Patents
Literature
213 results about "Diode voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
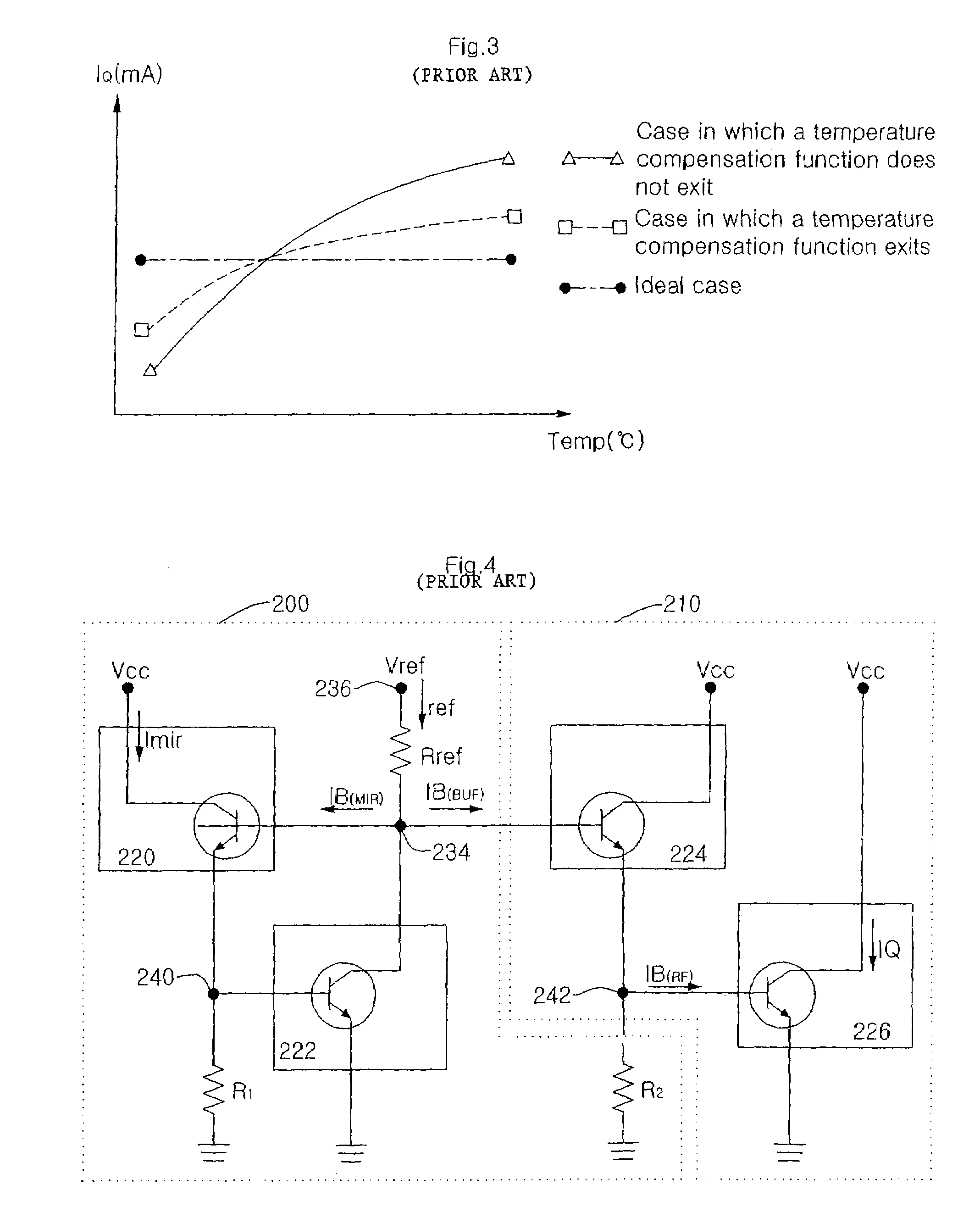
The normal diode may have a reverse-breakdown voltage of around 160 volts (V), and this voltage is the common peak level of a 110 volts alternating current (VAC) power line voltage.
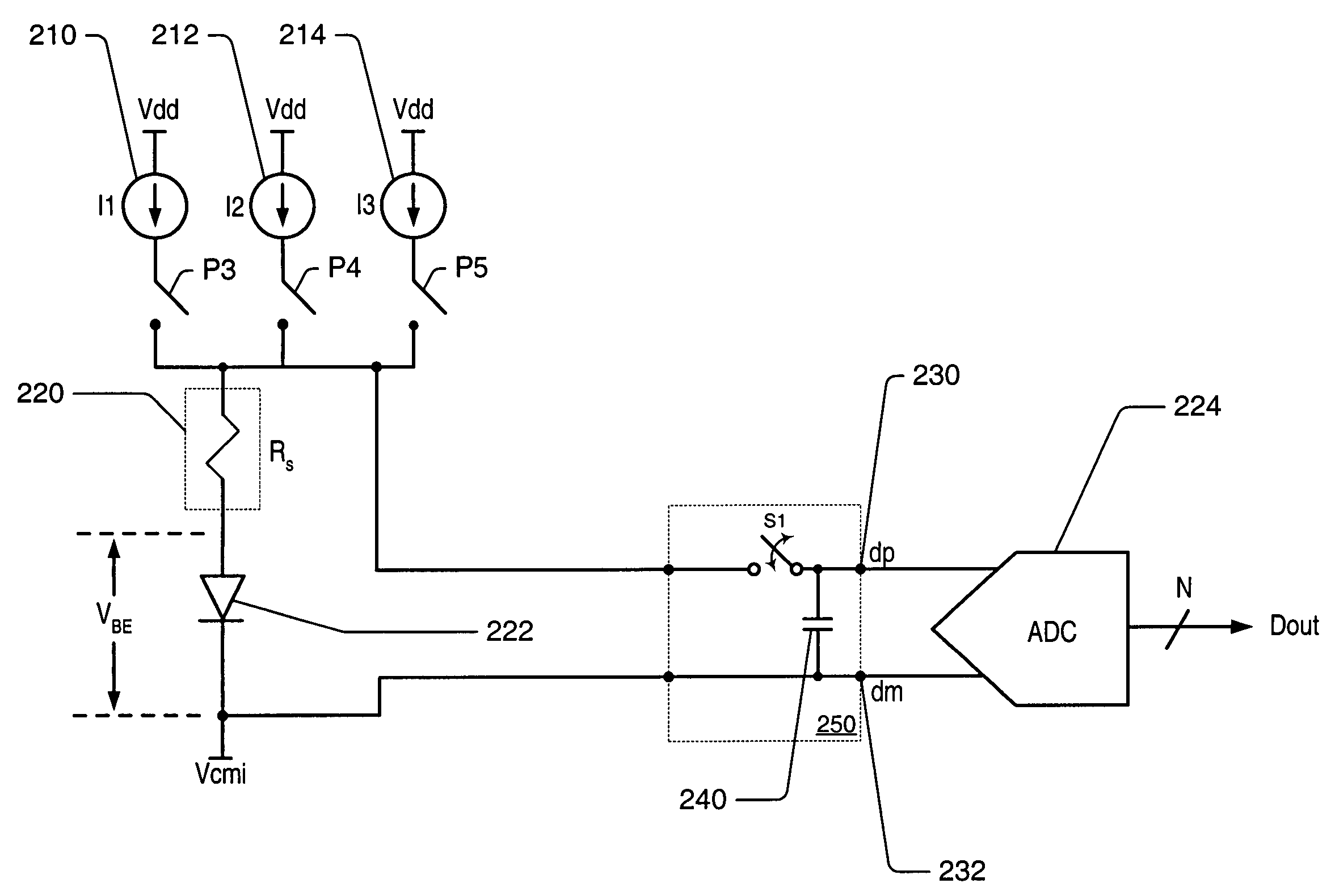
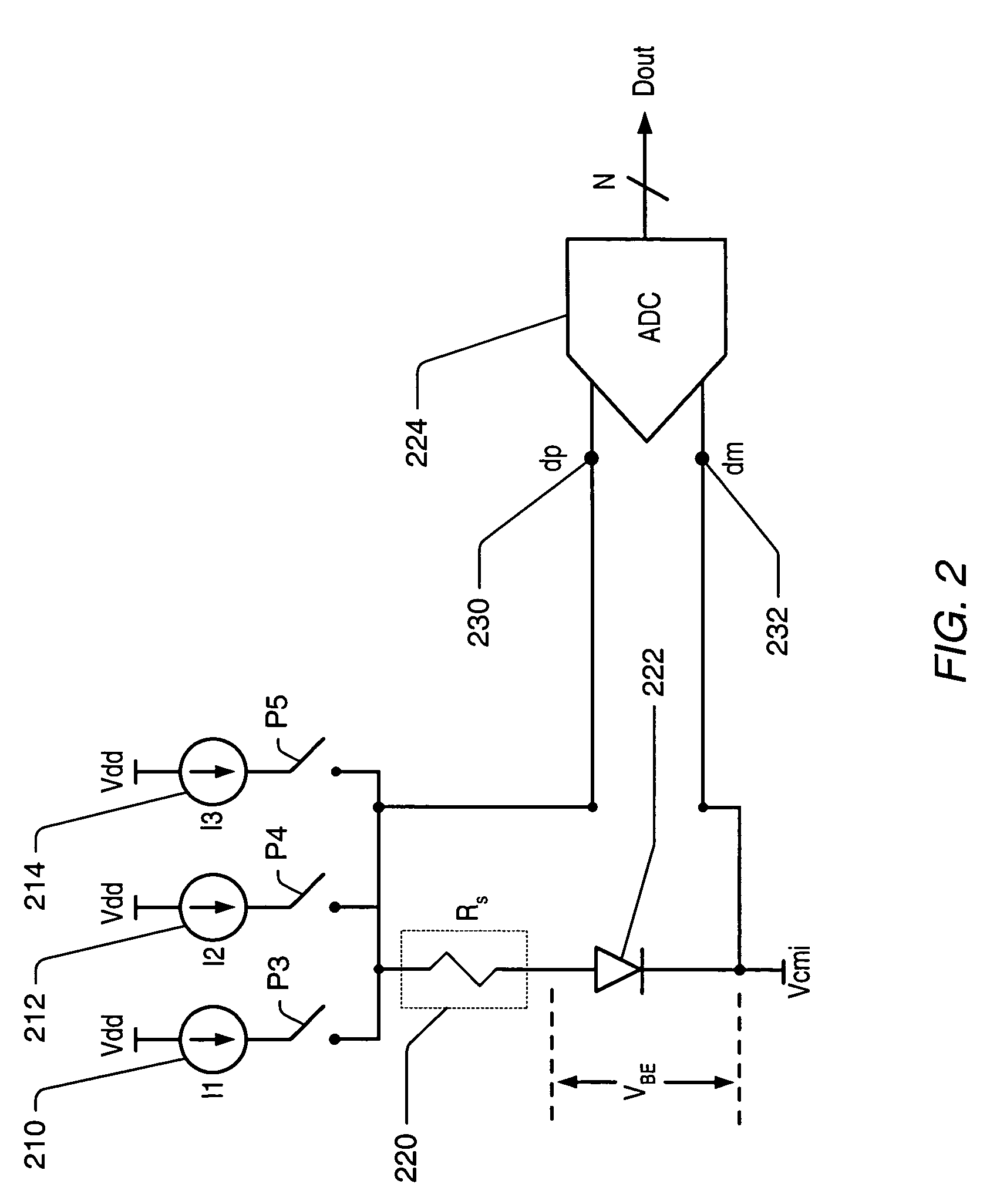
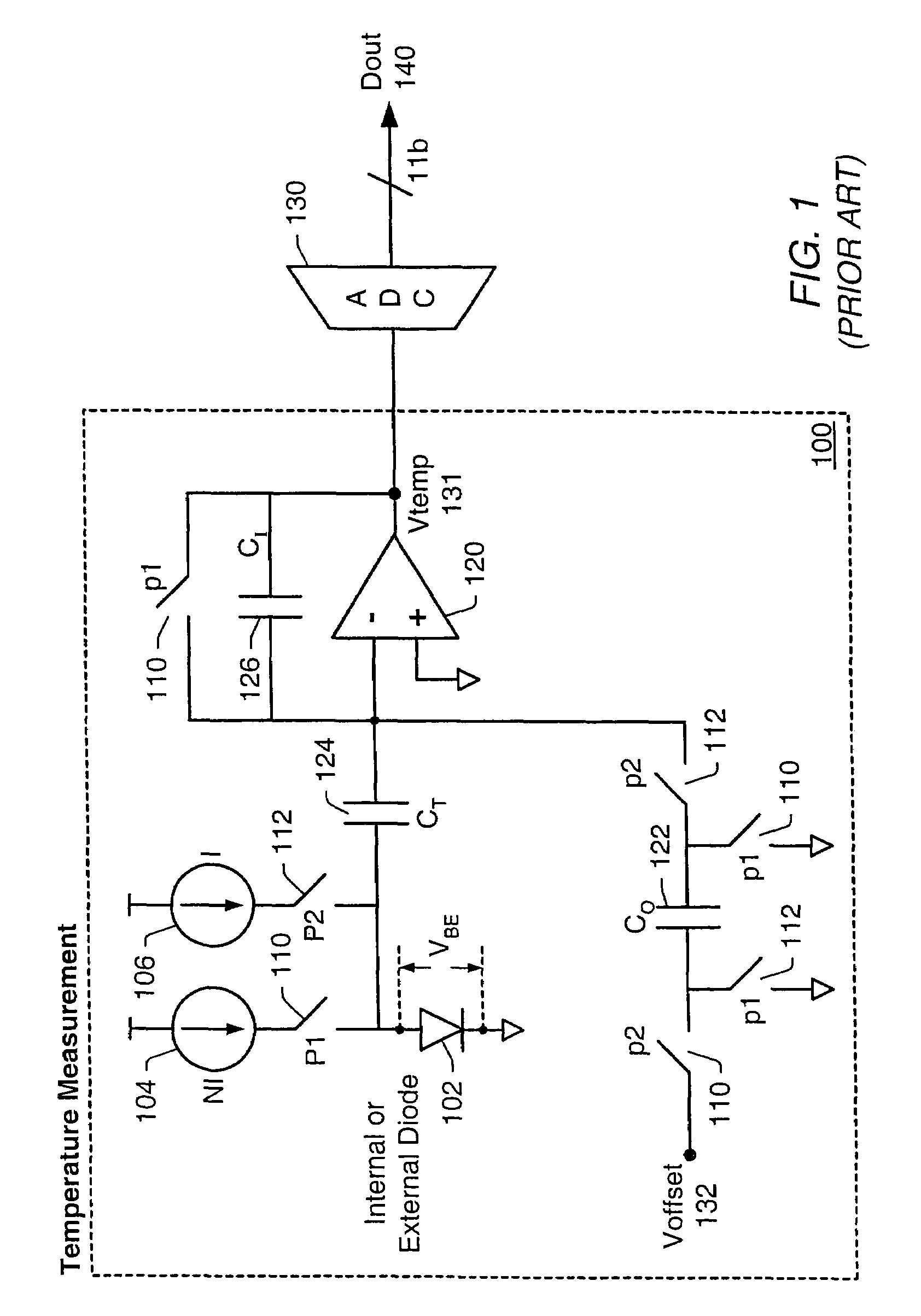
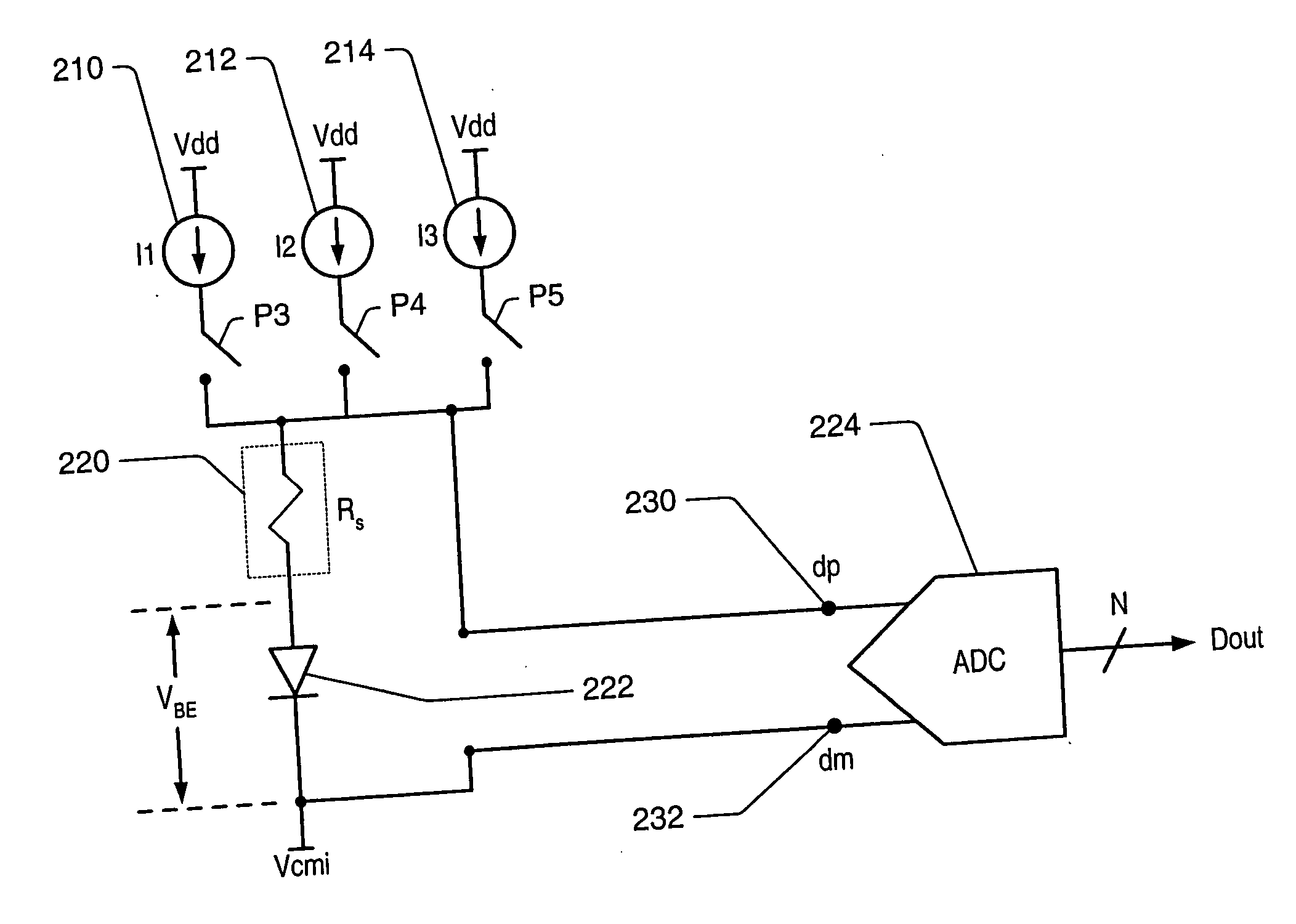
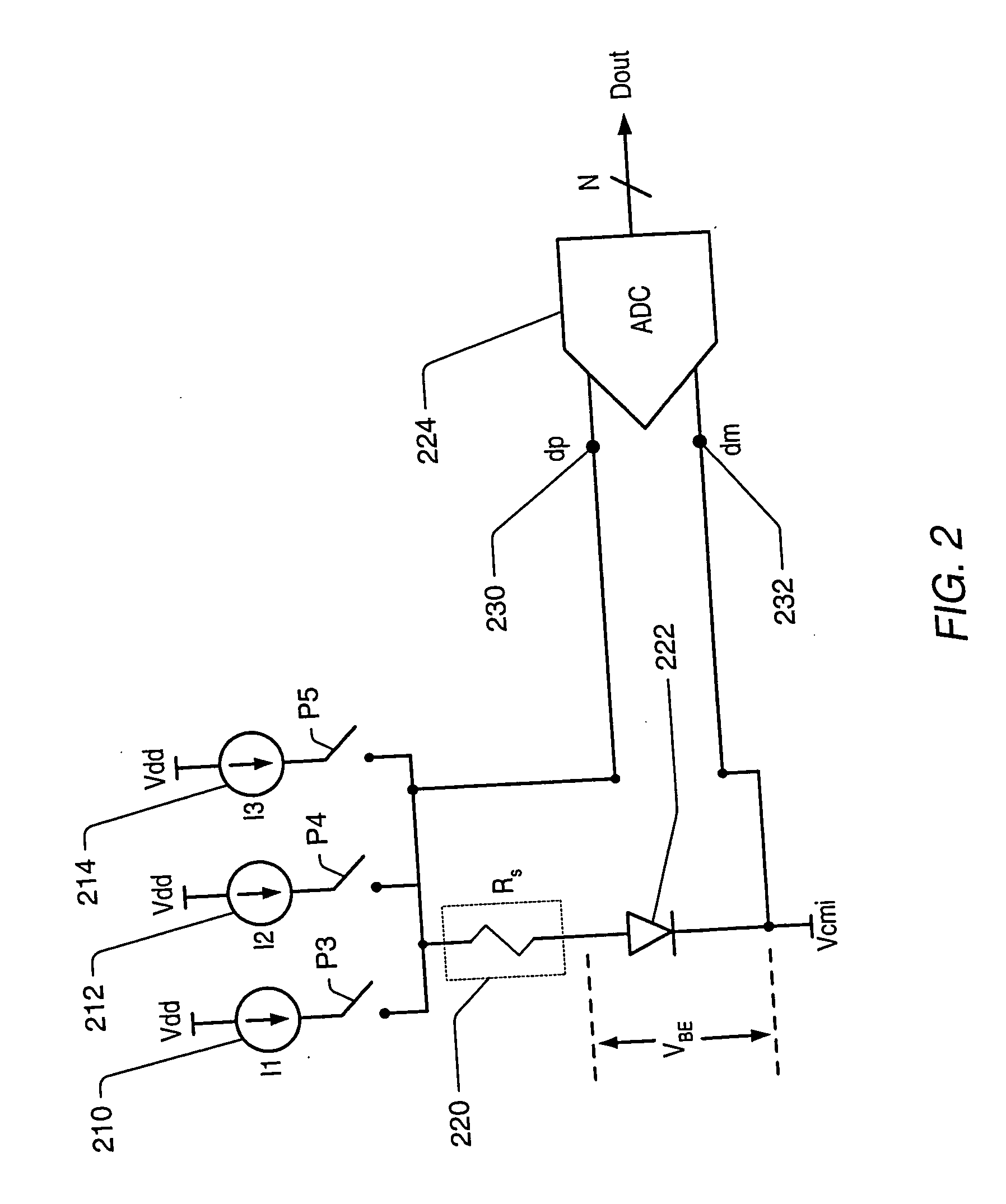
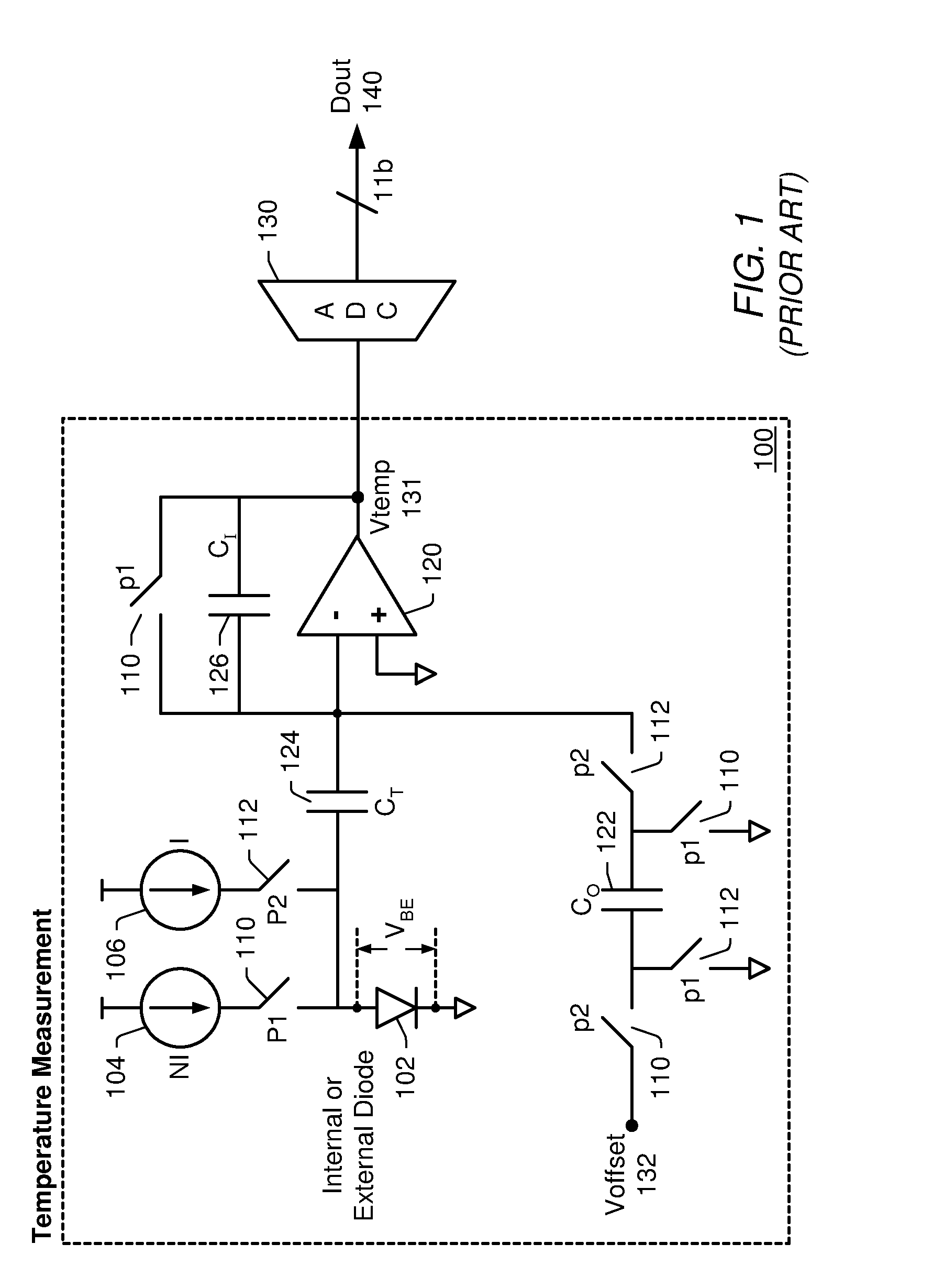
Integrated resistance cancellation in temperature measurement systems
ActiveUS7281846B2Eliminate needThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceIntegrator
A temperature measurement device may be implemented by coupling a PN-junction, which may be comprised in a diode, to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that comprises an integrator. Different currents may be successively applied to the diode, resulting in different VBE values across the diode. The ΔVBE values thus obtained may be successively integrated. Appropriate values for the different currents may be determined based on a set of mathematical equations, each equation relating the VBE value to the temperature of the diode, the current applied to the diode and parasitic series resistance associated with the diode. When the current sources with the appropriate values are sequentially applied to the diode and the resulting diode voltage differences are integrated by the integrator comprised in the ADC, the error in the temperature measurement caused by series resistance is canceled in the ADC, and an accurate temperature reading of the diode is obtained from the output of the ADC.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
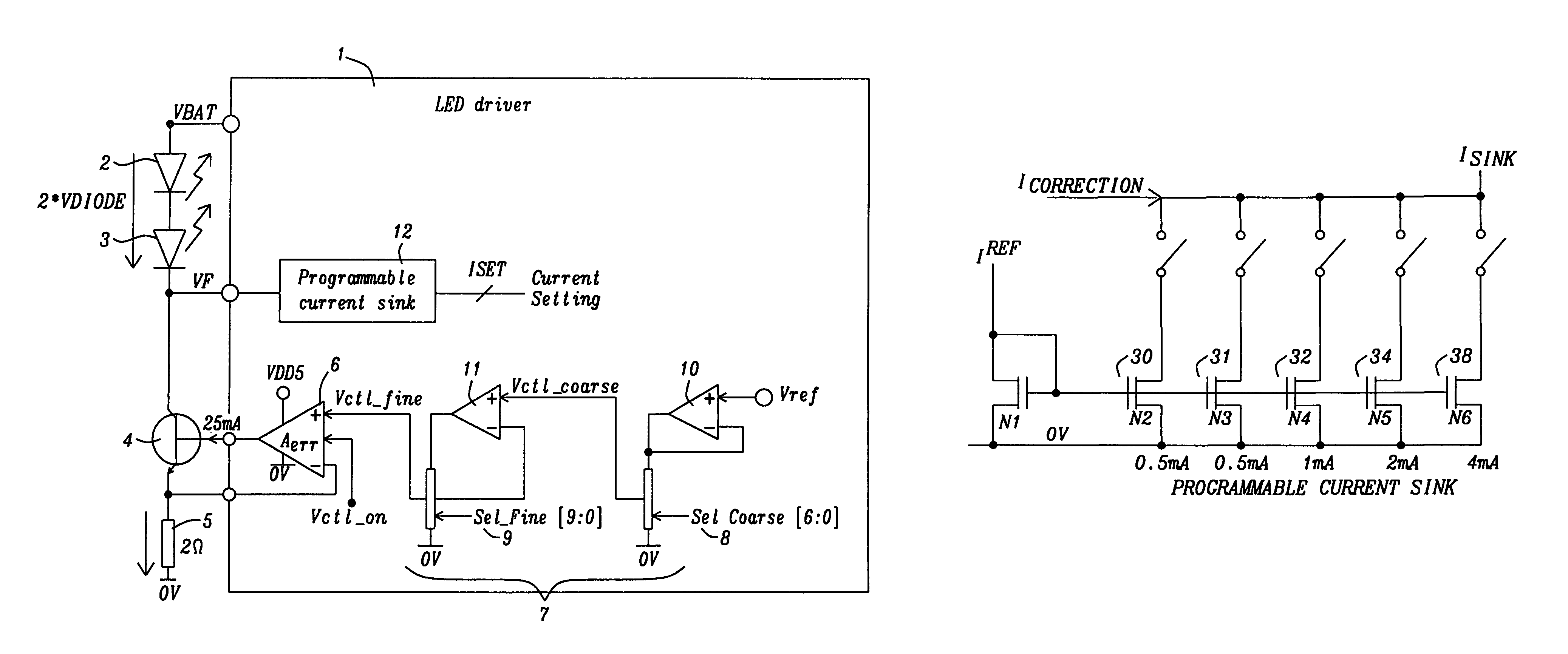
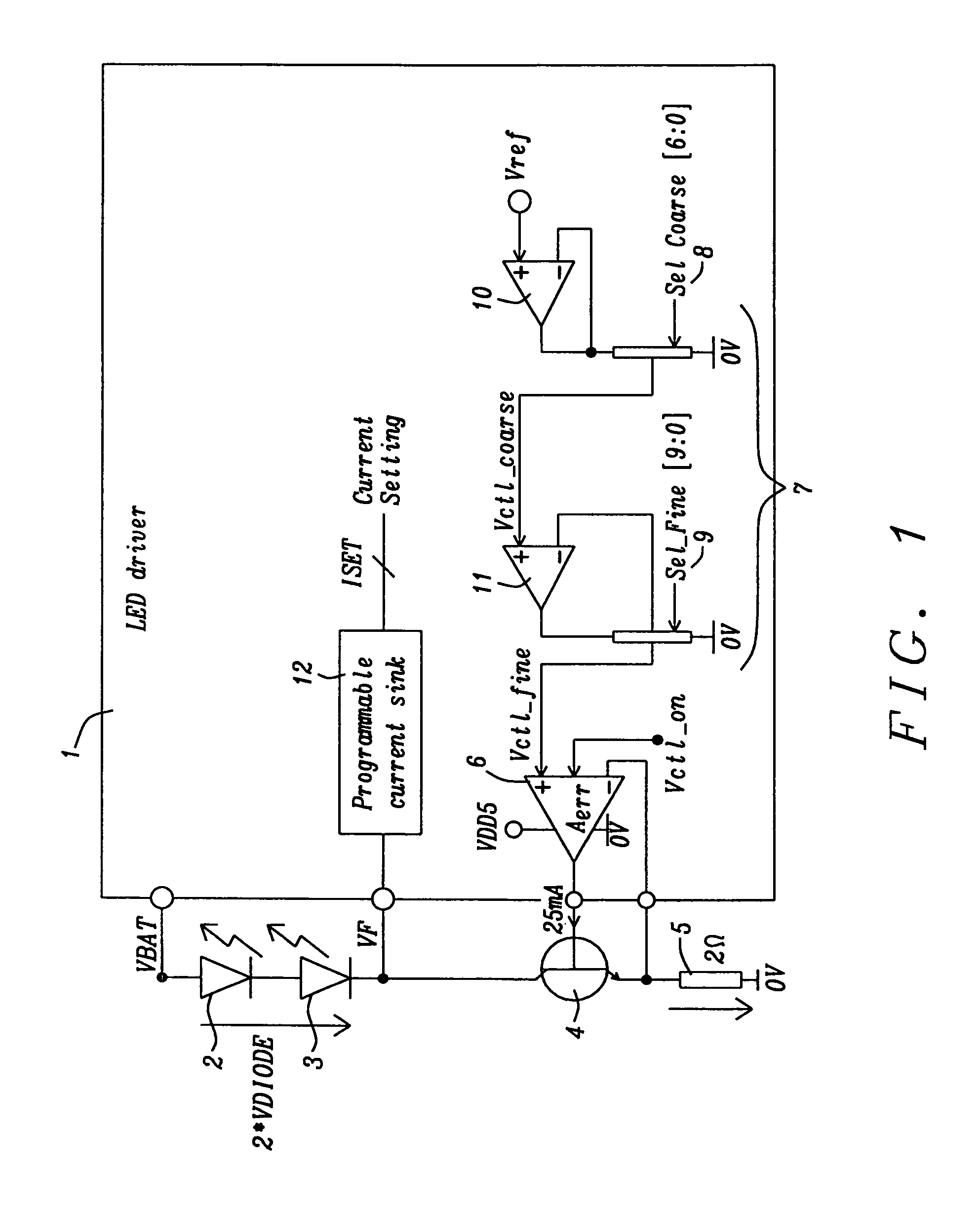
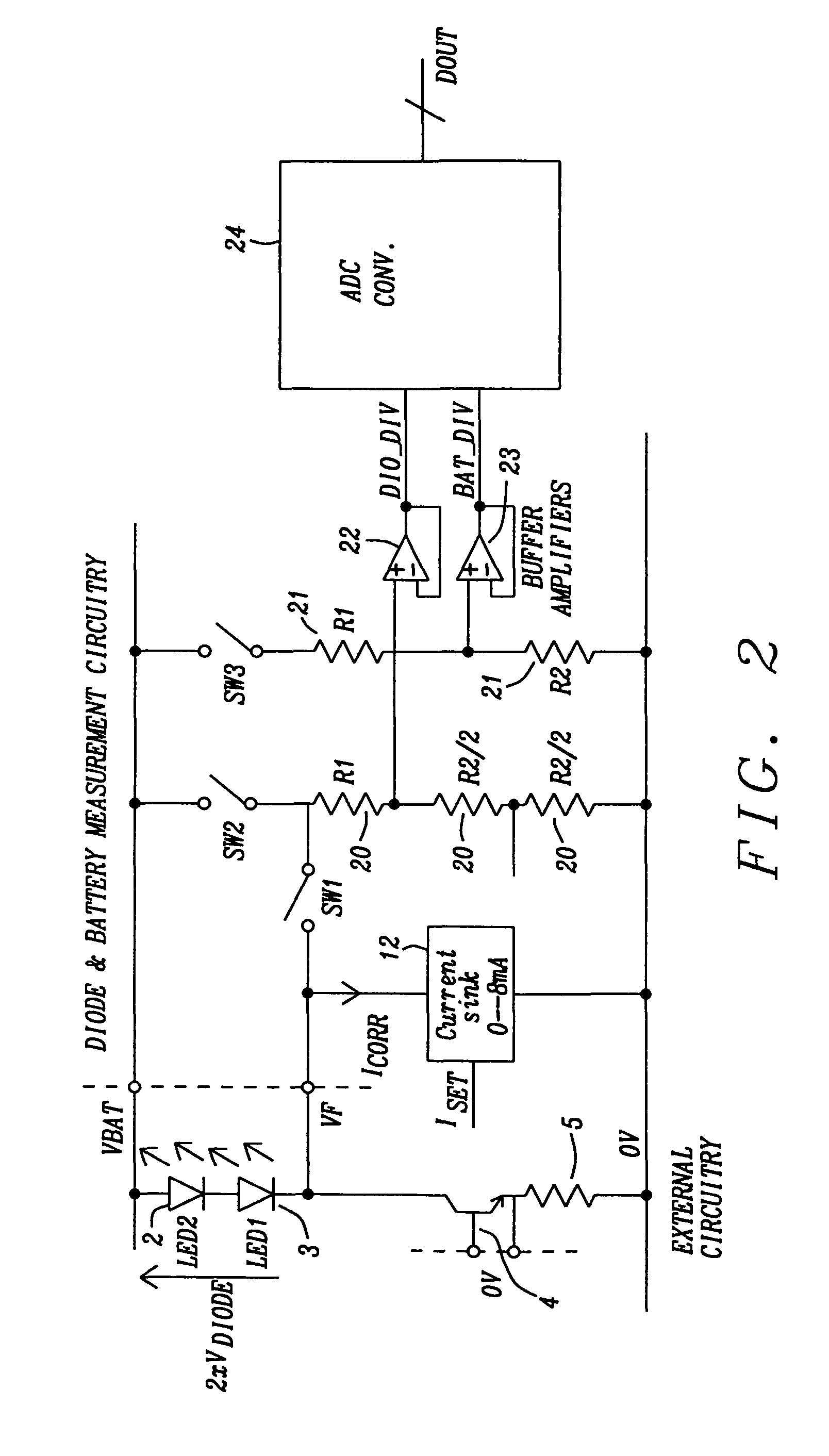
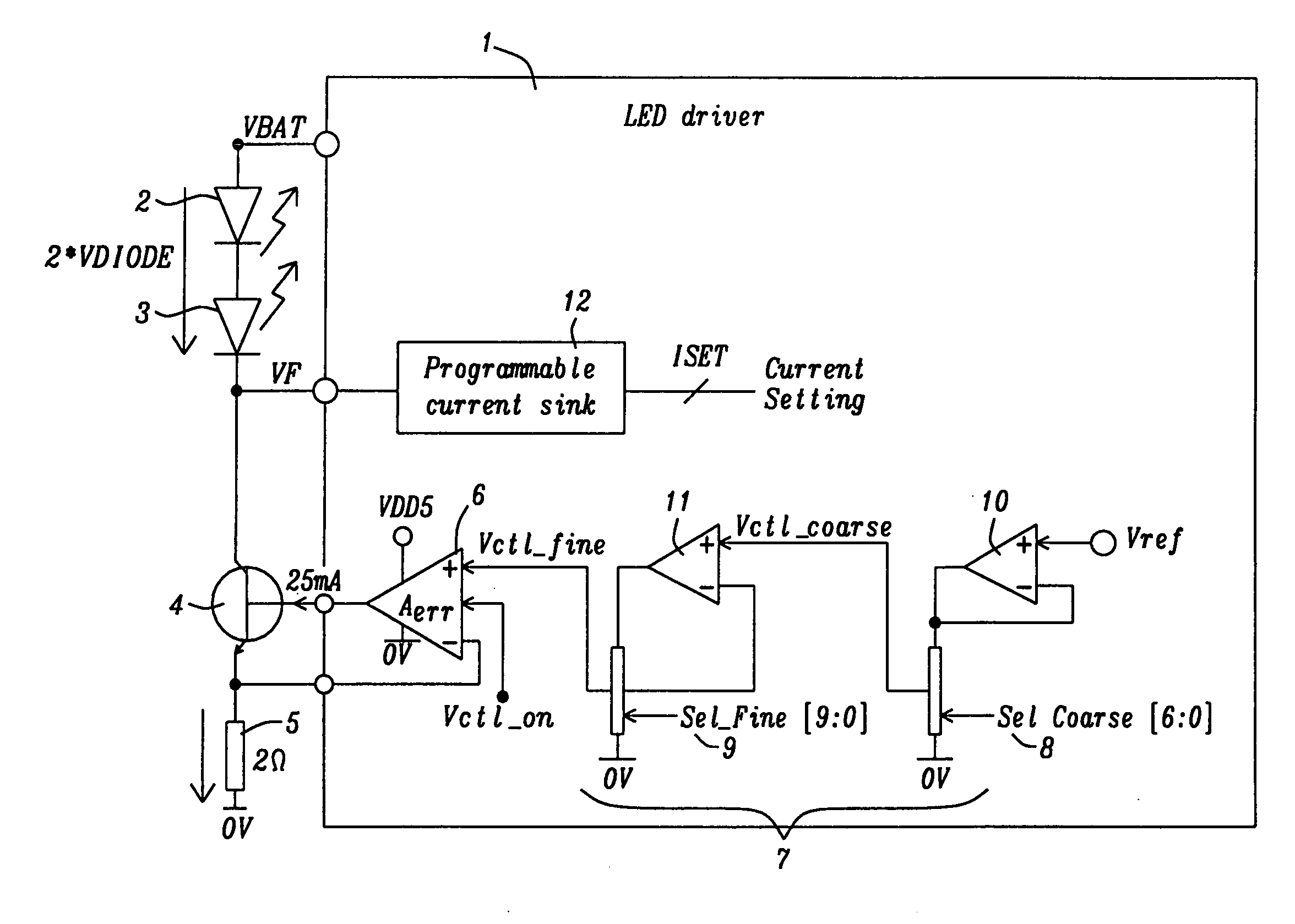
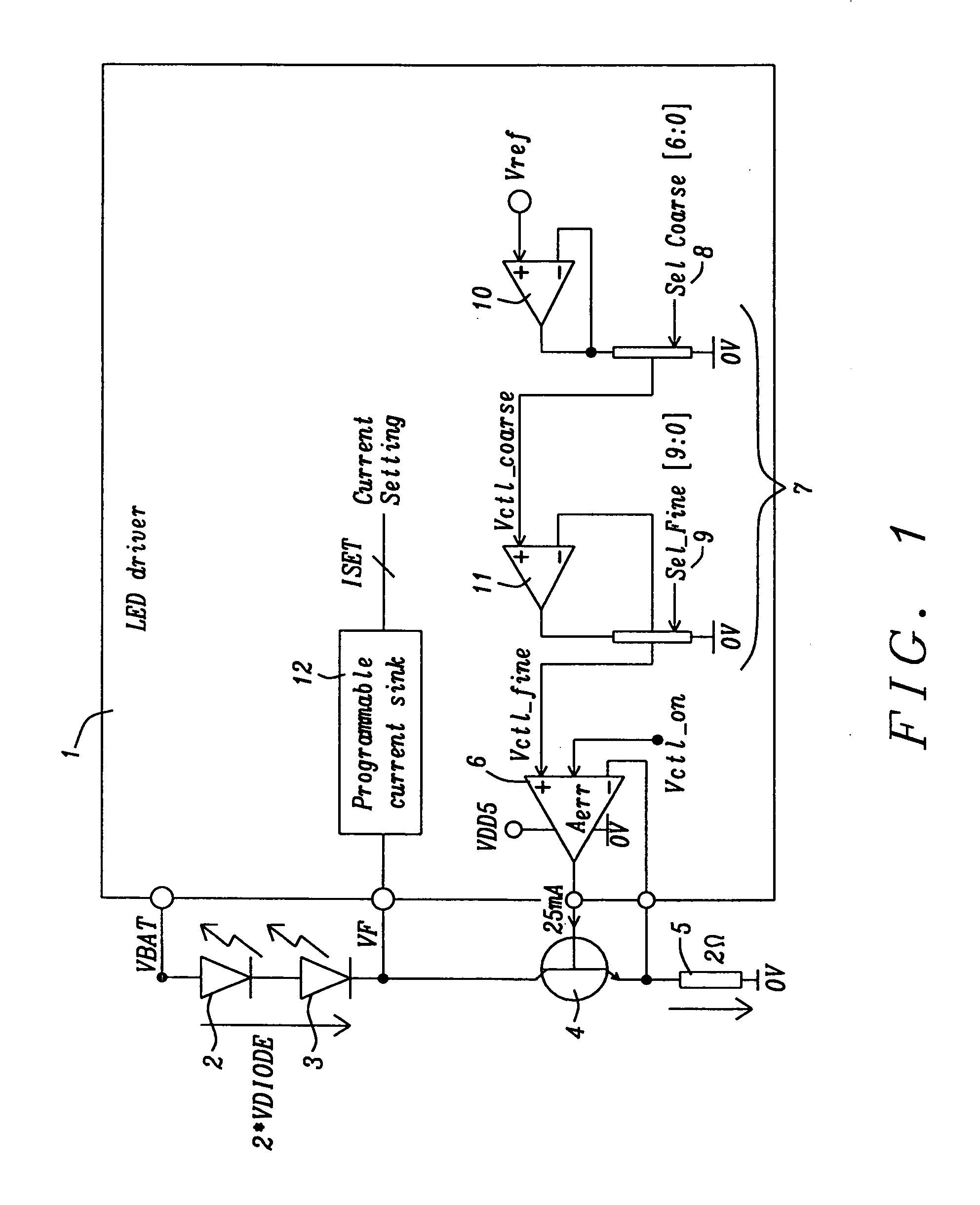
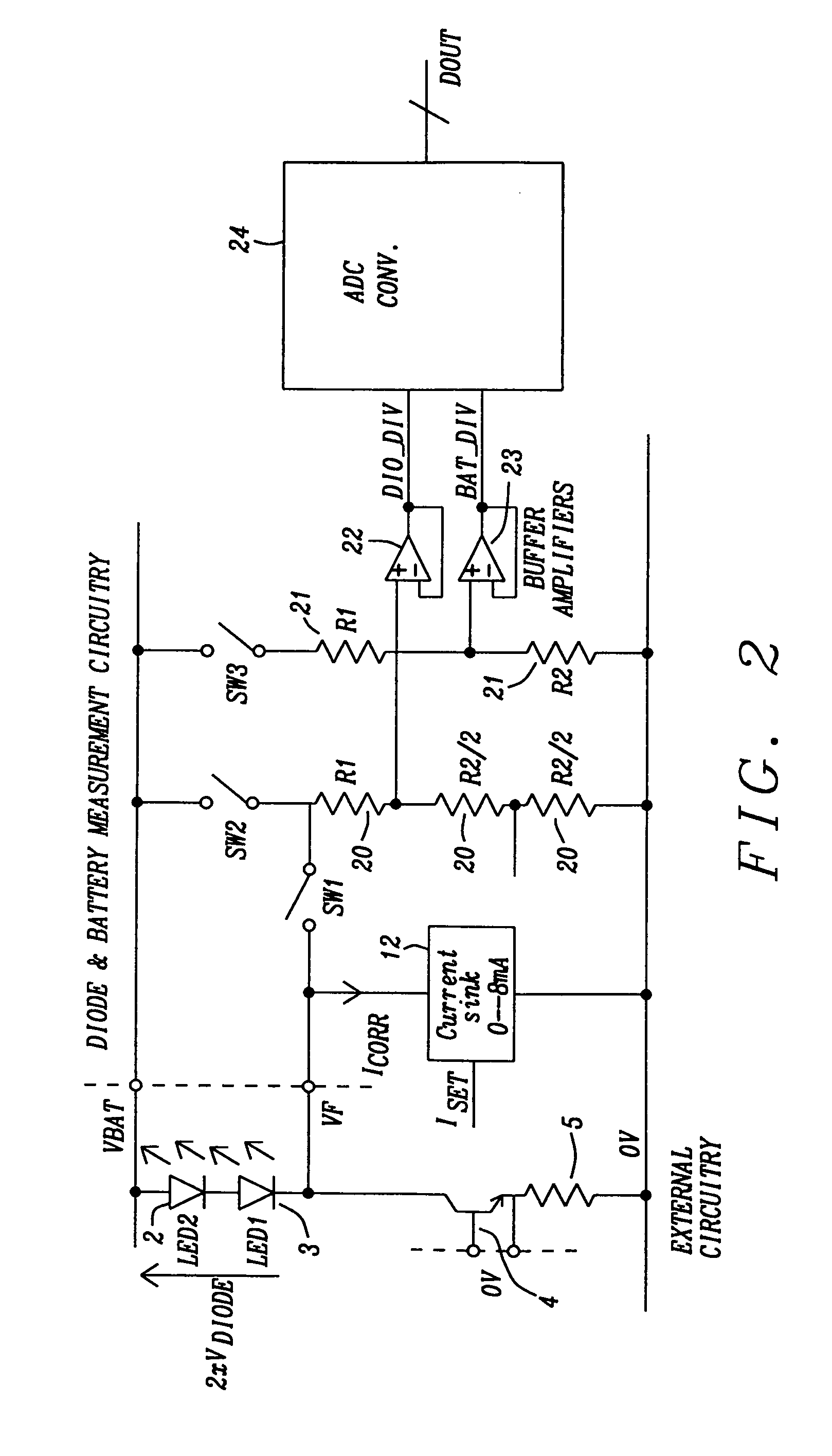
Circuit for driving an infrared transmitter LED with temperature compensation
ActiveUS8283876B2Eliminate currentElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDriving currentJunction temperature
Systems and methods to achieve a circuit for driving one or more infrared transmitter LEDs with temperature compensation have been disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention the circuit has been applied for a rain sensing system. The junction temperature of the LED is measured and compensated by adjusting the driver current of a voltage-to-current converter driving the LED. The LED junction temperature is measured by comparing the difference in the forward diode voltage at different current densities. This voltage difference is extracted when switching the drive currents between different constant values. The measurement results are converted to digital values, which are used by a buffered dual ladder resistive DAC structure to adjust the drive current to temperature variations.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
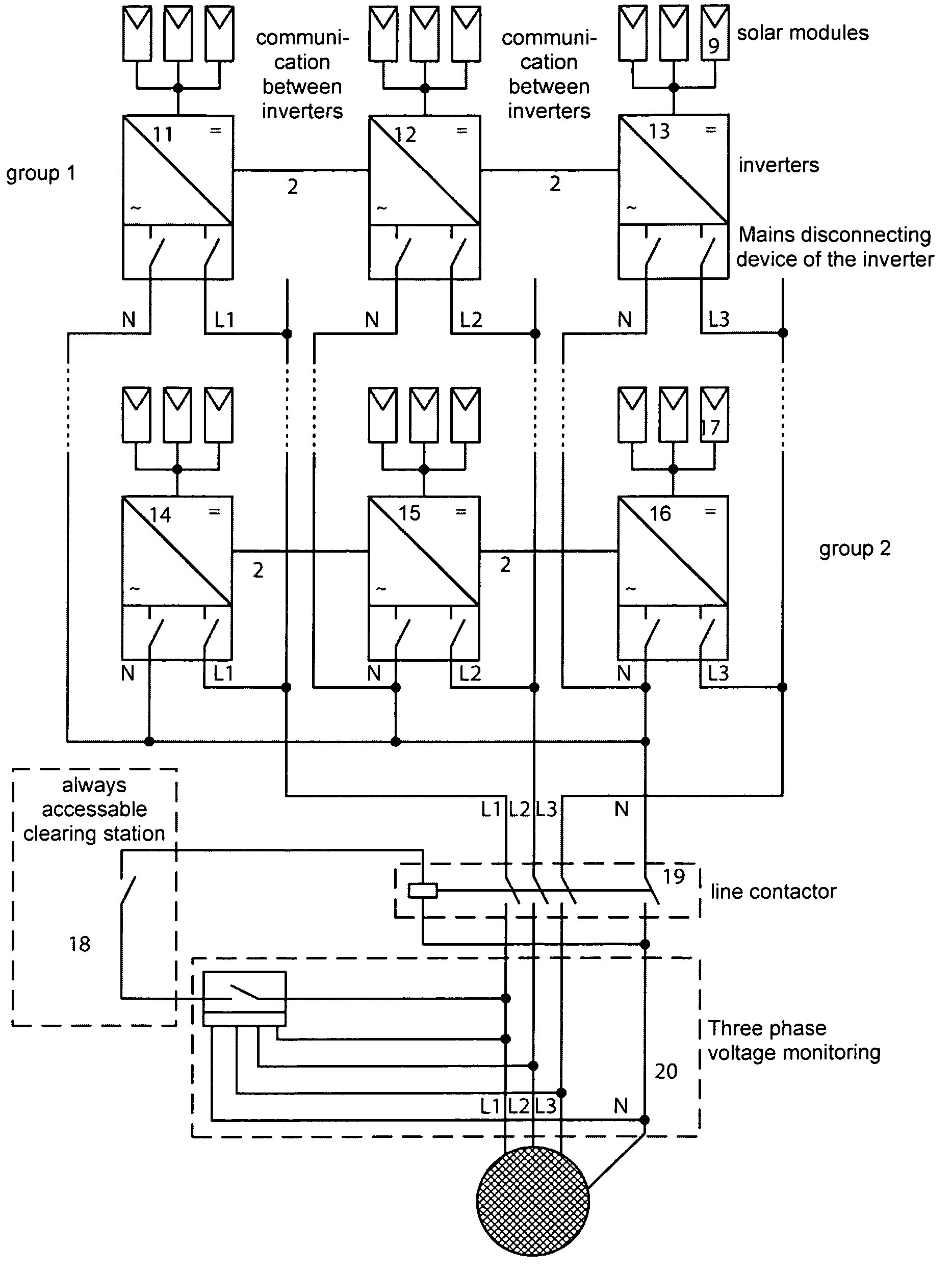
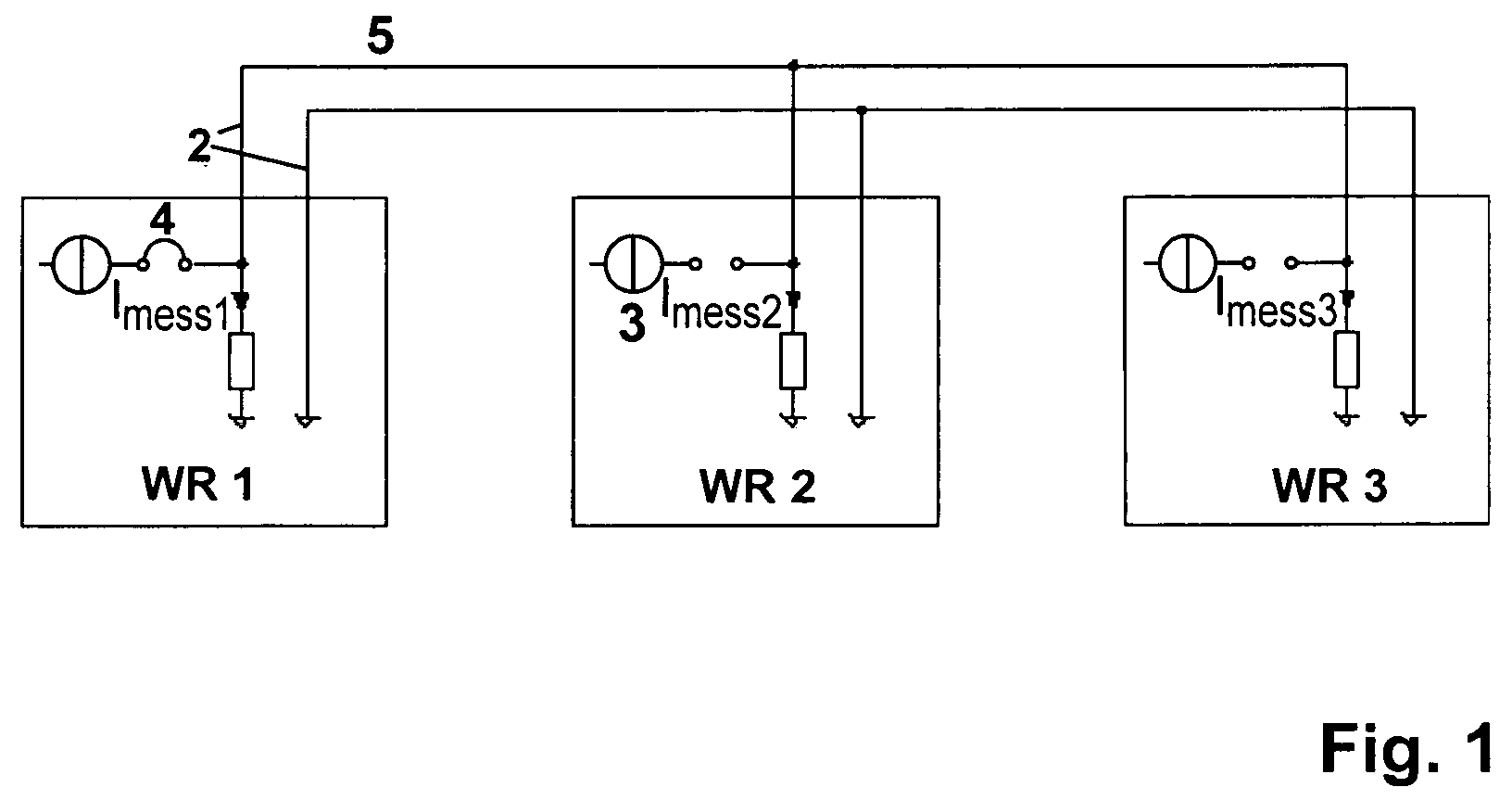
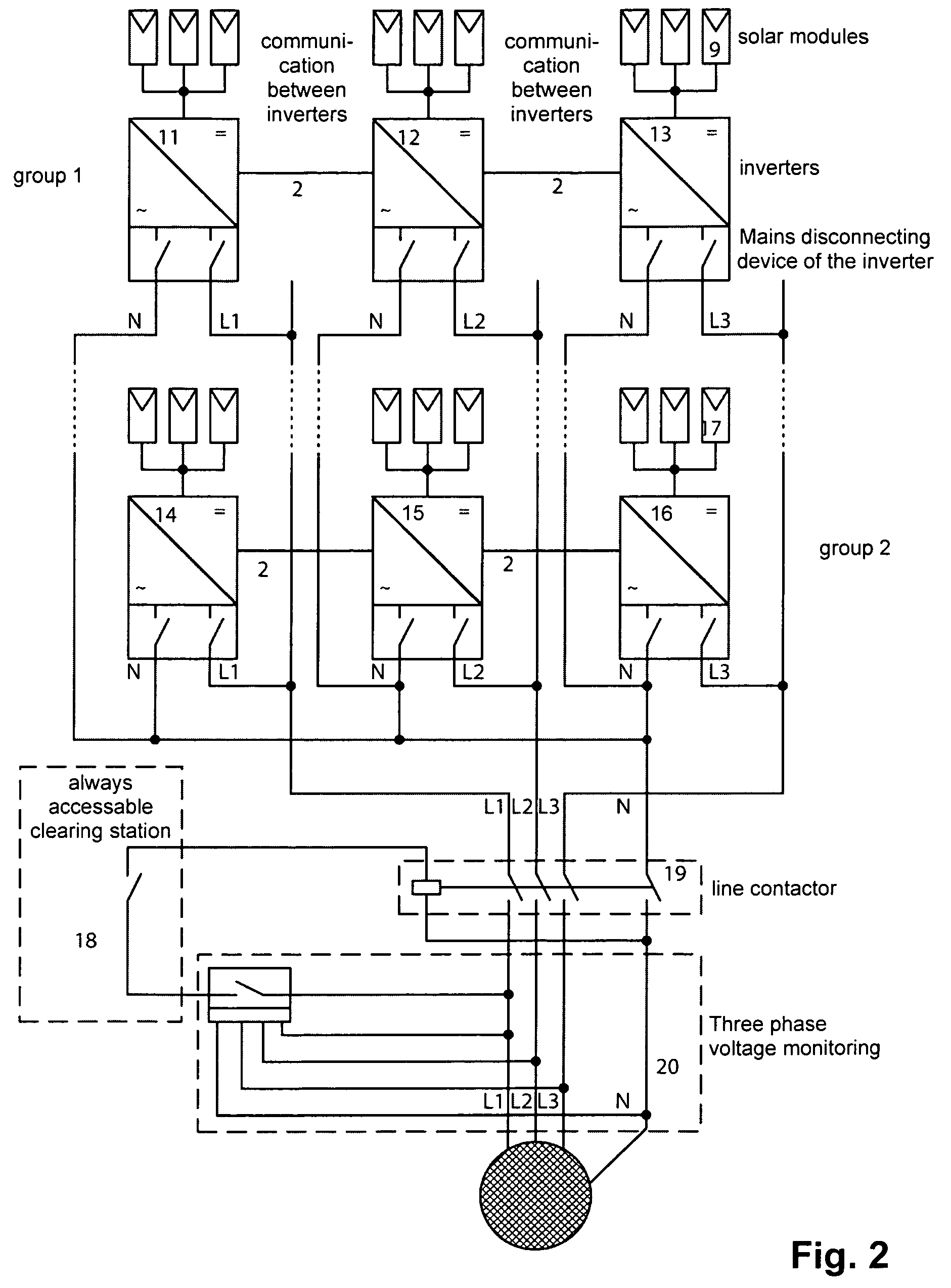
Method for converting direct voltage into three-phase alternating voltage
