Patents
Literature
116 results about "Thermal diode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term "thermal diode" is sometimes used for a (possibly non-electrical) device which allows heat to flow preferentially in one direction. Or, the term may be used to describe an electrical (semiconductor) diode in reference to a thermal effect or function. Or the term may be used to describe both situations, where an electrical diode is used as a heat-pump or thermoelectric cooler.
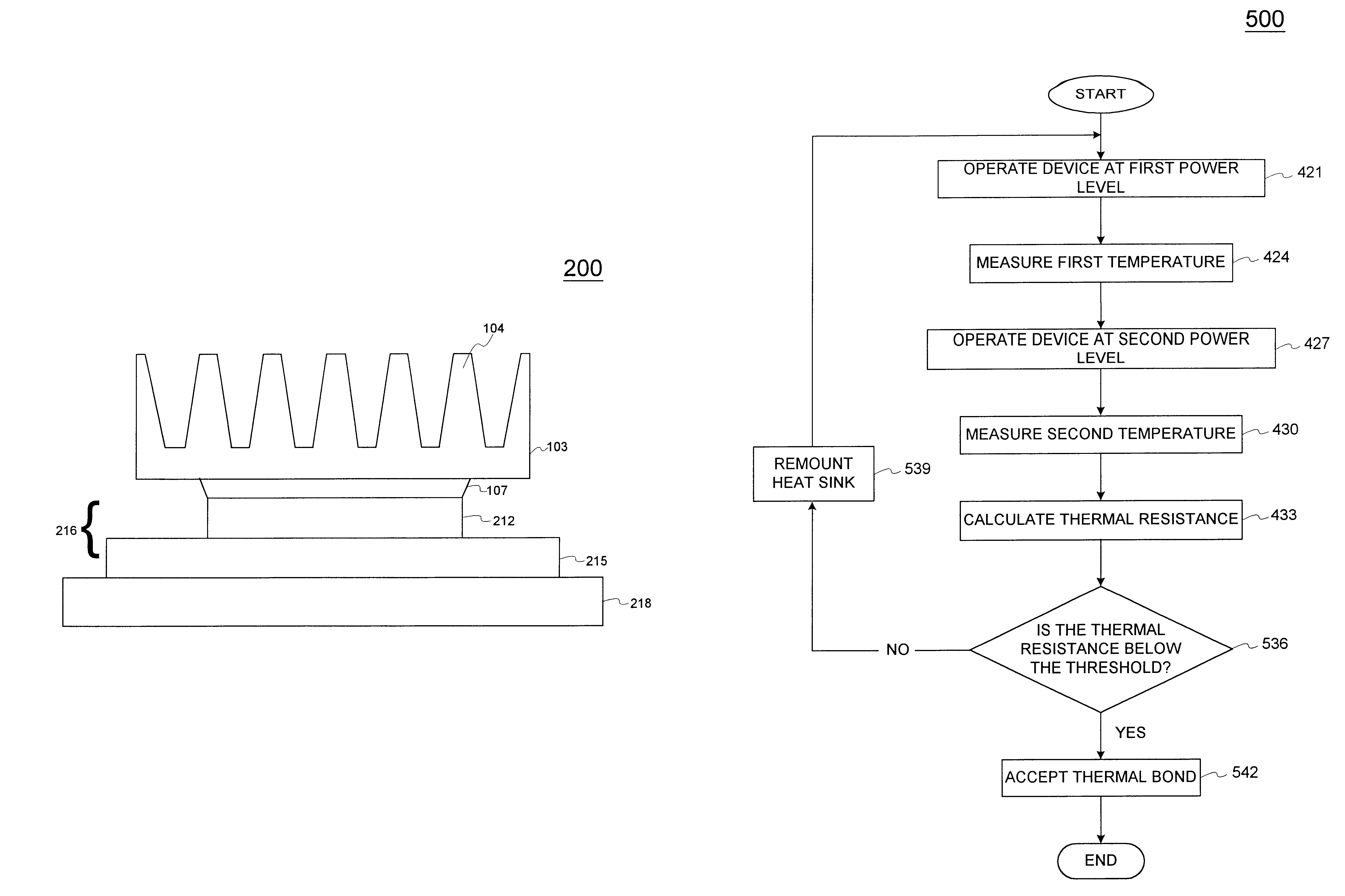
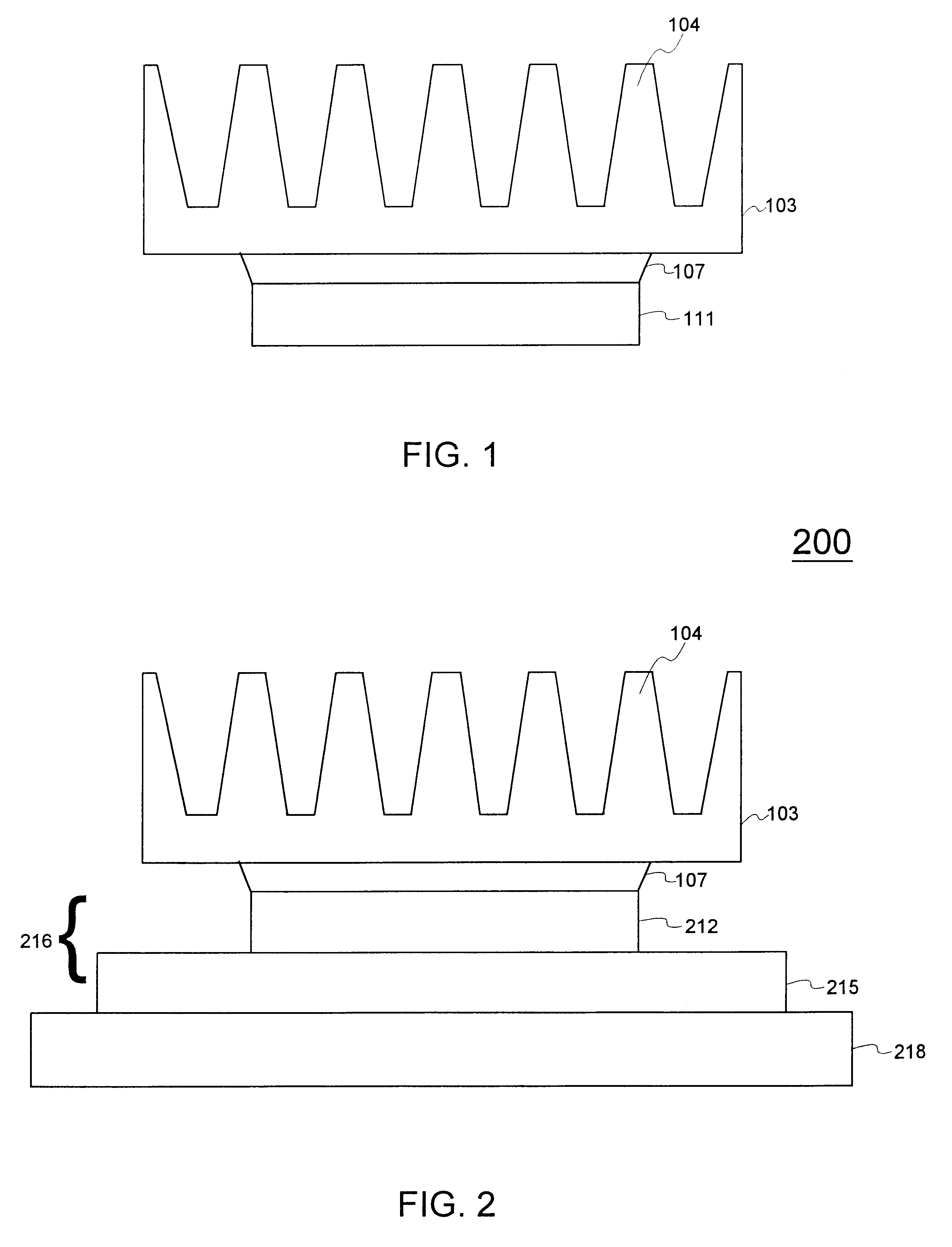
Thermal bond verification
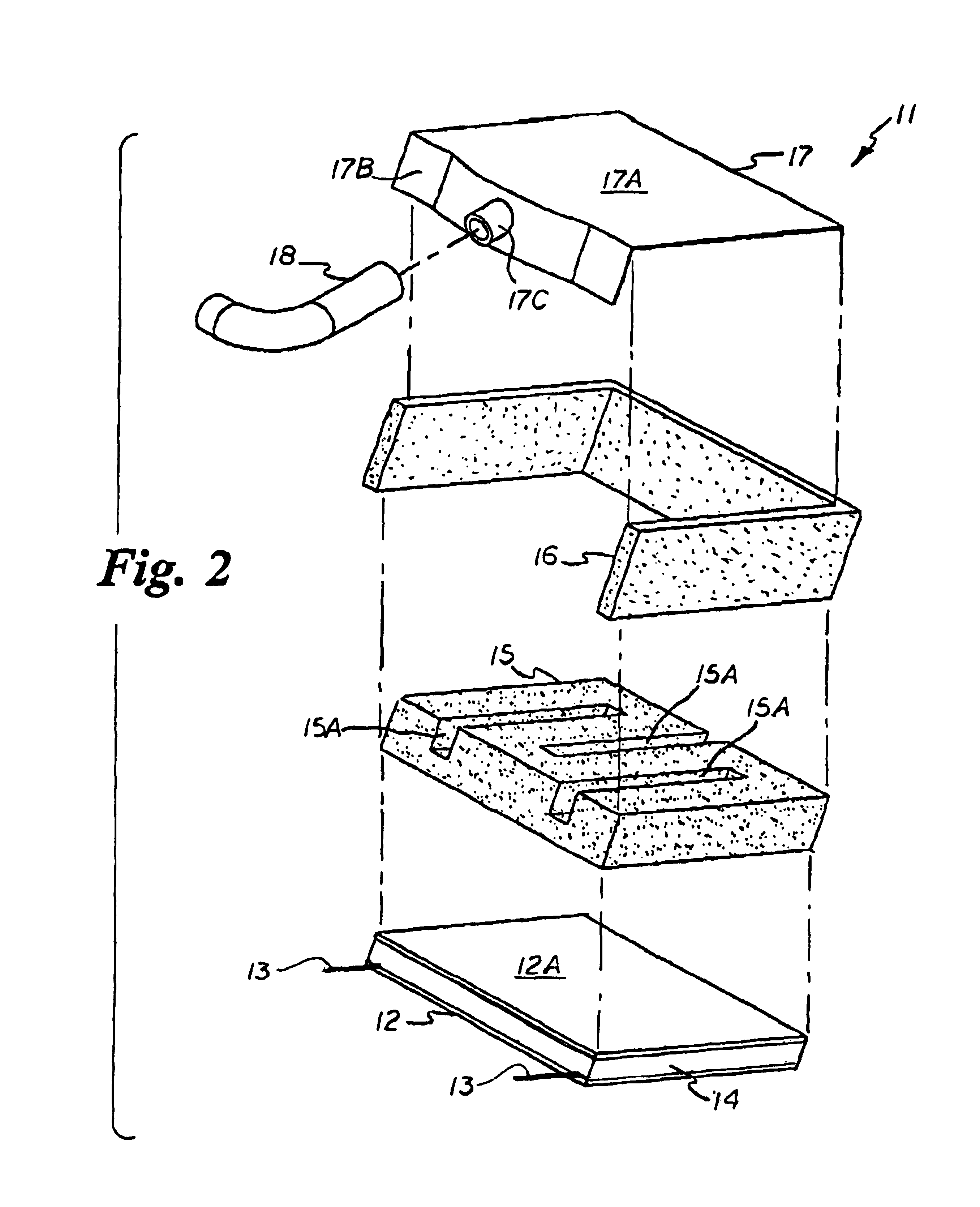
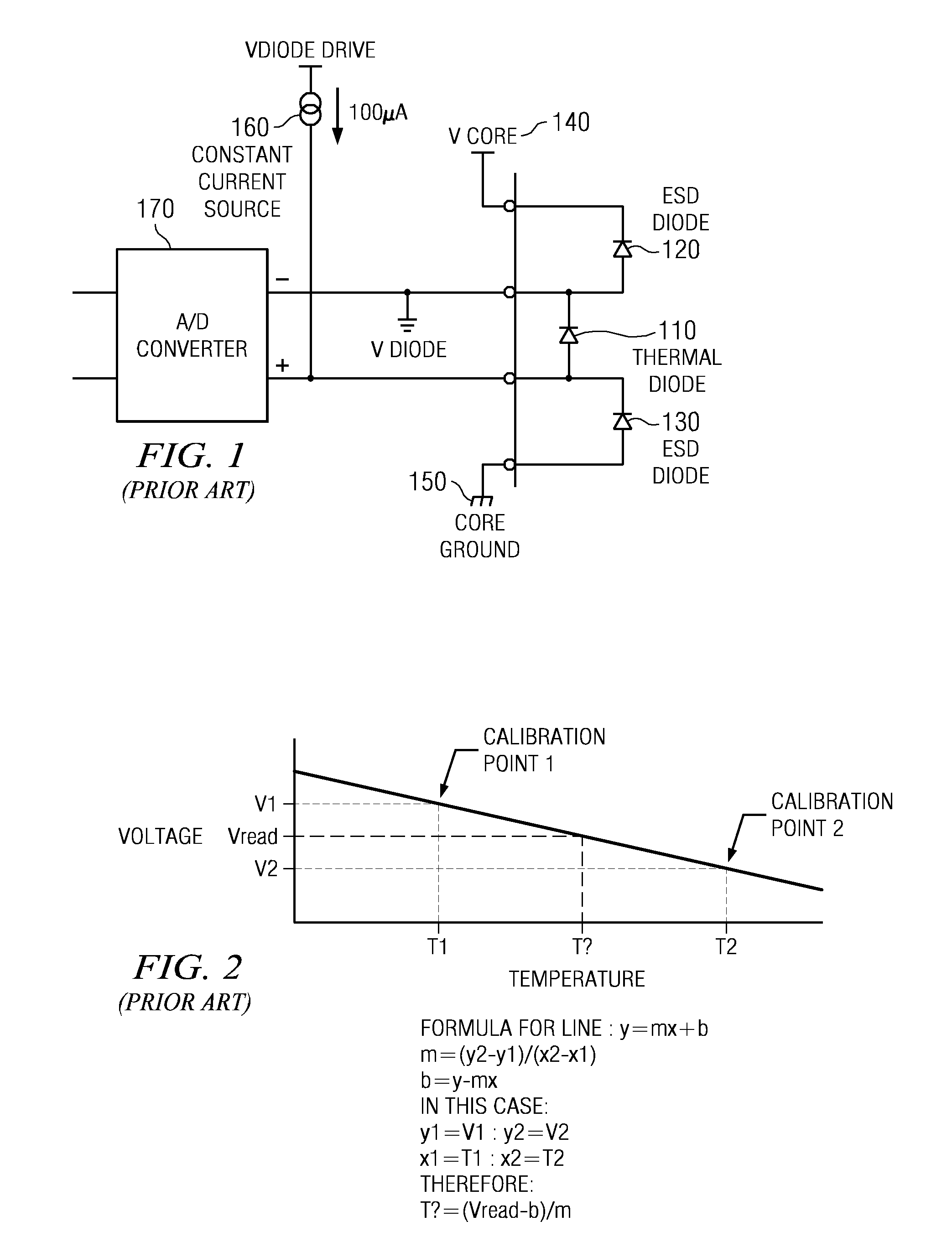
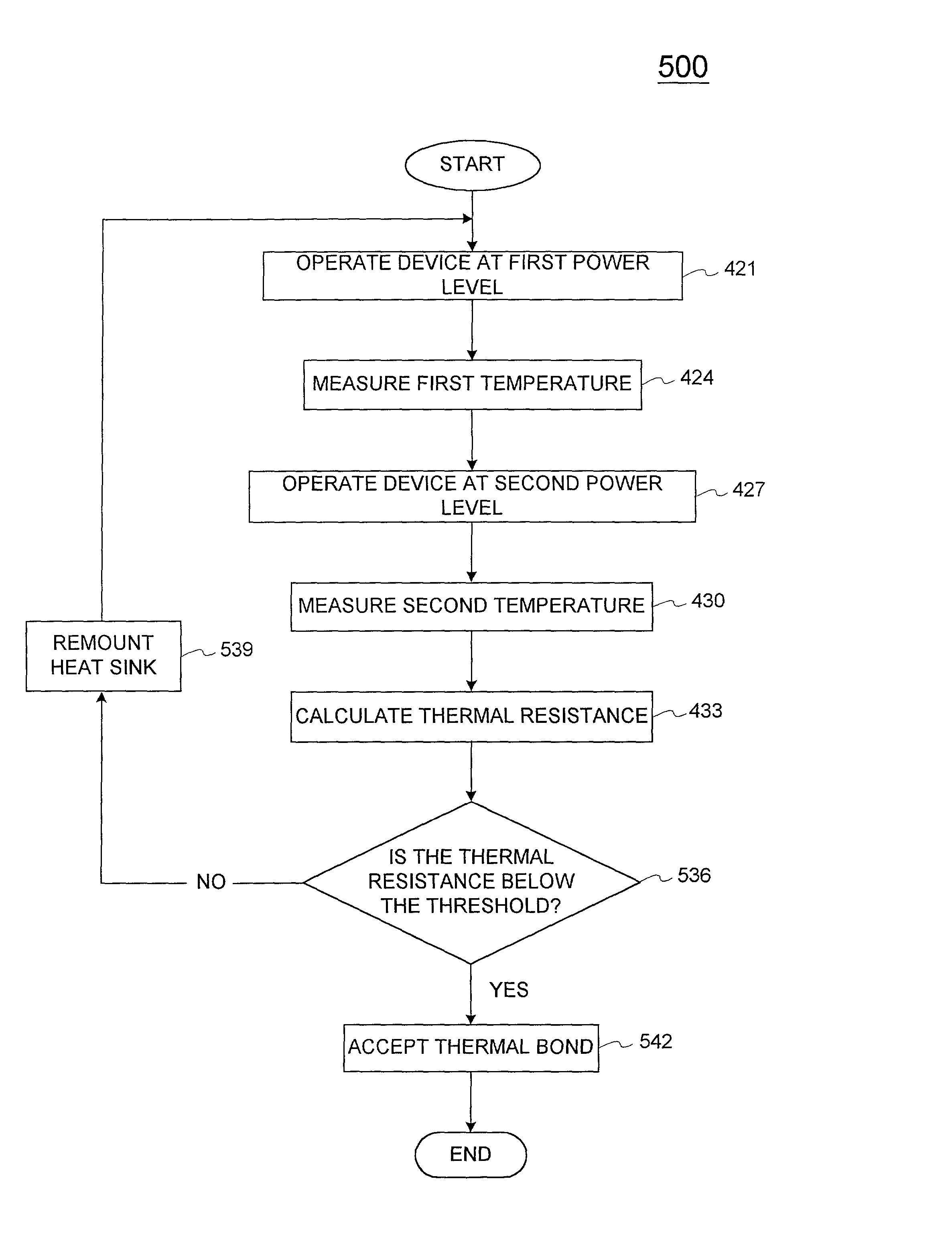
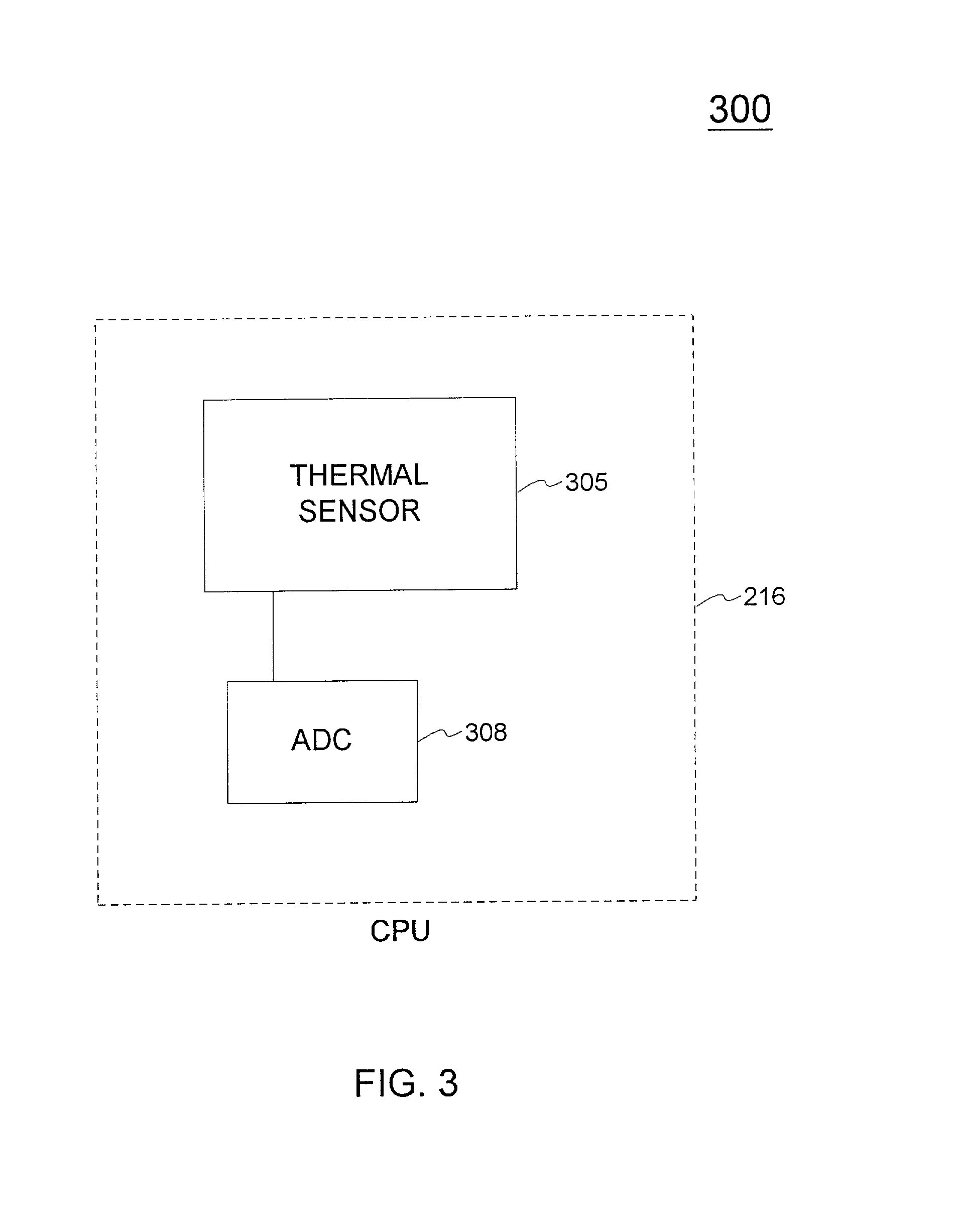
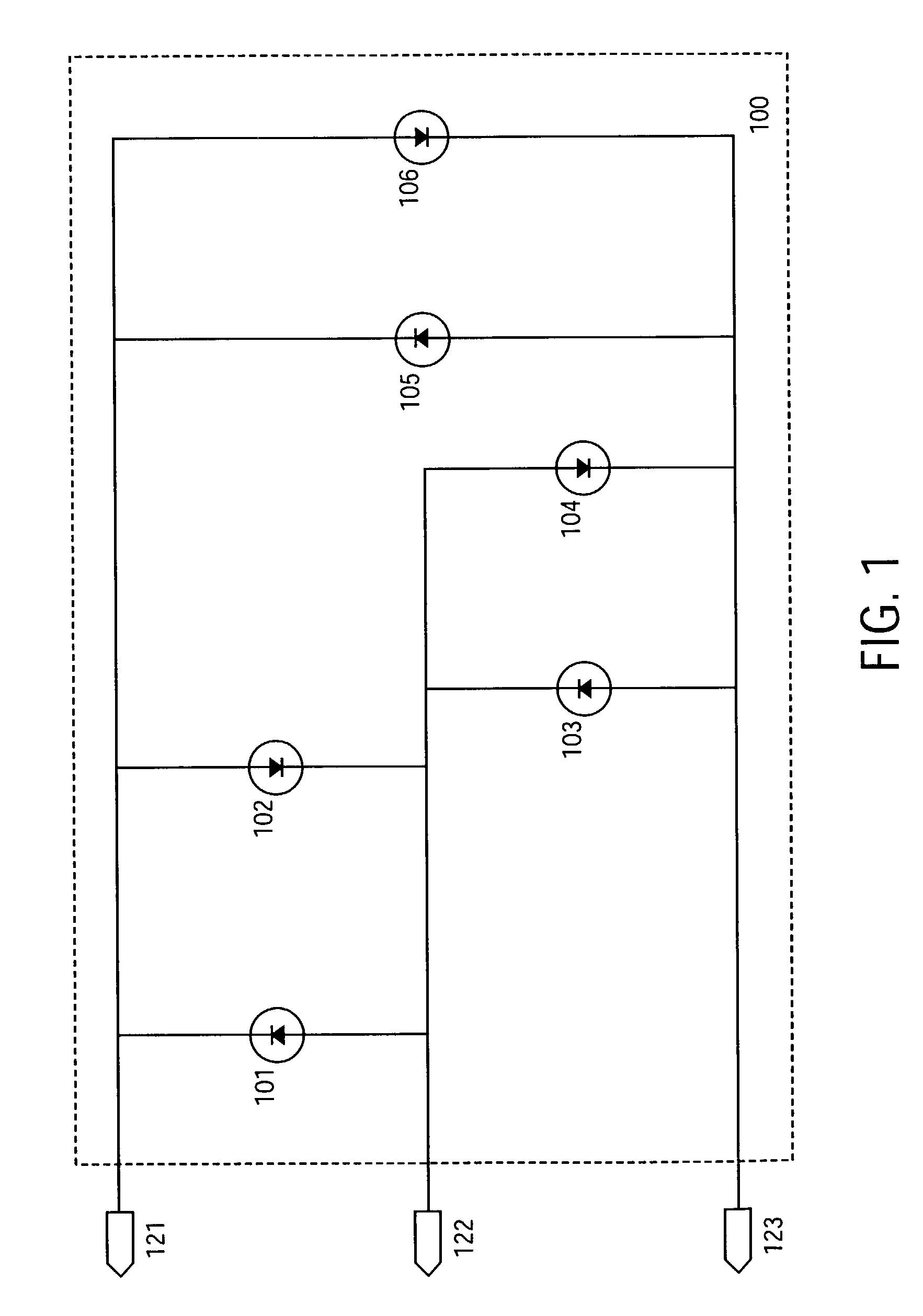
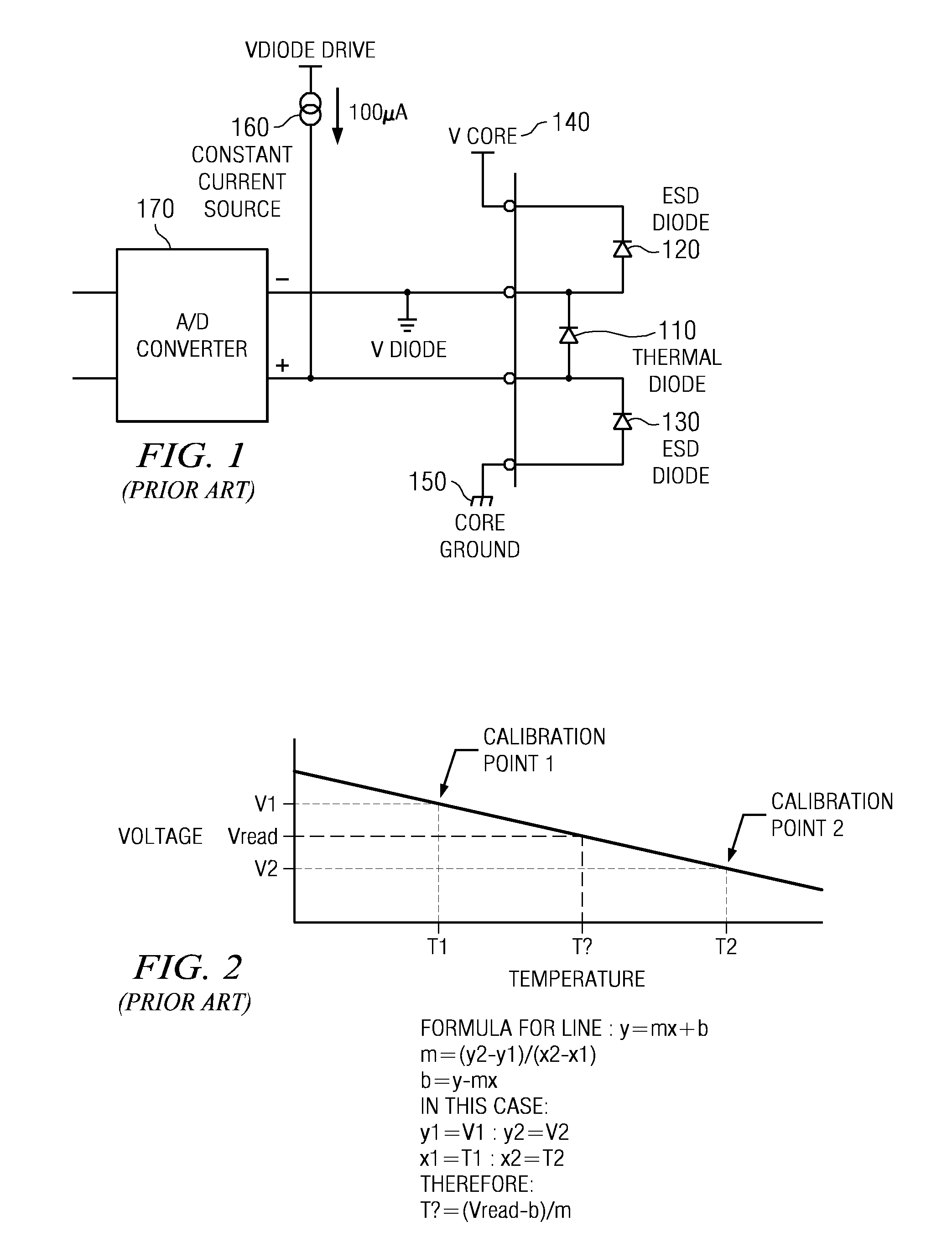
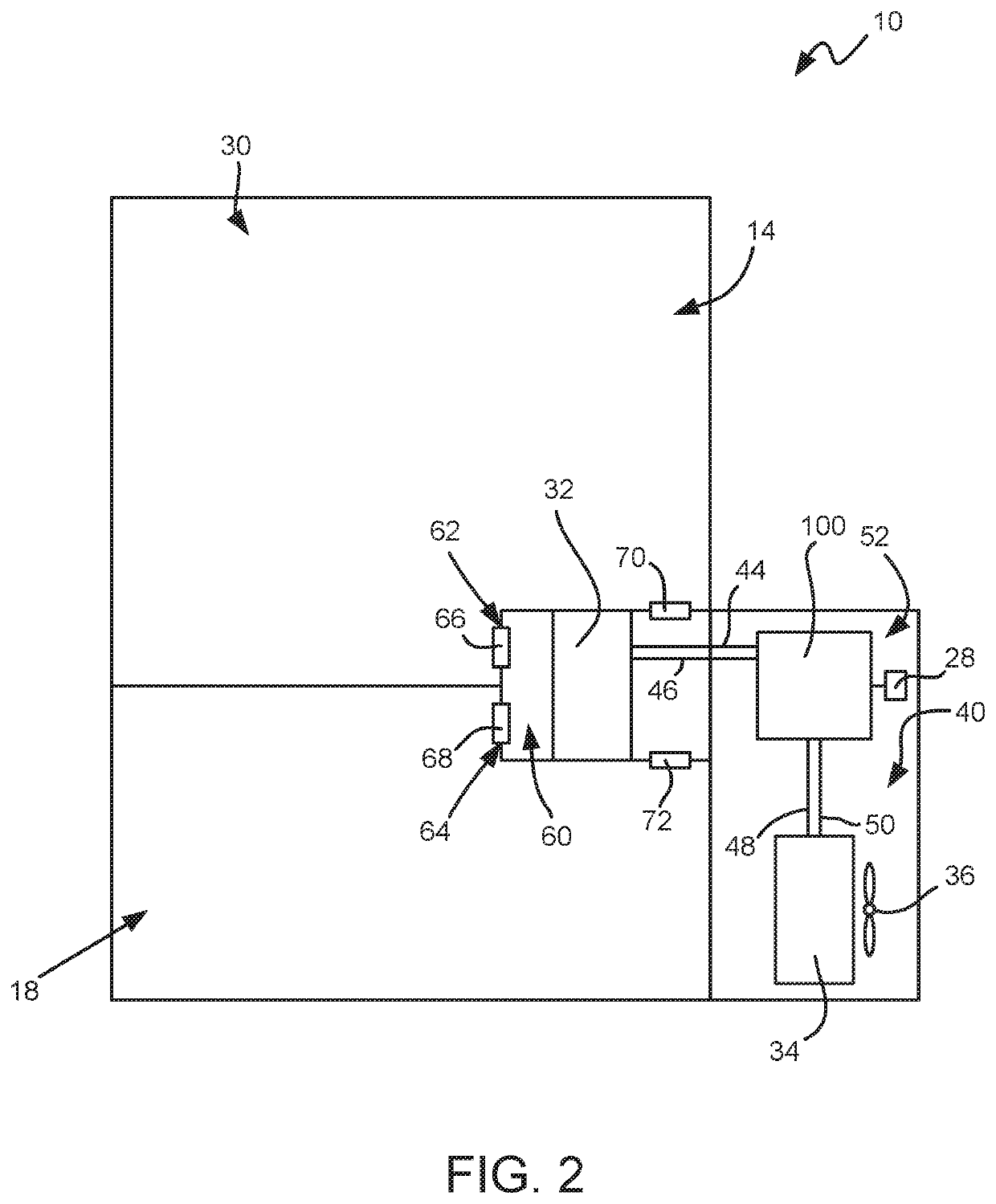
A system and method for evaluating the thermal bond between a heat-producing device and a heat-absorbing apparatus. The heat-producing device may be a CPU, such as an INTEL PENTIUM microprocessor, and the heat-absorbing apparatus may be a heat sink. The two may be joined with a heat-conducting substance such as thermal grease or adhesive. In one exemplary embodiment, the heat-producing device is operated at a first power level, a first temperature measurement is then taken, the device is operated at a second power level, and then a second temperature measurement is then taken. The thermal resistance is then calculated, which may involve subtracting the second temperature from the first, and may involve dividing by the power level. The first power level may be full power, and the second power level may be near zero. The first temperature may be measured when equilibrium temperatures have been reached, and the second temperature may be measured a predetermined amount of time after the second power level is initiated, which may be just enough time for the temperatures of the CPU and the heat sink to equalize. The CPU may perform the calculations, and the temperature may be measured with an on-board thermal sensor which may be a thermal diode.
