Apparatus and method for collecting and treating waste
a technology for collecting and treating waste materials, applied in the direction of liquid degasification, separation process, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of contaminating ground water, material leaching into the ground, and plant life at or around the area where sludge is dumped, etc., to reduce the air pressure within the conduit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
I. Introduction and Definitions
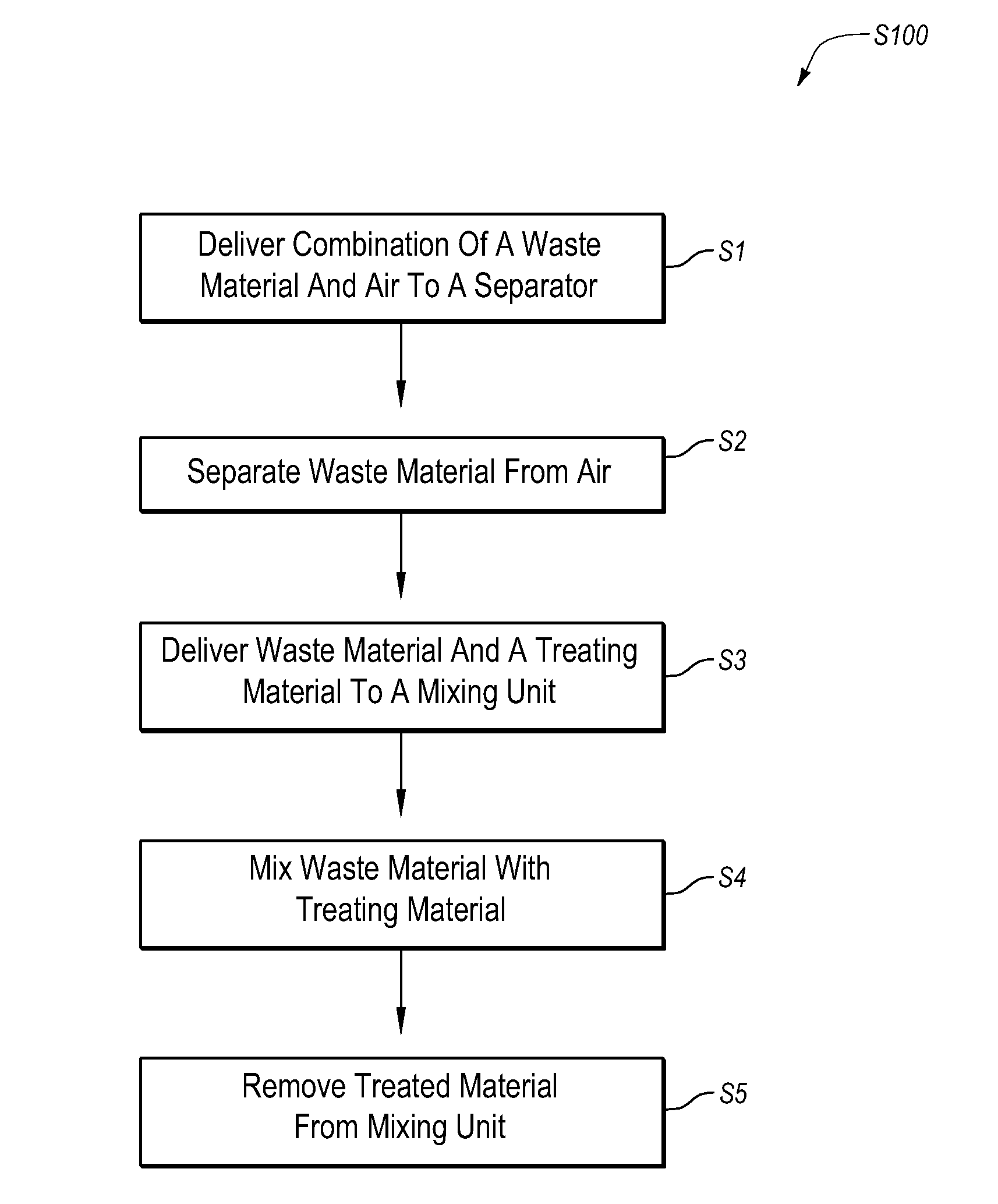