ActiveUS20070179720A1Avoids inadmissible load unbalanceAvoid loadBatteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlThree-phaseEngineering
A method of converting a direct voltage generated by a decentralized power supply system into three-phase alternating voltage by means of a plurality of single-phase inverters (WR1-WR3), said alternating voltage being provided for supplying an electric mains, is intended to avoid inadmissible load unbalances using single-phase inverters. This is achieved in that, upon failure of one inverter (WR1-WR3), an asymmetrical power supply distribution is reduced by limiting the output of the other inverters. The method makes it possible to simplify three-phase voltage monitoring.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
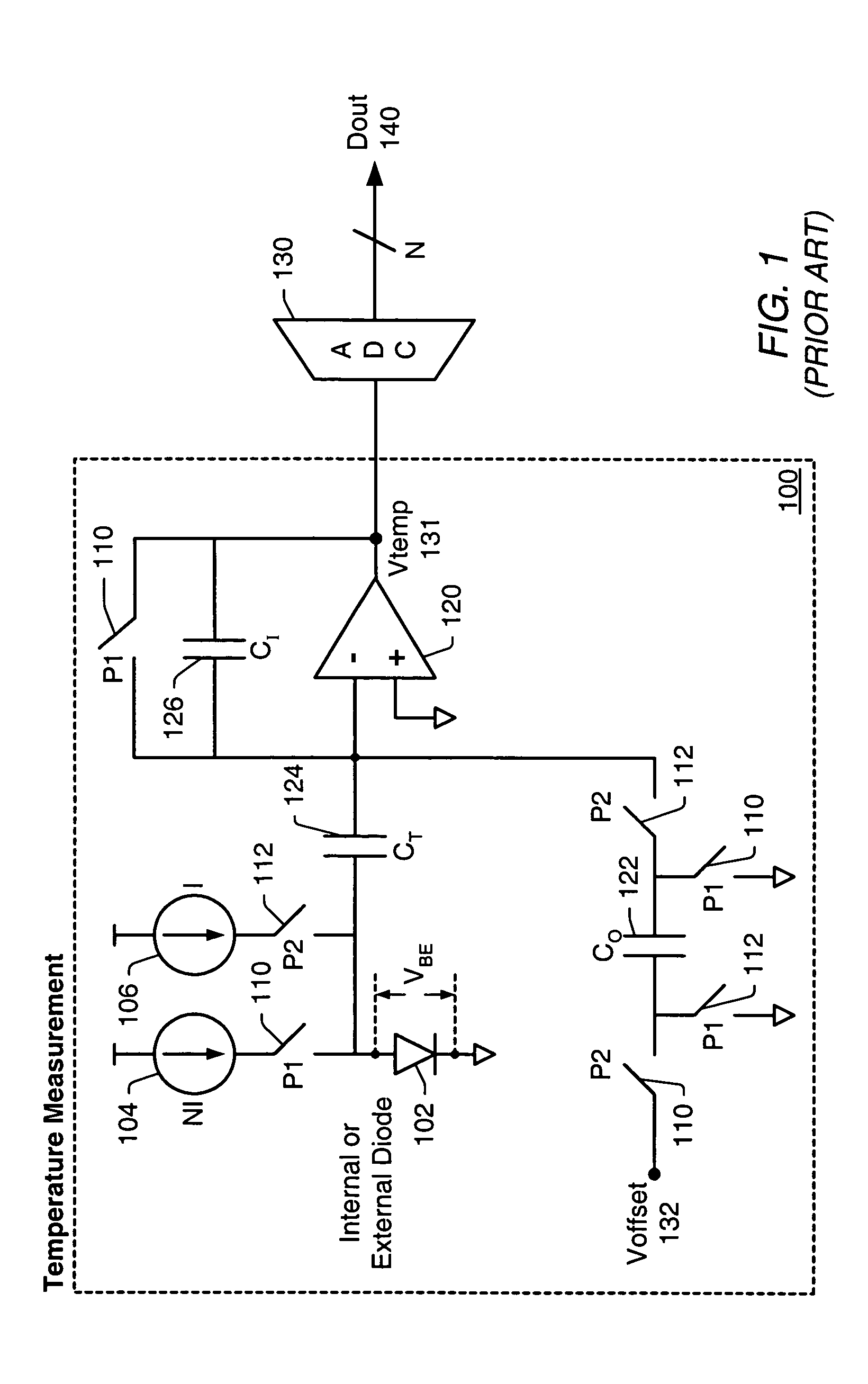
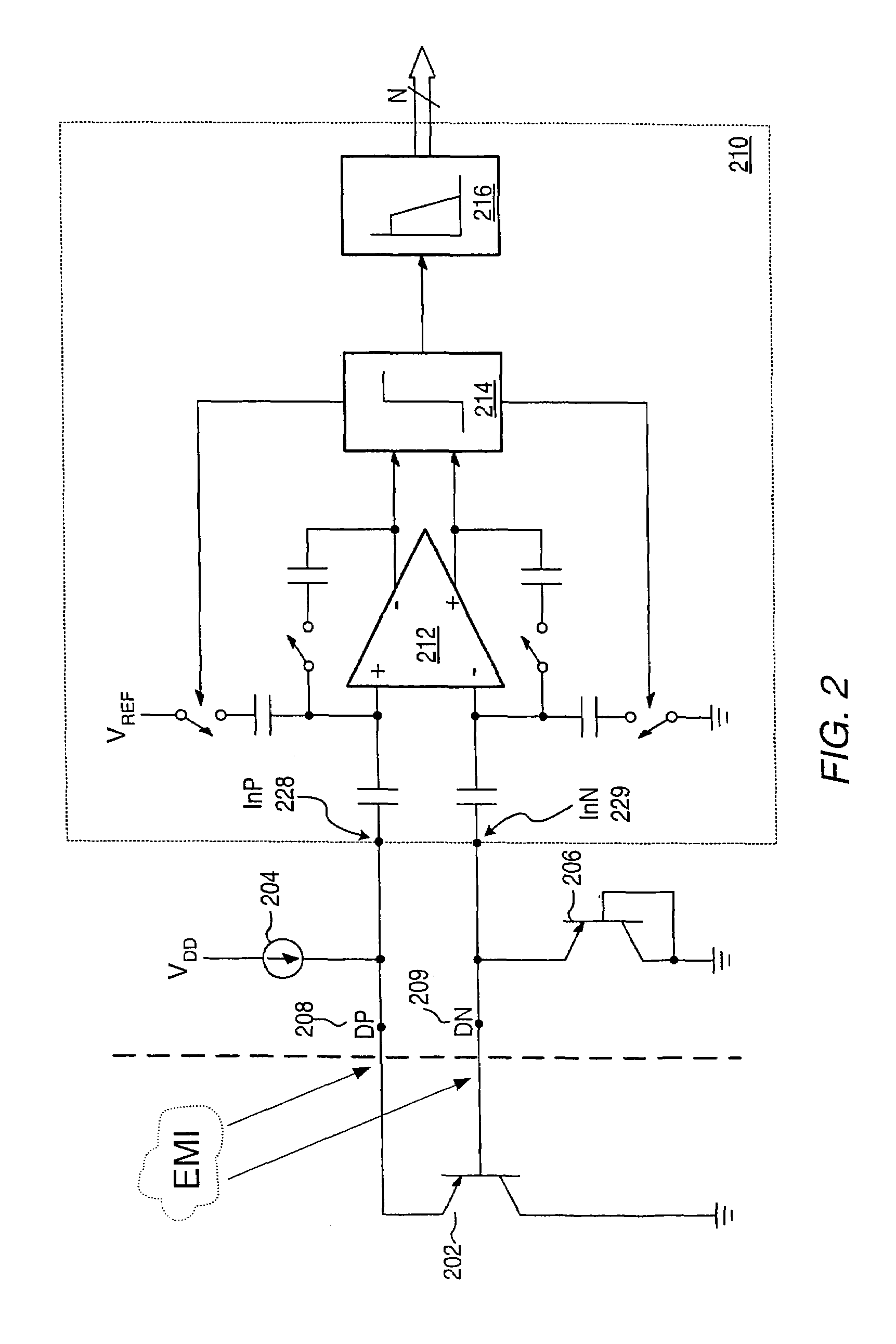
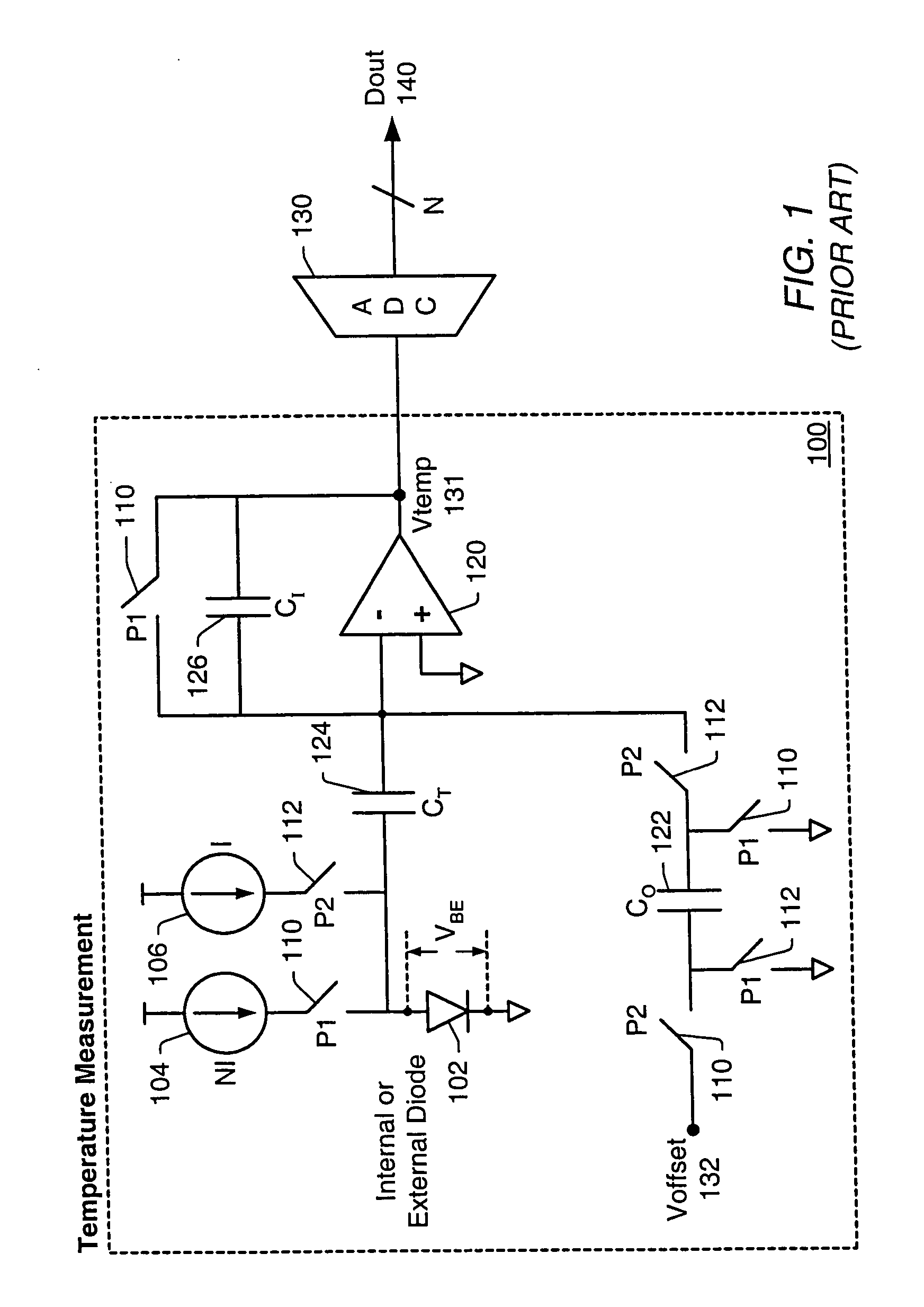
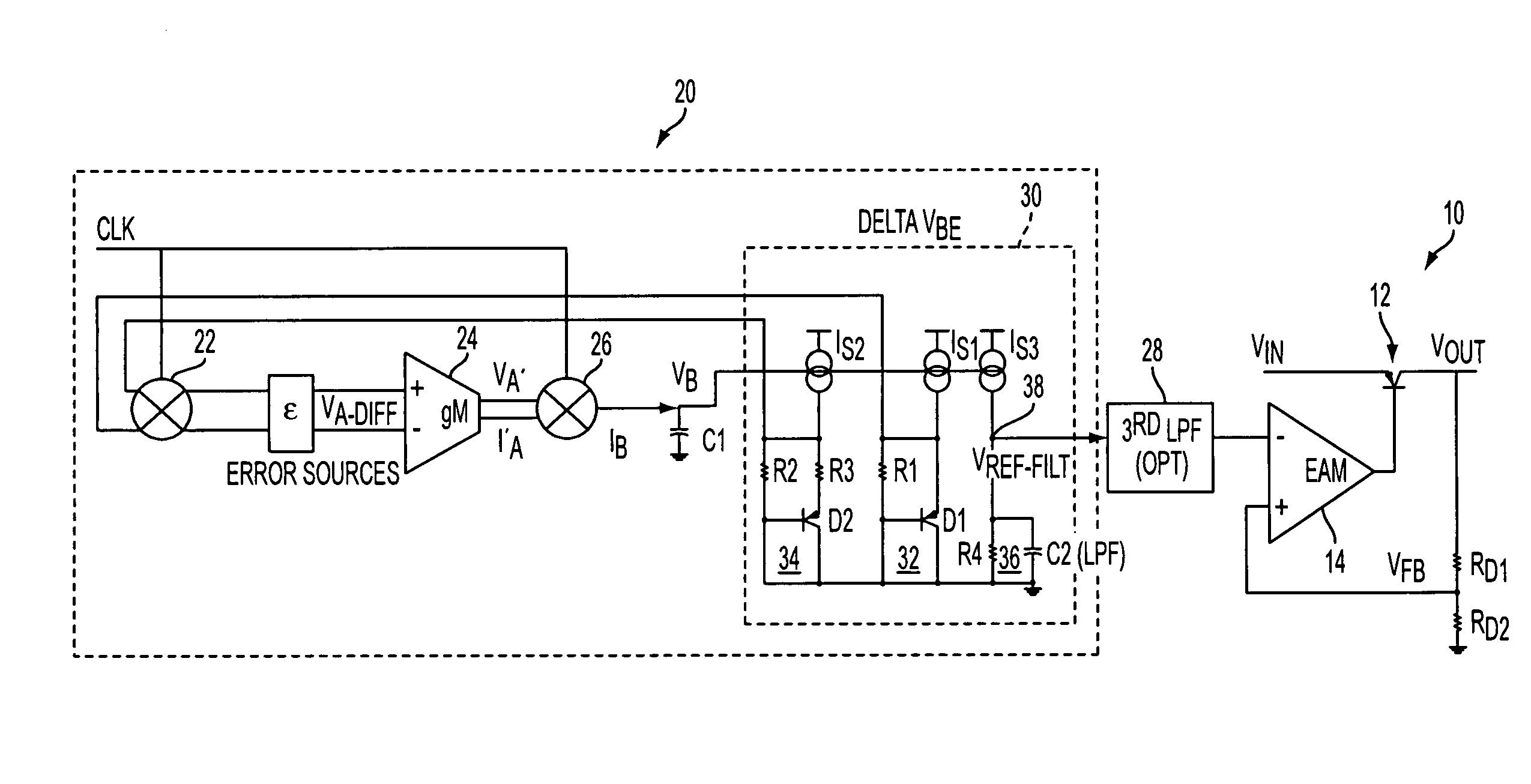
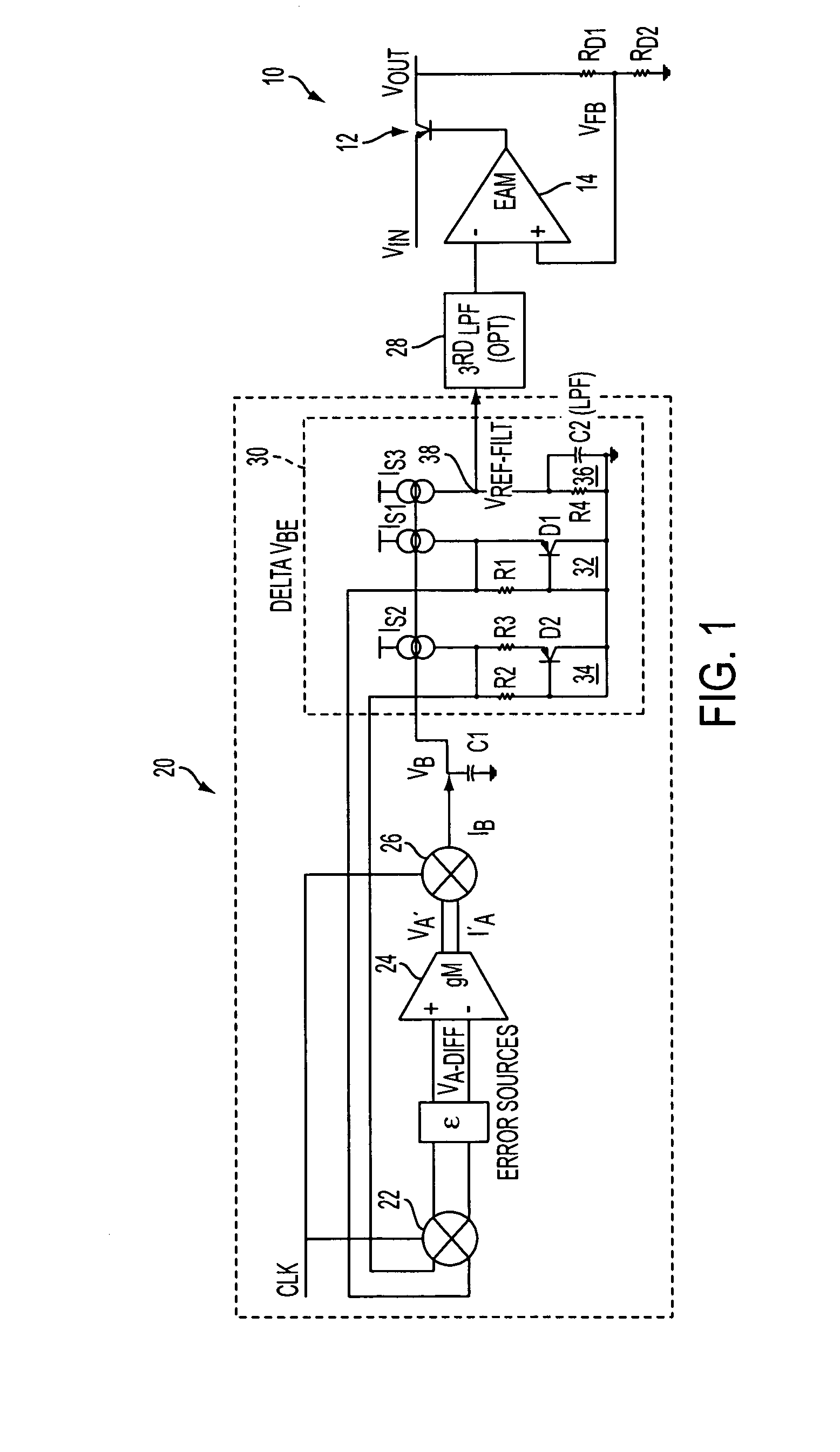
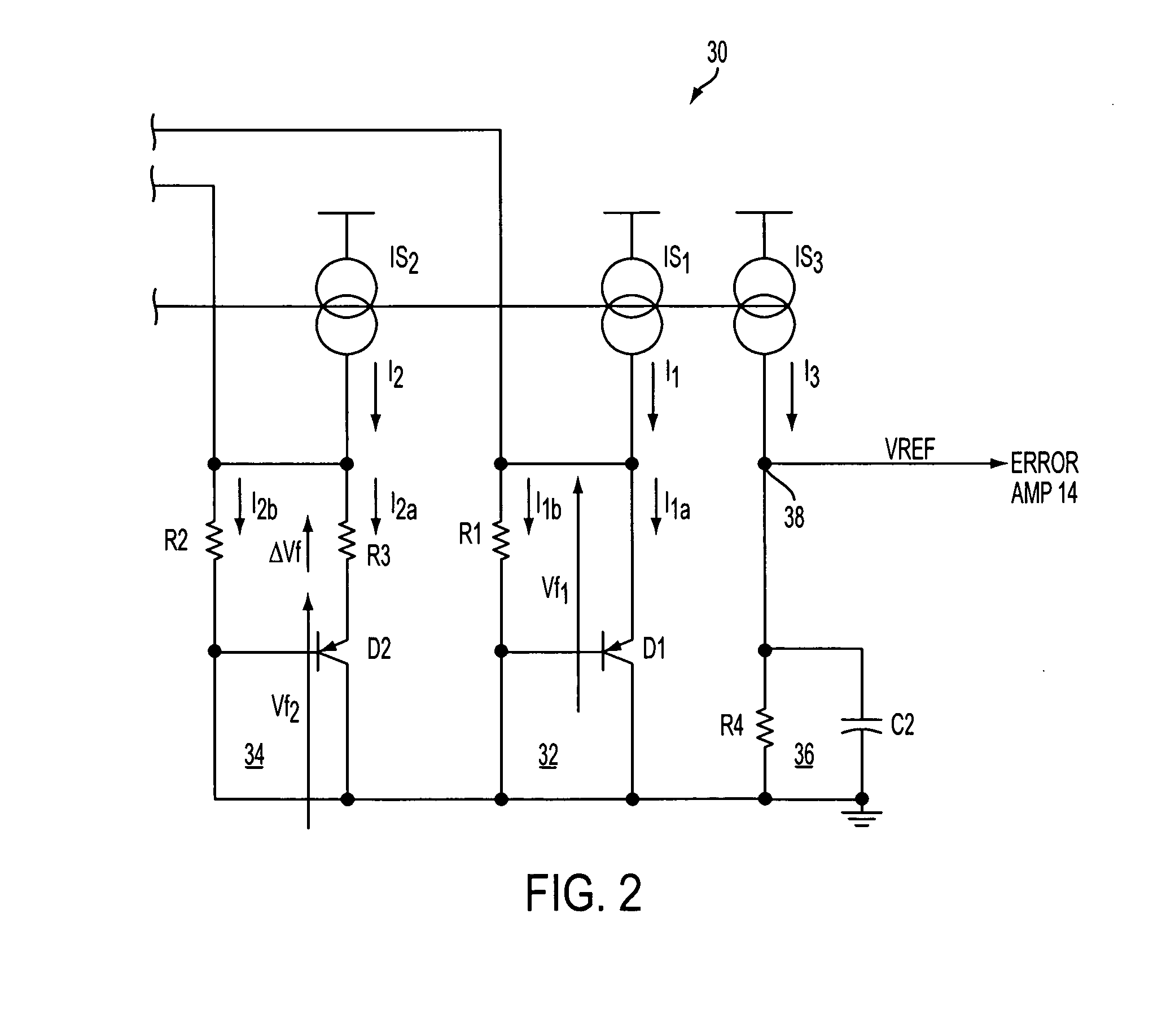
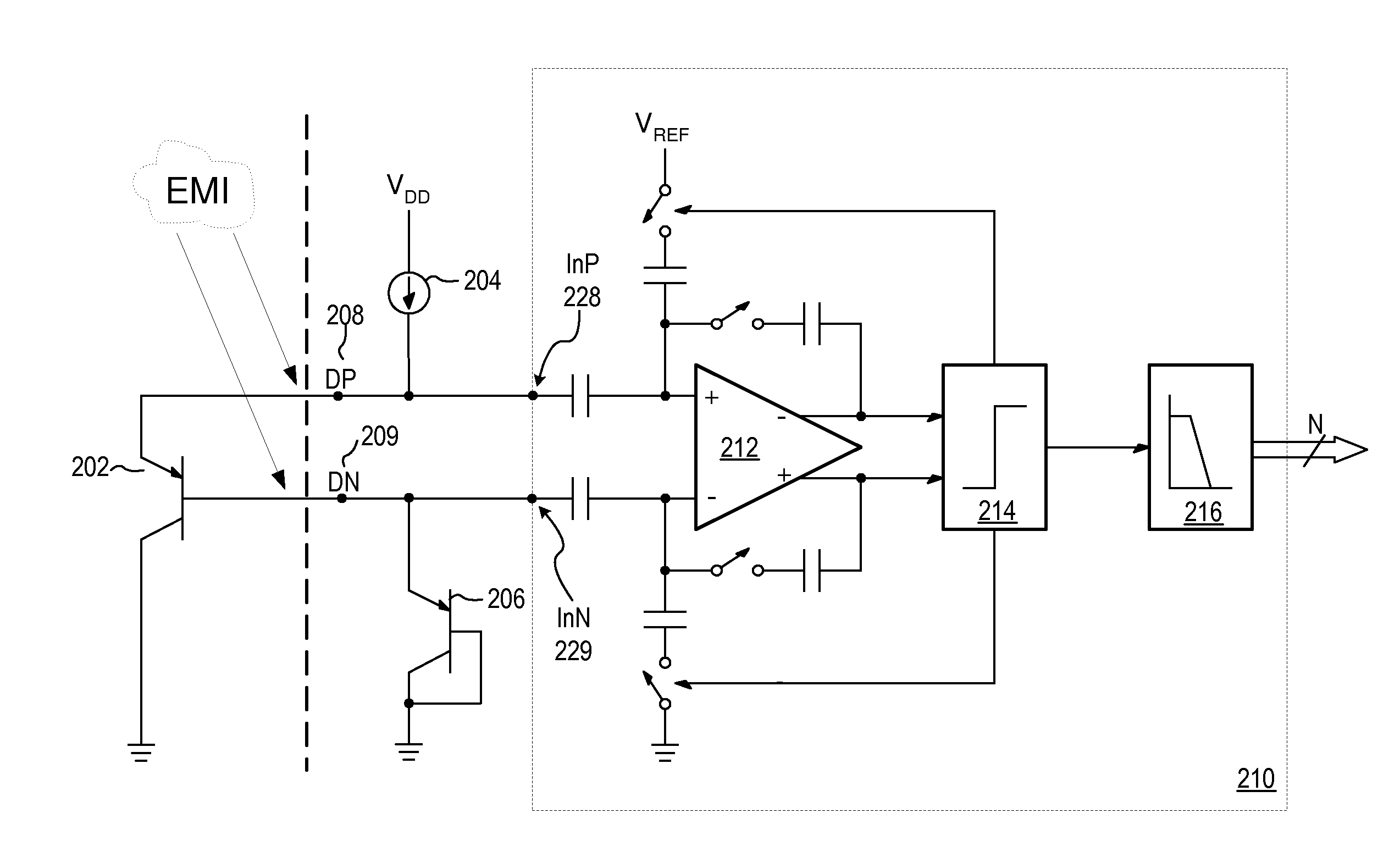
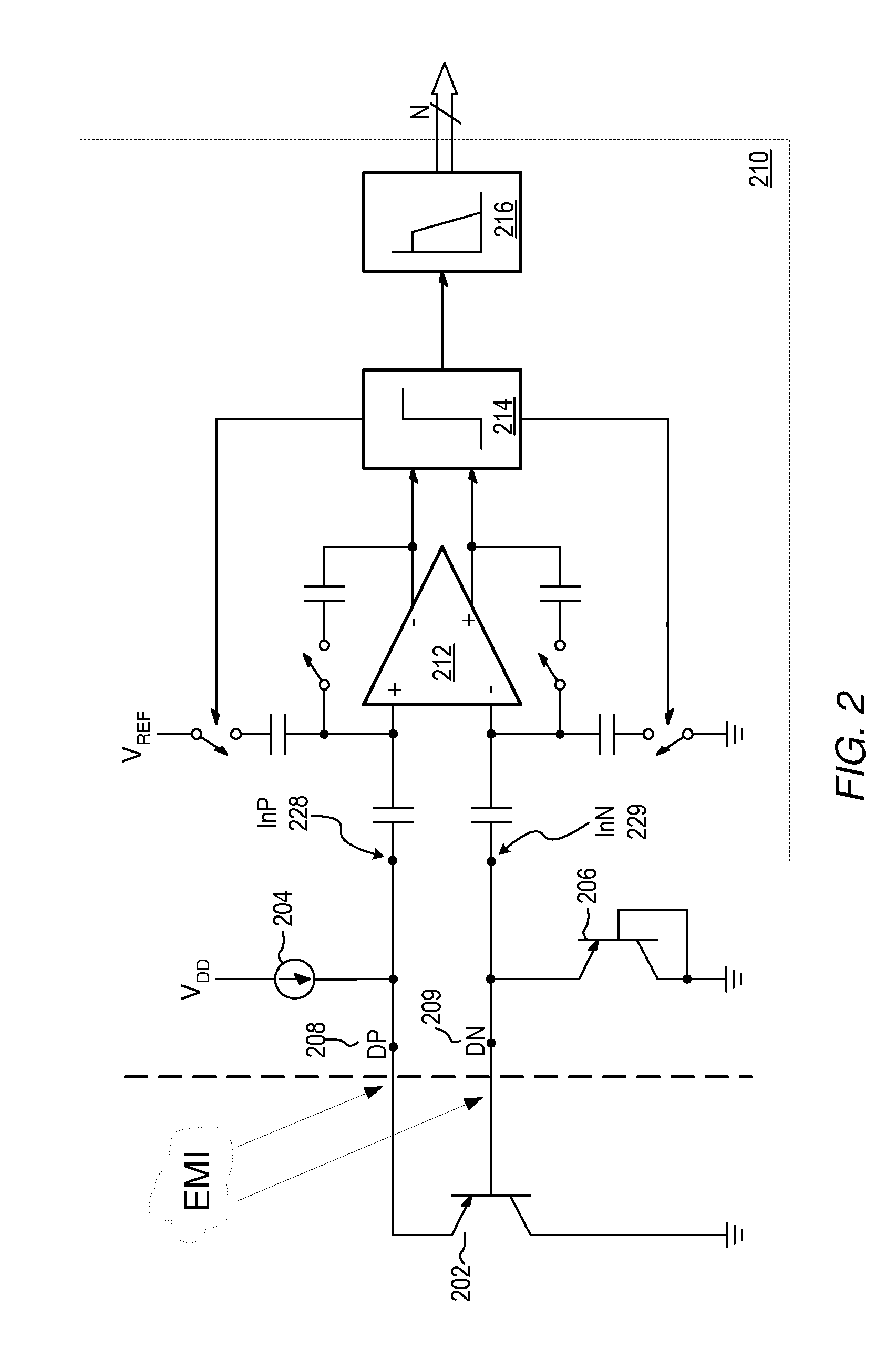
Proportional settling time adjustment for diode voltage and temperature measurements dependent on forced level current
ActiveUS7429129B2Increase conversion rateMinimizing temperature measurementThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionAc componentsShunt capacitors
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate digital temperature readings using a local or remote temperature diode. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an analog to digital converter (ADC), which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a digital output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. DC components of errors in the measured temperature that may result from EMI noise modulating the junction voltage (VBE) may be minimized through the use of a front-end sample-and-hold circuit coupled between the diode and the ADC, in combination with a shunt capacitor coupled across the diode junction. The sample-and-hold-circuit may sample VBE at a frequency that provides sufficient settling time for each VBE sample, and provide corresponding stable ΔVBE samples to the ADC at the ADC operating frequency. The ADC may therefore be operated at its preferred sampling frequency rate without incurring reading errors while still averaging out AC components of additional errors induced by sources other than EMI.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
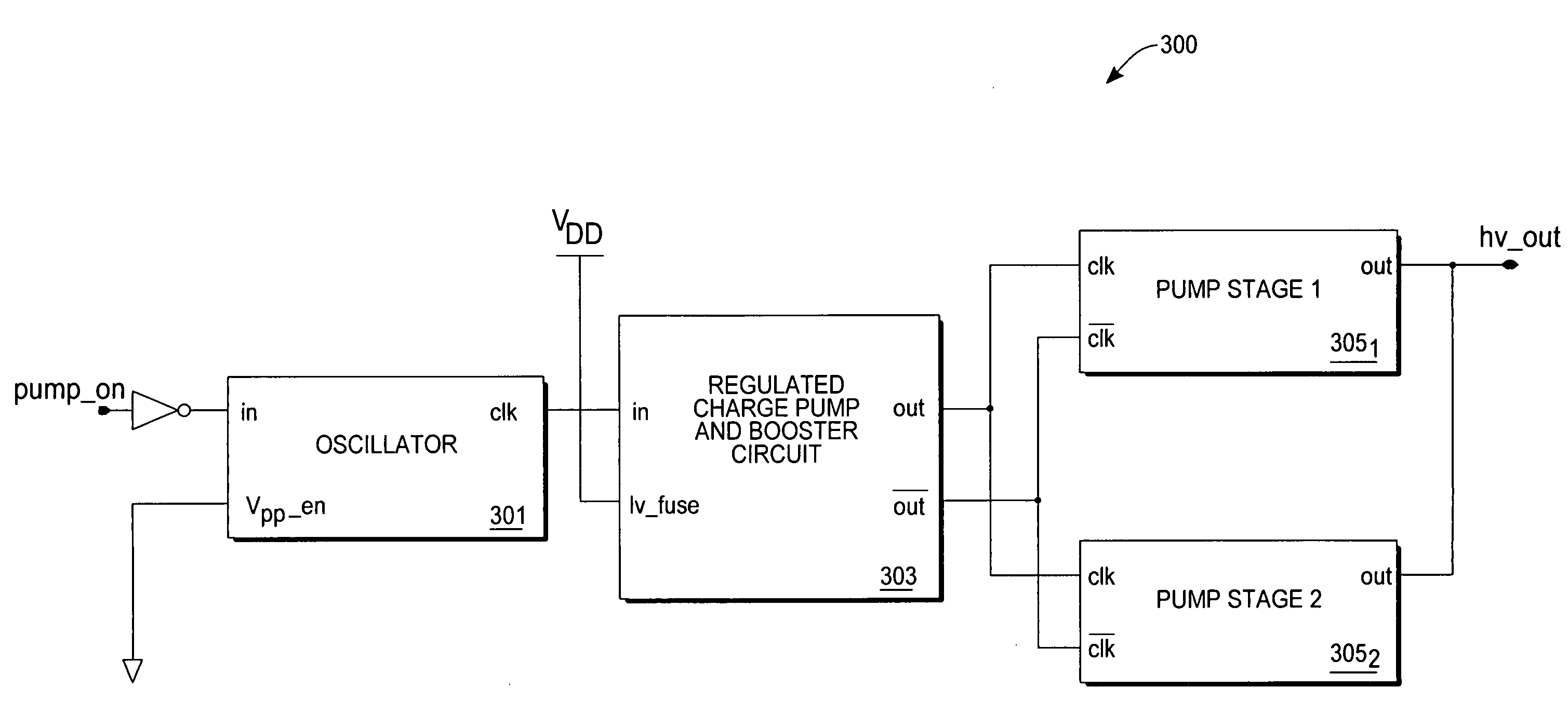
Efficient charge pump for a wide range of supply voltages
ActiveUS7259612B2Avoids inherent diode voltage dropEfficiency high and lowApparatus without intermediate ac conversionStatic storageLow voltageHigh pressure
A voltage booster and regulator usable with Dickson-type charge pump device is specifically adapted to maintain efficiency with both high and low supply voltages. For high voltage supplies (e.g., 2.6 volts or more), the charge pump reduces overall power consumption resulting in a more efficient design. For low voltage applications (e.g., for supply voltages less than 2.6 volts), the charge pump uses a booster circuit to increase a clock input potential beyond the supply voltage available to a typical Dickson array. Further, the charge pump avoids inherent diode voltage drops in a typical Dickson array.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
