Patents
Literature
61 results about "Amino acids/proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins. Amino acids and proteins are the building blocks of life. When proteins are digested or broken down, amino acids are left. The human body uses amino acids to make proteins to help the body: Amino acids can also be used as a source of energy by the body.
Direct molecular diagnosis of Friedreich ataxia
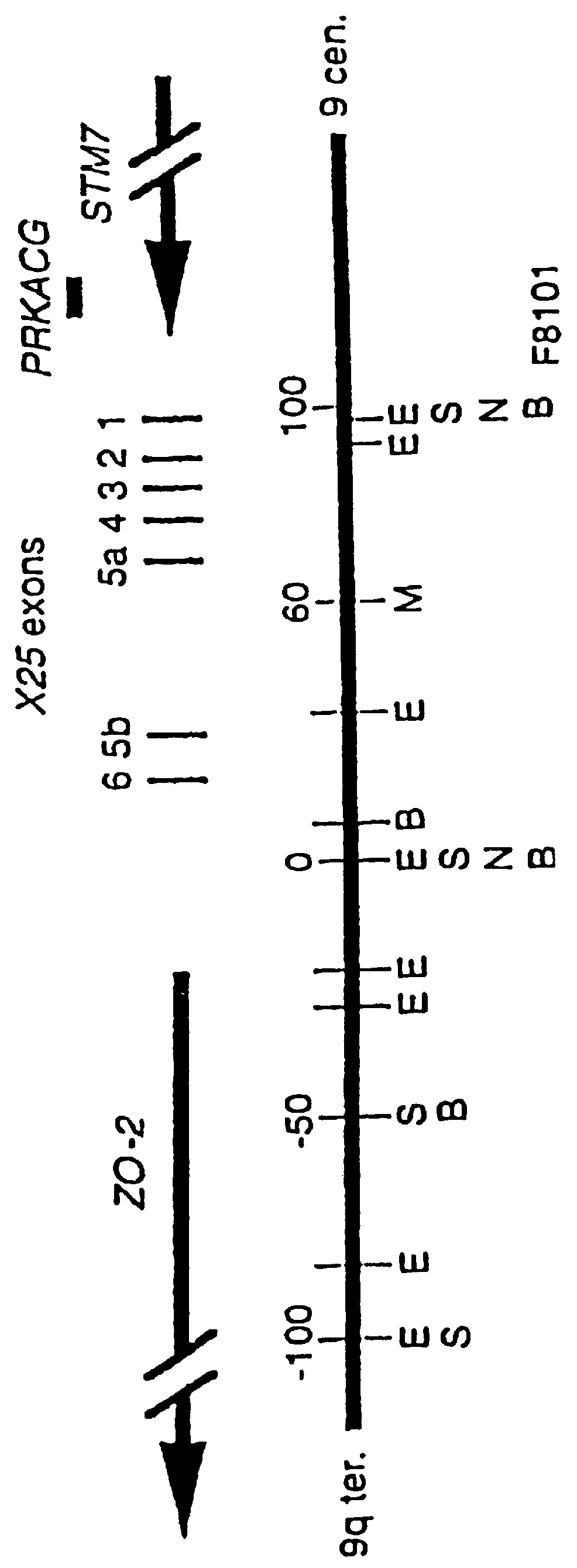
This invention relates generally to methods for the diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of Friedreich Ataxia. Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal recessive, degenerative disease that involves the central and peripheral nervous system and the heart. A gene, X25, was identified in the critical region for the FRDA locus on chromosome 9q13. The gene encodes a 210 amino acid protein, frataxin, that has homologues in distant species such as C. elegans and yeast. A few FRDA patients have been found to have point mutations in X25, but the vast majority are homozygous for a variable, unstable GAA trinucleotide expansion in the first X25 intron. Mature X25 mRNA was severely reduced in abundance in individuals with FRDA. Carriers and individuals at risk for developing FRDA can be ascertained by the methods of the present invention. Further, the methods of the present invention provide treatment to those individuals having FRDA.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Peptides derived from STEAP1
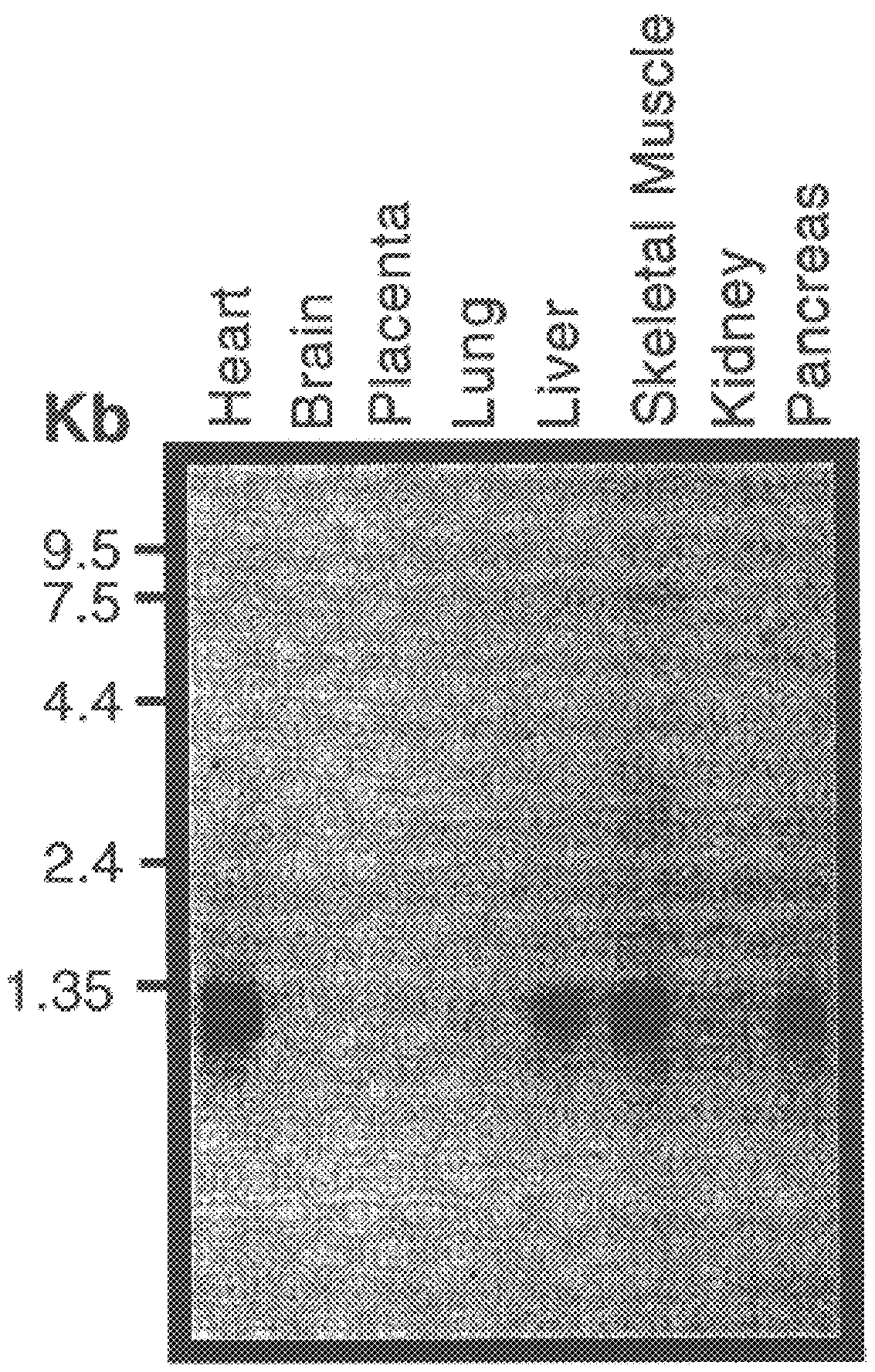
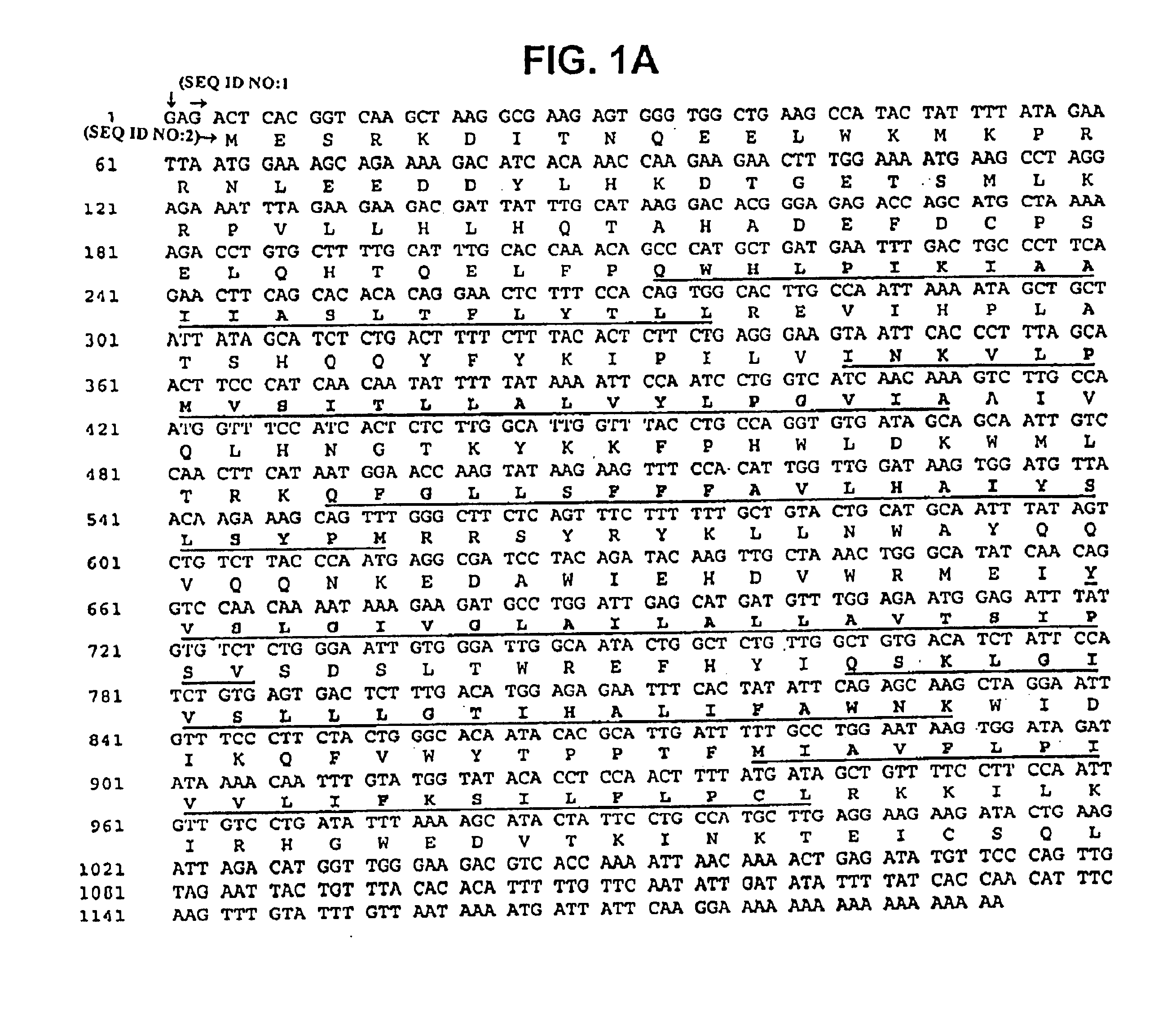
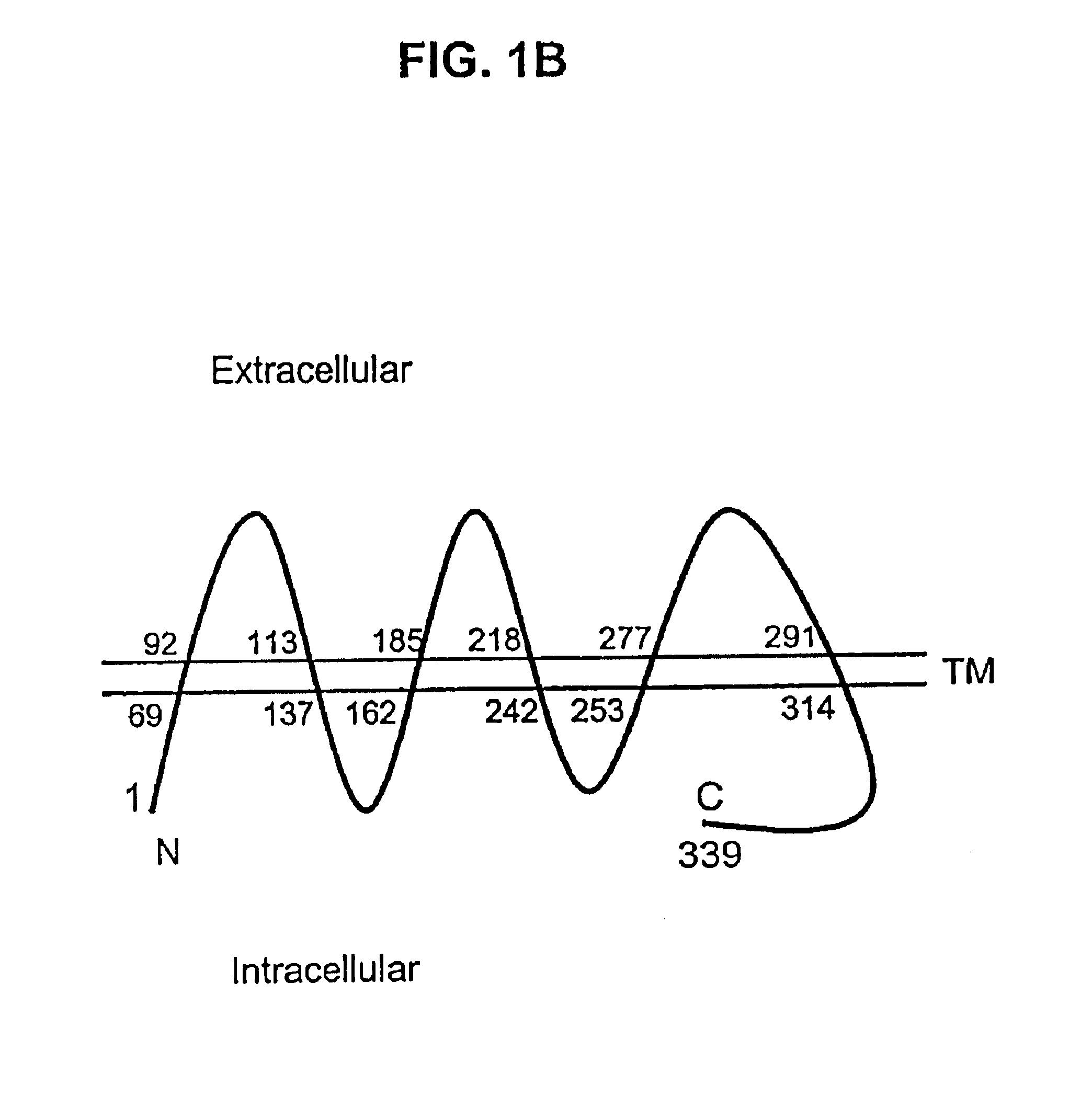
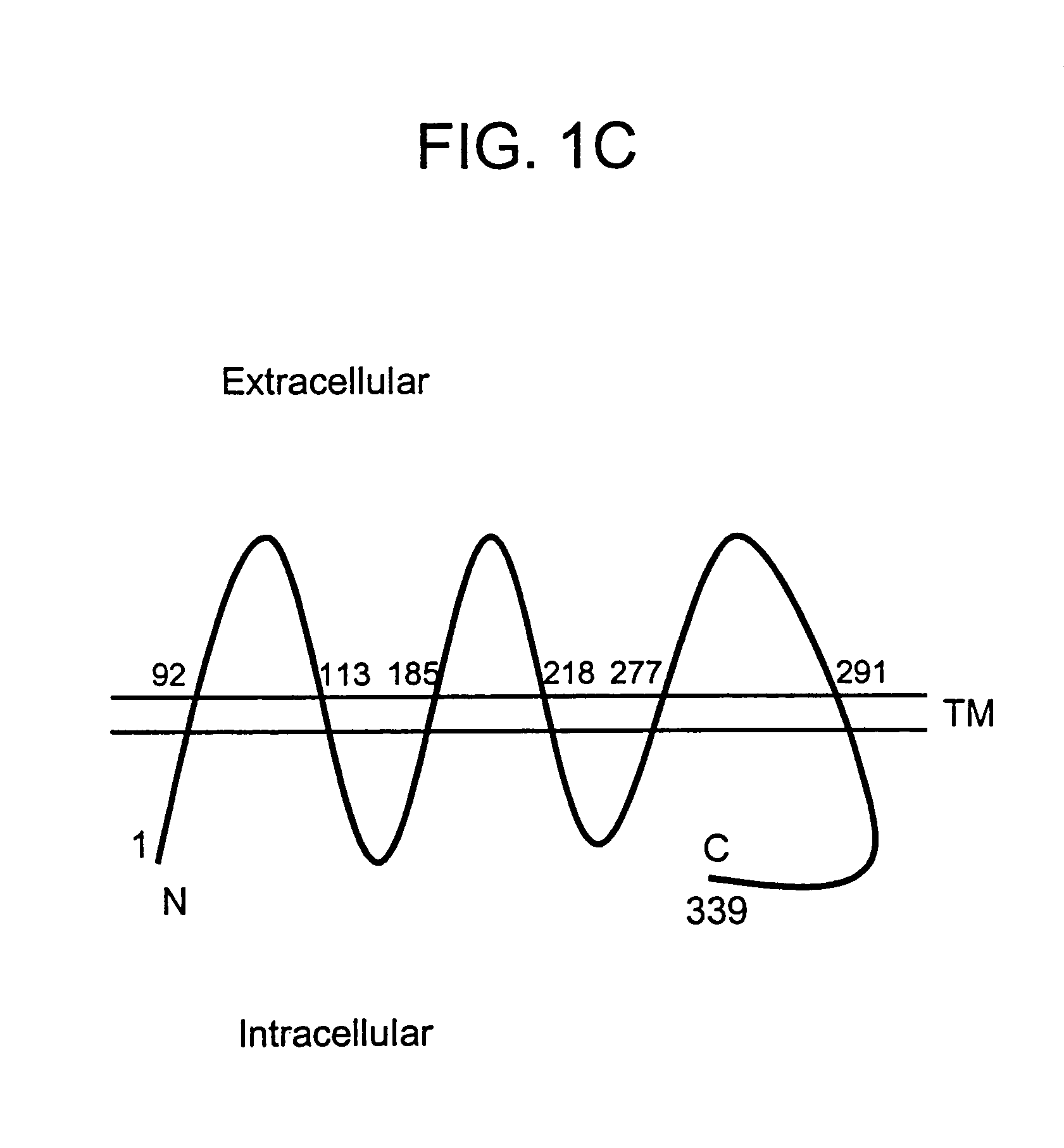
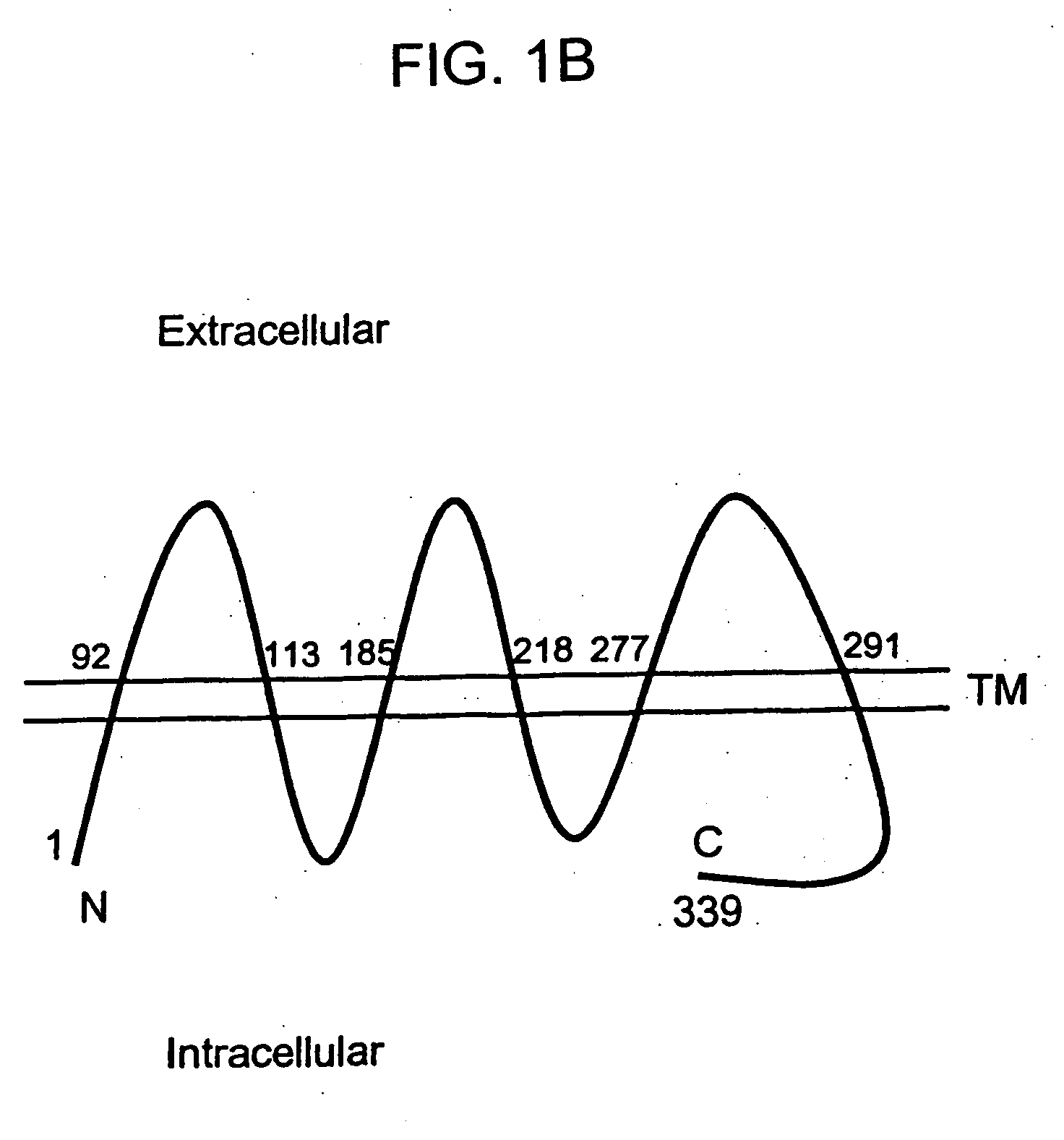
Described is a novel family of cell surface serpentine transmembrane antigens. Two of the proteins in this family are exclusively or predominantly expressed in the prostate, as well as in prostate cancer, and thus members of this family have been termed “STEAP” (serpentine transmembrane antigens of the prostate). Four particular human STEAPs are described and characterized herein. The human STEAPs exhibit a high degree of structural conservation among them but show no significant structural homology to any known human proteins. The prototype member of the STEAP family, STEAP-1, appears to be a type IIIa membrane protein expressed predominantly in prostate cells in normal human tissues. Structurally, STEAP-1 is a 339 amino acid protein characterized by a molecular topology of six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini, suggesting that it folds in a “serpentine” manner into three extracellular and two intracellular loops. STEAP-1 protein expression is maintained at high levels across various stages of prostate cancer. Moreover, STEAP-1 is highly over-expressed in certain other human cancers.