Owner:SBS TECH
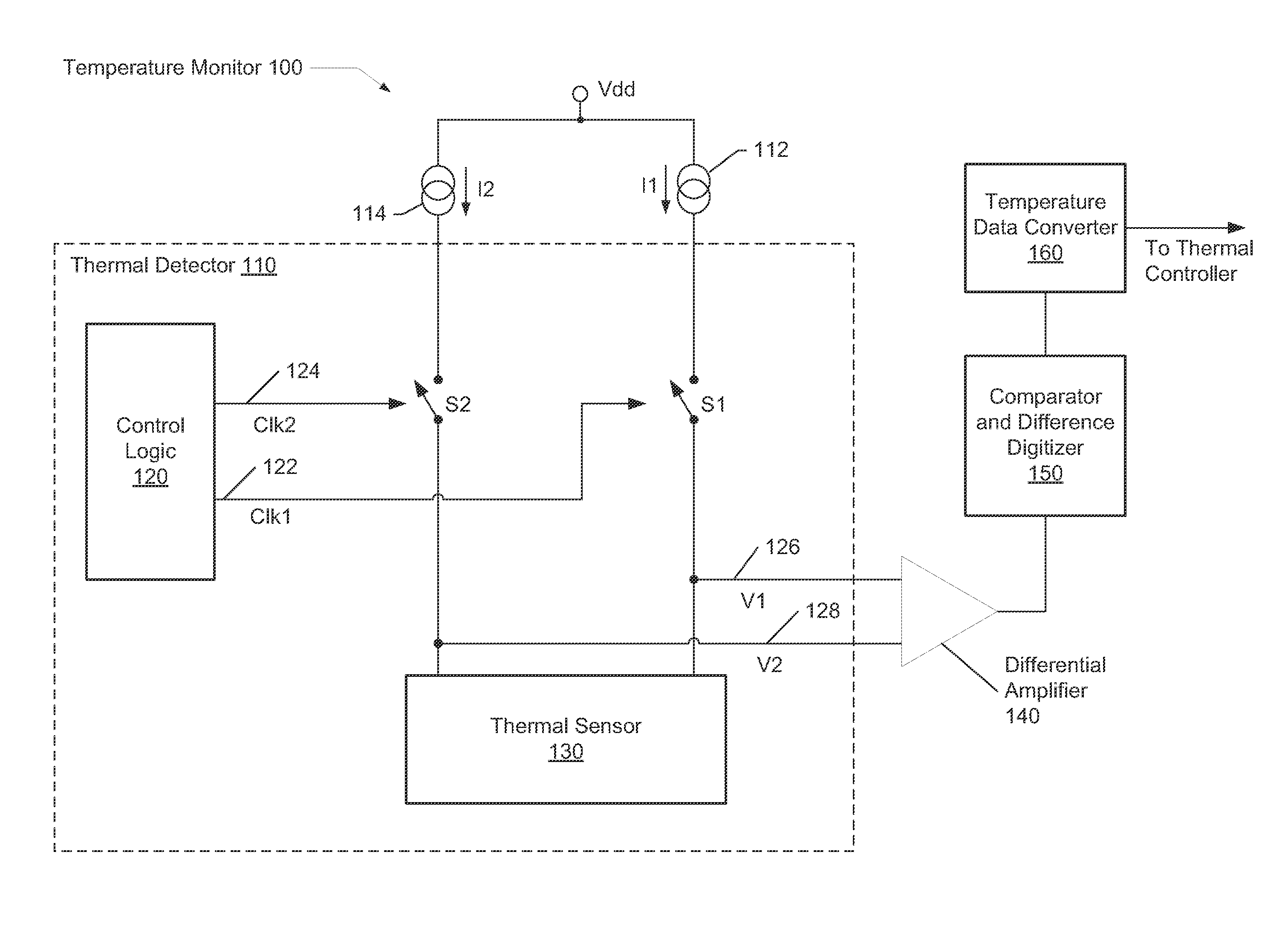
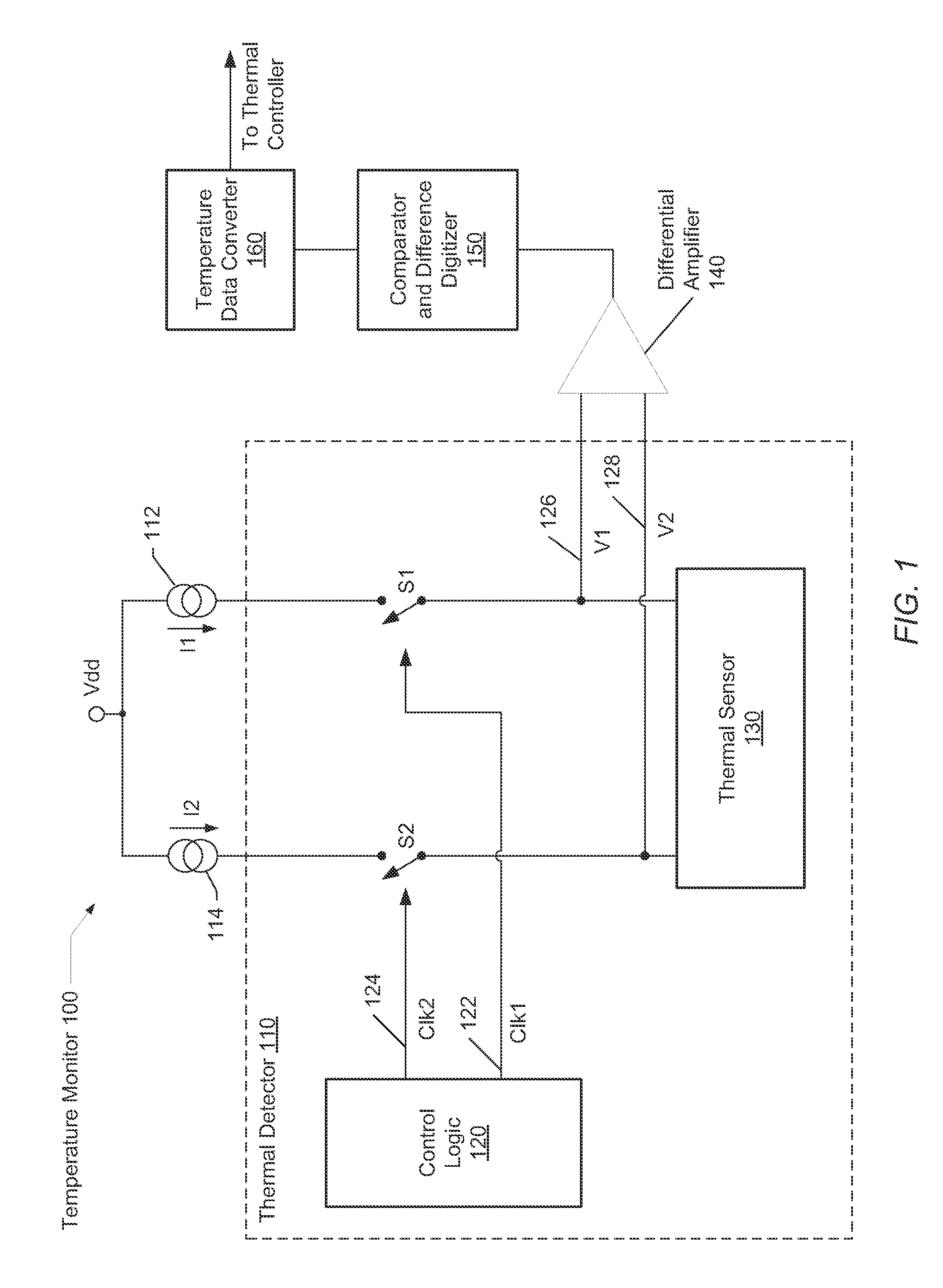
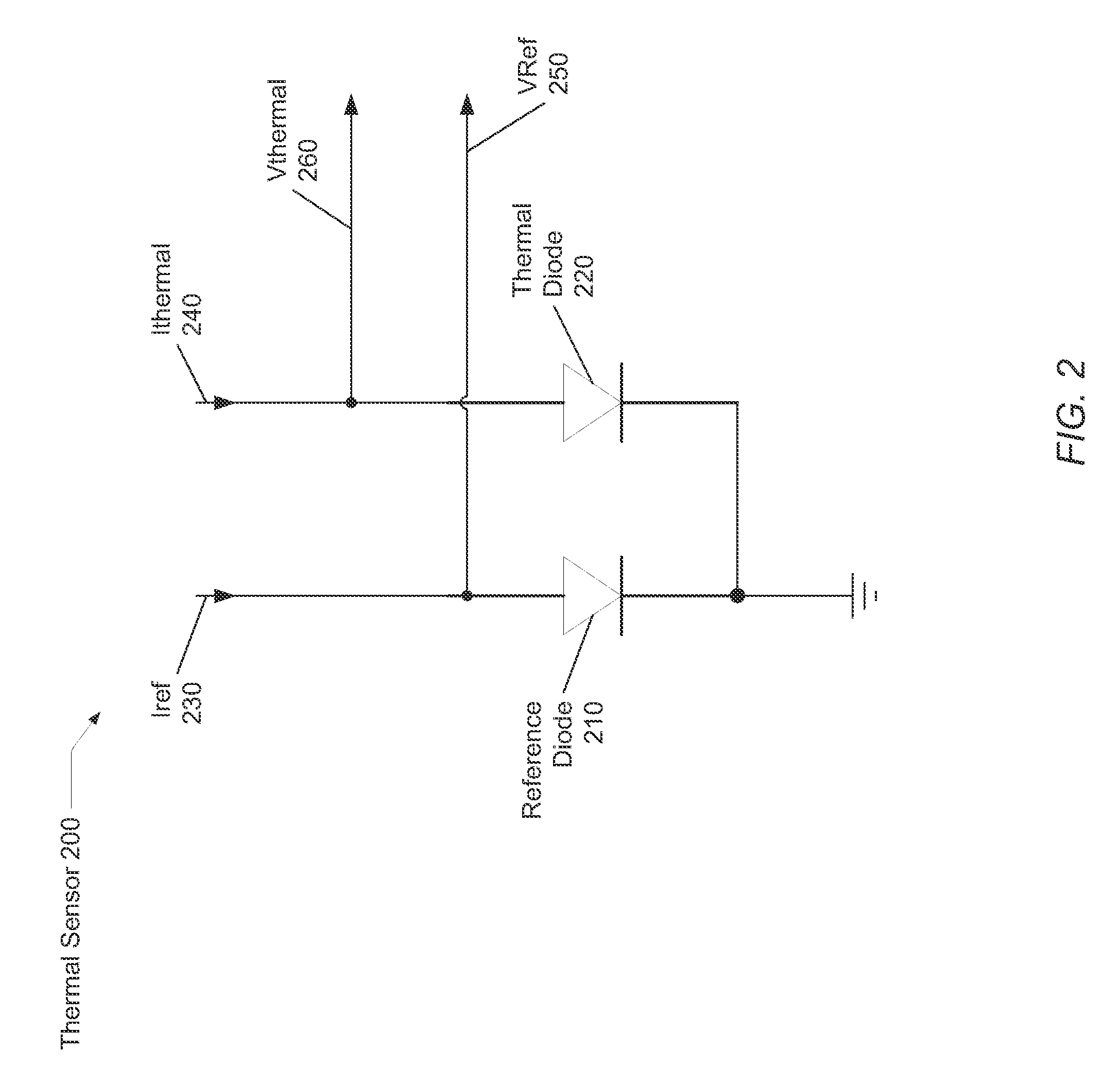
Dynamic voltage reference for sampling delta based temperature sensor
ActiveUS20130120930A1Efficient measurementDigital data processing detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVoltage referenceDiode voltage
A system and method for measuring integrated circuit (IC) temperature. An integrated circuit (IC) includes a thermal sensor and data processing circuitry. The thermal sensor utilizes switched currents provided to a reference diode and a thermal diode. The ratios of the currents provided to each of these diodes may be chosen to provide a given delta value between the resulting sampled diode voltages. At a later time, a different ratio of currents may be provided to each of these diodes to provide a second given delta value between the resulting sampled diode voltages. A differential amplifier within the data processing circuitry may receive the analog sampled voltages and determine the delta values. Other components within the data processing circuitry may at least digitize and store one or both of the delta values. A difference between the digitized delta values may calculated and used to determine an IC temperature digitized code.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
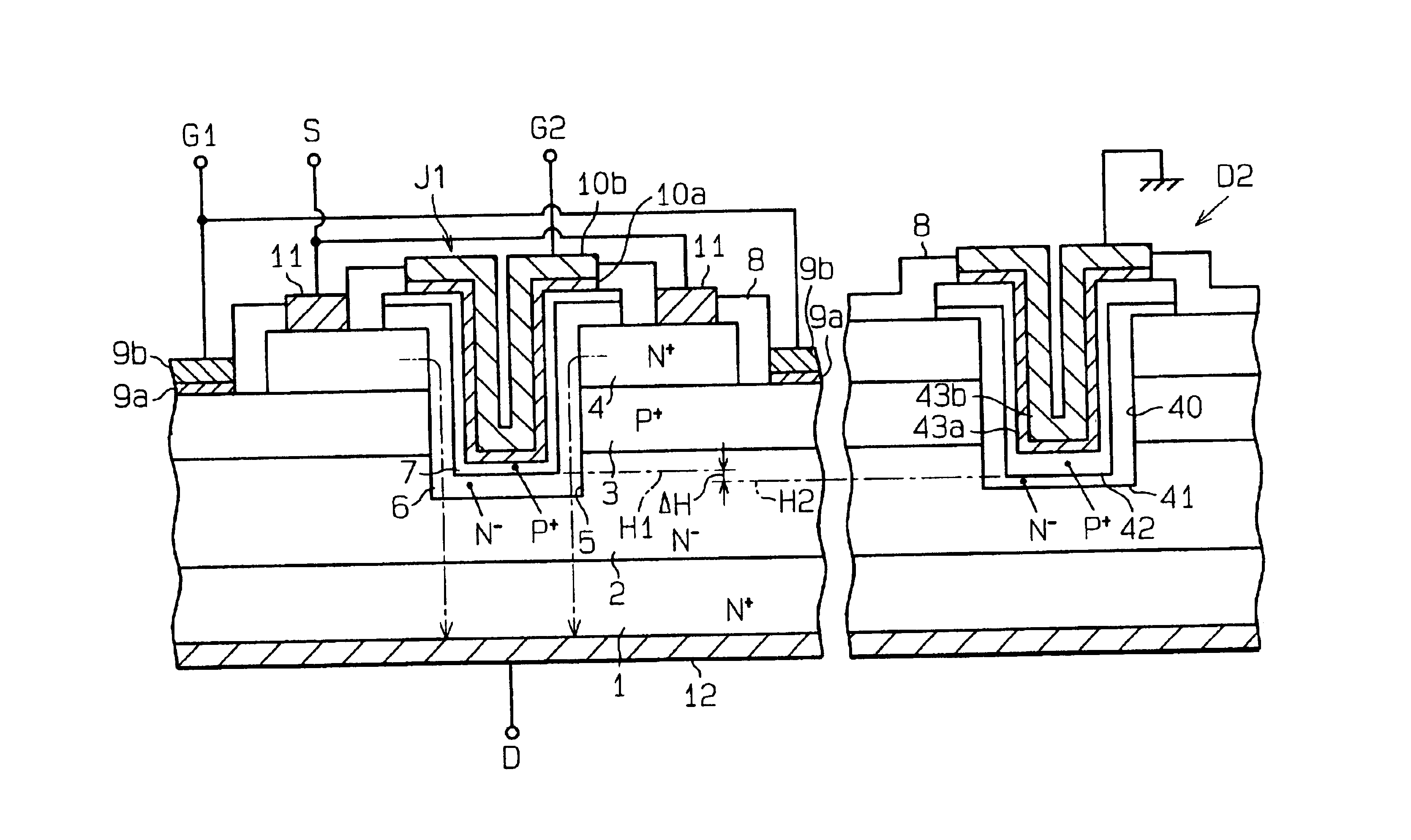
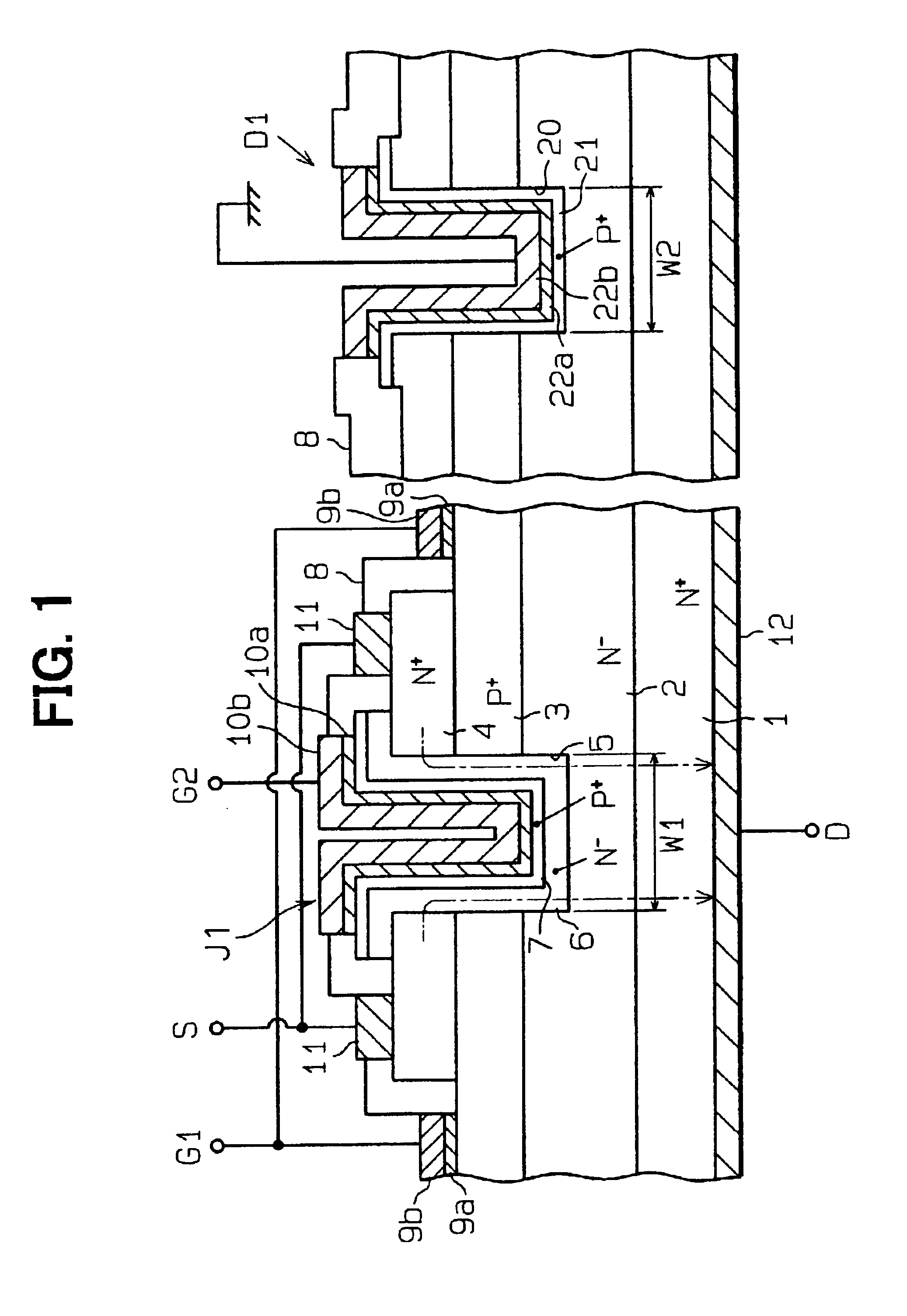
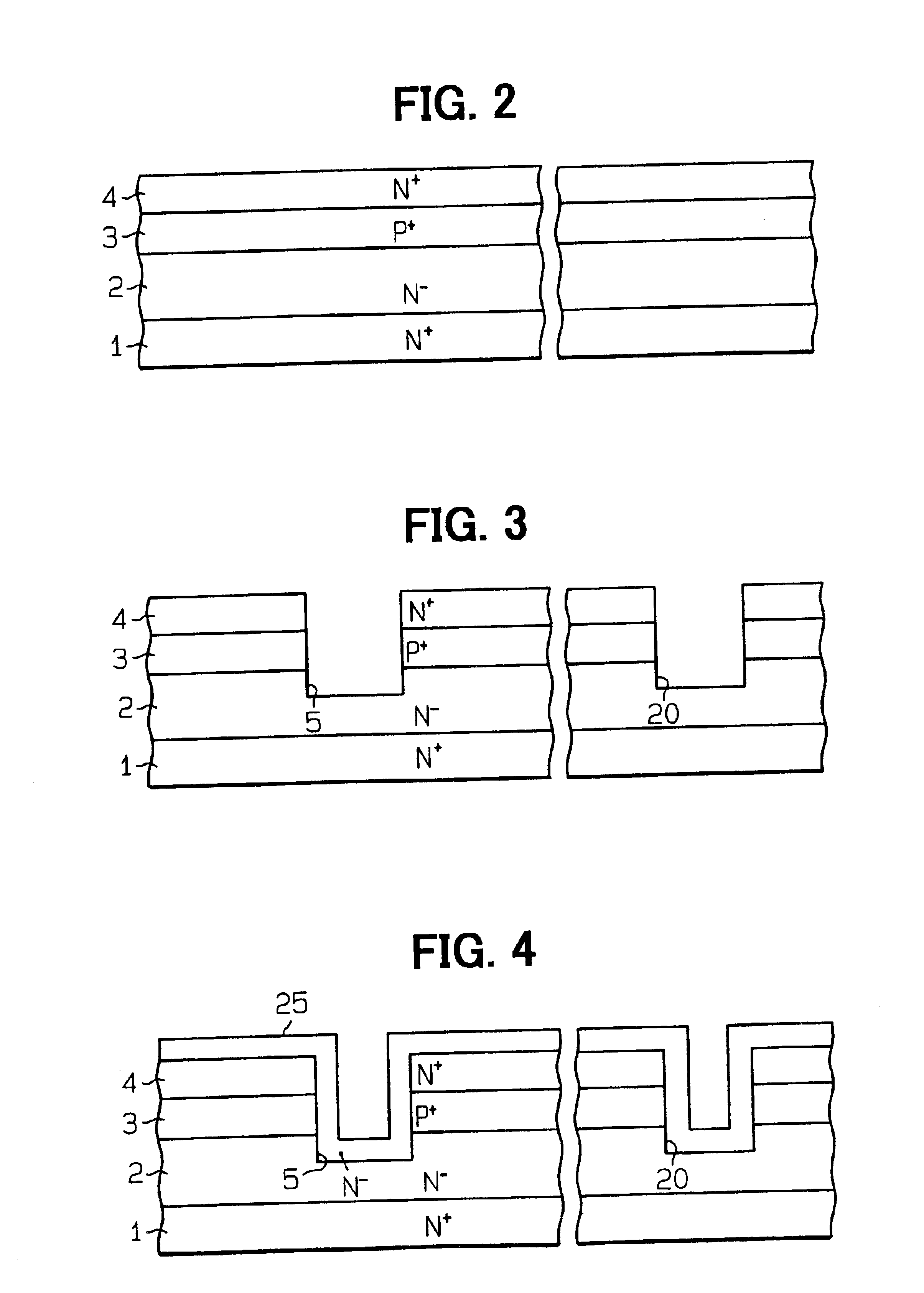
Silicon carbide power device having protective diode
InactiveUS6855981B2Avoid damageLower breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierZener diode
A silicon carbide power device includes a junction field effect transistor and a protective diode, which is a Zener or PN junction diode. The PN junction of the protective diode has a breakdown voltage lower than the PN junction of the transistor. Another silicon carbide power device includes a protective diode, which is a Schottky diode. The Schottky diode has a breakdown voltage lower than the PN junction of the transistor by adjusting Schottky barrier height or the depletion layer formed in the semiconductor included in the Schottky diode. Another silicon carbide power device includes three protective diodes, which are Zener diodes. Two of the protective diodes are used to clamp the voltages applied to the gate and the drain of the transistor due to surge energy and used to release the surge energy. The last diode is a thermo-sensitive diode, with which the temperature of the JFET is measured.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050121701A1Reduce stepsMinimizes risk of malfunctionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