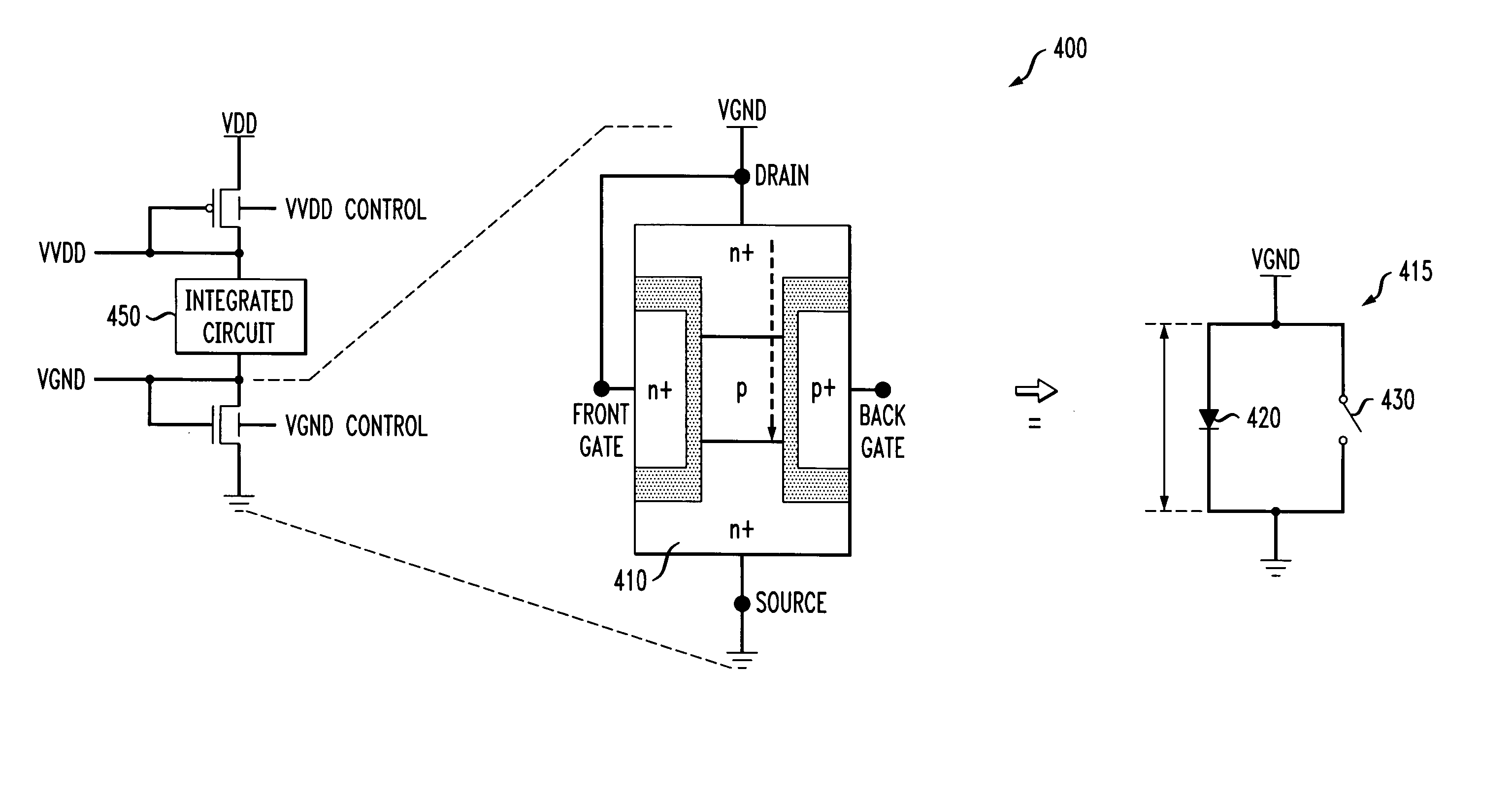
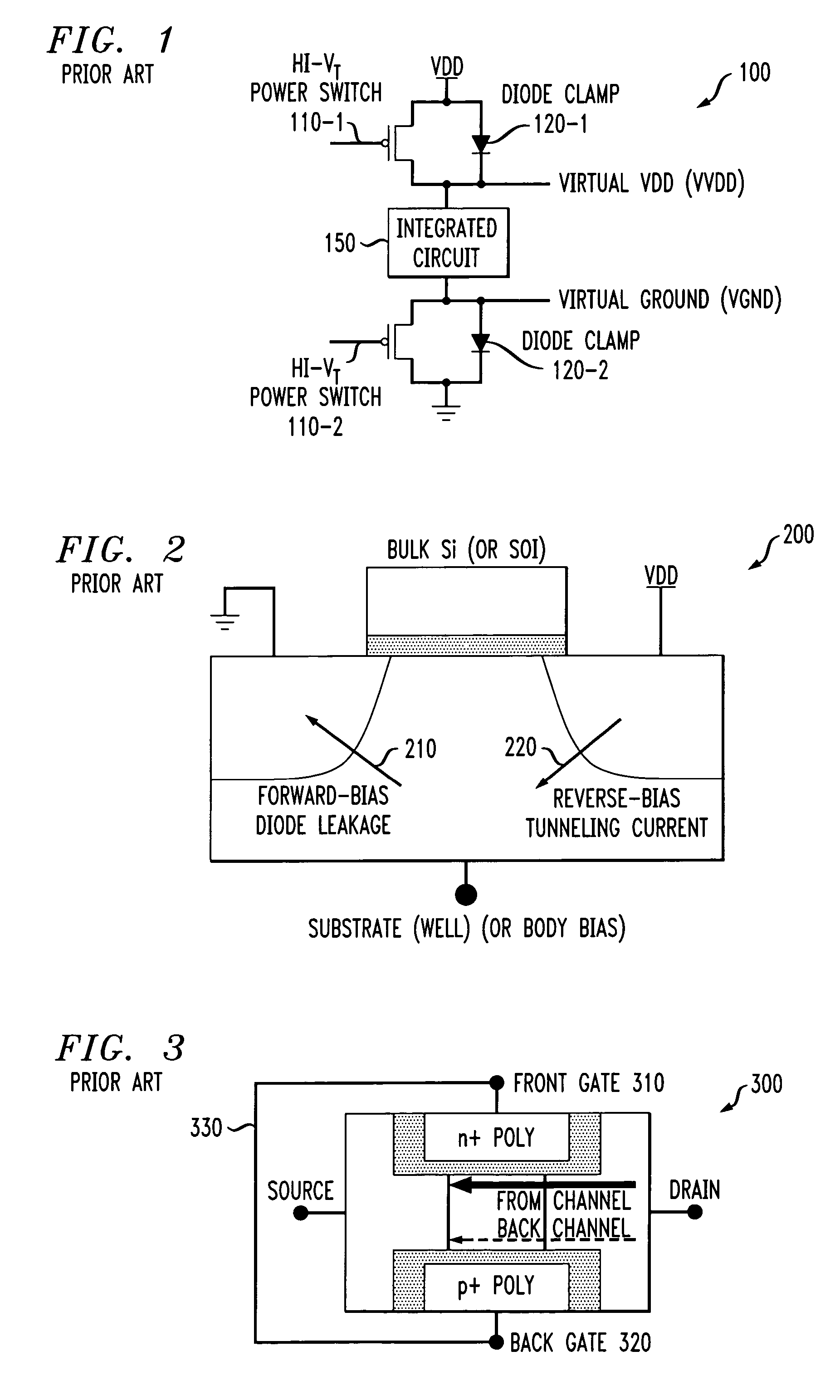
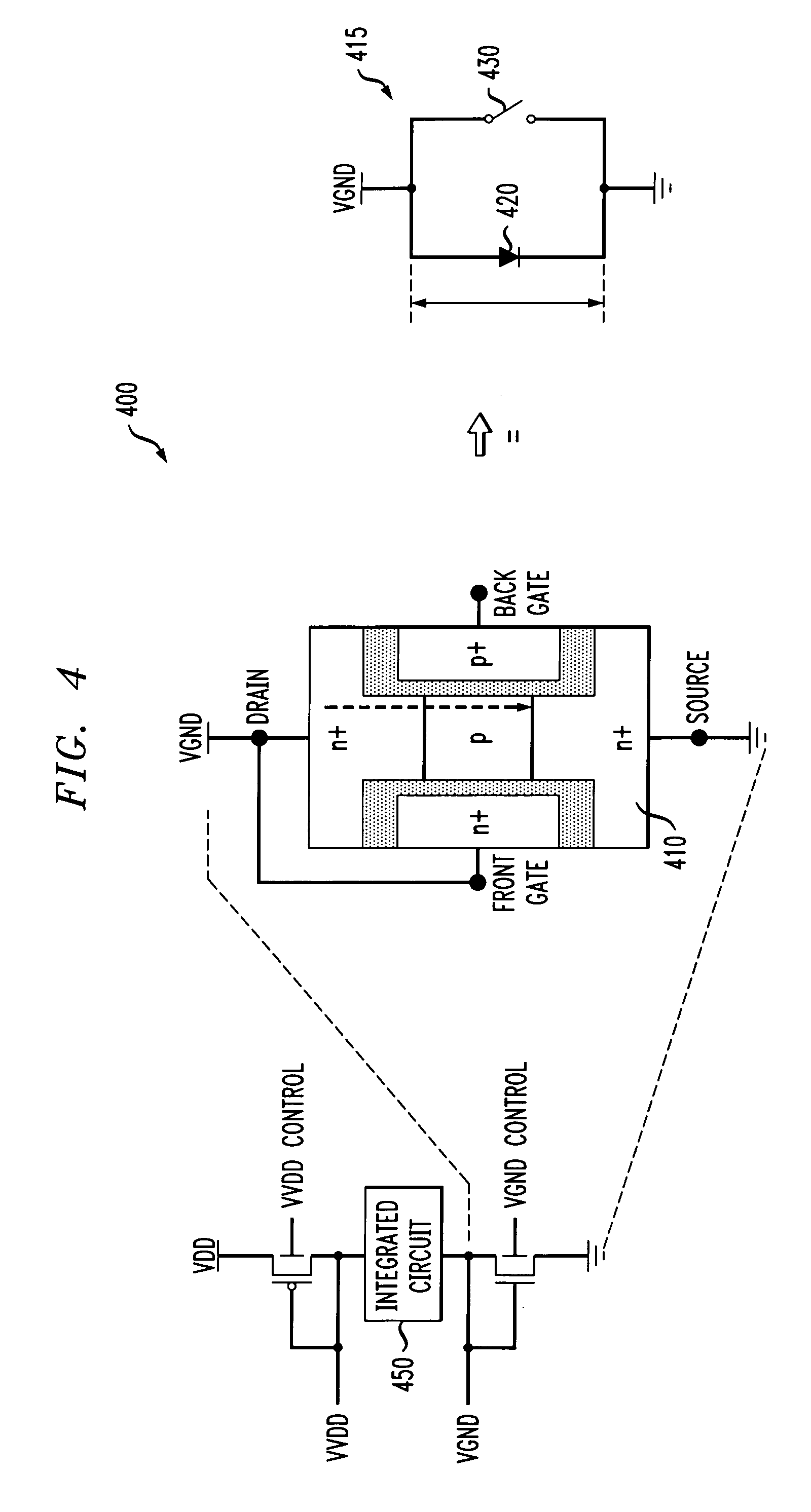
Methods and apparatus for varying a supply voltage or reference voltage using independent control of diode voltage in asymmetrical double-gate devices
Methods and apparatus are provided for varying one or more of a supply voltage and reference voltage in an integrated circuit, using independent control of a diode voltage in an asymmetrical double-gate device. An integrated circuit is provided that is controlled by one or more of a supply voltage and a reference voltage. The integrated circuit comprises an independently controlled asymmetrical double-gate device to adjust one or more of the supply voltage and the reference voltage. The independent control may comprise, for example, a back gate bias. The independently controlled asymmetrical double-gate device may be employed in a number of applications, including voltage islands, static RAM, and to improve the power and performance of a processing unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
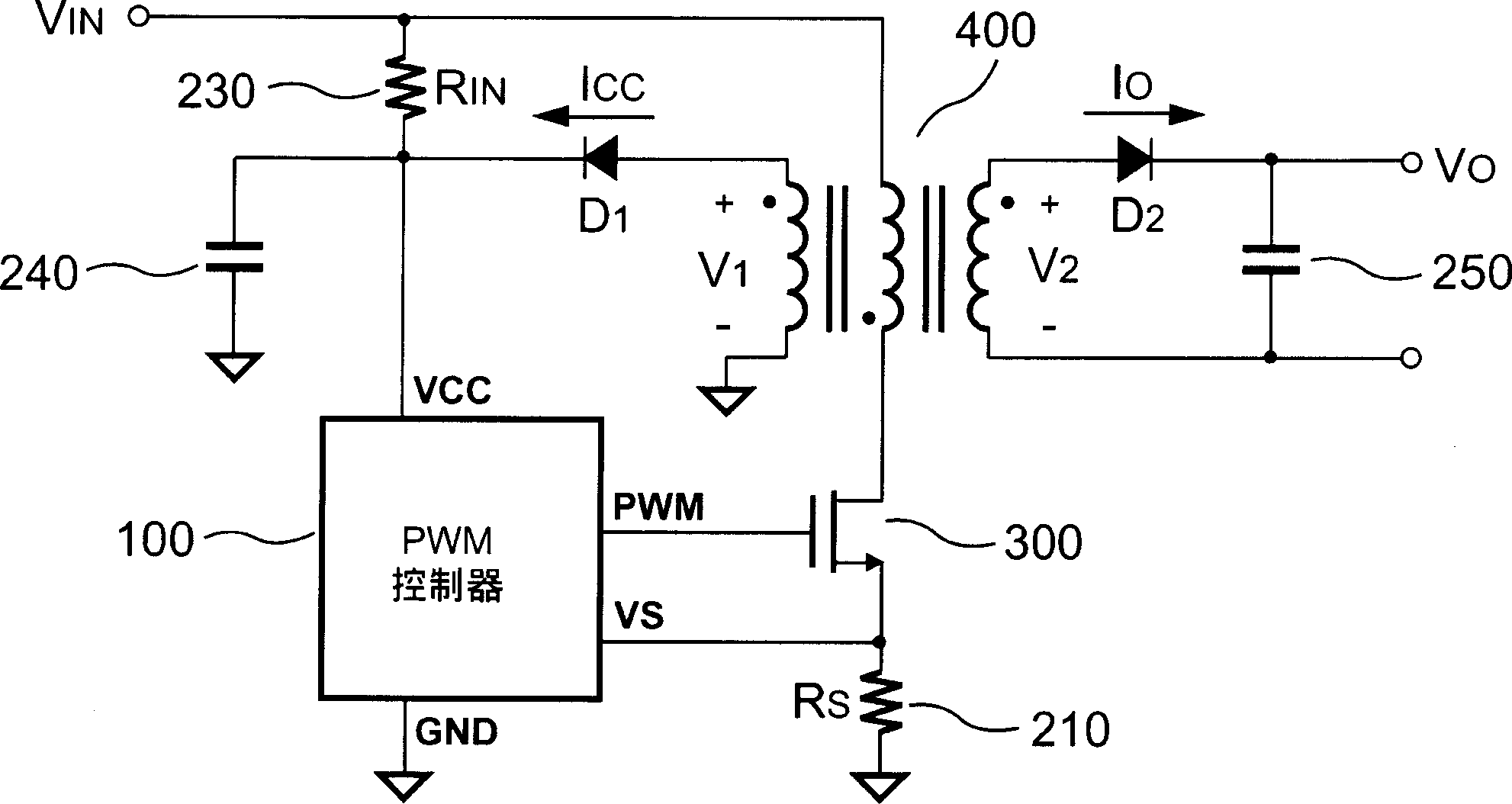
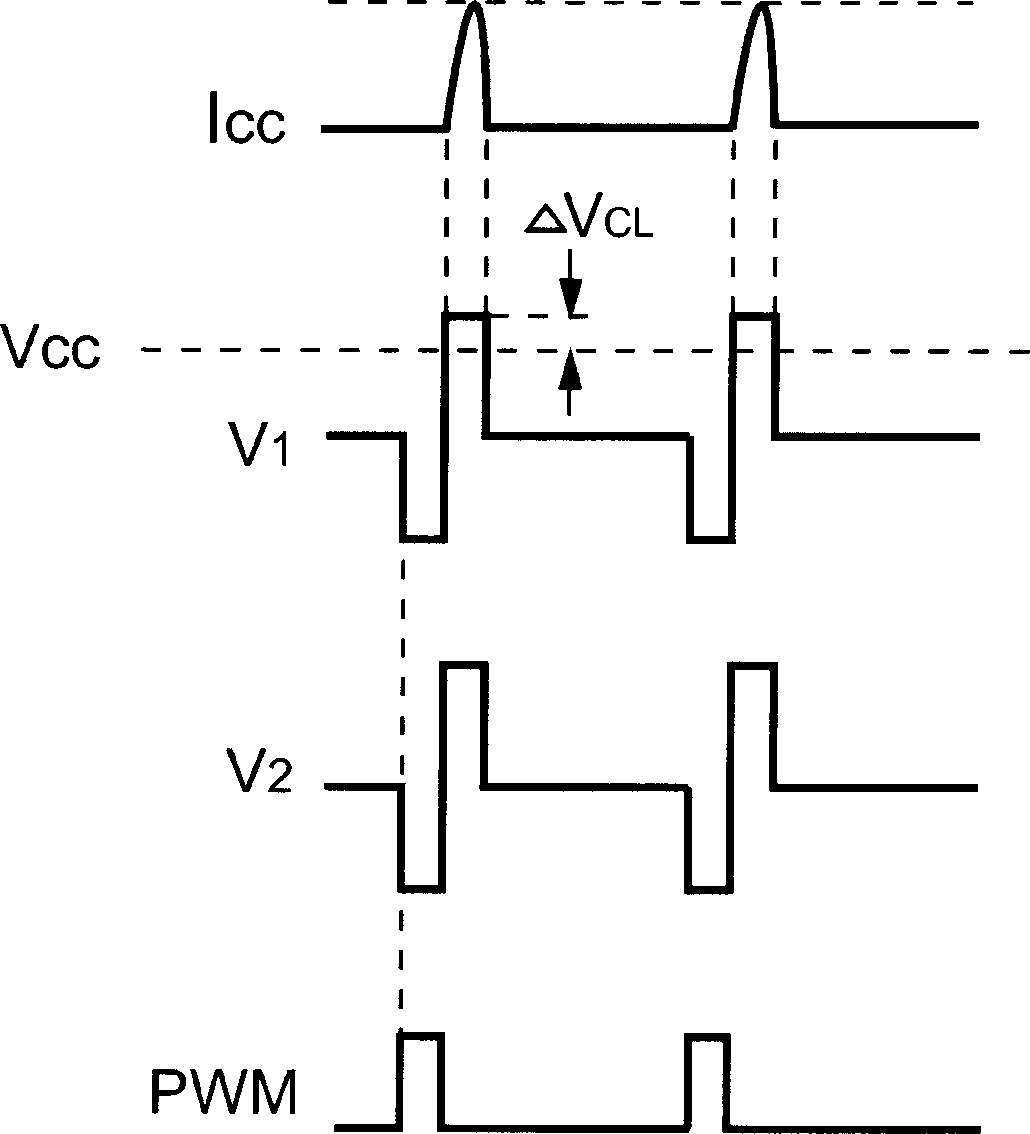
Primary-side regulated pulse width modulation controller with improved load regulation
ActiveCN1806380AImprove stabilityPrecise Feedback ControlTransformersApparatus with intermediate ac conversionVoltage generatorRectifier diodes
The present invention provides a primary-side regulated PWM (pulse width modulation, pulse width modulation) controller with improved load regulation. In each PWM cycle, a built-in feedback voltage generator samples and holds the flyback voltage from the auxiliary winding of the transformer through a sampling switch, and generates a feedback voltage accordingly. A bias current sink sinks a bias current proportional to the feedback voltage. When the output load changes, the bias current will generate a voltage drop through a sense resistor to compensate the voltage drop of the output rectifier diode. According to the present invention, the bias current may enable the PWM controller to regulate the output voltage very accurately without using a secondary feedback circuit.
Owner:SYST GEN
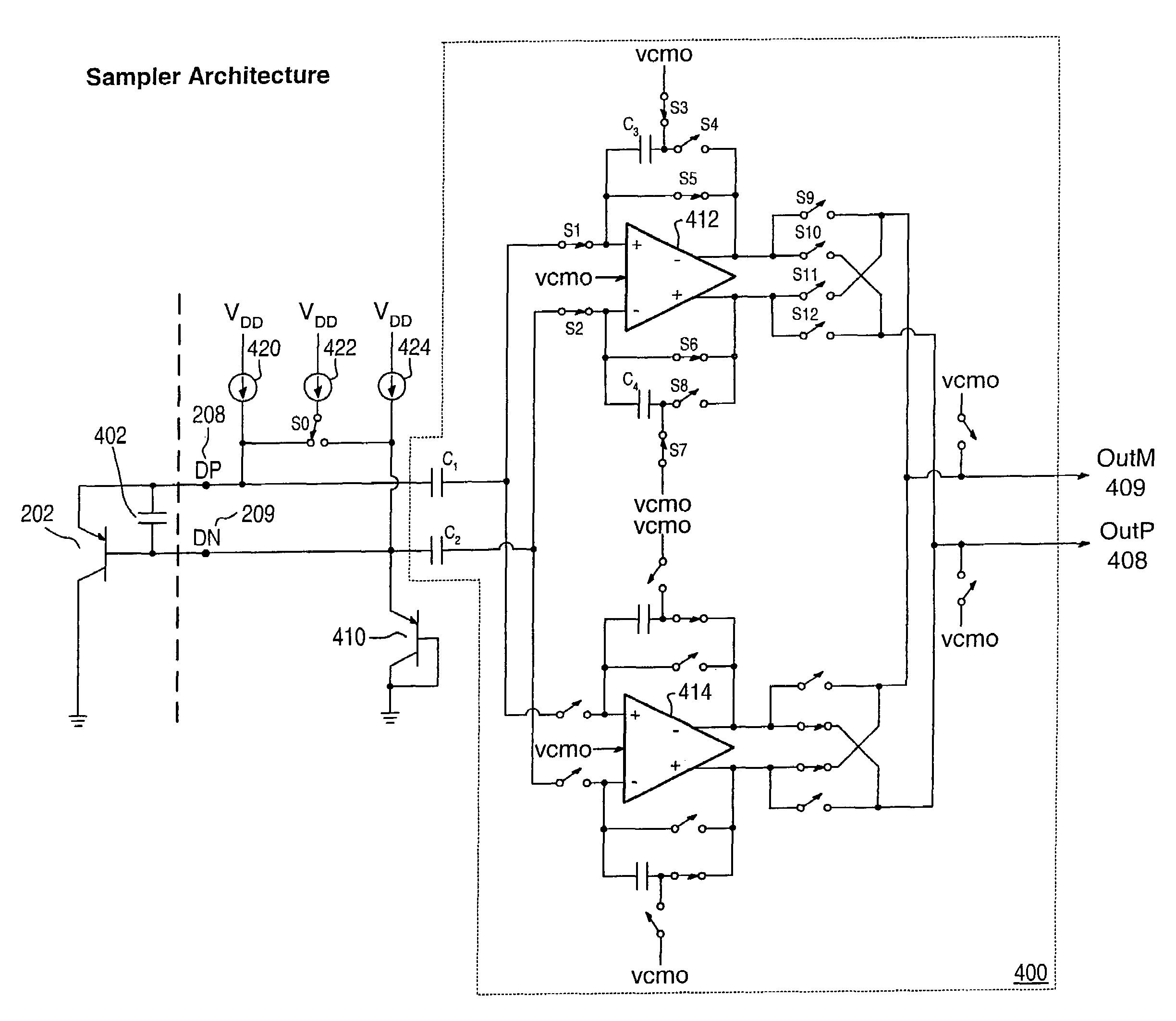
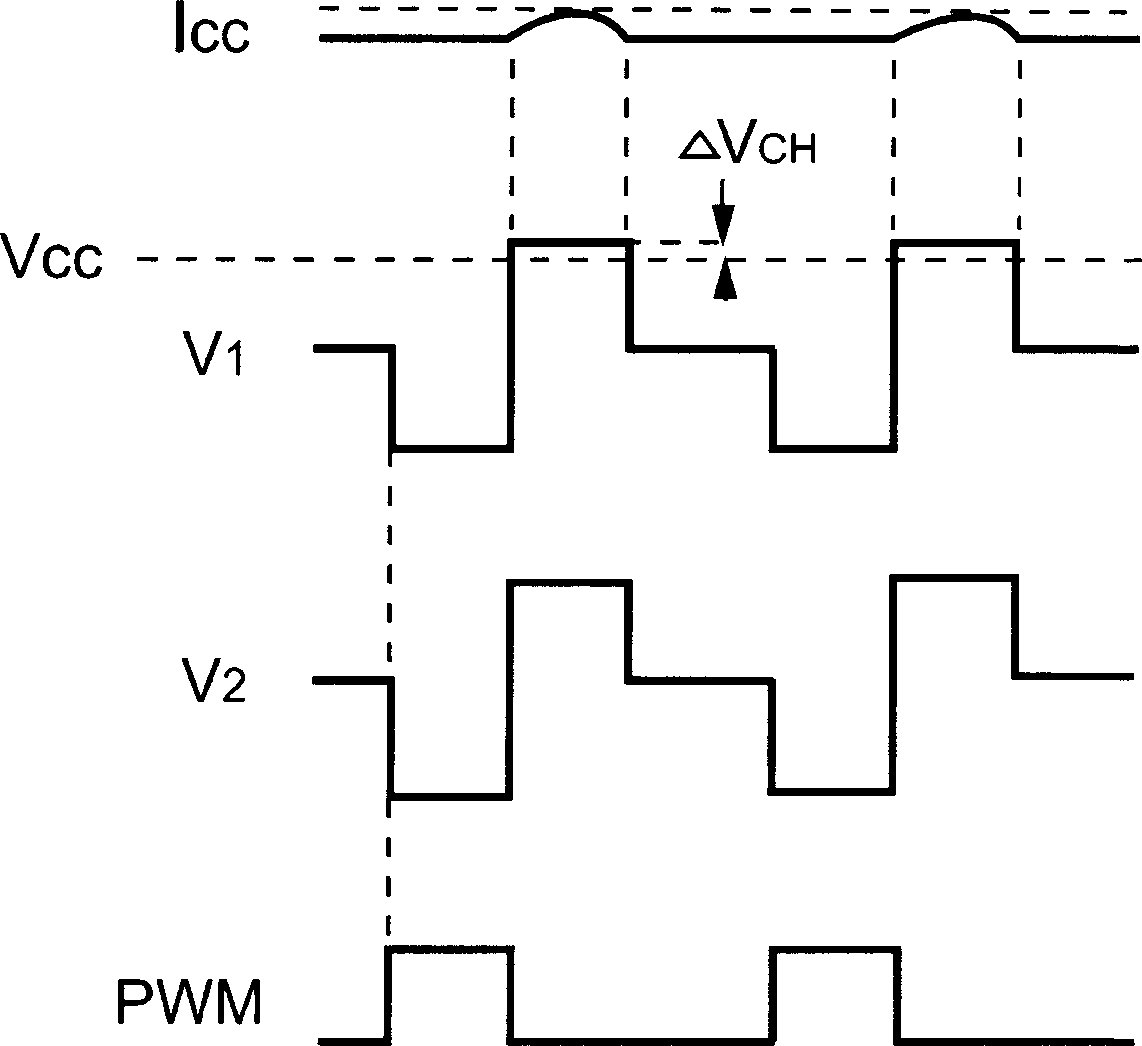
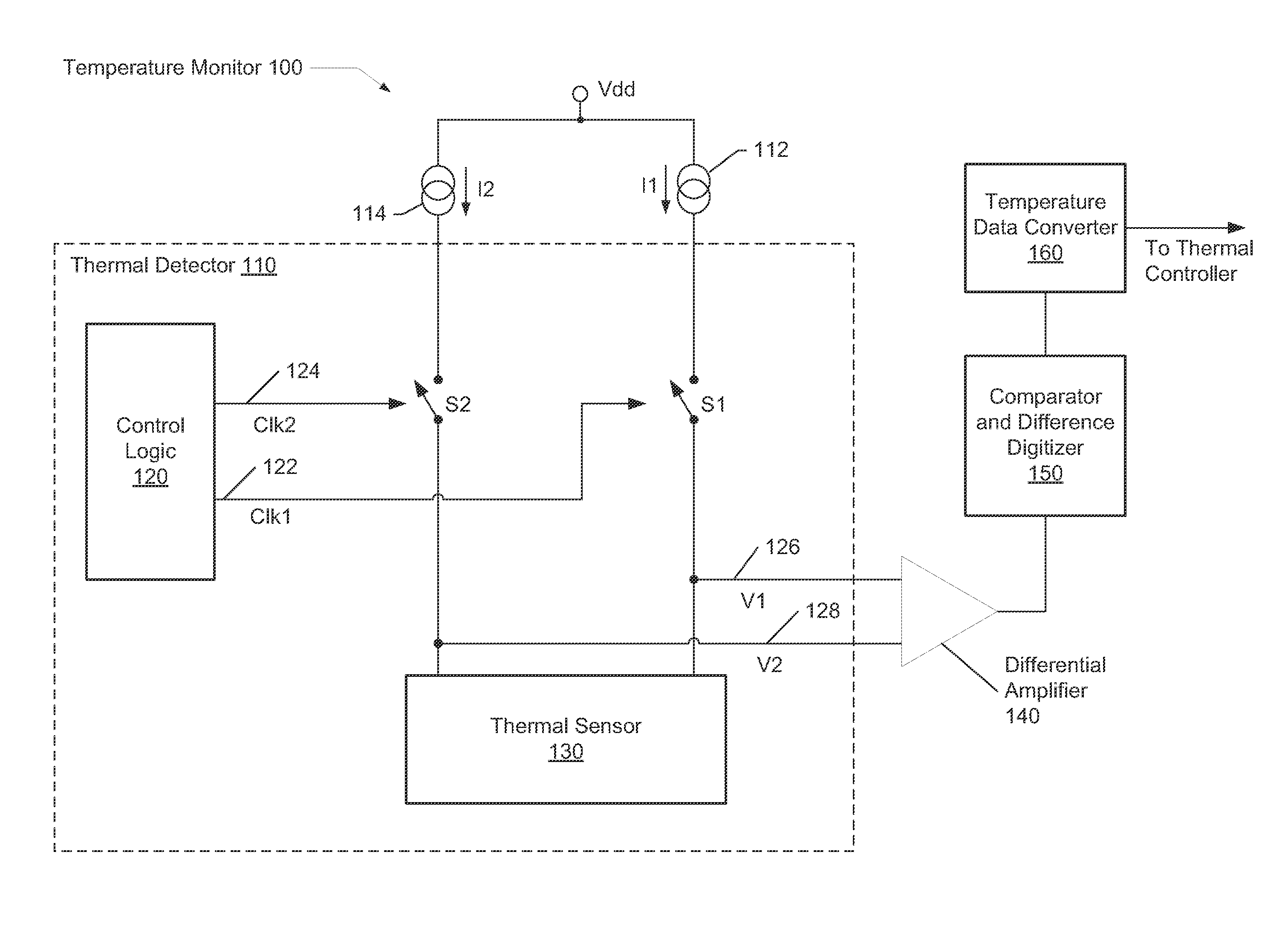
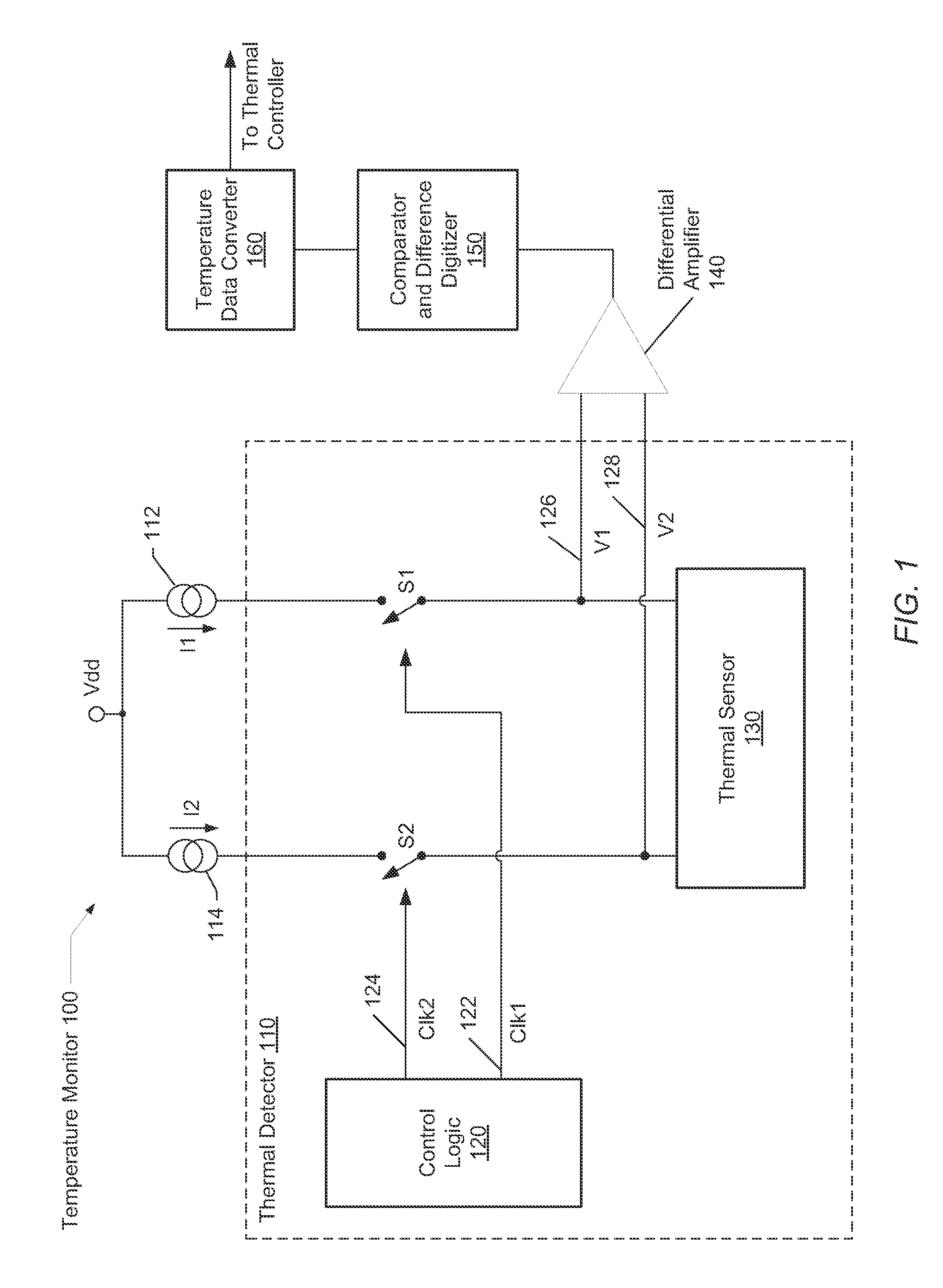
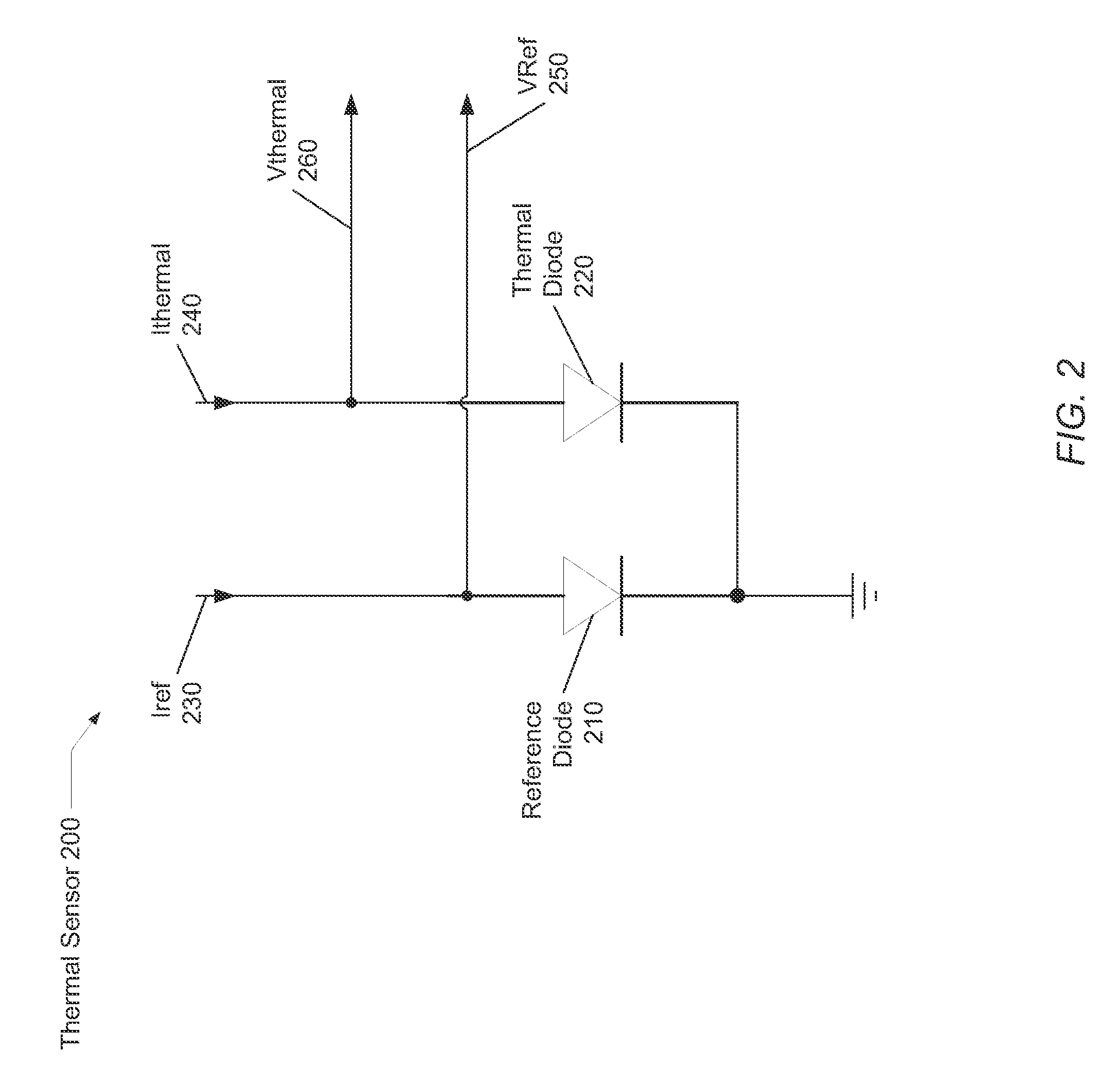
Dynamic voltage reference for sampling delta based temperature sensor
ActiveUS20130120930A1Efficient measurementDigital data processing detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVoltage referenceDiode voltage
A system and method for measuring integrated circuit (IC) temperature. An integrated circuit (IC) includes a thermal sensor and data processing circuitry. The thermal sensor utilizes switched currents provided to a reference diode and a thermal diode. The ratios of the currents provided to each of these diodes may be chosen to provide a given delta value between the resulting sampled diode voltages. At a later time, a different ratio of currents may be provided to each of these diodes to provide a second given delta value between the resulting sampled diode voltages. A differential amplifier within the data processing circuitry may receive the analog sampled voltages and determine the delta values. Other components within the data processing circuitry may at least digitize and store one or both of the delta values. A difference between the digitized delta values may calculated and used to determine an IC temperature digitized code.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Integrated resistance cancellation in temperature measurement systems