Owner:AGENSYS
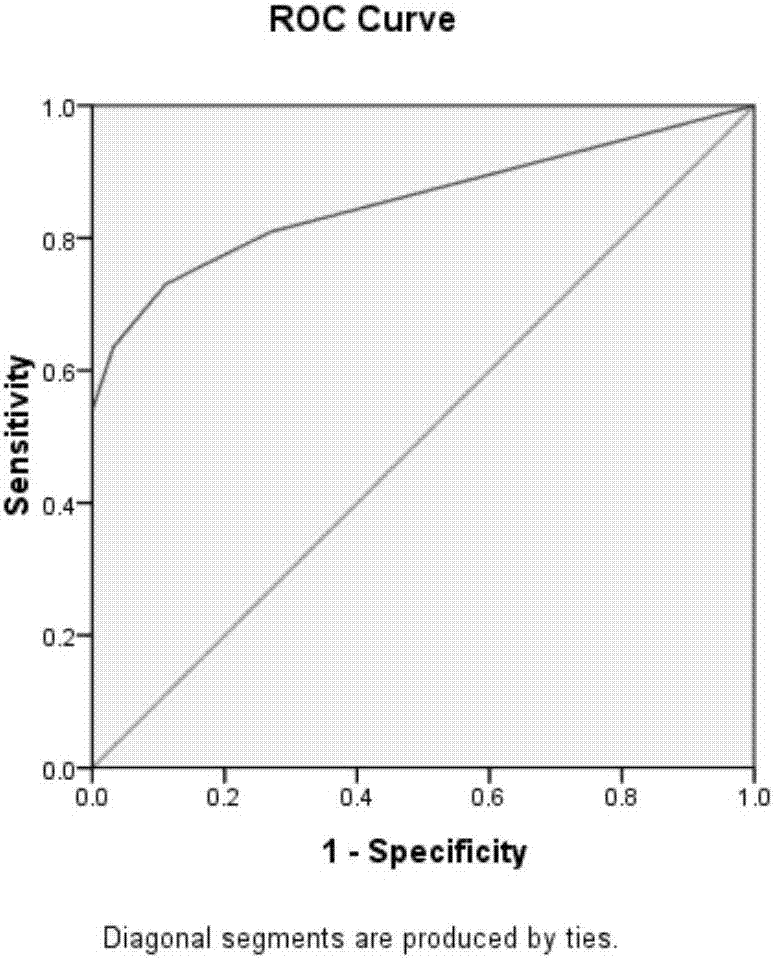
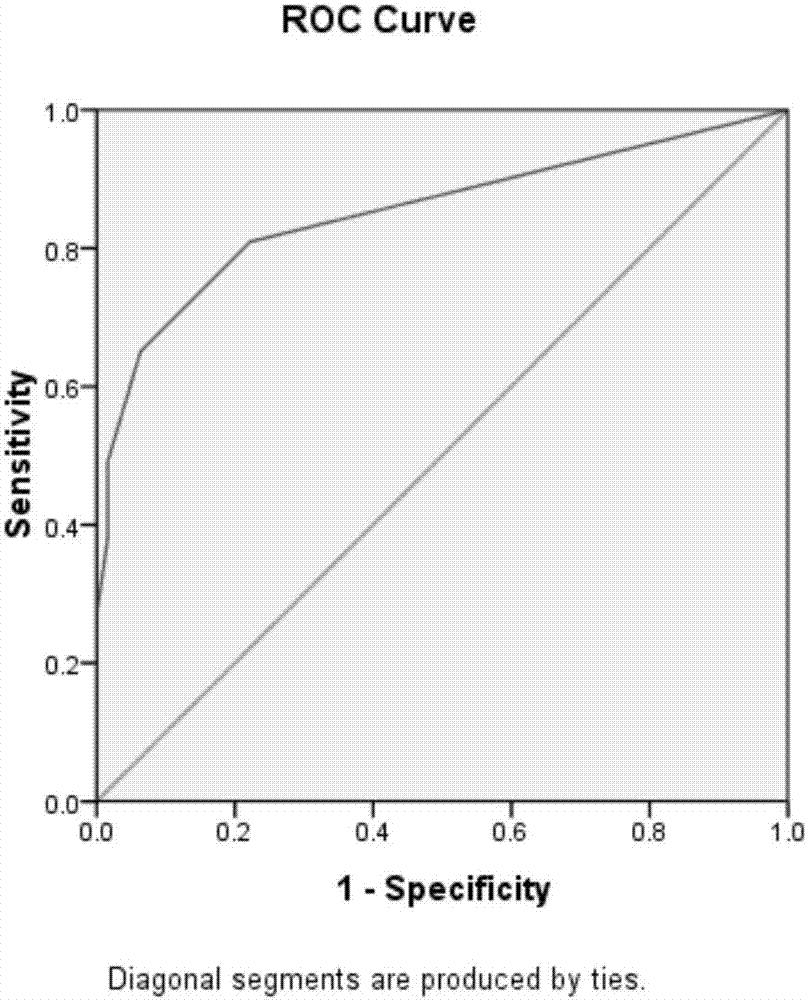
Screening method and use of biomarker related to severe oligoasthenospermia
The invention discloses a method for screening a biomarker related to severe oligoasthenospermia. The method comprises carrying out deep mass spectrometry on multiple sperm protein uncoded amino acids of severe oligoasthenospermia through a NanoHPLC-MS / MS mass spectrometry system and an unlabeled quantitative proteomics method, searching the mass spectrometry data through a nonfinite amino acid protein modification analysis method, carrying out multivariable gaussian mixture distribution clustering analysis to identify the non-coding amino acids in the sperm protein group as much as possible, and comparing the non-coding amino acids of the normal and patient sperm protein groups to obtain protein uncoded amino acid sites related to severe oligoasthenospermia, wherein the protein uncoded amino acid sites are used as molecular markers of severe oligoasthenospermia. The method provides novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for severe oligoasthenospermia.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
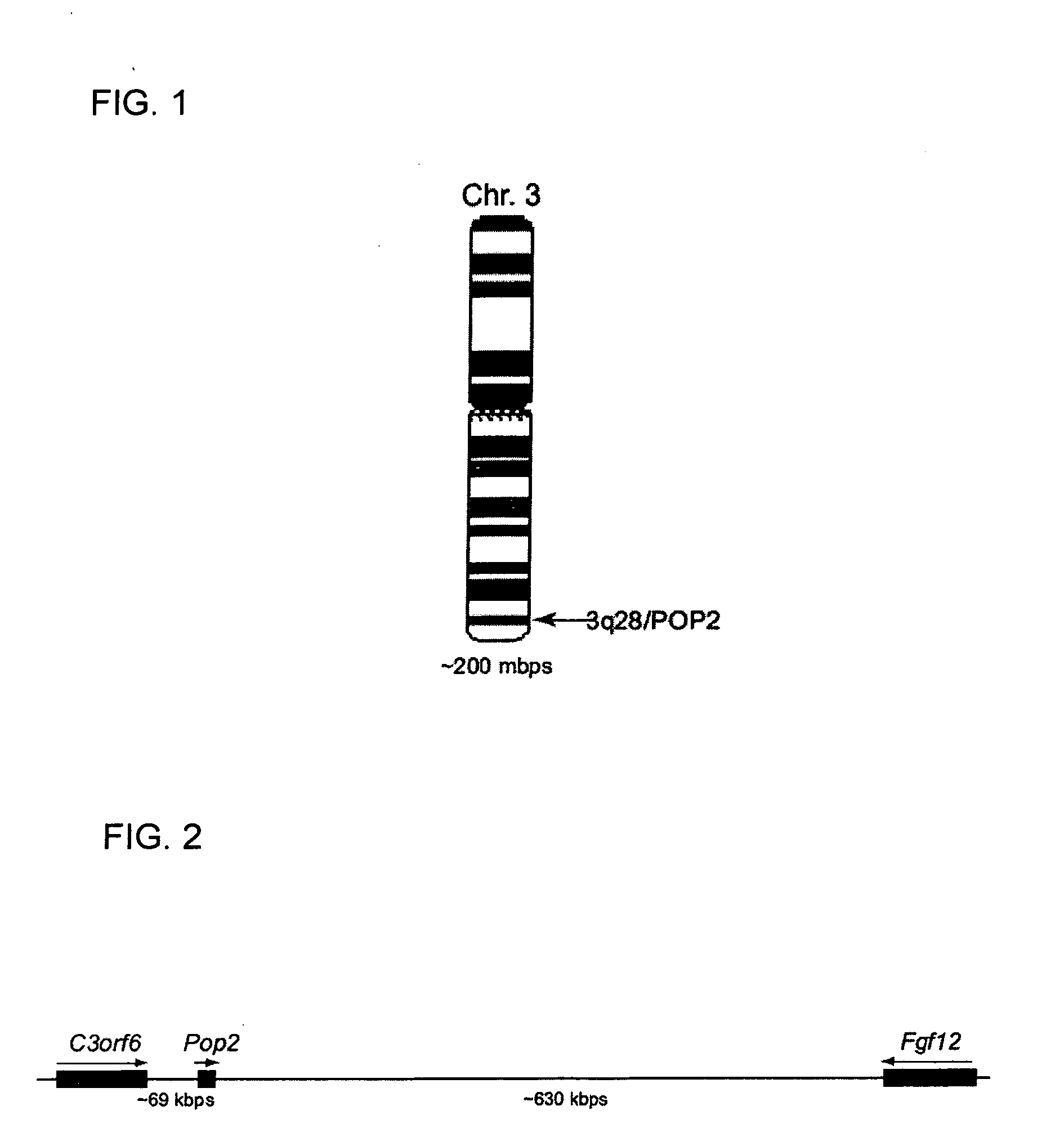
POP2: NFkB - Inhibiting Polypeptides, Nucleic Acids and Methods of Use
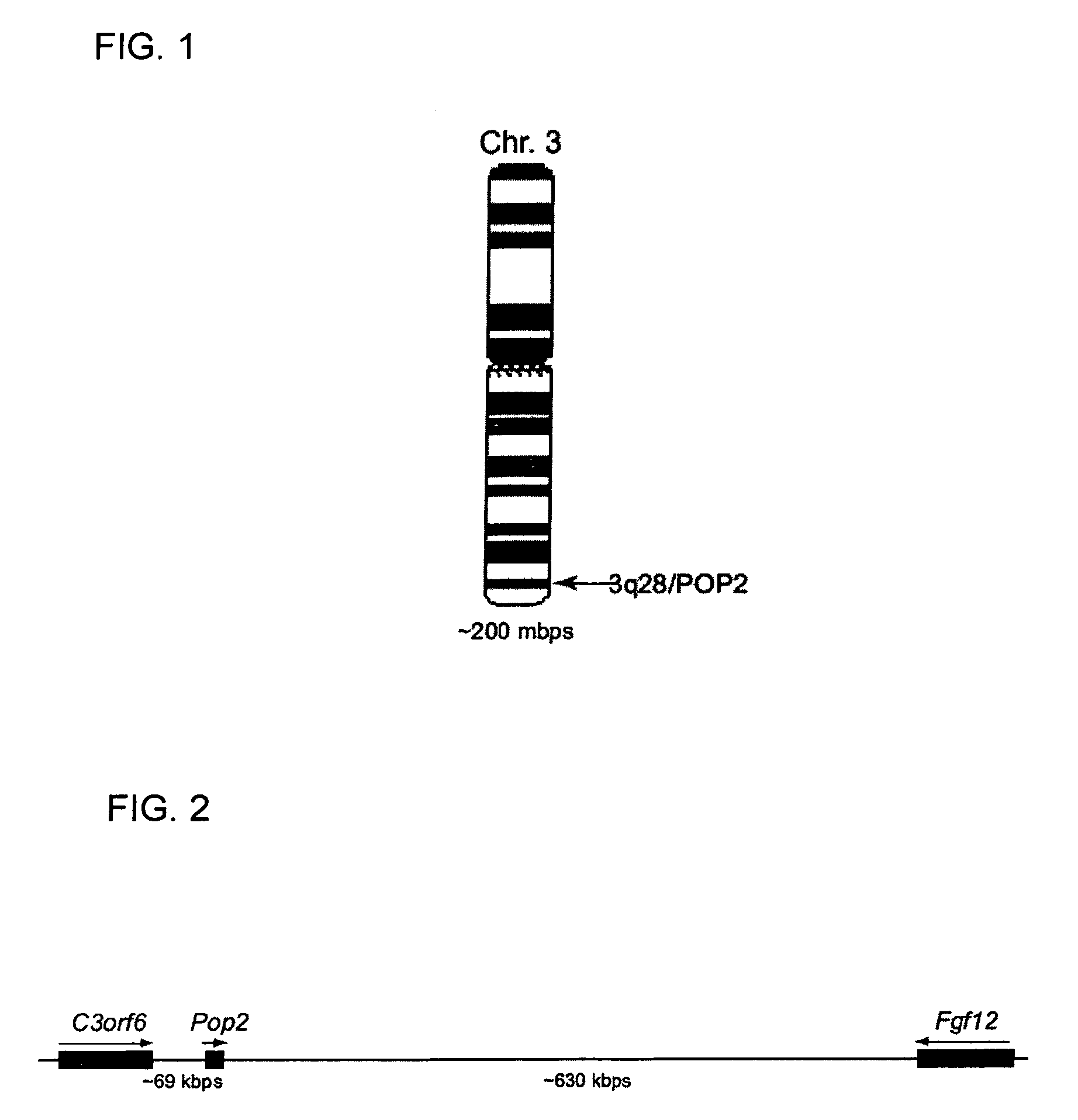
This invention provides a novel pyrin-only protein (POP2), polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them. The polypeptides of this invention have nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) modulating activity. NF-κB is pivotal for transactivation of cell-cycle regulatory, cytokine and adhesion molecule genes and is dysregulated in many cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory diseases. Proteins with Pyrin and / or caspase recruitment (CARD) domains have roles in apoptosis, innate immunity, and inflammation. Many pyrin domain proteins modulate NF-KB activity as well as participate in assembling both the perinuclear “apoptotic speck” and the pro-IL1β / IL-18 converting inflammasome complex. ‘Pyrin-only’ proteins are attractive as negative regulators of pyrin domain-mediated functions and one such protein, POP1, has been