Electronic endoscope apparatus and electronic endoscope system
a technology of electronic endoscope and endoscope, which is applied in the field of electronic endoscope apparatus and electronic endoscope system, can solve the problems of overcurrent flow, heat generation, and increase of image signal noise,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
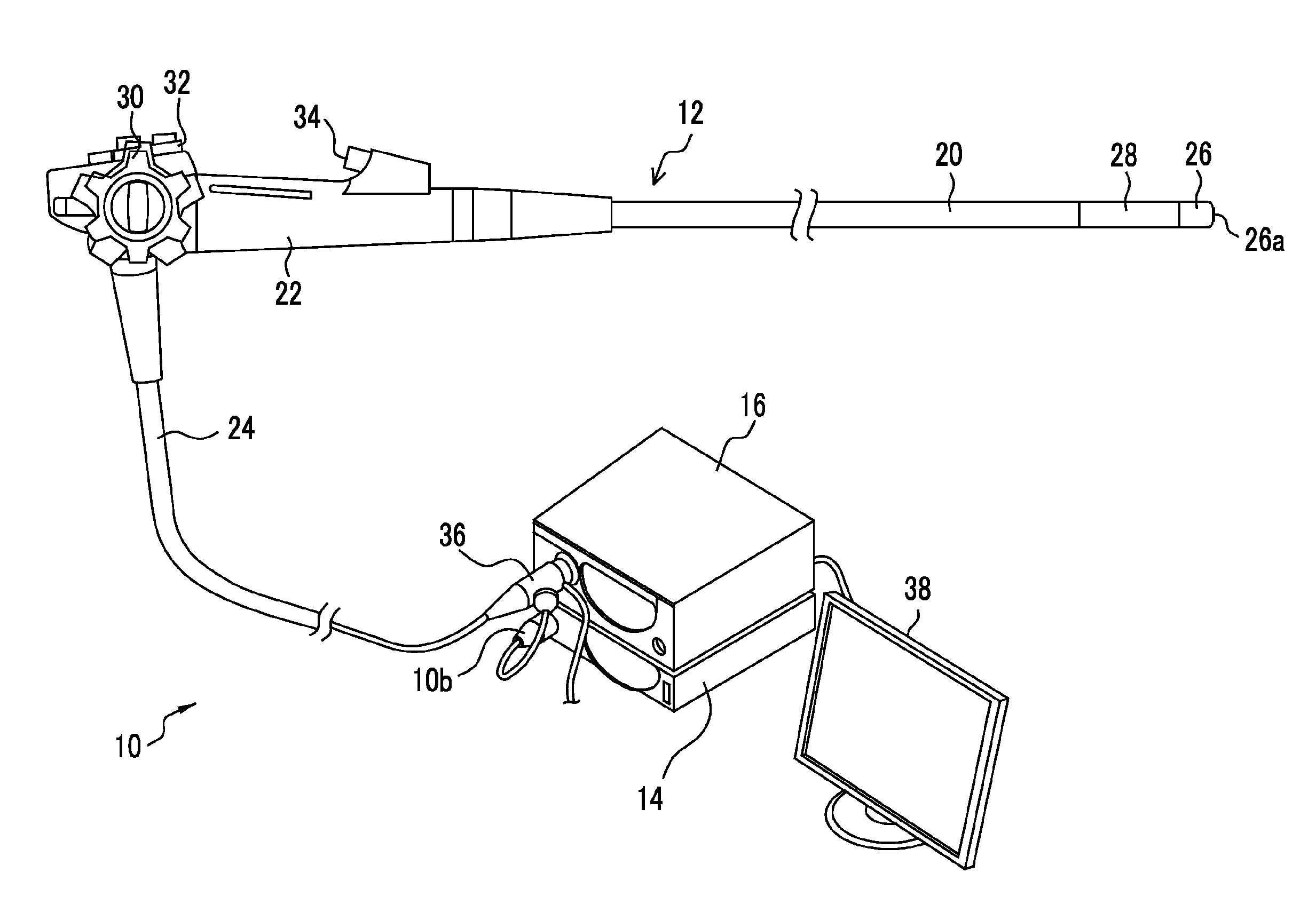
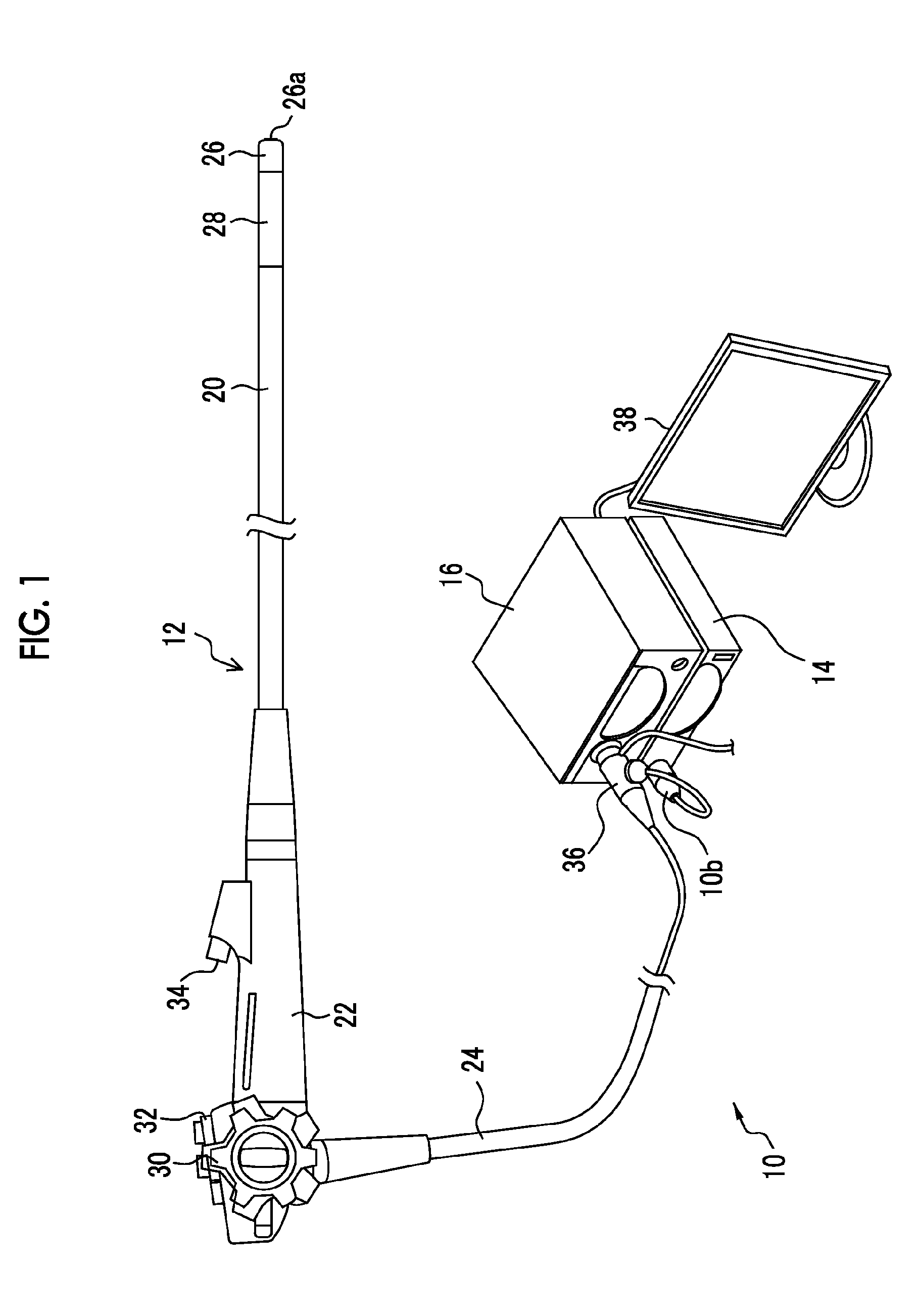
[0049]FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration view showing the schematic configuration of an electronic endoscope system related to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, an endoscope system 10 of the present embodiment is constituted by an electronic endoscope 12, a processor device 14, a light source device 16, or the like. The electronic endoscope 12 has a flexible insertion part 20 to be inserted into a body cavity of a patient (subject), a manipulating part 22 continuously provided at a proximal end portion of the insertion part 20, a flexible portion 24 connected to the processor device 14 and the light source device 16.