In a semiconductor device, risk of malfunction of a heat sensing diode on a main side of a vertical power semiconductor element is minimized by arranging the diode at the center of the element. Because the heat sensing diode is disposed at the center of the main side of the semiconductor element, the diode is protected from breakage and heat accumulation even when an excessive heat causes a crack at the periphery of a conductive bonding material that connects the element and the metal bodies on both sides of the element.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Solid state heat pump appliance with carbon foam heat sink
InactiveUS6948322B1Less power to operateImprove heat transfer efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectDomestic cooling apparatusAir filterPorous carbon
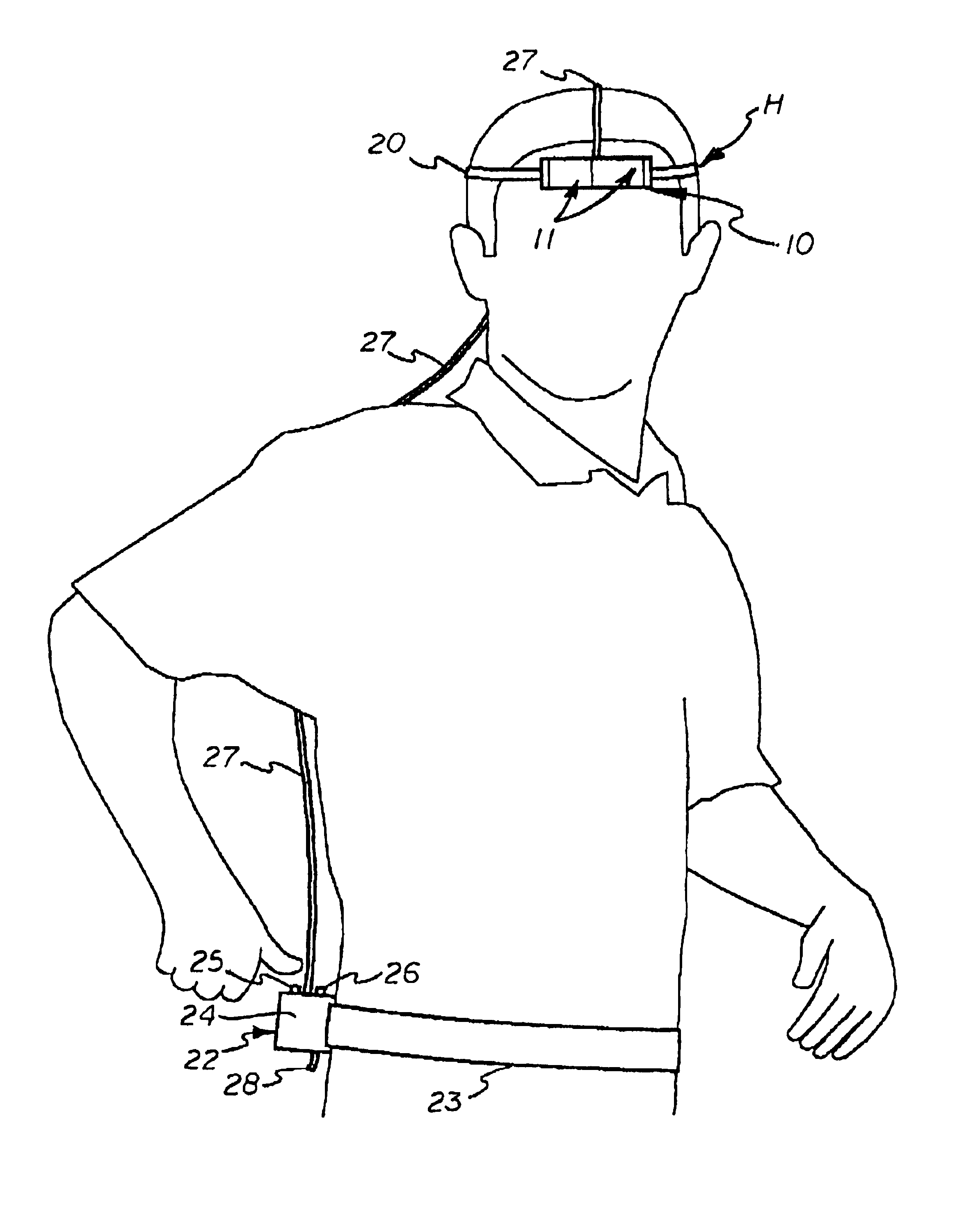
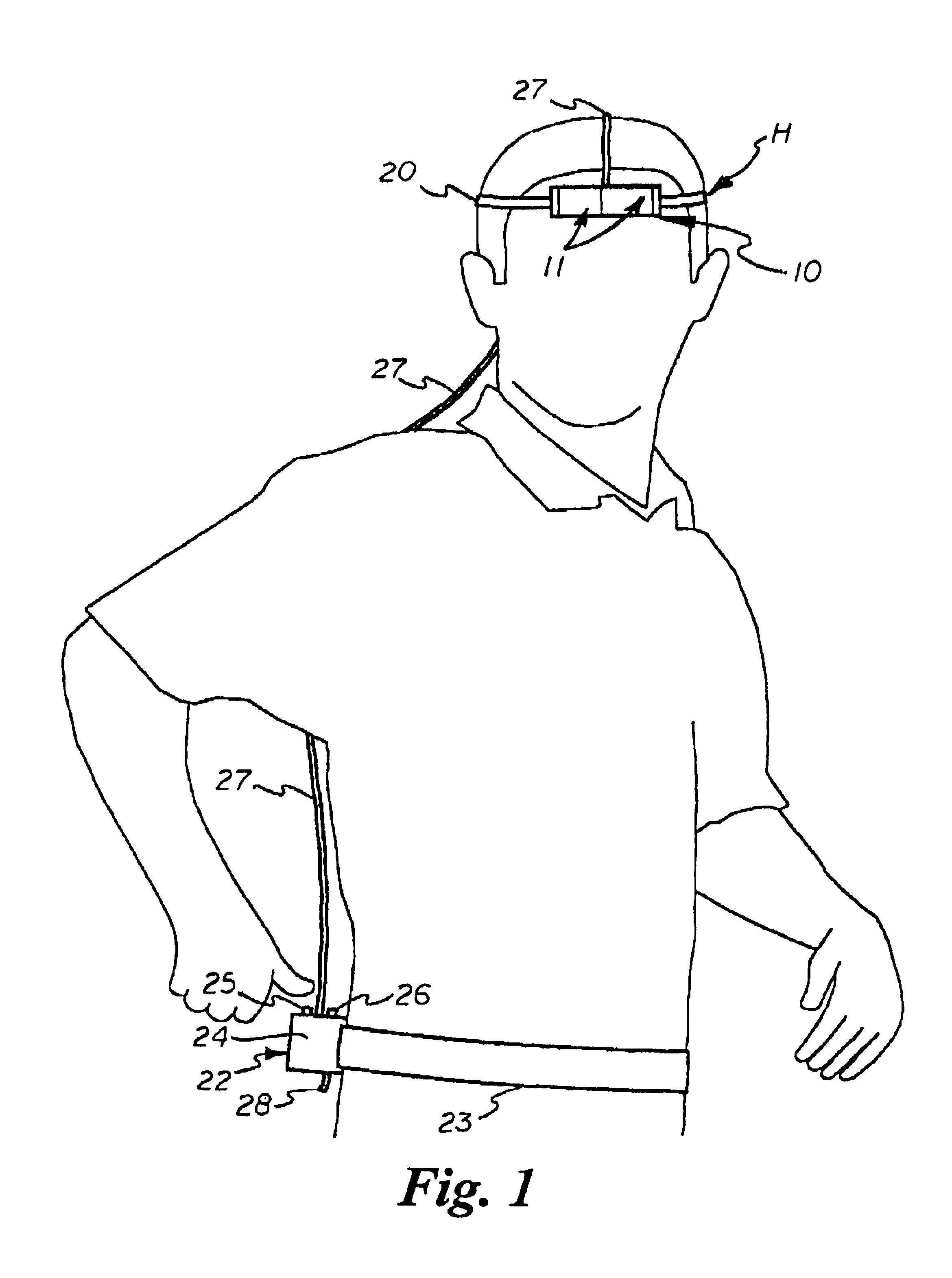
A thermionic heating and cooling device for heating or cooling a portion of a user's body utilizes thermal diodes having a first surface in thermal contact with a flexible thermal transfer band strapped to a portion of the user's body and a second surface spaced apart therefrom with a thermally conductive porous carbon foam heat sink secured to their second surface which is partially enclosed by a shroud and a surrounding air filter. A small enclosure worn by the user contains an air pump, a battery and a switch. A flexible conduit connects the air pump and shroud and draws ambient air through the porous carbon foam medium. The thermal diodes are connected to the battery by leads extending through the conduit. A voltage bias between the diode surfaces creates a cold surface and hot surface opposite each other and causes electrons to flow in one direction and transfer heat from the first surface to the second and into the heat exchanger, and the heat is prevented from returning to the first surface.
Owner:GIBLIN PERCY
Structure for a Phase Locked Loop with Adjustable Voltage Based on Temperature
InactiveUS20090021314A1Reduce usageImprove device yieldThermometer detailsTemperatue controlCircuit complexitySilicon
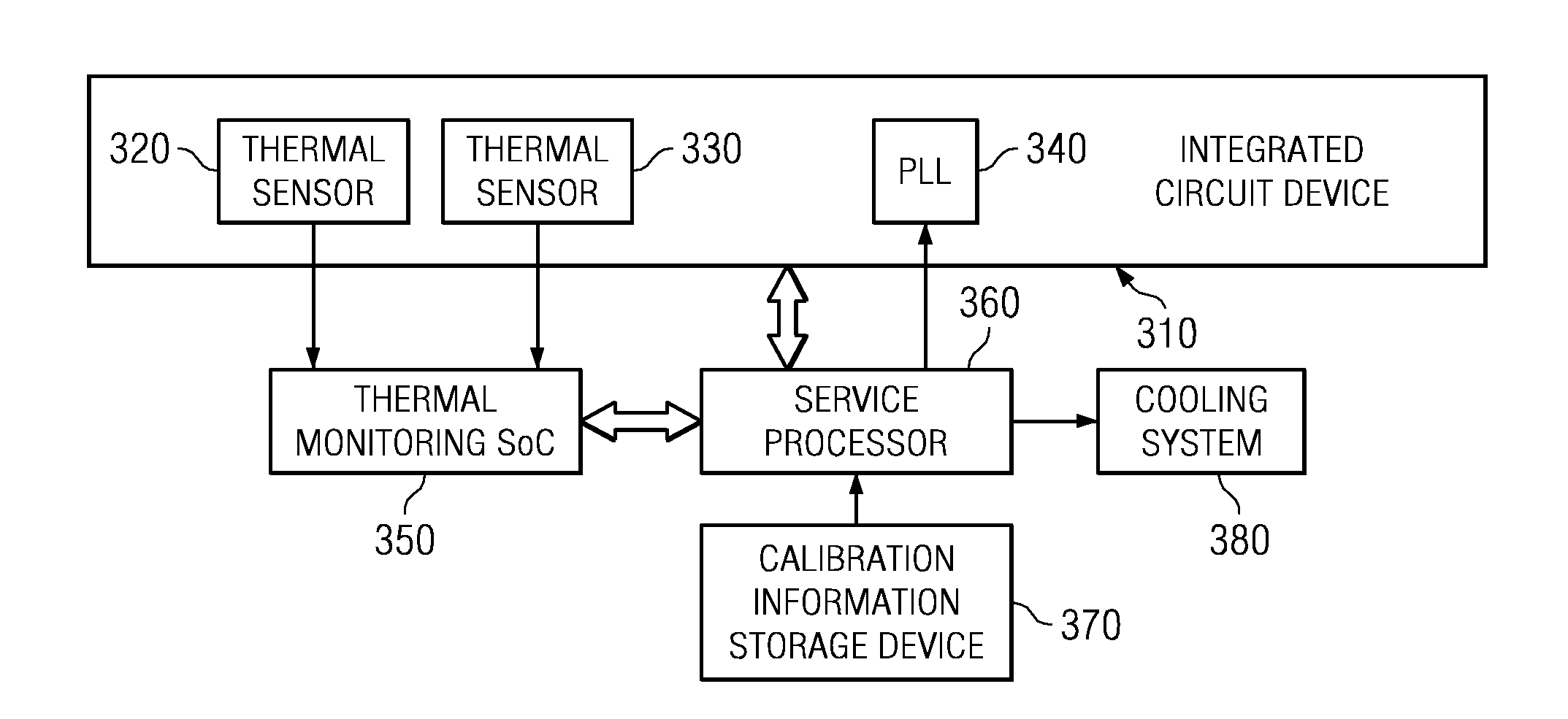
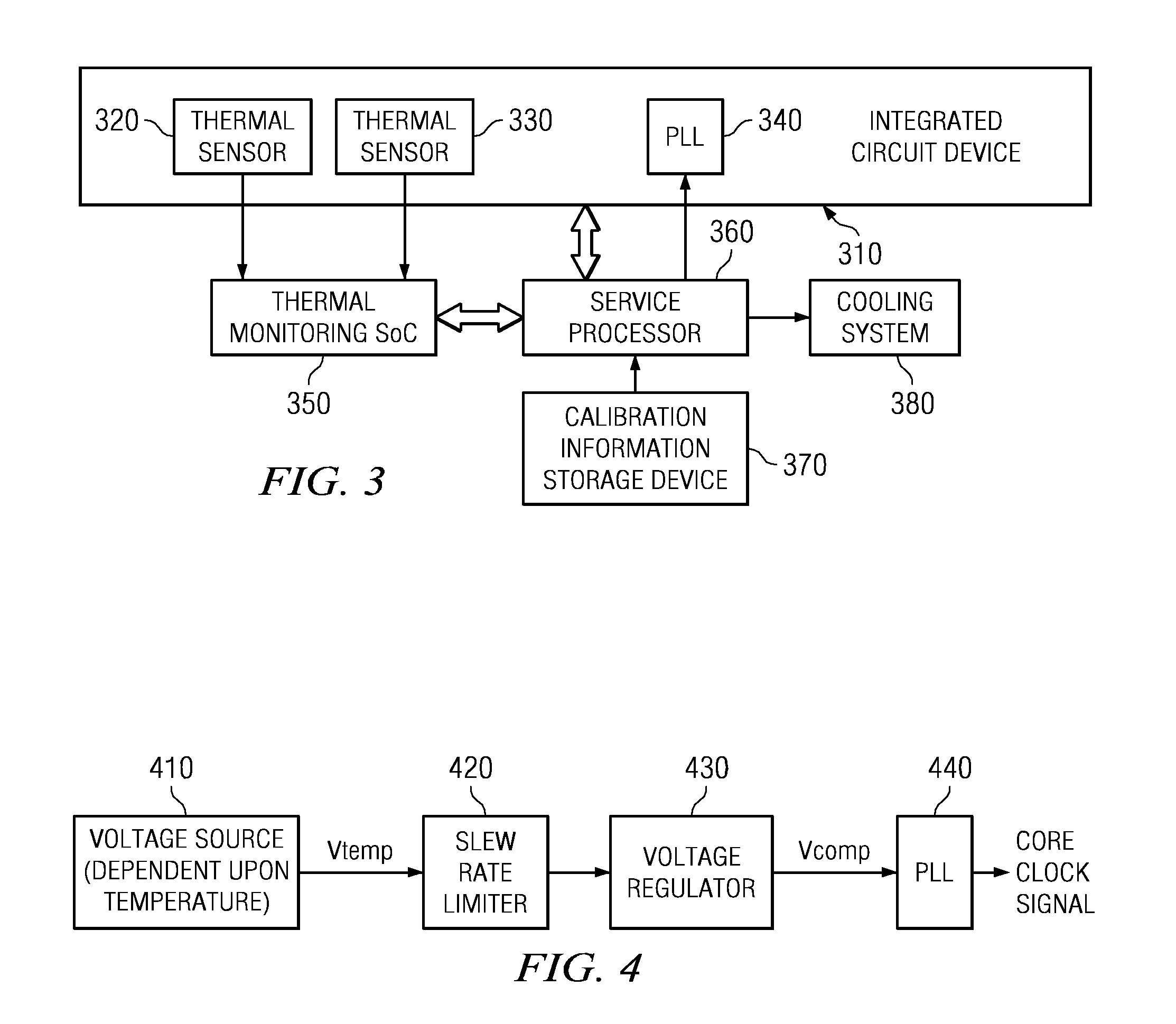
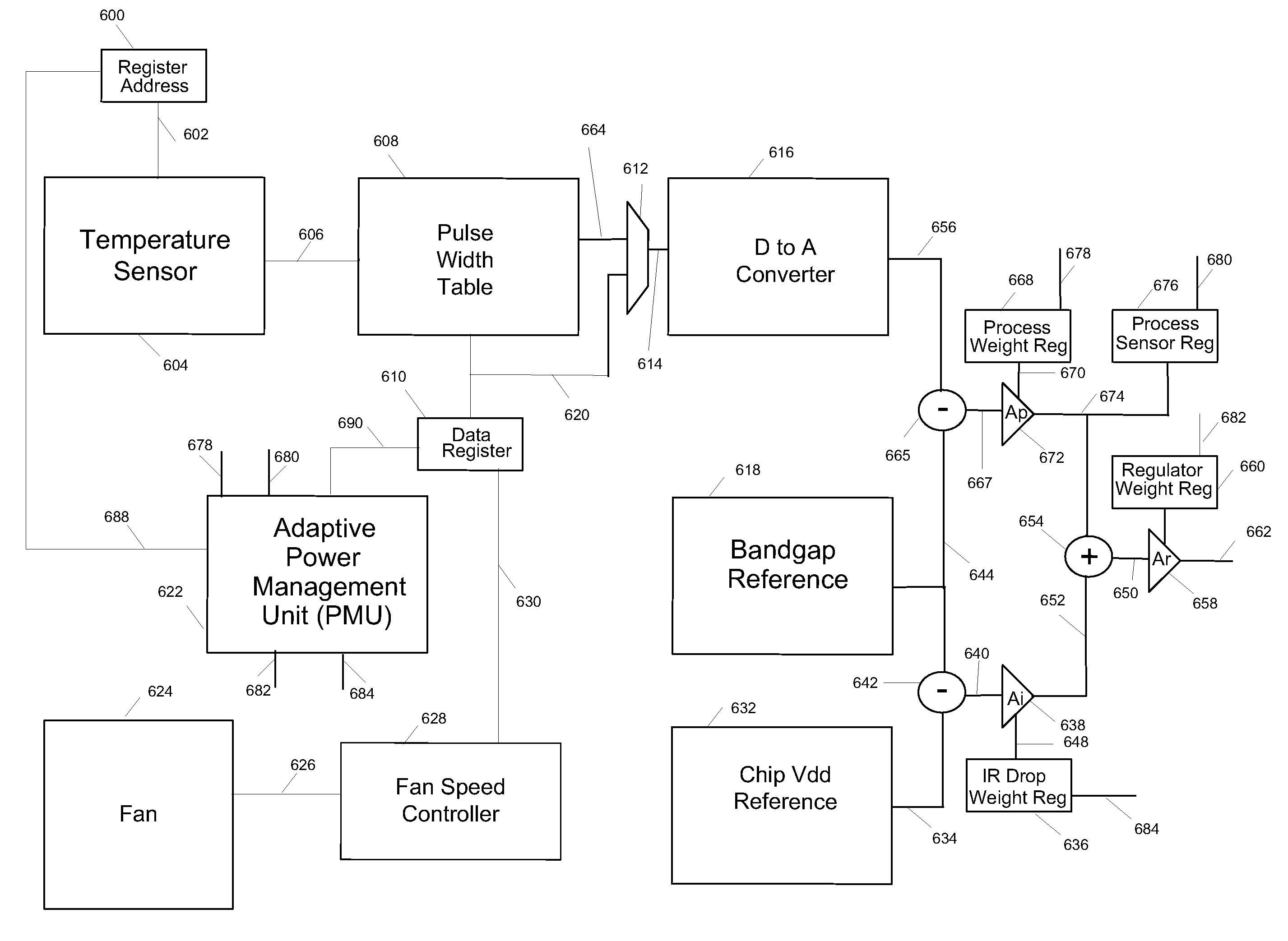
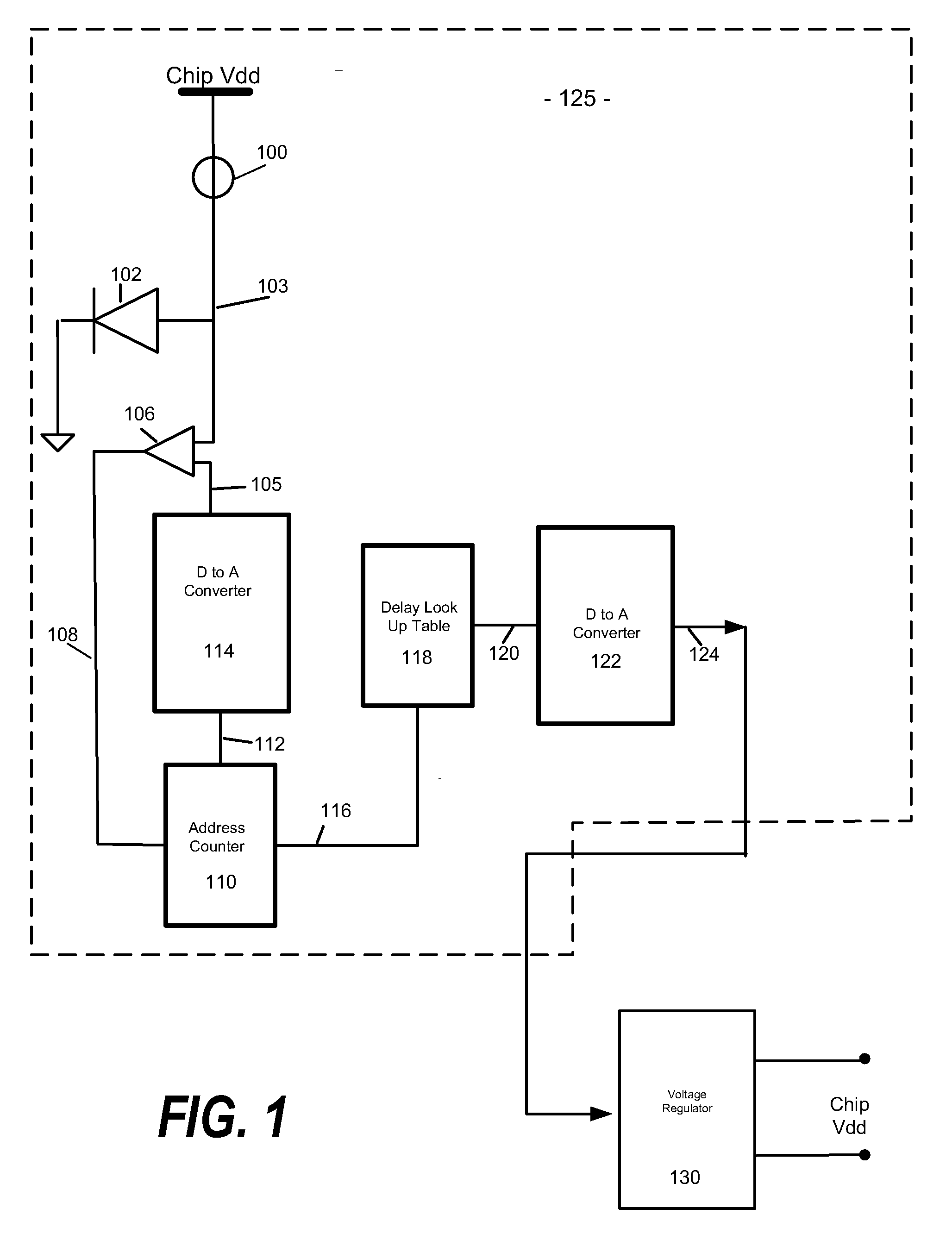
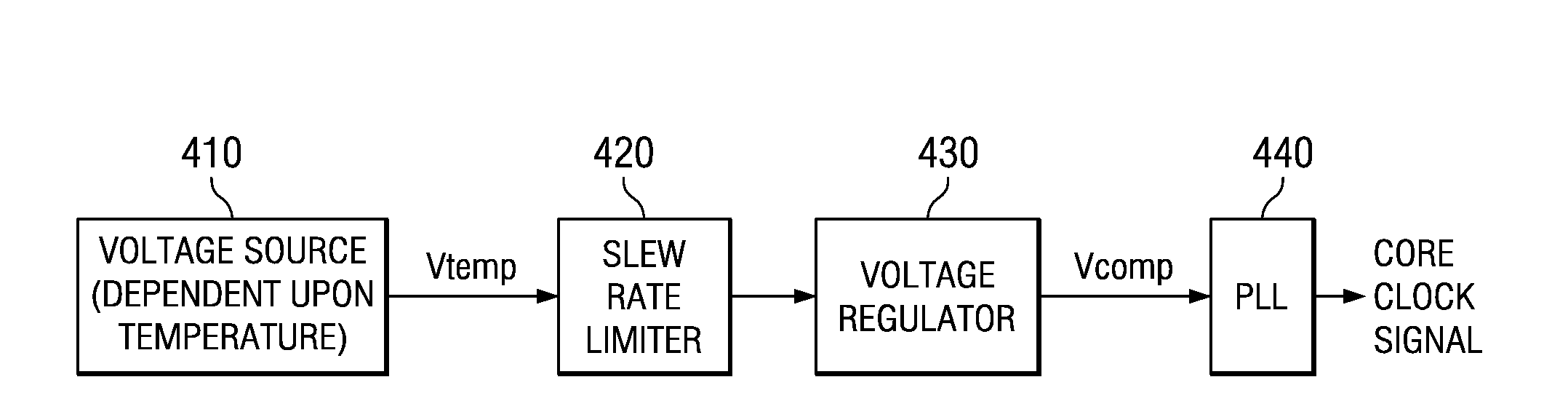
