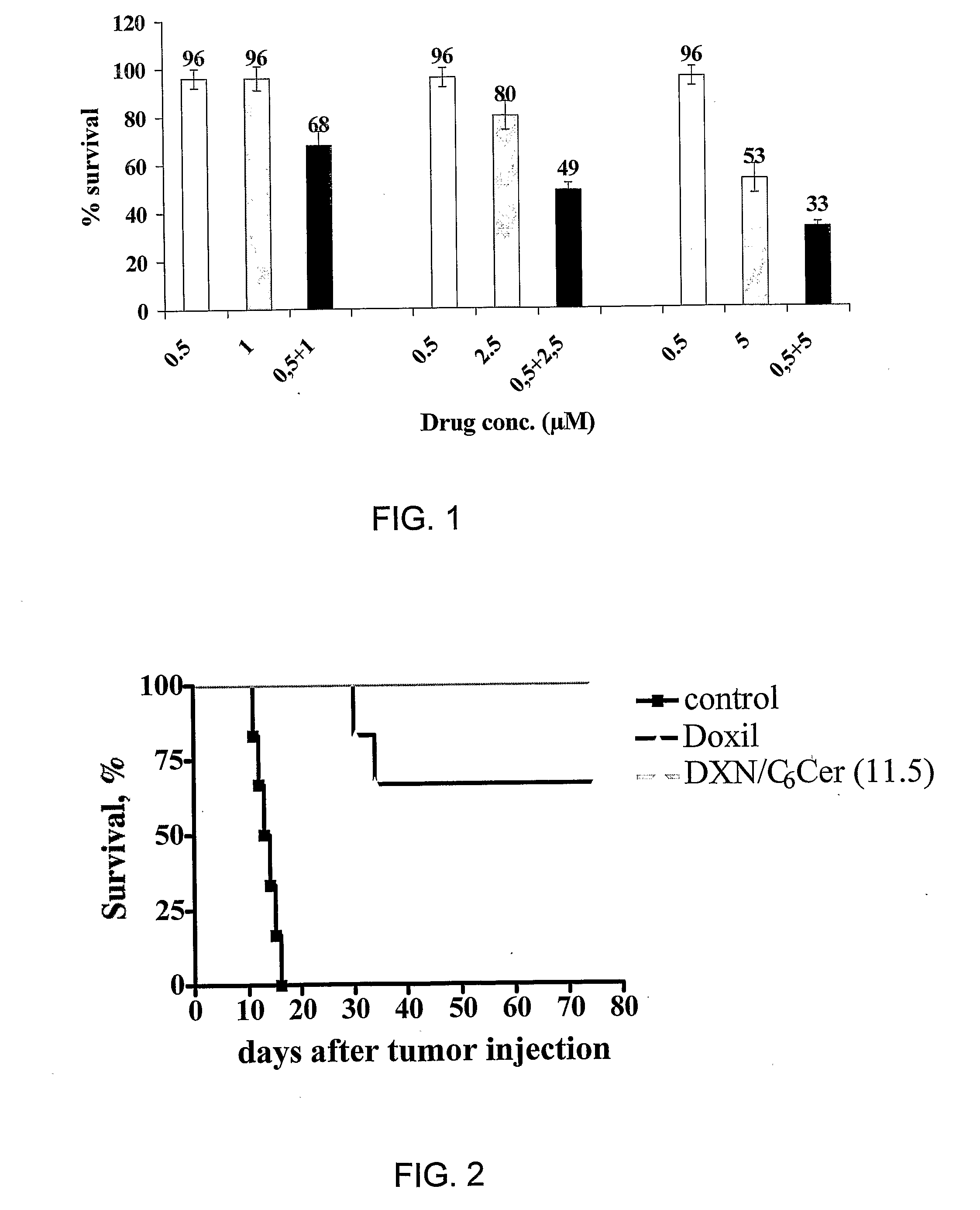
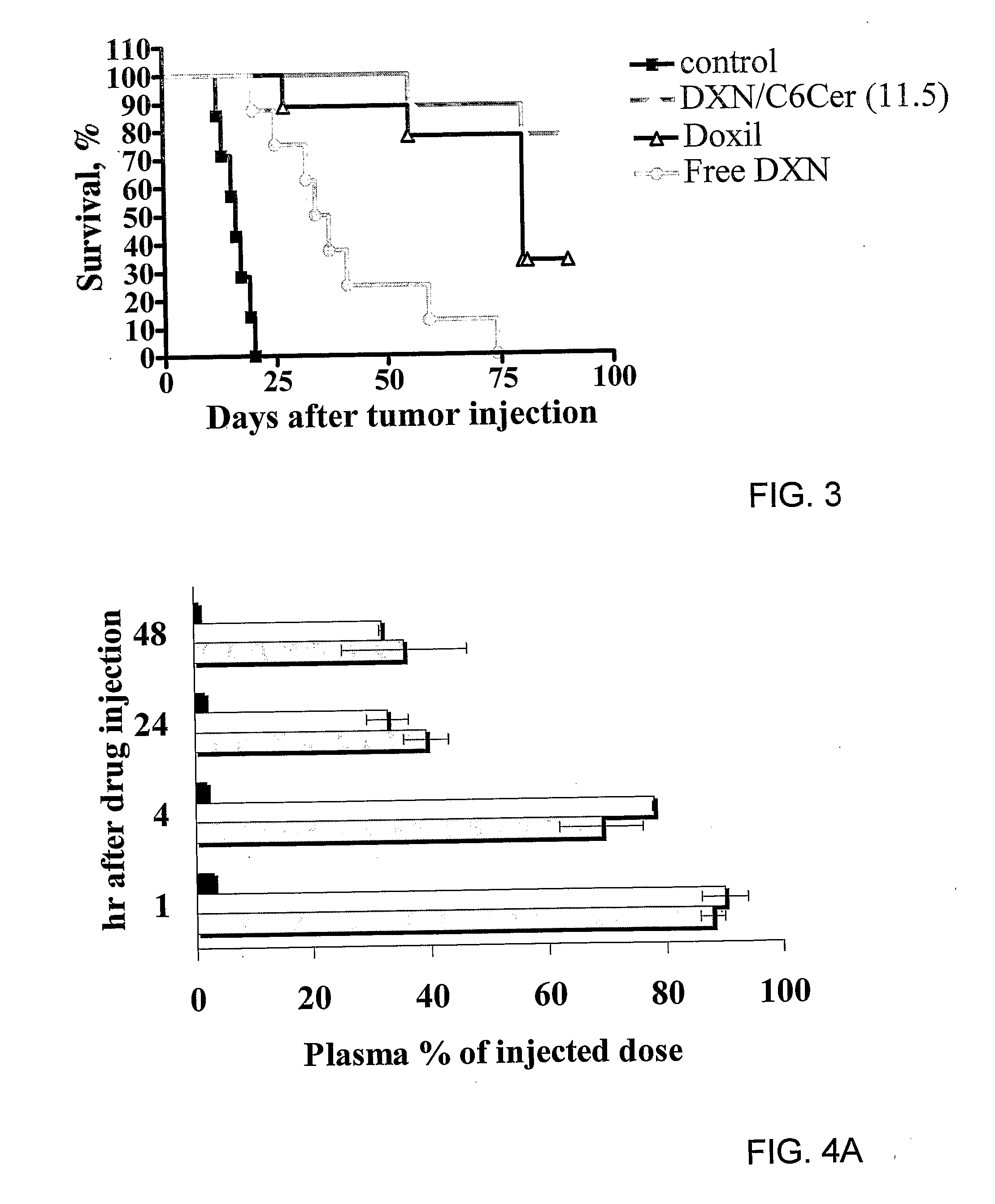
The present invention concerns a new medical treatment involving the combination of two active entities, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the two active entities. Specifically, the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a stable lipid assembly comprising as a first active entity an apoptosis-affecting lipid which does not self-aggregate in a polar environment to form liposomes and a lipopolymer. The pharmaceutical composition further comprises, as the second active entity, a cytotoxic amphipathic weak base drug carried by the lipid assembly or by a different liposome. According to one embodiment, the apoptotic-affecting lipid is a pro-apoptotic lipid. A preferred pro-apoptotic lipid is ceramide, preferably C6-ceramide. The cytotoxic amphipathic weak base drug is preferably doxorubicin or a biologically active, anthracyline-based doxorubicin analog thereof.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM LTD
Method of treating cancer using dichloroacetate
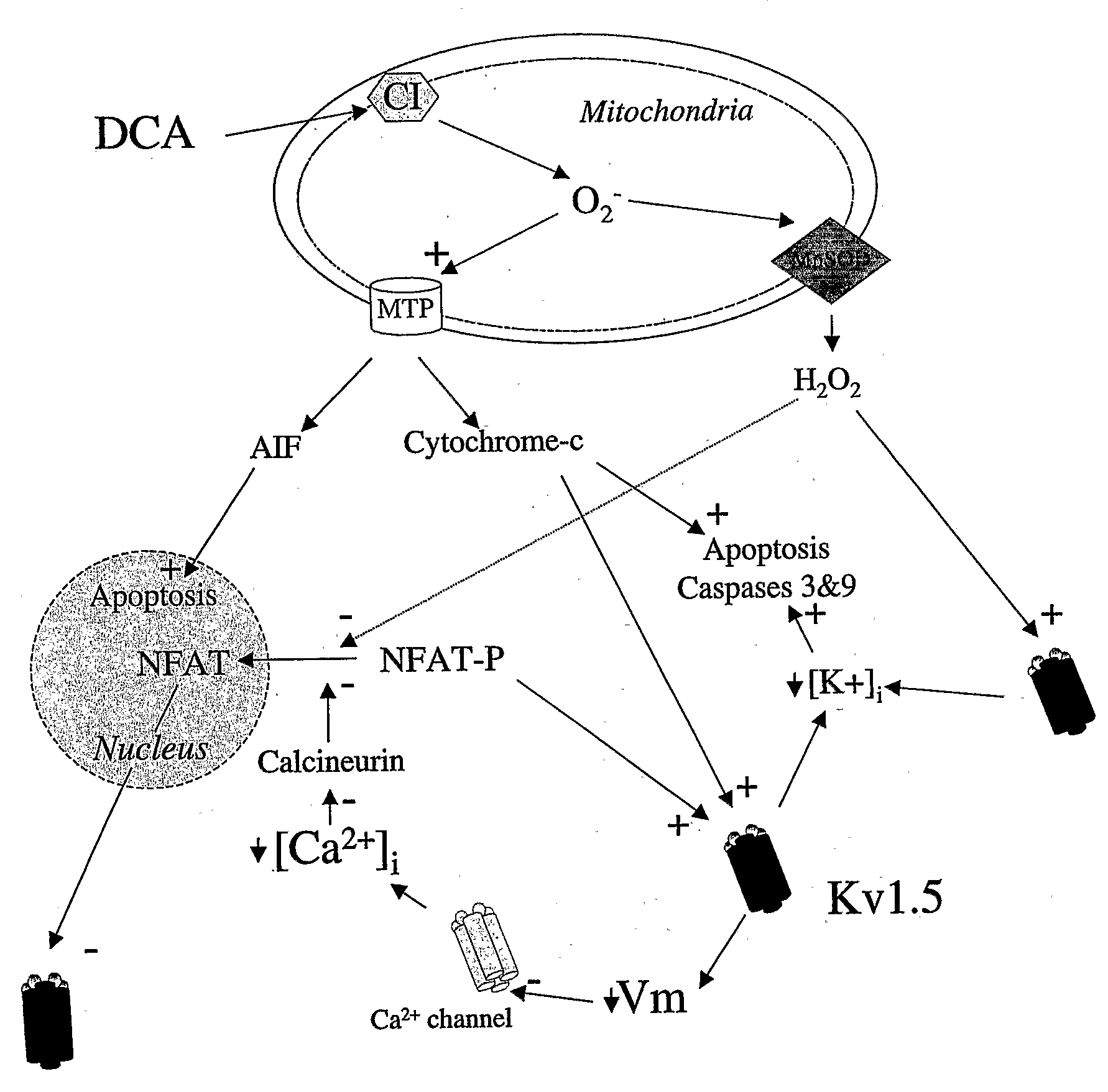
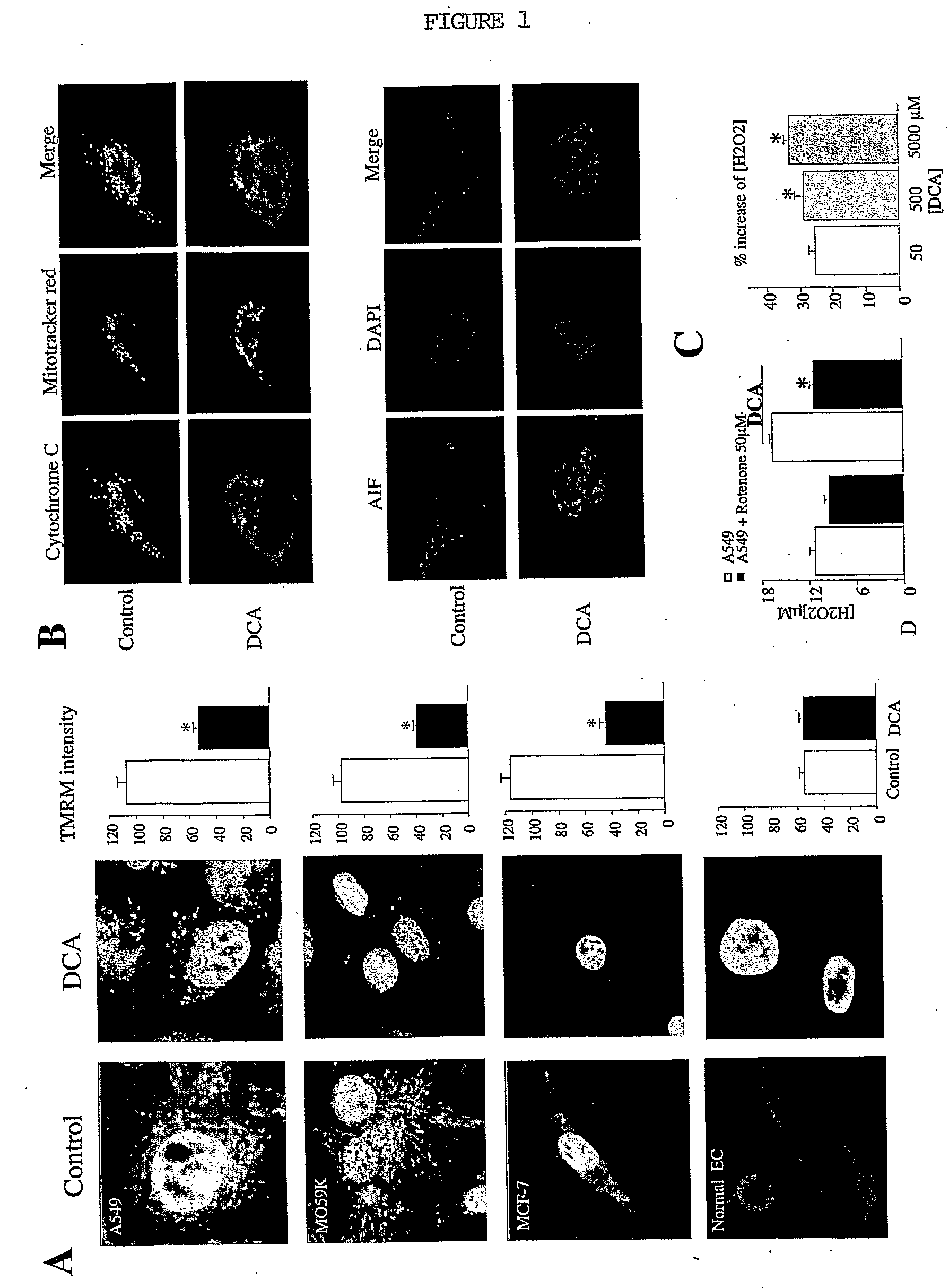
The invention relates to the use of dichloroacetate and chemical equivalents thereof for the treatment of cancer by inducing apoptosis or reversing apoptosis-resistance in a cell Preferably, the dosage is 10-100 mg / kg Preferably, sodium dichloroacetate is used. The dichloroacetate may optionally be given in combination with a pro-apoptotic agent and / or a chemotherapeutic agent Preferably, the cancers treated are non-small cell lung cancer, glioblastoma and breast carcinoma.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
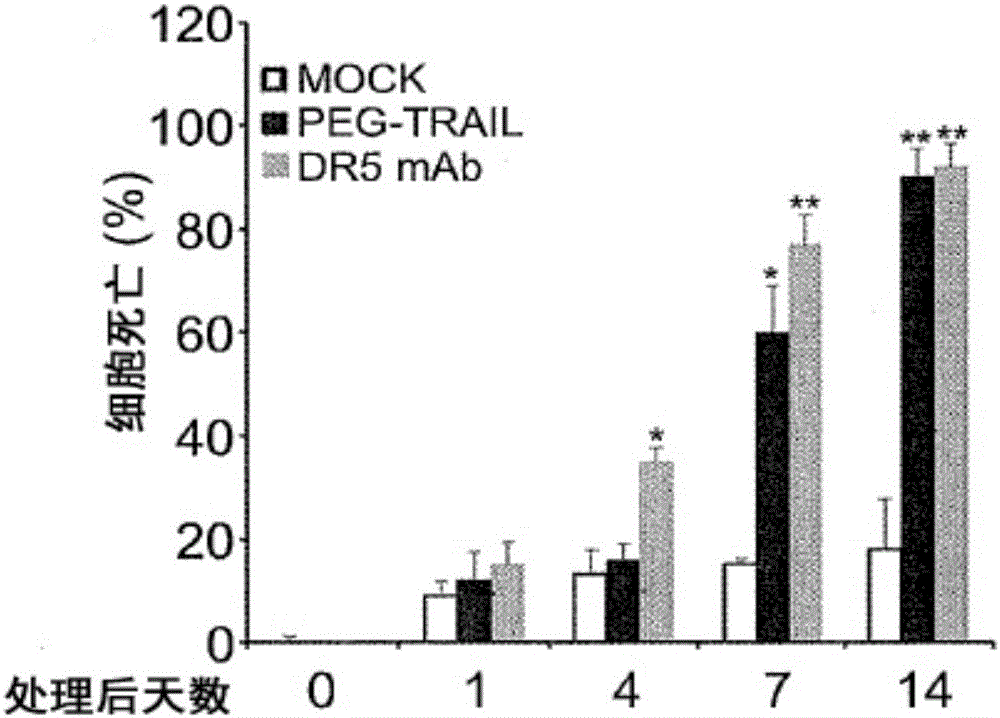
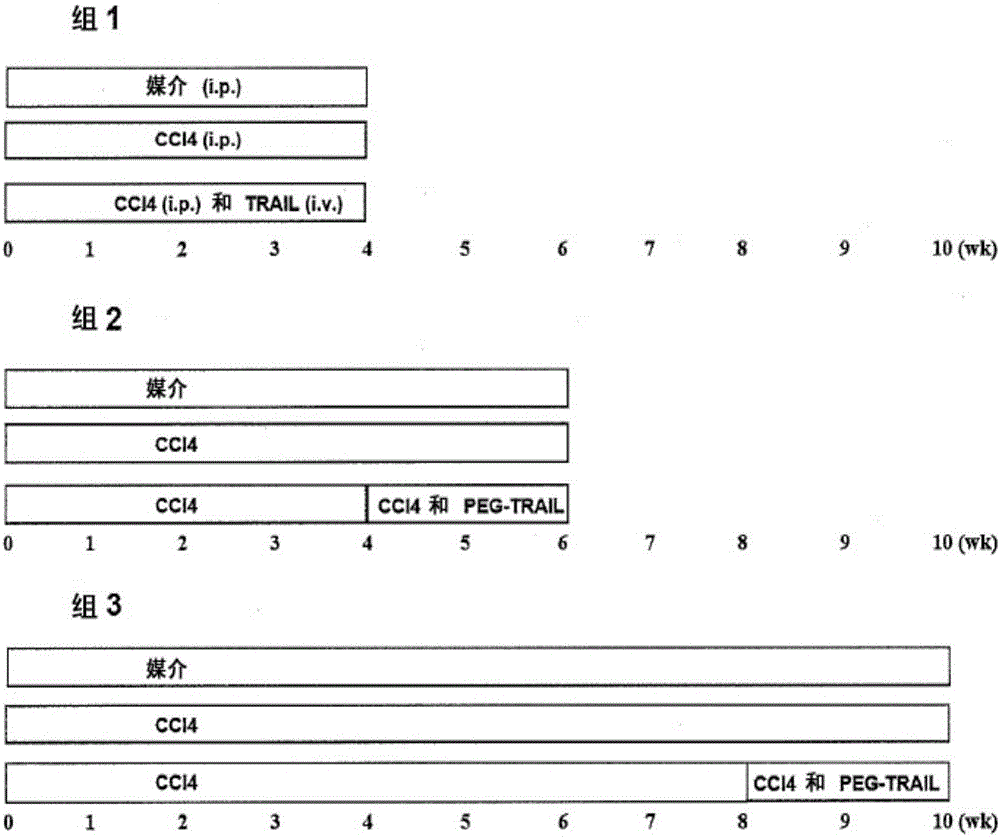
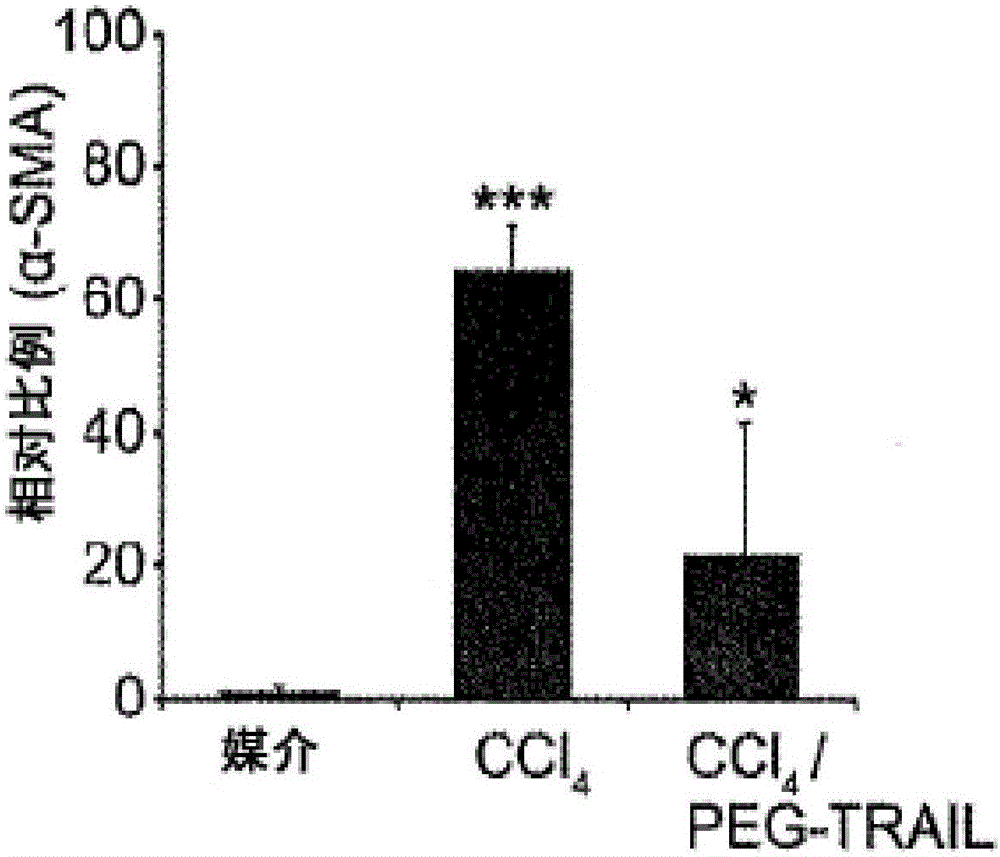
Trail receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic disease
ActiveUS20160022776A1Reduce the amount requiredUnwanted scarringPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTrail r1
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:D&D PHARMATECH INC
TRAIL receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic diseases
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:B&L DELIPHARM CORP
Alkoxyl terminal group oligo-PEG modified aminopyrimidine derivative and antitumor application