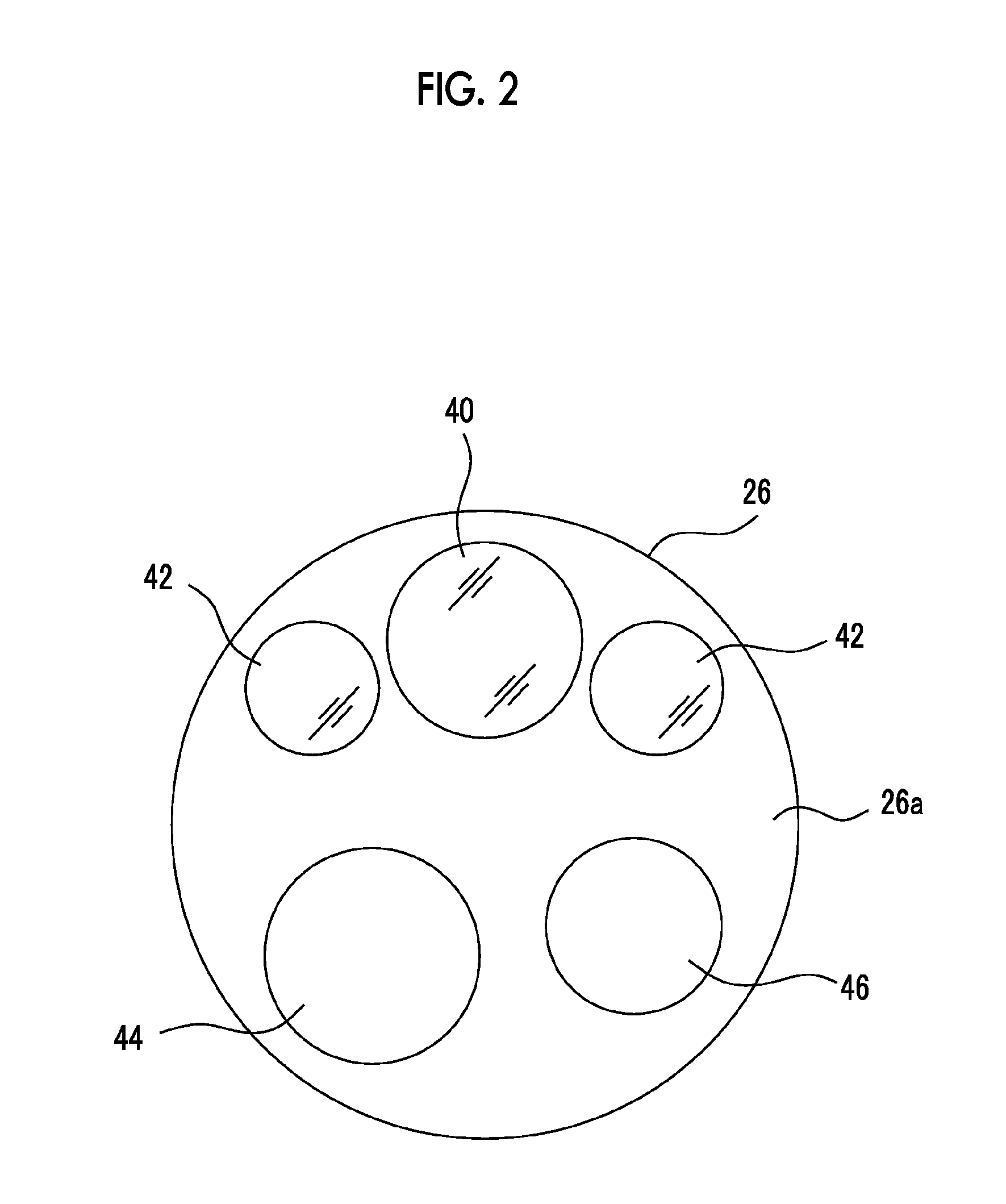
[0050]A distal end portion 26 in which a CMOS imaging device (imaging chip) 54 (refer to FIG. 3) for imaging the inside of a body cavity, or the like is built is continuously provided at the distal end of the insertion part 20. A curvable portion 28 in which a plurality of curved pieces are coupled together is provided behind the distal end por...
second embodiment
[0093]FIG. 6 is a block diagram of main parts of a second embodiment. In FIG. 6, elements that are the same or similar to the example described in FIG. 5 are designated by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted. In addition, in order to simplify illustration in FIG. 6, the description of the oscillator 116, the LVDS buffer 134, the A / D converter 138, the memory 140, and the feedback circuit 148, which are described in FIG. 5, is omitted. This is also the same in FIGS. 7 to 9.
[0094]The second embodiment of FIG. 6 is that a thermal diode (not shown) is assembled into the CMOS imaging device 54, instead of the temperature sensor 100 (thermistor) of FIG. 5. If abnormal heat generation is detected within the imaging element module (CMOS imaging device 54) in which a temperature detecting element is assembled, the detection information is notified to the CPU 132 within the scope board 130. The CPU 132 controls the second regulator 136 to stop the output of the...
third embodiment
[0095]FIG. 7 is a block diagram of main parts of a third embodiment. In FIG. 7, elements that are the same or similar to the example described in FIGS. 5 and 6 are designated by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted.
[0096]The third embodiment shown in FIG. 7 has a configuration in which elements for detecting temperature, such as the temperature sensor 100 described in FIG. 5 or the thermal diode described in FIG. 6, are not provided. While the configuration in which the temperature detecting element is omitted is adopted, the first regulator 150 to be mounted on the endoscope distal end portion includes an overcurrent detecting circuit 152, and a shutdown circuit 154 that performs a self-shutdown when overcurrent is detected. An overcurrent protection circuit is constituted by the combination of the overcurrent detecting circuit 152 and the shutdown circuit 154. That is, an overcurrent protection circuit, which monitors the amount of current that is ou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com