ActiveUS20060193370A1Eliminate needThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionElectrical resistance and conductanceIntegrator
A temperature measurement device may be implemented by coupling a PN-junction, which may be comprised in a diode, to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that comprises an integrator. Different currents may be successively applied to the diode, resulting in different VBE values across the diode. The ΔVBE values thus obtained may be successively integrated. Appropriate values for the different currents may be determined based on a set of mathematical equations, each equation relating the VBE value to the temperature of the diode, the current applied to the diode and parasitic series resistance associated with the diode. When the current sources with the appropriate values are sequentially applied to the diode and the resulting diode voltage differences are integrated by the integrator comprised in the ADC, the error in the temperature measurement caused by series resistance is canceled in the ADC, and an accurate temperature reading of the diode is obtained from the output of the ADC.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Circuit for driving an infrared transmitter LED with temperature compensation
ActiveUS20110062895A1EliminateEliminate currentElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDriving currentJunction temperature
Systems and methods to achieve a circuit for driving one or more infrared transmitter LEDs with temperature compensation have been disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention the circuit has been applied for a rain sensing system. The junction temperature of the LED is measured and compensated by adjusting the driver current of a voltage-to-current converter driving the LED. The LED junction temperature is measured by comparing the difference in the forward diode voltage at different current densities. This voltage difference is extracted when switching the drive currents between different constant values. The measurement results are converted to digital values, which are used by a buffered dual ladder resistive DAC structure to adjust the drive current to temperature variations.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
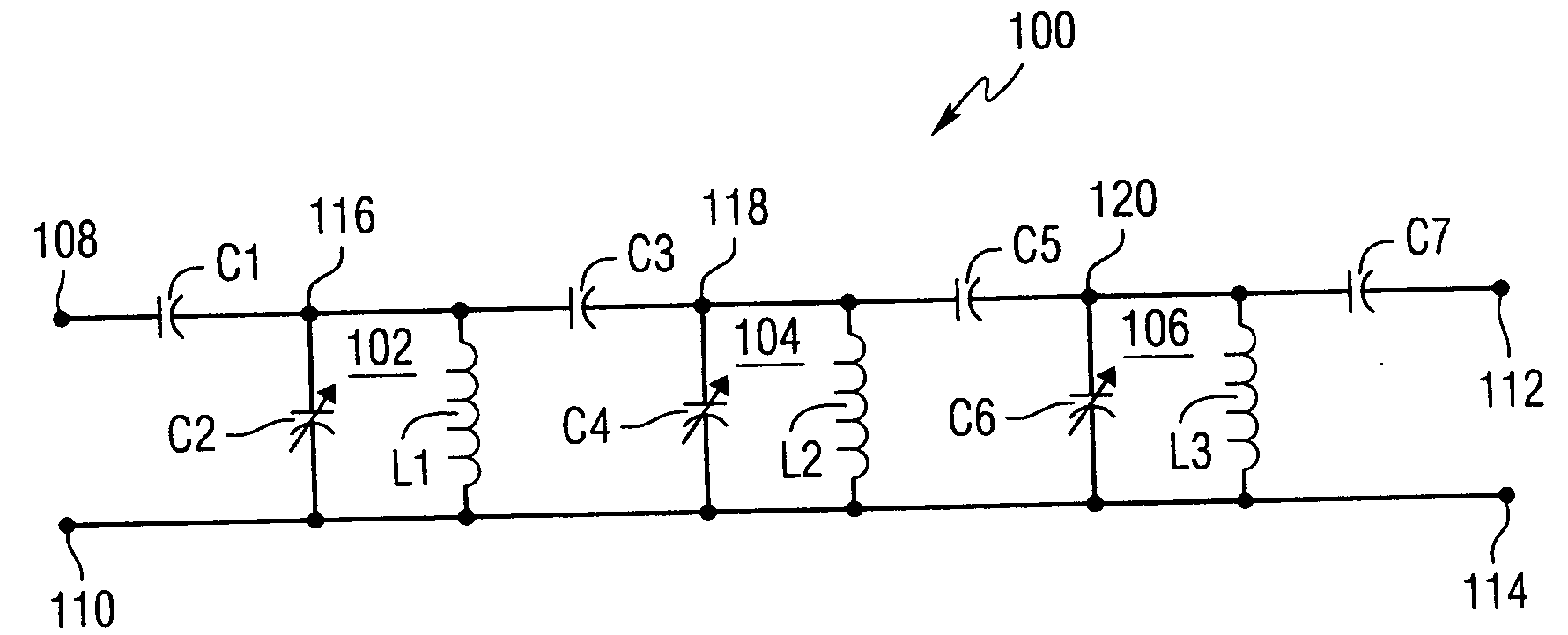
Electrically tunable filters with dielectric varactors
InactiveUS20050088255A1Increase powerReduce intermodulation distortionMultiple-port networksActive element networkInductorBand-stop filter
This invention provides a voltage tunable filter comprising an input connection point, an output connection point, and at least one circuit branch electrically coupled to the input connection point and the output connection point and including a voltage tunable dielectric varactor electrically connected to an inductor. The voltage tunable filter can be one of a low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop filter. The varactor can include built-in DC blocking capacitors.