ActiveCN107098909APromote apoptosisTherapeuticOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivative that is represented as the formula (I), which has significant growth inhibiting effect, apoptosis promoting effect and cell proliferation alleviating effect on tumor cells, can be used for preventing and / or treating tumor related diseases, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Gene therapy of tumors using non-viral delivery system
InactiveUS7157098B1Reduce lung cancer mortalityReduction in formation of tumorIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDispersion deliveryAbnormal tissue growthLipid formation
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising: (a) cationic lipids, wherein said lipids are a liposomal mixture of a diacyl-ethyl-phosphocholine and 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; and (b) a plasmid cDNA sequence encoding a protein having tumor suppressor or pro-apoptotic activity. This composition has a high gene transfection efficiency at non-toxic doses and is designed to transfect human bronchial premalignant lesions and early endo-bronchial malignancies. Also provided is a method of method of treating a cancerous or pre-cancerous condition of the respiratory tract in an individual in need of such treatment, comprising the step of administering to said individual a pharmacologically effective dose of a pharmaceutical composition, comprising: (a) cationic lipids, wherein said lipids are a liposomal mixture of a diacyl-ethyl-phosphocholine and 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; and (b) a plasmid cDNA sequence encoding a protein having tumor suppressor or pro-apoptotic activity.
Owner:PEREZ SOLER ROMAN +1
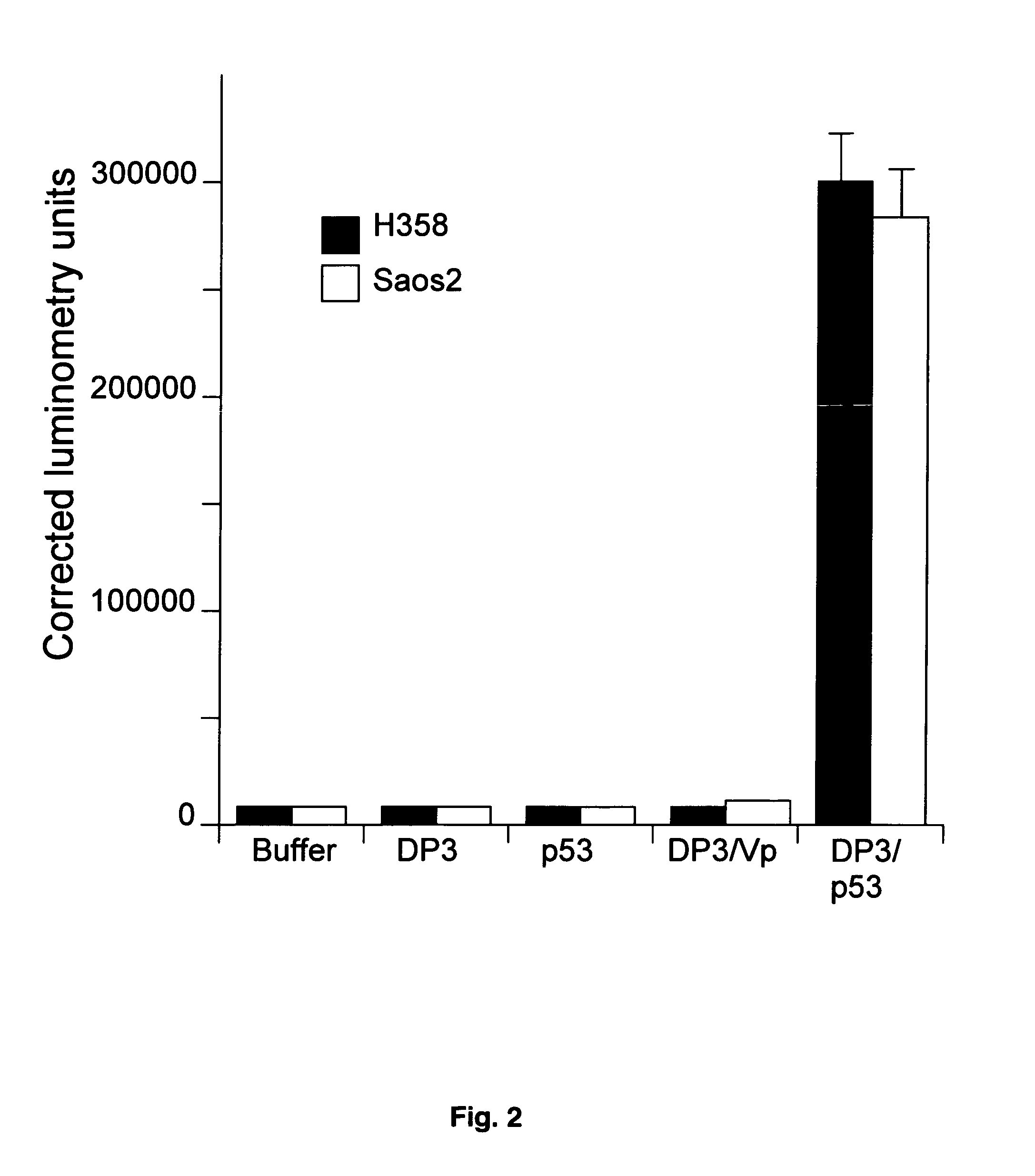
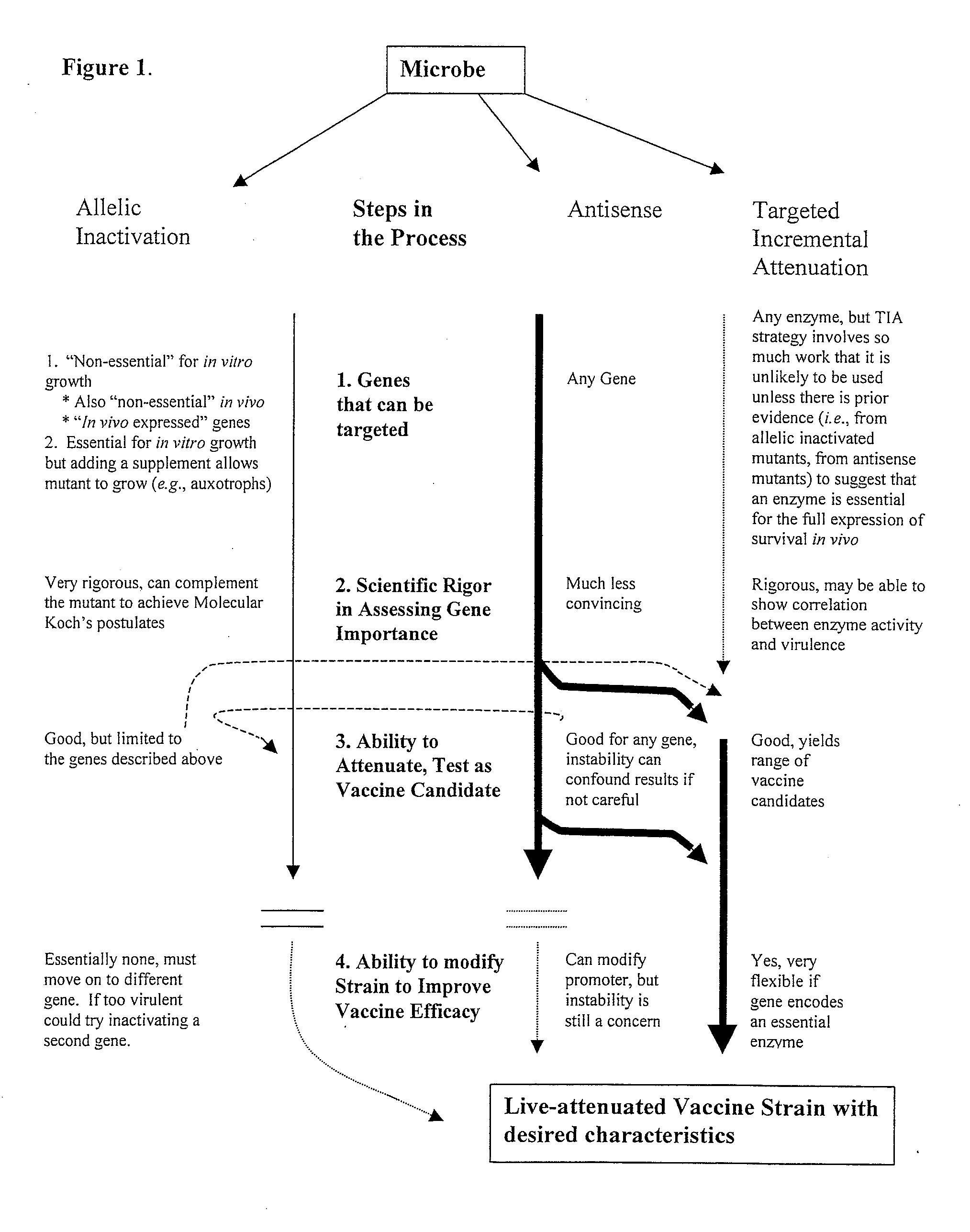
Pro-Apoptotic Bacterial Vaccines To Enhance Cellular Immune Responses
InactiveUS20120276144A1Diminishing intracellular survivalReduced activityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccine PotencyVaccine efficacy