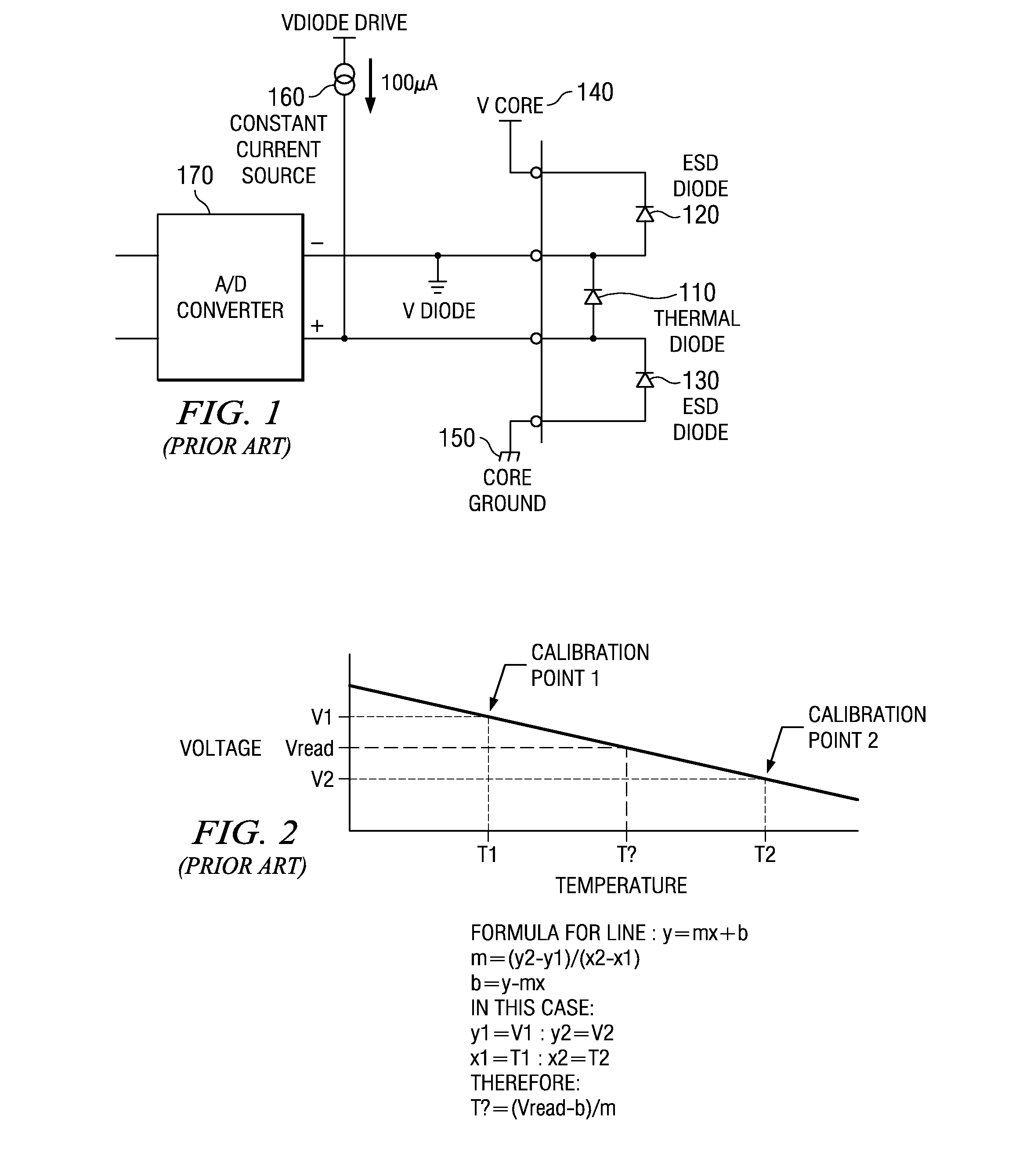
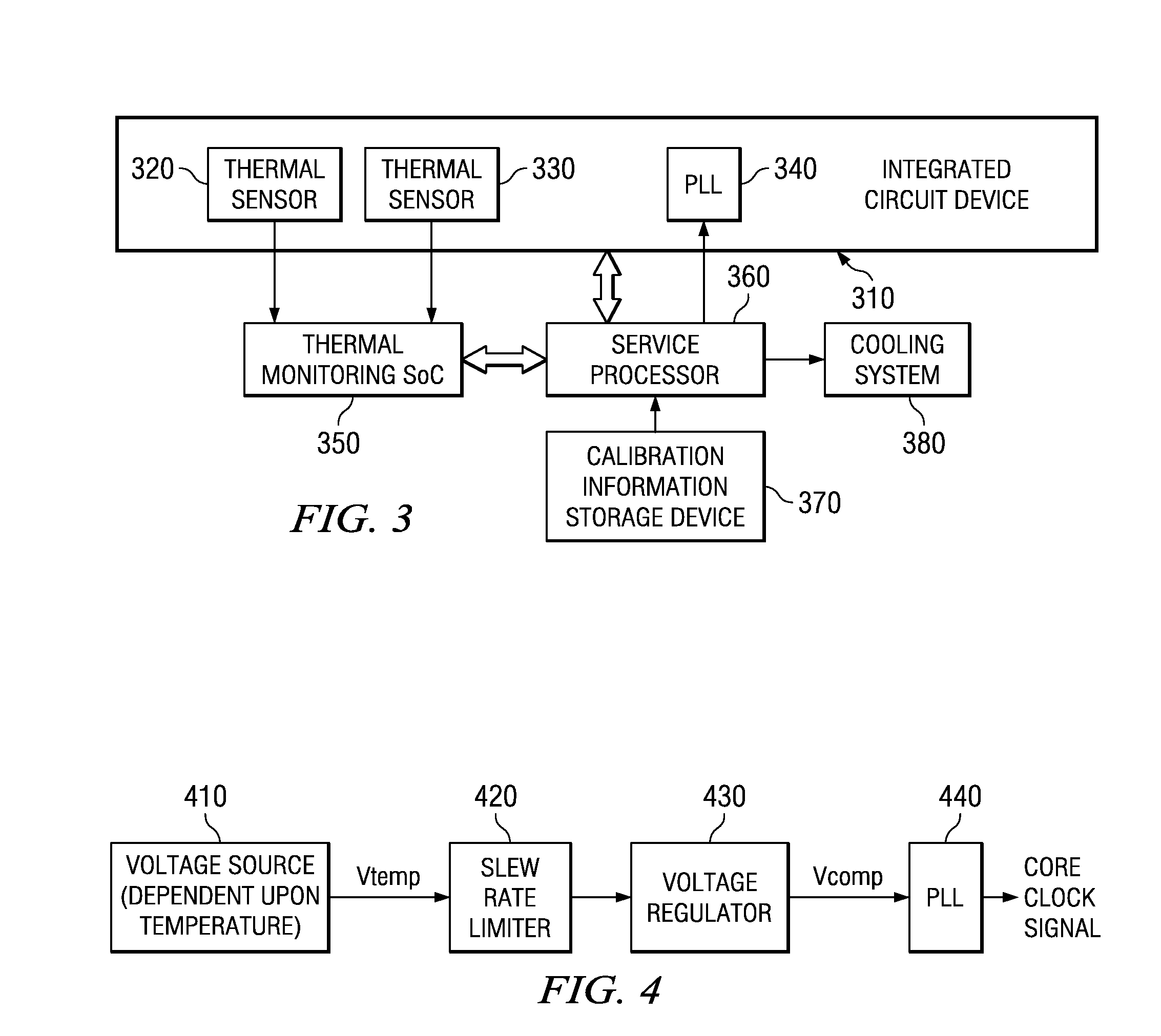
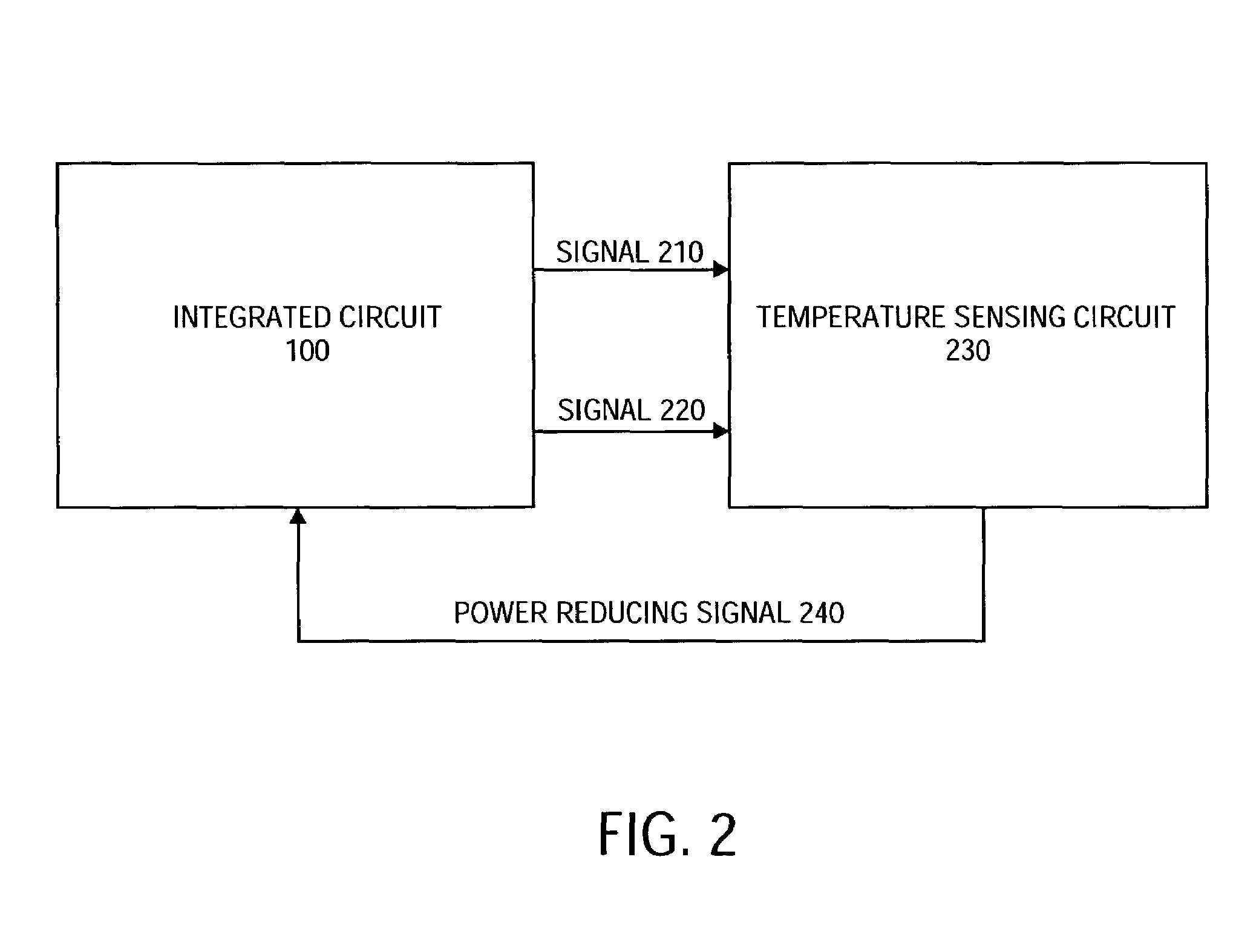
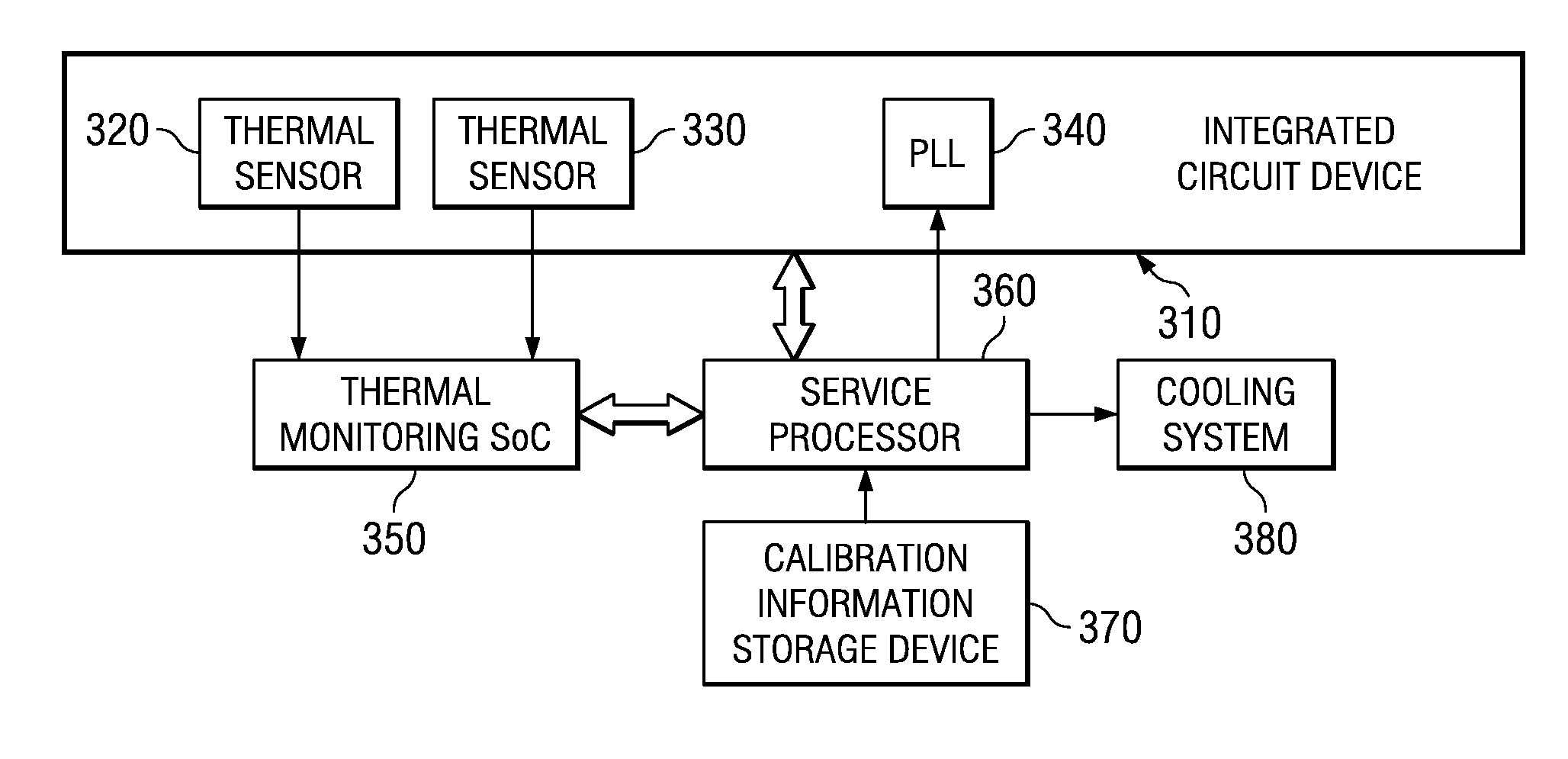
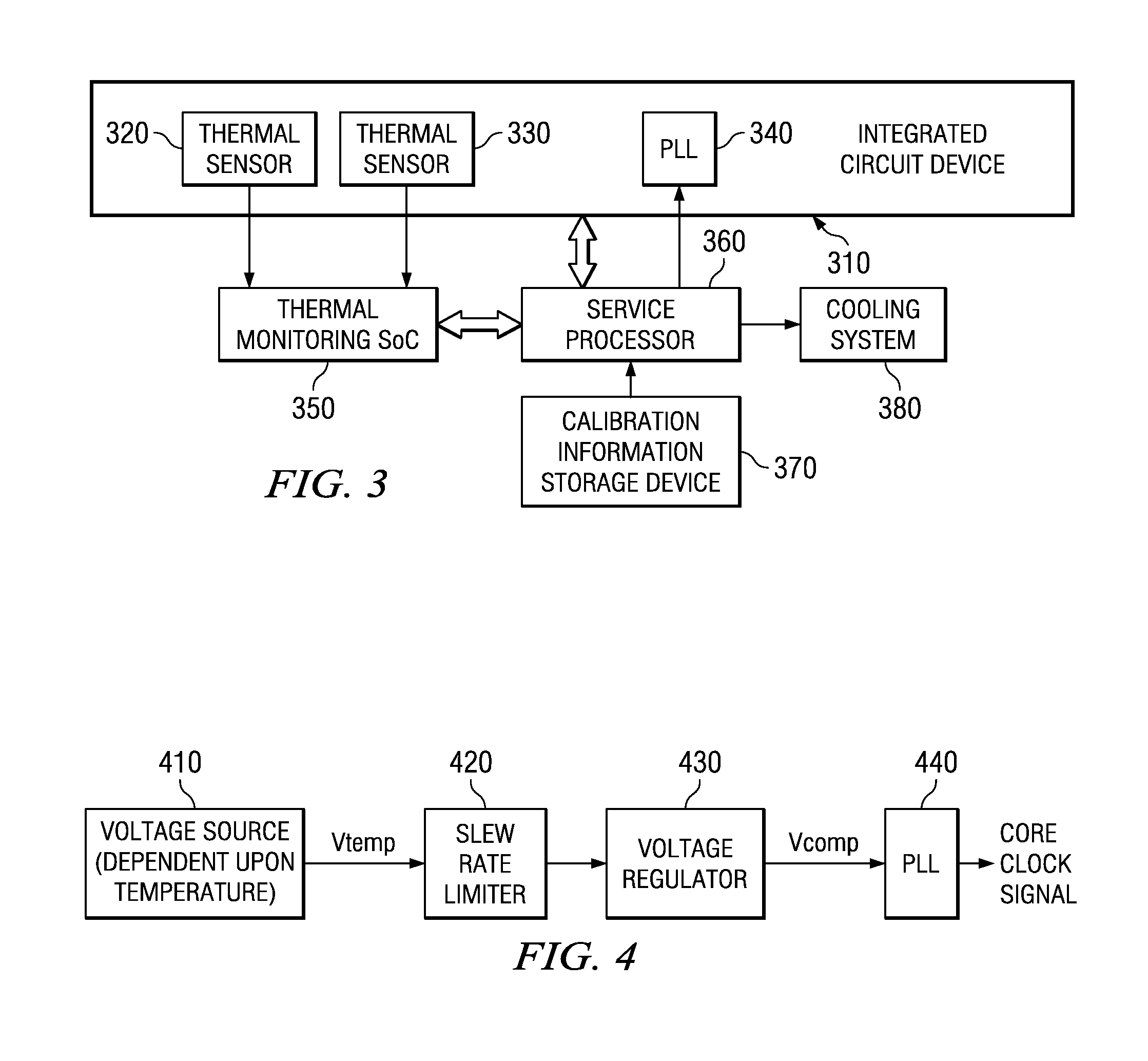
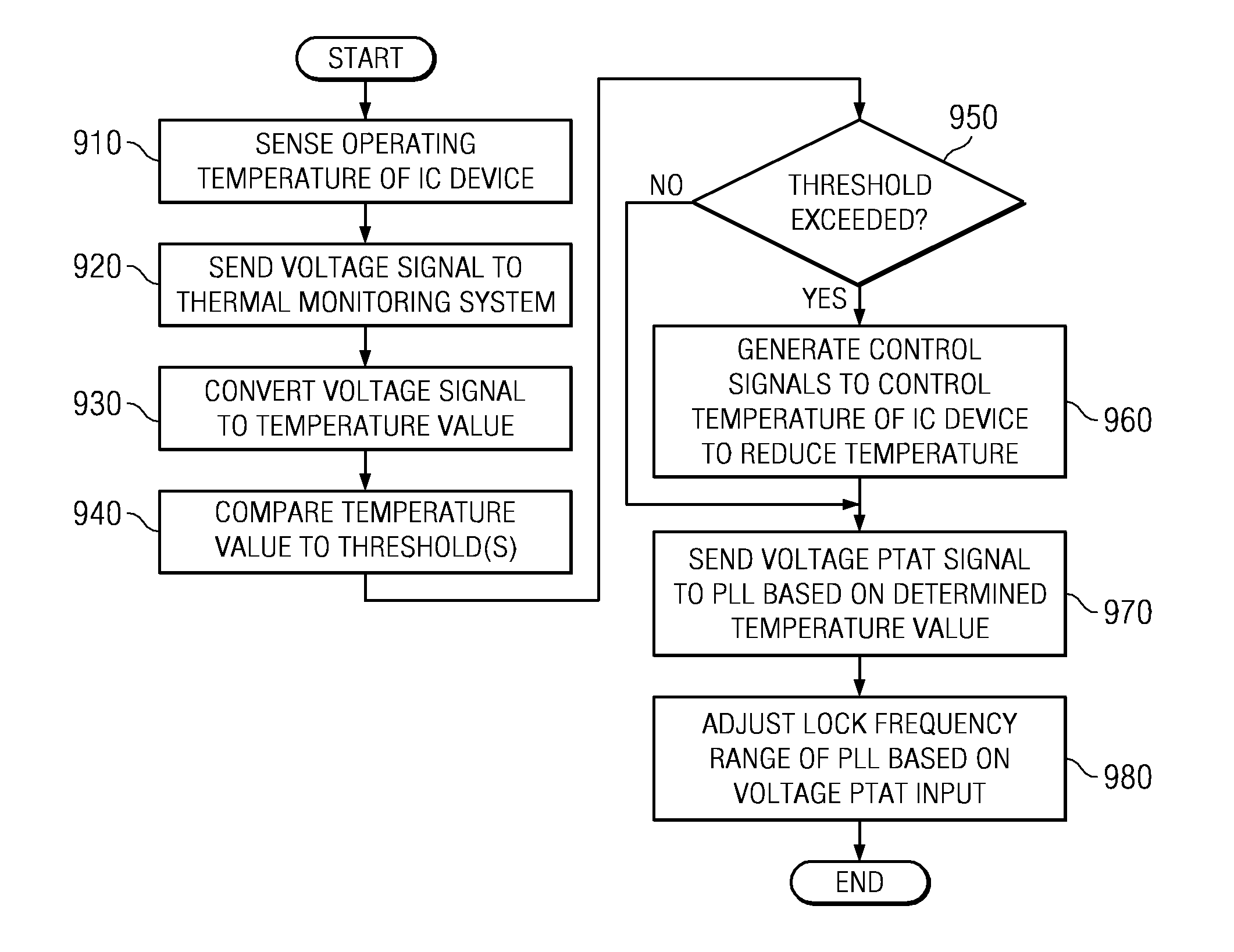
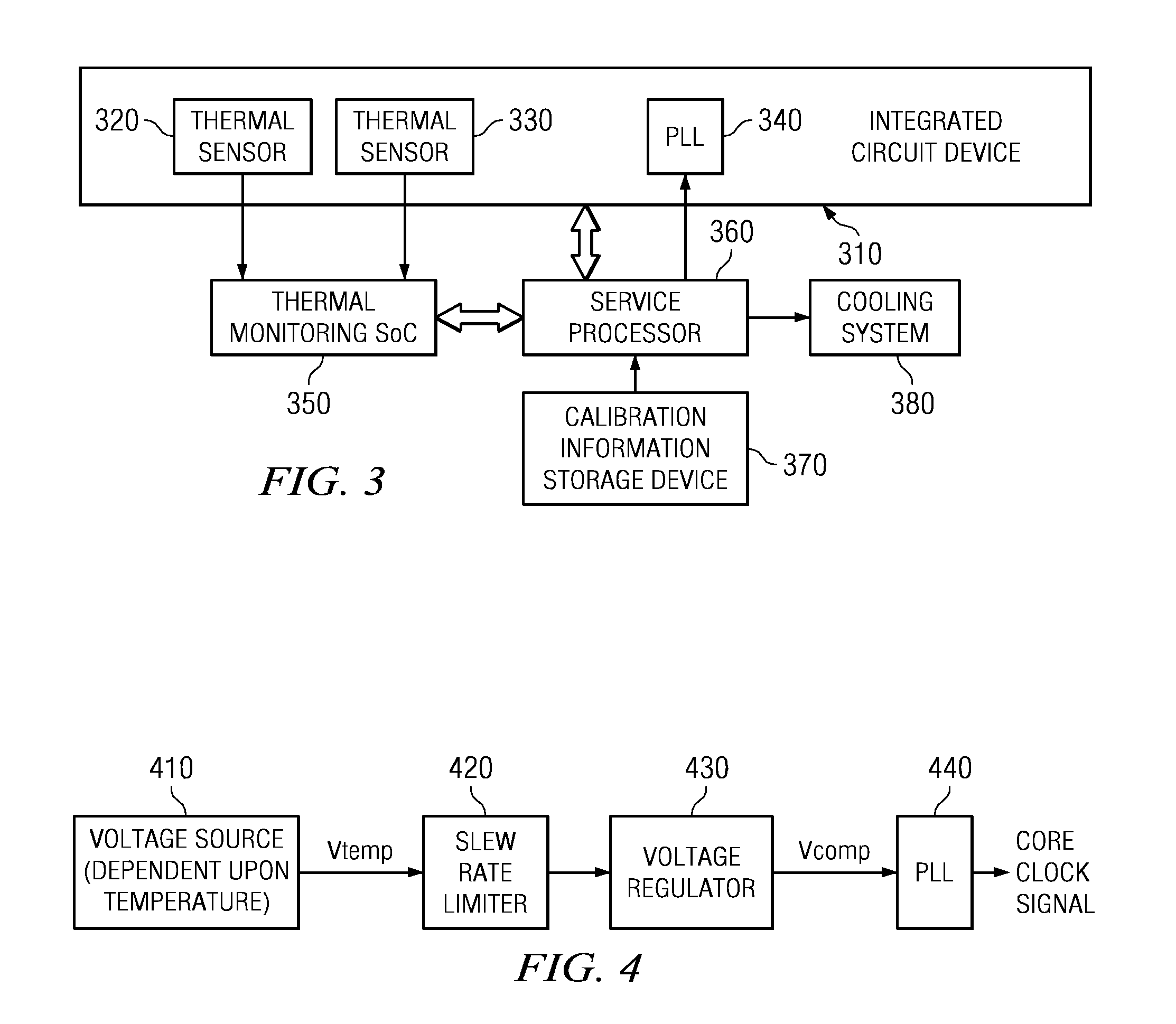
A design structure for an apparatus for utilizing a single set of one or more thermal sensors, e.g., thermal diodes, provided on the integrated circuit device, chip, etc., to control the operation of the integrated circuit device, associated cooling system, and high-frequency PLLs, is provided. By utilizing a single set of thermal sensors to provide multiple functions, e.g., controlling the operation of the integrated circuit device, the cooling system, and the PLLs, silicon real-estate usage is reduced through combining circuitry functionality. Moreover, the integrated circuit device yield is improved by reducing circuitry complexity and increasing PLL robustness to temperature. Furthermore, the PLL circuitry operating range is improved by compensating for temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Thermal bond verification
InactiveUS20020196835A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentOn boardHeat conducting
A system and method for evaluating the thermal bond between a heat-producing device and a heat-absorbing apparatus. The heat-producing device may be a CPU, such as an INTEL PENTIUM microprocessor, and the heat-absorbing apparatus may be a heat sink. The two may be joined with a heat-conducting substance such as thermal grease or adhesive. In one exemplary embodiment, the heat-producing device is operated at a first power level, a first temperature measurement is then taken, the device is operated at a second power level, and then a second temperature measurement is then taken. The thermal resistance is then calculated, which may involve subtracting the second temperature from the first, and may involve dividing by the power level. The first power level may be full power, and the second power level may be near zero. The first temperature may be measured when equilibrium temperatures have been reached, and the second temperature may be measured a predetermined amount of time after the second power level is initiated, which may be just enough time for the temperatures of the CPU and the heat sink to equalize. The CPU may perform the calculations, and the temperature may be measured with an on-board thermal sensor which may be a thermal diode.
