Flame Sense Circuit for Gas Pilot Control
a pilot control and flame sense technology, applied in the direction of lighting and heating apparatus, combustion process, combustion regulation, etc., can solve the problems of weak flame current, marginal flame, poor quality, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of fire, and reducing the safety of pilot control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
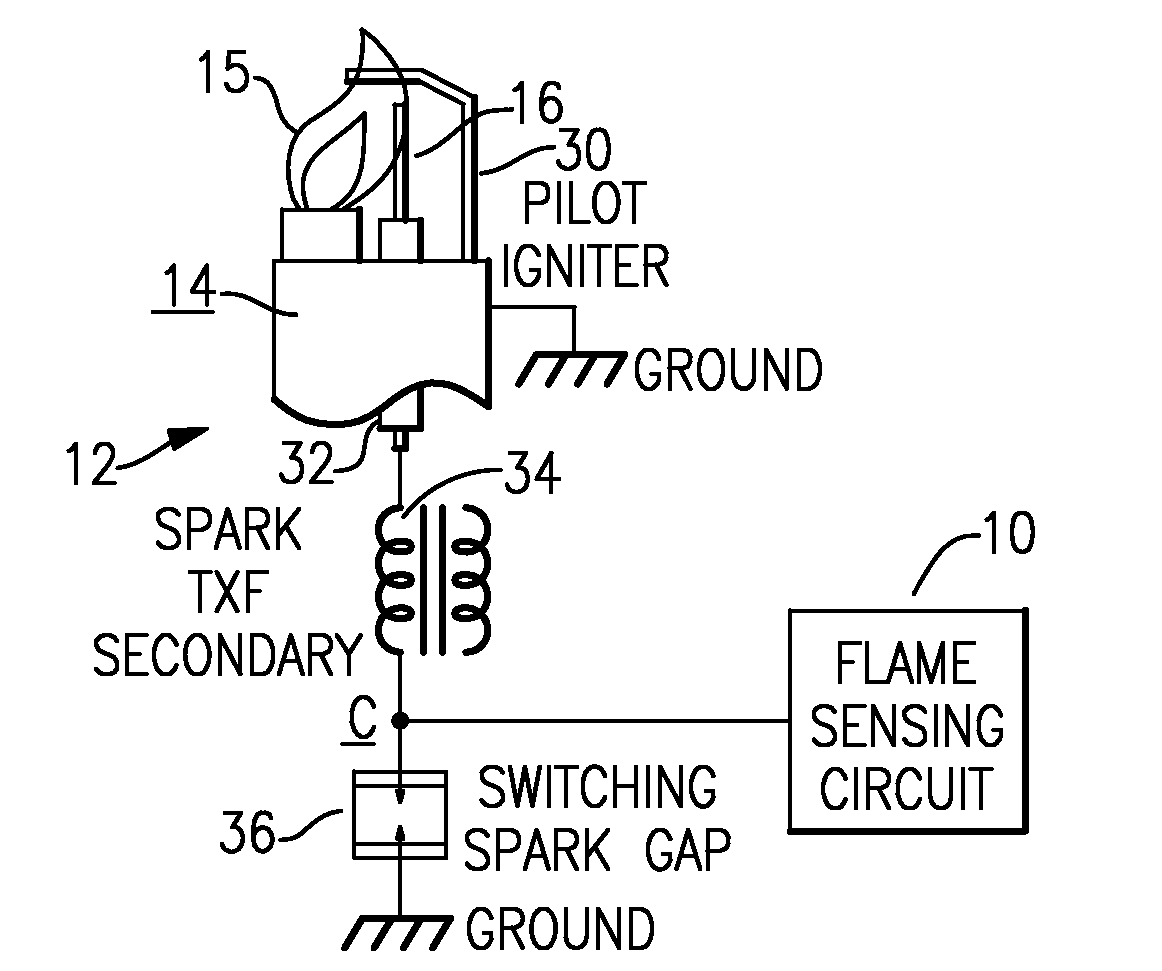
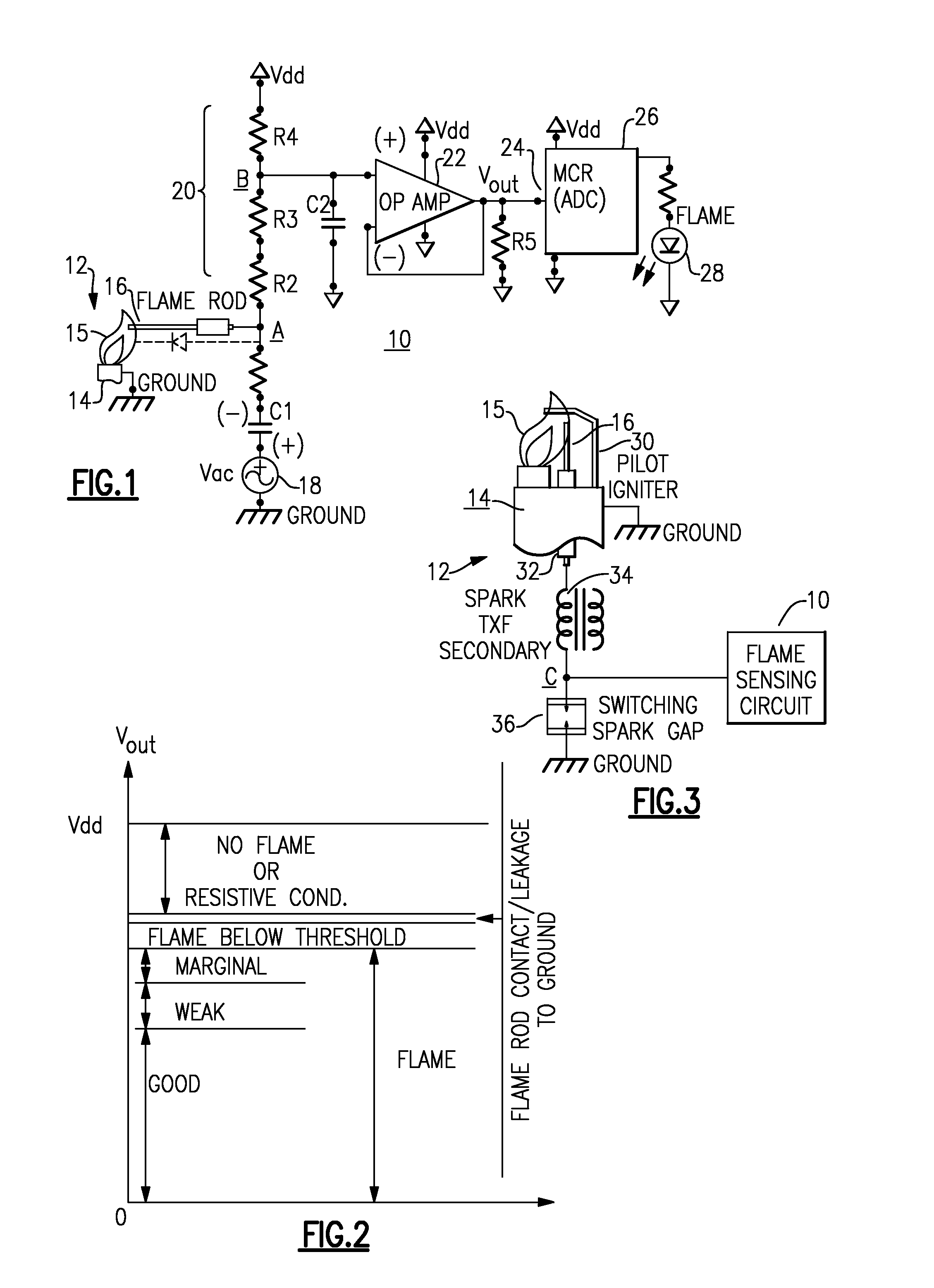
[0022]With reference now to the Drawing, FIG. 1 shows a general arrangement of a flame sense circuit 10, for monitoring the quality of flame of a gas burner pilot 12. The pilot 12 has a chassis 14, which is electrically grounded with a flame 15, when present, extending upward, and with a flame rod 16, which is electrically isolated, extending into the envelope of the flame 15.
[0023]In the flame sense circuit 10, there is an AC voltage source 18, e.g., 12-volt or 24-volt AC 60 Hz thermostat power, coupled between a ground point and one terminal of a capacitor C1. The other terminal of the capacitor C1 is coupled to a junction point or node A, which is in turn connected to the flame rod 16. Favorably, this capacitor has a capacitance value of about 2.2 nanofarads, and there may be a protective resistor R1 between the capacitor C1 and the flame rod 16 to limit current in the event that the flame rod touches the chassis and grounds. The resistor R1 favorably has a resistance value of ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com