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for their use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria. The present invention involves a method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme is reduced, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity. Also, the present invention provides a method of incrementally modifying enzyme activity to produce incrementally attenuated mutants of the microbe from which an effective vaccine candidate can be selected.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Application of pentacyclic triterpene compound and medicine composition
InactiveCN105497041AStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHalogenHydrogen
The invention discloses application of a pentacyclic triterpene compound and a medicine composition, and further discloses the pentacyclic triterpene compound shown in the formula A or the formula B in the specification, and application of a stereoisomer or a tautomer or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate or polymorph of the pentacyclic triterpene compound in preparing medicine for treating diseases (especially cancer) caused by cell apoptosis or cell damage and a BCL-XL inhibitor. R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, R8, R9, R10 and R11 are independently selected from one of hydroxyl, hydrogen, halogen, COR13, COOR14, C1-C4 alkoxy and C1-C4 alkyl, and R6, R12, R13 and R14 are independently selected from hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl. The pentacyclic triterpene compound has higher inhibitory activity on binding between BCL-XL and pro-apoptosis protein and has guiding significance on design and research and development of the medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
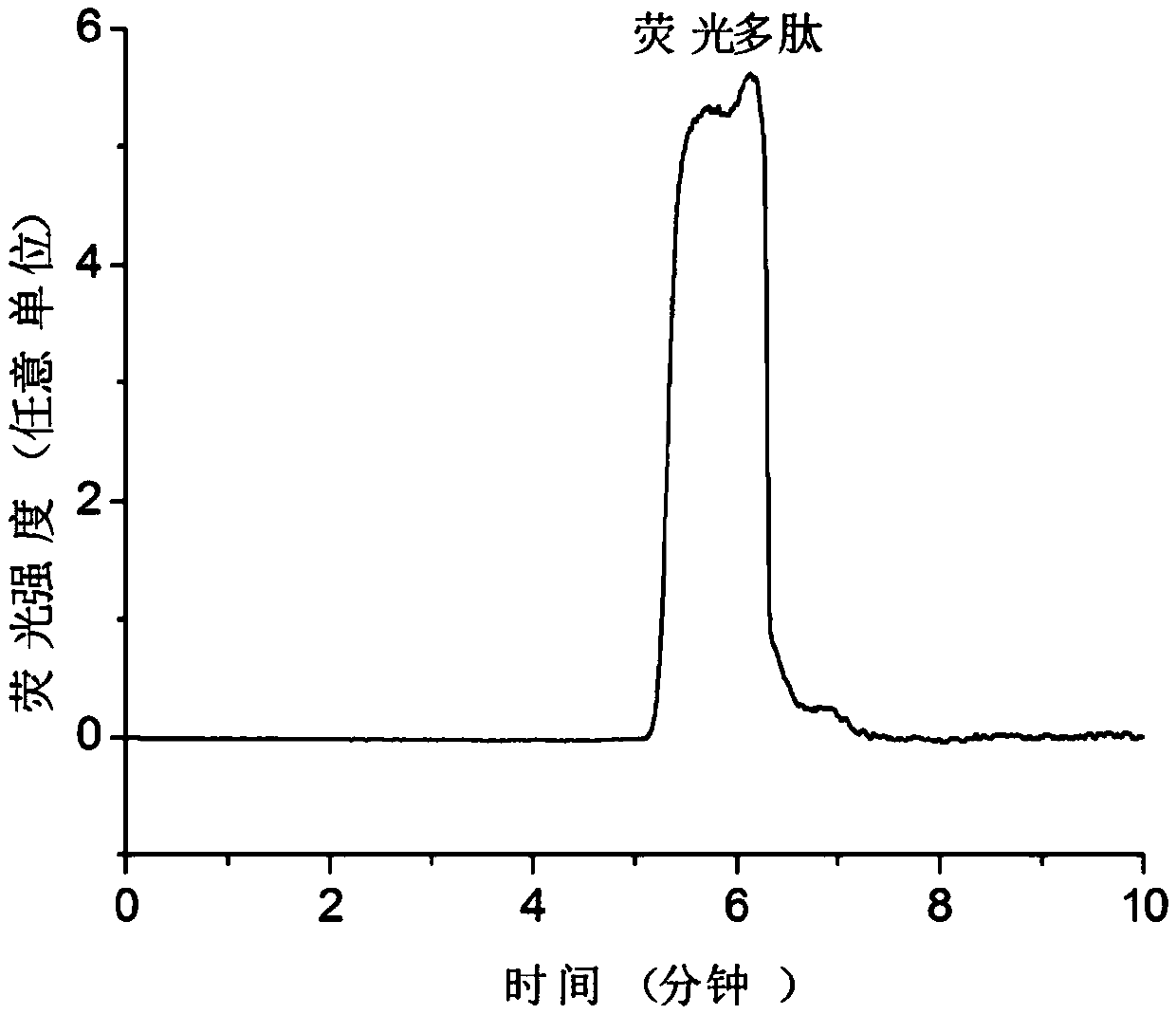
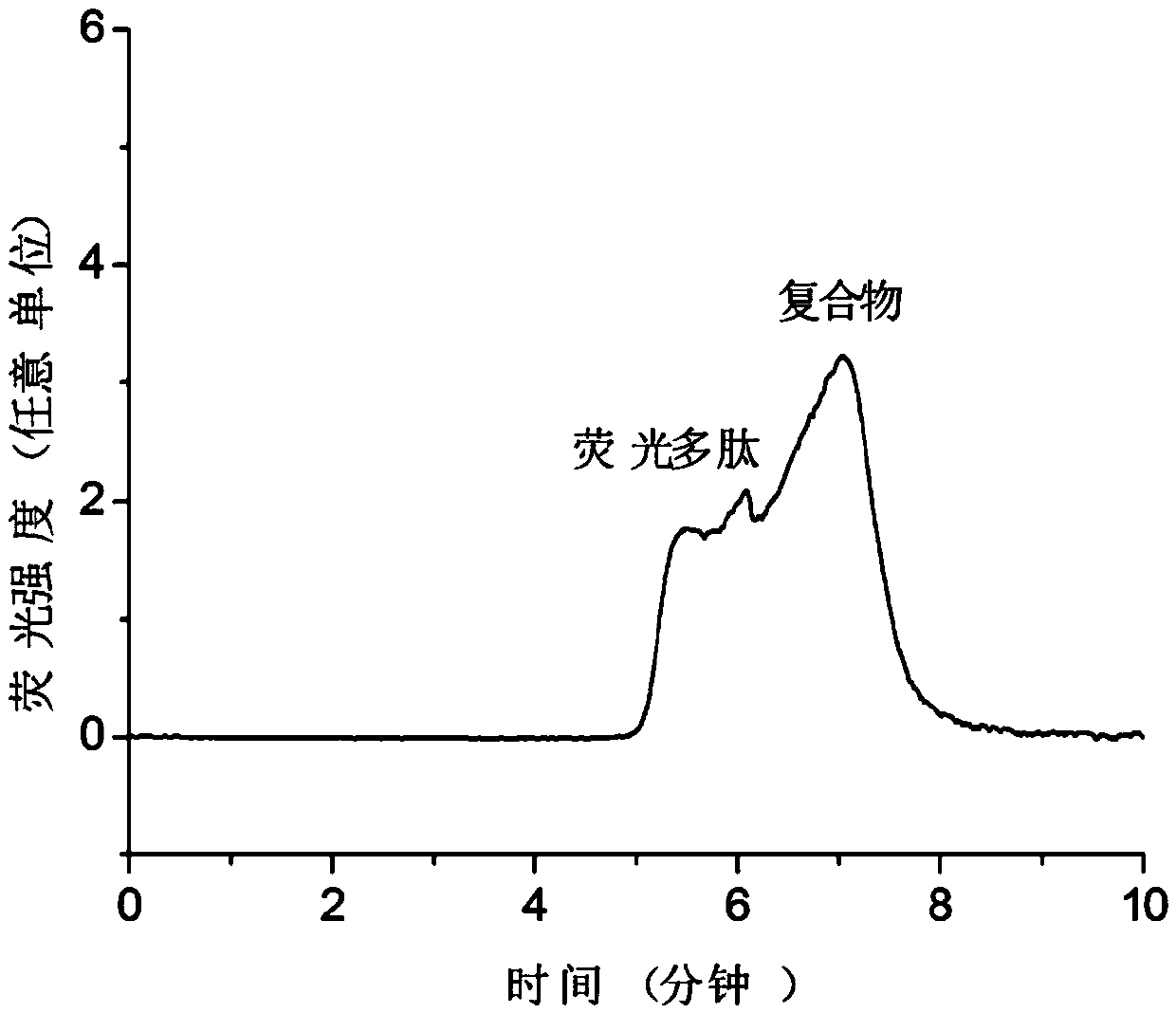
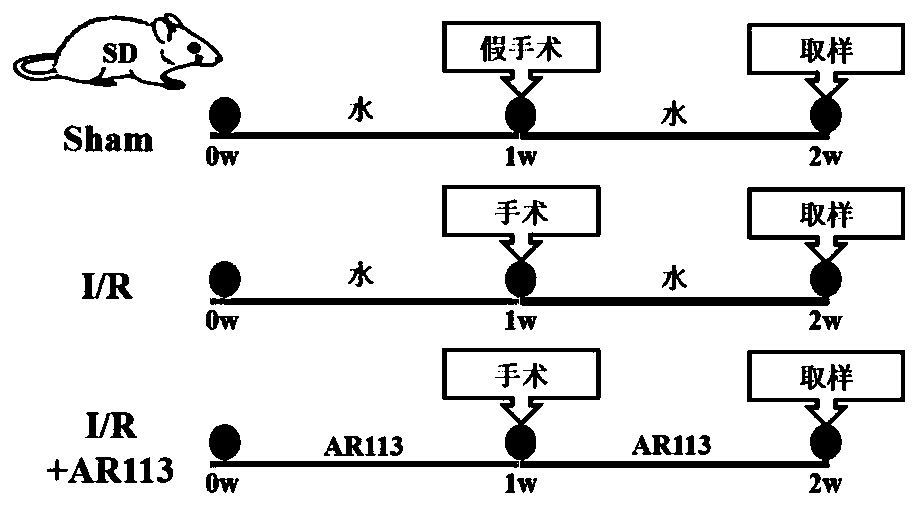
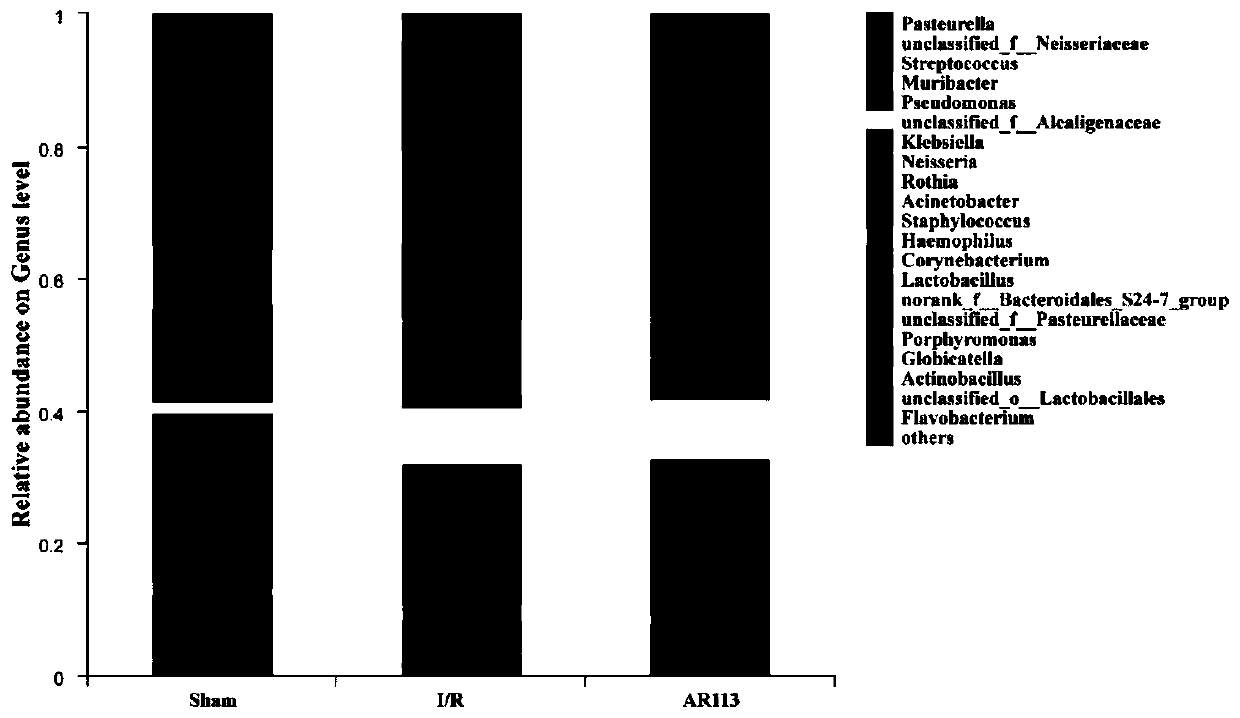
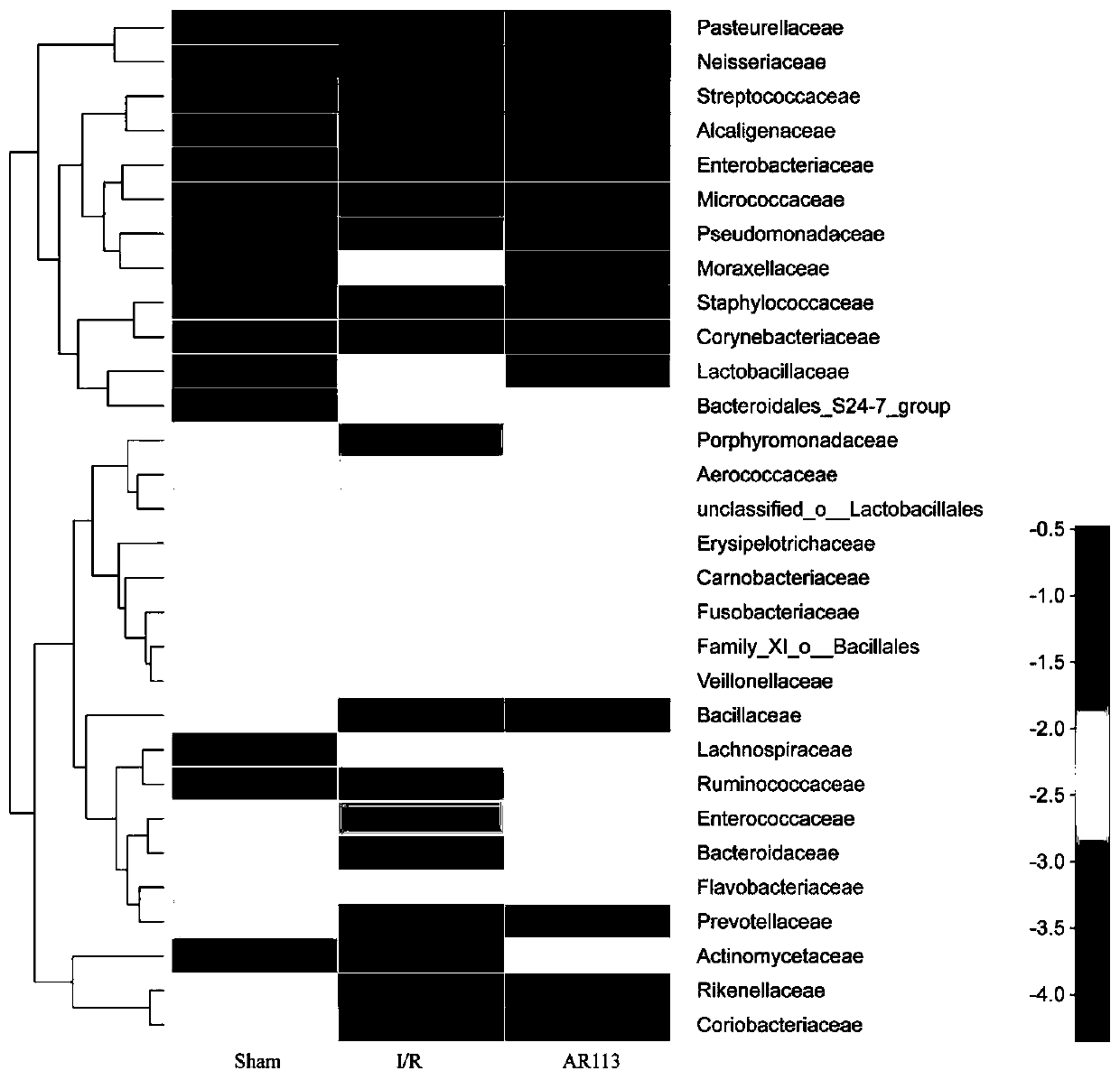
Lactobacillus plantarum with protection function on stroke
The invention provides a lactobacillus plantarum AR113 strain with a protection function on stroke. The lactobacillus plantarum AR113 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 22, 2017, and the preservation number is CGMCCC No.13909. By adopting the lactobacillus plantarum AR113 strain provided by the invention is capable of improving antioxidant enzyme activities of brain tissue, reducing levels of oxidation products, activating Nrf-ARE signal channels, regulating relative expression amounts of antioxidation factors Nrf2, NQO01 and HO-1, meanwhile, reducing miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) expression of apoptosis-promoting factors Cyt-C, Caspase-3 and Bax, increasing relative expression of an anti-apoptosis factor Bcl-2, and furthermore, relievingbran cell damage caused by cerebral ischemia reperfusion.