reported. We teach a second Pyrin-only protein (POP2). POP2 is a 294 nt single exon gene located on human chromosome 3 encoding a 97 amino acid protein with sequence and predicted structural similarity to other pyrin domains. Highly similar to pyrin domains in CATERPILLER (CLR, NLR, NALP) family proteins, POP2 is less like the prototypic Pyrin and ASC pyrin domains. POP2 is expressed principally in peripheral blood leukocytes and displays both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression patterns in transfected cells. TNFα-stimulated and p65 (RelA) induced NF-KB-dependent gene transcription is inhibited by POP2 in vitro by a mechanism involving changes in NF-κB nuclear import or distribution. While colocalizing with ASC in perinuclear specks, POP2 also inhibits the formation of specks by the CLR protein CIAS1 / NALP3. Together these observations indicate that POP2 is a negative regulator of NF-KB activity that may influence the assembly of pyrin-domain dependent complexes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Serpentine transmembrane antigens expressed in human cancers and uses thereof
Described is a novel family of cell surface serpentine transmembrane antigens. Two of the proteins in this family are exclusively or predominantly expressed in the prostate, as well as in prostate cancer, and thus members of this family have been termed “STEAP” (Six Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate). Four particular human STEAPs are described and characterized herein. The human STEAPs exhibit a high'degree of structural conservation among them but show no significant structural homology to any known human proteins. STEAP-2 is a 454 amino acid protein characterized by a predicted molecular topology of six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini, suggesting that it folds in a “serpentine” manner into three extracellular and two intracellular loops.
Owner:AGENSYS INC
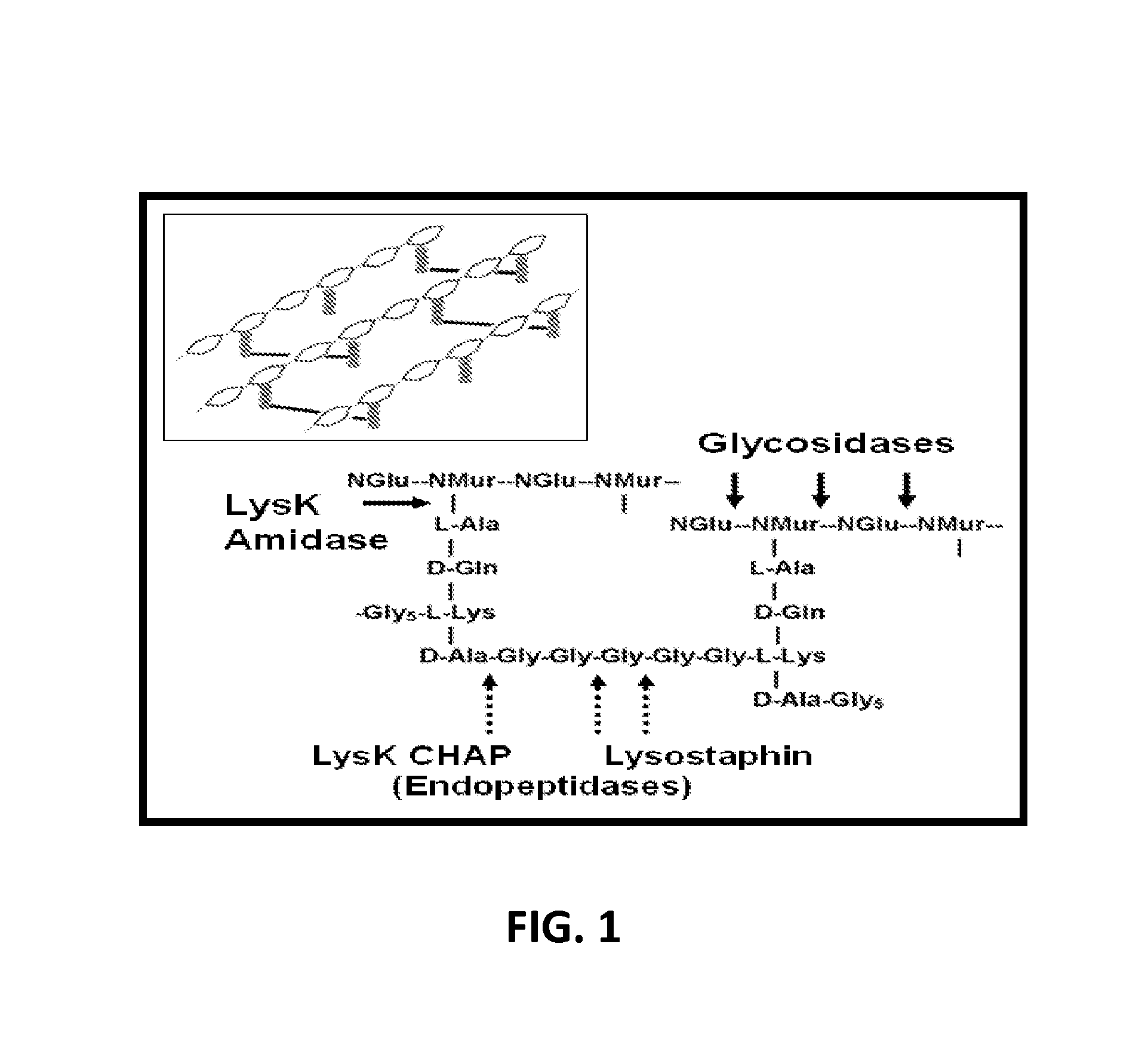
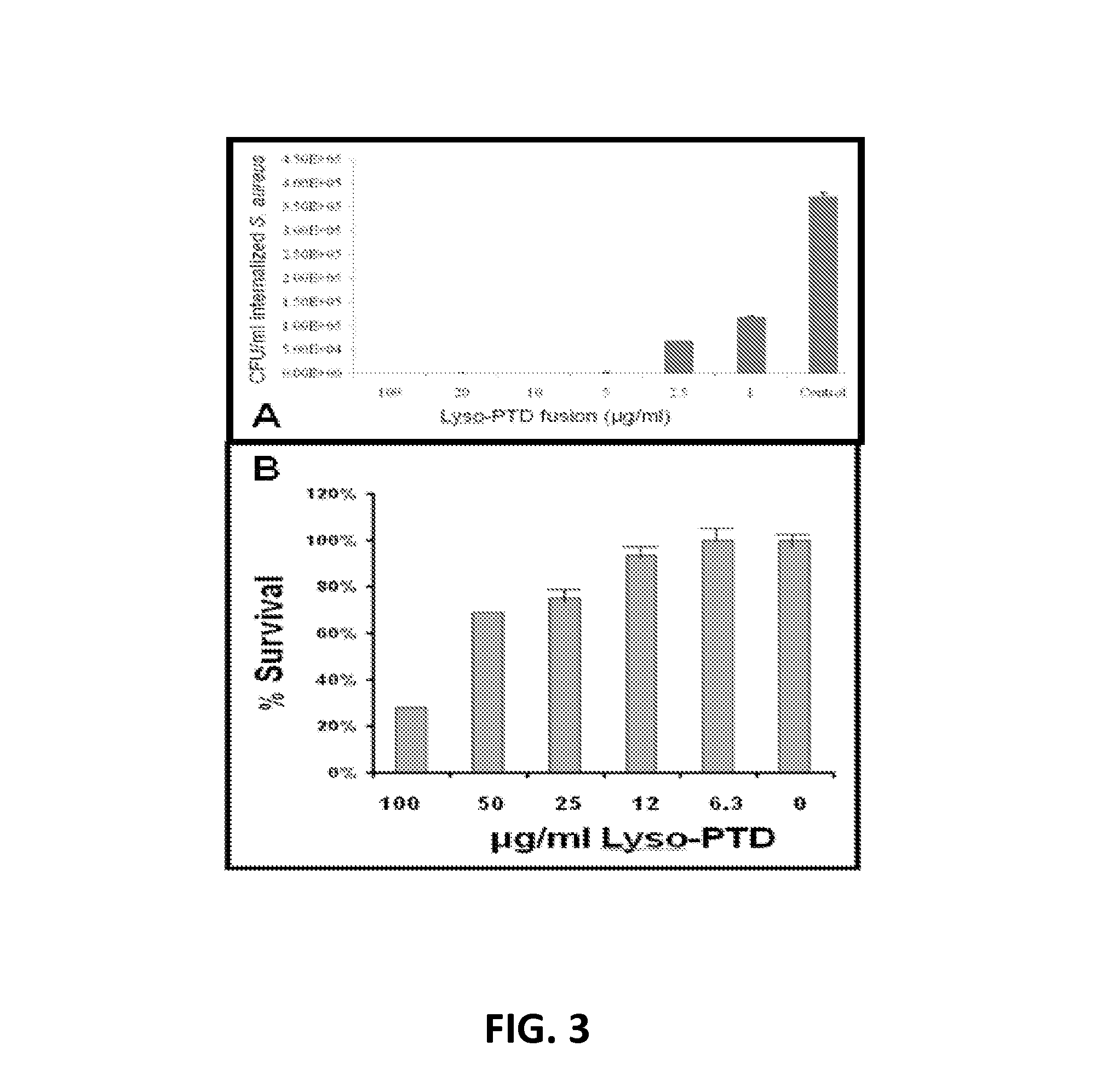
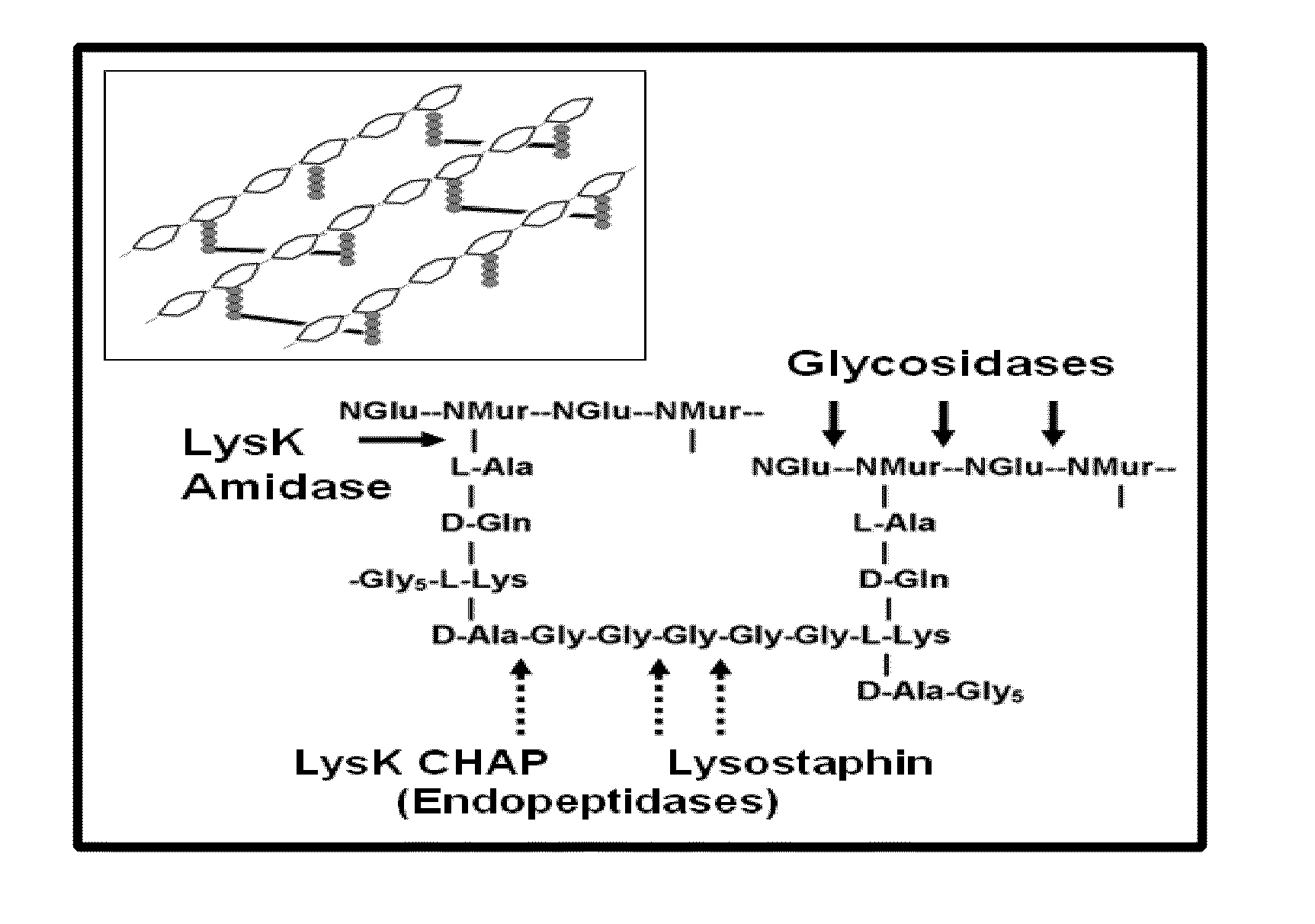
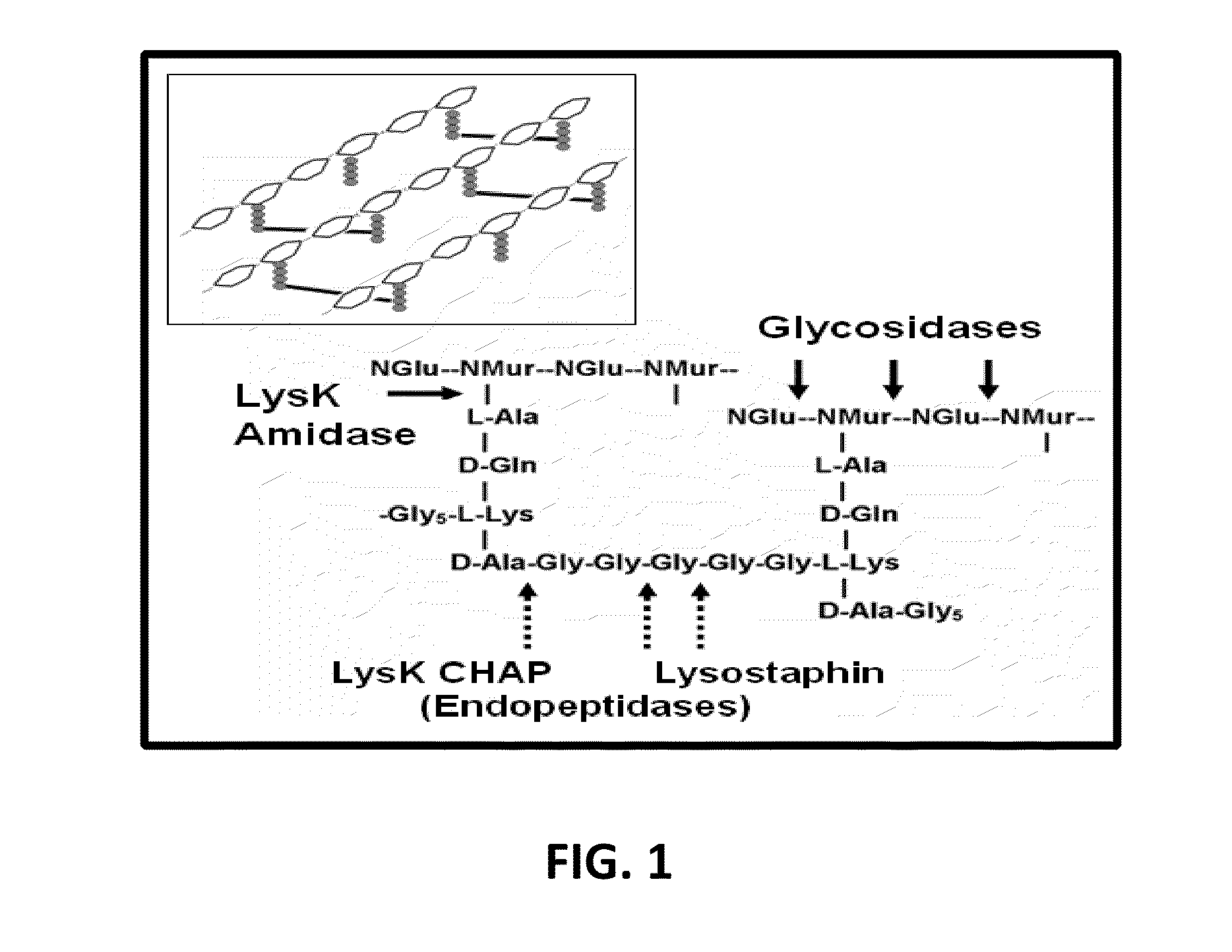
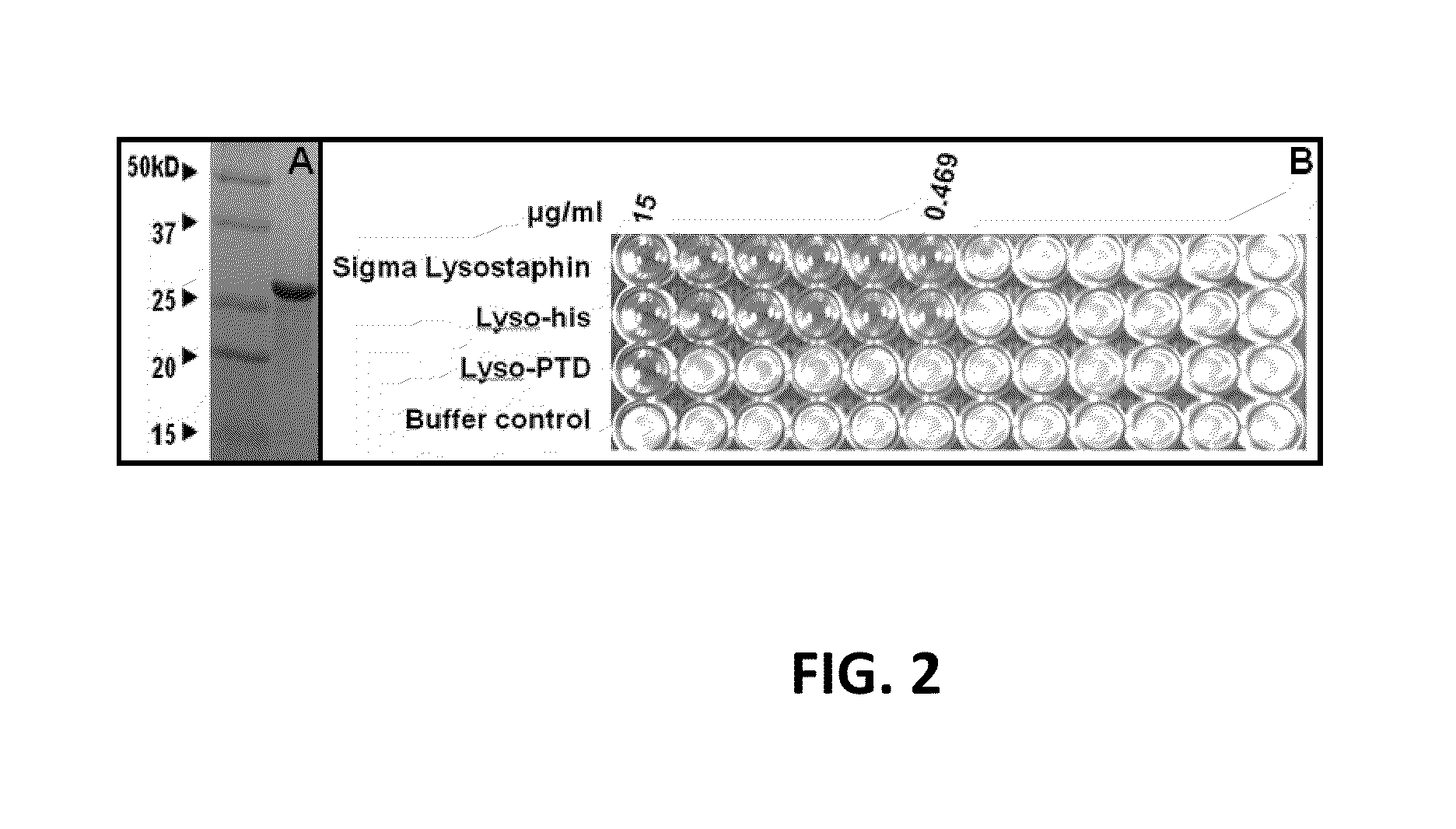
Fusion of peptidoglycan hydrolase enzymes to a protein transduction domain allows eradication of both extracellular and intracellular gram positive pathogens
InactiveUS8383102B2Facilitate its translocationEffective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibacterial agentsPeptidoglycan HydrolaseGram
