Catheter with sealed hydratable hemostatic occlusion element
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
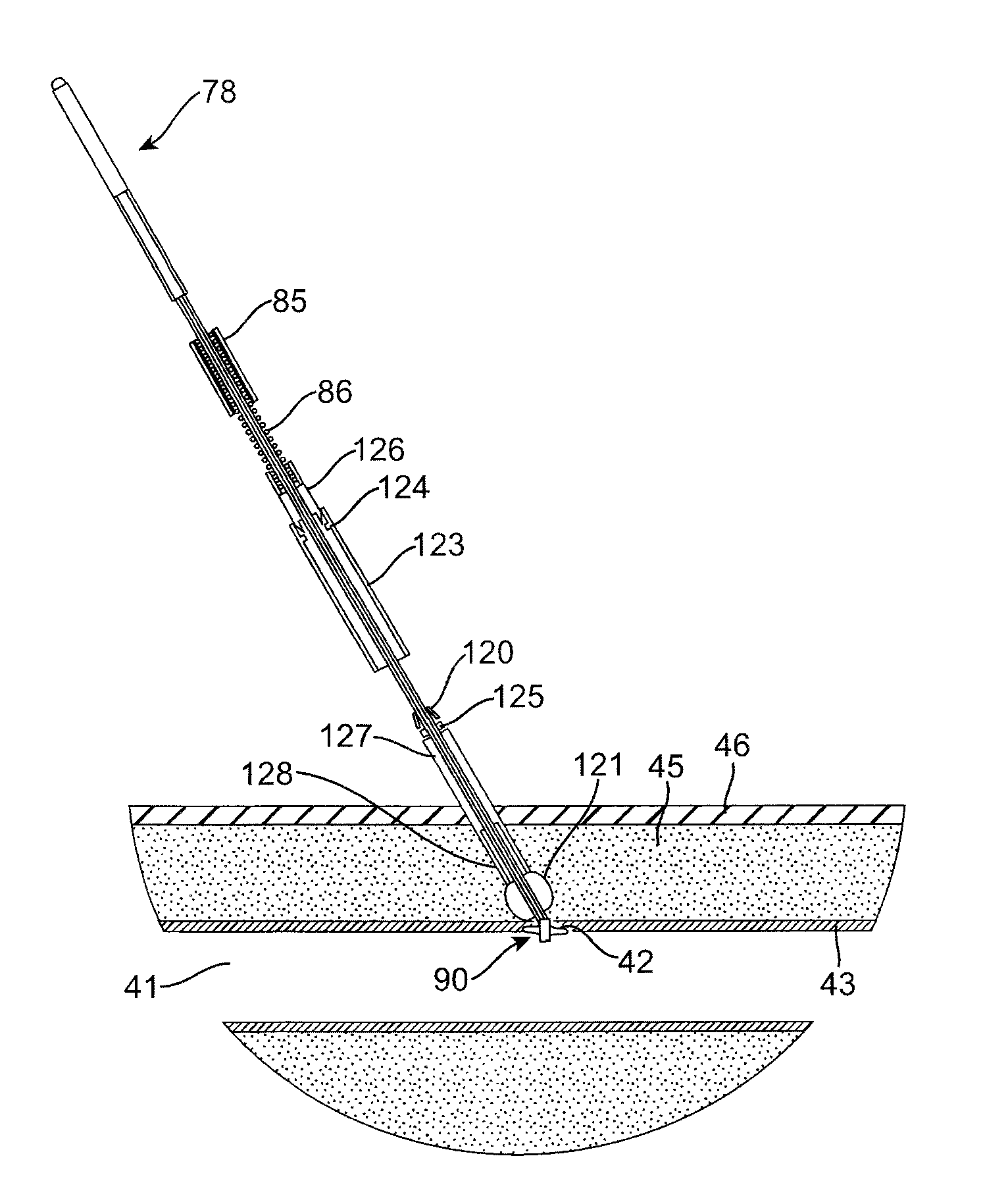
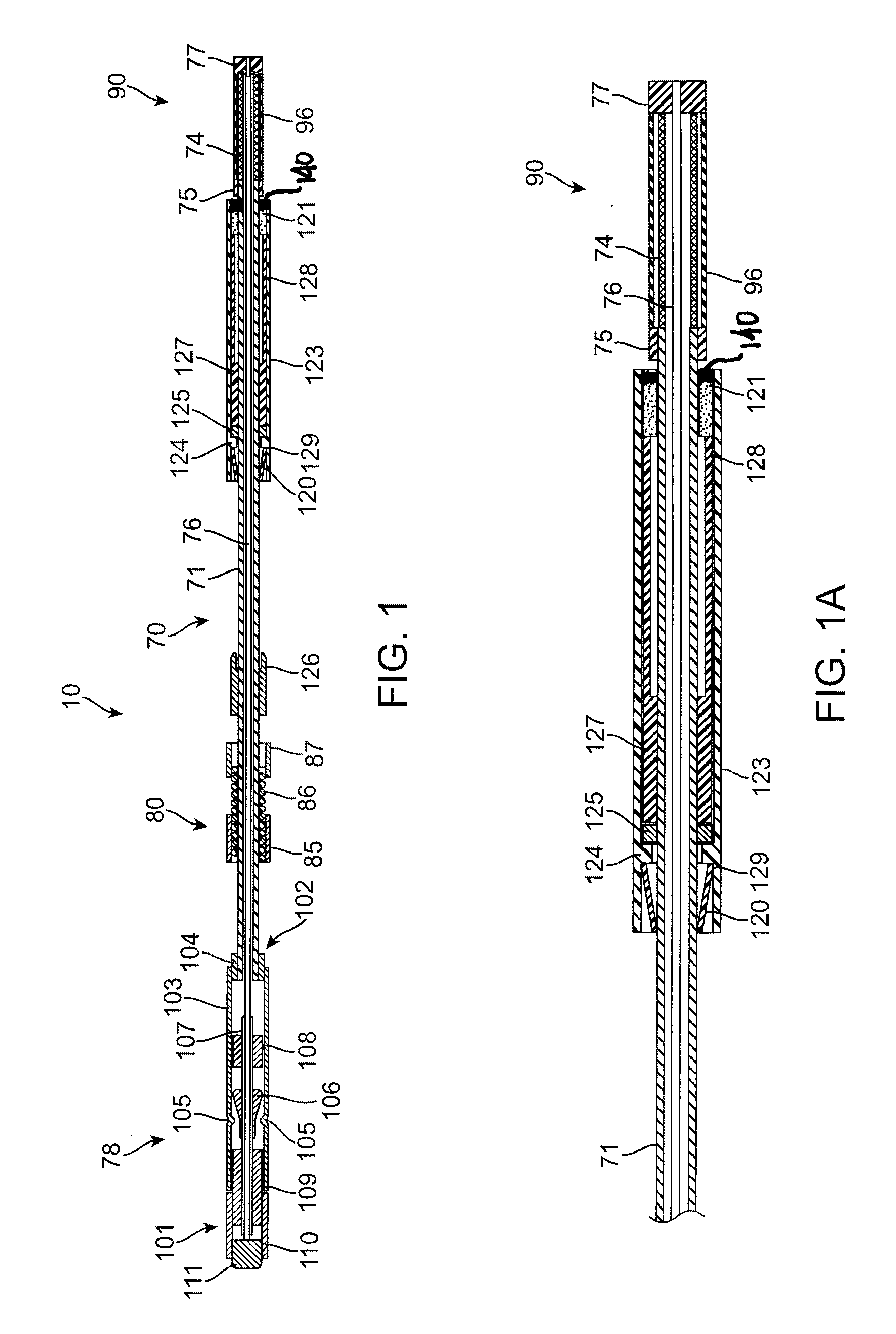
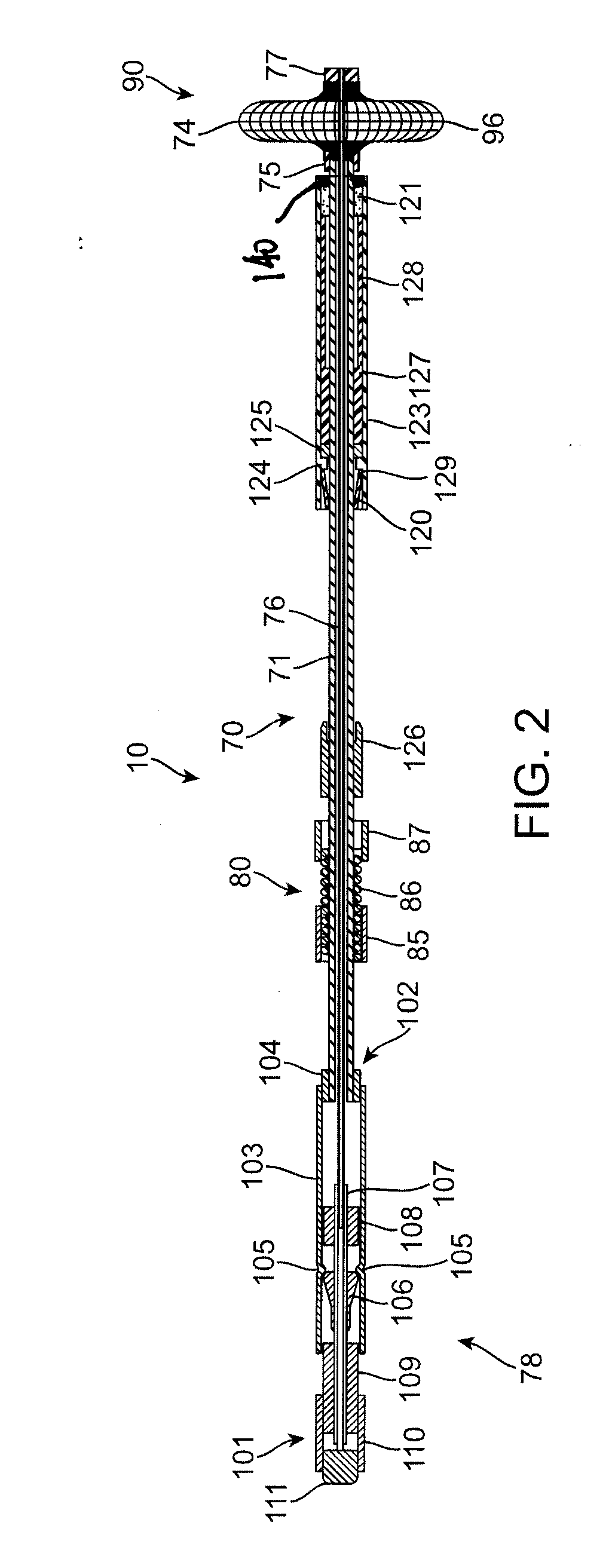
[0040]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 1A, an exemplary sealing apparatus 10 constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention comprises a shaft assembly 70 including an outer tube 71 and an inner rod 76. An expansible occlusion element 90 is mounted at a distal end (to the right in FIGS. 1 and 1A) of the shaft assembly 70 and includes a radially expansible mesh 74 covered by an elastomeric membrane 96. A handle assembly 78 is attached to a proximal end of the shaft assembly 70 and is operatively attached to both the outer tube 71 and inner rod 76 so that the inner rod can be axially advanced and retracted relative to the outer tube. The inner rod 76 and outer tube 71 are coupled together at the distal tip of the sealing apparatus 10 by a plug 77 and a proximal anchor 75, respectively. The occlusion element 90 is held between the plug 77 and the proximal anchor 75 so that axial retraction of the rod in the proximal direction (to the left as shown in FIGS. 1 and 1A) fore...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com