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
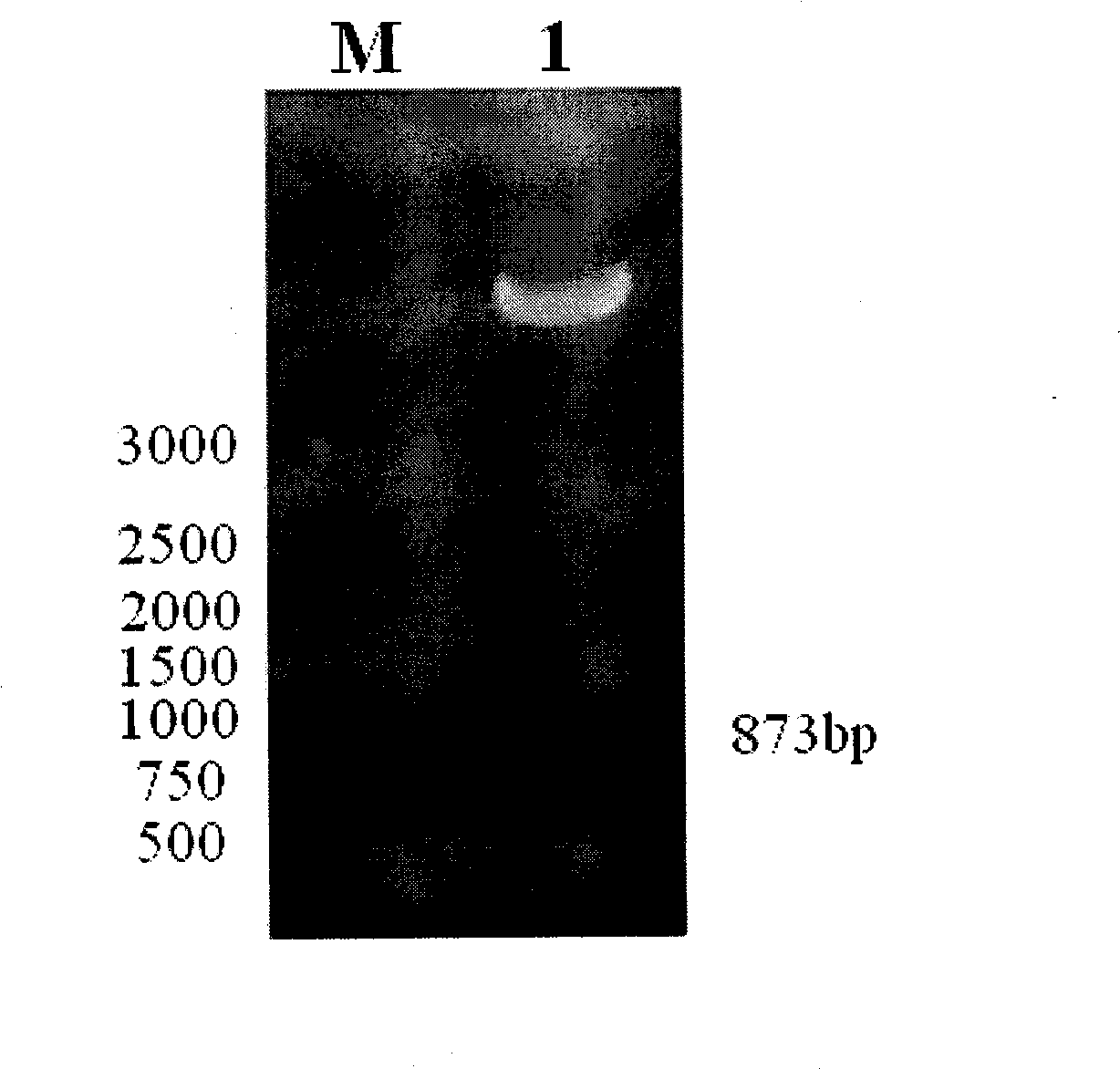
Human insulin-like growth factor conjugated protein 3 eucaryon expression vector, construction and use
InactiveCN101481705APro-apoptoticGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHuman fetalHuman insulin
The invention relates to the construction and the application of a eukaryotic expression vector of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 which is named as pCI-IGFBP-3. Sequence 1 is obtained through the recombination of human IGFBP-3 gene fragment and eukaryotic expression vector pCI-neo. The sequence 1 is summed up to 6399bp, wherein, IGFBP-3 sequence 3 containing 873bp is inserted between 1101bp and 1974bp. Primers are designed by the invention according to the cDNA sequence of human IGFBP-3 in Genbank. Human fetal liver cDNA library is used as a template to obtain an IGFBP-3cDNA sequence containing single peptide sequence by a pCR method in a cloning way. Target genes are directionally inserted into the eukaryotic expression vector pCI-neo by the double digestion of EcoR I and Xba I. The secretory IGFBP-3 eukaryotic expression vector is constructed successfully. Experimental results show that the eukaryotic expression vector of the human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 can secrete and express IGFBP-3 with biological activities in eukaryotic cells. The secreted and expressed IGFBP-3 directly acts on host cells to play a role of promoting apoptosis. The construction and the application of the eukaryotic expression vector of the human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 are clinically applied to the preparation of antitumor drugs with the IGFBP-3 eukaryotic expression vector as the effective component and lay the foundation for the development of naked plasmid anti-oncogene therapeutic drugs.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
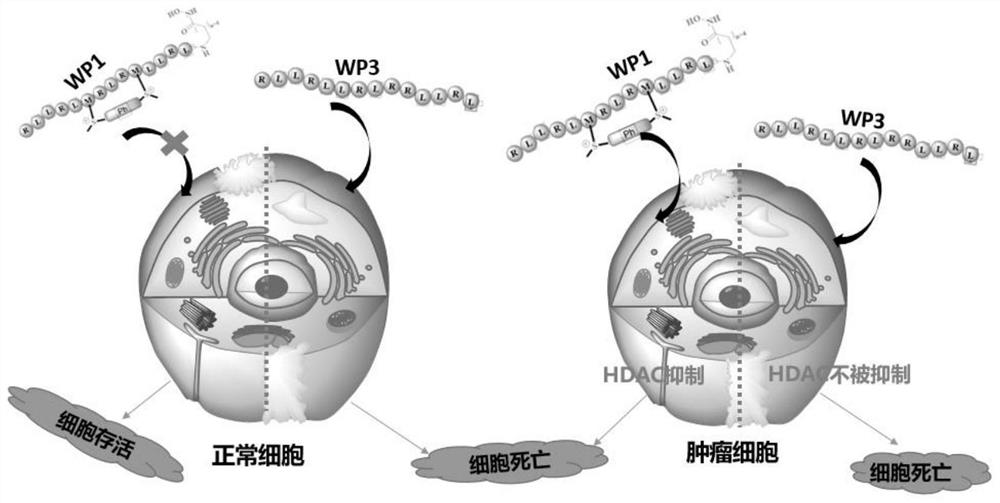