Lysostaphin is a bacteriocin secreted by S. simulans to kill S. aureus, and has been shown to also be a potent antimicrobial for many antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus. By adding a ˜13 amino acid protein transduction domain (PTD) from the HIV-TAT protein to lysostaphin to form lysostaphin-PTD, both extracellular and intracellular forms of S. aureus and MRSA are killed in all (multiple) cell types examined.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Color-enhancing feed for fancy carp
The invention relates to color-enhancing feed for fancy carp. The feed comprises the following components as per parts by weight: 75 to 85 parts of fish meal, 8 to 13 parts of shrimp meal, 20 to 40 parts of lucerne meal, 170 to 220 parts of spirulina, 120 to 180 parts of bran, 45 to 55 parts of beer yeast, 15 to 25 parts of seaweed powder, 1.8 to 2.2 parts of methionine, 15 to 25 parts of phospholipid oil, 8 to 13 parts of gluten powder, 55 to 65 parts of bean pulp, 45 to 55 parts of extruded soybean, 280 to 330 parts of flour and premix. The color-enhancing feed for the fancy carp is used together with various color-enhancing materials, feed base materials, nutrients abundant amino acid and protein and the like with proper proportion, so that the feed capable of quickly enhancing color of the fancy carp and with low cost can be obtained.
Owner:包卫空
Powdered oil feed and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102630818AImprove digestion and absorption rateIncrease enzyme activityAnimal feeding stuffOil and greaseAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to feed, and in particular relates to powdered oil feed and a preparation method thereof. The invention mainly solves the technical problems that the powdered oil in the prior art is easy to be fused, oxidized and deteriorated and is difficult to store, main nutritional ingredient of the powdered oil is fat, content of other nutritional ingredient is low and the powdered oil can be used as energy feed only in animal feed. The powdered oil feed disclosed by the invention comprises animal oil, plant oil, animal protein, plant protein, minerals, trace elements and vitamins. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: mixing the animal oil, plant oil, animal protein, plant protein and emulsifier and emulsifying at high speed; then carrying out high pressure homogenization; and carrying out instant variable frequency spray drying, adding the minerals, trace elements and vitamins and mixing; and finally packaging to obtain the finished product lipopeptid amino acid protein.