Owner:SBS TECH
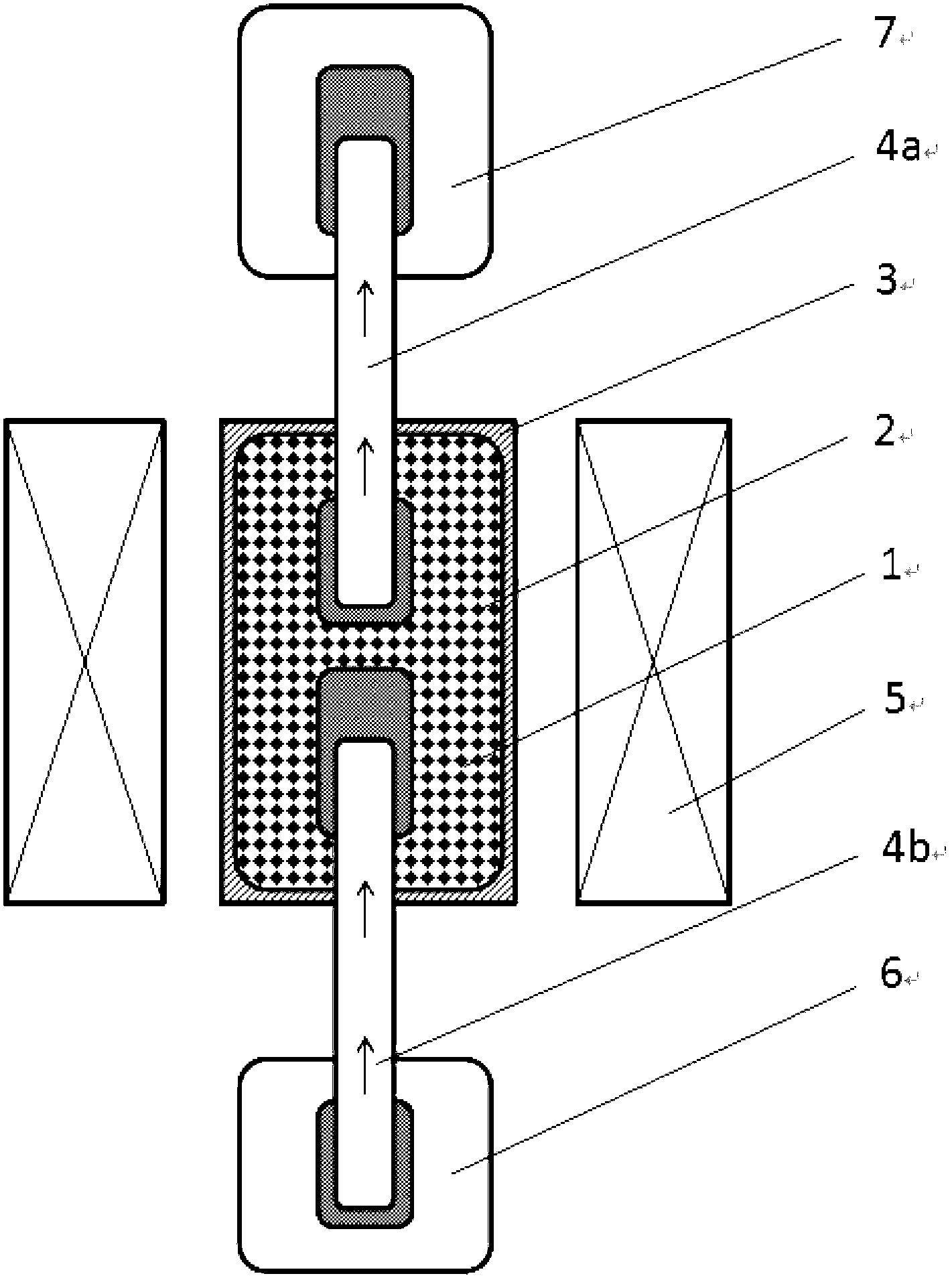
Magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly with a rotating heat exchanger
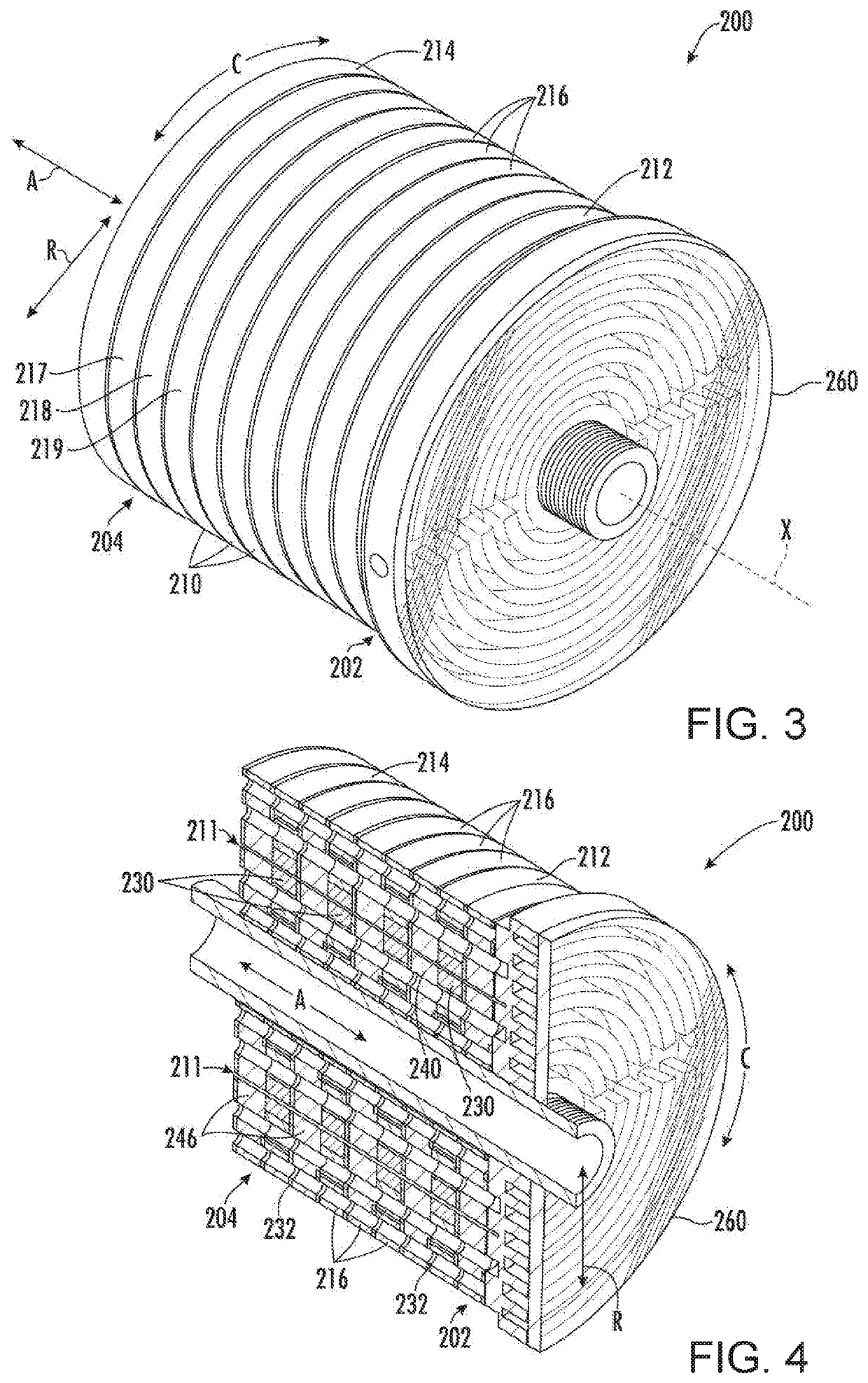
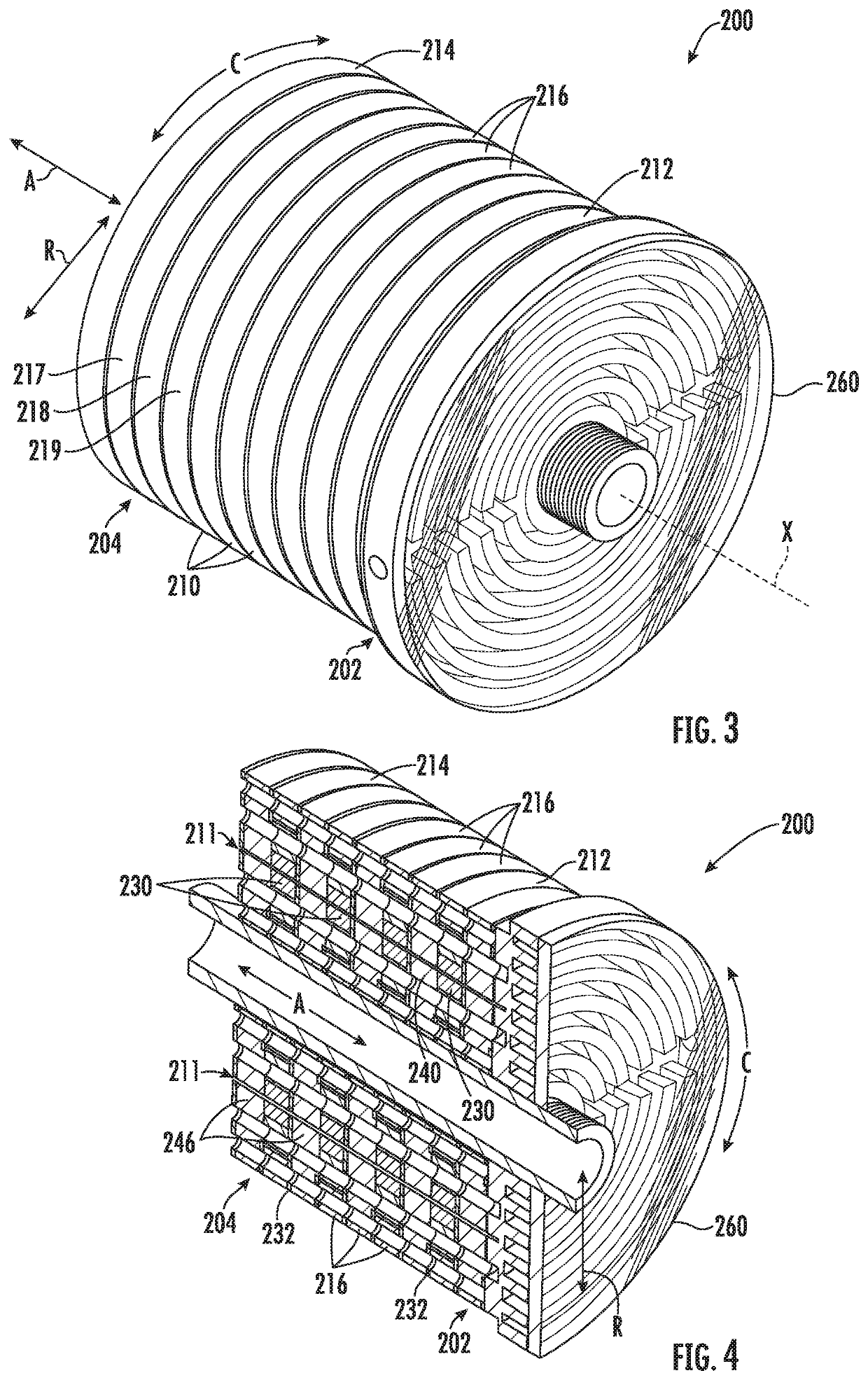
ActiveUS10684044B2Temperature control without auxillary powerDomestic refrigeratorsCold sideRotational axis
A magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly includes a magneto-caloric cylinder. A plurality of thermal stages is stacked along an axial direction between a cold side and a hot side. A heat exchanger includes a cylindrical stator positioned at and in thermal communication with the cold side or the hot side of the plurality of thermal stages. A cylindrical rotor is spaced from the cylindrical stator by a cylindrical gap. The cylindrical rotor is configured to rotate relative to the cylindrical stator about a rotation axis. A shearing liquid zone is defined between a surface of the cylindrical stator that faces the cylindrical gap and a surface of the cylindrical rotor that faces the cylindrical gap when the cylindrical gap is filled with a liquid.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
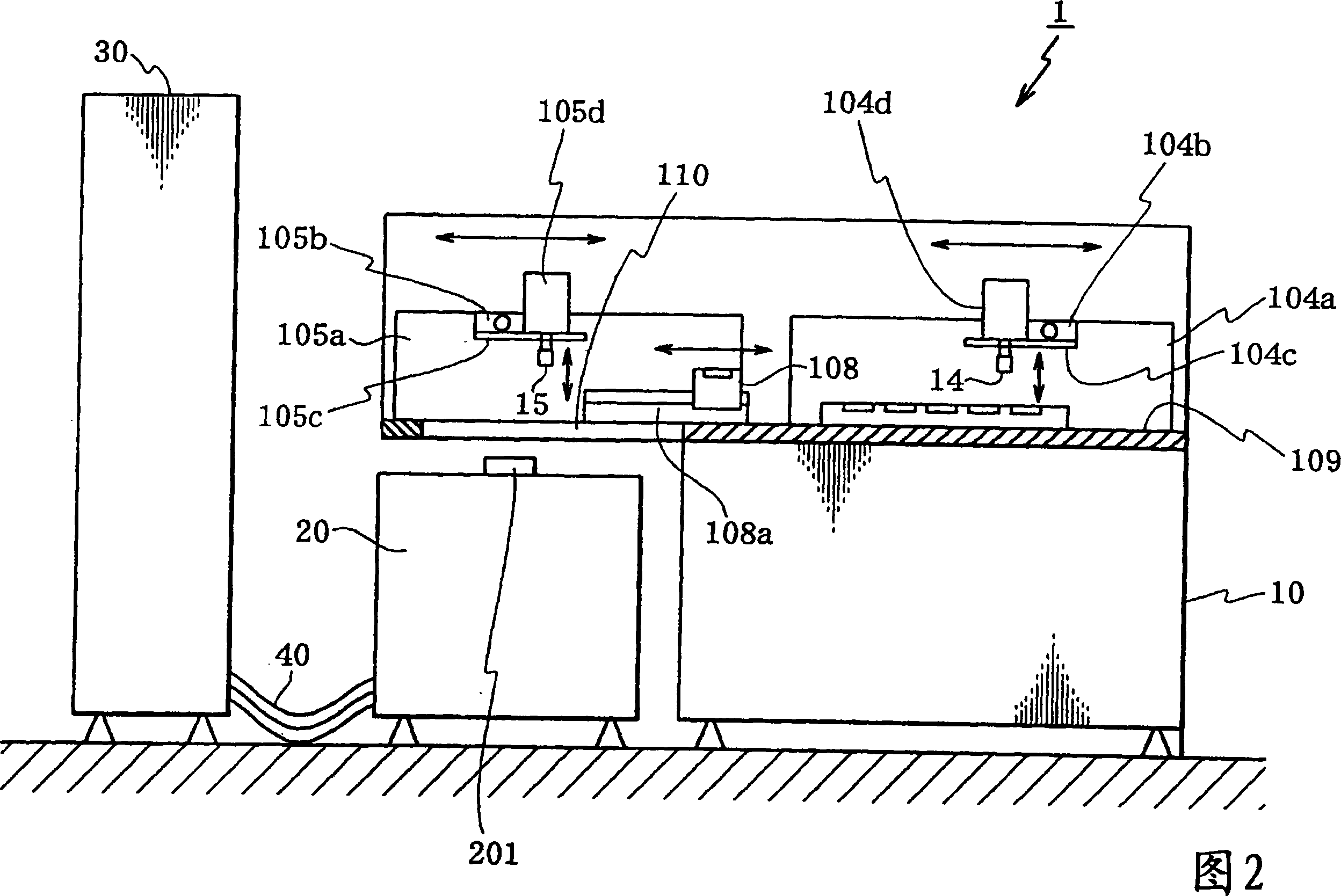
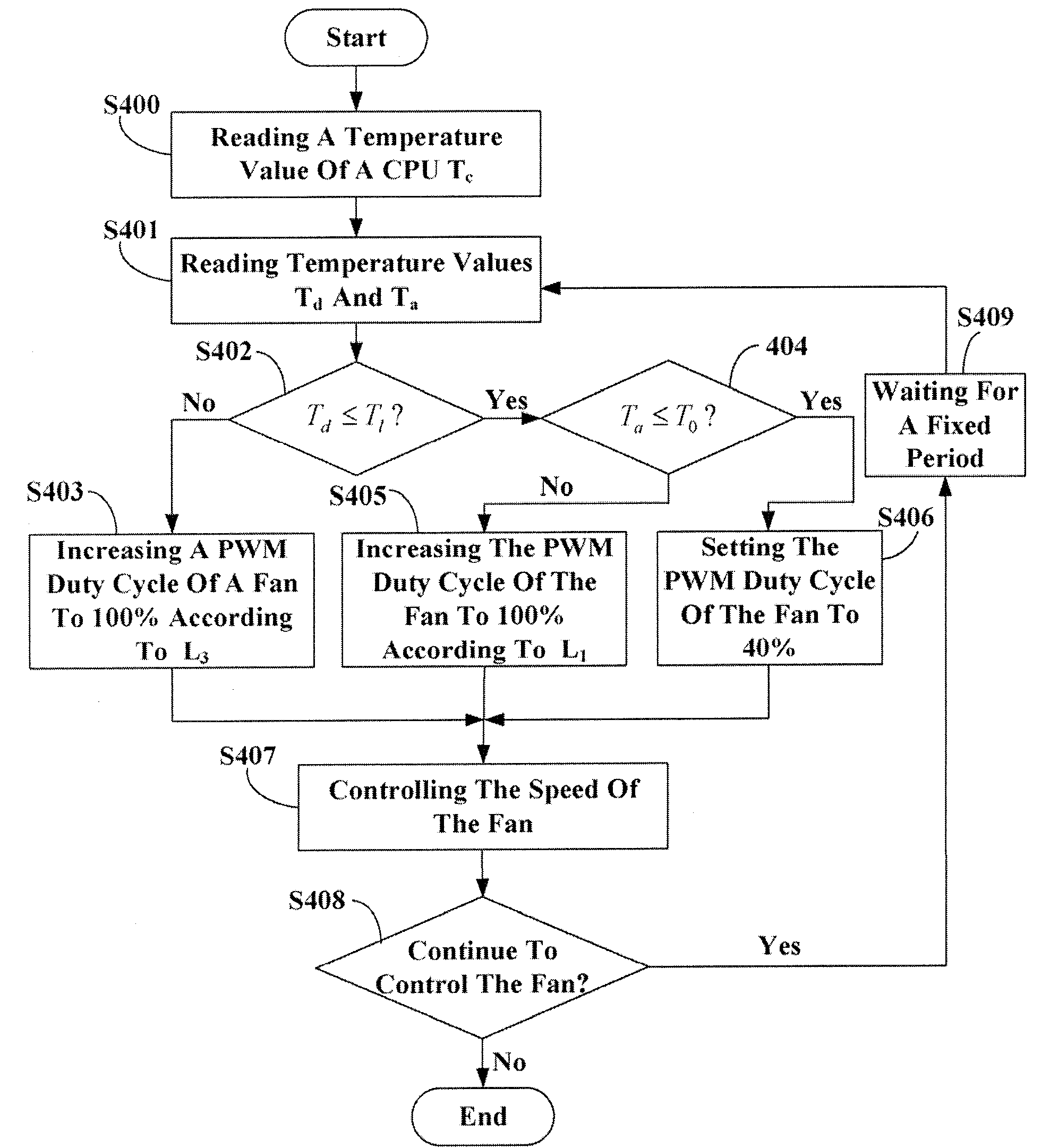
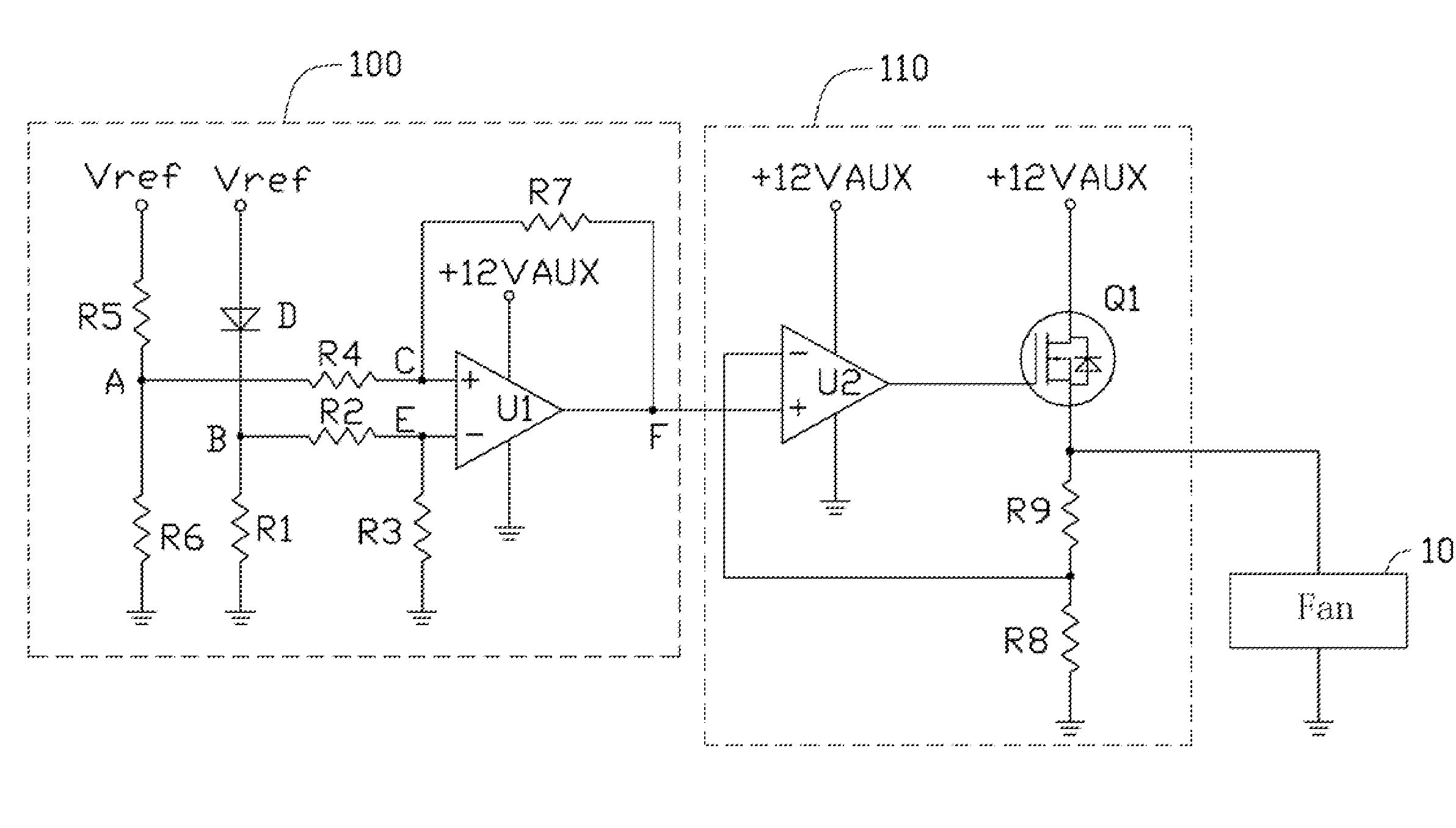
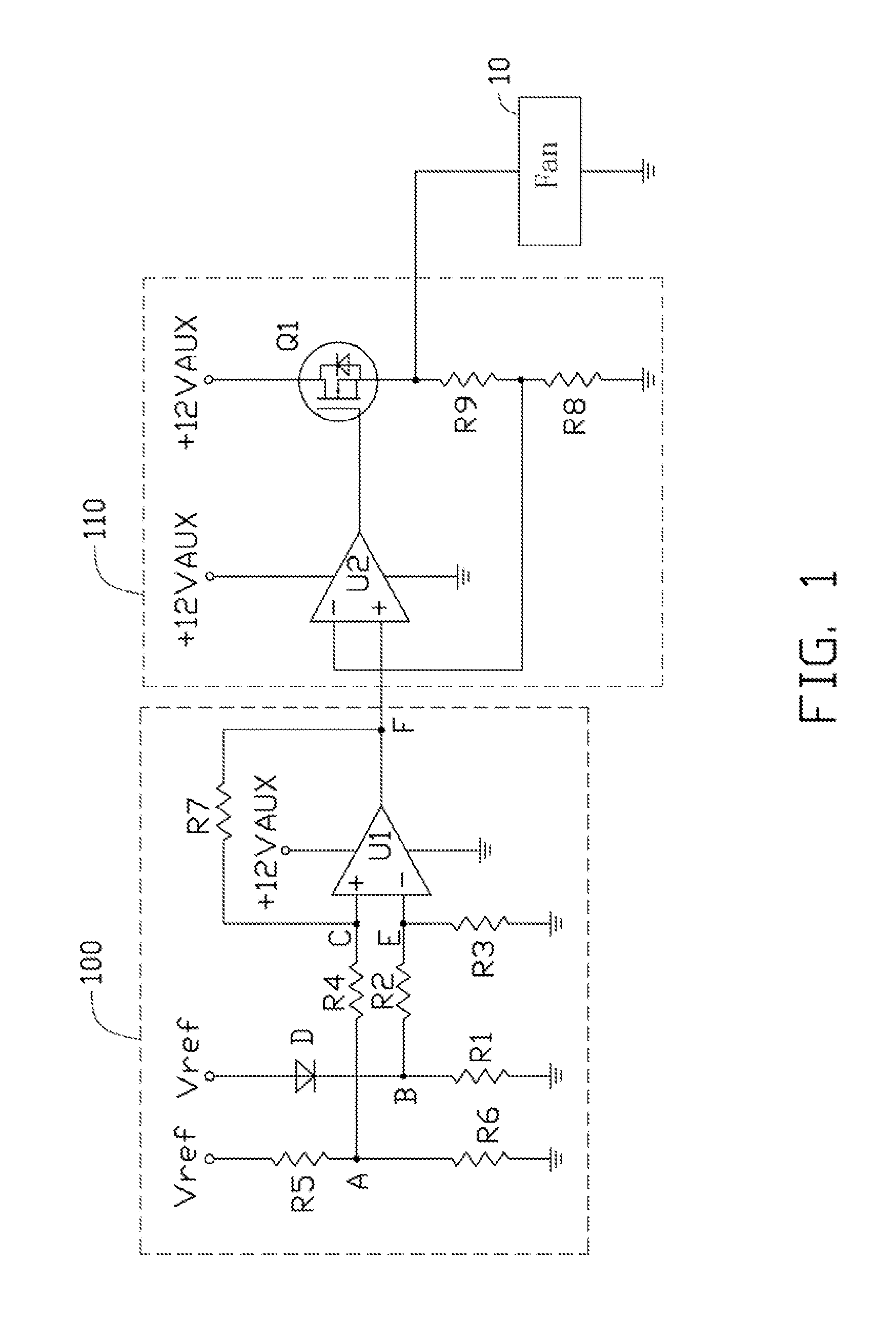
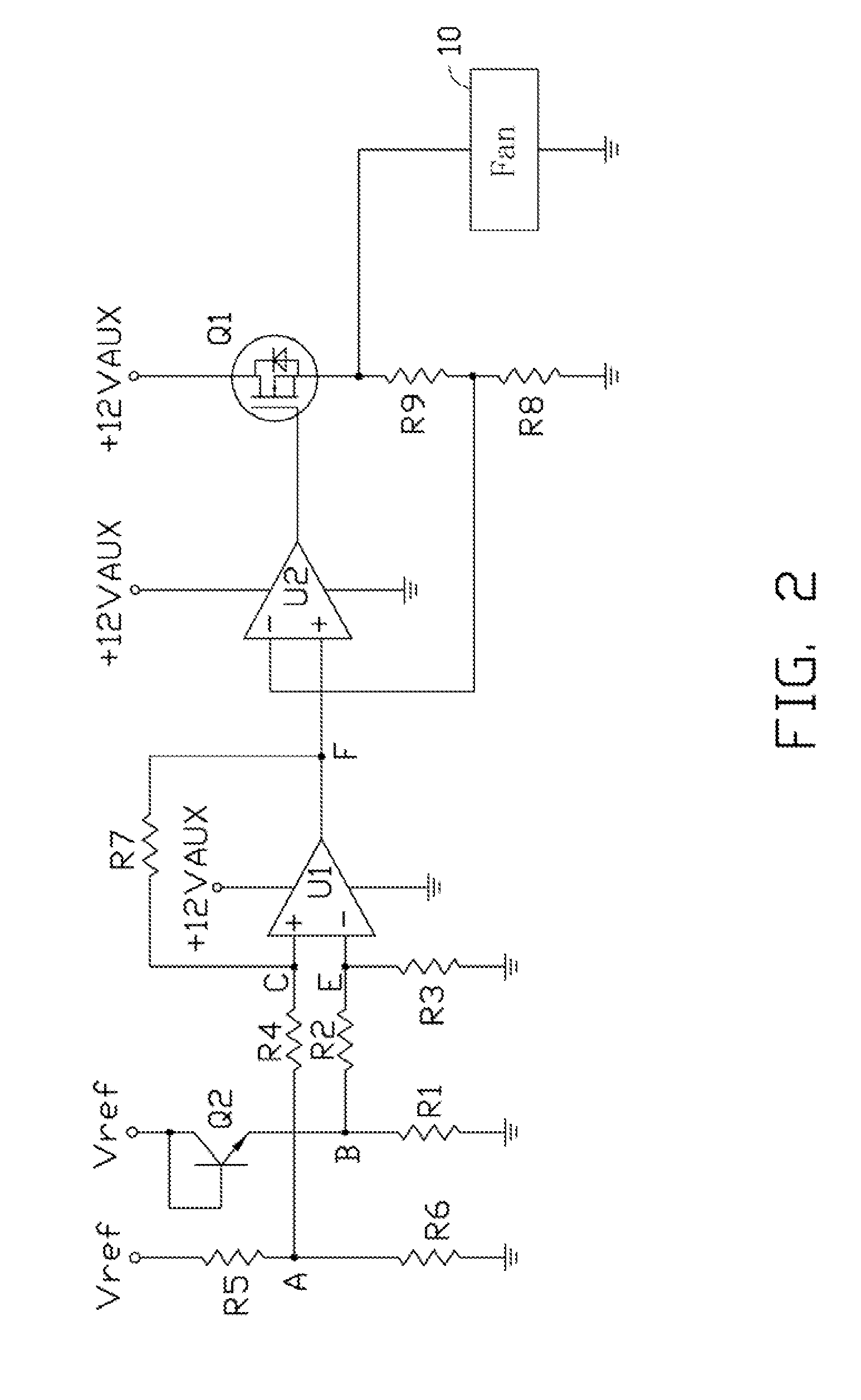
System and method for controlling the rotating speed of a fan
InactiveUS20070081800A1Rotation speed is limitedMotor/generator/converter stoppersDigital data processing detailsEngineeringControl theory
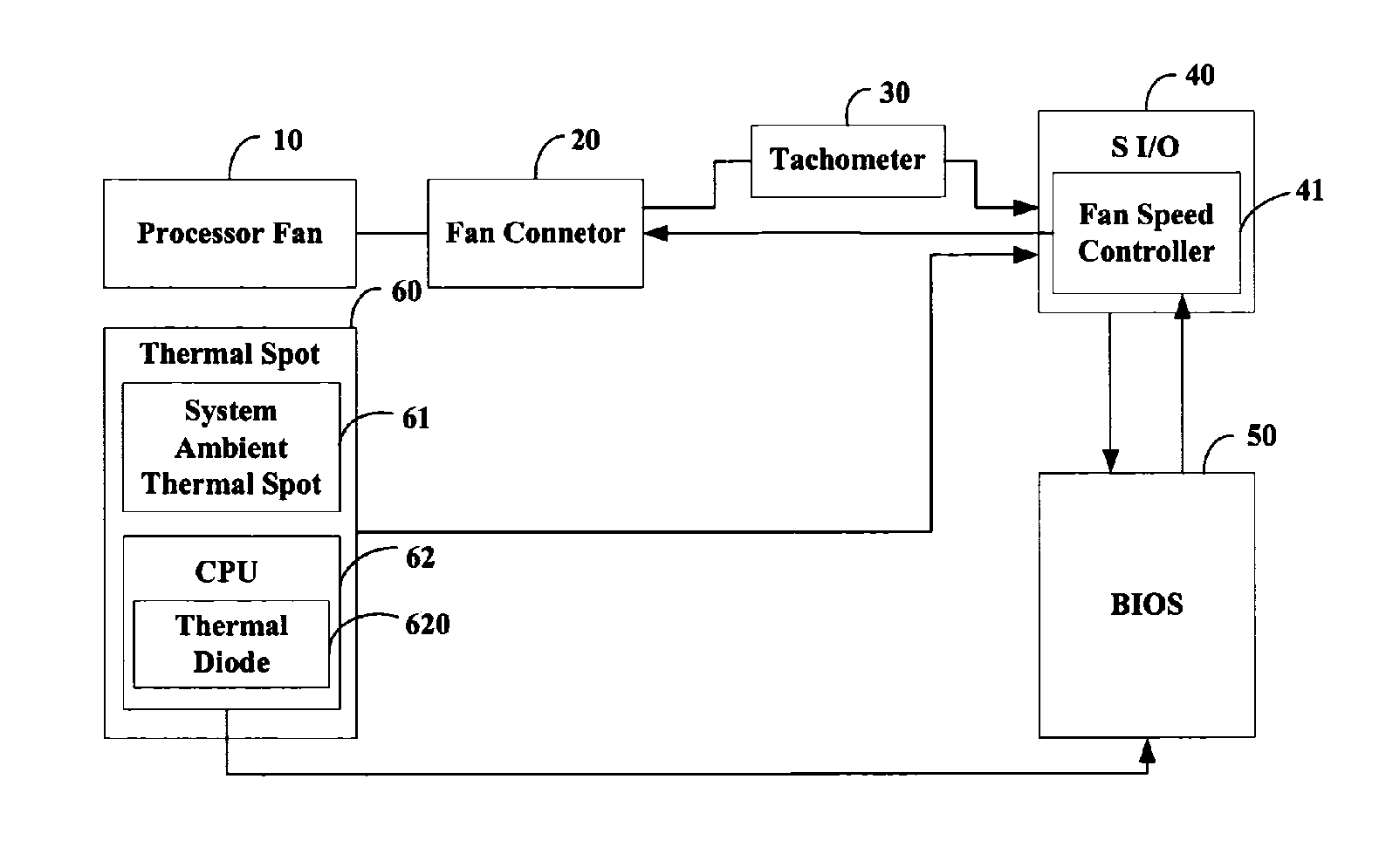
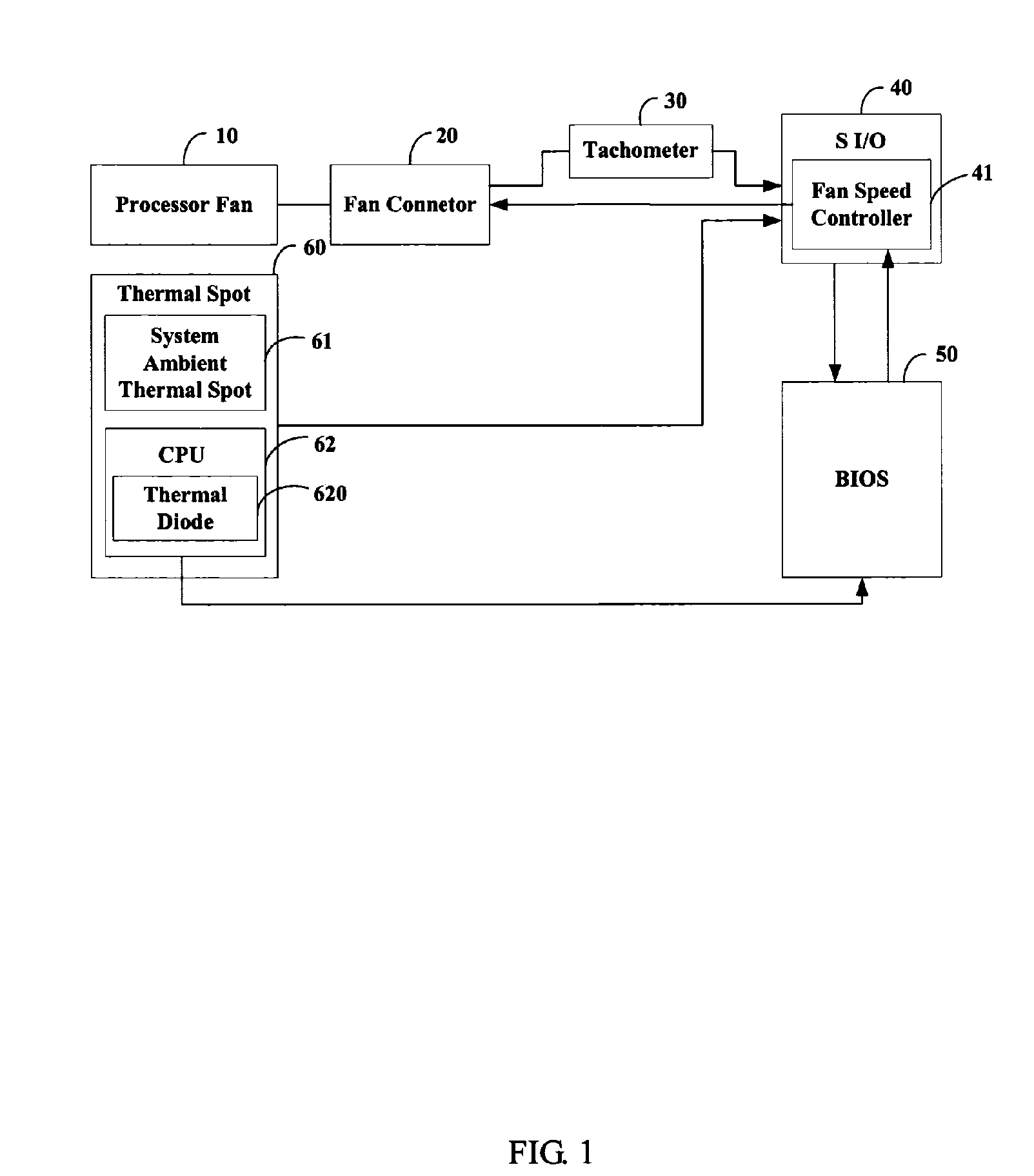
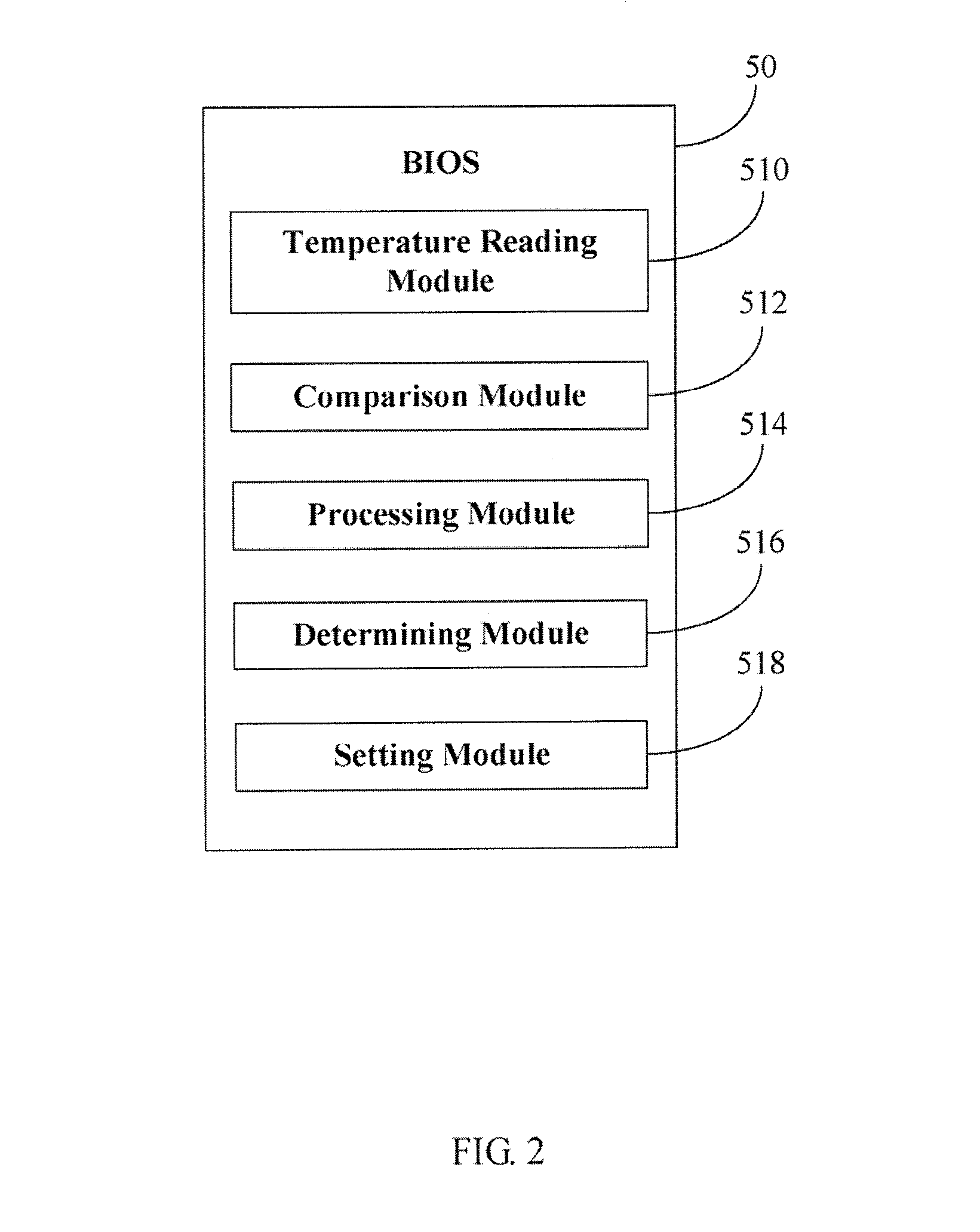
A method for controlling the rotating speed of a fan is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: reading a standard temperature Tc of a central processing unit (CPU); reading a thermal diode's temperature Td and a system ambient temperature Ta; comparing Td with a minimum temperature Tl, such that the fan begins processing the heat of the CPU begins; if Td>Tl, increasing pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty cycle of the fan to 100%; if Td<=Tl, comparing a critical temperature T0 with Ta; if Ta>T0, increasing PWM fan duty cycle to 100%; if Ta<=T0, setting the fan duty cycle at 40%; sending the PWM fan duty cycle to a fan speed controller.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Composite VDMOS device possessing temperature sampling and over-temperature protection function
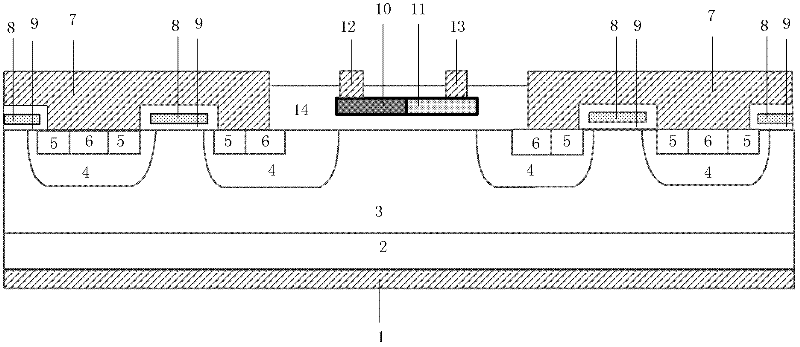
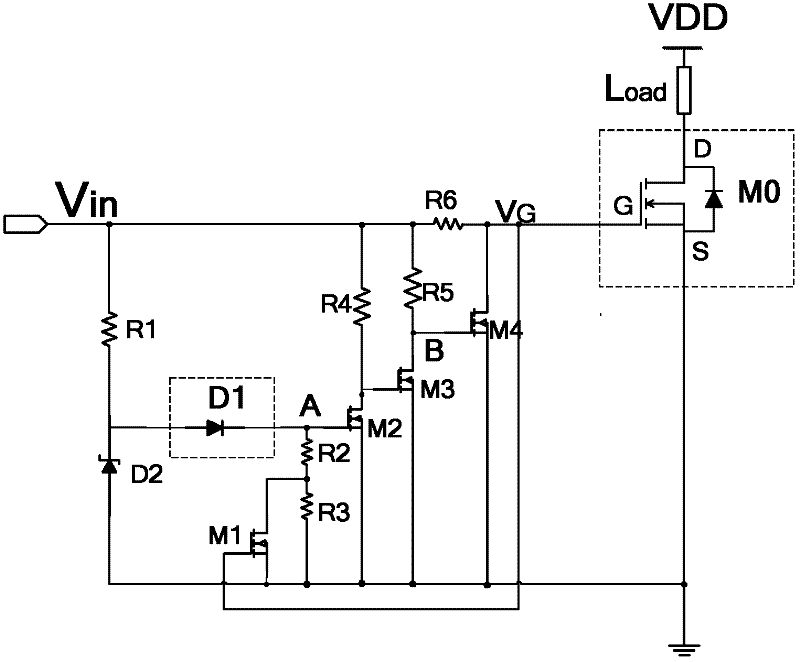
InactiveCN102394237AReduce failure rateAccurate samplingSolid-state devicesDiodePower semiconductor deviceNegative temperature
A composite VDMOS device possessing a temperature sampling and over-temperature protection function belongs to the power semiconductor device field. In the invention, a VDMOS device, a polysilicon thermal diode and an over-temperature protection circuit are integrated. Through using a negative temperature characteristic of forward voltage drop of the polysilicon thermal diode, the polysilicon thermal diode is made on an insulating layer of a VDMOS device surface so as to realize sampling of a VDMOS device operating temperature. Based on a temperature sampling signal of the polysilicon thermal diode, the over-temperature protection circuit carries out partial pressure to a gate input voltage Vin of the whole composite VDMOS device so as to obtain a gate control voltage VG of the VDMOS device. Therefore, the over-temperature protection can be performed to the VDMOS device, which is characterized by: when the operating temperature of the VDMOS device reaches TH, turning off the VDMOS device; when the internal temperature drops to TL after the VDMOS device is turned off, starting the VDMOS device, wherein temperature return difference can be represented as a following formula: Delta T=TH-TL. By using the composite VDMOS device of the invention, the accurate sampling and the over-temperature protection can be performed to the VDMOS device so that thermal failure of the device can be avoided and a service life of the device can be prolonged. A structure is simple and sampling accuracy is high. The device is compatible with a VDMOS device technology. The device is monolithic and has many other advantages.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Fan speed control from adaptive voltage supply
InactiveUS20080188994A1Digital data processing detailsEfficient regulation technologiesIntegrated circuit layoutSelf adaptive
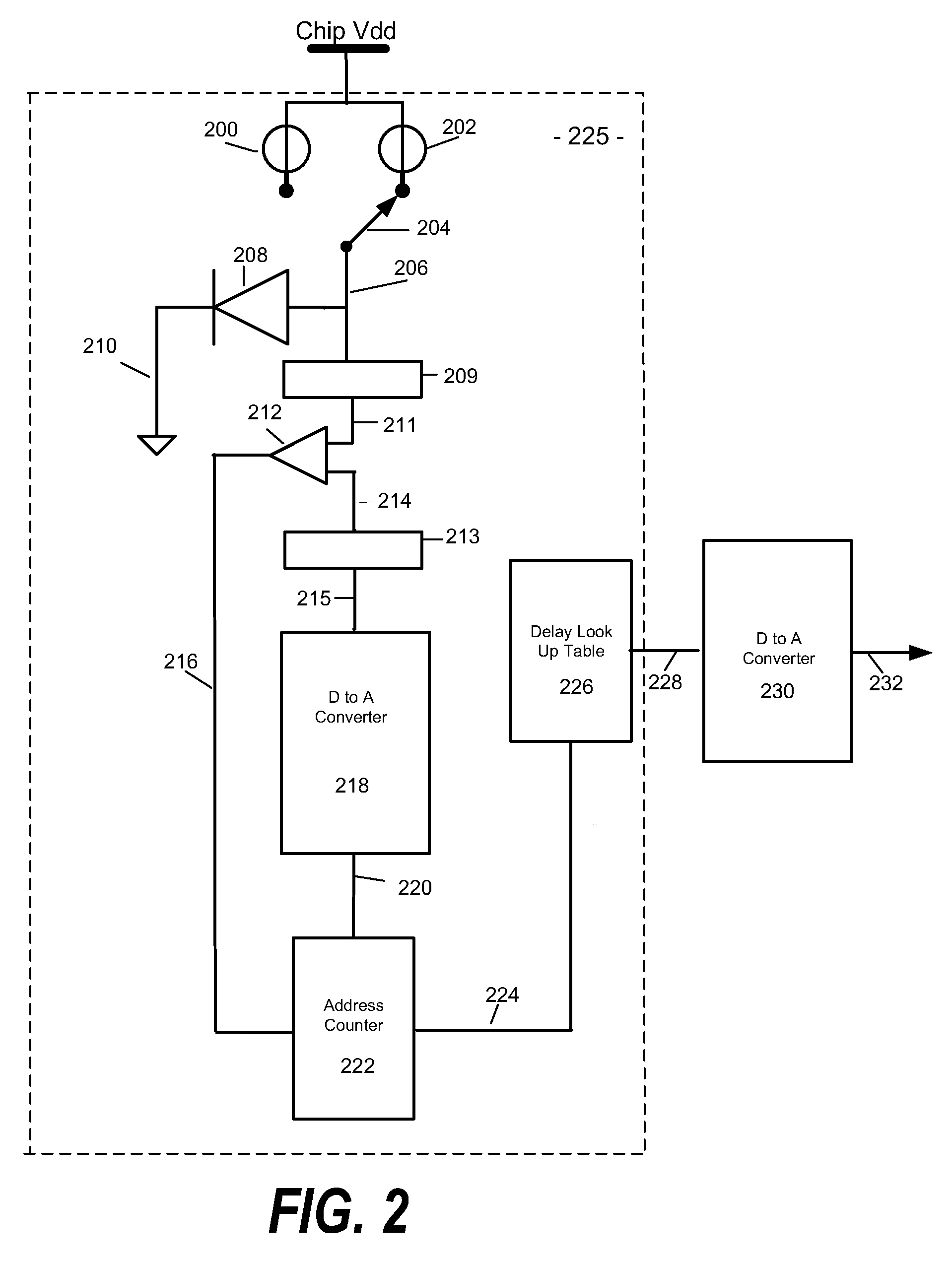
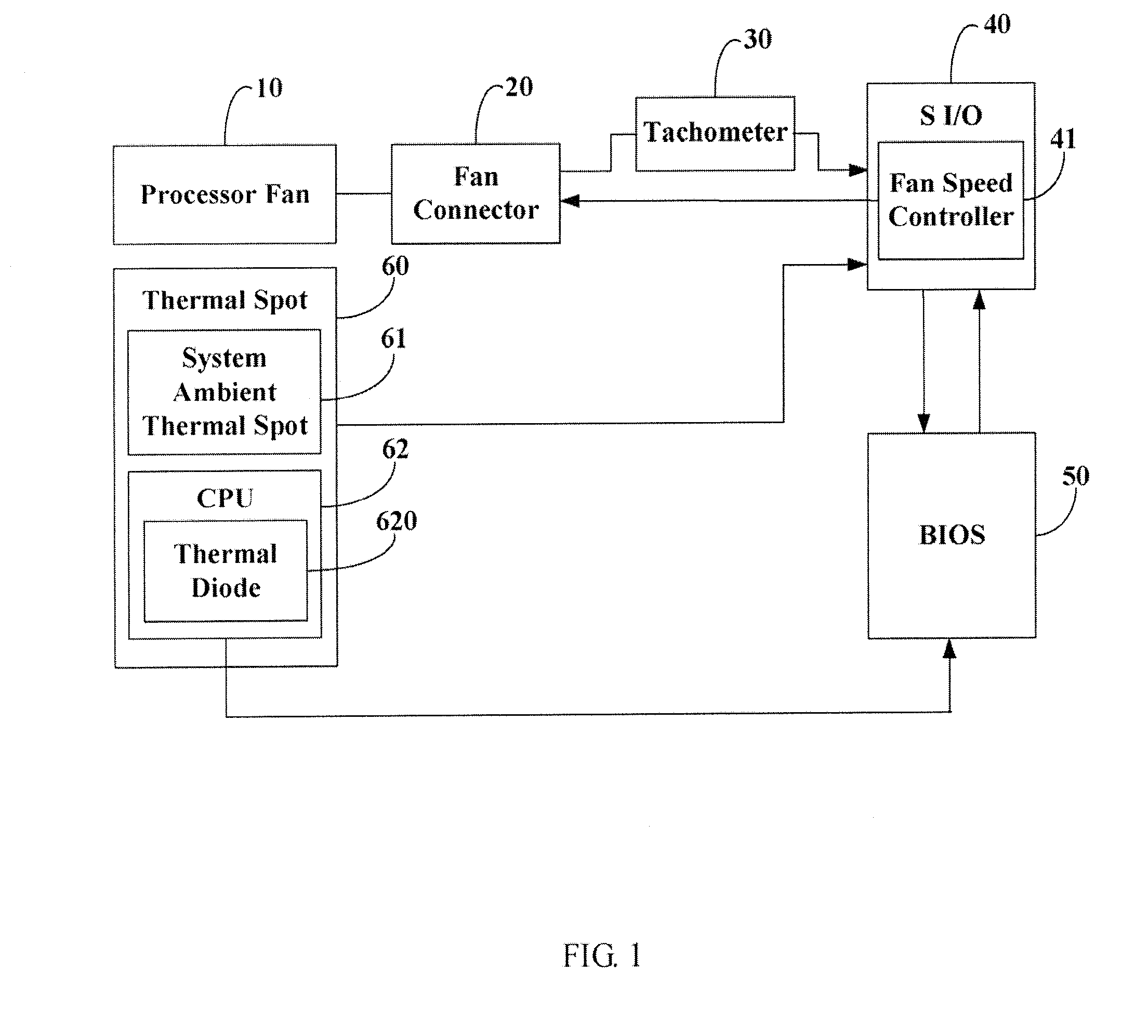
Measurement circuit components are included in an integrated circuit fabricated on a semiconductor substrate. A method is provided for controlling the speed of a cooling fan provided to cool an integrated circuit in which includes the steps of receiving a voltage from a thermal diode, addressing a table of digital temperatures by incrementing the address of the table entries every clock cycle of a circuit clock, converting the addressed data to a second voltage representing temperature, comparing the first voltage to the second voltage, providing a resulting temperature when both the first and second voltages are equal, and adjusting the fan speed accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and reference circuit for bias current switching for implementing an integrated temperature sensor
InactiveUS20050259718A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingReference currentReference circuit