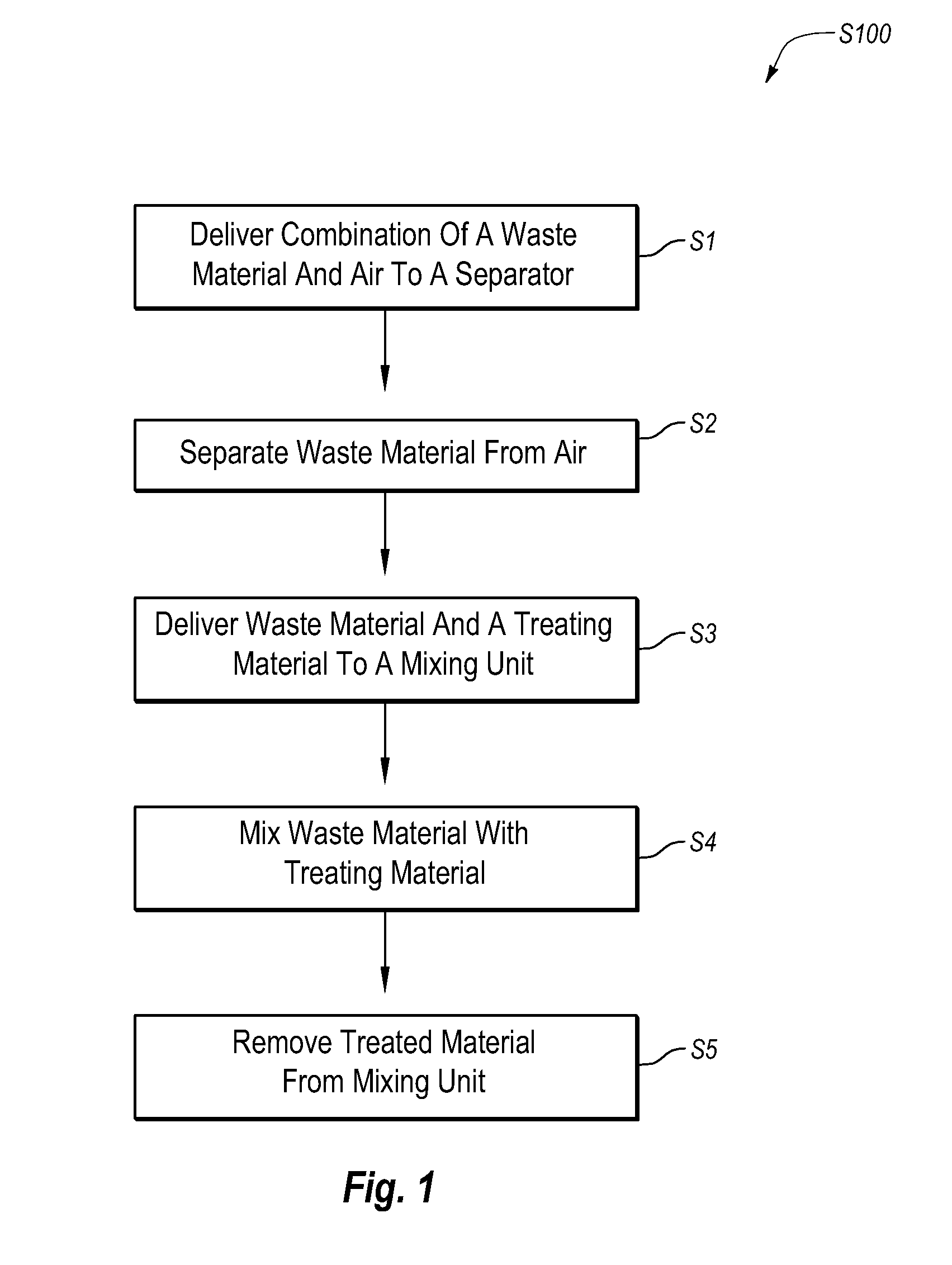
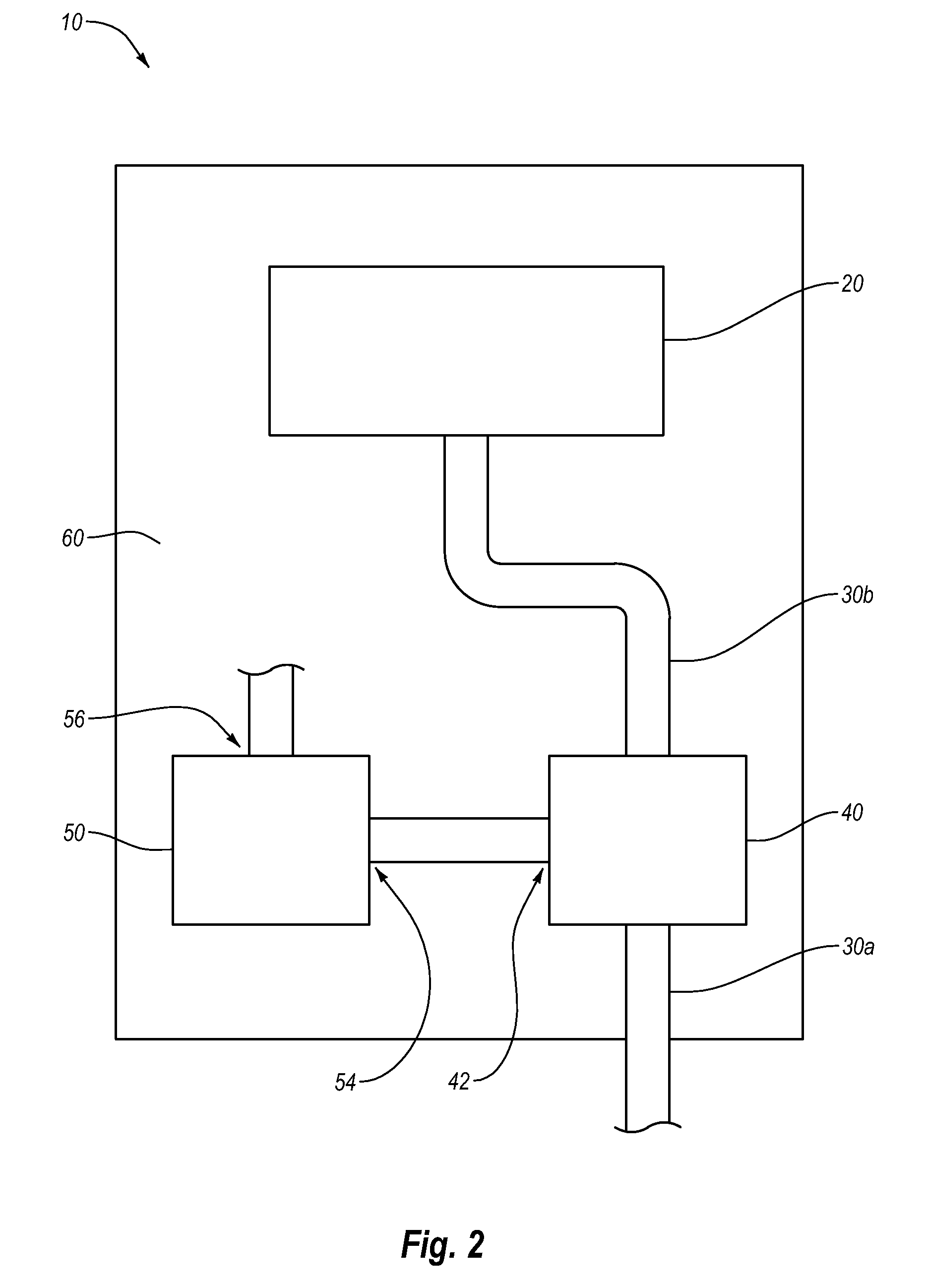
[0028]Implementations of the present invention solve one or more of the problems in the art with an apparatus for collecting and treating waste materials. In particular, one implementation of the present invention includes a mobile and integrated apparatus for continuously collecting and treating a waste material with a portable unit that can be stationed at a waste production site. The present invention also provides methods for collecting and treating waste material with a portable apparatus that continuously collects and treats a waste material.
[0029]Waste material, as that term is used herein, can include any material that requires some form of treatment before it can be disposed of at a landfill, used as a construction fill material, or otherwise discarded. A waste material can include a variety of materials in various forms. For example, a waste material can be wet or dry. A waste material may be a liquid, a solid, a slurry, or a gelatinous subst...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com