Owner:杭州禾太生物科技有限公司
Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Superhydrophilic Foam Membrane for Energy-Efficient Oil-Water Separation
ActiveUS20160243505A1Controlled hydrophilicity and stabilityEasy disposalMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCross-linkGenipin
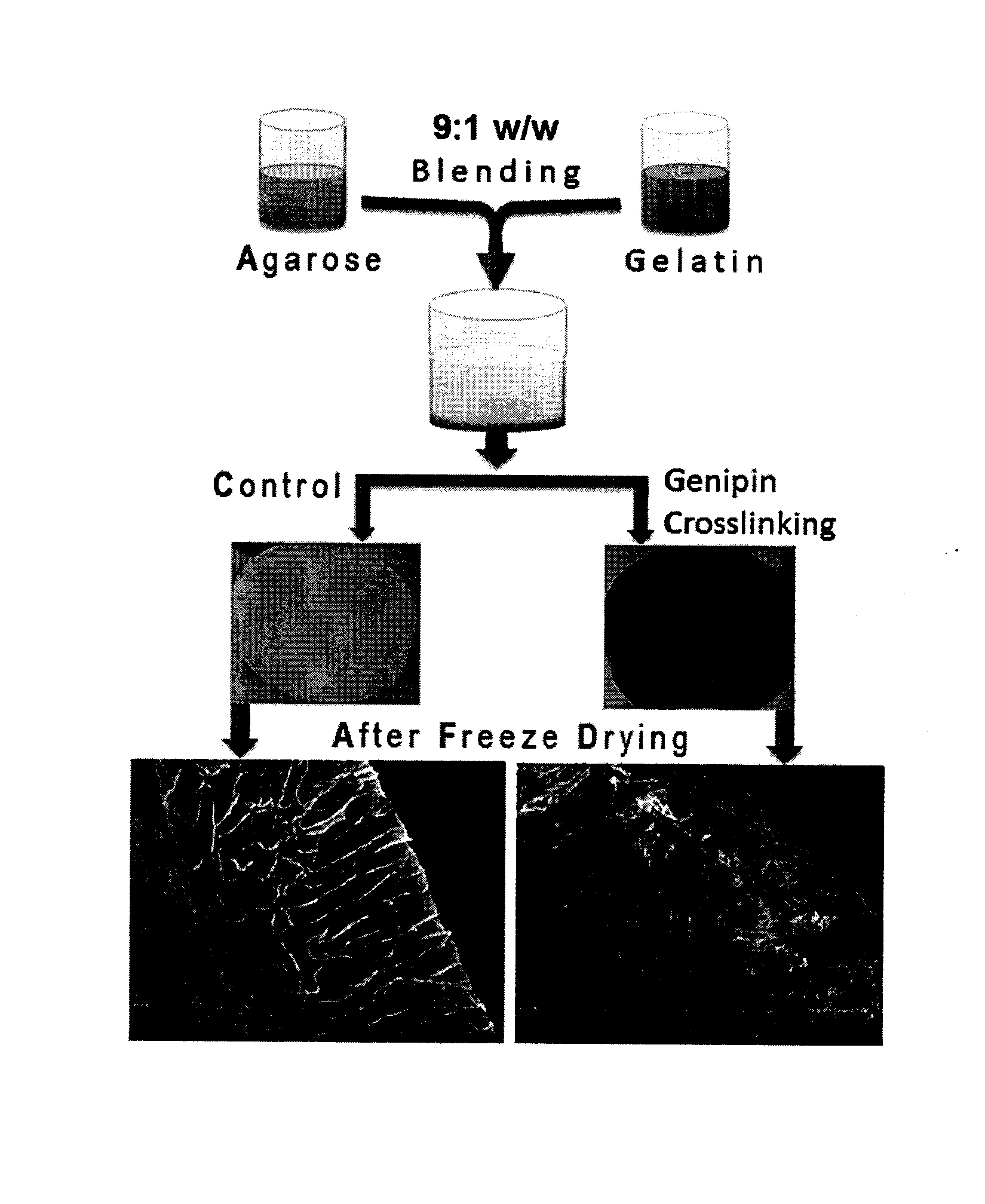
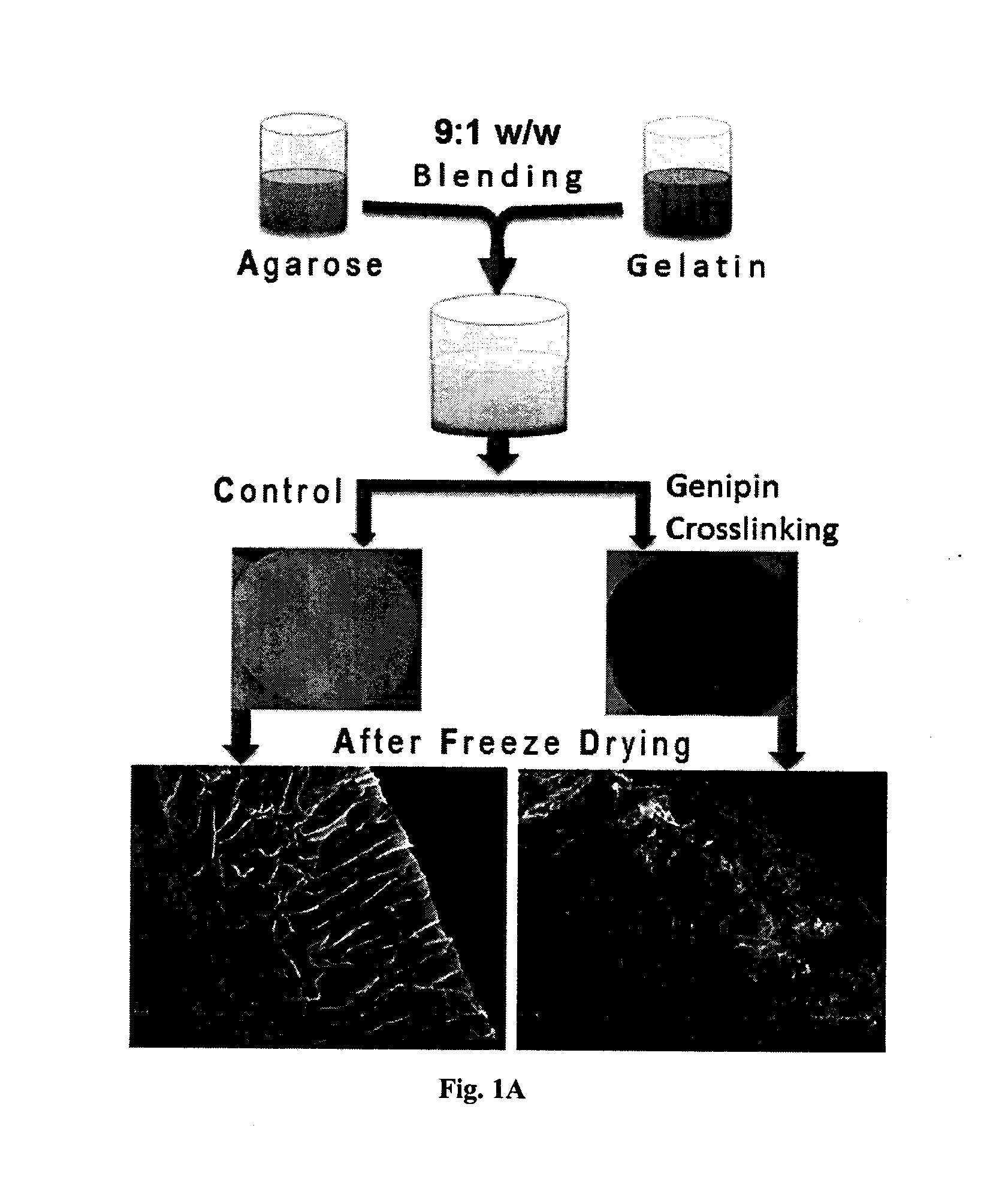
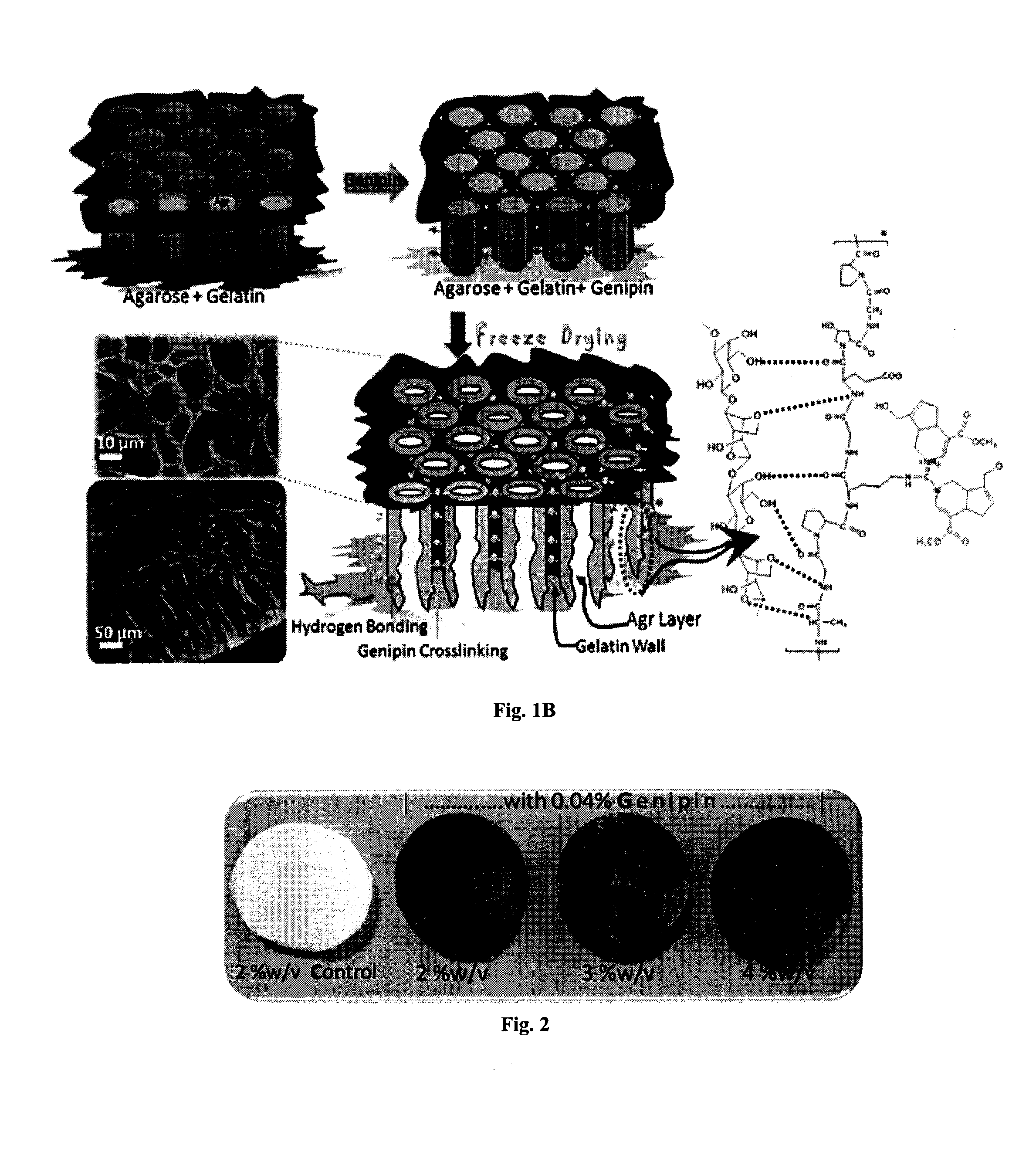
The present invention relates to a superhydrophilic biodegradable cross linked foam membrane and a process for preparation of said foam membrane from a seaweed polysaccharides by blending with amino biopolymers / amino acids / proteins / amino compounds followed by crosslinking with a naturally occurring cross linker, genipin. The foam membrane can be used as a substitute for synthetic membrane for varied applications including membrane separation for oil-water emulsions, oil-water mixtures and other aqueous-organic mixtures under ambient conditions. These foam membranes can be recycled and reused more than three times without considerable decrease in flux rate and stability. The separation methodology of the mixtures using the foam membrane of the present invention is gravity-driven and therefore, simple and energy-efficient.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Passivating of tin, zinc and steel surfaces
InactiveUS6830821B2Accelerated corrosionLess-expensive to produceHot-dipping/immersion processesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingBenzoic acidAlcohol
Owner:SAN FU CHEM CO LTD
Application for extration of glossy ganoderma in preparing medicine and health products for treating and improving depression symptoms a variety of causes resulting sleep disorder
The present invention provides one kind of glossy ganoderma extract for preventing and treating depression and sleep disorder of different causes. The glossy ganoderma extract contains glossy ganoderma polysaccharides, nucleosides, furans, sterols, alkaloids, amino acids and tritrepenes, as well as inorganic ions, organogermanium, etc. It may be mixed with various kinds of depression resisting, tranquilizing and hypnotic medicine and excipient to prepare medicine and health product for preventing and treating depression and sleep disorder of different causes.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Growth regulator for animals and preparation method of growth regulator
InactiveCN105211634AImprove immunityFast absorptionAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to a growth regulator for animals and a preparation method of the growth regulator. The growth regulator for the animals comprises preparation raw materials including mulberry leaf powder and a microbial agent and further comprises zeolite and microelements. The preparation method of the growth regulator for the animals comprises steps as follows: the raw materials are mixed, fermented and dried. According to the growth regulator for the animals, the natural mulberry leaf powder and the zeolite are taken as raw materials, and the growth regulator contains multiple amino acid proteins and microelements, can be an additive for various kinds of feed for the livestock and the poultry, for example, poultry, domestic animals and pigs and can be used for treating dyspepsia, enteritis, white diarrhea, asthma, scale damage and other diseases of the livestock and the poultry.
Owner:延川县富源康茶业专业合作社
Passivating of tin, zinc and steel surfaces
InactiveUS20040104122A1Accelerated corrosionLess-expensive to produceHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsBenzoic acidAlcohol
A method for coating zinc, zinc plated, or steel articles with a hydroxy benzoic acid protective coating by coating a cleaned zinc, zinc plated, or steel with a hydoxy benzoic acid composition having a pH of about 2.0 to 5.0; and coating cleaned tin surfaced articles with a composition having a PH of 2.0 to 12.0, and the composition having as its essential ingredients proteins, amino acids, amino acid-protein compounds and amine alcohols; and the articles produced thereby along with the coated articles having an appropriate paint thereon.