Owner:NXP USA INC
DC/DC converter
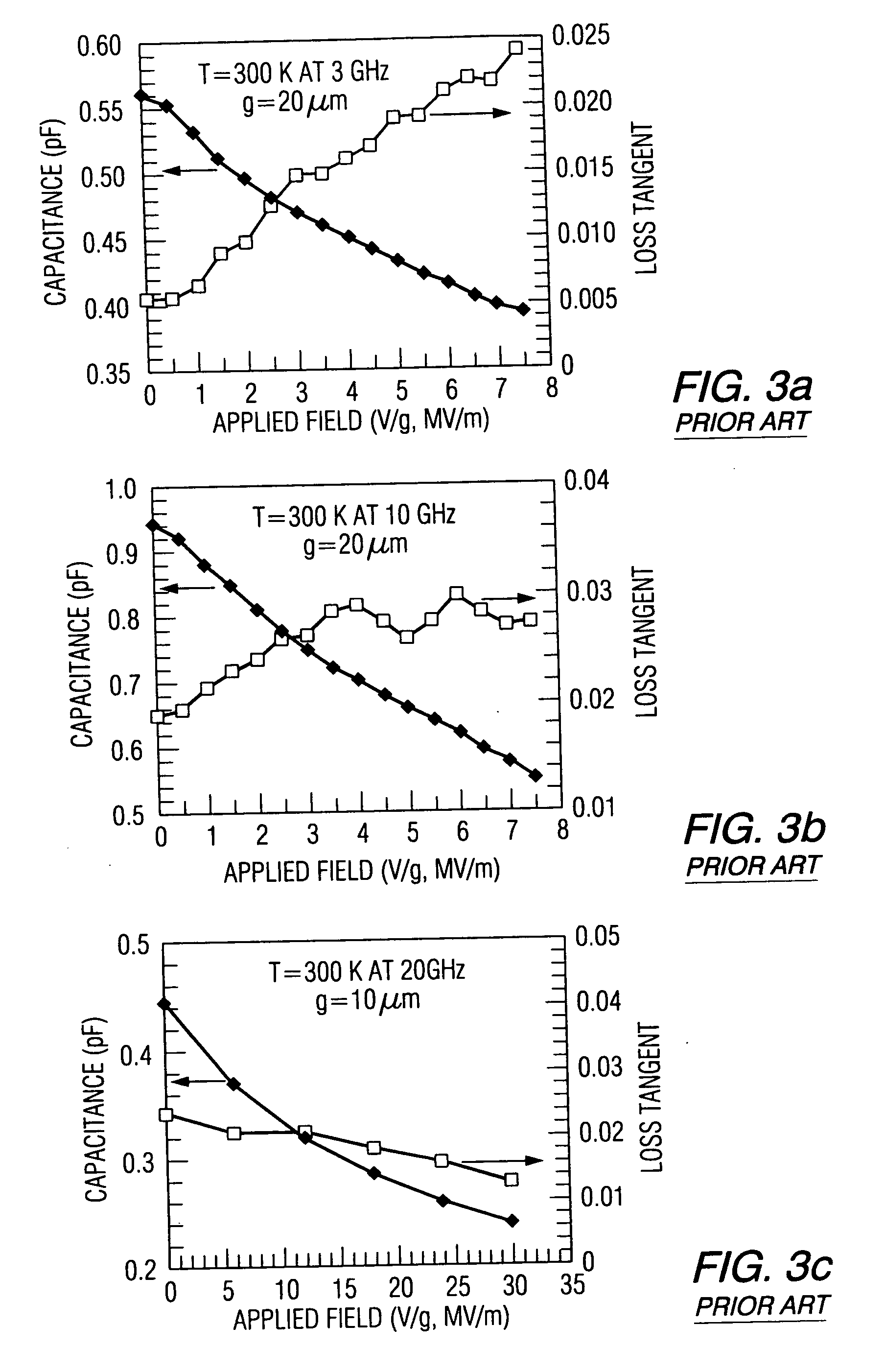
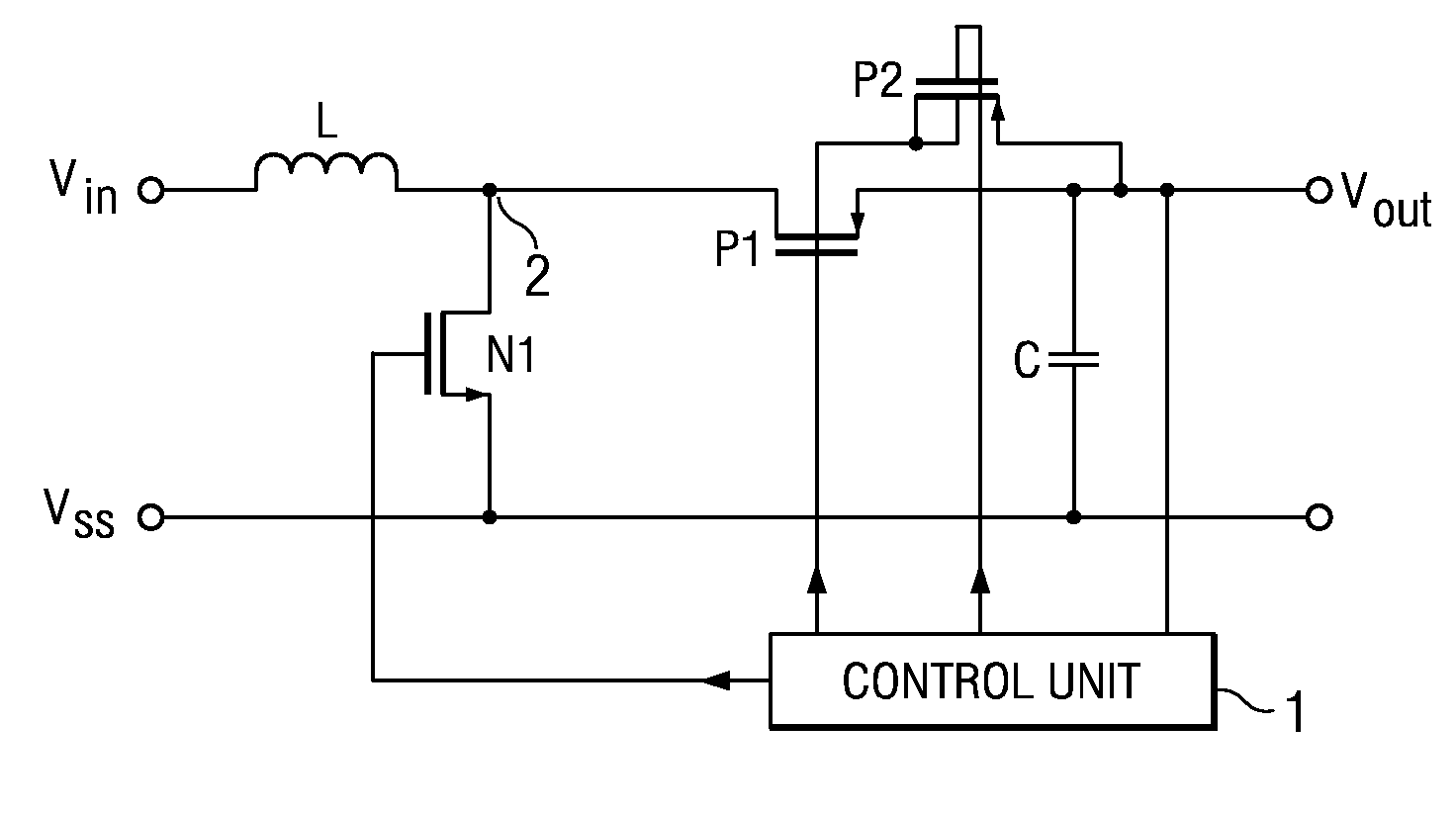
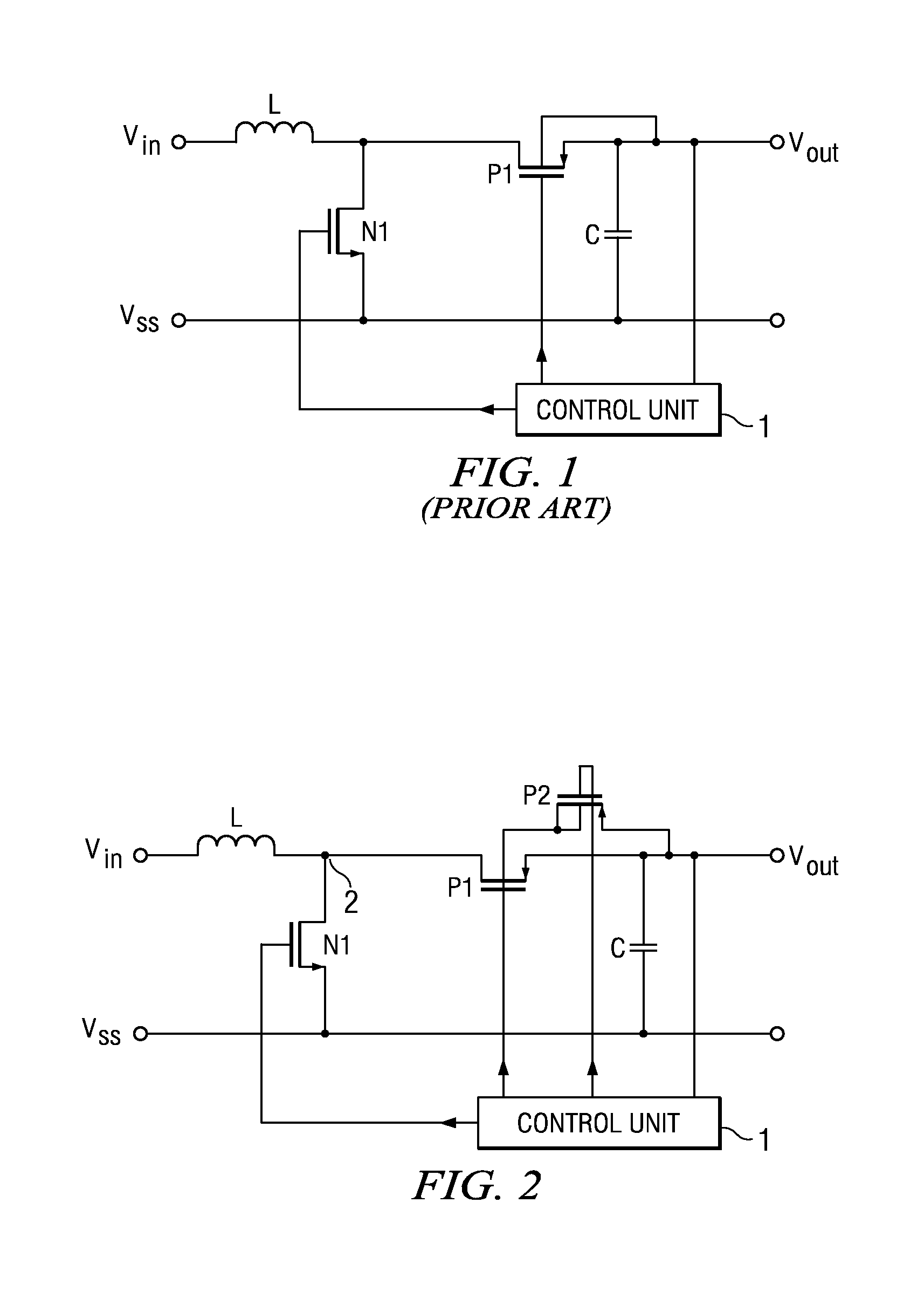
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter including an input to which an input voltage Vin is applied, a inductance L whose one terminal is connected to the input, a first controllable switch N1 via which the other terminal of the inductance is connectable to a reference potential Vss, a second controllable switch P1 via which the other terminal of the inductance is connectable to the output of the converter, and a regulator circuit 1 configured so that it is able to control the two switches in regulating the output voltage of the DC / DC converter to a predetermined wanted value. The second controllable switch is a PMOS-FET. The regulator circuit is configured so that when the input voltage is higher than the desired value of the output voltage, the gate of the PMOS-FET is permanently connected to a voltage which is larger than the difference between the input voltage and the threshold voltage of the PMOS-FET, it connecting the back gate of the PMOS-FET permanently to a voltage which is larger than the expression input voltage plus threshold voltage of the PMOS-FET minus the diode voltage of a pn junction of the PMOS-FET and timing the first controllable switch with a specific duty cycle so that the output voltage attains the wanted value. The converter in accordance with the invention now permits achieving both an increase and decrease in the input voltage. It can be put to use preferably in conjunction with battery-powered devices for which a wanted voltage is specified.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
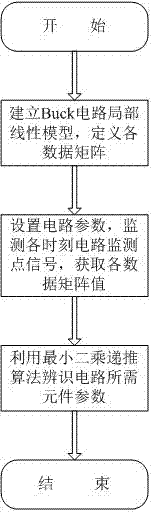
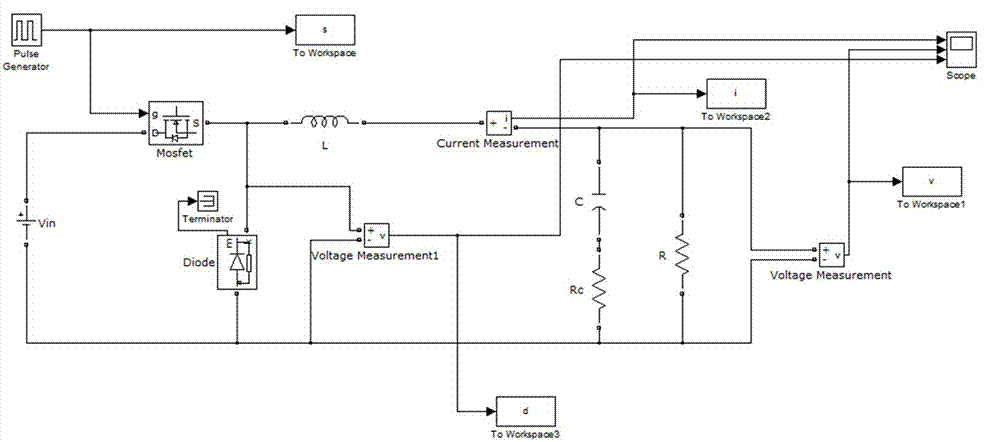
Buck circuit multiparameter on-line identification method
InactiveCN104750915AThe method is simple and reliableEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsLocal linear modelsState space equation
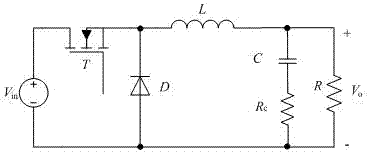
The invention discloses a Buck circuit multiparameter on-line identification method. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the Buck circuit is analyzed according to the Kirchhoff's law, and a state-space equation set of the Buck circuit is set up; secondly, according to the state-space equation set, a local linear model of the Buck circuit is set up; thirdly, according to the local linear model, a measurement matrix and a parameter matrix are defined; fourthly, different parameter values, monitoring inductive currents, output voltages and diode voltage signals of different elements in the Buck circuit are set; fifthly, estimated valve of the parameter matrix is obtained through least squares recursive algorithm. The parameter matrix obtained from the above estimated valve is used to calculating the parameter valves of the element need to be identified. According to the Buck circuit multiparameter on-line identification method, the influence of the diode and diode pre-stage circuit parameters including a non-ideal voltage and an input voltage on the precision of the parameter identification is removed, the practical operation is easy to achieve, and the identification precision is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
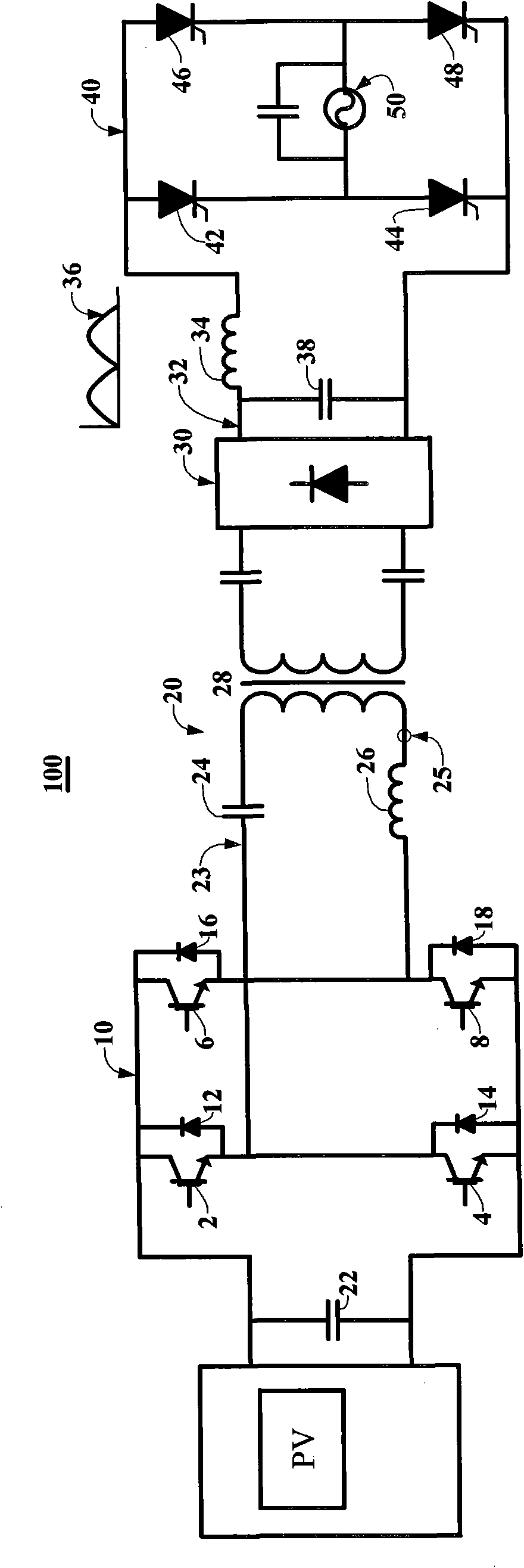
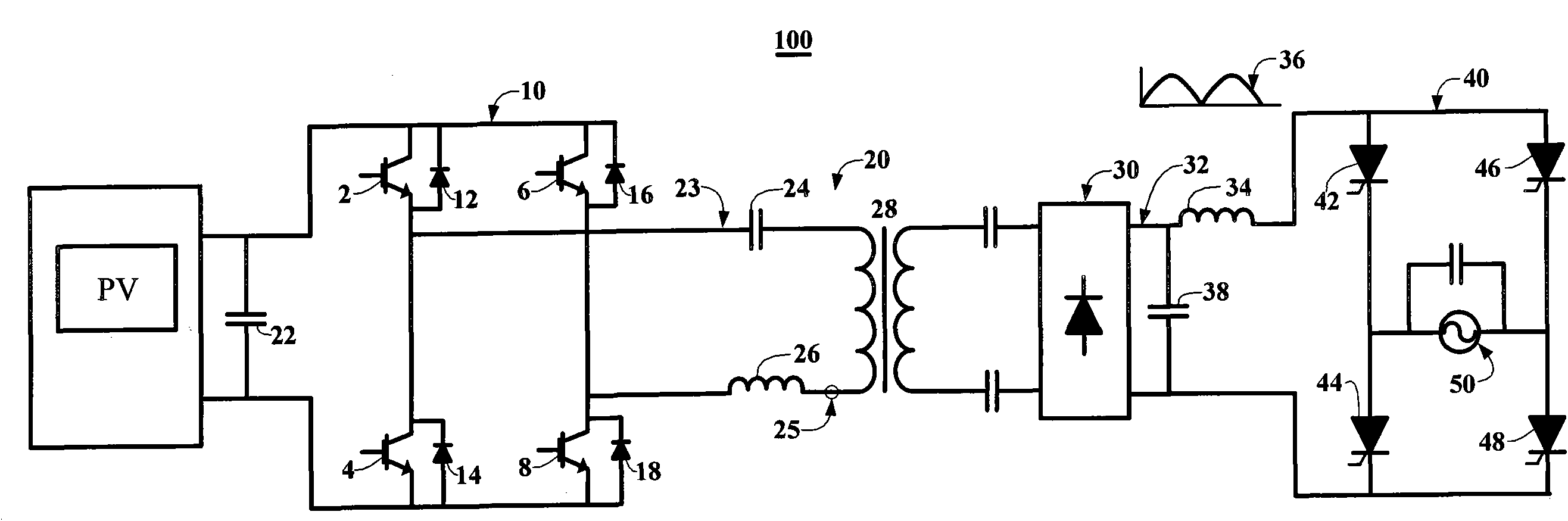
Direct-current tracing control high-power photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
ActiveCN101976965AImprove pressure resistanceHarmonic Distortion Rate CancellationAc-ac conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses a high-efficiency low-harmonic distortion rate high-power photovoltaic grid-connected inverter (100). The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter comprises a high frequency inverter (10), a series-connected resonance circuit (20), a fast incontrollable rectifier (30) and a power frequency inverter (40), wherein the high frequency inverter (10) is used for transforming the voltage of a photovoltaic array into impulse level; the series-connected resonance circuit (20) transforms the impulse level into sinusoidal voltage and current; the high frequency inverter (10) outputs a level impulse according to direct-current tracing control, so that the resonant amplitude of the series-connected resonance circuit (20) can be continuously adjusted, and traces the change of rectified grid voltage; the incontrollable rectifier (30) transforms the sinusoidal voltage with different amplitude values into direct-current voltage which traces the change of the rectified grid voltage;and the power frequency inverter (40) switches to trigger when the grid voltage crosses a zero point and is used for tracing the change of the grid voltage with output voltage. The inverter can be applied to the large-scale high voltage grid connection of photovoltaic electric power generating systems.
Owner:江苏博纬新能源科技有限公司
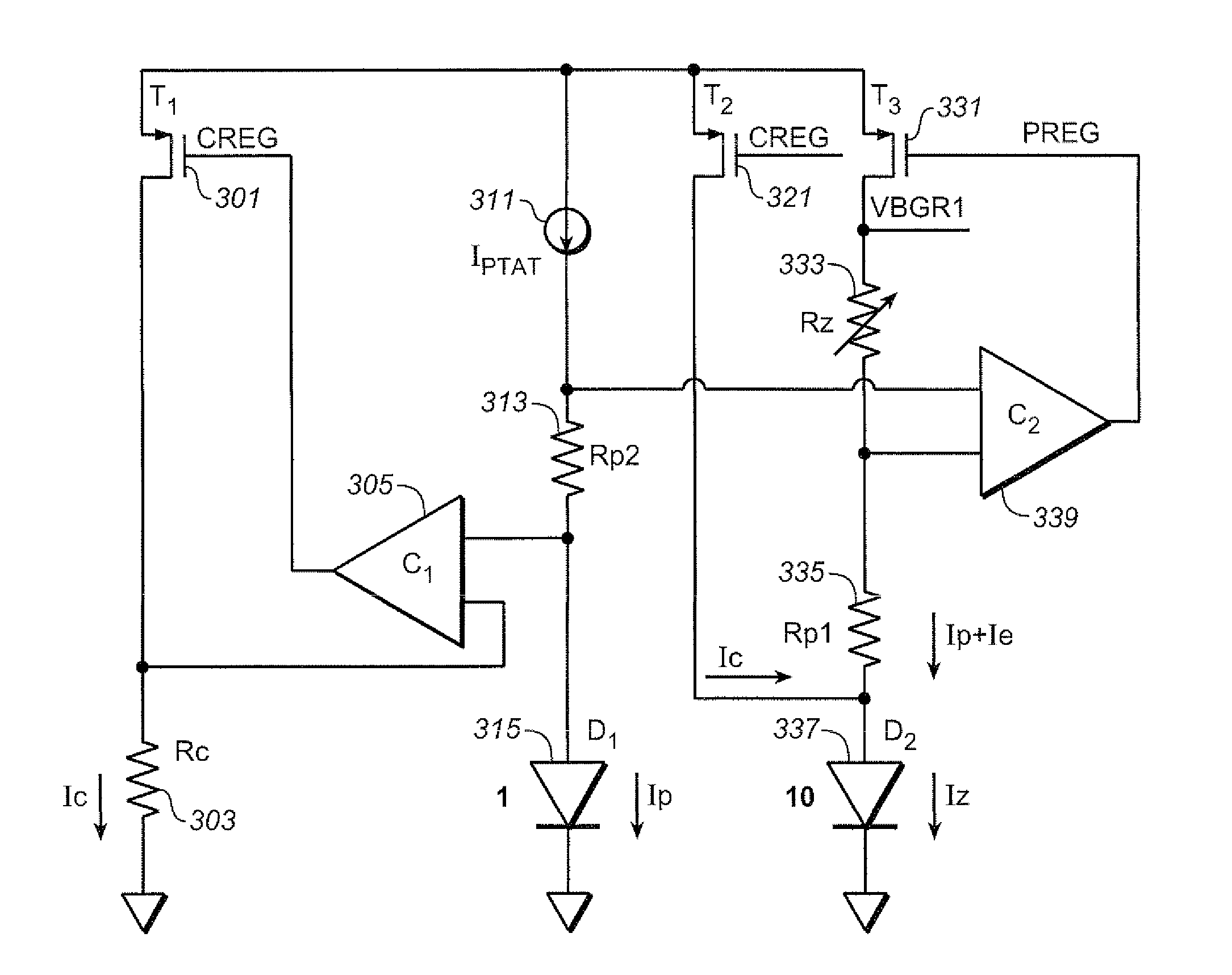
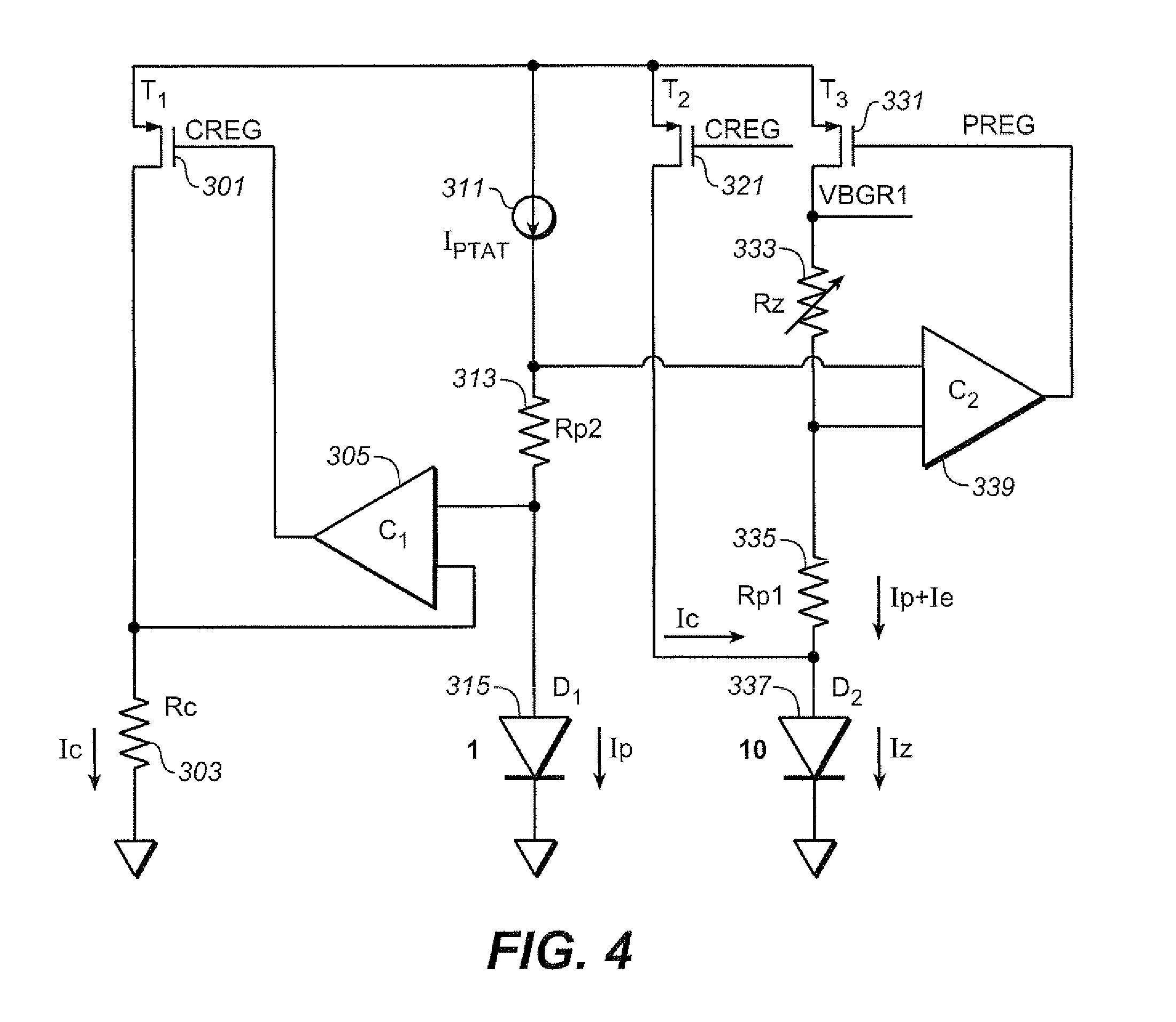
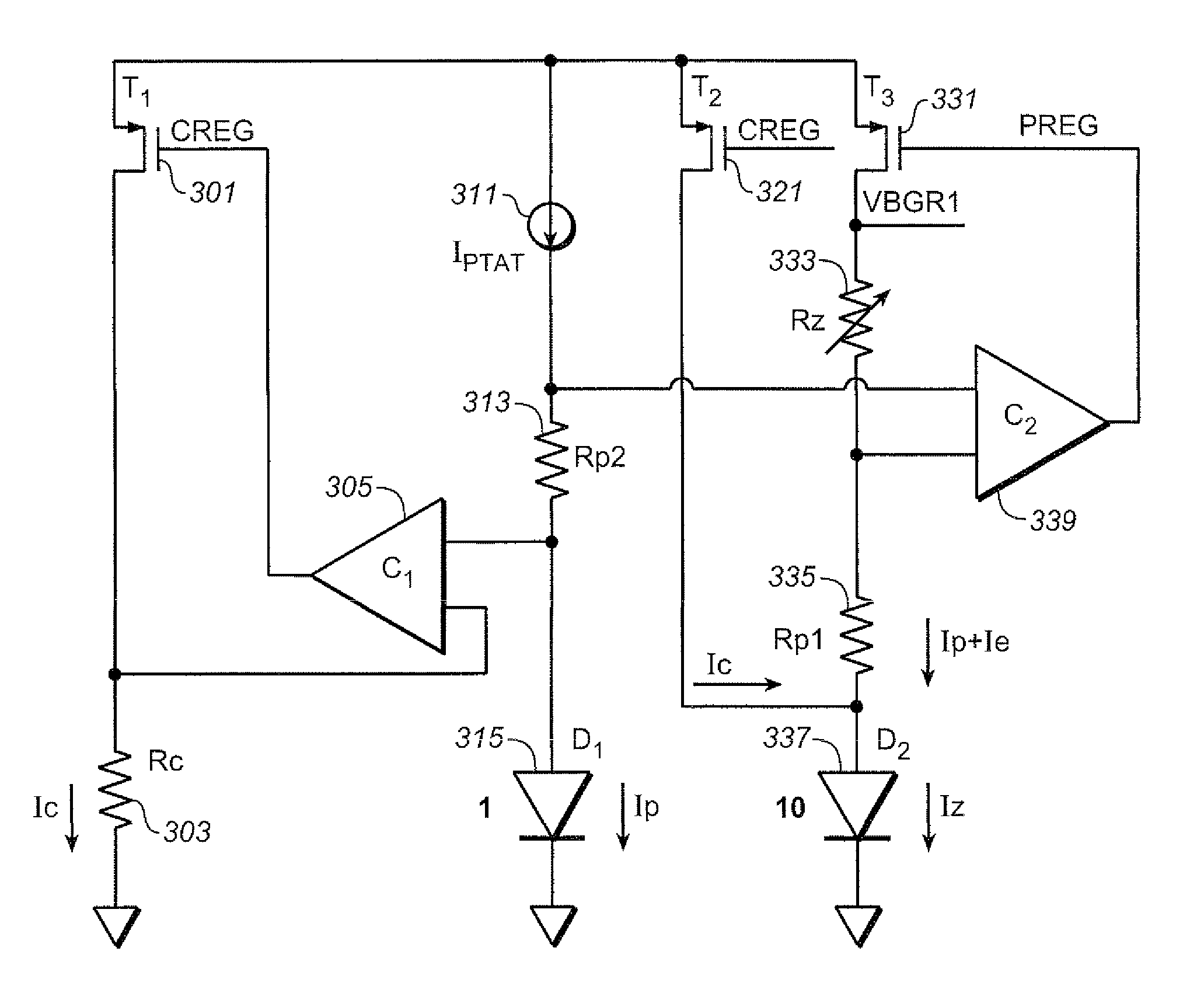
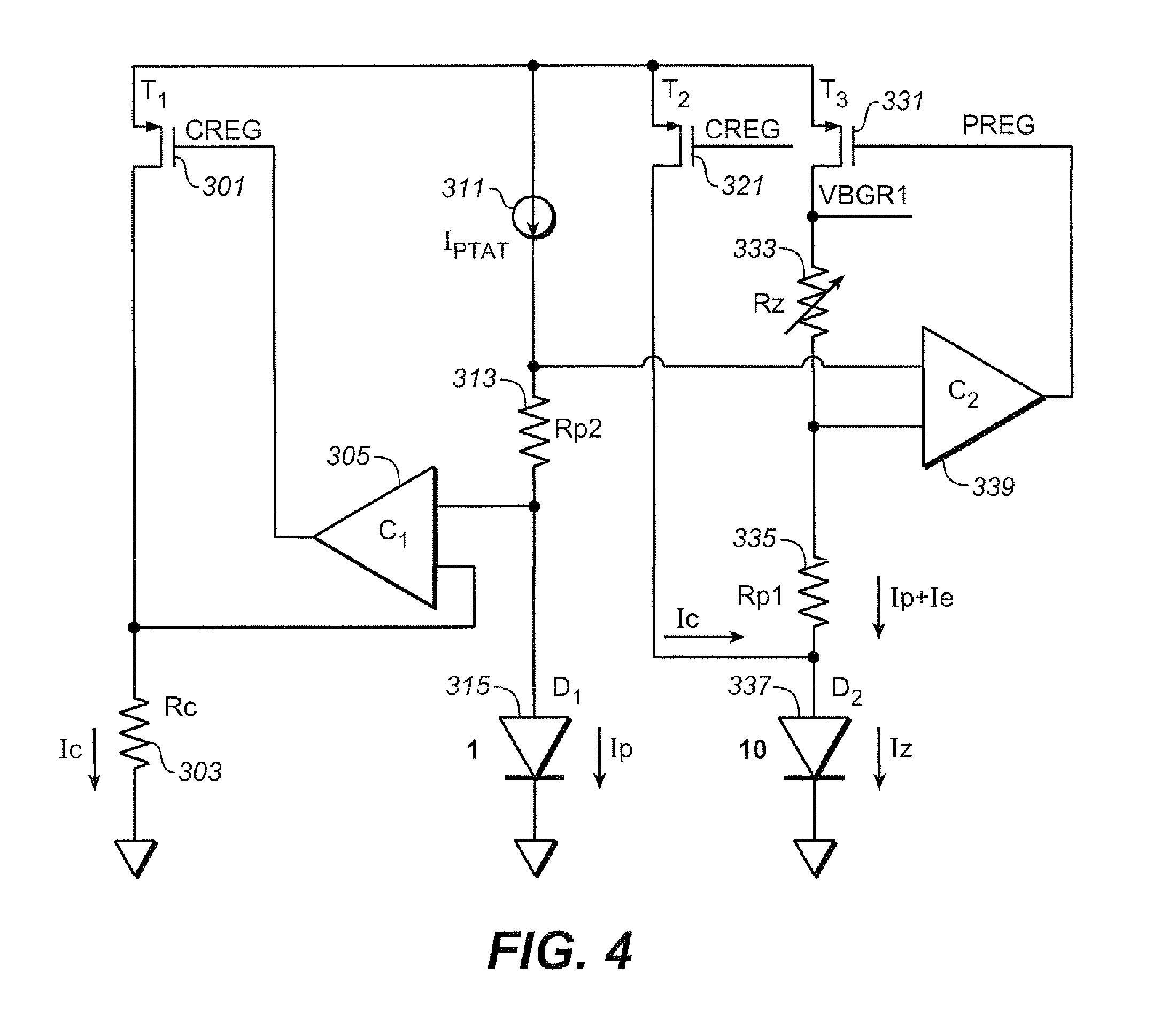
Chopper stabilized bandgap reference circuit and methodology for voltage regulators
InactiveUS20100295529A1Power supply linesDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A chopper stabilized bandgap voltage reference circuit comprises current mirror circuitry mirroring first and second currents into first and second networks to generate a forward diode voltage signal and a PTAT (proportional to absolute temperature) component signal, and a third current having a derived temperature coefficient into a third network to generate a reference voltage signal for a regulator. An amplifier amplifies a differential signal of the forward diode voltage signal and the PTAT component signal to output a fourth current to control the first and second currents. According to a chopper clock, a modulator modulates the differential signal to be supplied to the amplifier and a demodulator demodulates the fourth current. A gain loop compensation circuit is coupled to the demodulator to compensate the amplifier, and filter the fourth current for noise components, and a bypass circuit is also provided to the third network for filtering the third current.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Proportional Settling Time Adjustment For Diode Voltage And Temperature Measurements Dependent On Forced Level Current
ActiveUS20090009234A1Increase conversion rateMinimizing temperature measurementThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingAc componentsShunt capacitors
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate digital temperature readings using a local or remote temperature diode. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an analog to digital converter (ADC), which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a digital output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. DC components of errors in the measured temperature that may result from EMI noise modulating the junction voltage (VBE) may be minimized through the use of a front-end sample-and-hold circuit coupled between the diode and the ADC, in combination with a shunt capacitor coupled across the diode junction. The sample-and-hold-circuit may sample VBE at a frequency that provides sufficient settling time for each VBE sample, and provide corresponding stable ΔVBE samples to the ADC at the ADC operating frequency. The ADC may therefore be operated at its preferred sampling frequency rate without incurring reading errors while still averaging out AC components of additional errors induced by sources other than EMI.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
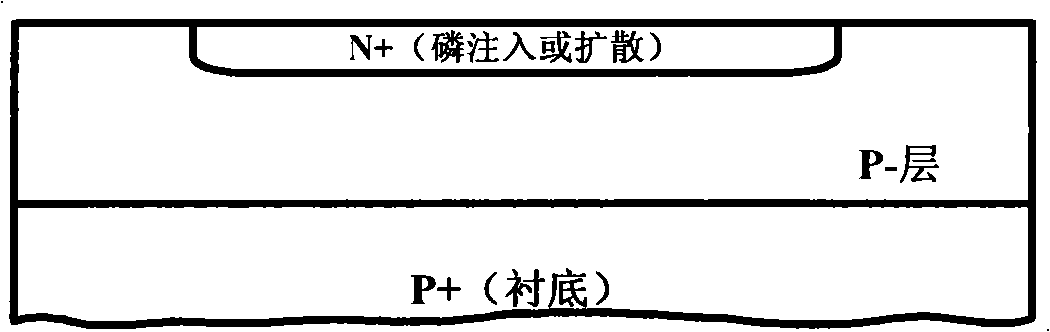
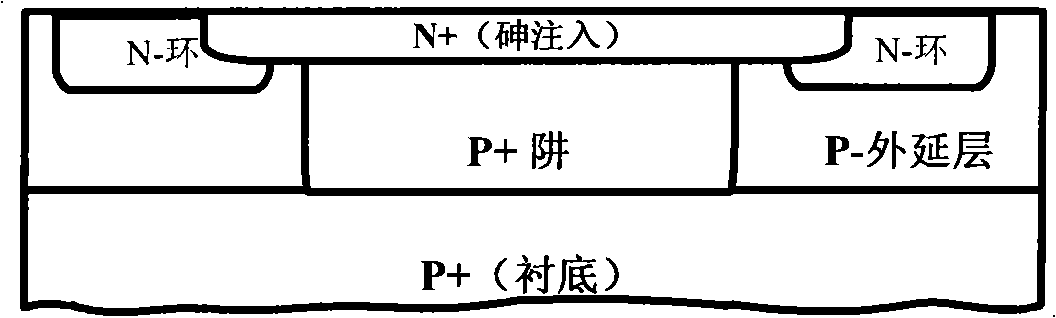
Preparation method of diode chip on P+ substrate and structure of diode chip
ActiveCN102142370AGuaranteed uniformityAvoid side penetrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRing deviceLow voltage
The invention discloses a preparation method of a diode chip on a P+ substrate and a structure of the diode chip. The method comprises the following steps of: directly forming a P- epitaxial layer on the P+ substrate through epitaxy; forming a P+ well through filling boron; annealing a P well; forming an N- ring region through photoetching and etching; annealing the N- ring; forming an N+ main junction region through photoetching and etching; annealing the N+ main junction region; evaporating or sputtering A1 as a positive electrode and the like. In the structure, special structures of the P-epitaxial layer, the P+ well and an N- voltage dividing ring device, and an N+ arsenic filling process are adopted to ensure that the N+ / P+ is broken down on a plane and to avoid lateral breakdown; the voltage of a diode formed on the P+ substrate is reduced to be lower than 5.1V, the lowest voltage can reach 2.0V, and leakage current is within 100uA, so that the uniformity of the voltage in the chip is ensured to be within 5%; and in fact the diode is a P-N junction formed by the P well and an N+ region. The structure is successfully applied to the fields of a low-voltage voltage-regulator diode and a low-voltage transient voltage suppressor diode.