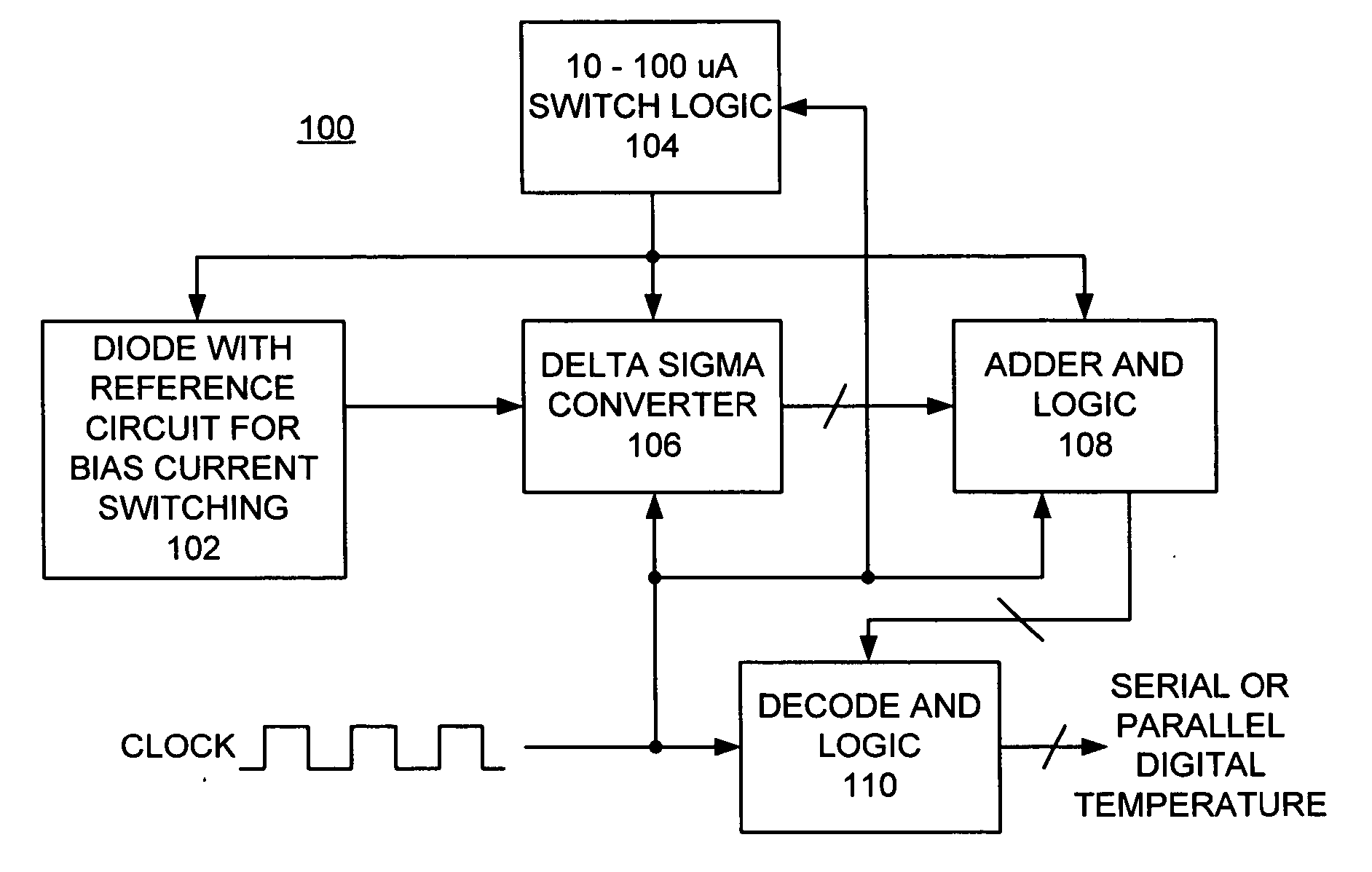
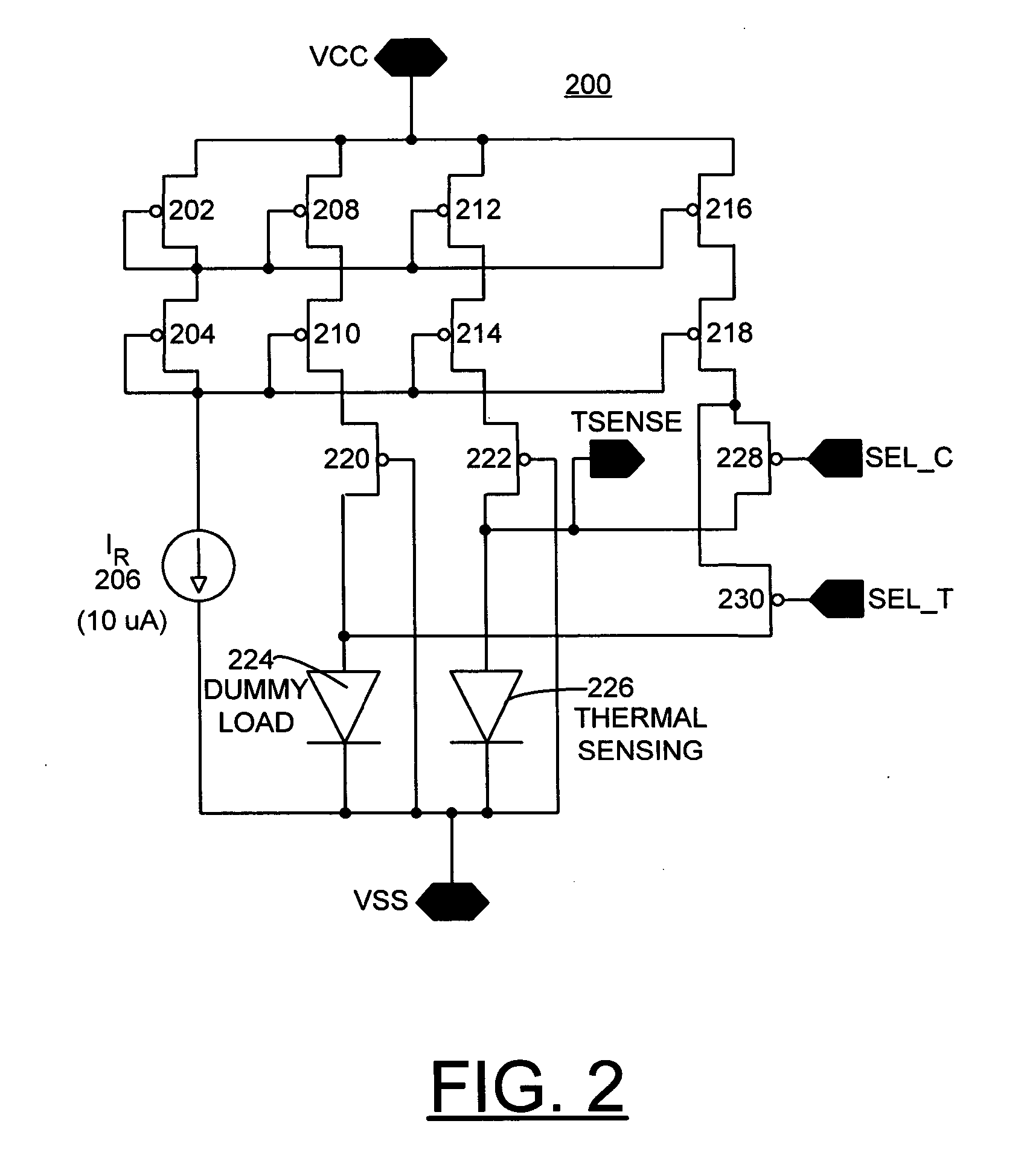
A method and a reference circuit for bias current switching are provided for implementing an integrated temperature sensor. A first bias current is generated and constantly applied to a thermal sensing diode. A second bias current is provided to the thermal sensing diode by selectively switching a multiplied current from a current multiplier to the thermal sensing diode or to a load diode. The reference circuit includes a reference current source coupled to current mirror. The current mirror provides a first bias current to a thermal sensing diode. The current mirror is coupled to a current multiplier that provides a multiplied current. A second bias current to the thermal sensing diode includes the first bias current and the multiplied current from the current multiplier. The second bias current to the thermal sensing diode is provided by selectively switching the multiplied current between the thermal sensing diode and a dummy load diode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adjusting voltage for a phase locked loop based on temperature
InactiveUS20090024349A1Reduce usageImprove device yieldThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryCircuit complexitySilicon
A mechanism for utilizing a single set of one or more thermal sensors, e.g., thermal diodes, provided on the integrated circuit device, chip, etc., to control the operation of the integrated circuit device, associated cooling system, and high-frequency PLLs is provided. By utilizing a single set of thermal sensors to provide multiple functions, e.g., controlling the operation of the integrated circuit device, the cooling system, and the PLLs, silicon real-estate usage is reduced through combining circuitry functionality. Moreover, the integrated circuit device yield is improved by reducing circuitry complexity and increasing PLL robustness to temperature. Furthermore, the PLL circuitry operating range is improved by compensating for temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Electronic device testing device and its temperature control method
InactiveCN101248361APrecise temperature controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsTemperature controlEngineering
An electronic device testing apparatus is described that includes a temperature measurement device for measuring a temperature of an IC device based on a voltage of a thermal diode provided inside the IC device, a temperature sensor and a temperature applying device provided to a pusher, and a temperature control portion for calculating a correction value from a difference of a measurement temperature of a predetermined IC device by the temperature measurement device and that by the temperature sensor. A temperature of the IC device to be tested is measured by the temperature measurement device at an actual operation, and the temperature applying device is controlled based on the obtained measurement temperature and the correction value calculated by the temperature control portion.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
System and method for controlling the rotating speed of a fan
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
High contrast far-field radiative thermal diode
InactiveUS20190027615A1Indirect heat exchangersThermoelectric device detailsReflected wavesPartial reflection
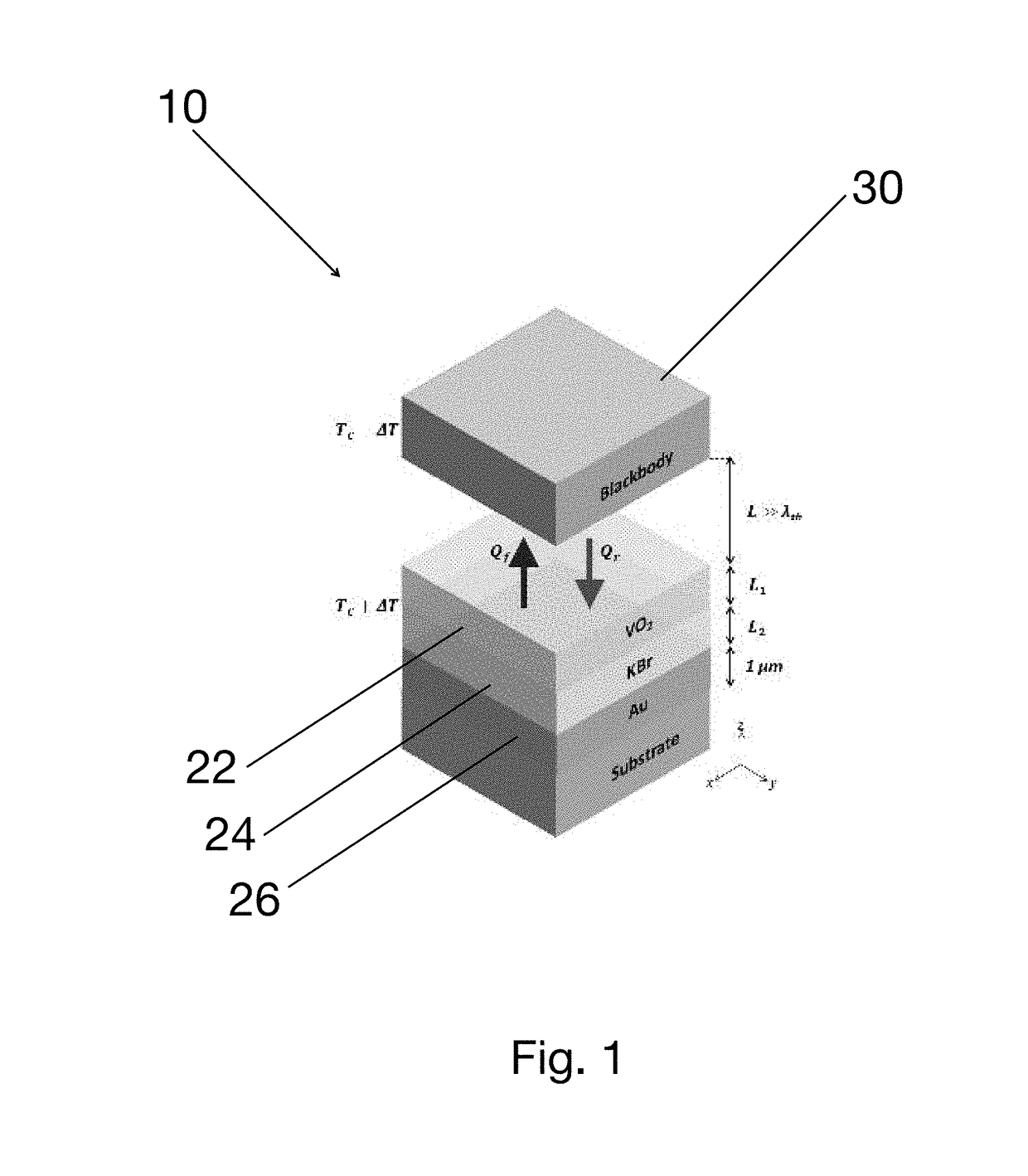
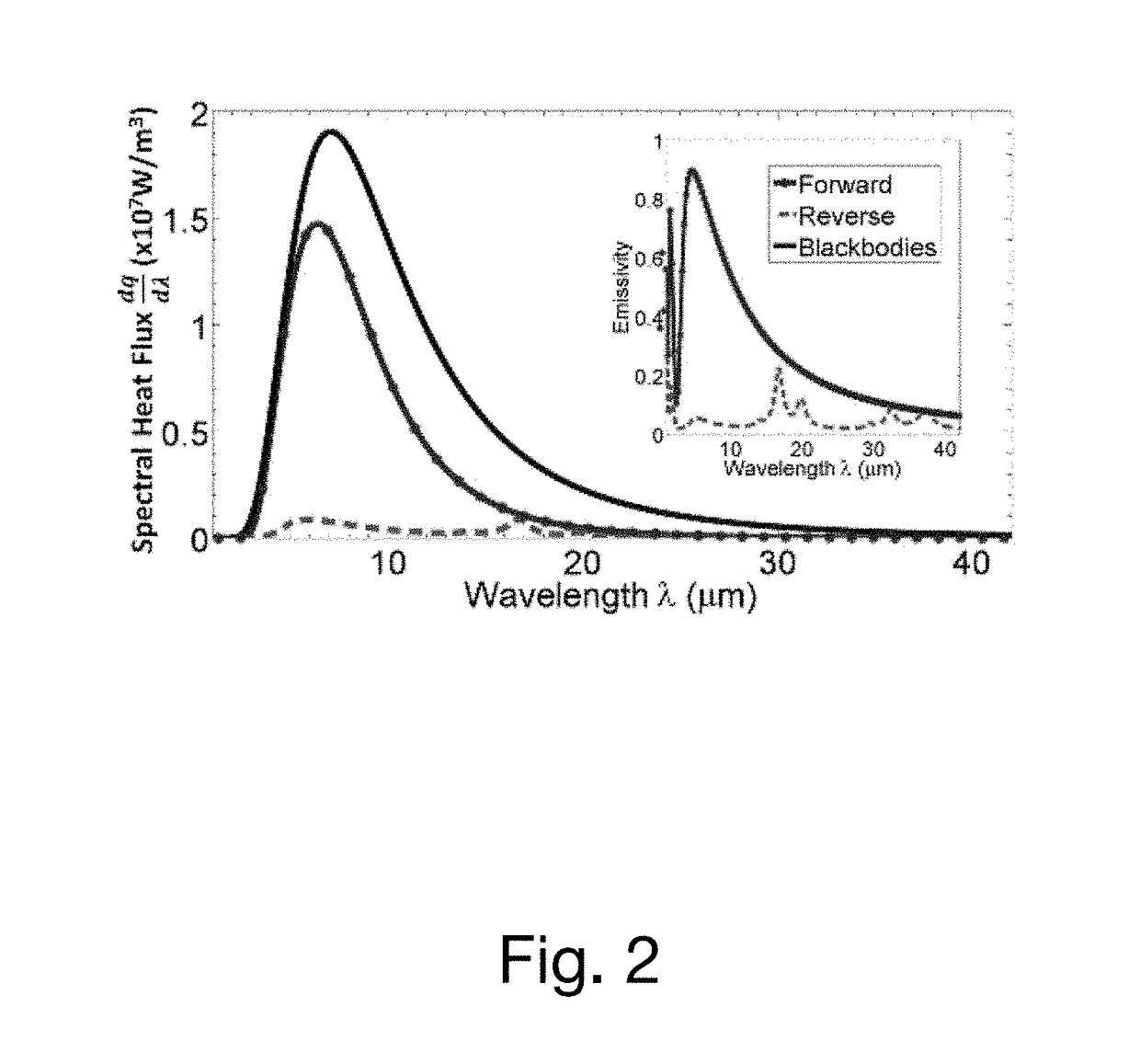
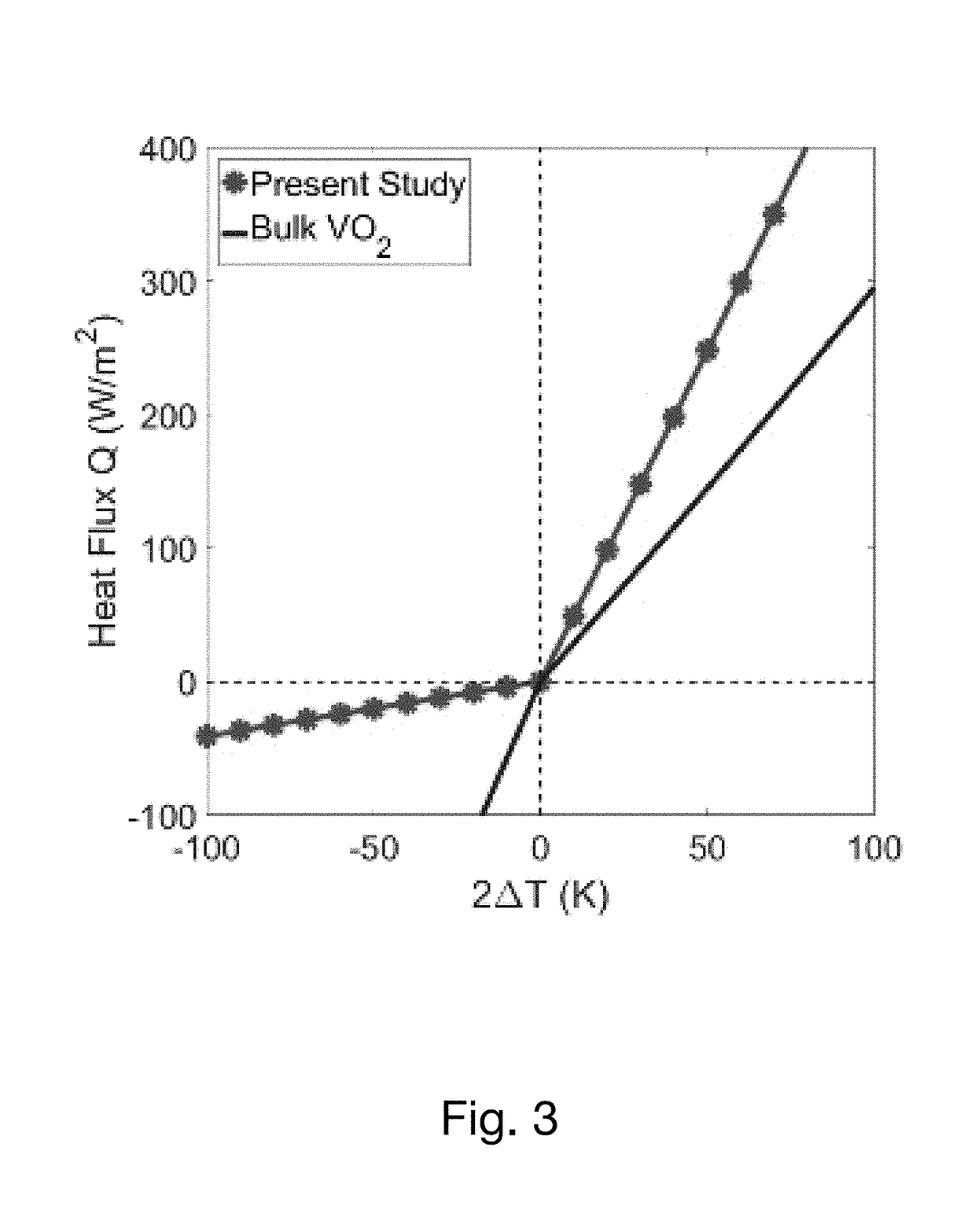
A far-field radiative thermal rectification device uses a phase change material to achieve a high degree of asymmetry in radiative heat transfer. The device has a multilayer structure on one side and a blackbody on other side. The multilayer structure can consist of a transparent thin film of KBr sandwiched between a thin film of VO2 and a reflecting layer of gold. When VO2 is in its insulating phase, the structure is highly reflective due to the two transparent layers on highly reflective gold. When VO2 is in the metallic phase, Fabry-Perot type of resonance occurs and the tri-layer structure acts like a wide-angle antireflection coating achieved by destructive interference of partially reflected waves making it highly absorptive for majority of spectral range of thermal radiation. The instant structure can form the active part of a configuration that acts like a far-field radiative thermal diode.
Owner:UNIV OF RHODE ISLAND BOARD OF TRUSTEES
Fan control system
InactiveUS20110101903A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlAudio power amplifierControl system
A fan control system includes a temperature detecting circuit and a rotation rate control circuit. The detecting circuit includes an amplifier and a thermal diode. The detecting circuit detects temperature and outputs a voltage signal. The control circuit receives the voltage signal and controls the rotation rate of the fan according to the voltage signal.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Circuit for sensing on-die temperature at multiple locations
InactiveUS7018095B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical polarityEngineering
A circuit for sensing on-die temperature at multiple locations using a minimum number of pins is described. Thermal diodes coupled to pins are placed on a die to measure the temperature at various die locations. Voltage is applied to the pins to determine the temperature at each given diode location. The polarity of the voltage applied across the pins determines what diodes are selected for measurement.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hot pipe deposited horizontally