Sulfonium salt-based stable HDAC-targeting polypeptide drug conjugate and application thereof
ActiveCN114146186AIncrease lethalityMaintain anti-tumor effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMalignancySulfonium
The invention relates to a sulfonium salt stable targeting HDAC polypeptide drug conjugate and application thereof, a sulfonium salt stable apoptosis-promoting polypeptide is coupled with an HDAC inhibitor to form a stable polypeptide HDAC inhibitor with tumor selective toxicity, the nonspecific toxicity of apoptosis polypeptide chemically stabilized by sulfonium salt is remarkably reduced, the stability of protease is higher, and the tumor selective toxicity of the apoptosis polypeptide is remarkably reduced. When a polypeptide drug conjugate is formed by coupling with an HDAC inhibitor, the polypeptide drug can significantly improve the selective toxicity to tumor cells, and has weak toxicity to normal cells. Cell proliferation, cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest experiments prove that the polypeptide can effectively inhibit proliferation of malignant liver cancer, has relatively good biological safety and has a potential anti-tumor clinical application prospect.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Method for predicting tumor recurrence
InactiveUS7238492B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingComputational physiologyTumor recurrence
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Compound medicine composite with breast cancer resistance function, application of composite and medicine based on composite
ActiveCN109620836ASmall toxicityGood synergistic pharmacological effectAntineoplastic agentsSexual disorderDrugDoxorubicin
The invention discloses a compound medicine composite with a breast cancer resistance function, application of the composite and medicine based on the composite. The active content of the compound medicine composite is composed of doxorubicin and piperlongumine with the mole ratio of 1:5-1:15. According to an experiment, an MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell is used as a model, and through an MTTexperiment, by applying CompuSyn software analysis, it is discovered that a good synergistic effect is achieved during compatibility of doxorubicin and