Owner:CHENGDU SILAN SEMICON MFG
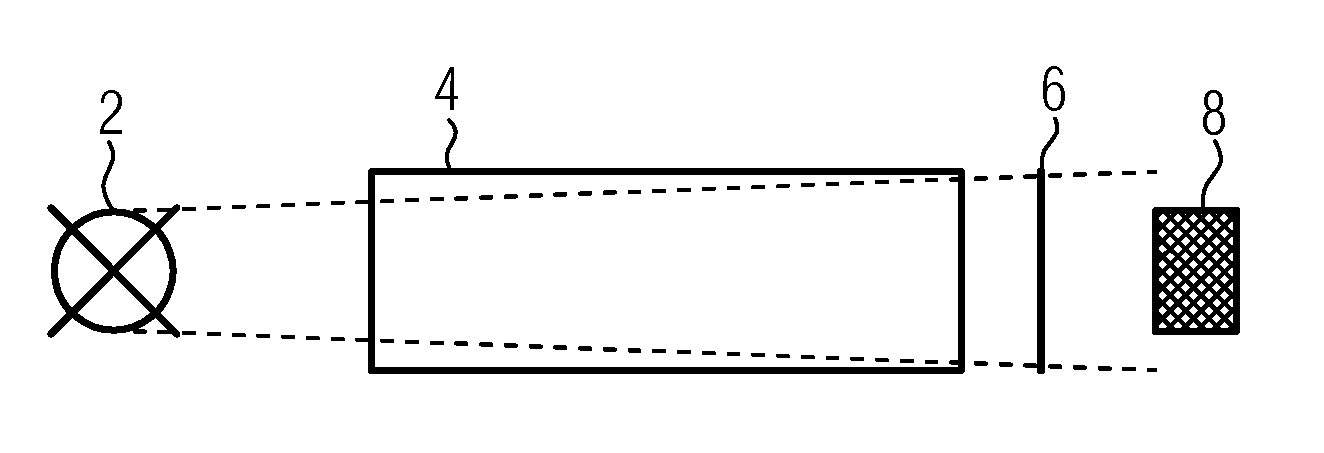
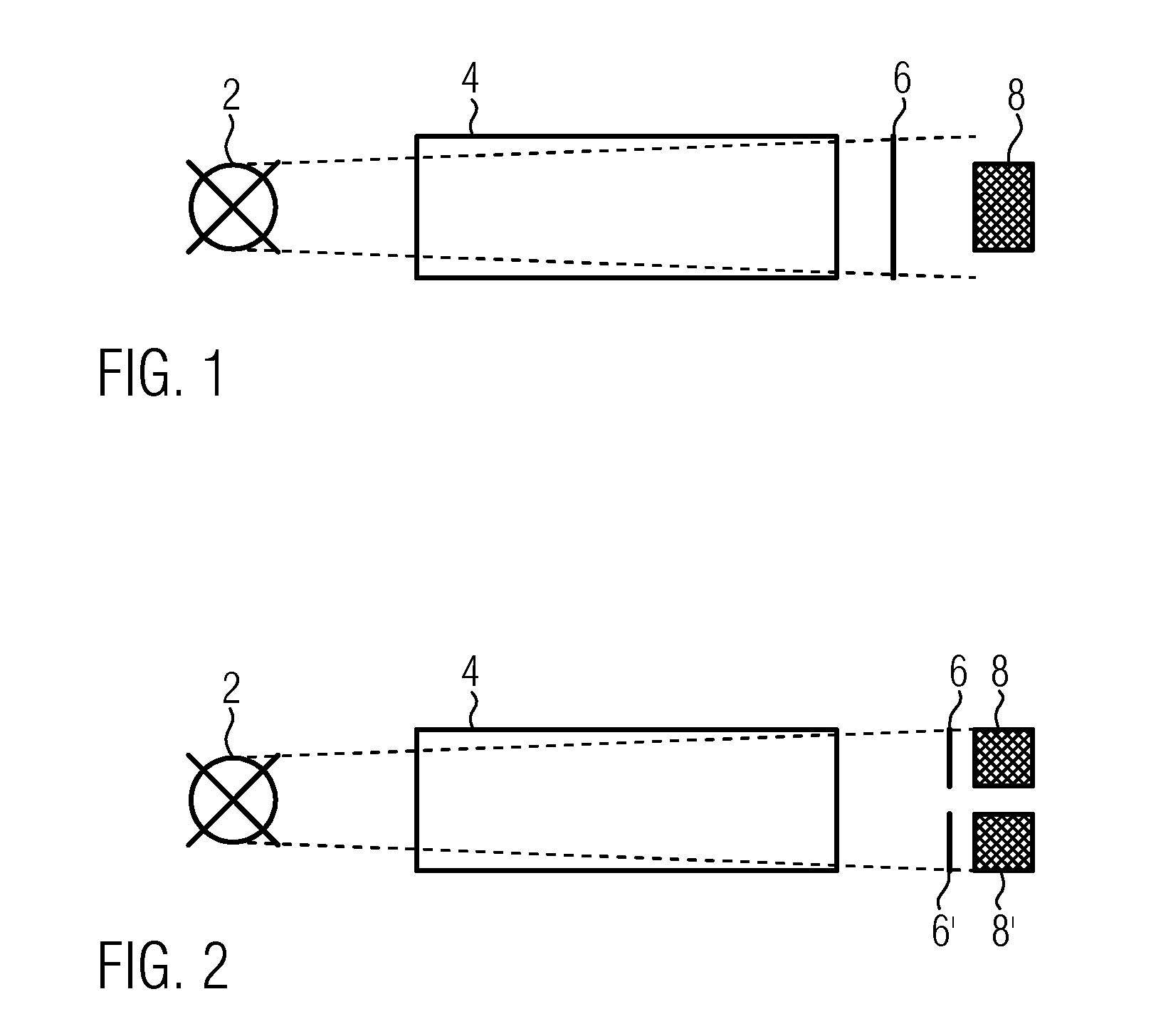
Optical gas sensor
ActiveUS20130265579A1Accurate measurementAnalysing gaseous mixturesMaterial analysis by optical meansOpto electronicDiode voltage
An optical gas sensor with a light-emitting diode (2), a photosensor (8), a measuring section between the light-emitting diode and the photosensor, and a control and analyzing unit (16), which is set up to determine the concentration of a gas in the measuring section from the light intensity measurement by the photosensor. The control and analyzing unit (16) is set up to measure the forward diode voltage over the light-emitting diode at a constant current, to determine the temperature of the light-emitting diode from the detected forward diode voltage over the light-emitting diode by means of a preset temperature dependence of the forward diode voltage, and to apply a correction function as a function of the light-emitting diode temperature determined, with which the measurement is converted to that of a preset temperature of the light-emitting diode.
Owner:DRAGER SAFETY
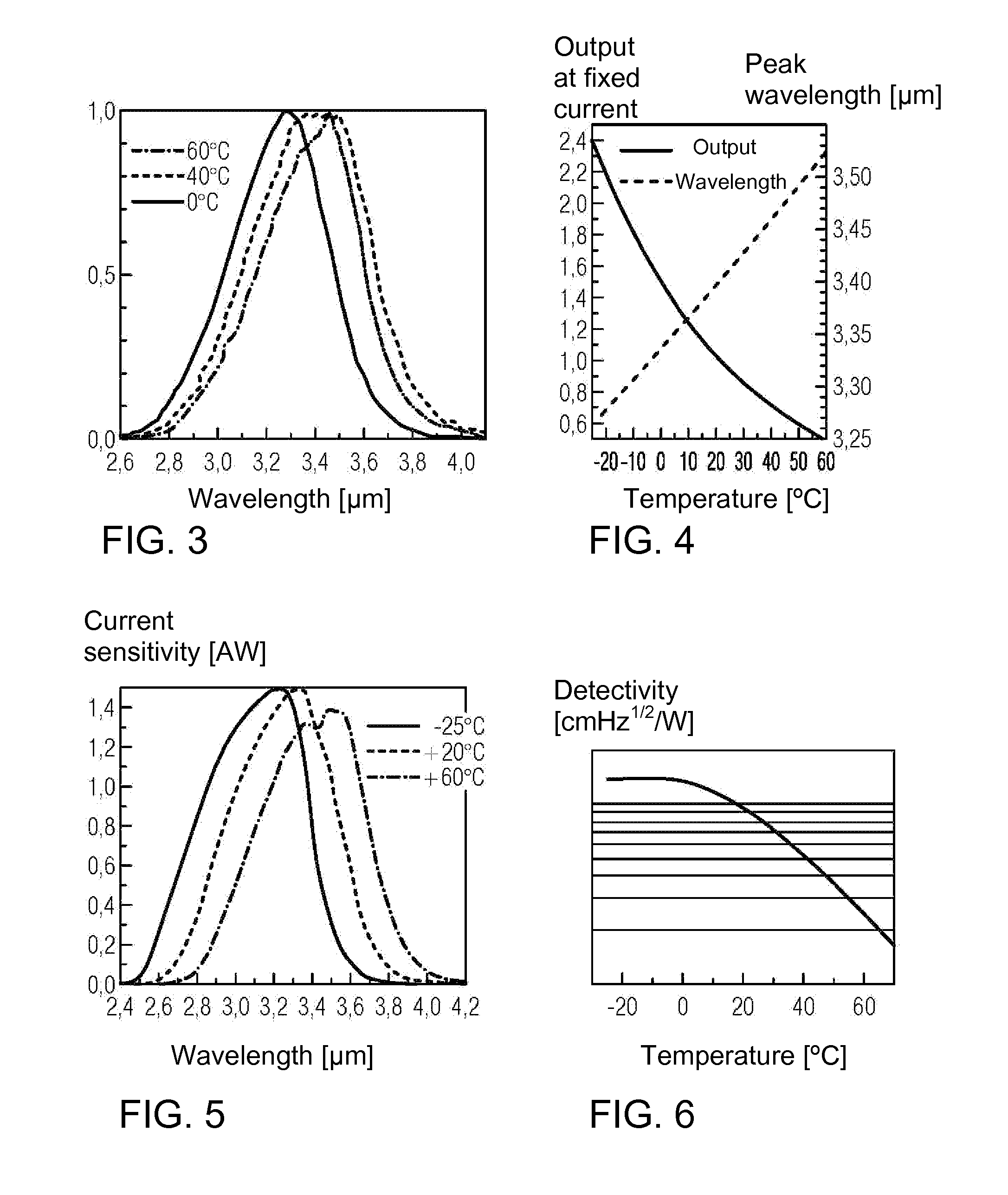
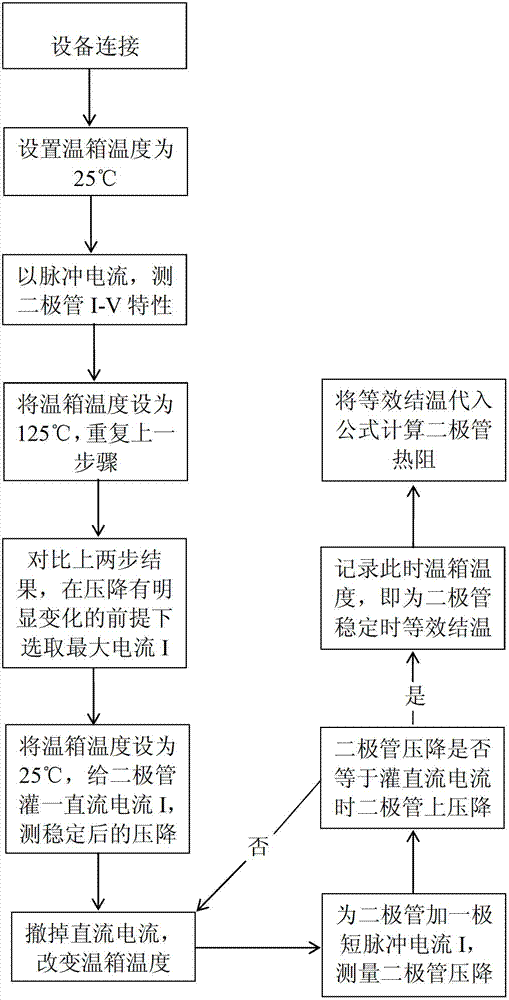
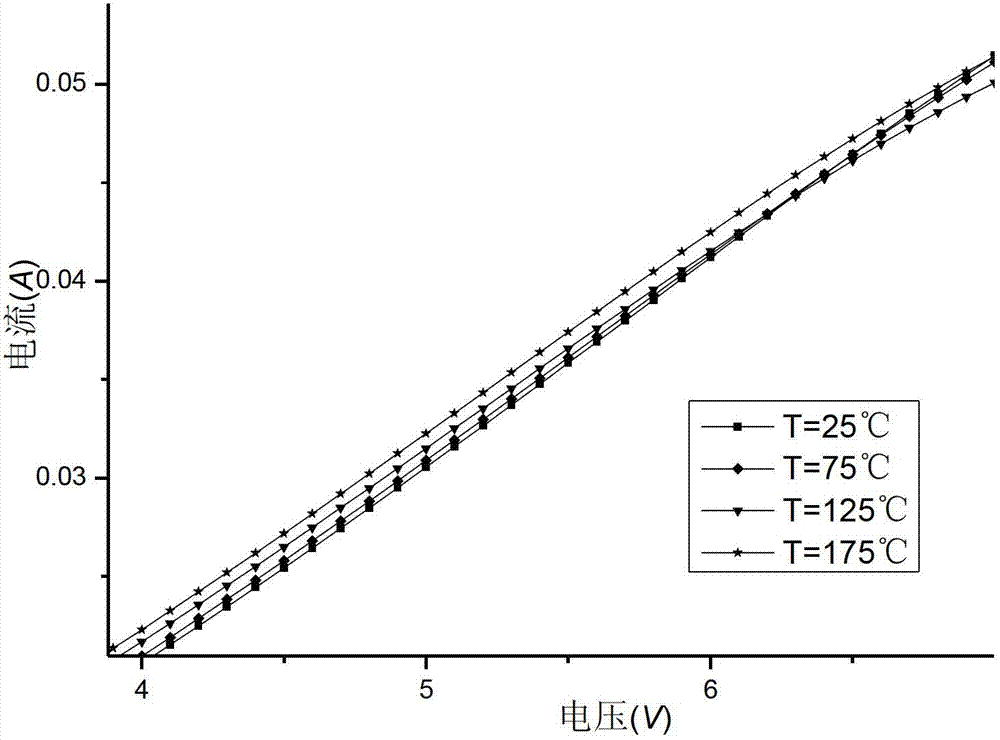
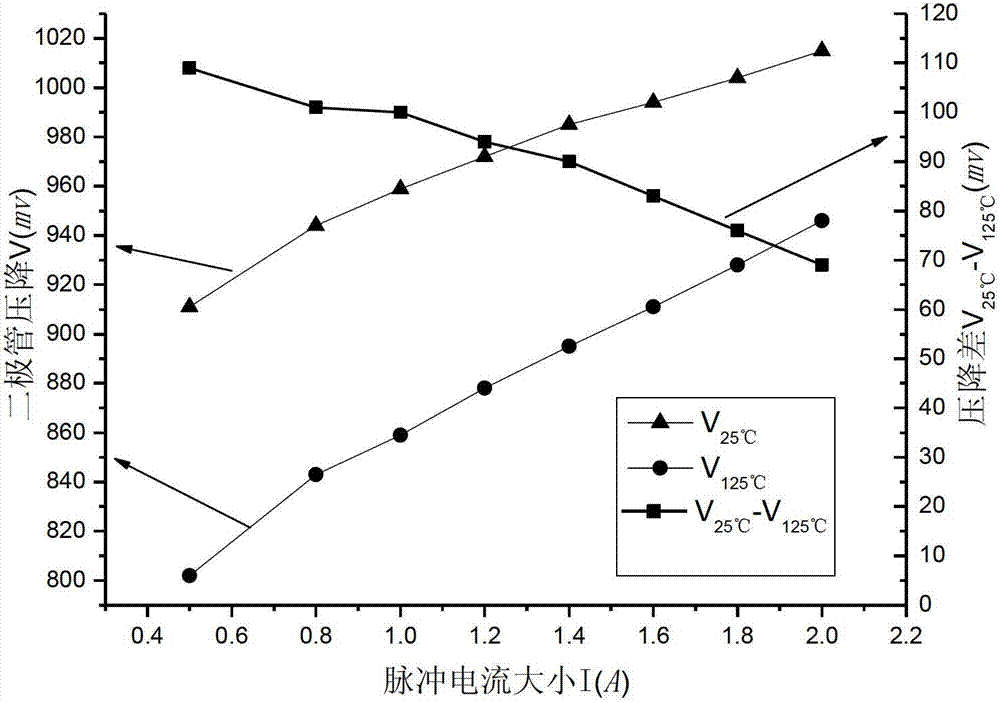
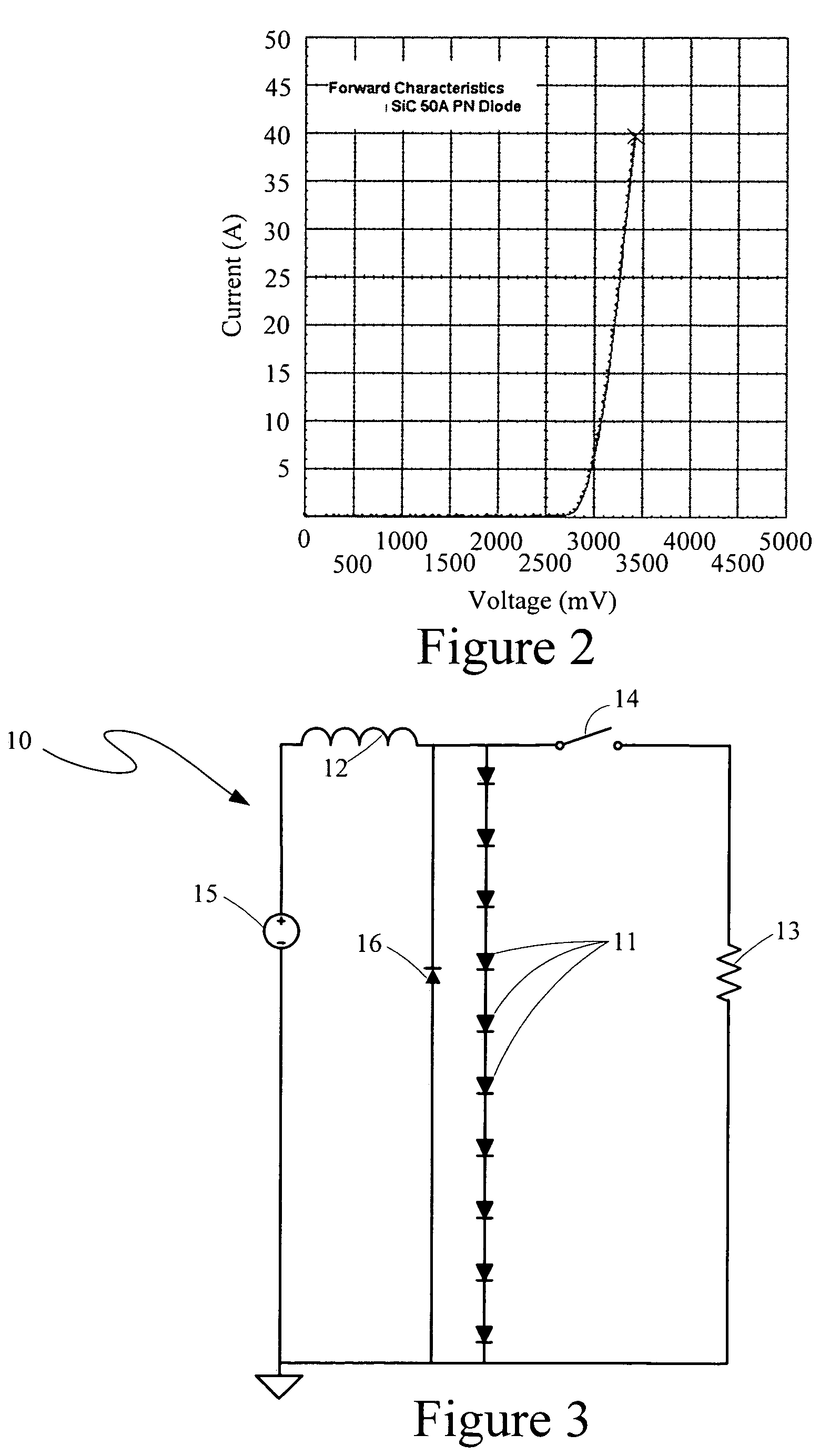
Method for testing thermal resistance of high-power silicon carbide diode
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
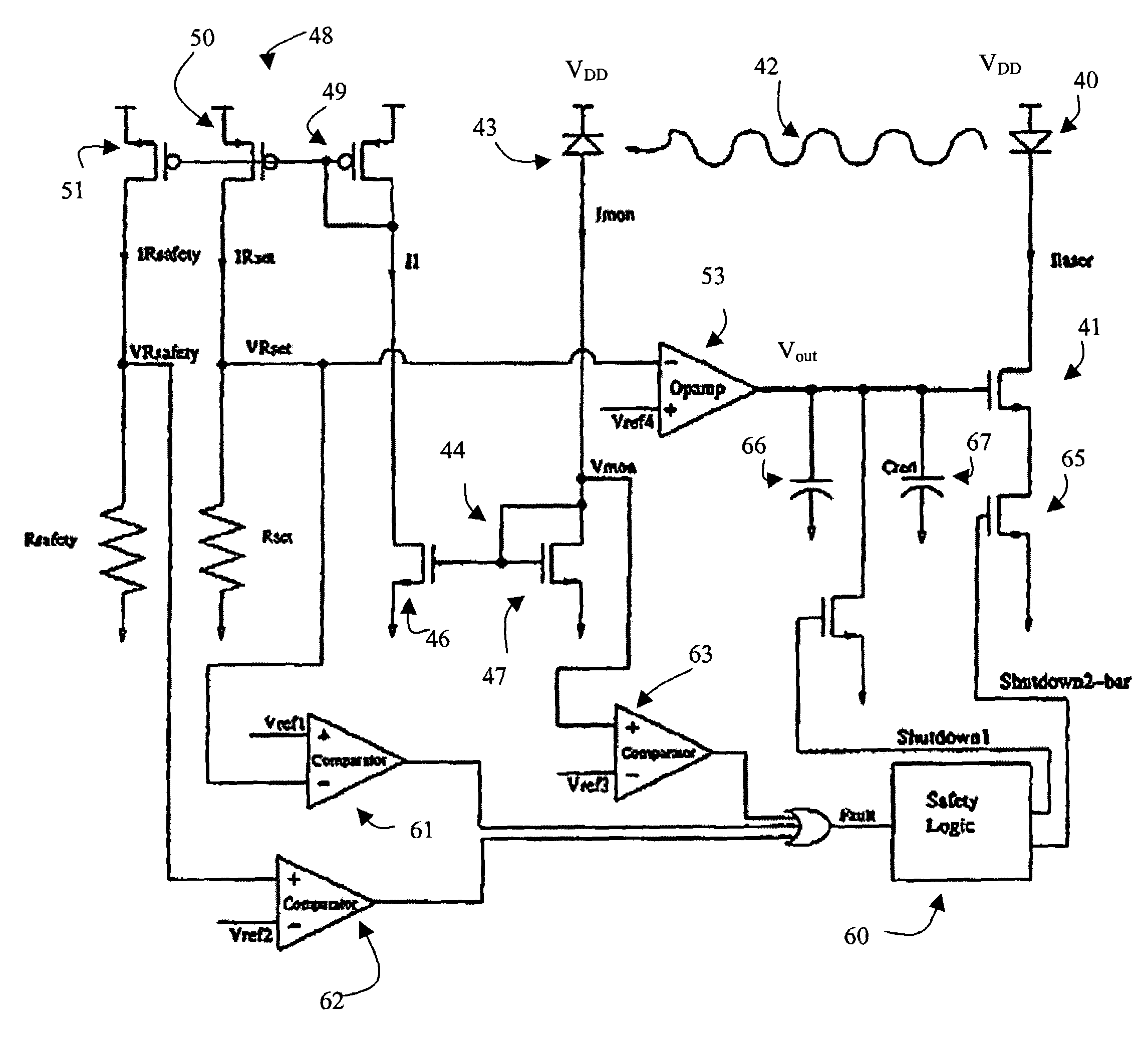
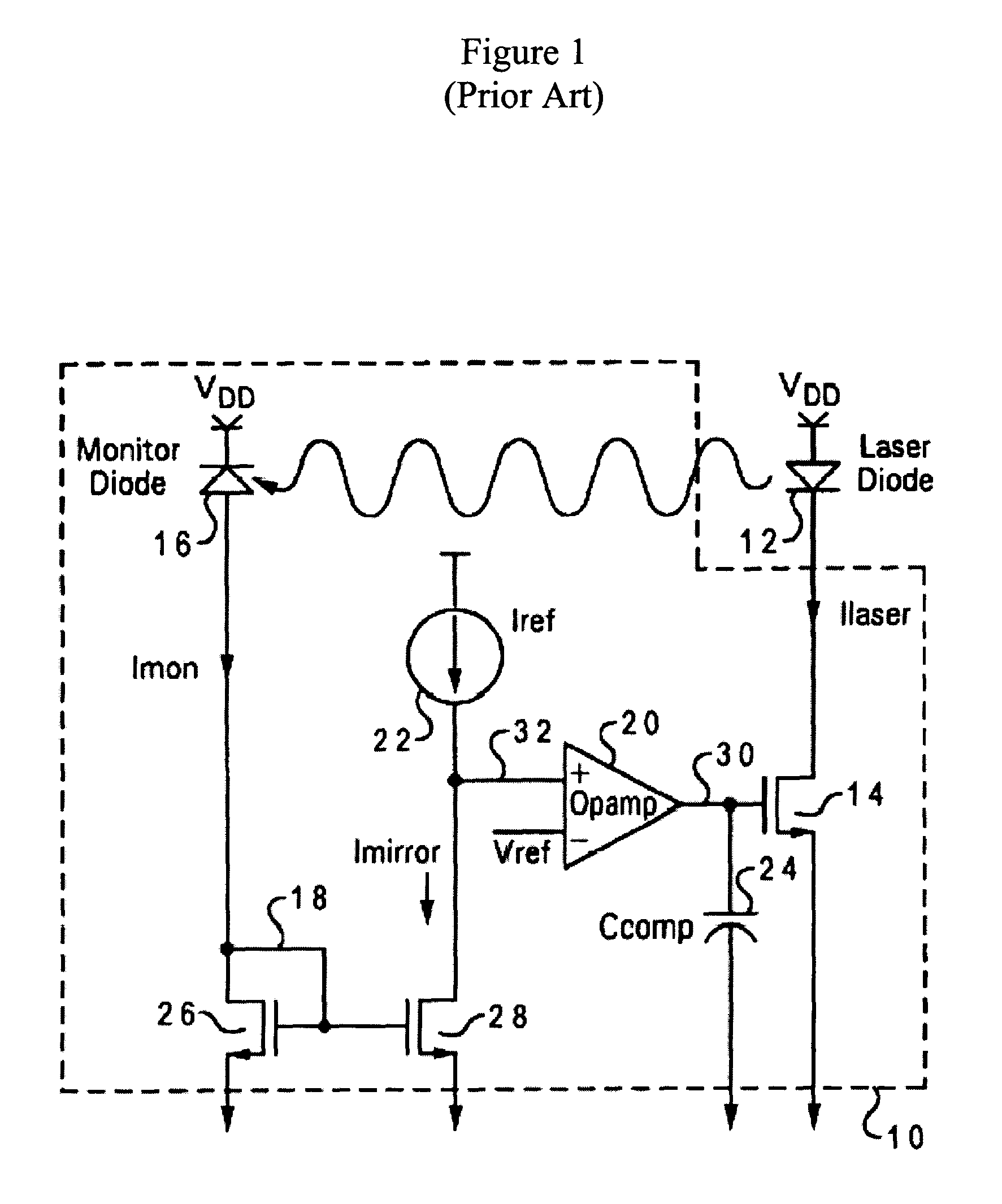
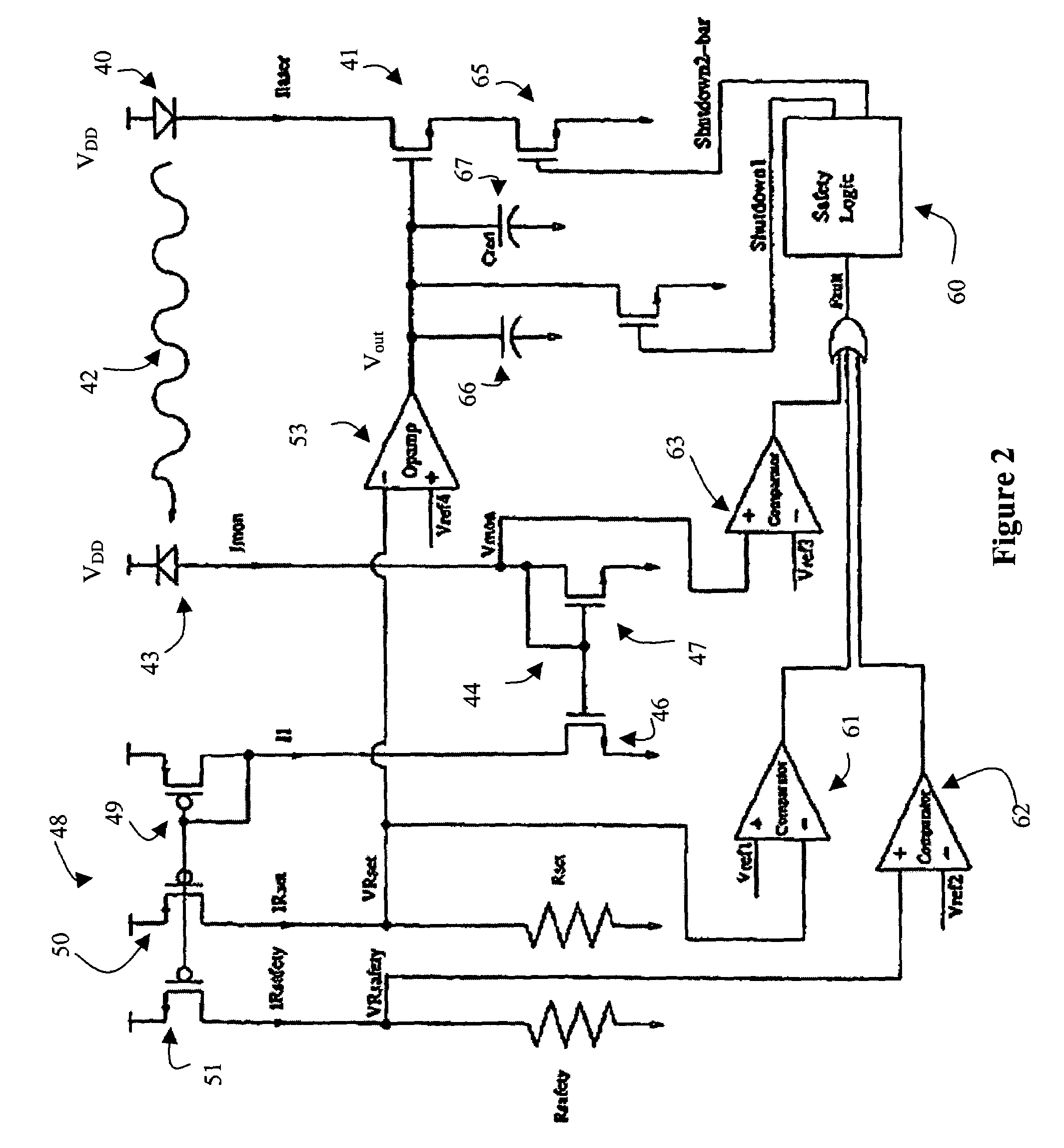
Laser diode driving circuit with safety feature
The invention relates to a feedback loop for a laser diode driving circuit for ensuring that the laser diode generates optical power at a constant safe level. The feedback loop includes a monitor diode, which generates a monitor current Imon, and a set resistance for generating a set voltage based on the monitor current and the set resistance. The set voltage is compared with a reference voltage in an operational amplifier, which generates a control signal for controlling the laser diode current source. The laser diode current source dictates the amount of bias current transmitted to the laser diode. Safety features, in the form of voltage comparators, are provided to ensure that: a) the feedback loop is closed, i.e. Imon is not too low; b) the optical power is not above standard safety threshold, i.e. Imon is not too high; and c) the monitor diode voltage is sufficient to provide specified optical power to electrical power conversion.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
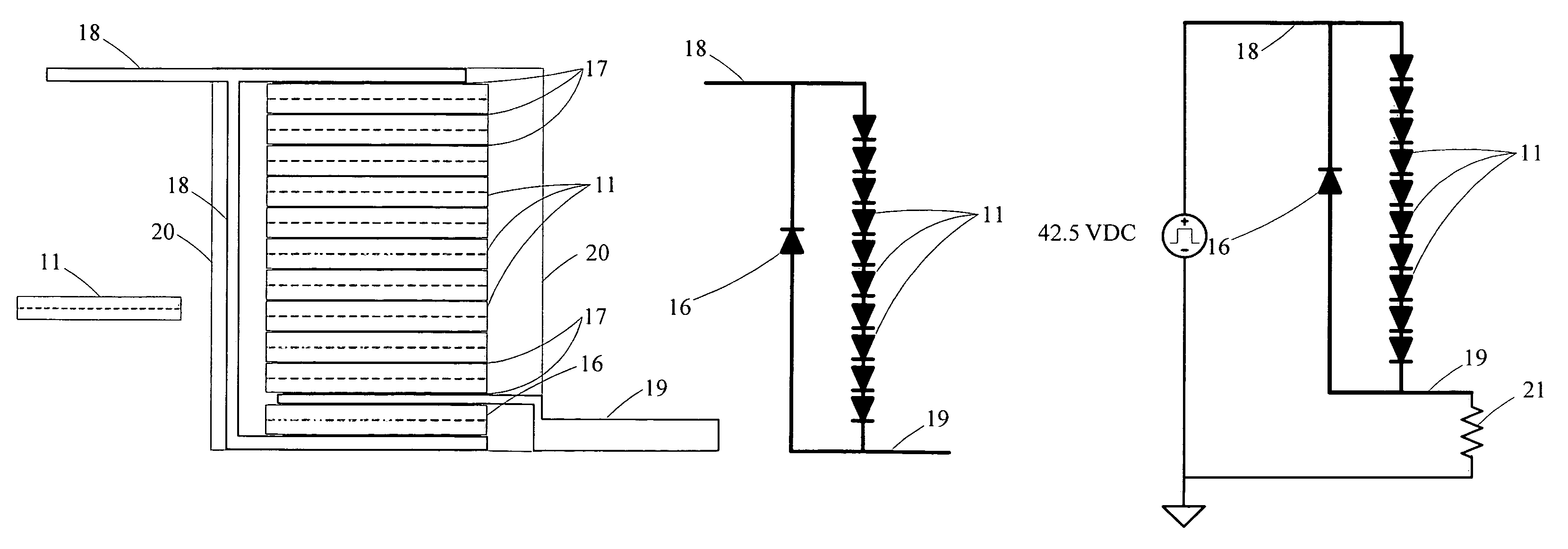
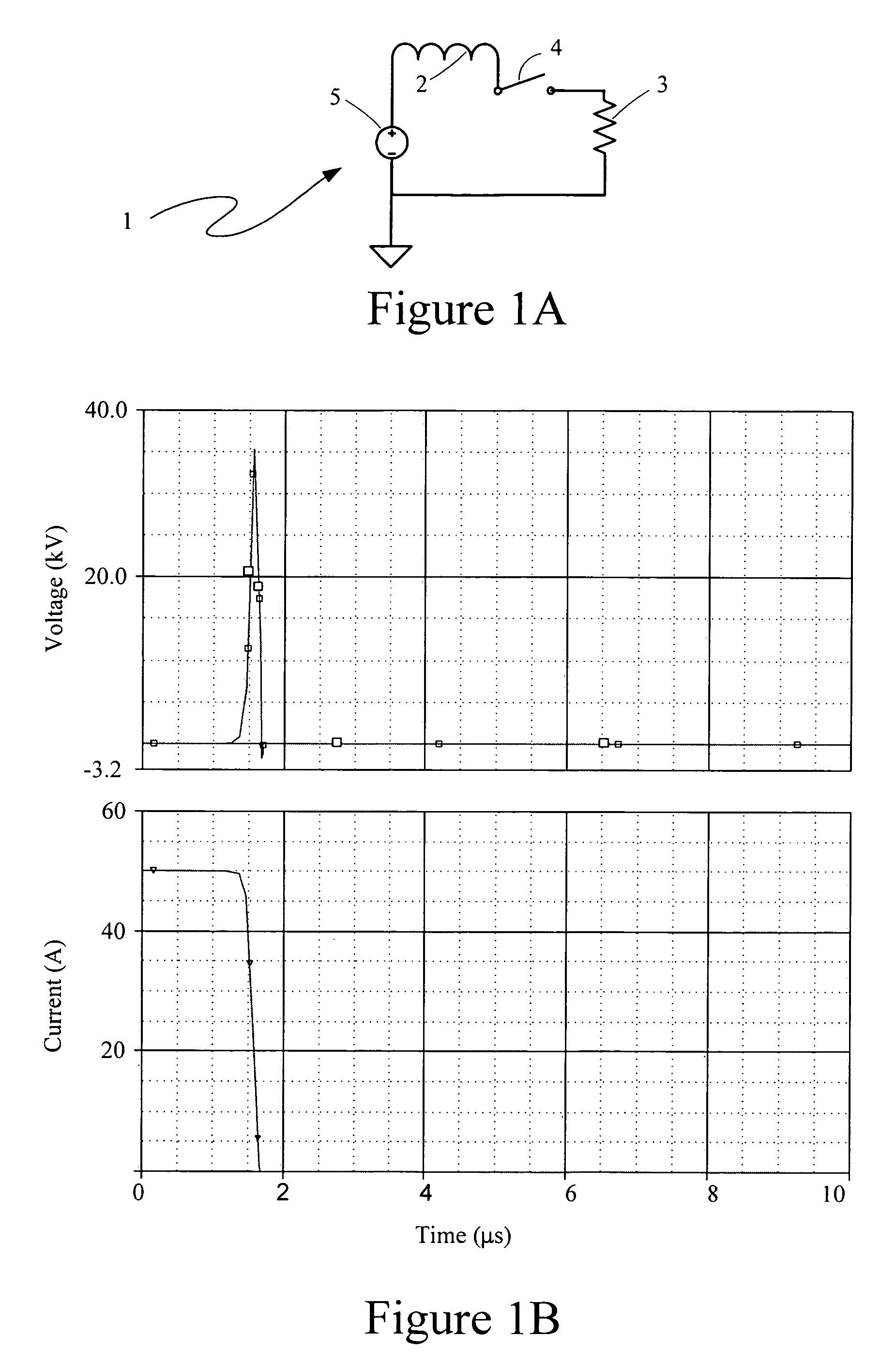
Silicon carbide diode voltage limiter
InactiveUS7339776B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityControl system
A voltage excursion control system for limiting transient voltage peaks in electrical circuits otherwise occurring across selected components therein in response to changing conditions in such circuits has a plurality of silicon carbide diode dice series-interconnected in a succession such that each cathode region of each die face toward a common end of the succession. First and second electrically conductive electrodes are each electrically interconnected with a corresponding one of the dice at opposite ends of the succession.