InactiveCN101324409AImprove heat transfer efficiencyAvoid backward passIndirect heat exchangersManufactured materialEvaporation
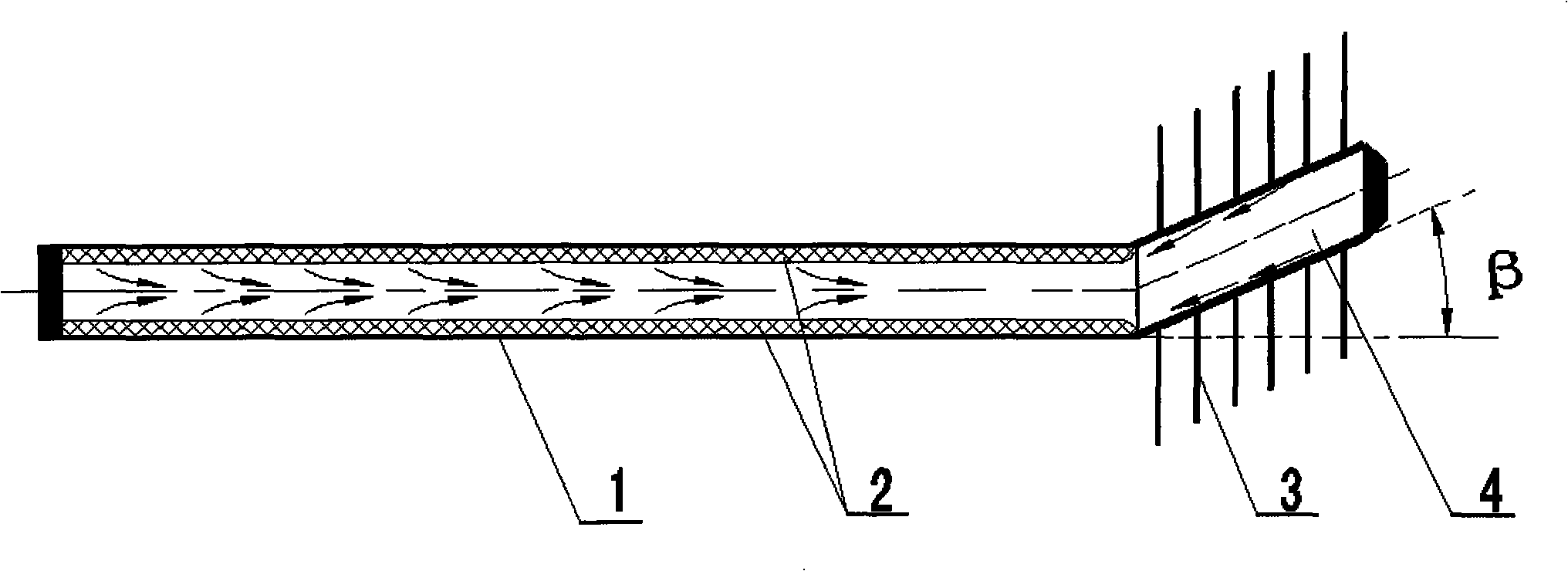
A heat pipe for horizontal arrangement, which belongs to a heat transfer element, comprises a pipe body and a medium fluid in the pipe body, wherein the pipe body comprises an evaporation segment, a heat insulation segment and a condensation segment, which are communicated with each other; and heat-dissipating fins are arranged on the outer circumference of the condensation segment. The condensation segment of the heat pipe is inclined upwards by an angle beta relative to the evaporation segment and the heat insulation segment, and a liquid absorption net is arranged on the inner walls of the evaporation segment and the heat insulation segment of the pipe body. When the heat pipe works normally, the medium fluid is repeatedly circulated in the heat pipe to carry out rapid heat exchange. When the temperature of the condensation segment is higher than the temperature of the evaporation segment, the inclination angle of the condensation segment can allow the gas to gather at the condensation segment and the liquid to gather at the evaporation segment to prevent the occurrence of heat blockage due to the flowing and circulation of the medium in the pipe and prevent reverse heat transfer, so that the heat pipe can achieve one-way heat transfer function of one-way thermal diode by injecting only one medium. The heat pipe has the advantages of improved heat transfer efficiency, reduced processing steps and saved manufacture material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
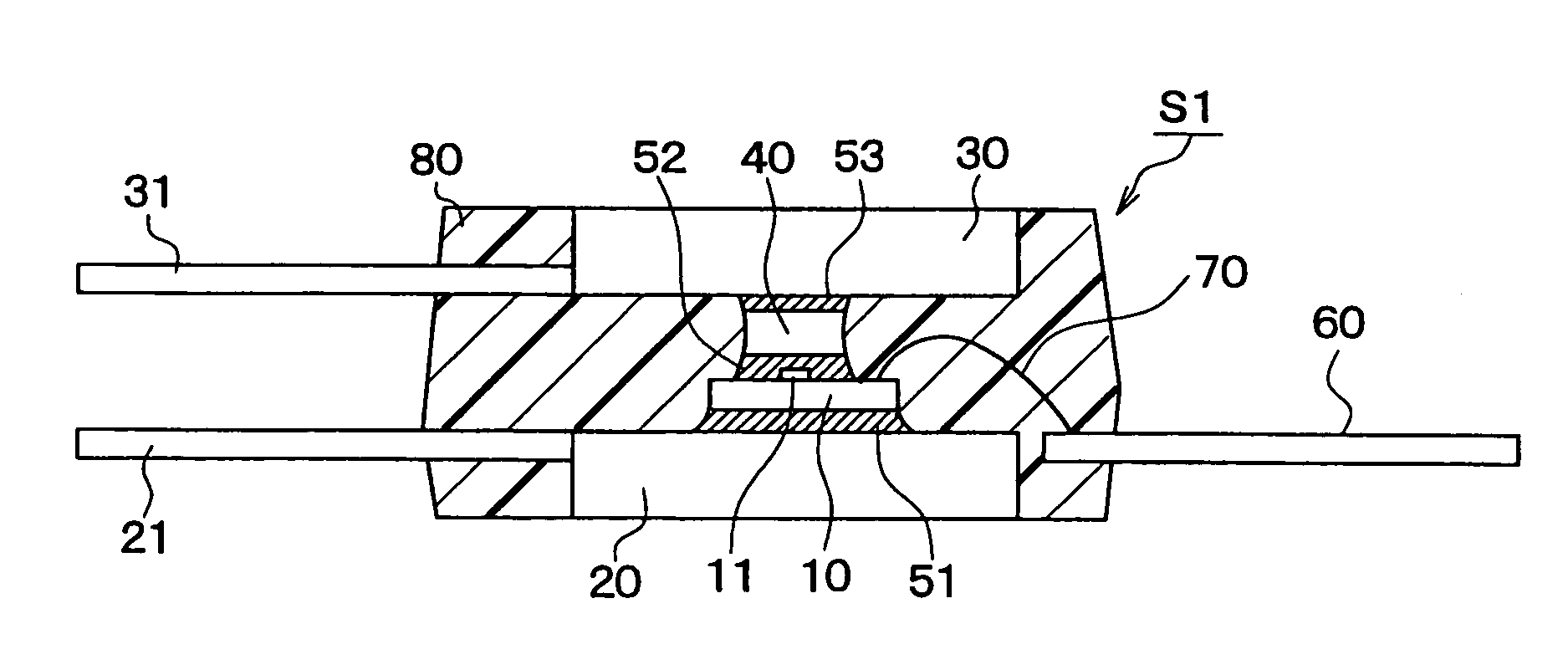
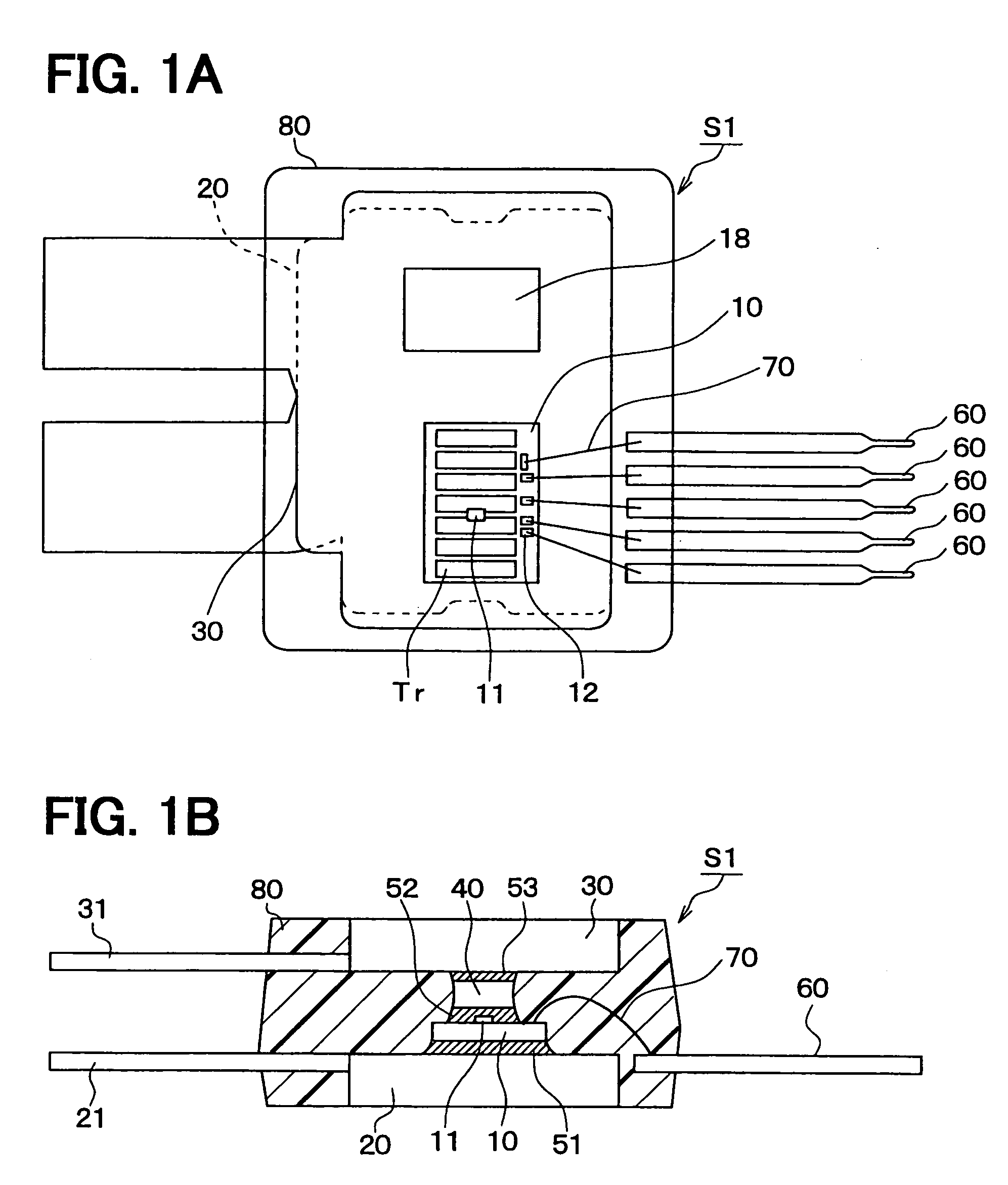
Temperature Sensor Module
InactiveUS20090207882A1Easy proofreadingAvoid temperature measurement errorsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansCMOSSemiconductor materials
A temperature sensor module includes a first temperature sensor configured for sensing the temperature of the environment, and a second temperature sensor configured for sensing the temperature of an eardrum. The first temperature sensor is a thermal diode, and the second temperature sensor is a thermopile. Preferably, the second temperature sensor may be a CMOS-infrared temperature sensor. The first temperature sensor and the second temperature sensor are both made of the semiconductor material such that they have same physical characters and same raising / falling temperature speeds even if entering into the environment with the different temperatures. Therefore, they are proofread easily, have a low manufacturing cost and consume low power.
Owner:FORTUNE SEMICON
Magnetic cold storage device for magnetic refrigerator
InactiveCN102706028AReduce lossesImprove conversion efficiencyEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic mediaCoupling
The invention discloses a thermal-switch magnetic cold storage device for a magnetic refrigerator. The device is arranged in a controllable magnetic field source and comprises a magnetic cold storage device which forms a heat transfer loop and a heat transfer assembly; the heat transfer assembly comprises at least one thermal switch unit; the magnetic cold storage device is a container filled with magnetic mediums; a portion of the thermal switch unit is arranged in the magnetic cold storage device to contact the magnetic mediums, and effectively enable the magnetic mediums to perform heat transport with the outside world during a magnetic field variation process. The thermal switch is a thermal diode, a superconductive switch or a heat transfer control device in the other modes; the magnetic mediums are solids, liquids or magnetic thermal materials in the other modes. The magnetic mediums give out heat to a heat source in a magnetizing stage and absorb heat from a cold source in a demagnetization stage by action of the controllable magnetic field so as to achieve the purpose of refrigeration. The device has good heat transport directivity and high-efficiency magnetic heat coupling mechanism; and the device has the advantages of high efficiency, compact structure, operation stability and good economical efficiency.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Temperature sensing module
InactiveCN101532886AReduce manufacturing costSave electricityThermometer applicationsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsManufacturing technologySemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a temperature sensing module which comprises a first temperature sensor and a second temperature sensor. The first temperature sensor is used for sensing the ambient temperature, while the second temperature sensor is used for sensing the temperature of eardrum. The first temperature sensor adopts a thermal diode, while the second temperature sensor can adopt a thermopile type thermal sensor or an infrared temperature sensor (CMOS-IR Detector) which is manufactured by the complementary metal-oxide semiconductor manufacturing technology. The temperature sensors are both made of semiconductor material so as to maintain identical physical properties. Even if the temperature sensors are simultaneously operated under the conditions with different temperature, the heating / cooling rates thereof are identical. The invention has the advantages of simple correction, low manufacturing cost and low power consumption.