piperlongumine with the mole ratio of 1:10; through a cell apoptosis experiment, it is discovered that the apoptosis-promoting effect is obviously superior that that of a single medicine group when the two kinds of medicines cooperate for use; through a naked mouse cancer-bearing medicine application experiment, it is discovered that growth of heterograft tumors of MDA-MB-231 cells in the naked mouse can be effectively inhibited through a medicine cooperation application group, and the effect of the medicine cooperation application group is obviously superior that that of the single medicine group. In this way, medicine cooperation application of doxorubicin and piperlongumine has the high function of inhibiting the breast cancer through cooperation, and accordingly the composite has good clinical medicine application development prospects.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Drug-loading nano-liposome, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104922067AImprove stabilityEasy to removeOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor therapyTherapeutic effect
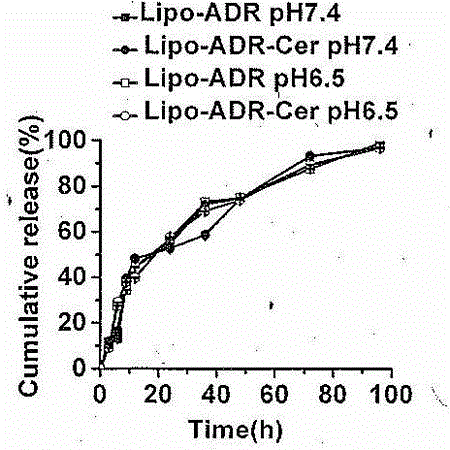
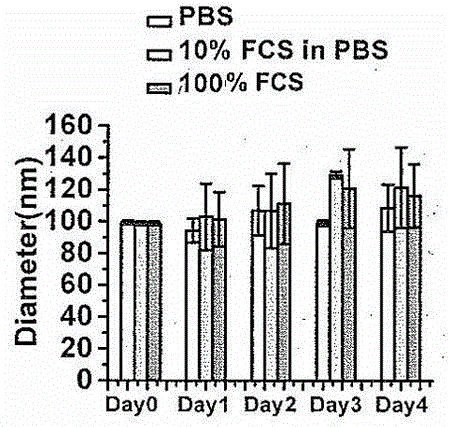
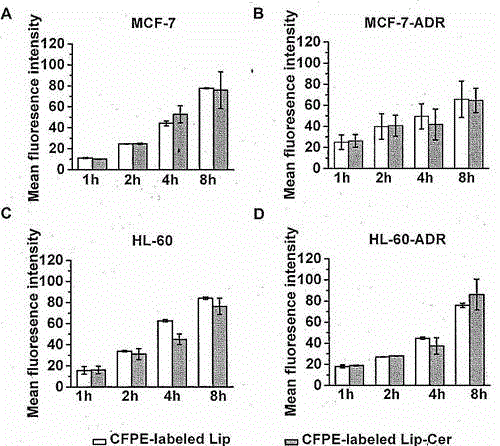
The invention discloses a drug-loading nano-liposome, and a preparation method and application thereof. The invention relates to the field of synthesis and treatment of nano-liposomes, in particular to a nano-liposome co-loading PEG-C16-ceramide and adriamycin, the preparation method of the nano-liposome, and the application of the nano-liposome to the field of tumor treatment. The nano-liposome (Lipo-ADR-Cer) co-loading the PEG-C16-ceramide and the adriamycin is constructed, the preparation method and the stability of the Lipo-ADR-Cer are disclosed, and the basic representation, the in-vitro release process and the in-vitro cell transfection endocytosis efficiency of the liposome are not changed. In terms of tumor drug-resistant cell strains, the in-vitro cytotoxicity, the in-vitro apoptosis-promoting ability and the in-vivo treatment effect of the Lipo-ADR-Cer are improved. The PEG-C16-ceramide and the adriamycin can be co-loaded, the adriamycin IC50 of the drug-resistant cells can be reduced, and the nano-liposome can be used for treating drug-resistant tumor cells.