Owner:ROCKETDYNE
Voltage injection single period control Buck converter and control method thereof
InactiveCN106887951AFast closed-loop dynamic responseSmall steady state errorDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorBuck converter
The invention discloses a voltage injection single period control Buck converter and a control method thereof and belongs to the control field of an electric power converter. The Buck converter comprises a Buck converter main power circuit, a single period control circuit and an output voltage sampling conditioning circuit, an output voltage signal is sampled, an output voltage and an output reference voltage are compared to acquire an error voltage, the error voltage is compensated through a compensator to acquire a compensation voltage, the compensation voltage and a diode voltage sampling signal add together, an addition result is inputted to a resettable integrator inverting end, and an integrator output signal and the output voltage reference are compared to acquire a duty ratio of a switch tube of the Buck converter. According to the Buck converter, on the basis of original single period control, the sampled output voltage signal is injected to a resettable integrator, response to input voltage disturbance and load disturbance can be simultaneously realized in a single period, and thereby disadvantages of single period control load adjusting performance can be solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
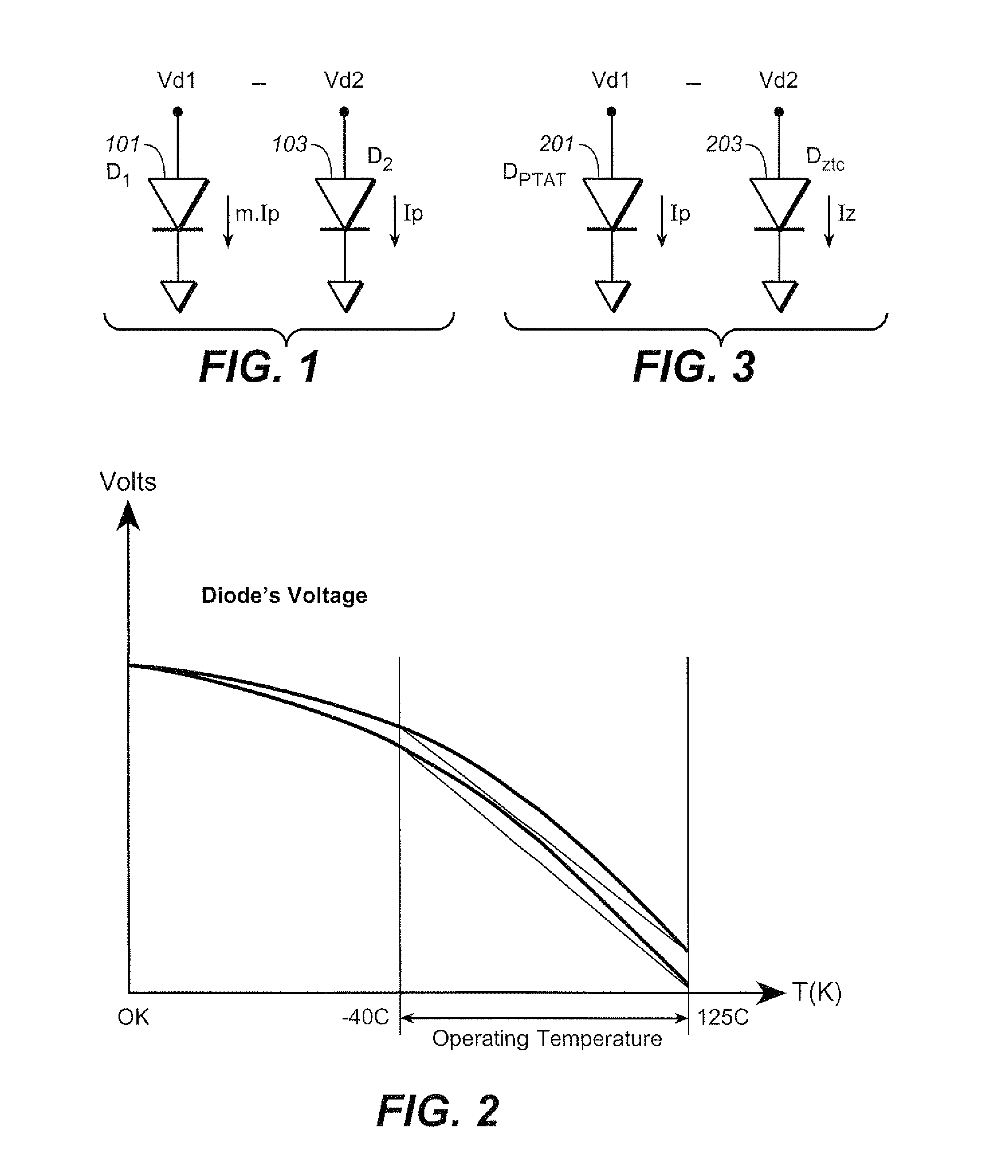
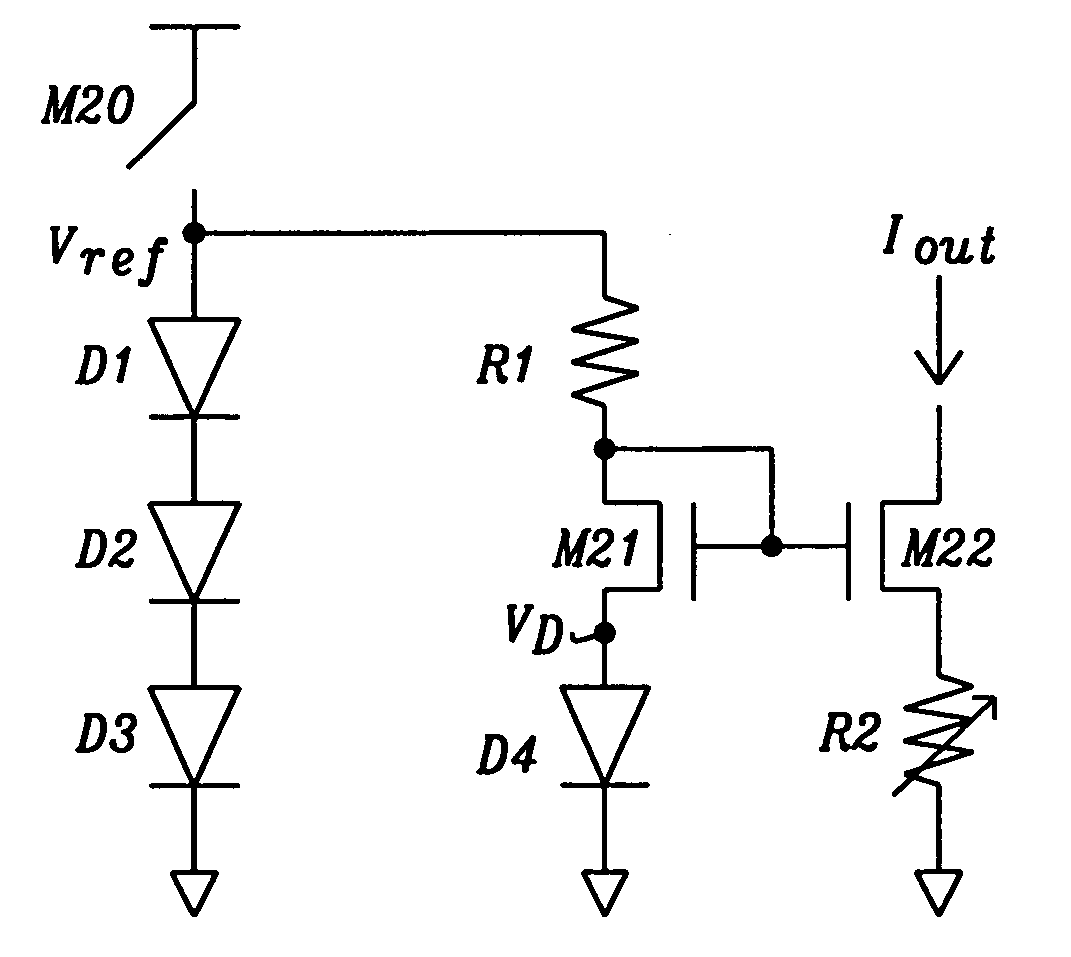
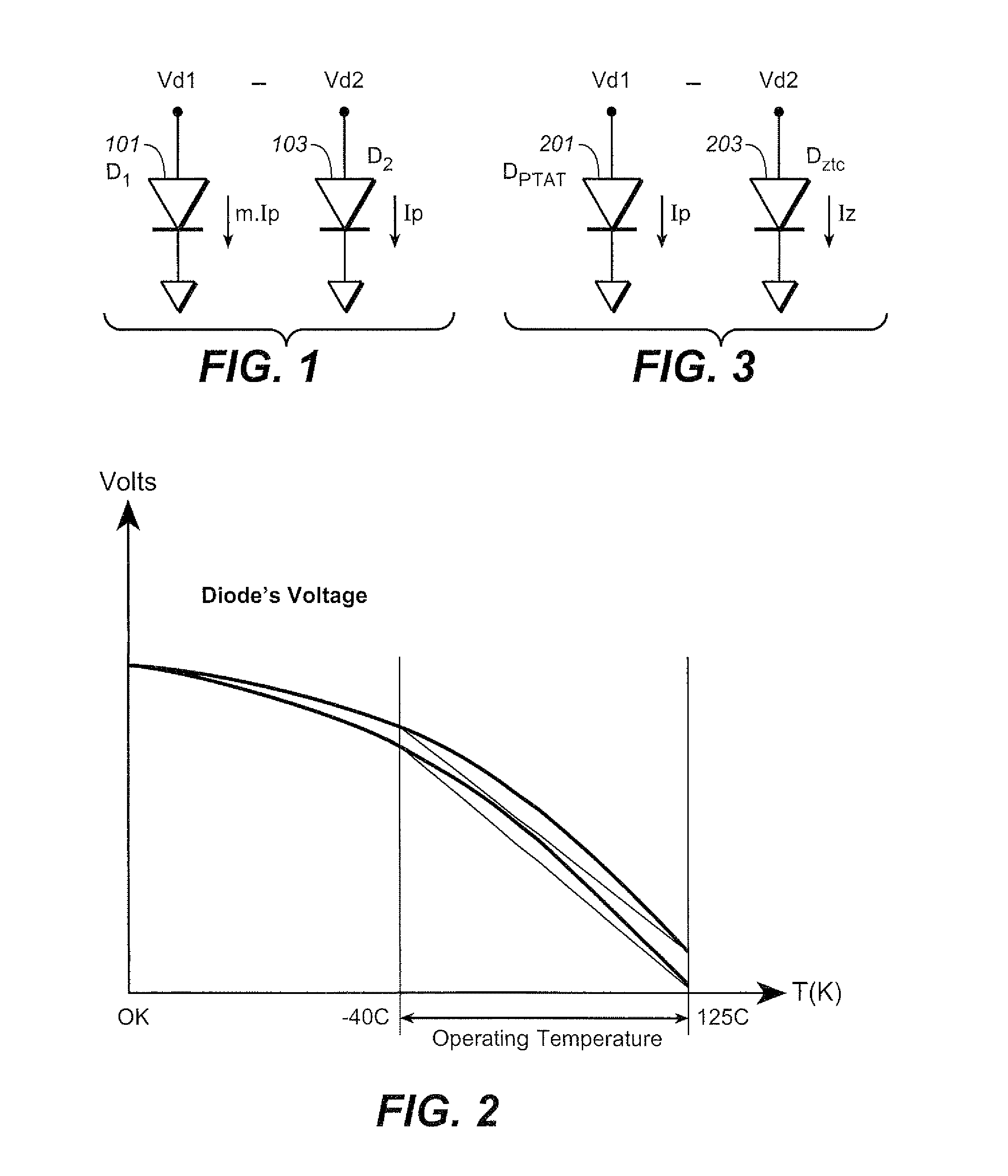
Curvature Compensated Band-Gap Design Trimmable at a Single Temperature
A band-gap reference circuit is compensated for temperature dependent curvature in its output. A voltage across a diode with a fixed current is subtracted from a voltage across a diode with a proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current. The resultant voltage is then magnified and added to a PTAT voltage and a diode's voltage that has a complementary-to-absolute temperature (CTAT) characteristic, resulting in a curvature corrected hand-gap voltage. This allows for the band-gap reference circuit to be trimmed at a single temperature. This allows the circuit to be made with only a single trimmable parameter, which, in the exemplary circuits, is a resistance value.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
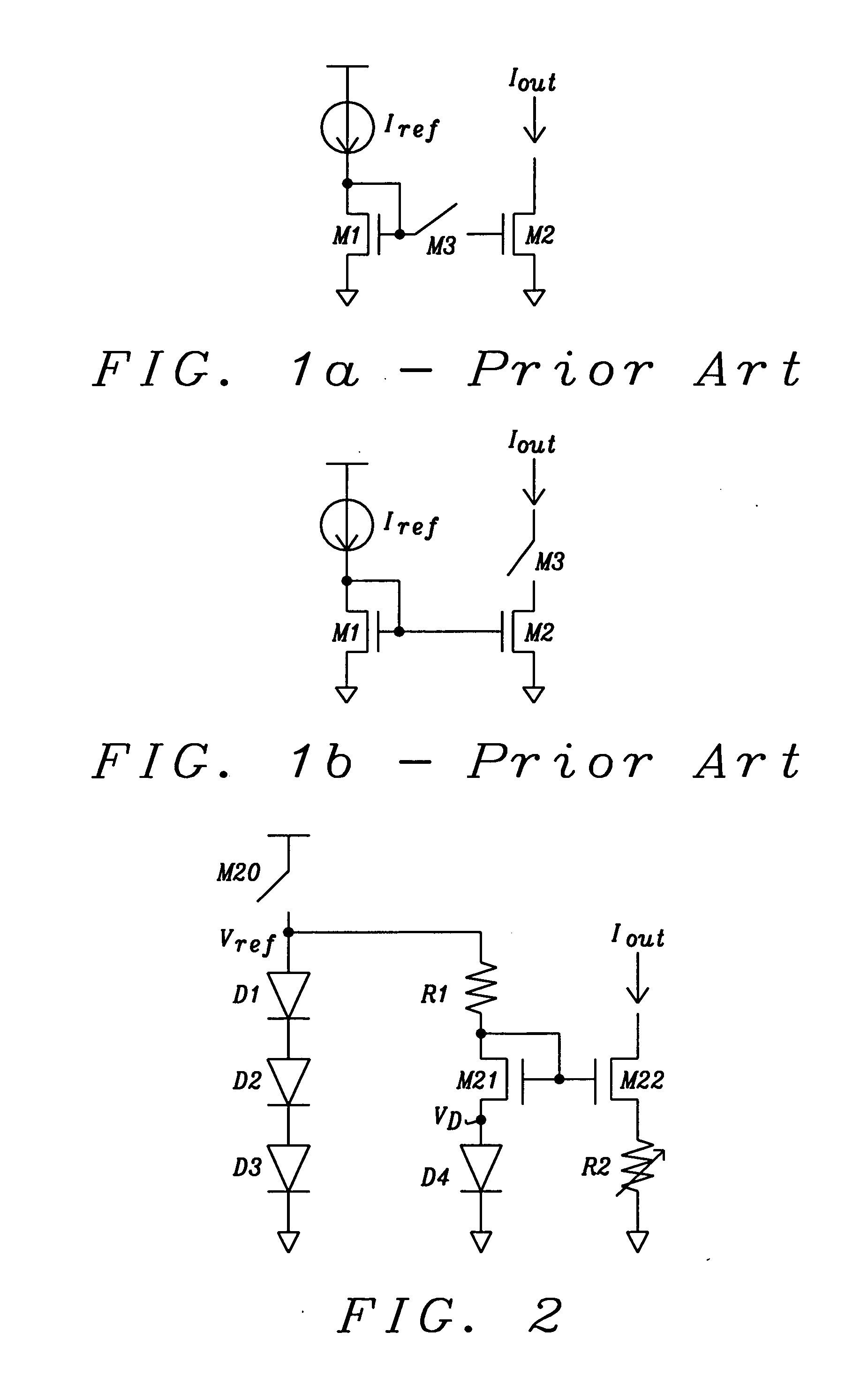
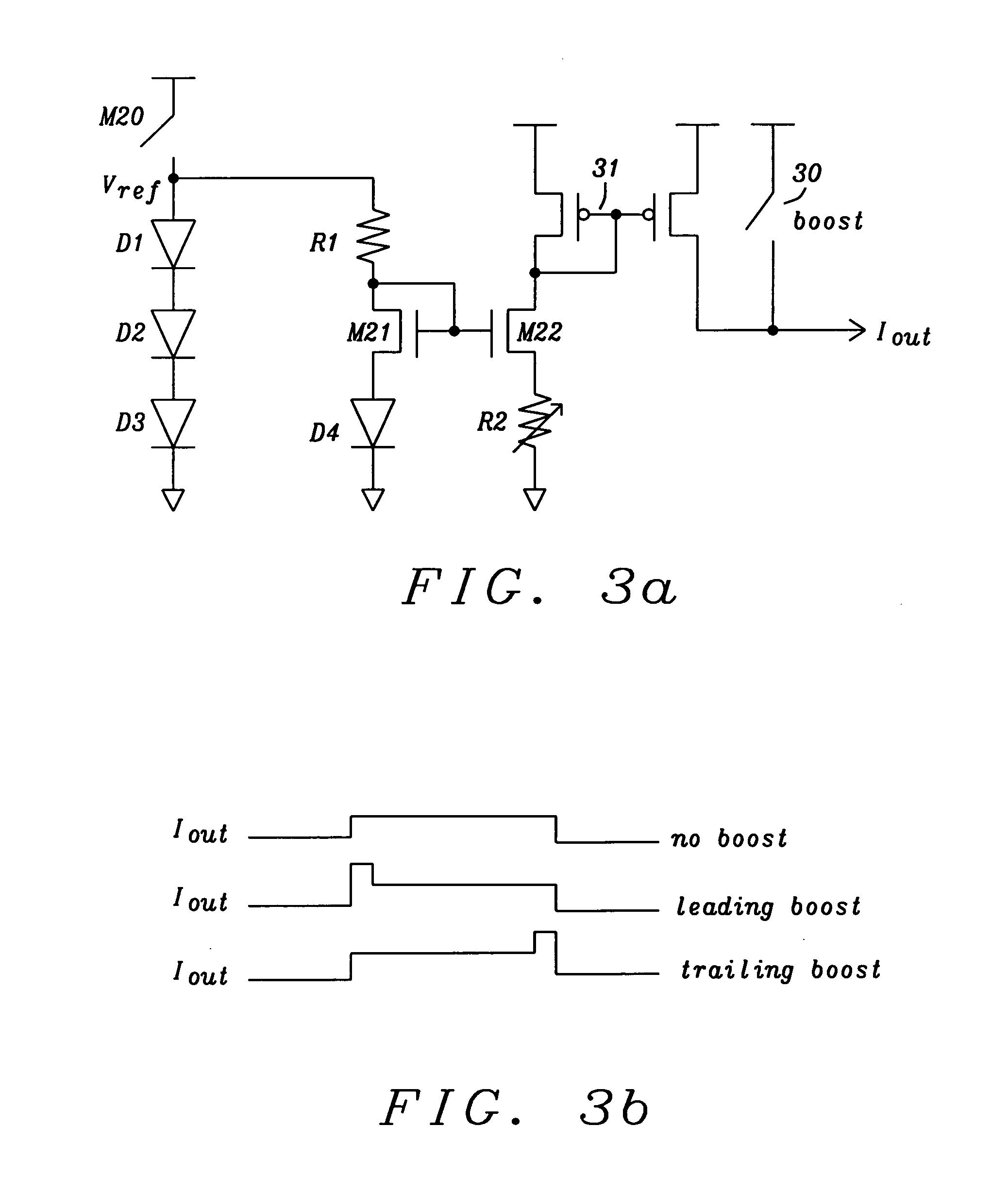
Fast and accurate current driver with zero standby current and features for boost and temperature compensation for MRAM write circuit
ActiveUS20120086476A1Fast and accurate current driverDigital storageElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceReference current
Systems and methods for realizing current drivers without current or voltage feedback for devices that require accurate current drive with zero standby current has been disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention this current driver is applied for write circuits for MRAMs. A fast and accurate reference current is generated by diode voltage divided by resistor without any feedback. The diode current is not fed back from the reference current. The diode current is generated from a regulated voltage. Temperature compensation of the write current is inherently built in the diode current reference. Fine-tuning of the temperature coefficient is achieved by mixing poly and diffusion resistors. A switch inserted in the current driver can turn on the driver fast and without a need for standby current. Leading boost in the current driver can fast charge the large coupling capacitance of word and bit lines and speed up write timing.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
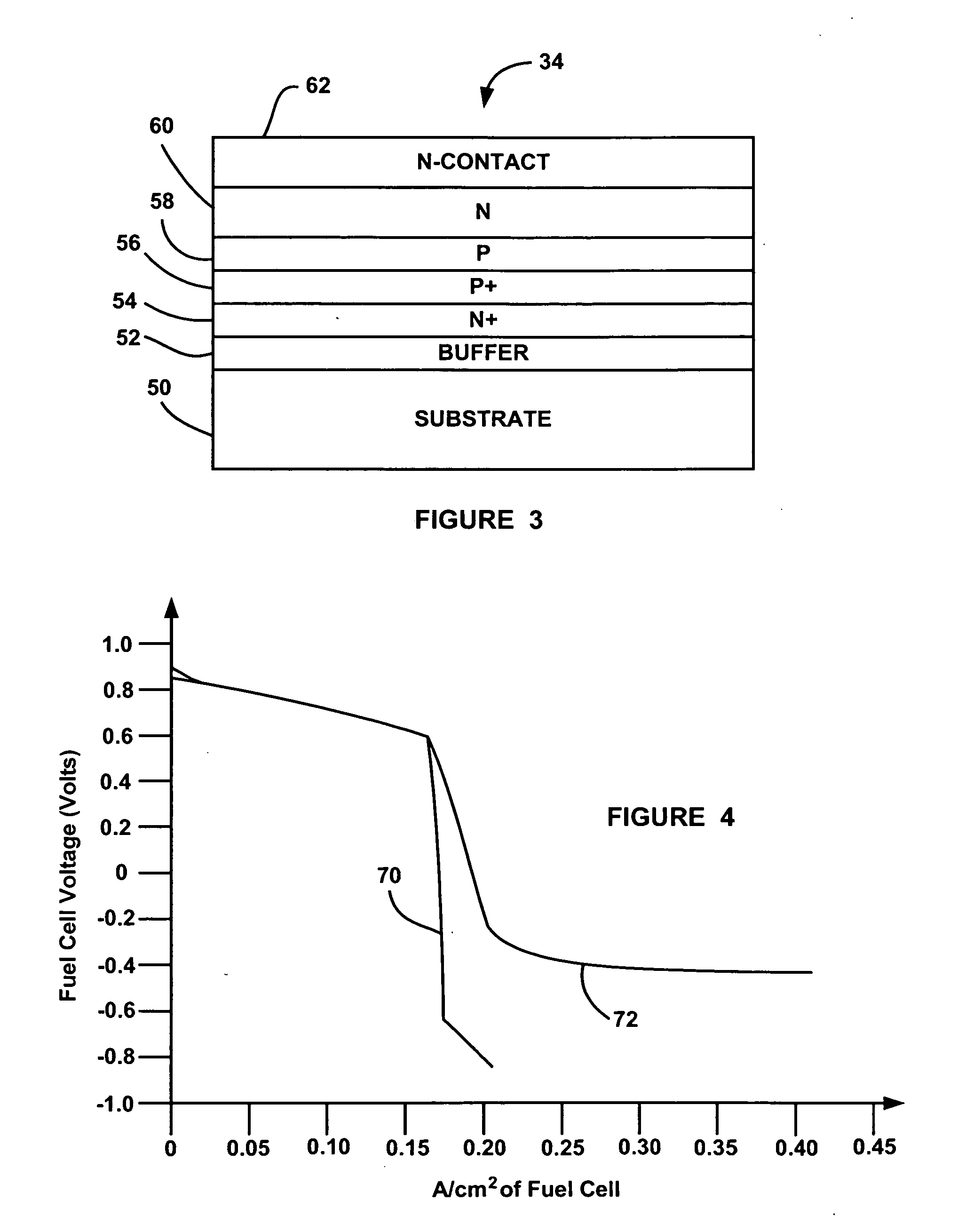
Integration of an electrical diode within a fuel cell
InactiveUS20060147769A1Reduce thicknessFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesElectricityFuel cells
A fuel cell system that employs a diode electrically coupled between bipolar plates in a fuel cell of a fuel cell stack for preventing the fuel cell between the plates from reversing its polarity. The diode is a thin-sheet p-n diode including doped semiconductor layers and has a thickness relative to the thickness of the MEA in the fuel cell so that the overall stack thickness does not increase. When the fuel cell is operating properly the diode does not conduct and all of the current through the fuel cell goes through the MEA. If the electric load on the stack increases to a level beyond the capability of the fuel cell, where the potential across the fuel cell goes significantly below zero, the diode will begin to conduct so that any current that cannot travel through the MEA with the cell voltage less than one negative forward diode voltage drop is able to go around the MEA through the diode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
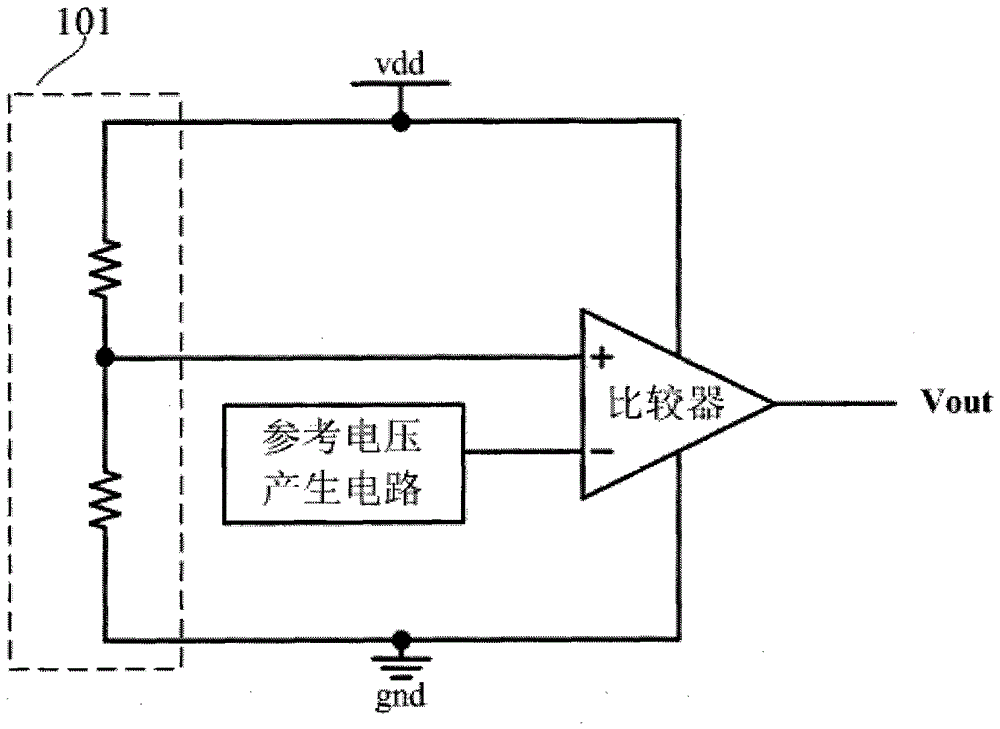
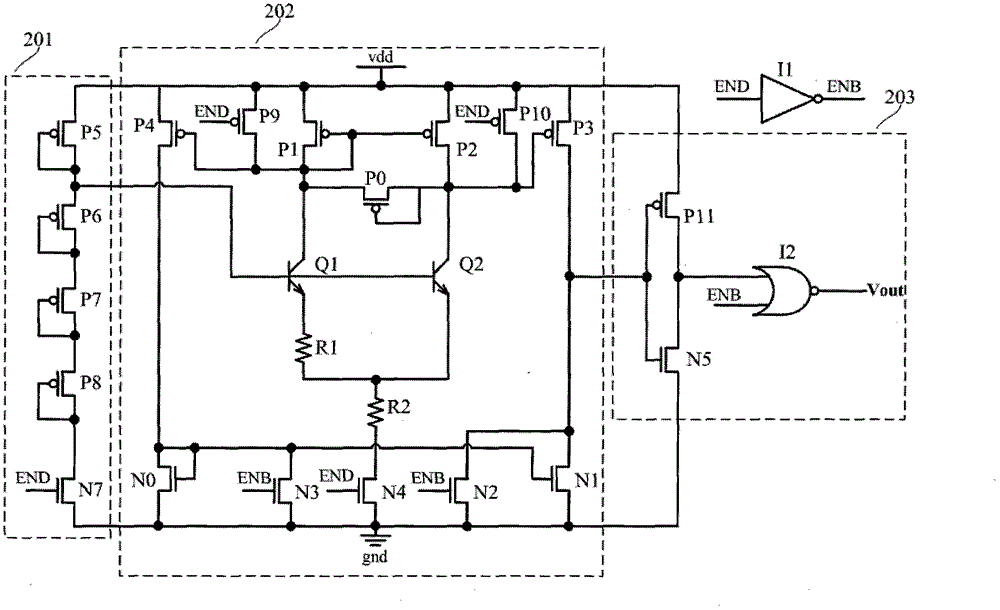
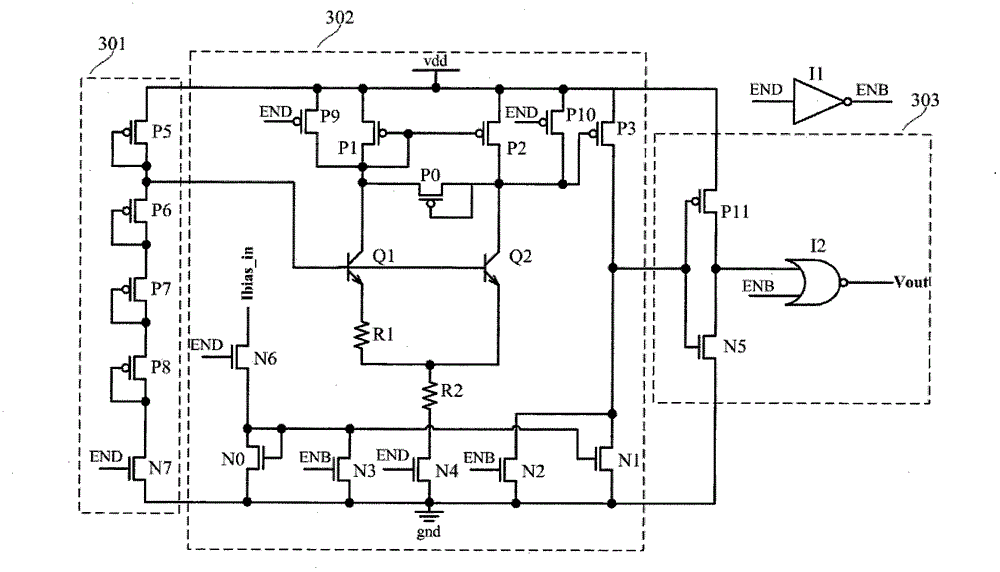
Ultra-low power consumption voltage detection circuit
InactiveCN105021862AAvoid it happening againGood precisionCurrent/voltage measurementDatum referenceSmart card
The invention discloses a ultra-low power consumption voltage detection circuit, which comprises an MOS diode voltage-dividing network, a level detection circuit and an output logic circuit. The main function of the MOS diode voltage-dividing network is to perform continuous sampling on a voltage to be detected, and provide a base input voltage and a base input current for an NPN triode in the level detection circuit; the level detection circuit is the core part of the ultra-low power consumption voltage detection circuit and utilizes the basic idea of band-gap reference, can realize accurate detection on the voltage to be detected under the condition that a reference voltage is not needed, and a voltage detection point has good temperature characteristics; and the output logic circuit is used for shaping a detection output signal at last. Compared with the traditional voltage detection technology, the ultra-low power consumption voltage detection circuit can operate at ultra-low power consumption (tens of nW) without an extra datum reference voltage, is low in area cost, and is very suitable for chip fields of radio frequency identification electronic tags, dual-interface intelligent cards and the like.