Owner:FORTUNE SEMICON
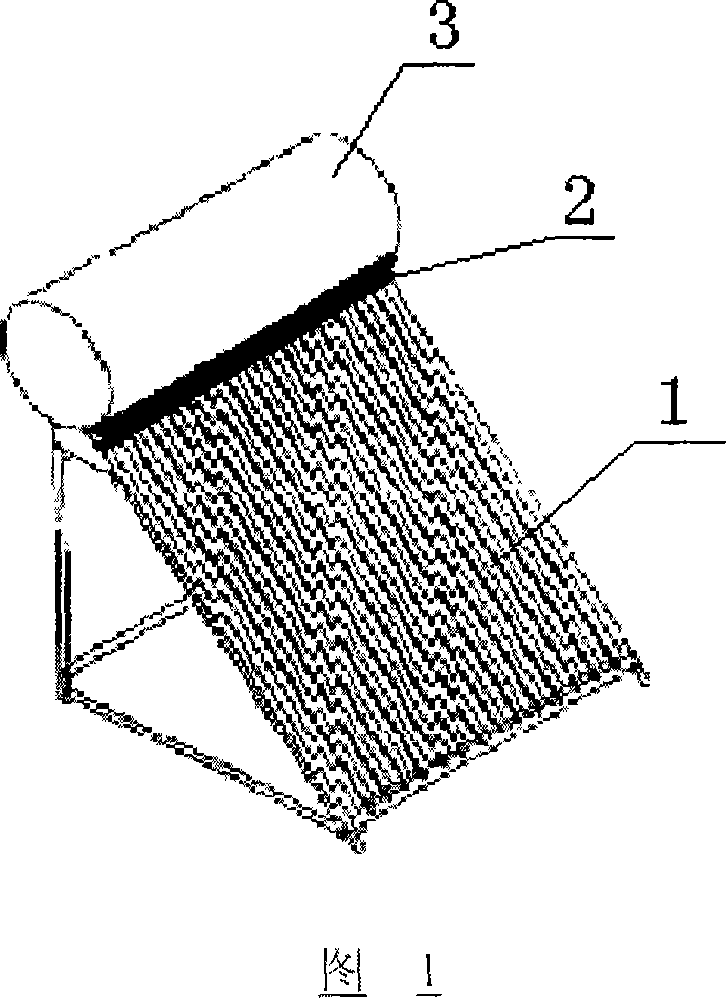
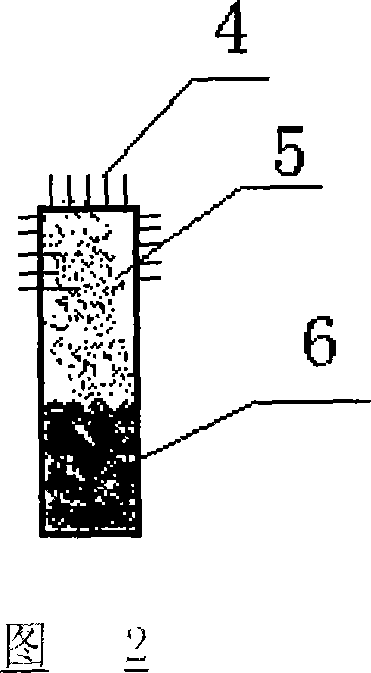
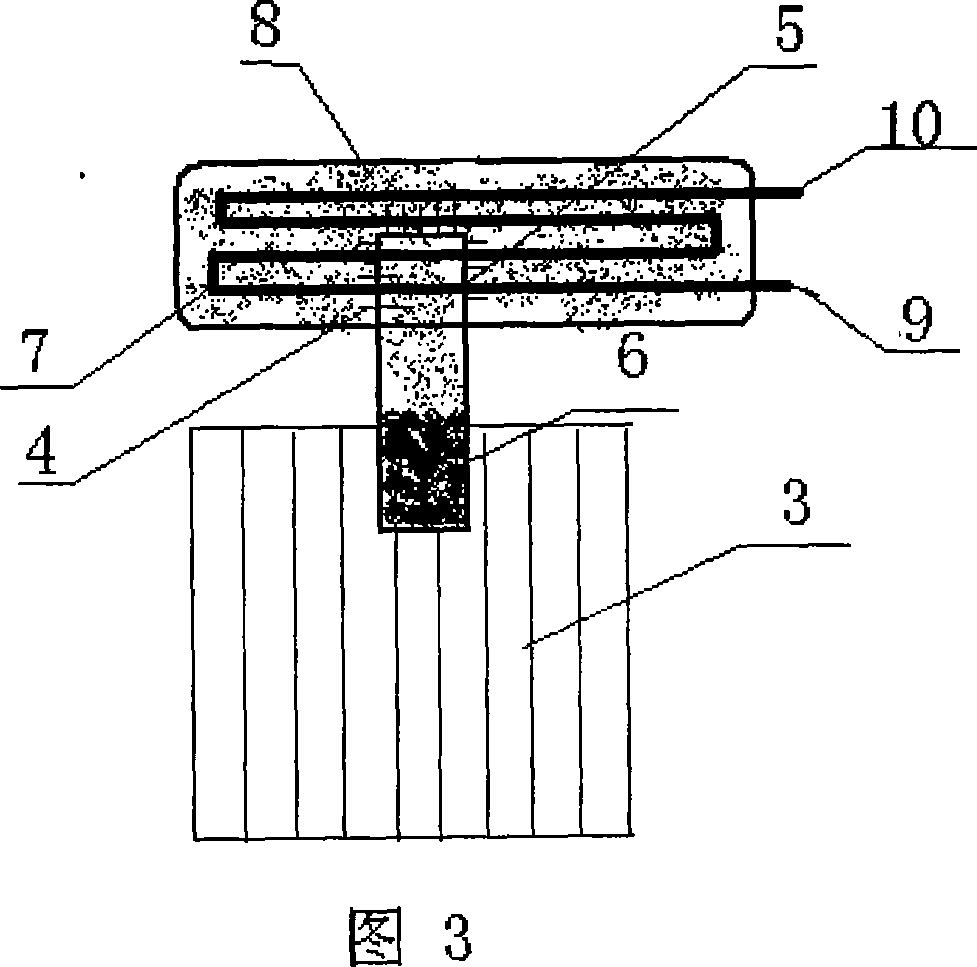
Solar energy heat utilization system combining thermal diode and phase change energy-storage material
InactiveCN101059285ASpeed up heat transferTake advantage ofSolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationThermal insulationSolar water heating system
The present invention provides a solar energy heat utilizing system combining thermal diode and phase-change energy-storing materials, it is characterized by it combines the thermal diode technology and the phase-change energy-storing technology, at the same time utilizes them in solar energy heat utilization to provide life hot water for people. When solar radiation is absorbed by heat-collecting sheet, the temperature of heat-collecting sheet one side is increased swiftly, the temperature of phase-change materials in heat-storing device is relative lower, so the solar energy heat quantity is transmitted into heat-storing device through thermal diode to make phase-change materials absorb heat and unfreeze and store heat quantity; when life hot water is needed, tap water flows over the heat transferring coil pipe in phase-change materials, and absorbs heat quantity for warming-up. The system has simple structure, it is easy to be combined with buildings, due to the utilization of thermal diode technology and the phase-change energy-storing technology, the heat-collecting performance and thermal insulation performance of the system are improved greatly. Compared with all-glass vacuum tube solar water heating system, the system has characteristics of no freezing, bearing more, fast start, high sensitivity and fast heat transfer speed.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
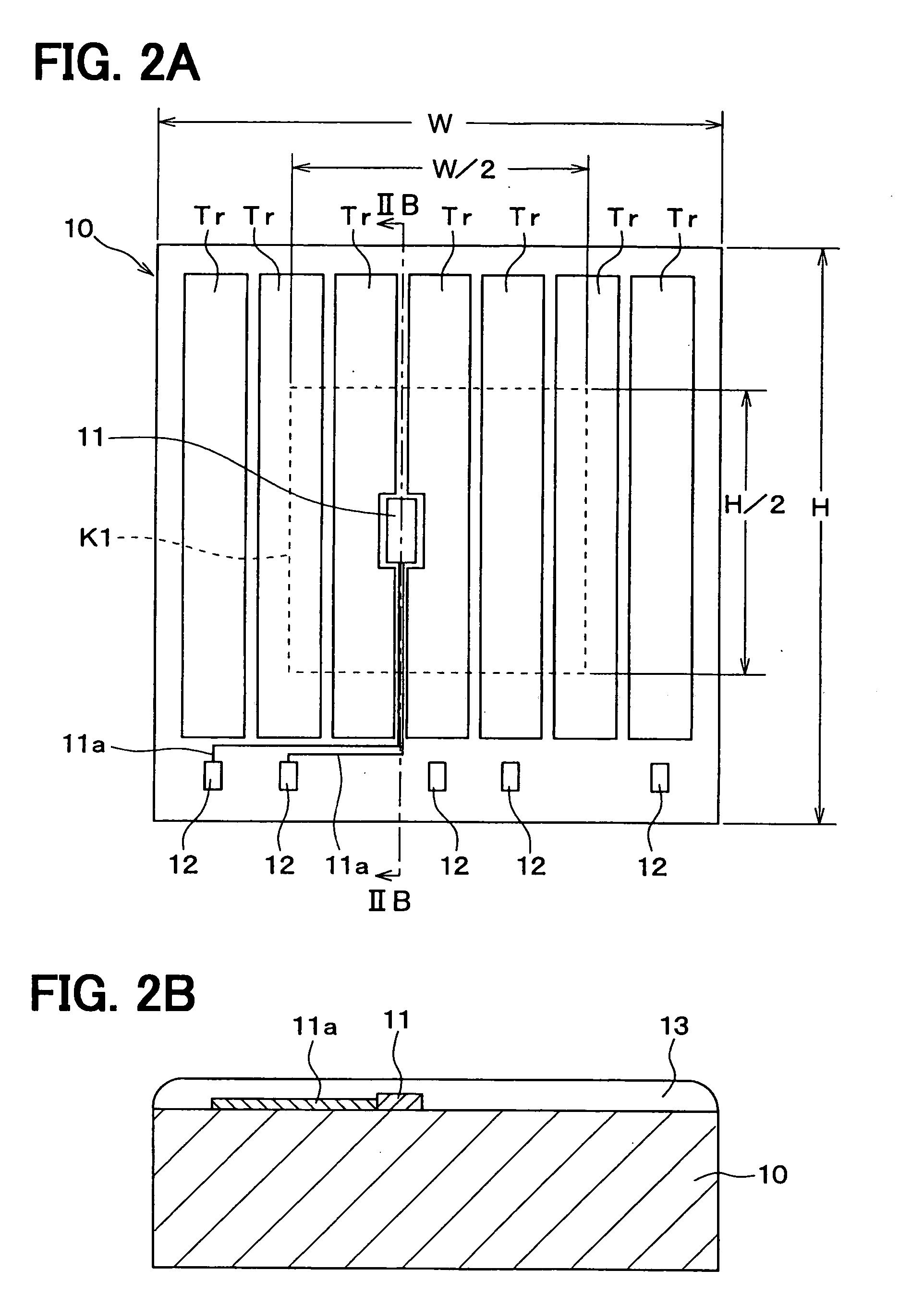
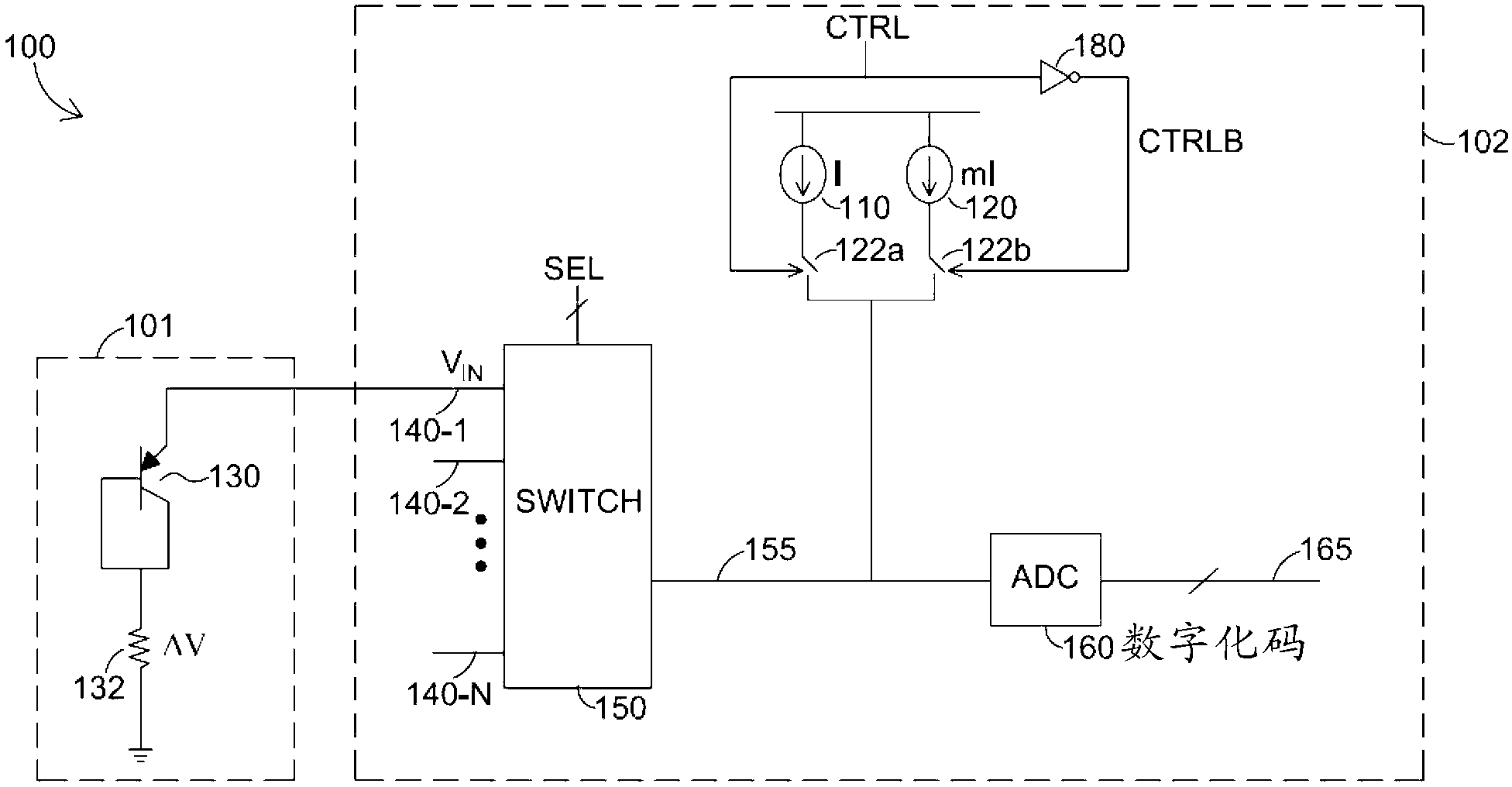
Small area high performance cell-based thermal diode
ActiveCN103226044AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansControl signalComputer module
A thermal sensing system includes a circuit having a layout including standard cells arranged in rows and columns. First and second current sources provide first and second currents, respectively. The thermal sensing system includes thermal sensing units, first and second switching modules, and an analog to digital converter (ADC). Each thermal sensing unit is configured to provide a voltage drop dependent on a temperature at that thermal sensing unit. The first switching module is configured to select one of the thermal sensing units. The second switching module includes at least one switch controllable by a control signal. The at least one switch is configured to selectively couple the thermal sensing units, based on the control signal, to one of the first and second current sources, via the first switching module. The ADC is configured to convert an analog voltage, provided by the selected thermal sensing unit, to a digital value. The invention also provides a small area high performance cell-based thermal diode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Variable temperature magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly
ActiveUS10557649B2Thermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeDomestic refrigeratorsThermodynamicsMagneto
A magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly includes a magneto-caloric cylinder with a plurality of magneto-caloric stages. Each of the plurality of magneto-caloric stages has a respective Currie temperature. The magneto-caloric cylinder has a length along an axial direction. The plurality of magneto-caloric stages is distributed along the length of the magneto-caloric cylinder. A plurality of thermal stages also has a length along the axial direction. The length of the plurality of thermal stages is less than the length of the magneto-caloric cylinder. The magneto-caloric cylinder is received within the plurality of thermal stages such that the magneto-caloric cylinder is movable along the axial direction relative to the plurality of thermal stages.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Adjusting voltage for a phase locked loop based on temperature
InactiveUS7493229B2Reduce usageImprove device yieldThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryCircuit complexityEngineering
A mechanism for utilizing a single set of one or more thermal sensors, e.g., thermal diodes, provided on the integrated circuit device, chip, etc., to control the operation of the integrated circuit device, associated cooling system, and high-frequency PLLs is provided. By utilizing a single set of thermal sensors to provide multiple functions, e.g., controlling the operation of the integrated circuit device, the cooling system, and the PLLs, silicon real-estate usage is reduced through combining circuitry functionality. Moreover, the integrated circuit device yield is improved by reducing circuitry complexity and increasing PLL robustness to temperature. Furthermore, the PLL circuitry operating range is improved by compensating for temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Structure for a phase locked loop with adjustable voltage based on temperature
InactiveUS7877222B2Reduce usageImprove device yieldThermometer detailsTemperatue controlCircuit complexityEngineering
A design structure for an apparatus for utilizing a single set of one or more thermal sensors, e.g., thermal diodes, provided on the integrated circuit device, chip, etc., to control the operation of the integrated circuit device, associated cooling system, and high-frequency PLLs, is provided. By utilizing a single set of thermal sensors to provide multiple functions, e.g., controlling the operation of the integrated circuit device, the cooling system, and the PLLs, silicon real-estate usage is reduced through combining circuitry functionality. Moreover, the integrated circuit device yield is improved by reducing circuitry complexity and increasing PLL robustness to temperature. Furthermore, the PLL circuitry operating range is improved by compensating for temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Methods for monitoring chip temperature during test
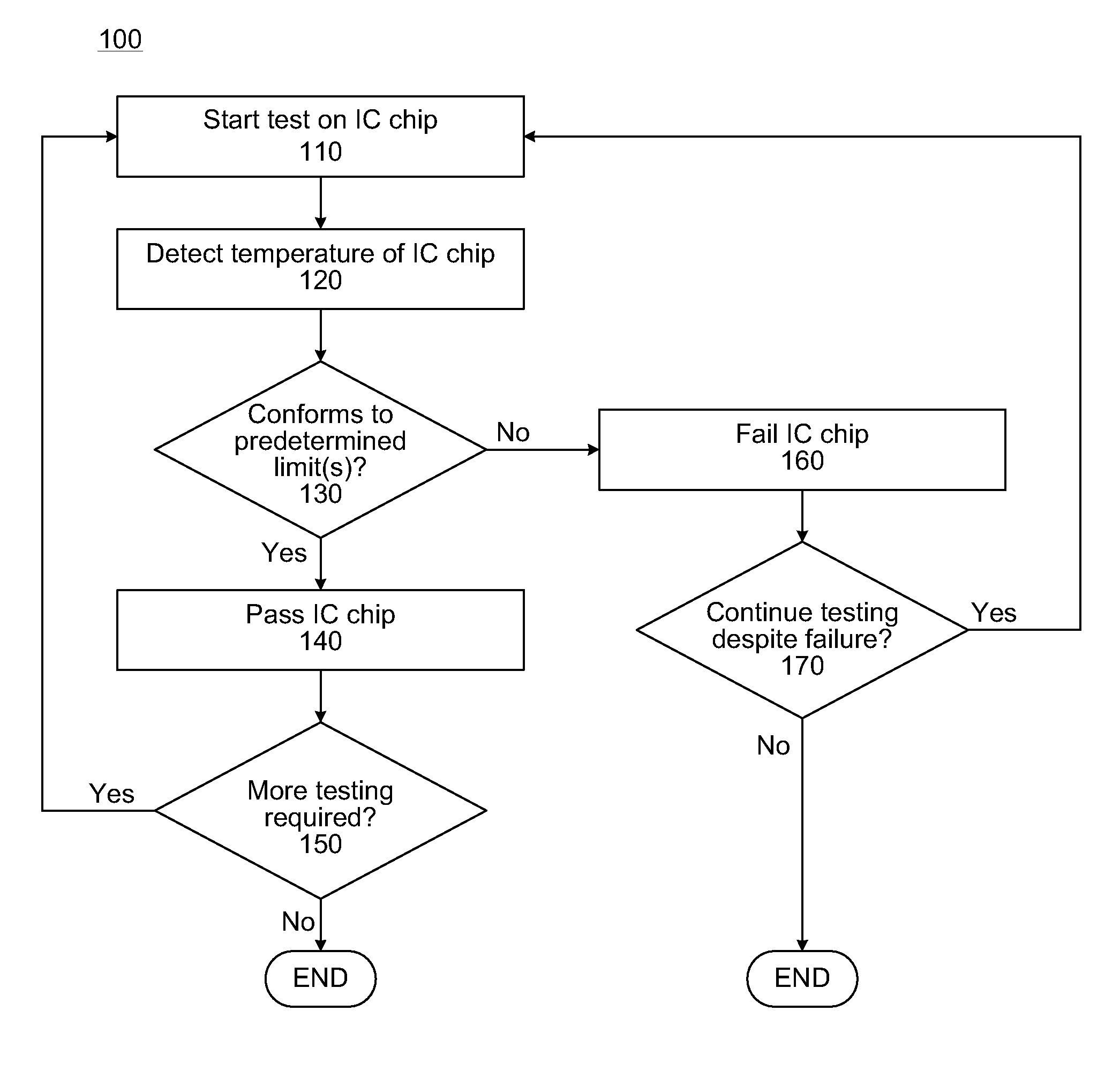
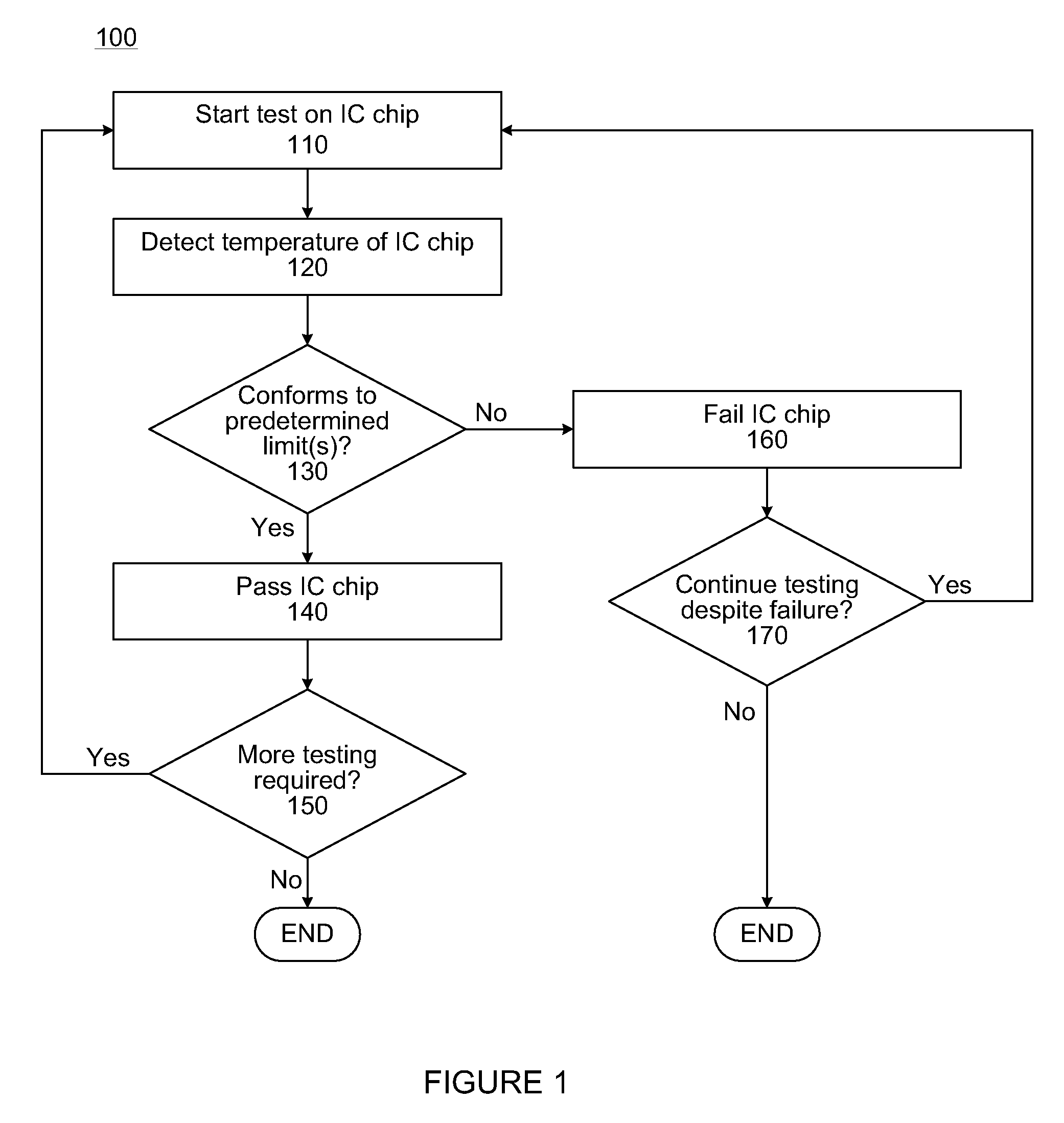
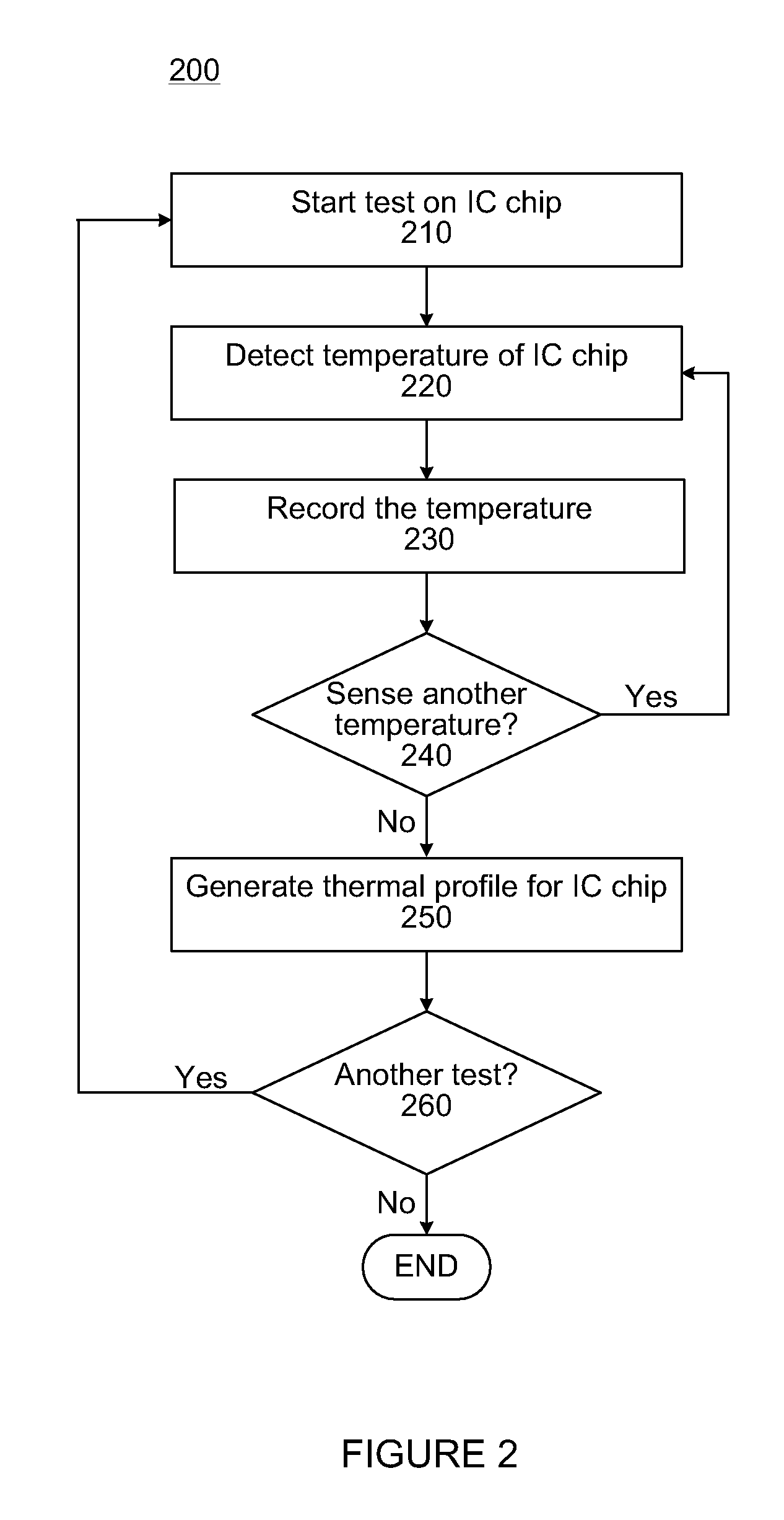
InactiveUS8152372B1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical testingThermal diodeIntegrated circuit
Described herein are methods and apparatuses for testing an integrated circuit chip including a thermal diode. According to various embodiments, a method for testing an integrated circuit chip including a thermal diode may comprise performing a test operation on the integrated circuit chip, and during the test operation, detecting a signal representative of a temperature sensed by a thermal diode embedded in the integrated circuit chip. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly
A magneto-caloric thermal diode assembly includes a magneto-caloric cylinder with a plurality of magneto-caloric stages. A length of one of the plurality of magneto-caloric stages is different than a length of another of the plurality of magneto-caloric stages. Each of a plurality of thermal stages includes a plurality of magnets and a non-magnetic ring. The plurality of magnets is distributed along a circumferential direction within the non-magnetic ring in each of the plurality of thermal stages. The length of each of the plurality of thermal stages corresponds to a respective one of the plurality of magneto-caloric stages.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com