System for the torrefaction of lignocellulosic material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
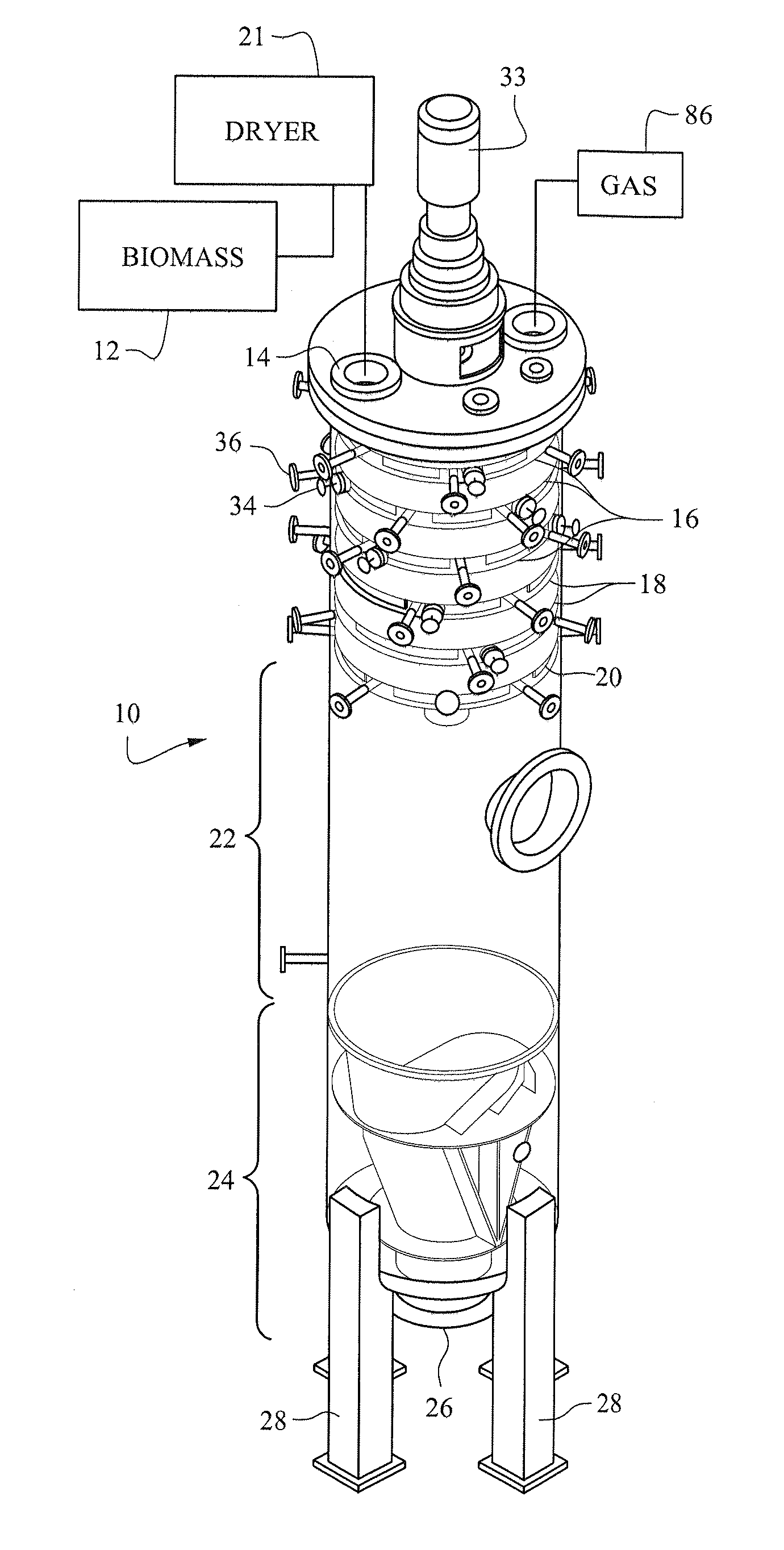
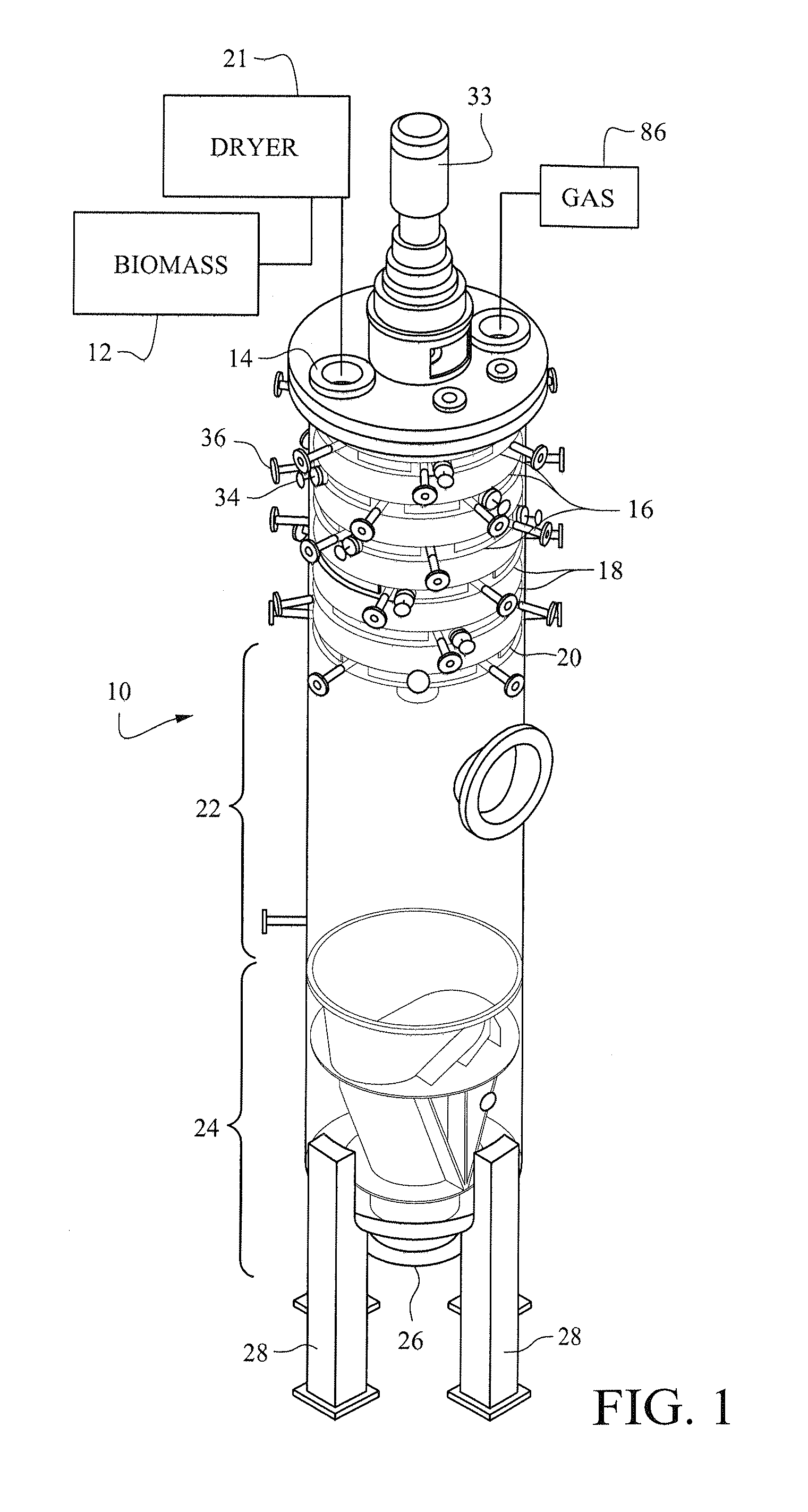
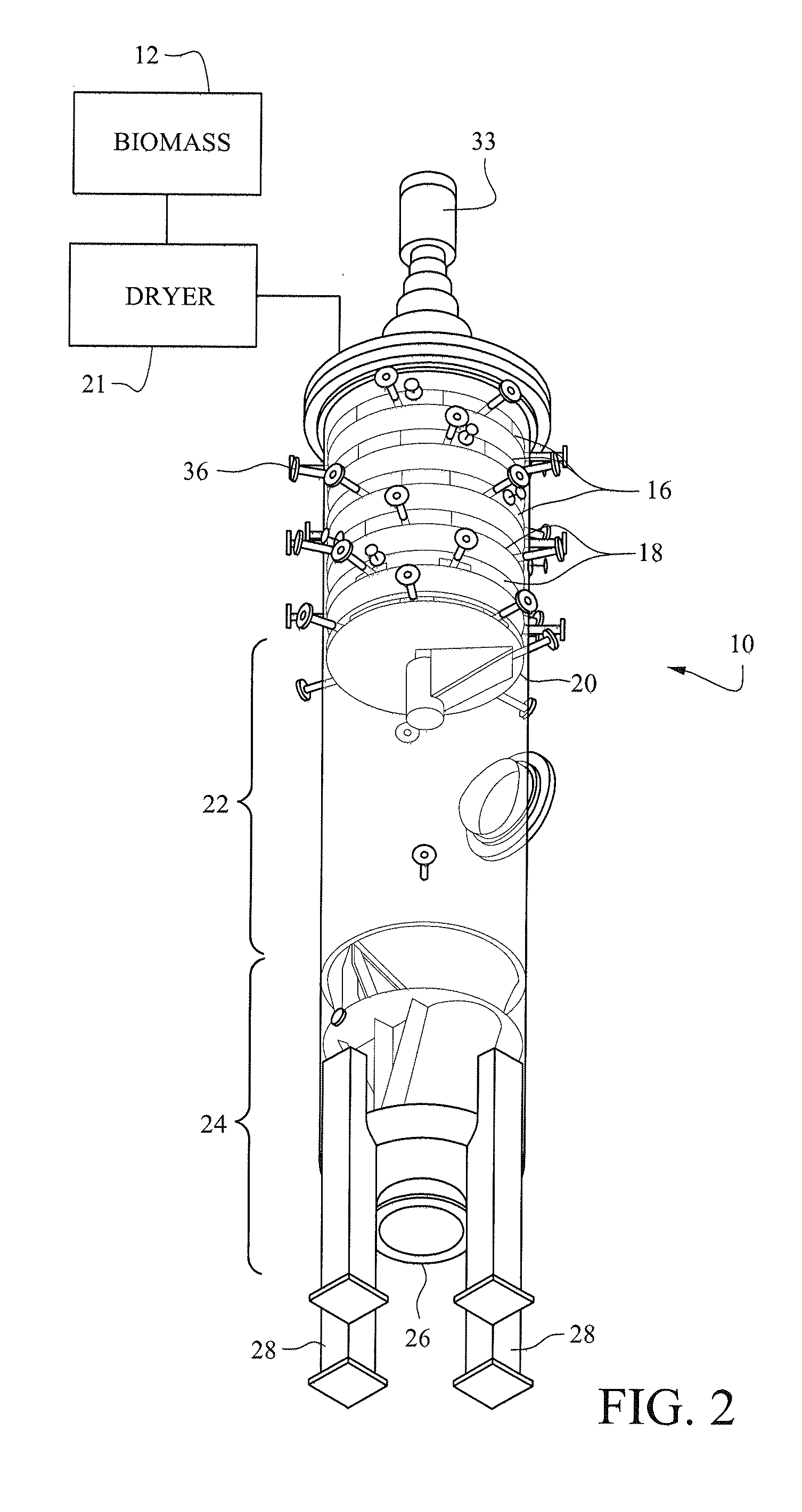
[0041]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate a pressurized treatment vessel 10 for receiving, treating, drying and cooling biomass material from a supply of biomass 12 through an upper inlet 14. The biomass may be wood chips, wood pulp or other comminuted cellulosic material. While moving over an upper series of drying tray assemblies 16 in the vessel, the biomass is dried. In addition or alternatively, the biomass may be dried prior to being introduced into the vessel 10.
[0042]The upper inlet 14 to the pressurized vessel may be coupled to a continuous feed, pressure isolation device, such as a conventional rotary valve or plug screw feeder, to feed the biomass into the pressurized vessel from a source of biomass at atmospheric pressure. The vessel 10 operates in a gas phase in which the dried biomass remains dry in the vessel.
[0043]The biomass may be fed to the inlet 14 to the vessel at a temperature of ambient temperature or, if a dryer 21 preheats the biomass, at 80° C. to 120° C., or higher, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com