Owner:SAN FU CHEM CO LTD
Fusion of Peptidoglycan Hydrolase Enzymes to a Protein Transduction Domain Allows Eradication of both Extracellular and Intracellular Gram Positive Pathogens
InactiveUS20110027249A1Effective antimicrobial treatmentFacilitate its translocationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibacterial agentsPeptidoglycan HydrolaseADAMTS Proteins
Lysostaphin is a bacteriocin secreted by S. simulans to kill S. aureus, and has been shown to also be a potent antimicrobial for many antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus. By adding a ˜13 amino acid protein transduction domain (PTD) from the HIV-TAT protein to lysostaphin to form lysostaphin-PTD, both extracellular and intracellular forms of S. aureus and MRSA are killed in all (multiple) cell types examined.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method for extraction of heparin sodium and co-production of polypeptide protein powder and amino acid protein powder by utilizing porcine and bovine lungs
ActiveCN103951768APreserve integrityEliminate hidden dangers of insecurityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationEconomic benefitsWastewater
The invention discloses a method for extraction of heparin sodium and co-production of polypeptide protein powder and amino acid protein powder by utilizing porcine and bovine lungs, belonging to the technical field of manufacturing of biomedicines. The method adopts the steps of (1) pulping; (2) salt solution; (3) enzymolysis; (4) precipitation and adsorption; (5) elution and drying; (6) preparation of the polypeptide protein powder; (7) preparation of the amino acid protein powder. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reasonable process design, no emission of waste gas, waste water and waste residue and no environmental pollution and is suitable for large-scale production; waste liquid and the waste residue produced in the production process are recycled and turned into treasure, so that economic benefits are improved; the operation is simple, the production period is short, the production yield is high and the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:GUIZHOU HUIJING BIOTECH
Extraction process of acetylisovaleryltylosin
ActiveCN103408623ALow viscosityHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationOrganic solventButyl acetate
The invention relates to the field of chemistry, and particularly relates to an extraction process of acetylisovaleryltylosin. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating an acetylisovaleryltylosin fermentation liquid to remove amino acid proteins with the isoelectric points of 4-4.5 and 2-2.5; carrying out scraper filtration, and collecting a first filtrate; carrying out membrane filtration at 30-40 DEG C, and collecting a second filtrate; carrying out nanofiltration at 25-30 DEG C, and collecting a third filtrate; precipitating a solid acetylisovaleryltylosin crystal from the third filtrate at 10-15 DEG C, culturing, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain solid acetylisovaleryltylosin; washing with water repeatedly; reacting the washed acetylisovaleryltylosin and tartaric acid to obtain an acetylisovaleryltylosin tartrate solution; and carrying out spray drying to obtain acetylisovaleryltylosin tartrate powder. The invention can avoid using the traditional extraction method using organic solvent and butyl acetate, and has the advantage of higher yield.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