Owner:TAIZHOU MABTECH PHARM CO LTD
Therapeutic pro-apoptotic BH3-like molecules and methods for generating and/or selecting the same
InactiveUS8686110B2Inhibit functioningInhibitory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesApoptosisCancer cell apoptosis
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
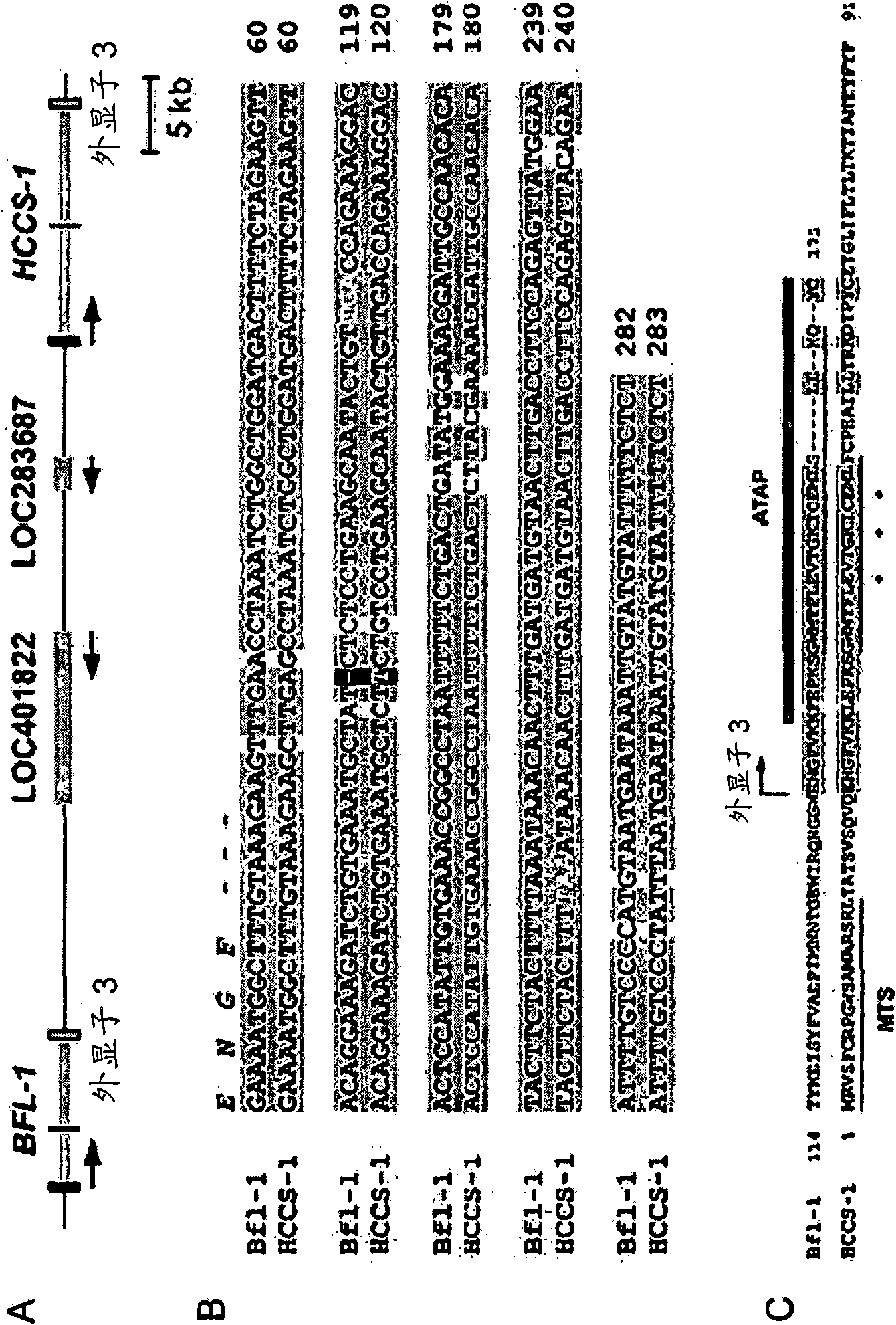
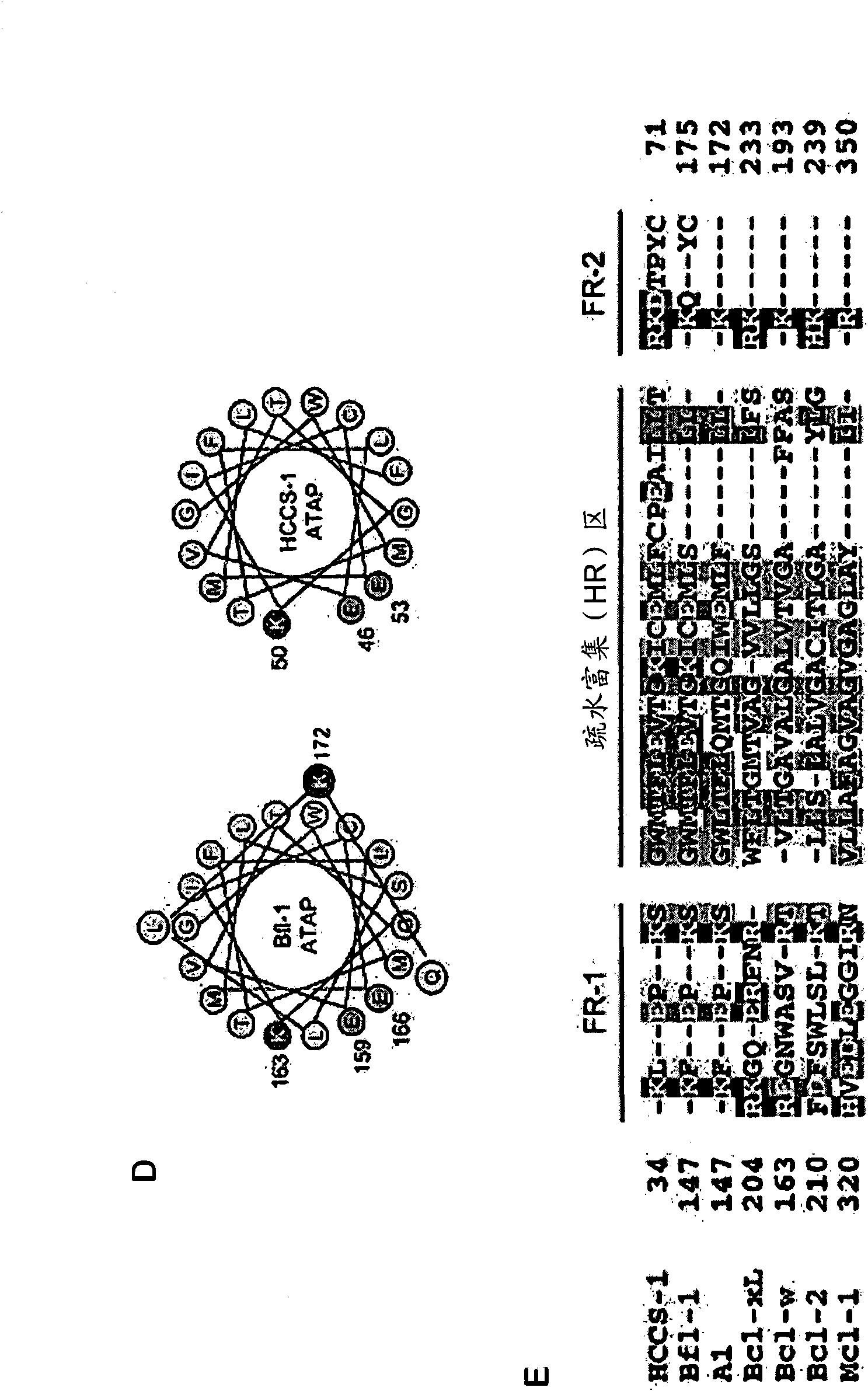
Atap peptides, nucleic acids encoding the same and associated methods of use
InactiveCN101557818AAntibacterial agentsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifADAMTS ProteinsNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are nucleic acid sequences that encode pro-apoptotic polypeptides. Also disclosed are polypeptides encoded by these nucleic acid sequences, and antibodies, which immunospecifically-bind to the polypeptide, as well as derivatives, variants, mutants, or fragments of the aforementioned polypeptide, polynucleotide, or antibody. The invention further discloses therapeutic, diagnostic and research methods for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of proliferative disorders and bacterial infections using the nucleic acids and proteins of the invention.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Solid dispersions containing an apoptosis-promoting agent
InactiveCN102802607AConvenient route of administrationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOral medication
A pro-apoptotic solid dispersion comprises, in essentially non-crystalline form, a Bcl-2 family protein inhibitory compound, e.g., ABT-263, dispersed in a solid matrix that comprises (a) a pharmaceutically acceptable water-soluble polymeric carrier and (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable surfactant. A process for preparing such a solid dispersion comprises dissolving the compound, the polymeric carrier and the surfactant in a suitable solvent, and removing the solvent to provide a solid matrix comprising the polymeric carrier and the surfactant and having the compound dispersed in essentially non-crystalline form therein. The solid dispersion is suitable for oral administration to a subject in need thereof for treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Use of pro-apoptotic factors in treatment of atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20010053769A1Reduce inflammationIncreased apoptosisBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAtheromaLesion
The present invention features a novel method of treating vascular disease that involves modifying smooth muscle cells to express a gene encoding a protein having both anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic activity. Preferably, the protein of the invention also has an anti-proliferative effect in smooth muscle cells. In general, the method is useful in preparing vascularized organs and vessels for transplant into a patient. Alternatively, the present invention can be applied to treat atherosclerotic lesions in damaged vessels.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Pro-apoptotic bacterial vaccines to enhance cellular immune responses
InactiveUS8021671B2Improves vaccine efficacyDiminishing intracellular survivalAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesApoptosis
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for their use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria. The present invention involves a method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme is reduced, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity. Also, the present invention provides a method of incrementally modifying enzyme activity to produce incrementally attenuated mutants of the microbe from which an effective vaccine candidate can be selected.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
Influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide-containing targeted recombinant molecule gene, protein encoded thereby and application thereof