Owner:BEIJING CEC HUADA ELECTRONIC DESIGN CO LTD
Curvature compensated band-gap design trimmable at a single temperature
A band-gap reference circuit is compensated for temperature dependent curvature in its output. A voltage across a diode with a fixed current is subtracted from a voltage across a diode with a proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current. The resultant voltage is then magnified and added to a PTAT voltage and a diode's voltage that has a complementary-to-absolute temperature (CTAT) characteristic, resulting in a curvature corrected hand-gap voltage. This allows for the band-gap reference circuit to be trimmed at a single temperature. This allows the circuit to be made with only a single trimmable parameter, which, in the exemplary circuits, is a resistance value.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
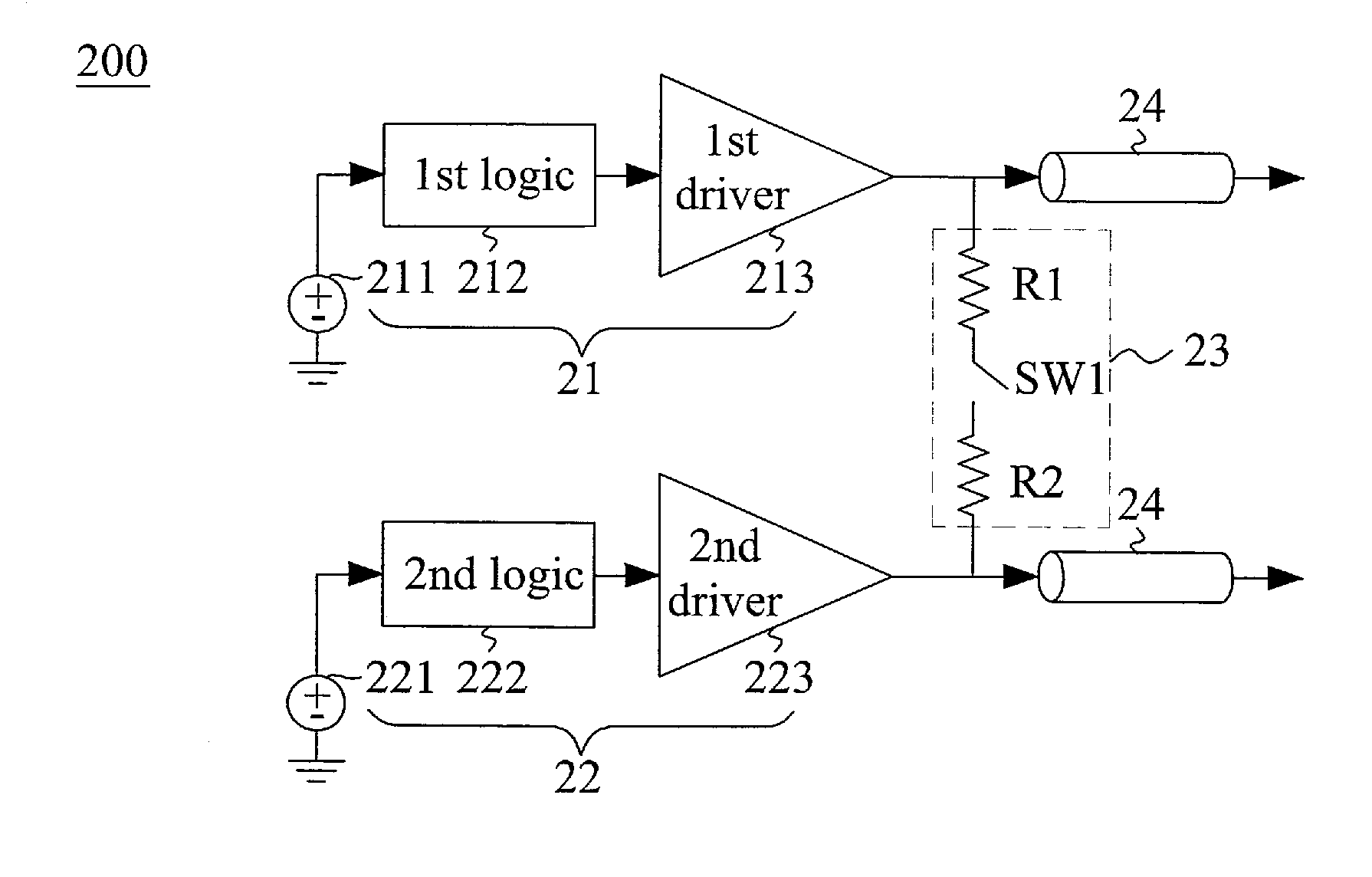
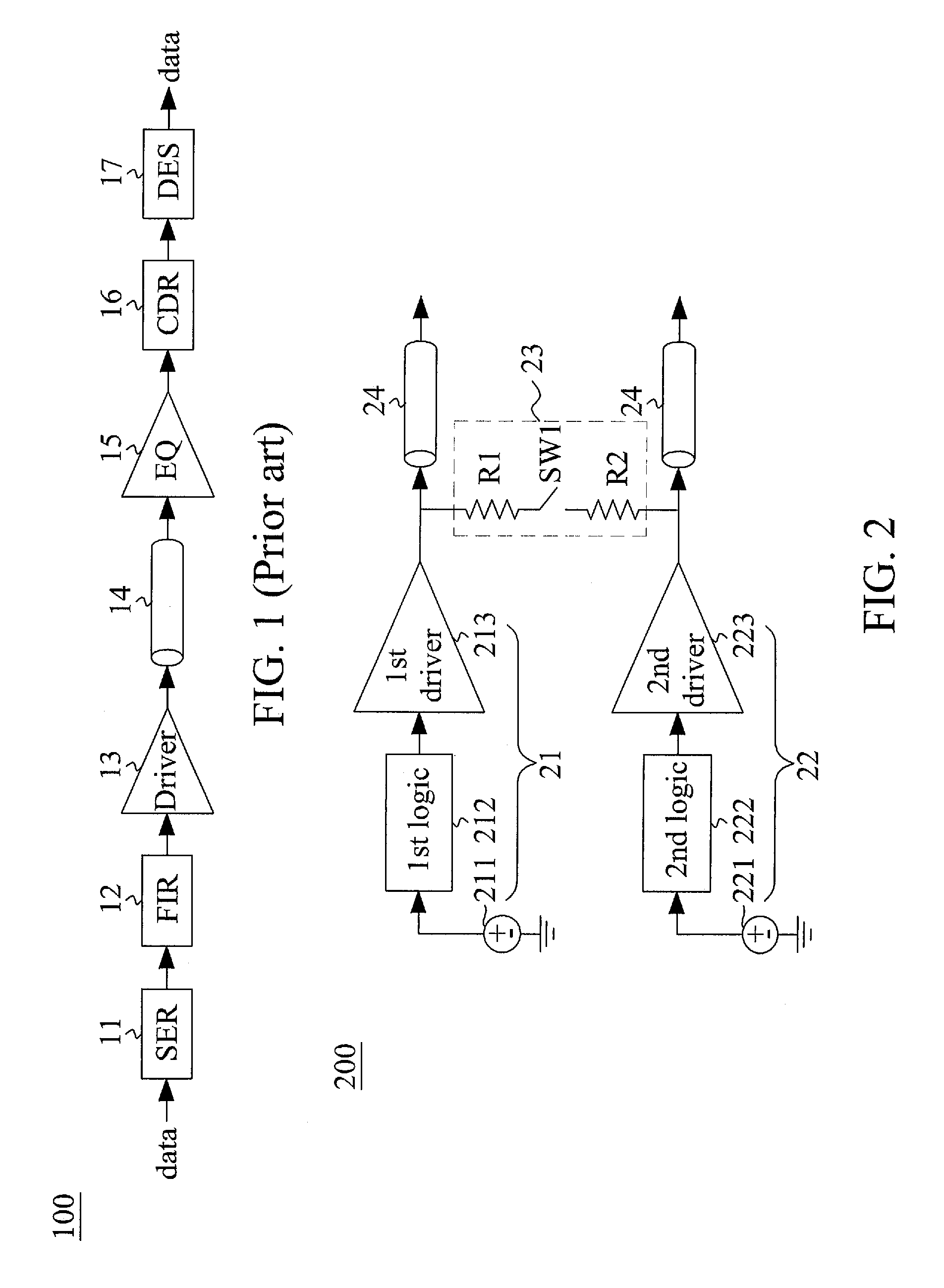
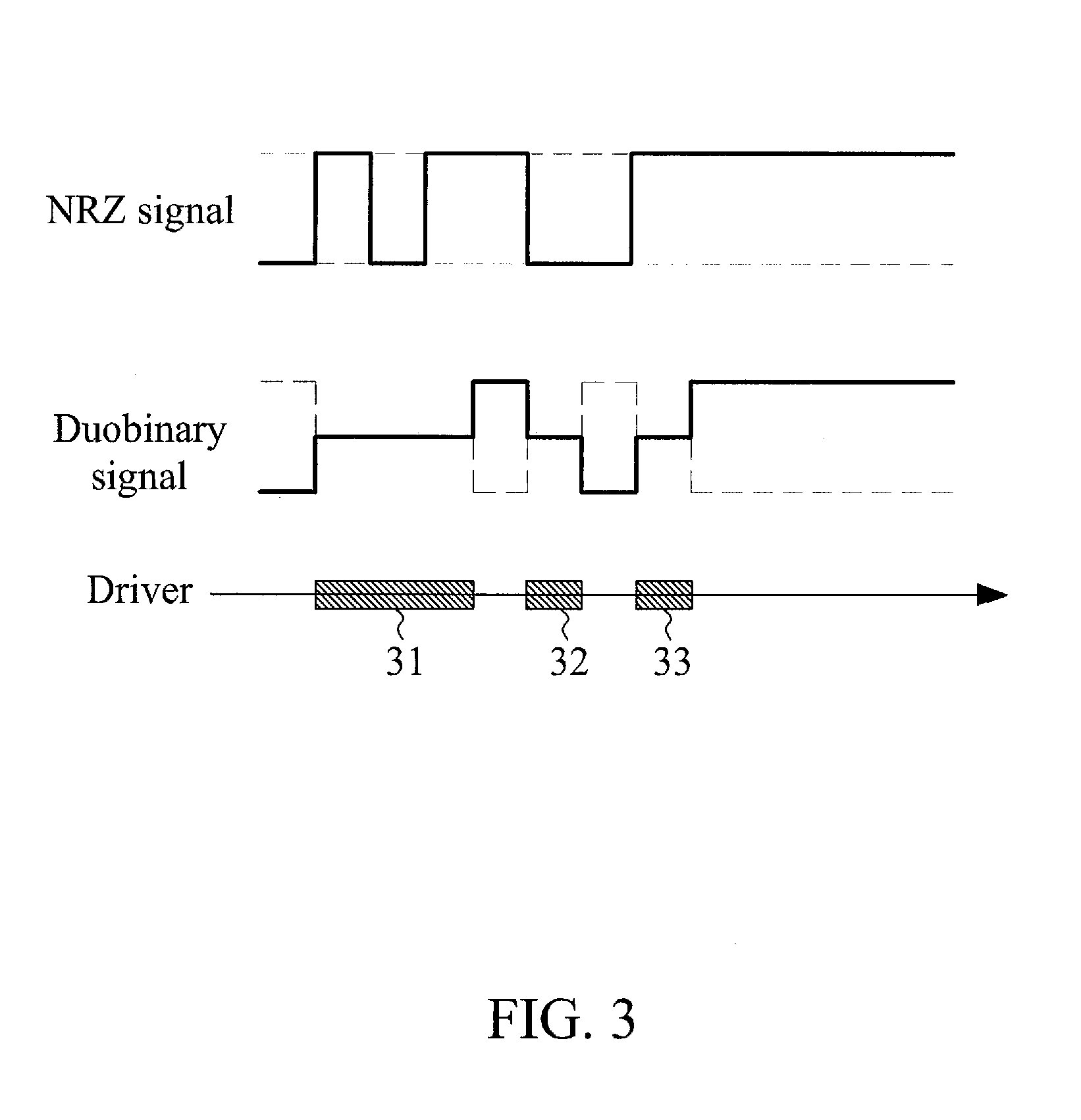
Duobinary voltage-mode transmitter
ActiveUS9143171B1Reduce power consumptionImproving Impedance MatchingSubstation remote connection/disconnectionHigh level techniquesEngineeringDiode voltage
A duobinary voltage-mode transmitter comprises a first branch including a first logic circuit and a first driver, and a second branch including a second logic circuit and a second driver. When a transition occurs between NRZ signals, two ends of a first match circuit are electrically coupled between the output nodes of the first driver and the second driver, respectively, and the first driver and the second driver are turned off.
Owner:NCKU RES & DEV FOUND +1
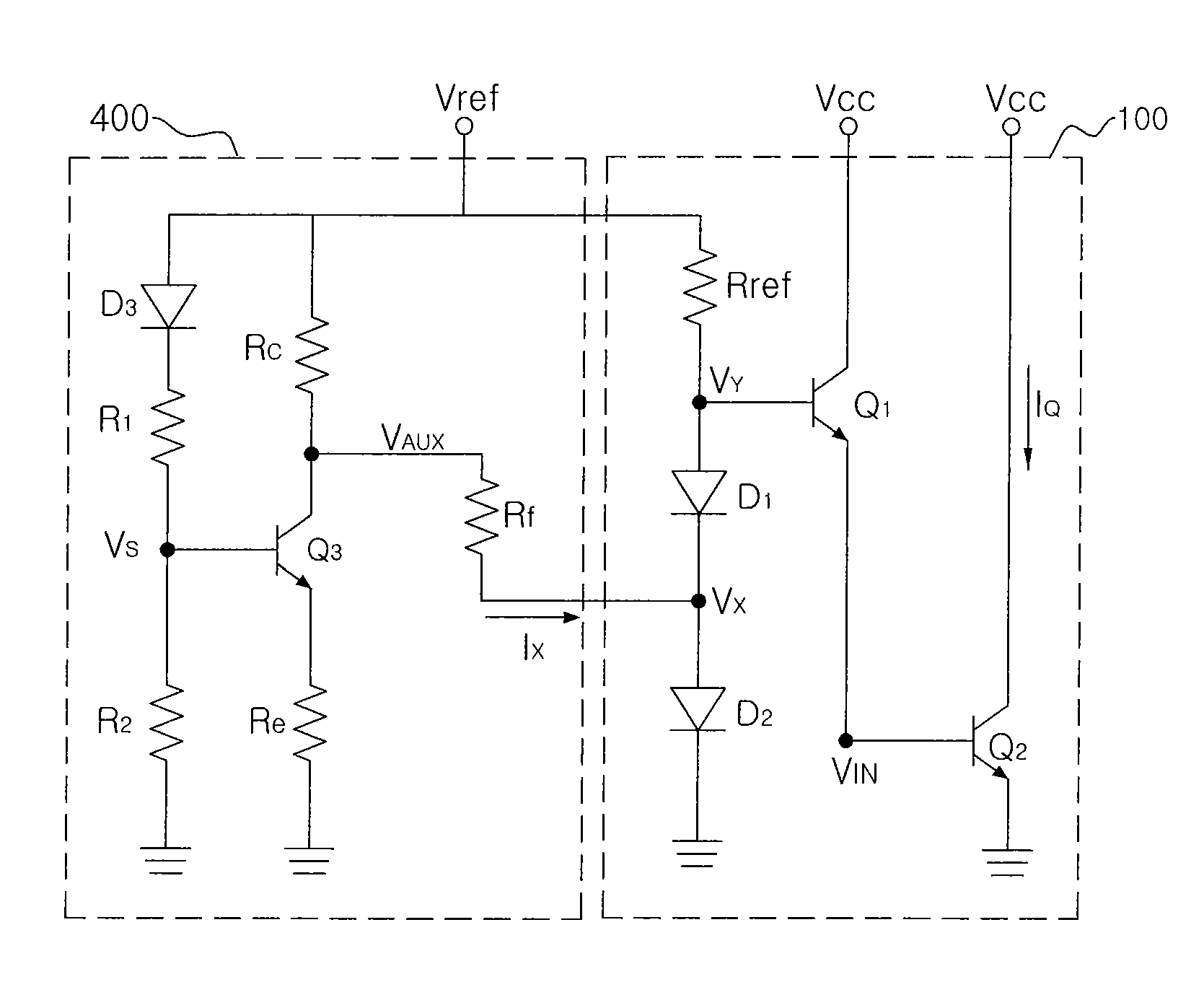
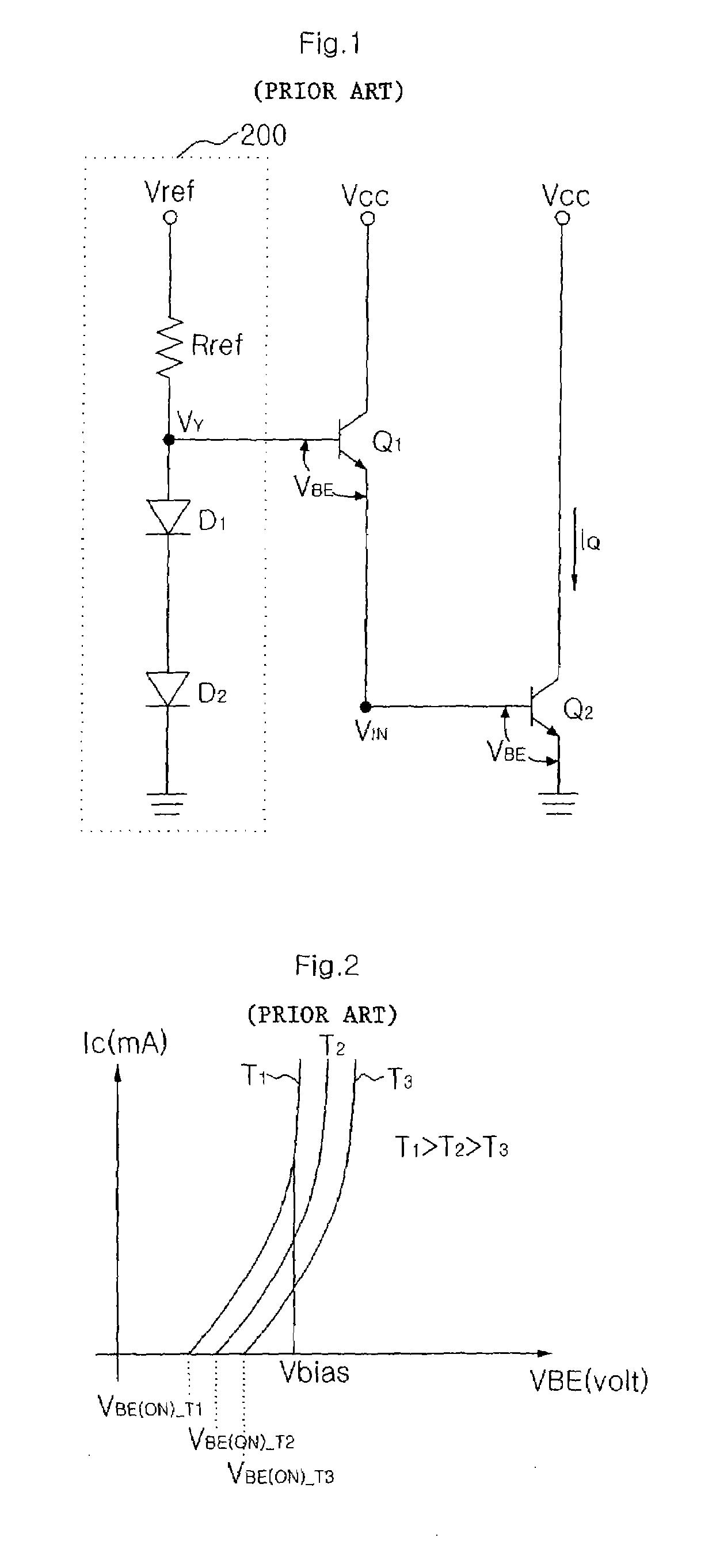
Temperature-compensated circuit for power amplifier using diode voltage control
ActiveUS7310015B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
Provided is a temperature-compensated circuit for a power amplifier through diode voltage control, in which a first resistor (Rref), a first diode (D1), and a second diode (D2) are connected to a reference voltage in series. The temperature-compensated circuit includes a second resistor (R1) connected to the reference voltage, a third resistor (R2) connected to the second resistor in series, a fourth resistor (Rc) having one terminal connected to the reference voltage, a fifth resistor (Re) having one terminal connected to ground, a bias transistor having a base terminal connected to a contact point (VS) between the second resistor and the third resistor, a collector terminal connected to the other terminal of the fourth resistor, and an emitter terminal connected to the other terminal of the fifth resistor, and a sixth resistor (Rf) connected between a series connection terminal between the first diode and the second diode, and the collector terminal of the bias transistor. The voltage of the collector terminal changes for compensation of a temperature.
Owner:WAVICS
Light emitting diode voltage adjusting device and driving system with same
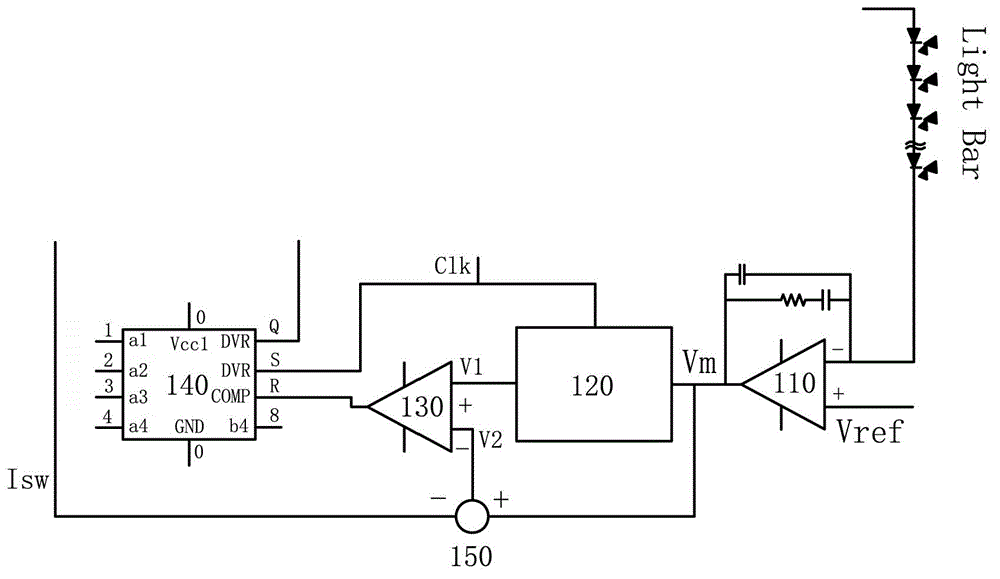
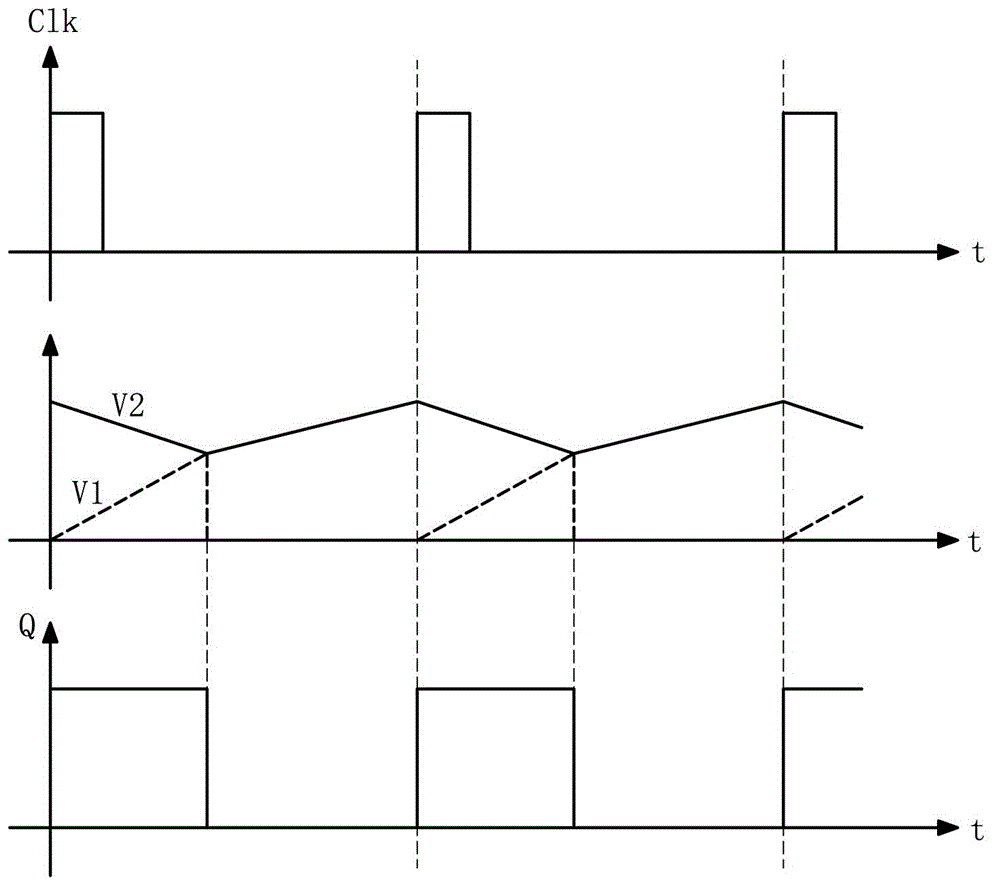
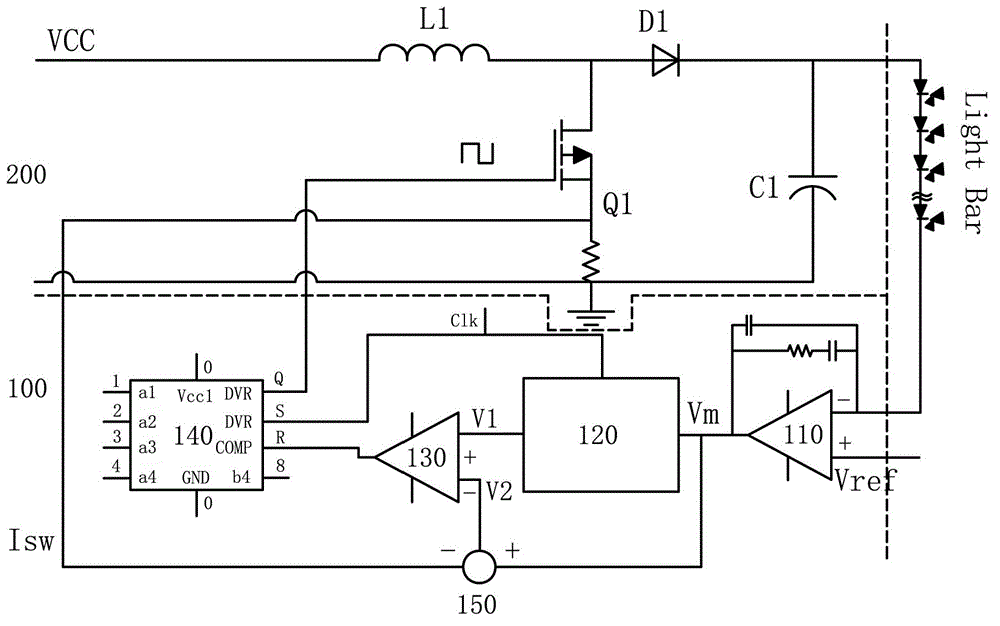
ActiveCN102945655AImprove protectionPrevent heat problemsElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesIntegratorControl signal
The invention discloses a light emitting diode voltage adjusting device and a driving system with the same. The light emitting diode voltage adjusting device comprises a PI (proportional-integral) adjuster, an integrator, a subtractor, a comparer and an integrated circuit module, wherein the negative input end of the PI adjustor is connected with the negative end of a light emitting diode light bar so as to receive the voltage of the negative end of the light bar; the positive input end of the PI adjustor is used for receiving the reference voltage; the integrator is used for integrating output signals of the PI adjustor; the positive input end of the subtractor is used for receiving output signals of the PI adjustor; the negative input end of the subtractor is used for receiving the over-current protecting and detecting voltage which is obtained from a boost converter for driving the light bar, and subtracting the over-current protecting and detecting voltage from the output signals of the PI adjustor; the positive input end of the comparer is used for receiving output signals of the integrator; the negative input end of the comparer is used for receiving output signals of the subtractor; and the integrated circuit module is used for receiving output signals of the comparer and outputting control signals for controlling a switch transistor of the boost converter to be powered on or powered off based on received signals.
Owner:CHANGSHA HKC OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com