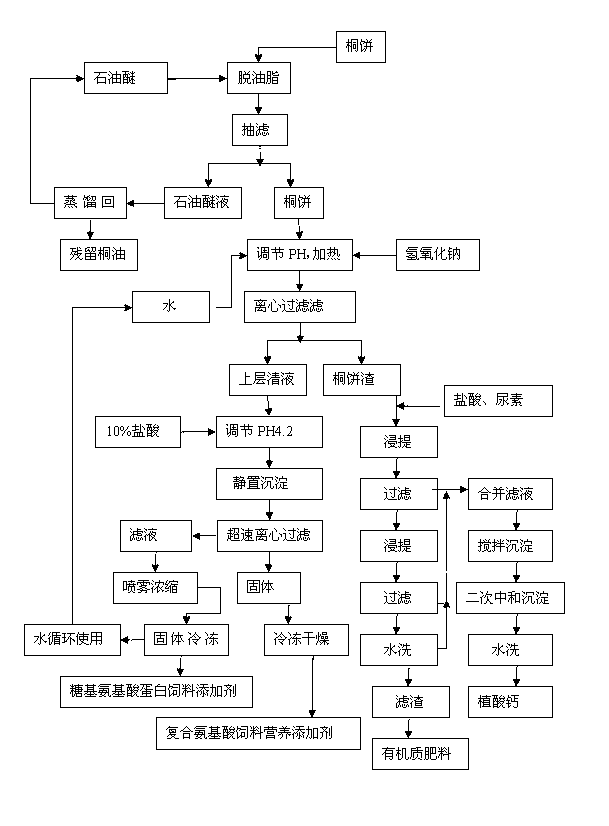
Processing method comprehensively utilizing plant oil cake
InactiveCN102793063AHigh protein contentNo toxic ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffVegetable oilNutrition
The invention discloses a processing method comprehensively utilizing a plant oil cake and belongs to the technical field of subsidiary agricultural products processing. Composite amino acid feed nutritional additive, glycosyl amino acid protein feed additive, organic matter fertilizer and calcium phytic acid are prepared by 8 steps of preparing raw materials, preparing cake powder, extraction, hydrolyzation, decoloration, crystallization, digestion and secondary neutralization and sedimentation. The processing method has the following beneficial effects that the obtained products are safe and contain no toxic component or saponin; meanwhile, the products have high nutrition and the protein content is as high as 92.1%; the additives are animal feed nutritional additives with high digestibility and can improve the protein content of feed products and the nutrition utilization rate and lower feeding cost; and in addition, the operation is simple and the method is easy for popularization, thus a great quantity of resources can be saved for society, the environmental pollution can be effectively lessened and the economic benefits can be increased.
Owner:重庆油桐产业研究中心
Trehalose transporter gene and method of introducing trehalose into cells
InactiveUS20090111176A1Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsConcentration gradientMembrane potential
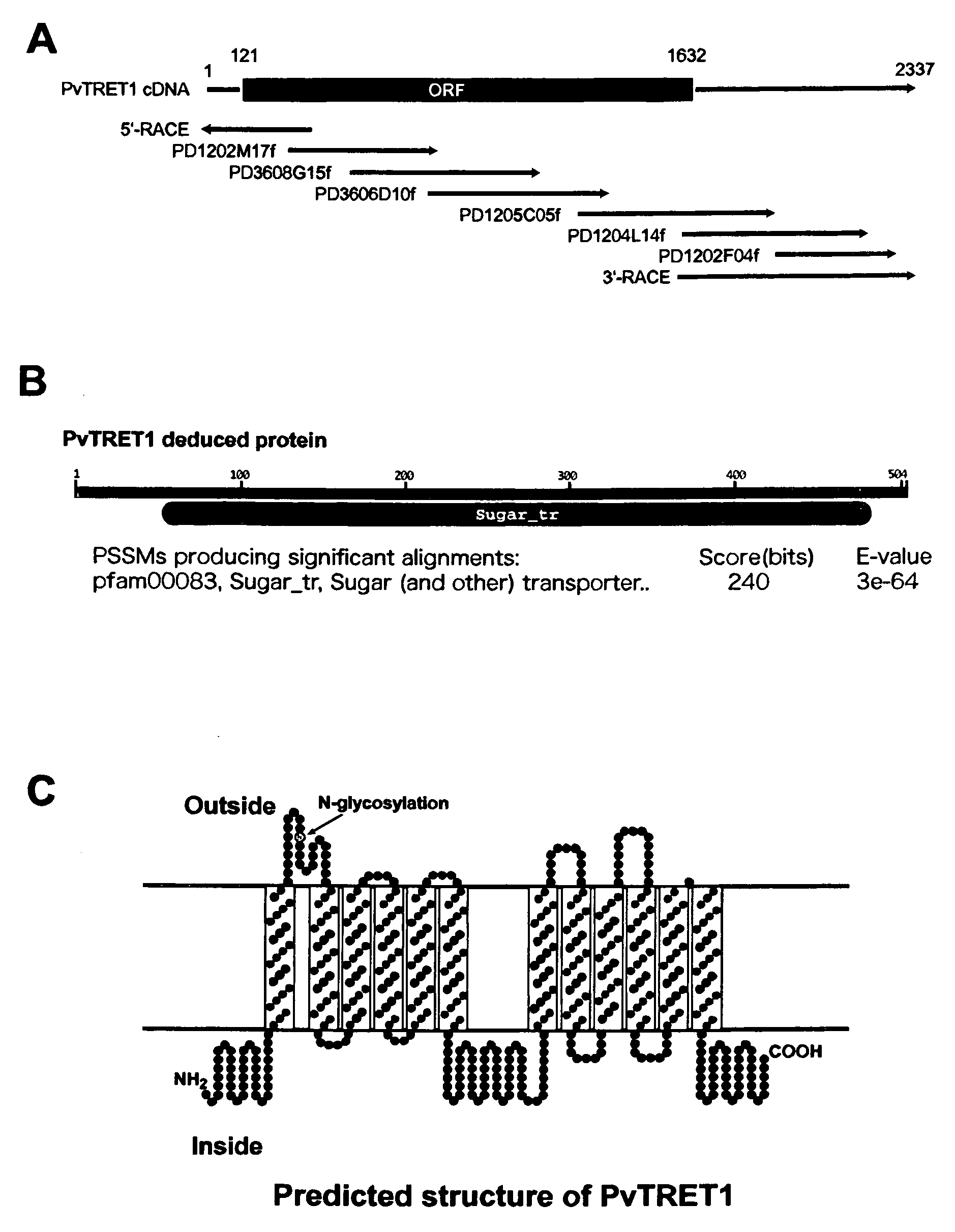
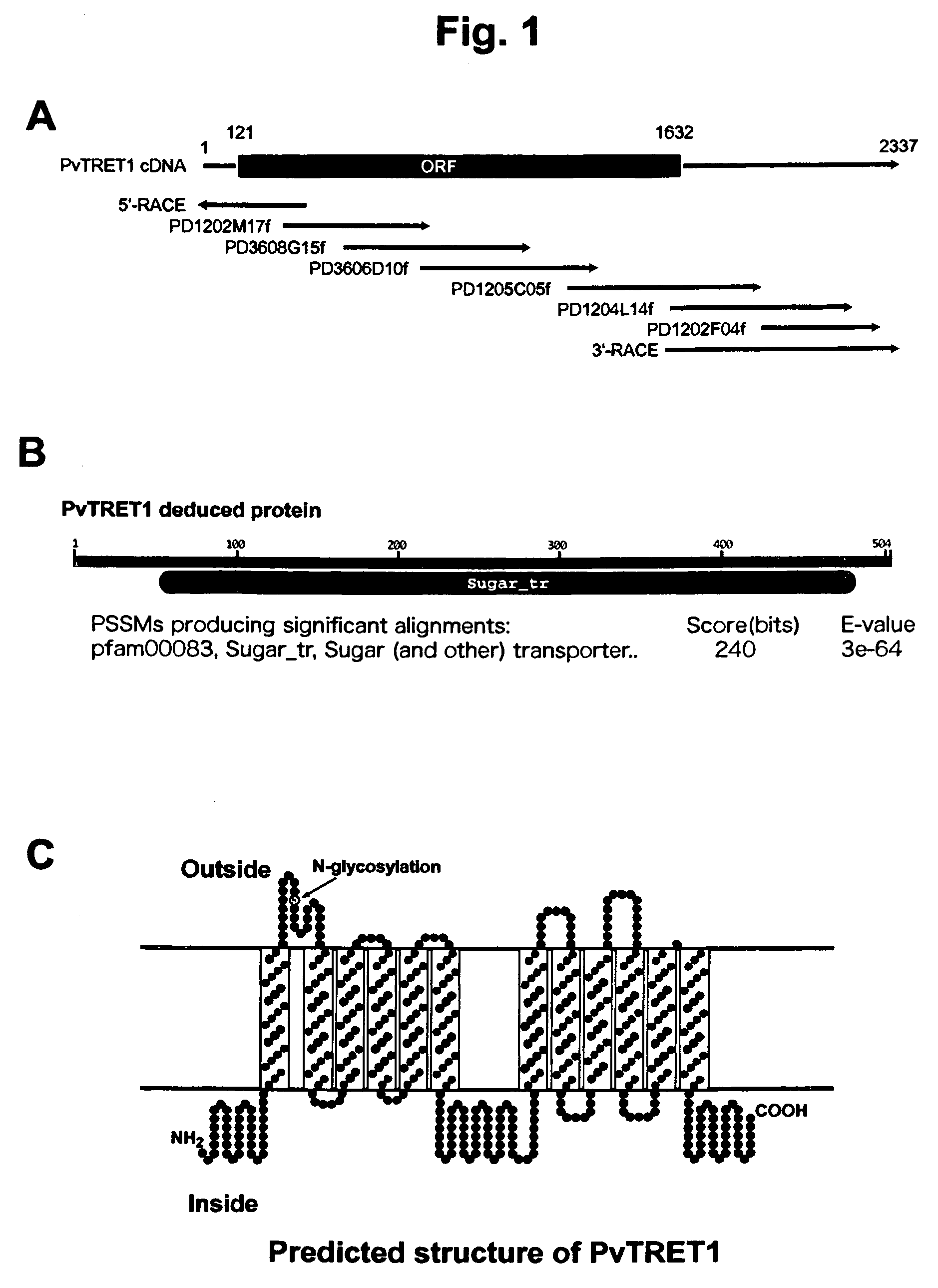
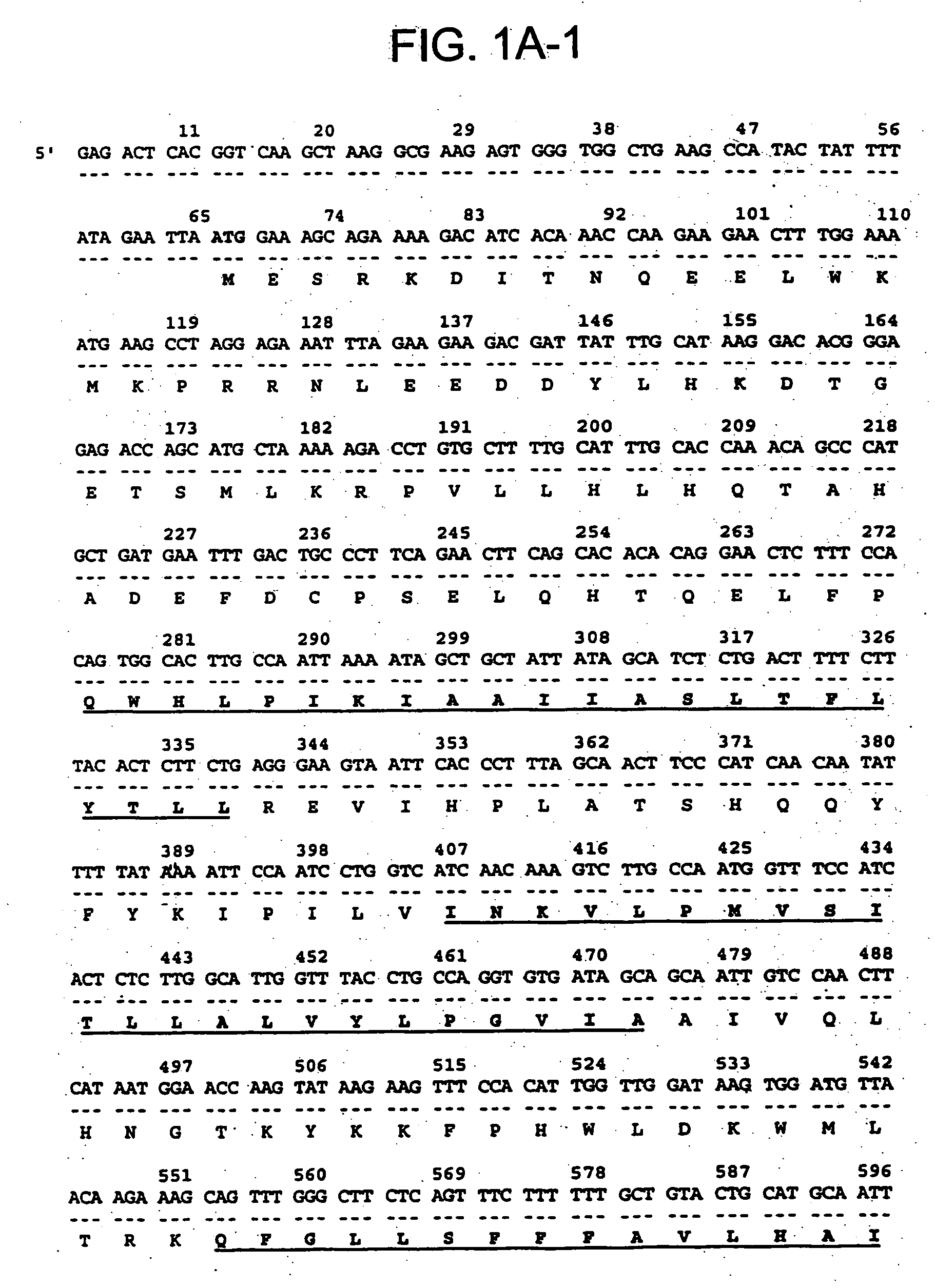
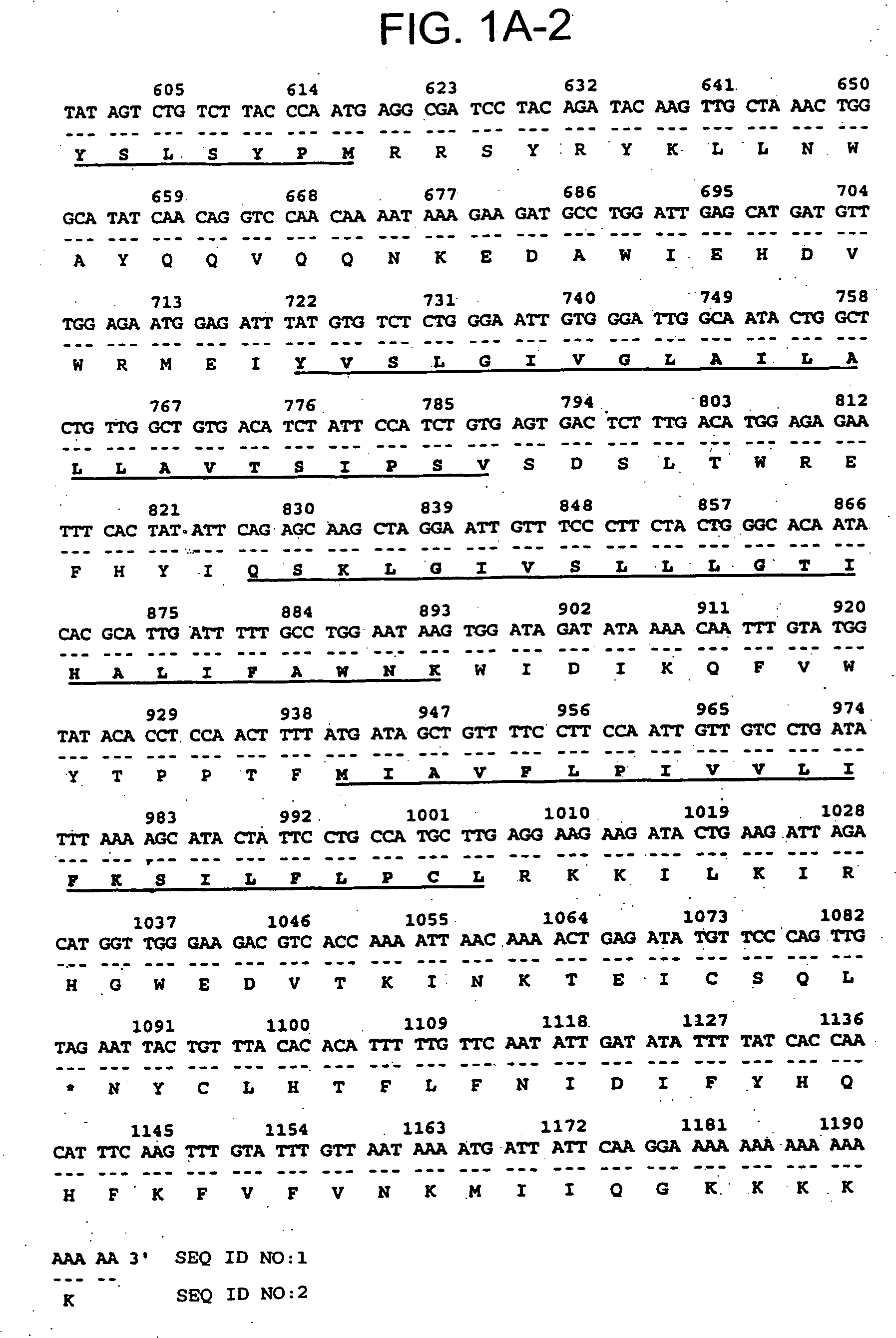
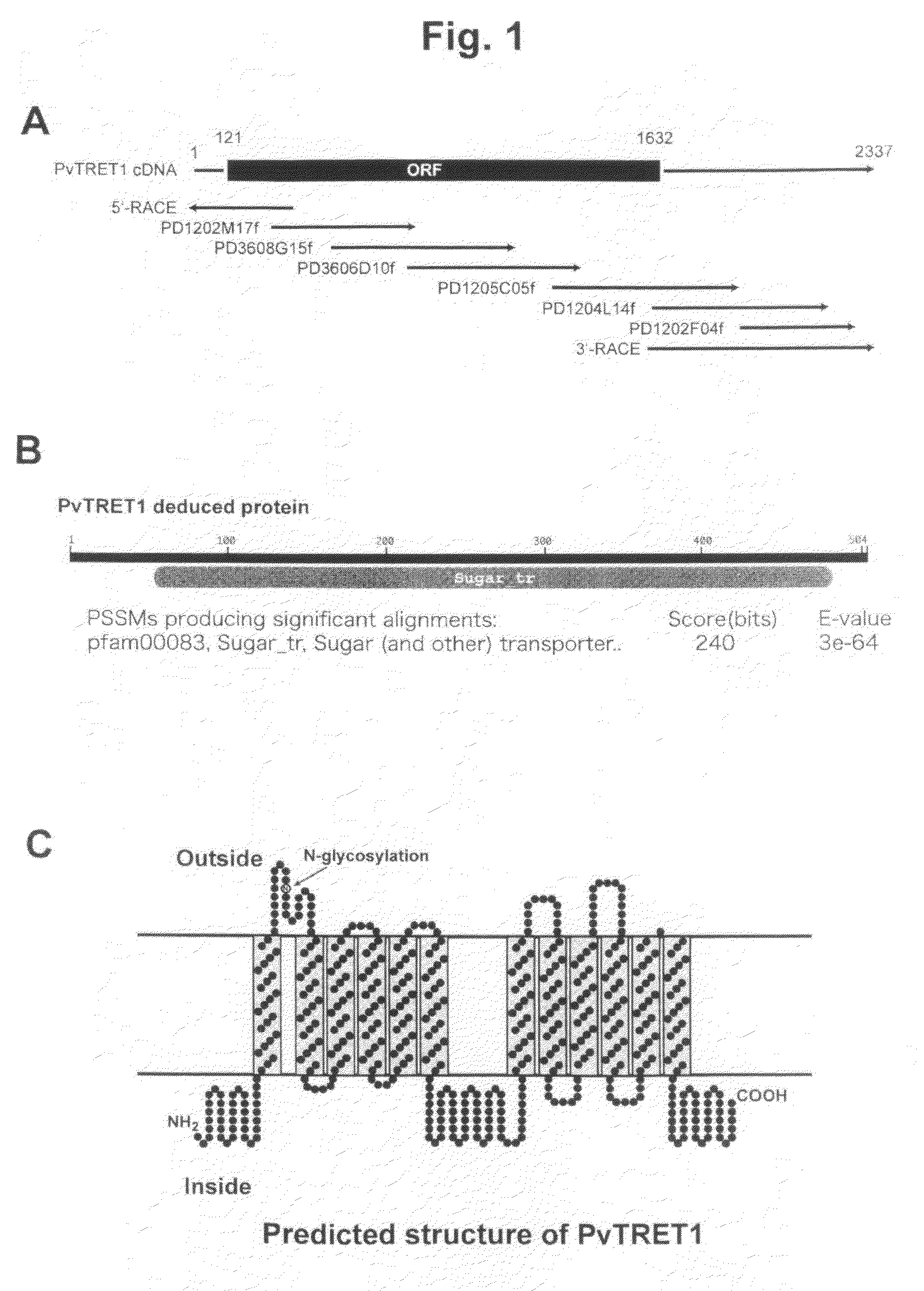
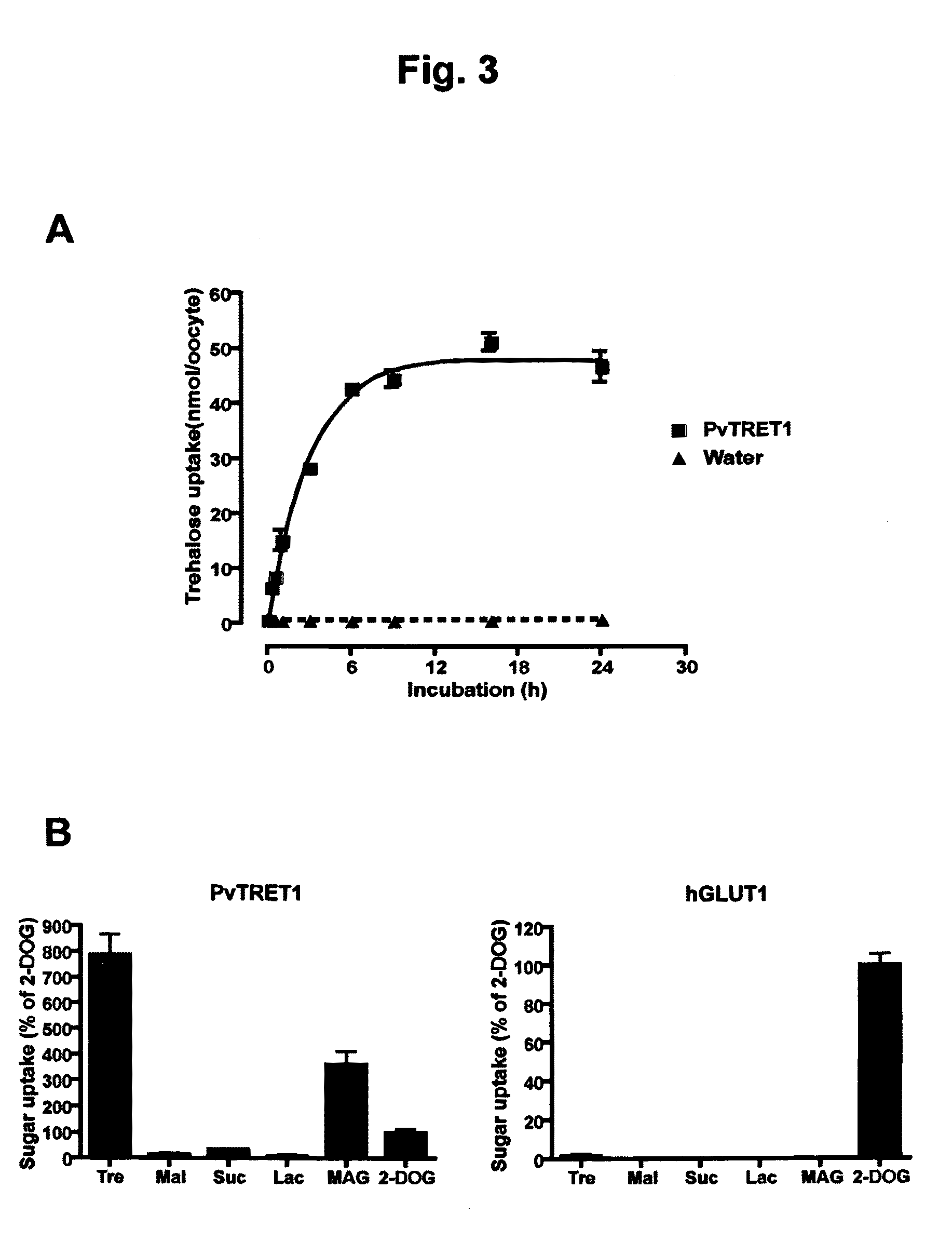
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
Novel serpentine transmembrane antigens expressed in human cancers and uses thereof
Described is a novel family of cell surface serpentine transmembrane antigens. Two of the proteins in this family are exclusively or predominantly expressed in the prostate, as well as in prostate cancer, and thus members of this family have been termed “STEAP” (Six Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate). Four particular human STEAPs are described and characterized herein. The human STEAPs exhibit a high degree of structural conservation among them but show no significant structural homology to any known human proteins. The prototype member of the STEAP family, STEAP-1, appears to be a type IIIa membrane protein expressed predominantly in prostate cells in normal human tissues. Structurally, STEAP-1 is a 339 amino acid protein characterized by a molecular topology of six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini, suggesting that it folds in a “serpentine” manner into three extracellular and two intracellular loops. STEAP-1 protein expression is maintained at high levels across various stages of prostate cancer. Moreover, STEAP-1 is highly over-expressed in certain other human cancers.