InactiveCN101979594AEfficient pro-apoptotic biological activityLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHemagglutininSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention provides an influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide-containing targeted recombinant molecule gene. The influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide-containing targeted recombinant molecule gene is formed by recombining an internalizing single-chain antibody gene, an influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide gene and an apoptotic molecule gene, wherein a gene sequence for encoding a furin protease recognition site is inserted between the internalizing single-chain antibody gene and the influenza virus hemagglutinin fusion peptide gene. A single-chain antibody part of an expression product of the targeted recombinant molecule gene of the kind can identify specificity, combines a target cell expressing a specific antigen and mediates the recombination protein internalization into the endosome of the target cell; the single-chain antibody is separated from the other parts after the recombination protein is cut by the furin protease in the endosome; the hemagglutinin fusion peptide is exposed; and the apoptotic molecule is released to cytoplasm by damaging the stability of an endosome membrane under the action of the hemagglutinin fusion peptide; and finally, the apoptotic molecule effectively induces the target cell into atopsis in the cytoplasm and embodies the biological activity of the hemagglutinin fusion peptide.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cell-penetrating peptides
ActiveUS20140364376A1Reduce doseOvercome problemsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCell biologyPro-apoptosis
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +1
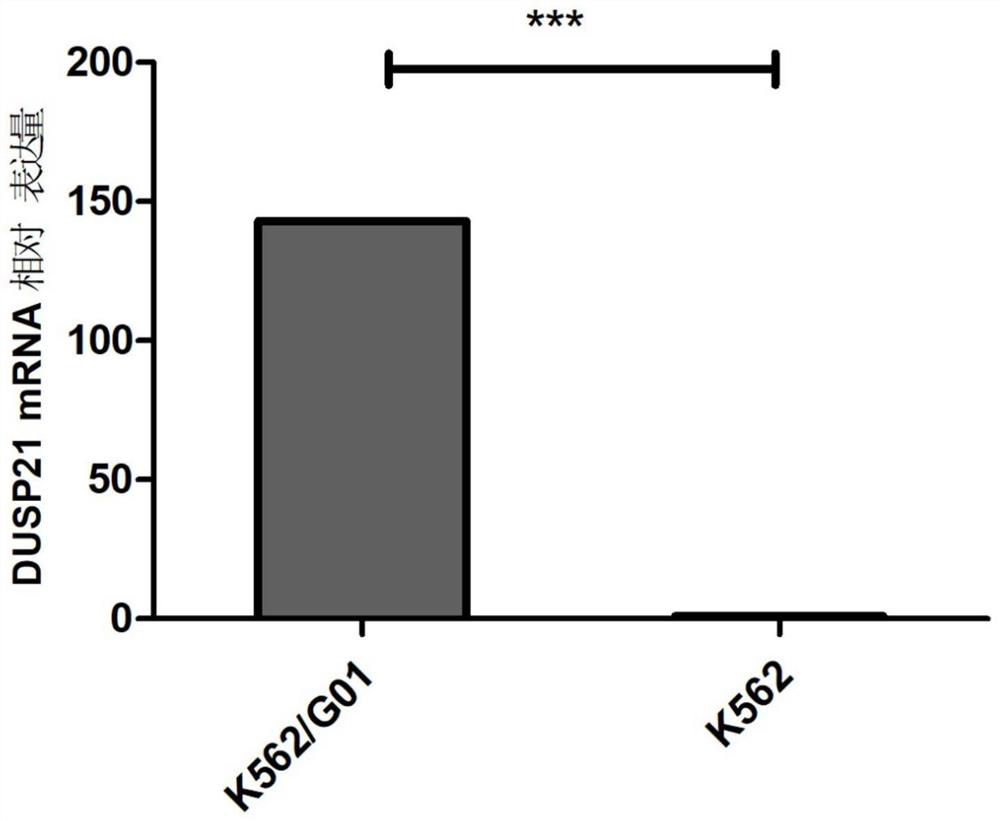
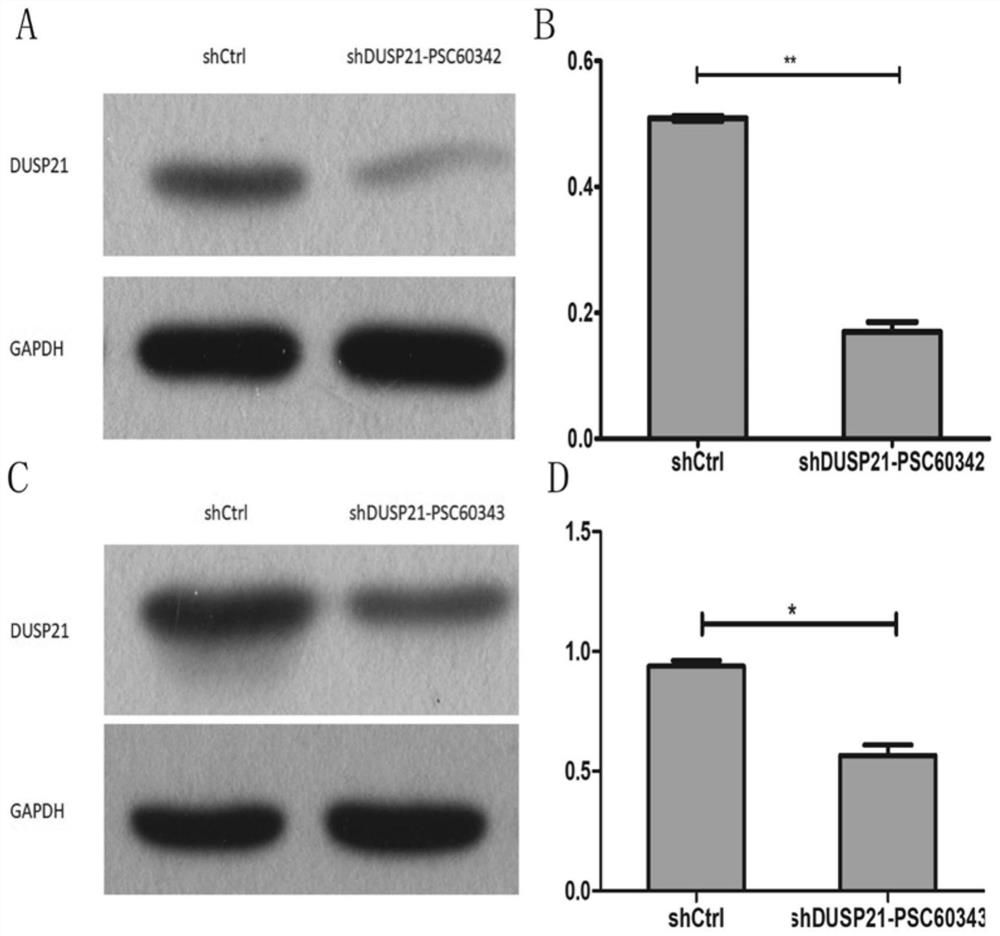
ShRNA for promoting apoptosis of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cell K562/G01 and application thereof
ActiveCN113528528APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesNew medicationsPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a novel molecular target DUSP21 for promoting apoptosis of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells (K562 / G01), and correspondingly provides shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) for inhibiting target molecules and application of the shRNA. The shRNA is psc60342 or psc60343, is a targeted DUSP21 gene and interferes with the expression of DUSP21, can inhibit the expression of DUSP21 in K562 / G01 and promote the apoptosis of K562 / G01 cells, can be applied to preparation of drugs for inhibiting the proliferation of human imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells and promoting the apoptosis, and a new way is provided for the development of new drugs for treating imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL TO NANCHANG UNIV
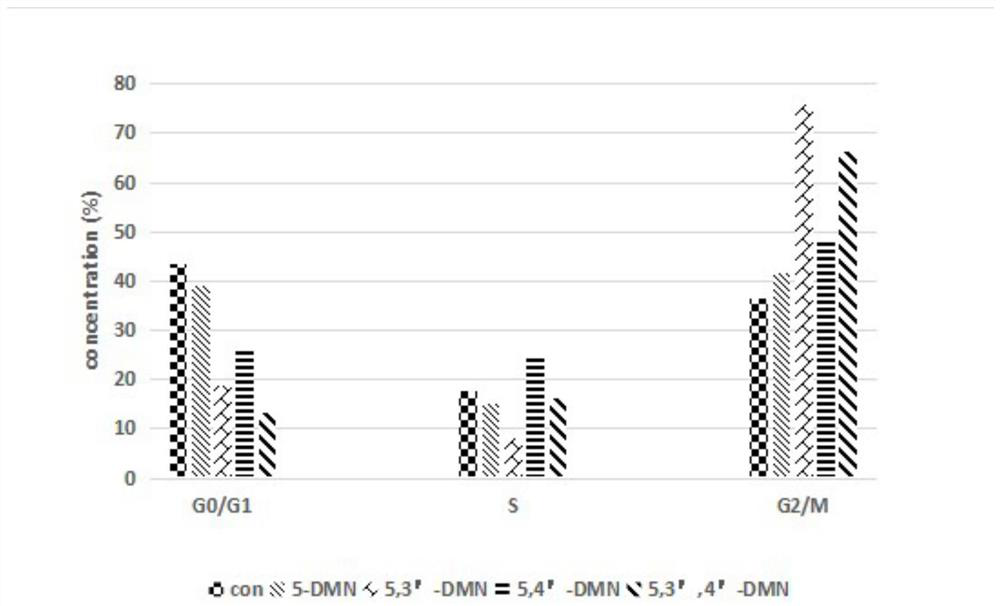
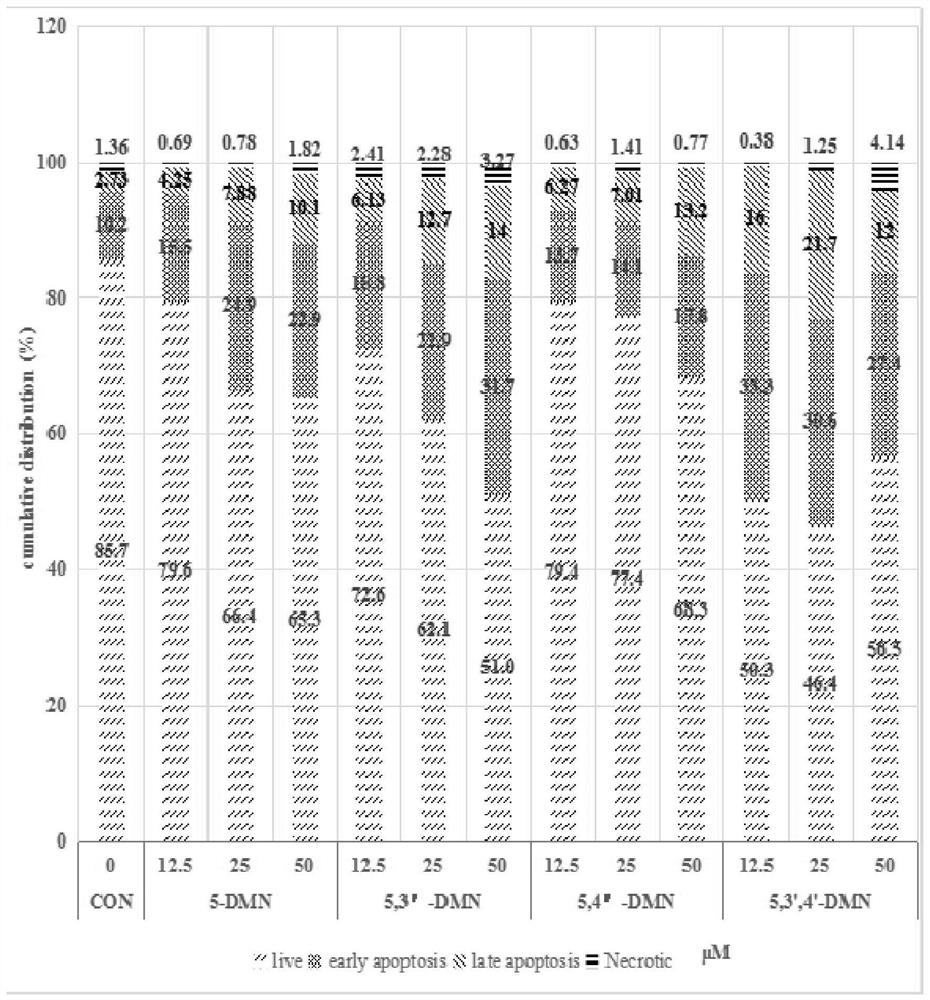
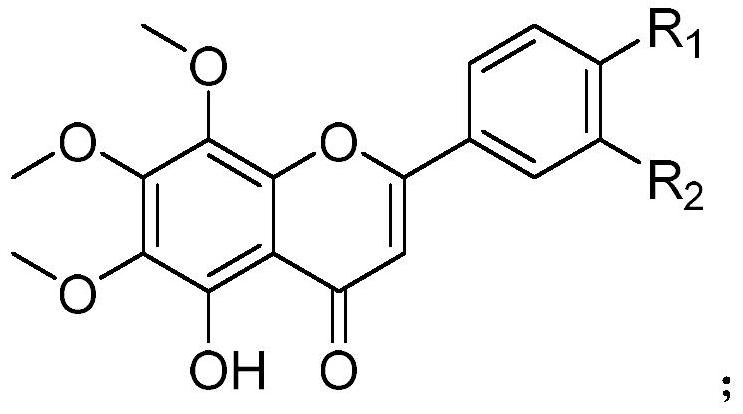
Hydroxylated polymethoxylated flavone and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112830917AHigh activityPro-apoptotic effect is goodOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsAluminium chlorideEthyl acetate
The invention provides hydroxylated polymethoxylated flavone and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structure of a compound is shown as a formula (I). The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an intermediate product 2a by using an intermediate product 1a, dissolving the intermediate product 2a in anhydrous acetonitrile, adding anhydrous aluminum chloride, adding a hydrochloric acid solution, cooling a reaction solution to room temperature, conducting extracting with ethyl acetate, carrying out drying with anhydrous Na2SO4, removing a solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product, separating and purifying the crude product with a silica gel chromatographic column, conducting recrystallizing with ethanol, and carrying out drying in vacuum to obtain a target product 3a. According to the invention, four compounds prepared in the invention are subjected to anti-proliferative activity screening, cell cycle capture experiments and cell apoptosis experiments of liver cancer cell HepG2, and the results show that the four compounds have good anti-proliferative activity and apoptosis promoting effect on HepG2 cells.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com