Glass, in particular solder glass or fusible glass
a technology of solder glass and fusible glass, which is applied in the field of solder glass or fusible glass, can solve the problems of low temperature resistance, high alkali content, and lead content of solder glass, and achieve the effect of sufficient chemical stability and high temperature resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
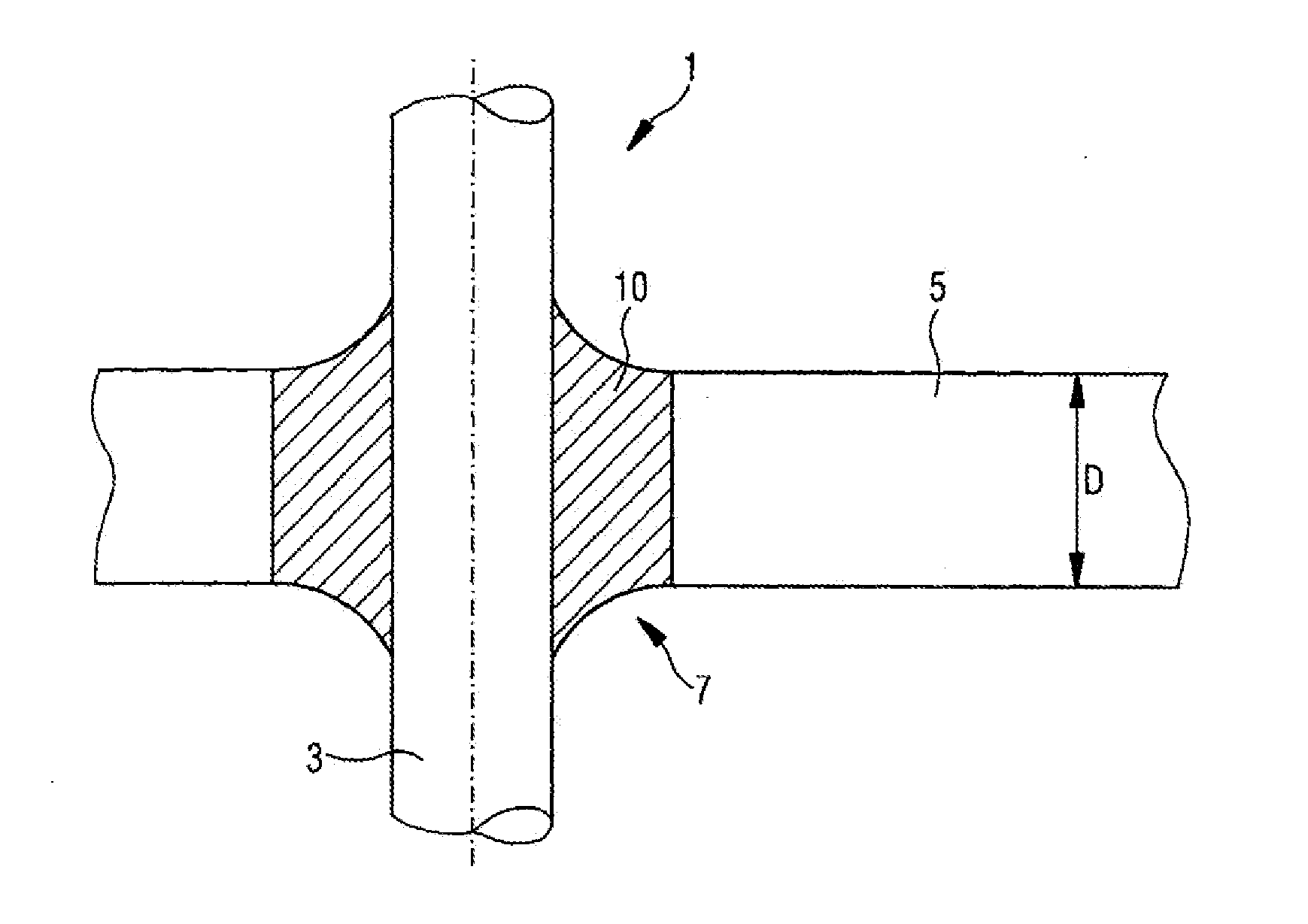
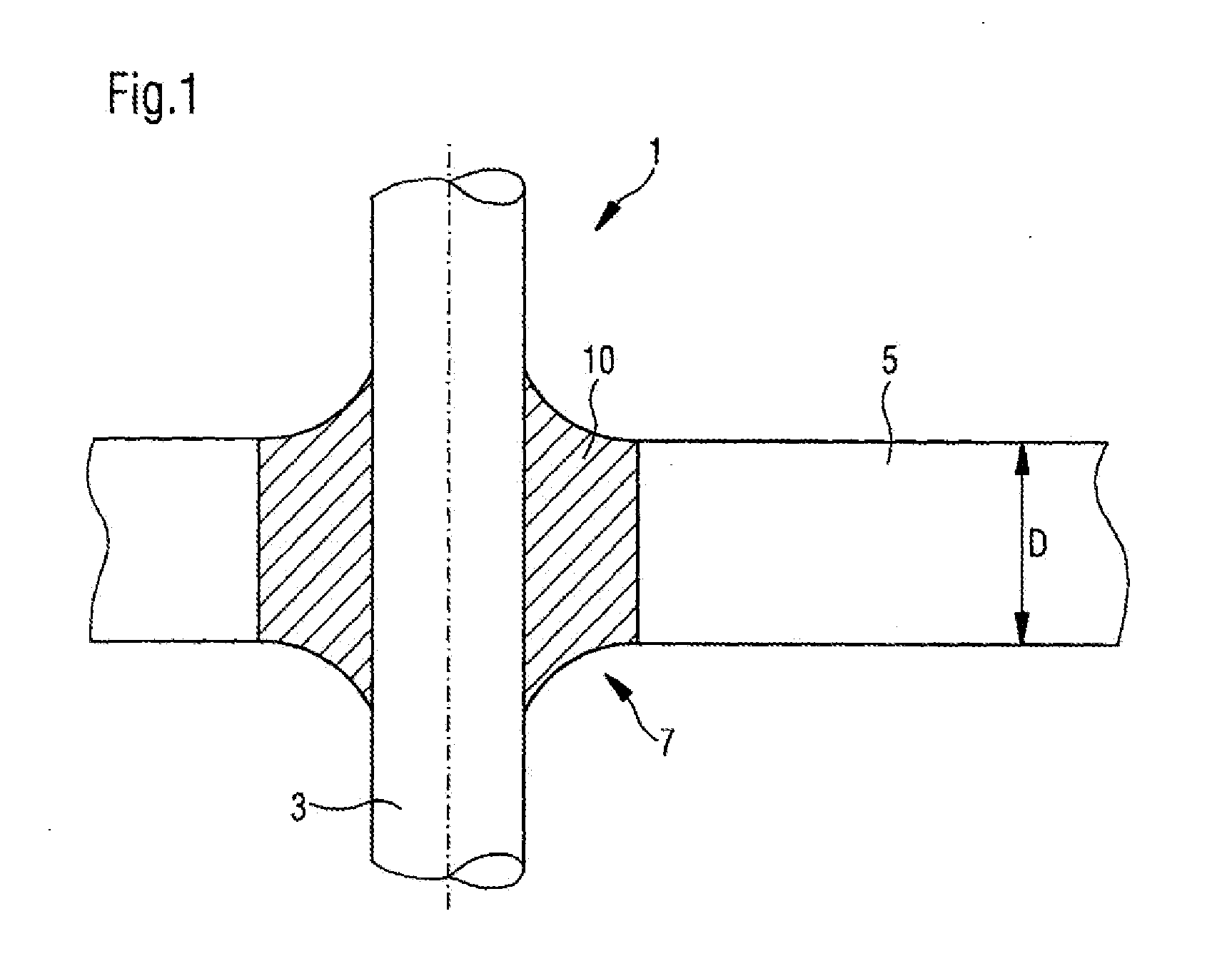
[0063]Referring now to the drawing, and more particularly to FIG. 1, there is shown a feed-through 1 according to the present invention. Feed-through 1 includes a metal pin 3 as a conductor, in particular as a pin shaped conductor which consists for example of a material, such as aluminum or copper. It further includes a base body 5 in the embodiment of a metal part consisting according to the present invention of a metal which has a low melting point, that is a light metal such as aluminum. Metal pin 3 is guided through an opening 7 which leads through metal part 5. Even though only the insertion of a single metal pin through the opening is illustrated, several metal pins could be inserted through the opening, without deviating from the present invention.
[0064]The outer contour of opening 7 can be round, but also oval. Opening 7 penetrates through the entire thickness D of base body 5, or respectively metal part 5. Metal pin 3 is sealed into a glass material 10 and is inserted insi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com