Owner:AFAR DANIEL E +4
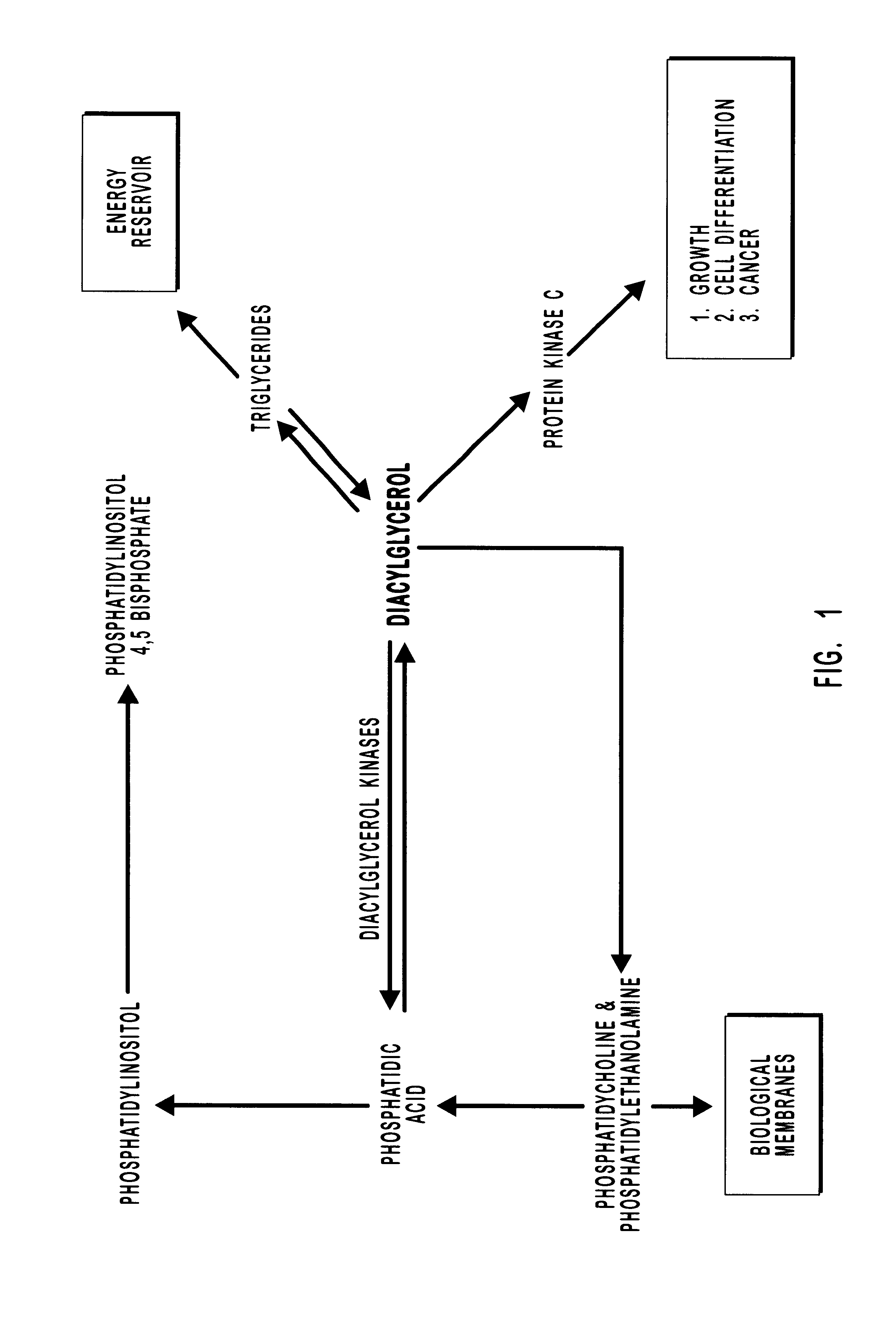
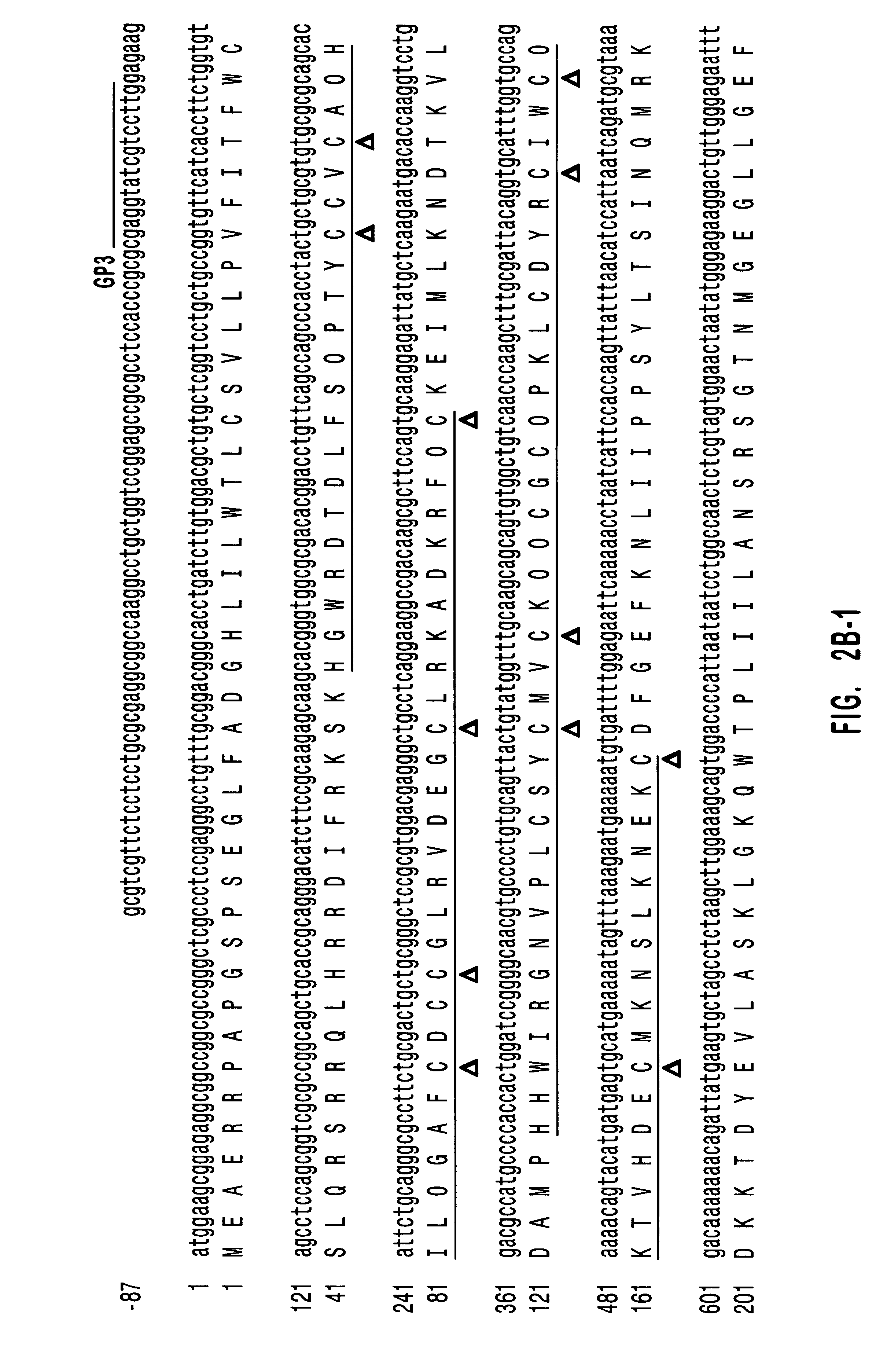
Diacylglycerol kinase isoforms epsilon and zeta and methods of use thereof
Two novel diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) isoforms are disclosed. The cDNA of one DGK isoform, designated DGKepsi, is about 2.6 kb in length. The DGKepsi cDNA has an open reading frame encoding 567 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 63 kDA. DAG kinase epsi is highly selective for arachidonate-containing diacylglycerol (DAG) substrates. The cDNA of the second isoform, designated DGK ζ, is 3.5 kb in length. The DGKζ cDNA contains a single large open reading frame encoding a 928-amino acid protein with a predicted molecular mass of 103.9 kDa. An alternatively spliced muscle specific species of DGKζ, DGKζ-2 is also disclosed and characterized. DGKζ is localized to the nucleus. A lysine-rich region with homology to the MARCKS protein is shown to be necessary and sufficient to confer nuclear localization to DGKζ via a protein kinase C phosphorylation.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Fermented glutinous rice mask and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107157869AIncrease elasticityPrevent black depositsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSide effectAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a fermented glutinous rice mask which is prepared from the following materials in parts by weight: 50-100 parts of fermented glutinous rice, 8-15 parts of pearl powder, 1-5 parts of radix notoginseng powder, 10-20 parts of beetroot juice, 5-10 parts of hyaluronic acid, 10-20 parts of milk, 1-2 parts of rice bran oil and 1-2 parts of tea tree essential oil. The fermented glutinous rice mask provided by the invention uses the fermented glutinous rice as a main component of the mask; the fermented glutinous rice contains rich vitamins and flavonoids, and contains free amino acids and proteins which are easily absorbed by the skin and can improve blood circulation of facial skin; the amino acids and the proteins can repair cells to improve elasticity of the skin; the fermented glutinous rice mask provided by the invention does not contain any chemical additive and is safe and free of side effects.
Owner:钦州市启仕教育咨询有限公司
Gene for coding, 1,3-propylene glycol reductase in E.aero strain
A coded 1,3-propylene-glycol redox enzyme gene of Eaero strain high-yielding mutant strain of aerogens 1.3-PD with number CGMCC 0532. The total length of the dhaT gene is 1164bp which codes 387 amino acid proteins, it begins with ATG initial codon and ends with TGA condon. The molecular weight of expressed protein is 43Kda and enzyme activity is 39muM / mg.
Owner:迟乃玉
Pearl protein fiber rich in amino acid protein and preparation method of pearl protein fiber
InactiveCN111764000ASilky touchMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentWet spinning methodsPolymer scienceBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of textiles, and particularly relates to pearl protein fiber rich in amino acid protein and a preparation method of the pearl protein fiber. The inventionprovides the pearl protein fiber rich in the amino acid protein, a preparation raw material comprises the following components of, in parts by weight, 20 parts of viscose fiber spinning solution, 1-5parts of pearl powder and 5.5-13.5 parts of auxiliaries. According to the pearl protein fiber rich in the amino acid protein and the preparation method of the pearl protein fiber, the technical solution that the pearl powder is dispersed in the viscose fiber by utilizing various amino acids and proteins of a pearl, and the characteristics of whitening skin, maintaining beauty and keeping young ofthe pearl can be given to a fiber material, so that the fiber material has the effects of being soft, fine and smooth in touch, and the effect is more obvious along with the increase of the pearl powder content in the viscose fiber.
Owner:深圳千维生态纺织有限公司
POP2: NKκB-inhibiting polypeptides, nucleic acids and methods of use
This invention provides a novel pyrin-only protein (POP2), polypeptides, and nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them. POP2 is a 294 nt single exon gene located on human chromosome 3 encoding a 97 amino acid protein with sequence and predicted structural similarity to other pyrin domains. Highly similar to pyrin domains in CATERPILLER (CLR, NLR, NALP) family proteins, POP2 is less like the prototypic Pyrin and ASC pyrin domains. POP2 is expressed principally in peripheral blood leukocytes and displays both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression patterns in transfected cells. TNFα-stimulated and p65 (RelA) induced NF-κB-dependent gene transcription is inhibited by POP2 in vitro by a mechanism involving changes in NF-κB nuclear import or distribution. While colocalizing with ASC in perinuclear specks, POP2 also inhibits the formation of specks by the CLR protein CIAS1 / NALP3. POP2 is a negative regulator of NF-κB activity that may influence the assembly of pyrin-domain dependent complexes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Chinese berbal medicine oral liquid for treating diabetes and its preparation method
InactiveCN1785353APromote generationImprove immunityMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsWhite blood cellFreeze-drying
A Chinese medicine in the form of oral liquid for treating diabetes and improving immunity and resistance to virus and infection is prepared from amino acid protein, water and 10 Chinese-medicinal materials including eucommia bark, astragalus root, wolfberry fruit, pueraria root, etc through washing, immersing in alcohol, steaming, filering, baking, immersing in alcohol, filtering, baking, immersing in alcohol, filtering, baking, immersing in warm water, filtering, freeze drying, mixing with amino acid protein and water, and sterilizing.
Owner:钟厚禄
Preparation method of selenium-rich amino acid nutrient solution
InactiveCN107125431ASave resourcesPromote bowel movementFood processingAnimal feeding stuffStrong acidsNutrient solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a selenium-rich amino acid nutrient solution, comprising the following steps: step 1, cleaning and baking waste chicken and duck feathers; step 2, diluting concentrated sulfuric acid with water in ratio of 0.8:10 to obtain dilute sulfuric acid; step 3, adding the dilute sulfuric acid to a strong acid-proof stainless steel jar, then adding the baked waste chicken and duck feathers, heating to 100-110DEG C for carrying out chelating reaction, and after reaction, adding a pH regulator to regulate the pH value of the reaction liquid to be neutral to obtain an amino acid nutrient solution; and step 4, adding CM strains and brown sugar to the amino acid nutrient solution, sealing and fermenting to obtain the selenium-rich amino acid nutrient solution. The selenium-rich amino acid nutrient solution disclosed by the invention integrates three effects of an amino acid protein feed raw material, a biological-source organic selenium source and a micro-ecological formulation, has the advantages of rich contents of amino acid, protein and selenium, comprehensive nutrition, safety and nontoxicity, and opens up a new way for a green and environment-friendly raw material of feed.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION CENT FOR ANALYSIS & TEST RES
Method of increasing cell permeability to trehalose by recombinantly producing a trehalose transporter
InactiveUS7892789B2Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesVertebrate cellsConcentration gradientFat bodies
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
High protein powder and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112137093ADestructive activityUndamagedProteins working-up by texturisingFood ingredientsBiotechnologyPROTEIN S HEERLEN
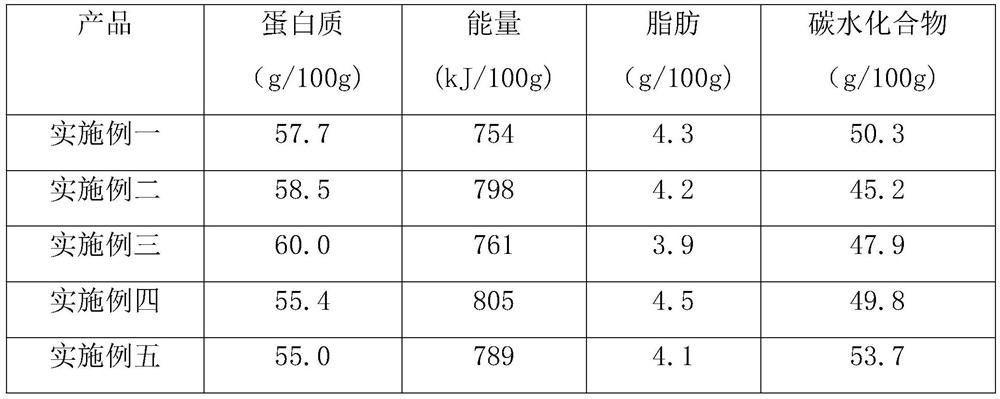
The invention discloses high protein powder and a preparation method thereof. By optimizing and improving existing food components and proportions, the protein content of the prepared high protein powder can be 55-60g per 100g, and the contents of calorie, fat and carbohydrate in every 100g of the high protein powder are lower than those of commercially available amino acid protein powder, whereinthe protein powder prepared in the third embodiment is highest in quality, the protein content reaches 60g / 100g, the calorie content is only 761kJ / 100g, the fat content is only 3.9g / 100g, and the carbohydrate content is only 47.9g / 100g. The high protein powder prepared by the method has the advantages of high protein content, comprehensive nutrition, wide raw material sources, low cost, caking prevention during brewing with water and the like. The high protein powder is suitable for supplementing nutrition for various populations and is especially suitable for sub-health people as sports food.
Owner:安徽海盛食品科技有限公司
Skin-care and moisturizing amino acid protein textile fabric
PendingCN113005601AKeep Feature PropertiesSkin-friendlyWeft knittingWarp knittingBiotechnologySkin sensitization
The invention relates to the technical field of textile fabrics, in particular to a skin-care and moisturizing amino acid protein textile fabric. The skin-care and moisturizing amino acid protein textile fabric is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5%-45% of cod-liver oil, 5%-45% of sunflower seed oil, 5%-10% of carrier fibers and 65%-75% of cotton fibers. Collagen extracted from fishes and plants is processed to coincide with carrier fibers, and then the fibers suitable for manufacturing the textile fabric are spun through the technology, so that the amino acid protein textile fabric is manufactured; and the fabric effectively keeps the original characteristics and attributes of the collagen, has the characteristics of skin friendliness, skin care, heat preservation and the like, the functions of the fabric can be permanently kept in the fibers, and the fabric cannot be lost after being washed for multiple times.
Owner:佛山奥轩科技有限公司
An Arabidopsis thaliana seed iron accumulation regulatory gene ino and its encoded protein and application
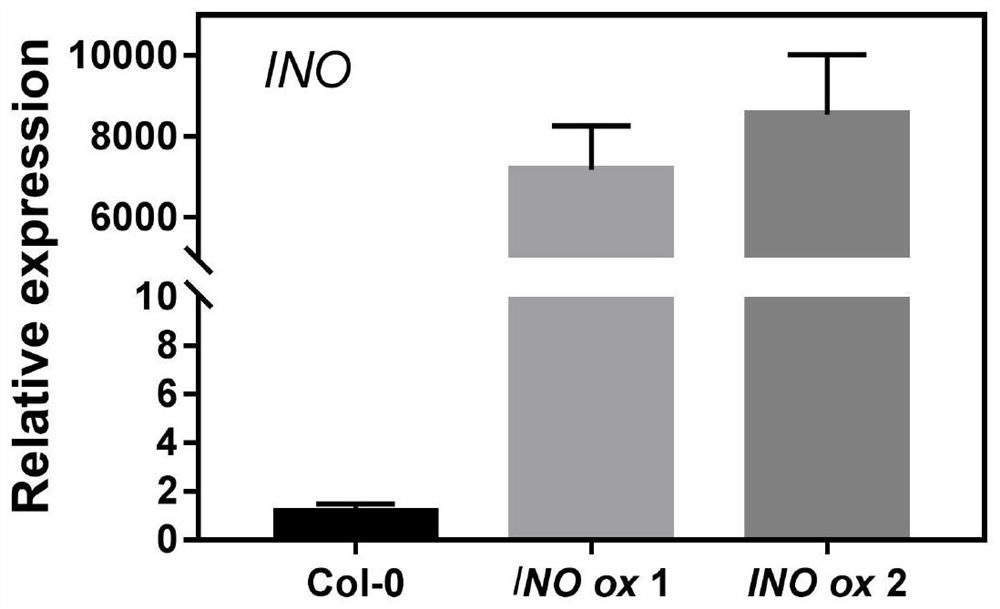
The invention provides an Arabidopsis thaliana seed iron accumulation regulating gene INO and its encoded protein and application, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The nucleotide sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana seed iron accumulation regulatory gene INO is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence listing. Arabidopsis seed iron accumulation regulatory gene INO encodes a 231-amino acid protein. Experiments of the present invention prove that the gene INO negatively regulates the loading of iron in plant seeds, so the application of the seed iron accumulation regulation gene INO or its encoded protein in the regulation of iron accumulation in plant seeds; Accumulation in seeds also improves the resistance of plants to iron-deficiency environments at the seedling stage. Therefore, the present invention also provides the application of the seed iron accumulation regulation gene INO or its coded protein in biofortifying iron or improving plant resistance to iron deficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com